生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 36-45.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.01.005
孙树娇1,2( ), 王秀英1,2, 陈奇1,2, 赵全宁1,2, 李甫1,2,*(
), 王秀英1,2, 陈奇1,2, 赵全宁1,2, 李甫1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-27
出版日期:2025-01-18
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
* 李甫。E-mail: 75243809@qq.com作者简介:孙树娇(1995年生),女,工程师,硕士,主要从事高寒生态气象研究。E-mail: sunshj17@lzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
SUN Shujiao1,2( ), WANG Xiuying1,2, CHEN Qi1,2, ZHAO Quanning1,2, LI Fu1,2,*(
), WANG Xiuying1,2, CHEN Qi1,2, ZHAO Quanning1,2, LI Fu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-27
Online:2025-01-18
Published:2025-01-21
摘要:
为实现利用植被光合呼吸模型(VPRM模型)在陆地生态系统估算大气与陆地生态系统之间净CO2交换量,需要针对不同生态系统进行VPRM模型参数的率定。基于位于典型高寒荒漠草原的沱沱河站2019年生长季(5—9月)的通量观测数据,结合遥感数据和气象数据,对VPRM的4个关键参数[最大光能利用率λ、光照为半饱和条件下光合有效辐射值P0和植被参数(α、β)]进行了率定,并对模型模拟效果进行了验证。结果表明,1)典型高寒荒漠草原生态系统VPRM模型的关键参数α、β、λ和P0值分别为0.034 μmol·m−2·s−1、0.217 μmol·m−2·s−1、0.119 μmol、64.920 μmol·m−2·s−1。2)VPRM模型在昼夜时间尺度上模拟效果最好,模拟值与观测值散点图的斜率接近0.918(R2=0.713),均方根误差为0.473,平均误差为0.342。3)VPRM模型和R程序包(REddyProc包)插补缺失值后两组数据相关性较高(昼R2=0.934;夜R2=0.975),两种方法插补精度类似。4)参数率定后的VPRM模型在晴天适用性最好(R2=0.829),均方根误差和平均误差均较小,分别是0.346和0.267。该文通过本地化参数率定和模拟效果验证,得到了典型高寒荒漠草原生态系统的VPRM模型,且具有较好的估算效果;该结果不仅为开展区域NEE估算奠定理论基础,而且还为地面观测数据的缺失值估算提供了新的思路。
中图分类号:
孙树娇, 王秀英, 陈奇, 赵全宁, 李甫. 植被光合呼吸模型在典型高寒荒漠草原生态系统的参数率定及验证[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 36-45.
SUN Shujiao, WANG Xiuying, CHEN Qi, ZHAO Quanning, LI Fu. Parameter Calibration and Validation of VPRM Model in Typical Alpine Desert Grassland Ecosystem[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(1): 36-45.
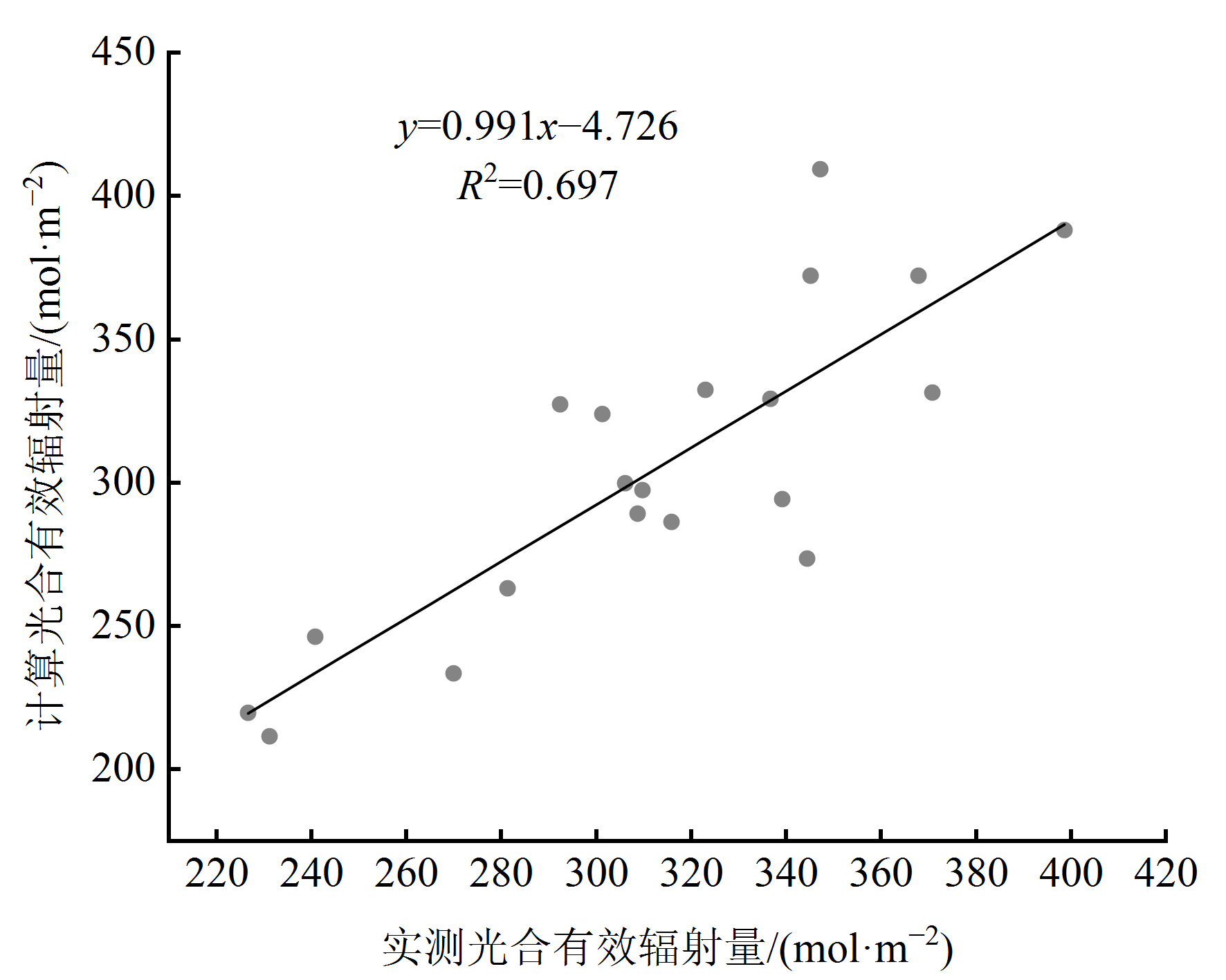
图2 隆宝站点观测得到的光合有效辐射与换算得到的光合有效辐射对比分析 黑色实线表示计算光合有效辐射量(y)与实测光合有效辐射量(x)的趋势线
Figure 2 Comparison analysis of measured PAR and calculated PAR of Longbao Station
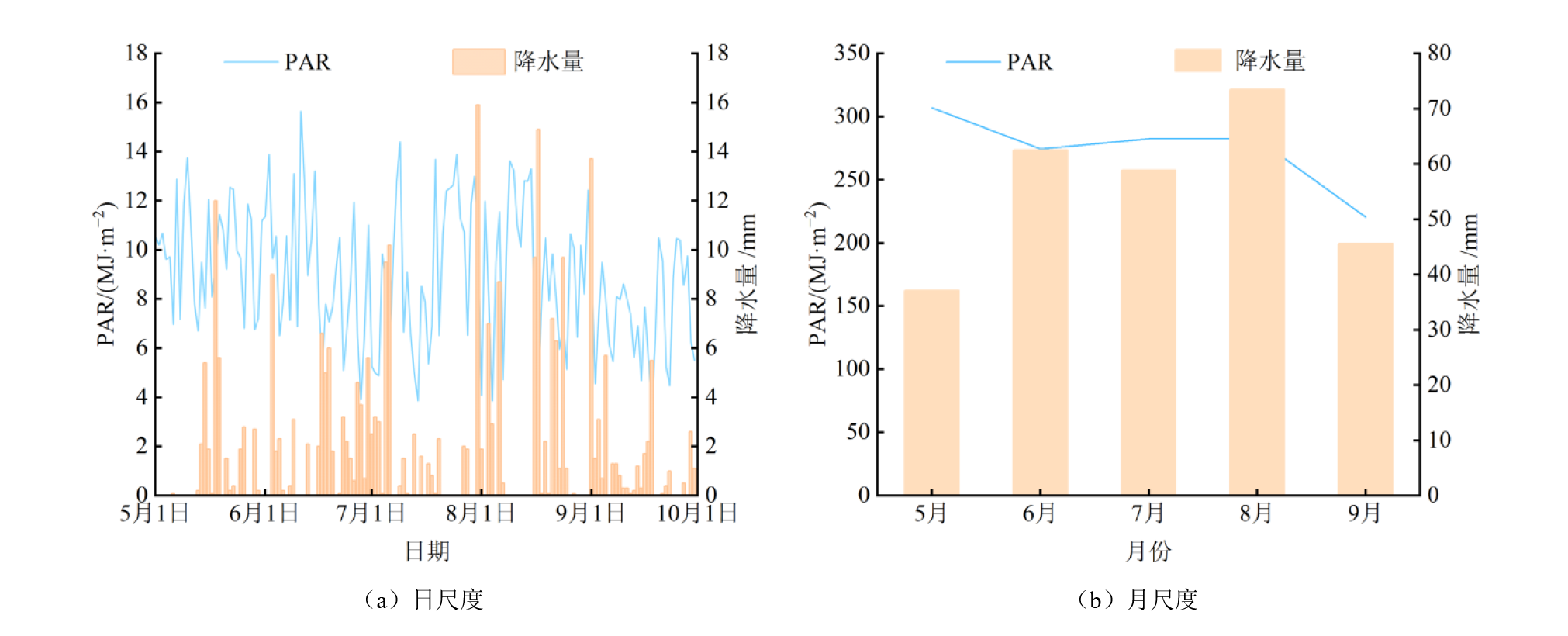
图3 2019年沱沱河生长季光合有效辐射PAR和降水量在日尺度和月尺度的分布特征
Figure 3 The daily and monthly distribution characteristics of the PAR and precipitation of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
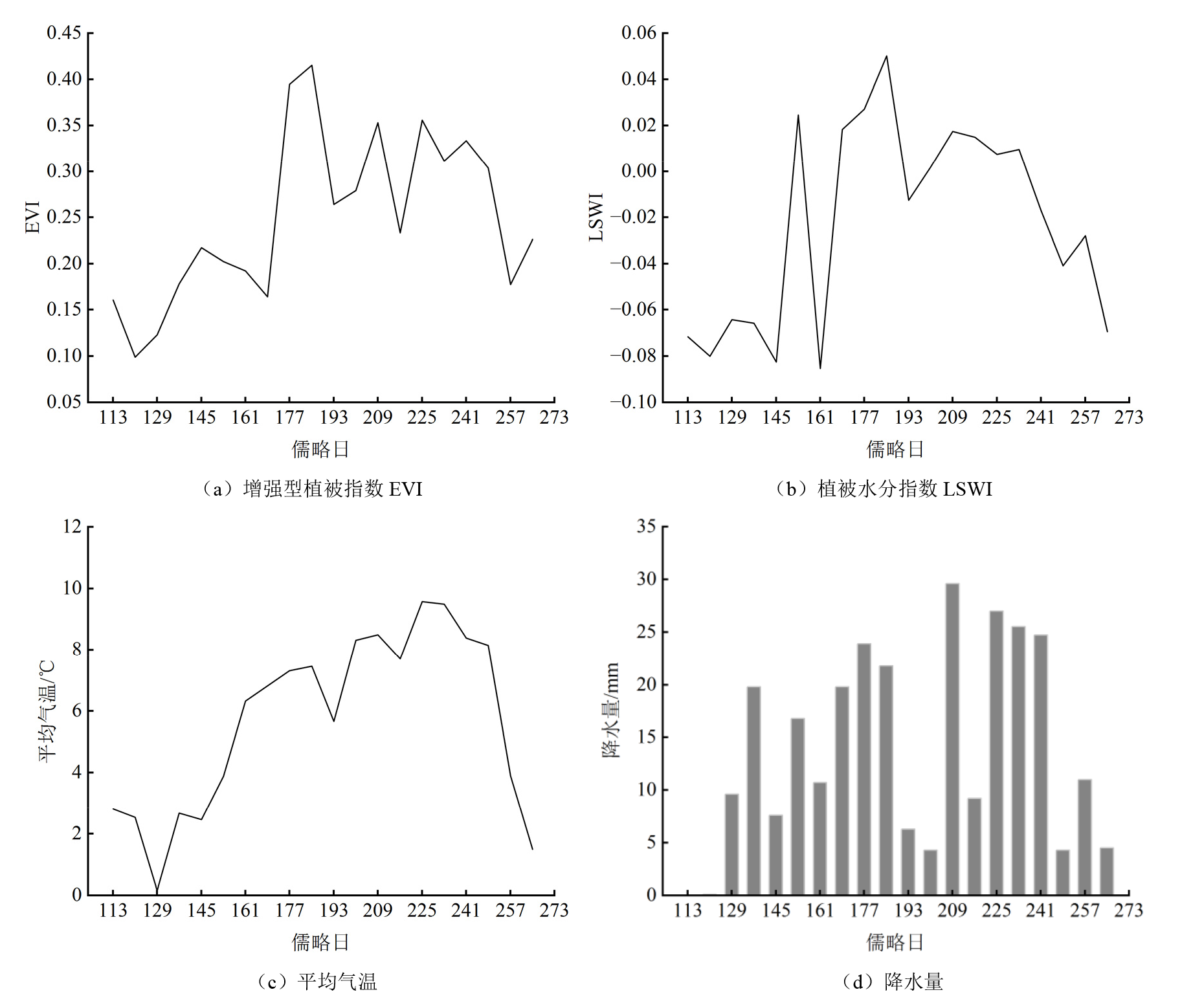
图4 2019年生长季沱沱河增强型植被指数EVI、植被水分指数LSWI、平均气温和降水量分布特征
Figure 4 The distribution characteristics of EVI, LSWI, mean temperature and precipitation of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
| 参数 | λ/(μmol) | P0/(μmol·m−2·s−1) | α/(μmol·m−2·s−1) | β/(μmol·m−2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0.119 | 64.920 | 0.034 | 0.217 |
表1 VPRM模型参数
Table 1 Parameters of VPRM
| 参数 | λ/(μmol) | P0/(μmol·m−2·s−1) | α/(μmol·m−2·s−1) | β/(μmol·m−2·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 值 | 0.119 | 64.920 | 0.034 | 0.217 |
| 不同时间尺度 | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE | 平均误差MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 0.462 | 0.805 | 0.561 |
| 昼夜 | 0.713 | 0.473 | 0.342 |
表2 2019年生长季沱沱河站点观测得到的NEE和模拟得到的NEE在30 min和昼夜时间尺度上的统计分析
Table 2 Statistical analysis between simulated NEE and measured NEE in 30min and day and night of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
| 不同时间尺度 | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE | 平均误差MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 0.462 | 0.805 | 0.561 |
| 昼夜 | 0.713 | 0.473 | 0.342 |
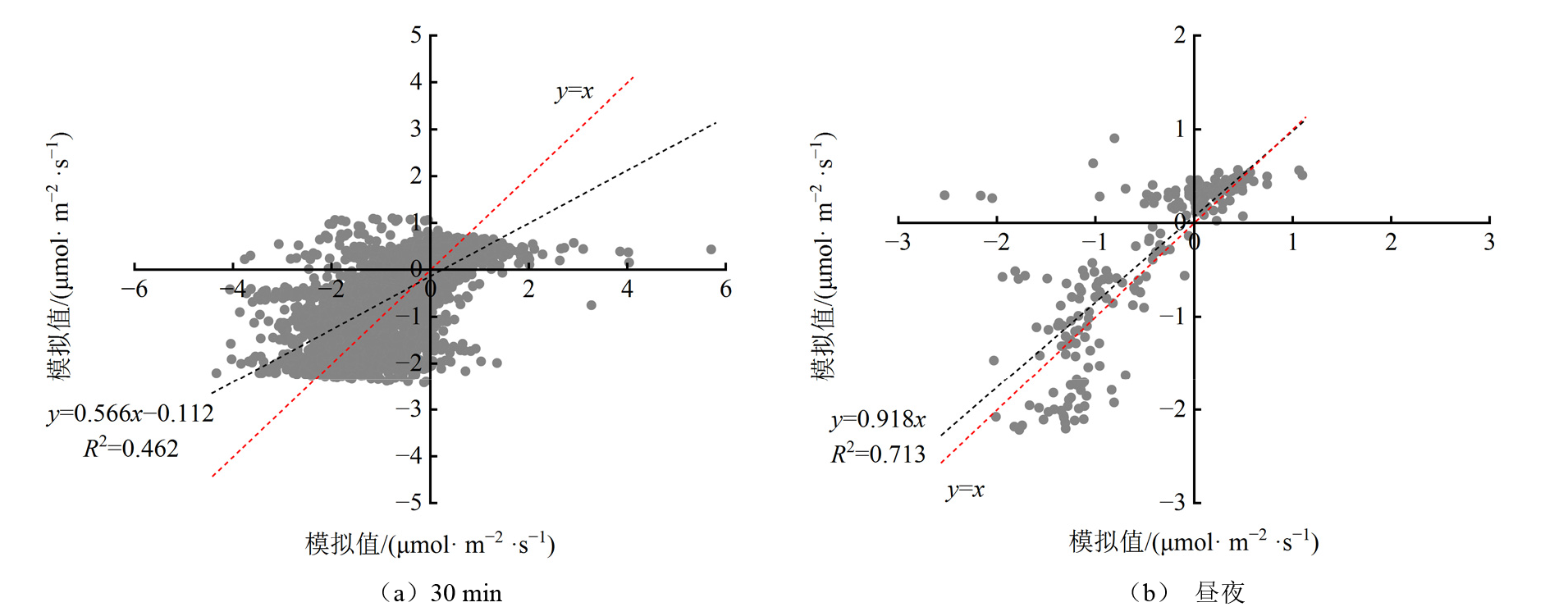
图7 2019年生长季沱沱河站点观测得到的NEE和模拟得到的NEE在30 min和昼夜时间尺度上对比分析 红色虚线表示y=x线,黑色虚线表示实测值与模拟值趋势线。下同
Figure 7 Comparative analysis between simulated NEE and measured NEE in 30min and day and night of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
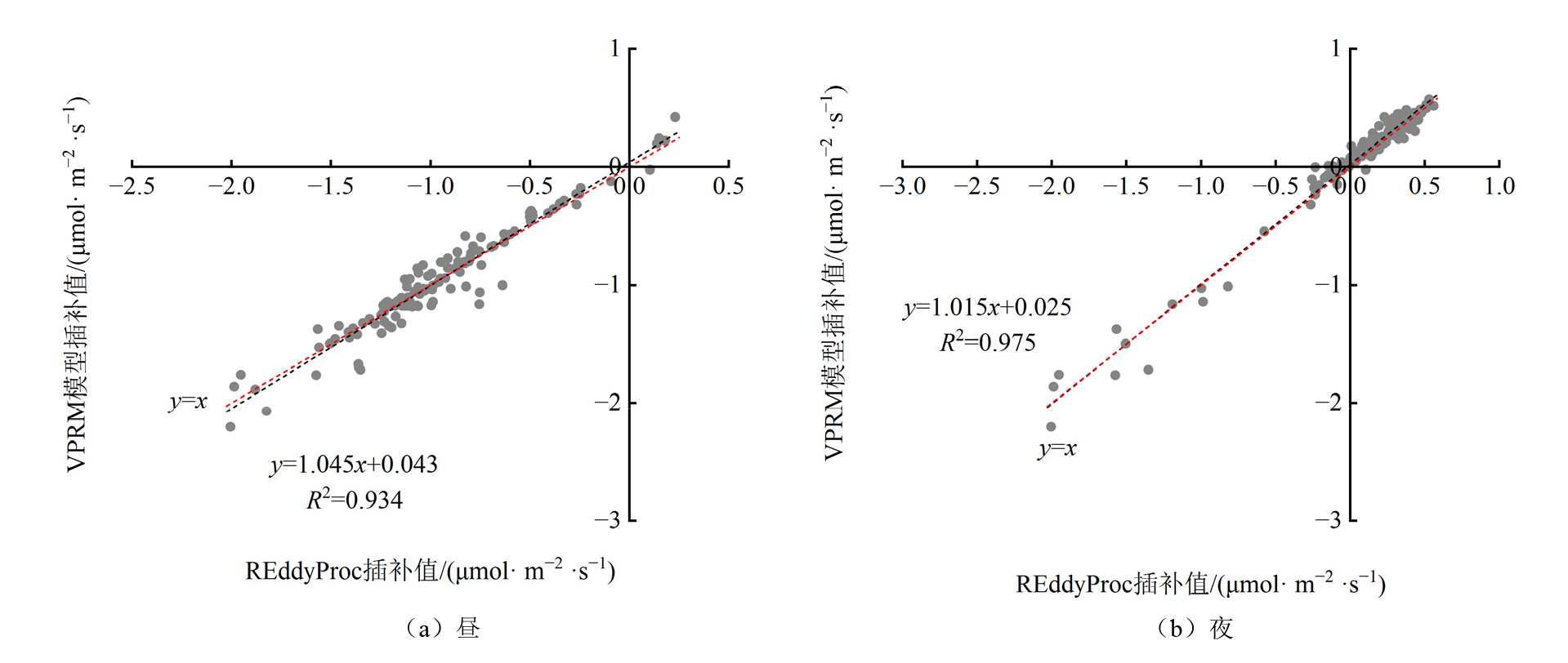
图8 2019年生长季昼和夜REddyProc程序和VPRM模型插补观测NEE数据分析
Figure 8 The analysis of measured NEE imputed by VPRM model and REddyProc in day and night of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
| 不同天气条件 | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE | 平均误差MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 晴天 | 0.829 | 0.346 | 0.267 |
| 多云 | 0.747 | 0.449 | 0.326 |
| 阴雨天 | 0.717 | 0.531 | 0.436 |
表3 2019年植被生长季晴天、多云和阴雨天模拟得到的NEE与通量站点观测的NEE之间的统计分析
Table 3 Statistical analysis between simulated NEE by VPRM model and measured NEE of sunny, cloudy and rainy days of the Tuotuohe during growing season in 2019
| 不同天气条件 | 决定系数R2 | 均方根误差RMSE | 平均误差MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 晴天 | 0.829 | 0.346 | 0.267 |
| 多云 | 0.747 | 0.449 | 0.326 |
| 阴雨天 | 0.717 | 0.531 | 0.436 |
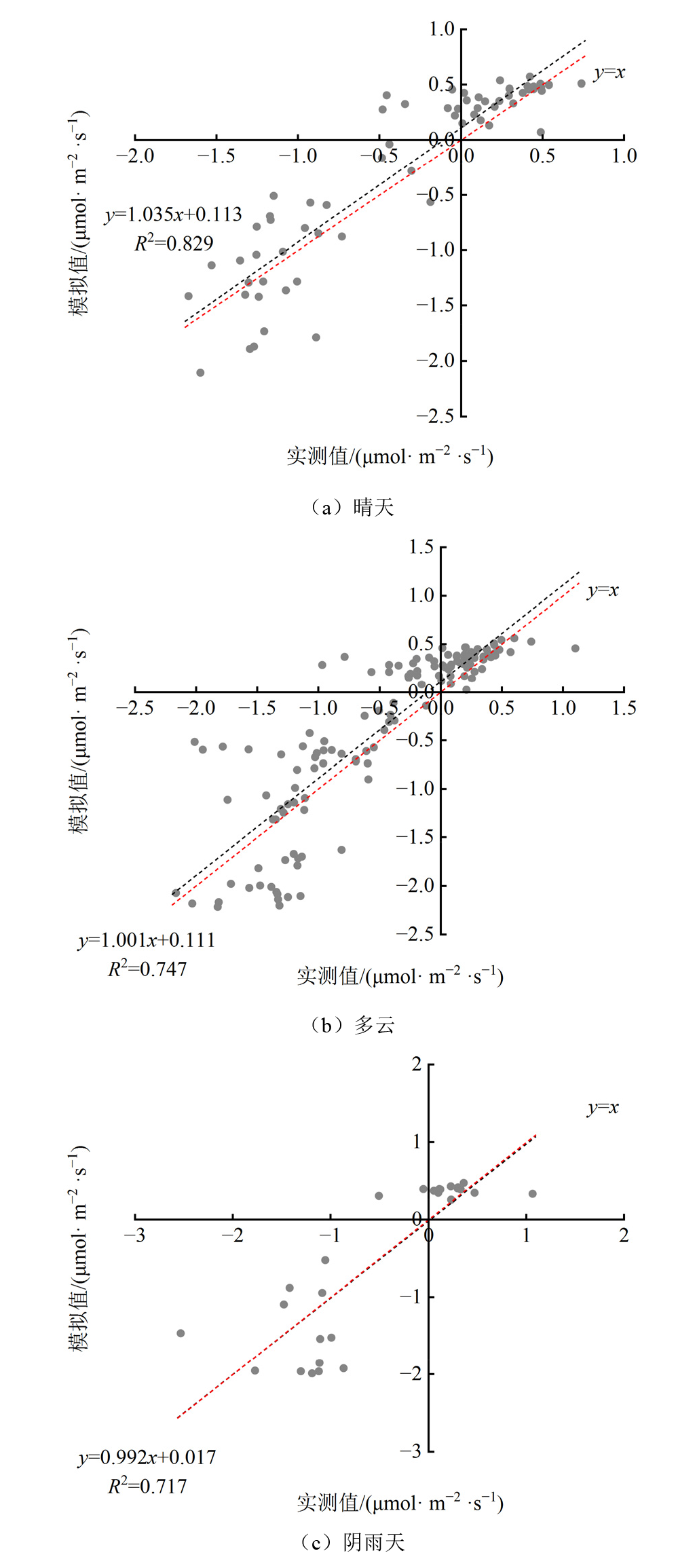
图9 2019年沱沱河晴天、多云和阴雨天实测NEE和模型模拟值对比分析
Figure 9 The comparison for NEE between measured and model simulated values on sunny, cloudy, and rainy days in the Tuotuo River in 2019
| [1] | FANG Q Q, WANG G Q, LIU T X, et al., 2018. Controls of carbon flux in a semi-arid grassland ecosystem experiencing wetland loss: Vegetation patterns and environmental variables[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 259(2):196-210. |
| [2] | HAN J G, ZHANG Y J, WANG C J, et al., 2008. Rangeland degradation and restoration management in China[J]. The Rangeland Journal, 30:233-239. |
| [3] | HARDIMAN B S, WANG J A, HUTYRA L R, et al., 2017. Accounting for urban biogenic fluxes in regional carbon budgets[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 592:366-372. |
| [4] | HILTON T W, DAVIS K J, KELLER K, et al., 2013. Improving North American terrestrial CO2 flux diagnosis using spatial structure in land surface model residuals[J]. Biogeosciences, 10(7):4607-4625. |
| [5] | MAHADEVAN P, WOFSY S C, MATROSS D M, et al., 2008. A satellite-based biosphere parameterization for net ecosystem CO2 exchange: Vegetation Photosynthesis and Respiration Model (VPRM)[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 22(2):1-17. |
| [6] | TURNER D, RITTS W, COHEN W, et al., 2006. Evaluation of MODIS NPP and GPP products across multiple biomes[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 102(3-4):282-292. |
| [7] | XIAO J F, CHEVALLIER F, GOMEZ C, et al., 2019. Remote sensing of the terrestrial carbon cycle: A review of advances over 50 years[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 233:111383. |
| [8] | XIAO X M, ZHANG Q Y, SALESKA S, et al., 2005. Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in a seasonally moist tropical evergreen forest[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 94(1):105-122. |
| [9] |
安克俭, 魏霞, 赵恒策, 等, 2021. 长江源区高寒草原和高寒草甸土壤粒径分布特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(2):433-440.
DOI |
| AN K J, WEI X, ZHAO H C, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of soil particle size in alpine steppe and alpine meadow in the source region of the Yangtze River[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(2):433-440. | |
| [10] | 常雅轩, 于颖, 崔绿园, 等, 2017. 基于HJ-1A星HSI数据的植被吸收光合有效辐射APAR估算[J]. 森林工程, 33(2):22-32. |
| CHANG Y X, YU Y, CUI L Y, et al., 2017. Vegetation absorbed photosynthetically active radiation estimates based on HJ 1A satellite HSI data[J]. Forest Engineering, 33(2):22-32. | |
| [11] | 丁蕾, 2021. 东北草地生产能力模拟与时空变化分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院: 1-15. |
| DING L, 2021. Simulating production capacity of grassland in northeastern china and analysising its spatiotemporal patterns[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: 1-15. | |
| [12] | 方精云, 于贵瑞, 任小波, 等, 2015. 中国陆地生态系统固碳效应——中国科学院战略性先导科技专项 “应对气候变化的碳收支认证及相关问题” 之生态系统固碳任务群研究进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 30(6):848-857. |
| FANG J Y, YU G R, REN X B, et al., 2015. Carbon sequestration in china's terrestrial ecosystems under climate change: Progress on ecosystem carbon sequestration from the CAS strategic priority research program[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 30(6):848-857. | |
| [13] | 高艳妮, 2014. 基于MODIS数据的陆地生态系统碳收支遥感模型研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 1-14. |
| GAO Y N, 2014. Modeling carbon budget of terrestrial ecosystem based solely on MODIS data[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-14. | |
| [14] | 郝勇, 2020. 典型陆地生态系统碳循环观测及模型优化[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学: 1-8. |
| HAO Y, 2020. Field observation and model optimization of carbon cycle in typical terrestrial ecosystems[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: 1-8. | |
| [15] | 江东, 王乃斌, 杨小唤, 等, 2002. 吸收光合有效辐射的时序变化特征及与作物产量之间的响应关系[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 18(1):51-54. |
| JIANG D, WANG N B, YANG X H, et al., 2002. Dynamic properties of absorbed photosynthetic active eadiation and its relation to crop yield[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 18(1):51-54. | |
| [16] | 兰垚, 2020. 基于VPRM模型的青海湖流域植被碳利用效率模拟研究[D]. 西宁: 青海师范大学: 1-7. |
| LAN Y, 2020. A simulation study on carbon use efficiency of vegetation in Qinghai Lake basin based on the VPRM model[D]. Xining: Qinghai Normal University: 1-7. | |
| [17] | 李宇环, 2013. 台湾亚热带云雾林碳通量模拟[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 1-8. |
| LI Y H, 2013. Modeling the net ecosystem exchange of carbon dioxide for a subtropical mountain cloud forest in Taiwan[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 1-8. | |
| [18] |
刘诚, 黄建平, 刁一伟, 2015. 植被光合呼吸模型在千烟洲亚热带常绿针叶林的优化及验证[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(4):388-397.
DOI |
|
LIU C, HUANG J P, DIAO Y W, et al., 2015. Optimization and evaluation of vegetation photosynthesis and respiration model using the measurements collected from the forest site of subtropical coniferous-evergreen[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(4):388-397.
DOI |
|
| [19] | 刘可群, 黎明锋, 杨文刚, 2008. 大棚小气候特征及其与大气候的关系[J]. 气象, 34(7):101-107. |
| LIU K Q, LI M F, YANG W G, 2008. Microclimatic characteristics under plastic film and relationship with macroclimate[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 34(7):101-107. | |
| [20] | 刘敏, 2008. 基于RS和GIS的陆地生态系统生产力估算及不确定性研究——以青藏高原草地样带为例[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学:41-76. |
| LIU M, 2008. Study on estimation and uncertainty of terrestrial ecosystem productivity based on RS and GIS: Take the grassland transect in Tibetan Plateau for example[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University:41-76. | |
| [21] | 刘宪锋, 任志远, 林志慧, 等, 2013. 2000-2011年三江源区植被覆盖时空变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 68(7):897-908. |
| LIU X F, REN Z Y, LIN Z H, et al., 2013. The spatial temporal changes of vegetation coverage in the Three River Headwater Region in recent 12 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(7):897-908. | |
| [22] | 乔英, 马英杰, 辛明亮, 2023. 基于REddyProc的干旱区枣林通量数据插补及能量平衡分析[J]. 林业科学, 59(8):1-11. |
| QIAO Y, MA Y J, XIN M L, 2023. Flux data interpolation and energy balance analysis of jujube forests in arid areas by employing REddyProc[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 59(8):1-11. | |
| [23] | 秦大河, 2014. 三江源区生态保护与可持续发展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-5. |
| QIN D H, 2014. Ecological protection and sustainable development in Sanjiangyuan[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-5. | |
| [24] | 王伟, 方青青, 王国强, 等, 2018. 呼伦贝尔草原区CO2源、汇及时空分布模拟研究[J]. 生态学报, 38(20):7288-7299. |
| WANG W, FANG Q Q, WANG G Q, et al., 2018. Simulation of CO2 source, sink, and flux temporal and spatial distributions in Hulun Buir grassland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(20):7288-7299. | |
| [25] | 王秀英, 周秉荣, 苏淑兰, 等, 2023. 青藏高原高寒草甸和荒漠碳交换特征及其气象影响机制[J]. 生态学报, 43(3):1194-1208. |
| WANG X Y, ZHOU B R, SU S L, et al., 2023. Carbon exchange characteristics and meteorological influence mechanism of Alpine Meadow and Desert in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(3):1194-1208. | |
| [26] |
项子源, 王钧, 王伟民, 2020. 亚热带城市高温对城市生态系统碳通量的抑制作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(9):1810-1821.
DOI |
| XIANG Z Y, WANG J, WANG W M, 2020. Study on high temperature constraints on urban ecosystem carbon fluxes in a subtropical city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(9):1810-1821. | |
| [27] | 许学莲, 许圆圆, 何生录, 等, 2020. 长江源头气候变化及其对牧草生育期的影响分析[J]. 青海草业, 29(4):18-29. |
| XU X L, XU Y Y, HE S L, et al., 2020. Analysis of climate change at the source of Yangtze River and its influence on herbage growth period[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 29(4):18-29. | |
| [28] | 岳广阳, 赵林, 赵拥华, 等, 2010. 青藏高原草地生态系统碳通量研究进展[J]. 冰川冻土, 32(1):166-174. |
| YUE G Y, ZHAO L, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2010. Research advances of grassland ecosystem CO2 flux on Qinghai-Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 32(1):166-174. | |
| [29] | 张嘉荣, 王咏薇, 张弥, 等, 2017. 植被光合呼吸模型在长白山温带阔叶红松林的优化及验证[J]. 生态学报, 37(20):6679-6690. |
| ZHANG J R, WANG Y W, ZHANG M, et al., 2017. Optimization and validation of the vegetation photosynthesis and respiration model in a temperate broad-leaved Korean pine forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(20):6679-6690. | |
| [30] |
张琦, 苏永红, 冯起, 等, 2022. 以地下水位估算的荒漠河岸胡杨 (Populus euphratica) 林生态系统地下水蒸散发[J]. 中国沙漠, 42(6):243-254.
DOI |
| ZHANG Q, SU Y H, FENG Q, et al., 2022. Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration of Populus euphratica forest ecosystem along desert river banks based on groundwater level dynamics[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 42(6):243-254. | |
| [31] |
张文奇, 赵媛媛, 赖宗锐, 等, 2024. 基于ANUSPLIN模型的柴达木盆地2000-2019年降水时空格局[J]. 高原气象, 43(3):737-748.
DOI |
|
ZHANG W Q, ZHAO Y Y, LAI Z R, et al., 2024. Spatiotemporal patterns of precipitation in Qaidam Basin from 2000 to 2019 base on the ANUSPLIN model[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 43(3):737-748.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 赵宁, 周蕾, 庄杰, 等, 2021. 中国陆地生态系统碳源/汇整合分析[J]. 生态学报, 41(19):7648-7658. |
| ZHAO N, ZHOU L, ZHUANG J, et al., 2021. Integration analysis of the carbon sources and sinks in terrestrial ecosystems, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(19):7648-7658. |
| [1] | 夏凡, 韩怡蒙, 周剑兴, 谢丹妮. 氮和硫在人为扰动的青藏高原高寒森林中的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 689-698. |
| [2] | 陈弘杰, 廖洪凯, 龙健, 赵雨鑫, 湛凯翔, 冉泰山, 杨国梅. 强还原土壤灭菌对土壤原生生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 539-547. |
| [3] | 张传光, 沈艳, 张珊珊, 李玉文, 陈剑, 杨文忠. 原生与迁地毛枝五针松根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1544-1553. |
| [4] | 李勋, 张艳, 宋思梦, 周扬, 张健. 西南地区马尾松与乡土阔叶树种凋落叶混合分解过程中的细菌群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 12-27. |
| [5] | 袁茜, 傅开道, 陶雨晨, 张年, 杨丽莎. 澜沧江(云南段)水-气界面氧化亚氮释放通量时空分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 54-61. |
| [6] | 苗敬杰, 张开, 孟钰博, 王乃加, 李海楠, 郭康军, 张君, 高西宁, 王立为. 覆膜垄作对旱地雨养马铃薯田N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 62-71. |
| [7] | 顾美英, 唐光木, 张云舒, 黄建, 张志东, 张丽娟, 朱静, 唐琦勇, 楚敏, 徐万里. 有机肥与生物炭对新疆盐碱沙化土壤微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1392-1404. |
| [8] | 刘紫薇, 葛继稳, 王月环, 杨诗雨, 姚东, 谢金林. 大九湖泥炭湿地甲烷通量变异特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 706-714. |
| [9] | 朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [10] | 张涵, 唐常源, 禤映雪, 江涛, 黄品怡, 杨秋, 曹英杰. 珠江口红树林土壤甲烷和二氧化碳通量特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 939-948. |
| [11] | 陈丽娟, 周文君, 易艳芸, 宋清海, 张一平, 梁乃申, 鲁志云, 温韩东, MOHD Zeeshan, 沙丽清. 云南哀牢山亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤CH4通量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 949-960. |
| [12] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [13] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [14] | 杨贤房, 陈朝, 郑林, 万智巍, 陈永林, 王远东. 稀土矿区不同土地利用类型土壤细菌群落特征及网络分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 793-801. |
| [15] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
