生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1495-1505.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.10.001
• 碳循环与碳减排专栏 •
下一篇
常博然1,*( ), 陈茹岚1,*, 王彪1, 蓝天2, 邓琳2, 薛会英3,**(
), 陈茹岚1,*, 王彪1, 蓝天2, 邓琳2, 薛会英3,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-16
出版日期:2024-10-18
发布日期:2024-11-15
通讯作者:
**薛会英。E-mial: xhytibetan@xza.edu.cn作者简介:常博然(1999年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为森林土壤资源化。E-mial: 1139844860@qq.com第一联系人:*陈茹岚为共同第一作者
基金资助:
CHANG Boran1,*( ), CHEN Rulan1,*, WANG Biao1, LAN Tian2, DENG Lin2, XUE Huiying3,**(
), CHEN Rulan1,*, WANG Biao1, LAN Tian2, DENG Lin2, XUE Huiying3,**( )
)
Received:2024-07-16
Online:2024-10-18
Published:2024-11-15
摘要:
了解藏东南折拉山森林土壤有机碳及其组分分布特征,对区域内森林可持续发展和管理保护具有重要意义。在研究区折拉山选取川滇高山栎(Quercus aquifolioides)、察隅冷杉(Abies chayuensis)、密枝圆柏(Juniperus convallium)、大果红杉(Larix potaninii)等4种森林,采集林下0-20、20-40 cm土壤样品,探究森林类型和不同深度土壤有机碳(SOC)、微生物量碳(MBC)、水溶解性土壤有机碳(WSOC)、土壤易氧化有机碳(ROC)、土壤颗粒有机碳(POC)、矿质结合态有机碳(MAOC)、稳定态有机碳(NOC)的分布情况,阐明SOC及其组分与土壤理化性质的相关性和主要影响因子。结果表明:4种森林类型土壤SOC及其组分(MBC除外)含量随土层深度的增加而减小,且不同土层间差异显著(p<0.05);各层土壤中密枝圆柏的各项碳组分在不同森林类型间均为最高。0-40 cm土层,土壤ROC、NOC、POC含量均表现为:密枝圆柏林>察隅冷杉林>大果红杉林>川滇高山栎林。相关性分析表明:土壤SOC与ROC和NOC、ROC与POC呈极显著正相关(p<0.01);WSOC与POC和ROC、NOC与POC呈极显著正相关(p<0.01);土壤酸碱性(pH)与SOC、WSOC、ROC、POC呈极显著正相关(p<0.01);土壤全钾(TK)与WSOC、POC和MOAC呈极显著负相关(p<0.01)。冗余分析表明:土壤硝态氮(NO3−-N)、全氮(TN)、土壤含水率(SWC)、电导率(EC)是影响4种森林类型土壤SOC及其组分的主要影响因子。综上,折拉山4种森林类型间土壤SOC及其组分的含量存在差异性,且受到土层深度的影响呈现出表聚性;土壤SOC及其组分的含量受土壤理化指标影响较大,其他因子对其影响较小。
中图分类号:
常博然, 陈茹岚, 王彪, 蓝天, 邓琳, 薛会英. 藏东南折拉山不同林分类型土壤有机碳及其组分分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1495-1505.
CHANG Boran, CHEN Rulan, WANG Biao, LAN Tian, DENG Lin, XUE Huiying. Characteristics of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Component Distribution in Different Forest Stand Types on Mount Zola in Southeastern Tibet[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(10): 1495-1505.
| 森林类型 | 川滇高山栎 Quercus aquifolioides | 察隅冷杉 Abies chayuensis | 密枝圆柏 Juniperus convallium | 大果红杉 Larix potaninii |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编号 | GSL | LS | YB | HS |
| 土壤质地 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 砂壤土 |
| 海拔/m | 3351‒3405 | 3790‒3850 | 4073‒4165 | 4291‒4320 |
| 坡度/(°) 坡位 | 42‒48 中下 | 46‒50 中 | 26‒39 中下 | 35‒44 上 |
| 坡向/(°) | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 |
| 郁闭度 | 76‒78 | 60‒66 | 47‒59 | 36‒43 |
| 树高/m | 12.8±1.6 | 24.9±2.9 | 15.2±1.3 | 19.5±2.7 |
| 胸径/cm 林下主要物种 | 65.2±5.2 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、 8、9、10、11、12、13、14 | 114.5±2.5 15、16、17、18、19、20、 21、22、23、9、14 | 49.6±3.8 24、25、26、27、28、29、30、31、32、33、4、14、34、35、36 | 106.1±2.9 33、37、38、39、40、41 |
表1 样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic information about the sample plots
| 森林类型 | 川滇高山栎 Quercus aquifolioides | 察隅冷杉 Abies chayuensis | 密枝圆柏 Juniperus convallium | 大果红杉 Larix potaninii |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 编号 | GSL | LS | YB | HS |
| 土壤质地 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 壤土 | 砂壤土 |
| 海拔/m | 3351‒3405 | 3790‒3850 | 4073‒4165 | 4291‒4320 |
| 坡度/(°) 坡位 | 42‒48 中下 | 46‒50 中 | 26‒39 中下 | 35‒44 上 |
| 坡向/(°) | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 | 阳坡、半阳坡 |
| 郁闭度 | 76‒78 | 60‒66 | 47‒59 | 36‒43 |
| 树高/m | 12.8±1.6 | 24.9±2.9 | 15.2±1.3 | 19.5±2.7 |
| 胸径/cm 林下主要物种 | 65.2±5.2 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、 8、9、10、11、12、13、14 | 114.5±2.5 15、16、17、18、19、20、 21、22、23、9、14 | 49.6±3.8 24、25、26、27、28、29、30、31、32、33、4、14、34、35、36 | 106.1±2.9 33、37、38、39、40、41 |
| 森林 类型 | 土层/ cm | pH | 含水率 SWC/% | 电导率EC/ (μS∙cm−1) | 全钾 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 全磷 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 全氮 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 铵态氮 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | 硝态氮 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | 碳氮比 C/N | 微生物熵 qMB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 川滇高山栎 (GSL) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 5.25±0.03Ab 5.56±0.16Bb | 9.36±0.59Ac 10.30±1.04Ab | 14.31±0.69Ac 9.81±0.66Bc | 16.41±0.49Ac 22.42±1.16Bb | 0.77±0.14Ab 0.49±0.07Bb | 2.51±0.31Ac 1.06±0.13Ba | 11.08±1.81Ac 4.74±1.08Bc | 2.07±0.36Ac 0.85±0.25Bc | 15.63±2.93Ab 9.72±1.68Bb | 32.57±7.66Aa 18.56±1.90Ba |
| 察隅冷杉(LS) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 5.29±0.2Ab 5.75±0.11Bb | 12.73±0.98Ab 14.18±0.71Aa | 32.90±1.89Ab 17.41±1.17Bb | 20.29±0.86Ab 19.09±0.77Bc | 0.79±0.1Ab 0.44±0.12Bc | 2.25±0.09Ad 1.863±0.10Bb | 19.47±2.36Ab 11.32±1.13Ba | 2.16±0.31Ac 1.42±0.21Bb | 20.69±3.26Aa 18.73±2.48Ba | 28.86±3.31Aa 21.50±5.66Ba |
| 密枝圆柏(YB) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 6.71±0.15Aa 6.91±0.26Aa | 16.76±0.21Aa 8.13±0.28Bc | 56.84±1.51Aa 36.20±0.52Ba | 14.91±0.49Ad 16.55±0.67Bd | 1.17±0.06Aa 0.77±0.14Ba | 5.61±0.22Aa 2.60±0.206Bc | 67.02±6.08Aa 11.10±1.12Ba | 5.61±0.41Aa 3.02±0.46Ba | 14.74±0.70Abc 14.21±0.50Aab | 16.07±1.36Ab 10.03±1.46Bb |
| 大果红杉(HS) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 4.82±0.21Ac 5.40±0.21Bb | 9.49±0.59Ac 9.82±0.35Ab | 12.29±0.39Ac 6.27±0.49Bd | 31.74±0.92Aa 35.42±2.46Ba | 0.50±0.07Ac 0.49±0.09Ad | 3.21±0.14Ad 1.48±0.18Bd | 7.29±0.68Ad 6.75±0.68Ab | 2.61±0.40Ab 1.38±0.33Bb | 11.82±1.21Ac 17.60±5.05Ba | 14.16±0.30Ac 7.70±0.06Bb |
表2 不同森林类型下土壤理化性质及碳组分的特征值
Table 2 Characteristic values of soil physicochemical properties and carbon components under different forest types
| 森林 类型 | 土层/ cm | pH | 含水率 SWC/% | 电导率EC/ (μS∙cm−1) | 全钾 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 全磷 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 全氮 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | 铵态氮 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | 硝态氮 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | 碳氮比 C/N | 微生物熵 qMB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 川滇高山栎 (GSL) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 5.25±0.03Ab 5.56±0.16Bb | 9.36±0.59Ac 10.30±1.04Ab | 14.31±0.69Ac 9.81±0.66Bc | 16.41±0.49Ac 22.42±1.16Bb | 0.77±0.14Ab 0.49±0.07Bb | 2.51±0.31Ac 1.06±0.13Ba | 11.08±1.81Ac 4.74±1.08Bc | 2.07±0.36Ac 0.85±0.25Bc | 15.63±2.93Ab 9.72±1.68Bb | 32.57±7.66Aa 18.56±1.90Ba |
| 察隅冷杉(LS) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 5.29±0.2Ab 5.75±0.11Bb | 12.73±0.98Ab 14.18±0.71Aa | 32.90±1.89Ab 17.41±1.17Bb | 20.29±0.86Ab 19.09±0.77Bc | 0.79±0.1Ab 0.44±0.12Bc | 2.25±0.09Ad 1.863±0.10Bb | 19.47±2.36Ab 11.32±1.13Ba | 2.16±0.31Ac 1.42±0.21Bb | 20.69±3.26Aa 18.73±2.48Ba | 28.86±3.31Aa 21.50±5.66Ba |
| 密枝圆柏(YB) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 6.71±0.15Aa 6.91±0.26Aa | 16.76±0.21Aa 8.13±0.28Bc | 56.84±1.51Aa 36.20±0.52Ba | 14.91±0.49Ad 16.55±0.67Bd | 1.17±0.06Aa 0.77±0.14Ba | 5.61±0.22Aa 2.60±0.206Bc | 67.02±6.08Aa 11.10±1.12Ba | 5.61±0.41Aa 3.02±0.46Ba | 14.74±0.70Abc 14.21±0.50Aab | 16.07±1.36Ab 10.03±1.46Bb |
| 大果红杉(HS) | 0‒20 20‒40 | 4.82±0.21Ac 5.40±0.21Bb | 9.49±0.59Ac 9.82±0.35Ab | 12.29±0.39Ac 6.27±0.49Bd | 31.74±0.92Aa 35.42±2.46Ba | 0.50±0.07Ac 0.49±0.09Ad | 3.21±0.14Ad 1.48±0.18Bd | 7.29±0.68Ad 6.75±0.68Ab | 2.61±0.40Ab 1.38±0.33Bb | 11.82±1.21Ac 17.60±5.05Ba | 14.16±0.30Ac 7.70±0.06Bb |
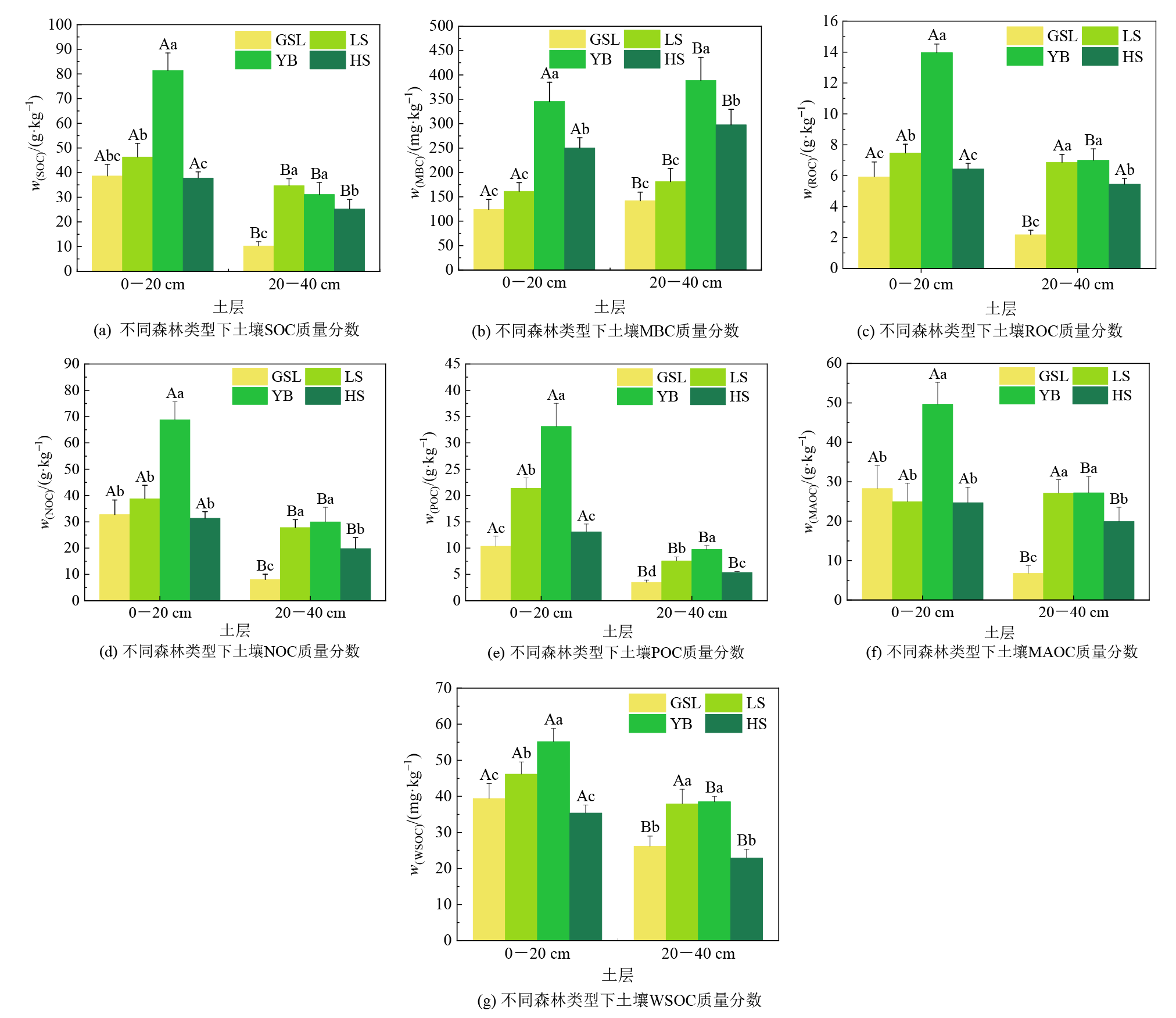
图2 不同森林类型下土壤有机碳及其组分质量分数 图中不同大写字母表示相同森林类型不同土层深度间差异显著(p<0.05),不同小写字母表示相同土层深度不同森林类型间差异显著(p<0.05)
Figure 2 Soil organic carbon and its component contents under different forest types

图3 不同森林类型下土壤有机碳组分及其特征值与理化性质的相关性特征 *表示在0.05水平呈显著相关性(p<0.05);**表示在0.01水平呈极显著相关性(p<0.01)
Figure 3 Characterization of soil organic carbon fractions and their eigenvalues in correlation with physicochemical properties under different forest types
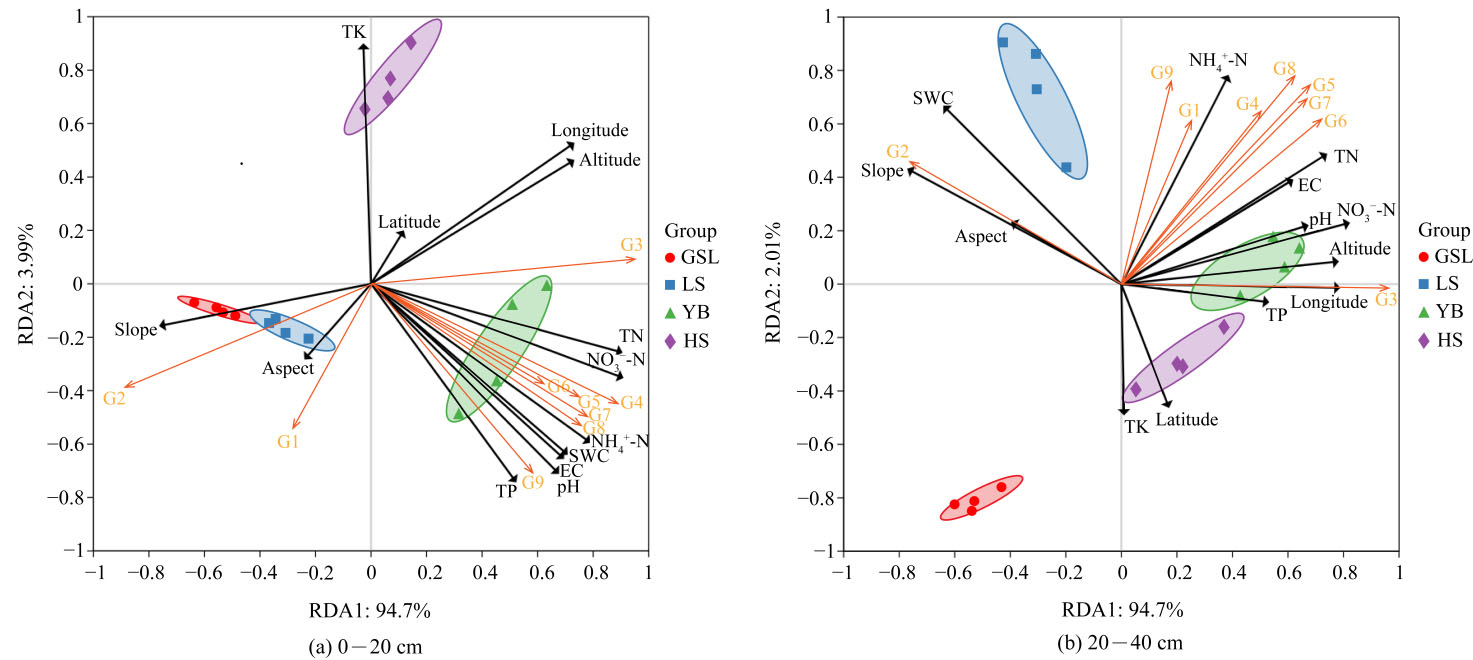
图4 土壤有机碳组分及其特征值与影响因子冗余分析(RDA) G1:qMB;G2:C/N;G3:MBC;G4:ROC;G5:SOC;G6:POC;G7:NOC;G8:MAOC;G9:WSOC;土壤含水量(SWC);pH:土壤酸碱度;EC:土壤电导率;TK:土壤全钾;TP:土壤全磷;TN:土壤全氮;NH4+-N:土壤铵态氮;NO3—N:土壤硝态氮;Longitude:经度;Latitude:纬度;Altitude:海拔;Slope:坡度;Aspect:坡向
Figure 4 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil organic carbon components, their characteristic values, and influencing factors
| [1] | BLAIR G J, LEFROY R, LISLE L, 1995. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems[J]. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 46(7): 1459. |
| [2] | CAMBARDELLA C A, ELLIOTT E T, 1992. Particulate soil organic-matter changes across a grassland cultivation sequence[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56(3): 777-783. |
| [3] |
CASTRO H F, CLASSEN A T, AUSTIN E E, et al., 2010. Soil microbial community responses to multiple experimental climate change drivers[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(4): 999-1007.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | CHEN X, TAYLOR A R, REICH P B, et al., 2023. Tree diversity increases decadal forest soil carbon and nitrogen accrual[J]. Nature, 618(7963): 94-101. |
| [5] | FANG C, MONCRIEFF J B, 2001. The dependence of soil CO2 effiux on temperature[J]. Soil Biology Biochemistry, 33(2): 155-165. |
| [6] |
HU M J, REN H C, REN P, et al., 2017. Response of gaseous carbon emissions to low-level salinity increase in tidal marsh ecosystem of the Min River estuary, southeastern China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 52: 210-222.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | KACHURINA O M, ZHANG H L, RAUN W R, et al., 2000. Simultaneous determination of soil aluminum, ammonium‐ and nitrate‐nitrogen using 1 M potassium chloride extraction[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. 31(7-8): 893-903 |
| [8] | KOOCH Y, SANJI R, TABARI M, 2019. The effect of vegetation change in C and N contents in litter and soil organic fractions of a Northern Iran temperate forest[J]. Catena, 178: 32-39. |
| [9] |
LAL R, 2004. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security[J]. Science, 304(5677): 1623-1627.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | LI M, 2022. Carbon stock and sink economic values of forest ecosystem in the forest industry region of Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 33(3): 875-882. |
| [11] | LU S B, XU Y, FU X P, et al., 2019. Soil carbon stocks in plantations and natural forests of the sub-tropics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(6): 478-486. |
| [12] |
MAO Z, CORRALES A, ZHU K, et al., 2019. Tree mycorrhizal associations mediate soil fertility effects on forest community structure in a temperate forest[J]. New Phytologist, 223(1): 475-486.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | PRESTON C M, BHATTI J S, FLANAGAN B, et al., 2006. Stocks, chemistry, and sensitivity to climate change of dead organic matter along the Canadian boreal forest transect case study[J]. Climatic Change, 74(1): 223-251. |
| [14] | QI H S, ZHAO Y, WANG X, et al., 2021. Manganese dioxide driven the carbon and nitrogen transformation by activating the complementary effects of core bacteria in composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 330: 124960. |
| [15] | RATH K M, ROUSK J, 2015. Salt effects on the soil microbial decomposer community and their role in organic carbon cycling: A review[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 81: 108-123. |
| [16] | ROBLEDANO A F, ROMERO D A, BELMONTE S F, et al., 2014. Ecogeomorphological consequences of land abandonment in semiarid Mediterranean areas: Integrated assessment of physical evolution and biodiversity[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 197: 222-242. |
| [17] | SUN Y M, CHEN X L, ZHONG A N, et al., 2023. Variations in microbial residue and its contribution to SOC between organic and mineral soil layers along an altitude gradient in the Wuyi Mountains[J]. Forests, 14(8): 1678. |
| [18] | VANCE E D, BROOKES P C, JENKINSON D S, 1987. Microbial biomass measurements in forest soils: the use of the chloroform fumigation- incubation method in strongly acid soils[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 19(6): 697-702. |
| [19] | WYNN J G, BIRD M I, VELLEN L, et al., 2006. Continental-scale measurement of the soil organic carbon pool with climatic, edaphic, and biotic controls[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 20(1): GB1007. |
| [20] |
YANG M X, GUO Q W, TONG T L, et al., 2017. Vegetation type and layer depth influence nitrite-dependent methane-oxidizing bacteria in constructed wetland[J]. Archives of microbiology, 199(3): 505-511.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | ZHAO Z Z, ZHAO Z Y, FU B, et al., 2021. Characteristics of soil organic carbon fractions under different land use patterns in a tropical area[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21(2): 689-697. |
| [22] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 2022. 中国森林土壤有机碳活性组分及其影响因素[J]. 世界林业研究, 35(1): 76-81. |
| DU X, WANG H Y, 2022. Organic carbon activity fractions of Chinese forest soils and their influencing factors[J]. World Forestry Research, 35(1): 76-81. | |
| [23] |
樊廷录, 王淑英, 周广业, 等, 2013. 长期施肥下黑垆土有机碳变化特征及碳库组分差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 46(2): 300-309.
DOI |
| FAN T L, WANG S Y, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2013. Characteristics of organic carbon changes and differences in carbon pool fractions in black clay soil under long-term fertilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 46(2): 300-309. | |
| [24] | 樊子豪, 崔鸿侠, 沈琛琛, 等, 2024. 神农架林区天然次生林土壤有机碳分布及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 44(16): 1-10. |
| FAN Z H, CUI H X, SHEN C C, et al., 2024. Distribution and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in natural secondary forests of Shennongjia forest area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44(16): 1-10. | |
| [25] | 方华军, 耿静, 程淑兰, 等, 2019. 氮磷富集对森林土壤碳截存的影响研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 56(1): 1-11. |
| FANG H J, GENG J, CHENG S L, et al., 2019. Progress of research on the effect of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on carbon sequestration in forest soils[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 56(1): 1-11. | |
| [26] | 方晰, 2004. 杉木人工林生态系统碳贮量与碳平衡的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林学院. |
| FANG X, 2004. Research on carbon storage and carbon balance of fir plantation forest ecosystem[D]. Changsha: Central South Forestry University. | |
| [27] |
郭璐璐, 李安迪, 商宏莉, 等, 2018. 川西贡嘎山不同森林生态系统土壤有机碳垂直分布与组成特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 39(10): 636-643.
DOI |
| GUO L L, LI A D, SHANG H L, et al., 2018. Vertical distribution and compositional characteristics of soil organic carbon in different forest ecosystems of Gongga Mountain, West Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 39(10): 636-643. | |
| [28] | 黄斌, 王泉泉, 李定强, 等, 2022. 南岭山地土壤有机碳及组分海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 土壤通报, 53(2): 374-383. |
| HUANG B, WANG Q Q, LI D Q, et al., 2022. Characteristics of soil organic carbon and component changes along an altitudinal gradient in the Nanling mountain area[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 53(2): 374-383. | |
| [29] | 胡海清, 罗斯生, 罗碧珍, 等, 2020. 林火干扰对森林生态系统土壤有机碳的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 40(6): 1839-1850. |
| HU H Q, LUO S S, LUO B Z, et al., 2020. Progress of research on the effects of forest fire disturbance on soil organic carbon in forest ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(6): 1839-1850. | |
| [30] | 胡海清, 陆昕, 孙龙, 2012. 土壤活性有机碳分组及测定方法[J]. 森林工程, 28(5): 18-22. |
| HU H Q, LU X, SUN L, 2012. Soil reactive organic carbon grouping and determination[J]. Forest Engineering, 28(5): 18-22. | |
| [31] | 何吉成, 罗天祥, 徐雨晴, 2009. 藏东南色季拉山急尖长苞冷杉 (Abies georgei var. smithii) 林线的生态气候特征[J]. 生态学报, 29(1): 37-46. |
| HE J C, LUO T X, XU Y Q, 2009. Ecoclimatic characteristics of Abies georgei var. smithii forest line in the Sertila Mountains, Southeast Tibet[J]. Journal of Ecology, 29(1): 37-46. | |
| [32] | 李双智, 2016. 中国岩须属植物分类与分布[D]. 昆明: 西南林业大学. |
| LI S Z, 2016. Classification and geographical distribution of cassiope in China[D]. Kunming: Southwest Forestry University. | |
| [33] | 黎萱, 陈东毅, 李良安, 等, 2024. 高寒草甸土壤有机碳活性组分对灌丛化的响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 44(3): 317-325, 334. |
| LI X, CHEN D Y, LI L A, et al., 2024. Response of soil organic carbon active fractions to scrub fertilization in alpine meadows[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Bulletin, 44(3): 317-325, 334. | |
| [34] | 李永涛, 魏海霞, 王莉莉, 等, 2024. 凋落物输入变化对黄河三角洲柽柳人工林土壤有机碳及其组分的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 52(7): 64-70. |
| LI Y T, WEI H X, WANG L L, et al., 2024. Effects of changes in apoplastic inputs on soil organic carbon and its fractions in tamarisk plantation forests in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 52(7): 64-70. | |
| [35] |
林丹丹, 毕华兴, 赵丹阳, 等, 2024. 晋西黄土区不同密度刺槐林土壤有机碳组分及碳库特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(3): 379-388.
DOI |
| LIN D D, BI H X, ZHAO D Y, et al., 2024. Soil organic carbon fractions and carbon pool characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia forests with different densities in the loess region of western Shanxi province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 33(3): 379-388. | |
| [36] | 刘江伟, 徐海东, 林同岳, 等, 2022. 海涂围垦区不同林分土壤活性有机碳垂直变化特征[J]. 林业科学研究, 35(3): 18-26. |
| LIU J W, XU H D, LIN T Y, et al., 2022. Characteristics of vertical changes in soil reactive organic carbon in different forest stands in a seawater swidden area[J]. Forest Research, 35(3): 18-26. | |
| [37] | 马和平, 郭其强, 刘合满, 等, 2013. 藏东南色季拉山西坡土壤有机碳库研究[J]. 生态学报, 33(10): 3122-3128. |
| MA H P, GUO Q Q, LIU H M, et al., 2013. Soil organic carbon pools on the western slopes of the Sertila Mountains, Southeast Tibet[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(10): 3122-3128. | |
| [38] | 申楷慧, 魏识广, 李林, 等, 2024. 漓江流域喀斯特森林土壤有机碳空间分布格局及其驱动因子[J]. 环境科学, 45(1): 323-334. |
| SHEN K H, WEI S G, LI L, et al., 2024. Spatial distribution patterns of soil organic carbon in Karst Forests of the Lijiang River basin and Its driving factors[J]. Environmental Science, 45(1): 323-334. | |
| [39] | 苏涵, 王维, 张巧凤, 等, 2023. 土壤矿质氮及其测定方法研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 51(24): 24-26, 30. |
| SU H, WANG W, ZHANG Q F, et al., 2023. Research progress of soil mineral nitrogen and its determination methods[J]. Anhui Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 51(24): 24-26, 30. | |
| [40] | 王春燕, 何念鹏, 吕瑜良, 2016. 中国东部森林土壤有机碳组分的纬度格局及其影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 36(11): 3176-3188. |
| WANG C Y, HE N P, LÜ Y L, 2016. Latitudinal patterns of soil organic carbon fractions in forests of eastern China and their influencing factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(11): 3176-3188. | |
| [41] | 肖思颖, 付芳伟, 李江荣, 等, 2023. 色季拉山6种典型林型土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 43(11): 120-130, 172. |
| XIAO X Y, FU F W, LI J R, et al., 2023. Characteristics of soil ecological stoichiometry in six typical forest types in the Sertila Mountains[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 43(11): 120-130, 172. | |
| [42] | 肖文发, 朱建华, 曾立雄, 等, 2023. 森林碳汇助力碳中和的几点认识[J]. 林业科学, 59(3): 1-11. |
| XIAO W F, ZHU J H, ZENG L X, et al., 2023. Several perspectives on forest carbon sink for promoting carbon neutrality[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 59(3): 1-11. | |
| [43] | 殷一丹, 鱼腾飞, 韩拓, 等, 2024. 黑河下游胡杨林土壤碳空间分异特征及其影响因素[J/OL]. 干旱区地理, 1-12 [2024-10-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/65.1103.X.20240809.1644.002.html. |
| YIN Y D, YU T F, HAN T, et al., 2024. Characteristics of spatial differentiation of soil carbon in poplar forests in the lower reaches of the Black River and its influencing factors[J/OL]. Geography of arid zones, 1-12 [2024-10-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/65.1103.X.20240809.1644.002.html. | |
| [44] | 杨静, 张耀艺, 谭思懿, 等, 2022. 中亚热带不同树种对土壤团聚体组成及其碳、氮含量的影响[J]. 林业科学, 58(4): 51-61. |
| YANG J, ZHANG Y Y, TAN S Y, et al., 2022. Effects of different tree species on the compositions of soil aggregates and their carbon and nitrogen concentrations in Mid-Subtropical Forests[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 58(4): 51-61. | |
| [45] | 袁毅, 2023. 长期不同施肥模式对土壤有机碳库的影响及其微生物作用机制[D]. 济南: 山东农业大学. |
| YUAN Y, 2023. Effects of different long-term fertilization patterns on soil organic carbon pools and their microbial mechanisms of action[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Agricultural University. | |
| [46] | 张常仁, 杨雅丽, 程全国, 等, 2020. 不同耕作模式对东北黑土微生物群落结构和酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 9(4): 335-347. |
| ZHANG C R, YANG Y L, CHENG Q G, et al., 2020. Effects of different tillage patterns on microbial community structure and enzyme activities in northeastern black soils of China[J]. Soils and Crops, 9(4): 335-347. | |
| [47] | 张敏, 2022. 刺槐人工林土壤有机碳库变化特征及其微生物驱动机制[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| ZHANG M, 2022. Changes of soil organic carbon pool in robinia locust plantation and its microbial driving mechanism[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University. | |
| [48] | 张鹏, 张涛, 陈年来, 2009. 祁连山北麓山体垂直带土壤碳氮分布特征及影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 20(3): 518-524. |
| ZHANG P, ZHANG T, CHEN N L, 2009. Characteristics of soil carbon and nitrogen distribution in the vertical zone of the northern Qilian Mountains and the factors affecting it[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(3): 518-524. | |
| [49] | 张莹, 2024. 贵州喀斯特地区马尾松林地下系统 (根系和土壤) 植硅体碳固存特征研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学. |
| ZHANG Y, 2024. Characterization of carbon sequestration in phyllosilicon bodies in the subsurface system (root system and soil) of the Mastodon pine forest in Karst region of Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University. | |
| [50] | 张于光, 宿秀江, 王敏, 等, 2014. 不同天然落叶阔叶林的土壤有机碳和微生物结构特征[J]. 土壤通报, 45(3): 625-629. |
| ZHANG Y G, SU X J, WANG M, et al., 2014. The characteristics of soil organic carbon and soil microbial community structure in two deciduous broadleaved forest types[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 45(3): 625-629. | |
| [51] | 赵彦坤, 张文胜, 王幼宁, 等, 2008. 高pH对植物生长发育的影响及其分子生物学研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 1(3): 783-787. |
| ZHAO Y K, ZHANG W S, WANG Y N, et al., 2008. Effects of high pH on plant growth and development and its progress in molecular biology[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 1(3): 783-787. | |
| [52] | 周晨霓, 马和平, 2013. 西藏色季拉山典型植被类型土壤活性有机碳分布特征[J]. 土壤学报, 50(6): 1246-1251. |
| ZHOU C N, MA H P, 2013. Characteristics of soil reactive organic carbon distribution in typical vegetation types of the Sertila Mountains, Tibet[J]. Soil Journal, 50(6): 1246-1251. |
| [1] | 李建付, 黄志霖, 和成忠, 姜昕, 宋琳, 刘佳鑫, 陈利顶. 滇东喀斯特断陷盆地土壤有机碳空间分布特征及其关键影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1339-1352. |
| [2] | 石含之, 熊振乾, 曹怡然, 吴志超, 文典, 李富荣, 李冬琴, 王旭. 外源秸秆添加对红壤及黑土有机碳固定的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1372-1383. |
| [3] | 罗庆, 何清, 吴慧秋, 寇力月, 方旭, 张鑫雨, 李缘, 柴育廷, 张瑞生, 代文举. 辽河口湿地土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 333-340. |
| [4] | 林丹丹, 毕华兴, 赵丹阳, 管凝, 韩金丹, 郭艳杰. 晋西黄土区不同密度刺槐林土壤有机碳组分及碳库特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 379-388. |
| [5] | 张桂芹, 王云博, 杜琪玥, 闫怀忠, 李思源, 石敬华, 刘仕杰, 朱文祺, 孙友敏. 济南市柴油型移动源排放颗粒物中碳组分特征和排放量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 408-417. |
| [6] | 李瑞, 王邵军, 兰梦杰, 罗双, 夏佳慧, 杨胜秋, 解玲玲, 肖博, 郭晓飞, 王郑钧, 郭志鹏. 石漠化土壤碳矿速率对丛枝菌根真菌接种的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1506-1515. |
| [7] | 王郑钧, 王邵军, 肖博, 解玲玲, 郭志鹏, 张昆凤, 张路路, 樊宇翔, 郭晓飞, 罗双, 夏佳慧, 李瑞, 杨胜秋, 兰梦杰. 西双版纳热带森林土壤有机碳积累-分配动态对蚂蚁筑巢活动的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 35-44. |
| [8] | 梁鑫, 韩亚峰, 郑柯, 王旭刚, 陈志怀, 杜鹃. 磁铁矿对稻田土壤碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1615-1622. |
| [9] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [10] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [11] | 张怀成, 韩红, 王在峰, 韩立钊, 刘克, 张桂芹, 范晶, 魏小锋. 济南市城市扬尘的微观形貌和化学组分特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 545-555. |
| [12] | 秦佳琪, 肖指柔, 明安刚, 朱豪, 滕金倩, 梁泽丽, 陶怡, 覃林. 针阔人工混交林及其纯林对土壤微生物碳循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1719-1731. |
| [13] | 肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764. |
| [14] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [15] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 李祥东, 陈静, 张晓龙, 陈金洁, 刘科学. 东南湿润区典型丹霞地貌土壤有机碳组分及其敏感性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1132-1140. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
