生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1326-1339.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.005
孙梦鑫1,2( ), 张岳1,2, 辛宇1,2, 钟鼎杰1,2, 杨存建1,2,*(
), 张岳1,2, 辛宇1,2, 钟鼎杰1,2, 杨存建1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-09-20
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*杨存建(1967年生),男,教授,博士研究生导师,主要从事遥感与GIS应用研究。E-mail: yangcj2008@126.com作者简介:孙梦鑫(1995年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事资源环境遥感与GIS应用研究。E-mail: mengxinsun916@gmail.com
基金资助:
SUN Mengxin1,2( ), ZHANG Yue1,2, XIN Yu1,2, ZHONG Dingjie1,2, YANG Cunjian1,2,*(
), ZHANG Yue1,2, XIN Yu1,2, ZHONG Dingjie1,2, YANG Cunjian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-20
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
植被物候是植被生长发育、枯萎凋落的周期性变化现象,揭示植被物候变化及其对水热因子的响应机制具有重要的生态意义。采用两种动态阈值分别提取川西高原近20 a森林植被、草地的生长季开始期(Start of Growing Season,SOS)和生长季结束期(End of Growing Season,EOS),利用Theil-Sen Median(Sen)趋势分析、偏相关系数分析植被物候的变化特征及其对季节性气温、降水的响应。结果表明,(1)川西高原植被平均SOS以70—130 d为主,平均EOS以260—290 d为主;植被SOS整体呈提前趋势、EOS整体呈推迟趋势,SOS的平均变化速率大于EOS;植被SOS平均提前速率为2.4 d∙(10 a)-1(α=0.05),EOS平均推迟速率为1.4 d∙(10 a)-1(α=0.05);草地和森林植被SOS平均提前速率大致相同,分别为2.4 d∙(10 a)-1、2.3 d∙(10 a)-1;草地EOS平均推迟速率1.4 d∙(10 a)-1,小于森林植被2.2 d∙(10 a)-1。(2)温度是影响植被SOS、EOS变化的主要因素。春季温度上升导致大部分植被SOS提前,这种现象在草地和森林植被间都很常见;冬季温度上升并不能使植被SOS出现普遍提前,且由于冬季温度升高可能会影响植被的春化作用,部分植被SOS甚至与冬季温度呈正相关;秋季温度上升是植被EOS推迟的主要因素,对草地的影响尤其显著;部分植被EOS与夏季温度呈负相关,这可能与夏季温度上升产生的水分胁迫以及植被生长周期的提前结束有关。(3)冬春季降水对植被SOS的影响不明显;夏季降水减少虽然对EOS有提前效应,但秋季降水增加以及升温对植被EOS的推迟作用强于夏季降水减少所带来的影响。
中图分类号:
孙梦鑫, 张岳, 辛宇, 钟鼎杰, 杨存建. 川西高原近20 a植被物候变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1326-1339.
SUN Mengxin, ZHANG Yue, XIN Yu, ZHONG Dingjie, YANG Cunjian. Changes of Vegetation Phenology and Its Response to Climate Change in the West Sichuan Plateau in the Past 20 Years[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1326-1339.
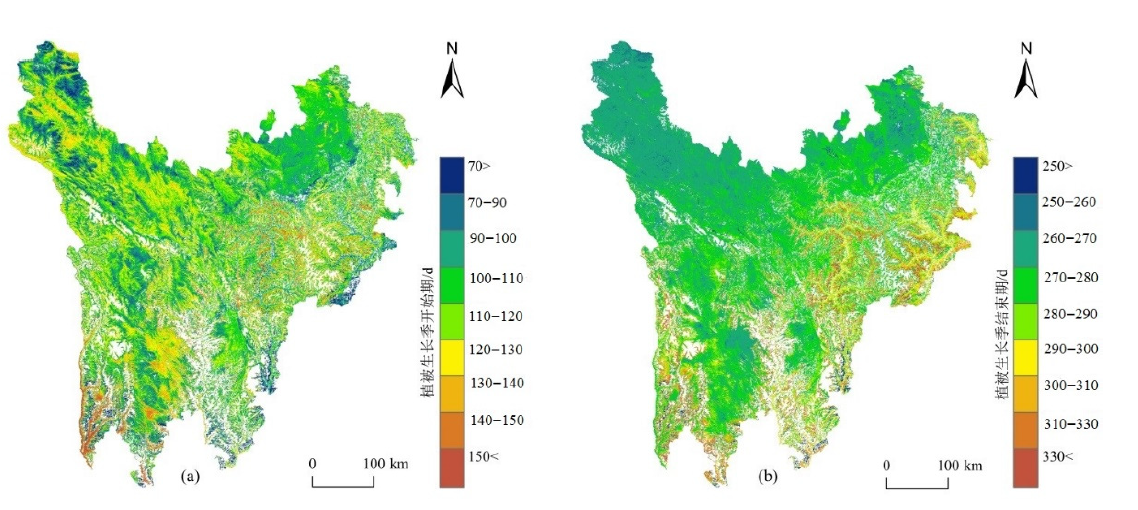
图4 2001—2020年川西高原植被SOS、EOS均值空间分布
Figure 4 Spatial distribution of mean values of SOS and EOS of vegetation on the western Sichuan Plateau from 2001 to 2020
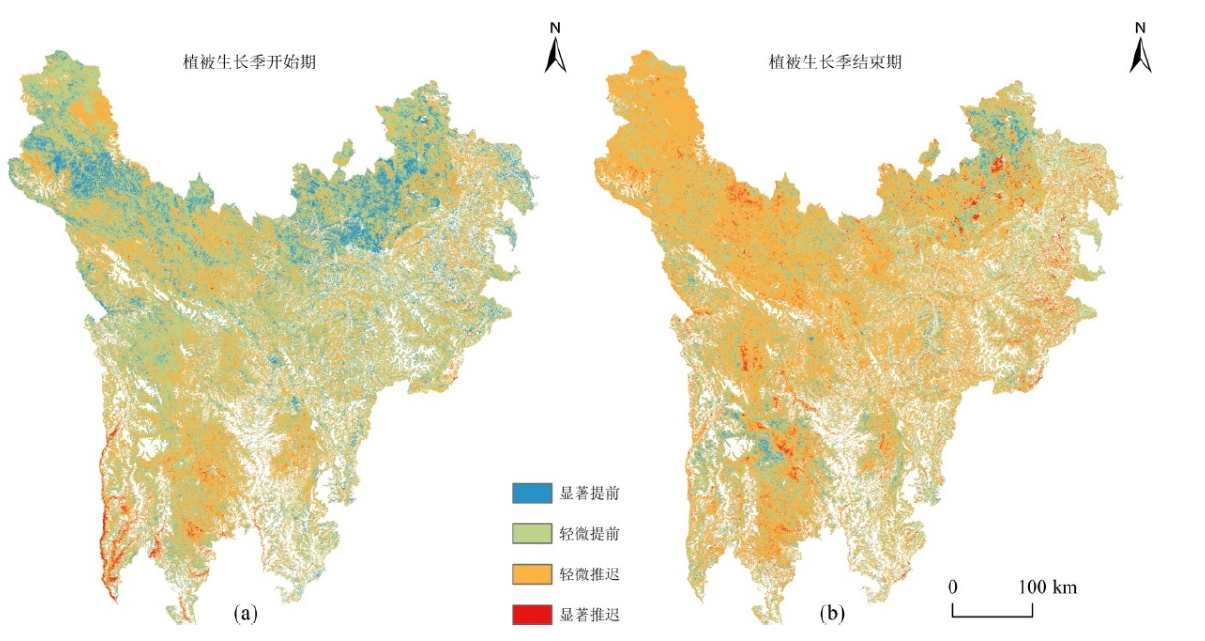
图9 2001—2020年川西高原植被物候变化空间分布特征
Figure 9 Spatial distribution characteristics of vegetation phenology changes in the Western Sichuan Plateau from 2001 to 2020
| 植被物候 Vegetation Phenology | 显著提前 Significant Advance | 轻微提前 Slight Advance | 显著推迟 Significant Delay | 轻微推迟 Slight Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草地Grassland SOS | 13.36 | 52.67 | 1.37 | 32.6 |
| 草地Grassland EOS | 4.3 | 33.71 | 3.08 | 58.91 |
| 森林植被 Forest SOS | 11.85 | 52.97 | 1 | 34.18 |
| 森林植被 Forest EOS | 4.17 | 42.54 | 5.23 | 48.06 |
表1 川西高原植被物候变化各类型所占百分比
Table 1 Percentage of various types of vegetation phenology changes in the Western Sichuan Plateau %
| 植被物候 Vegetation Phenology | 显著提前 Significant Advance | 轻微提前 Slight Advance | 显著推迟 Significant Delay | 轻微推迟 Slight Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草地Grassland SOS | 13.36 | 52.67 | 1.37 | 32.6 |
| 草地Grassland EOS | 4.3 | 33.71 | 3.08 | 58.91 |
| 森林植被 Forest SOS | 11.85 | 52.97 | 1 | 34.18 |
| 森林植被 Forest EOS | 4.17 | 42.54 | 5.23 | 48.06 |
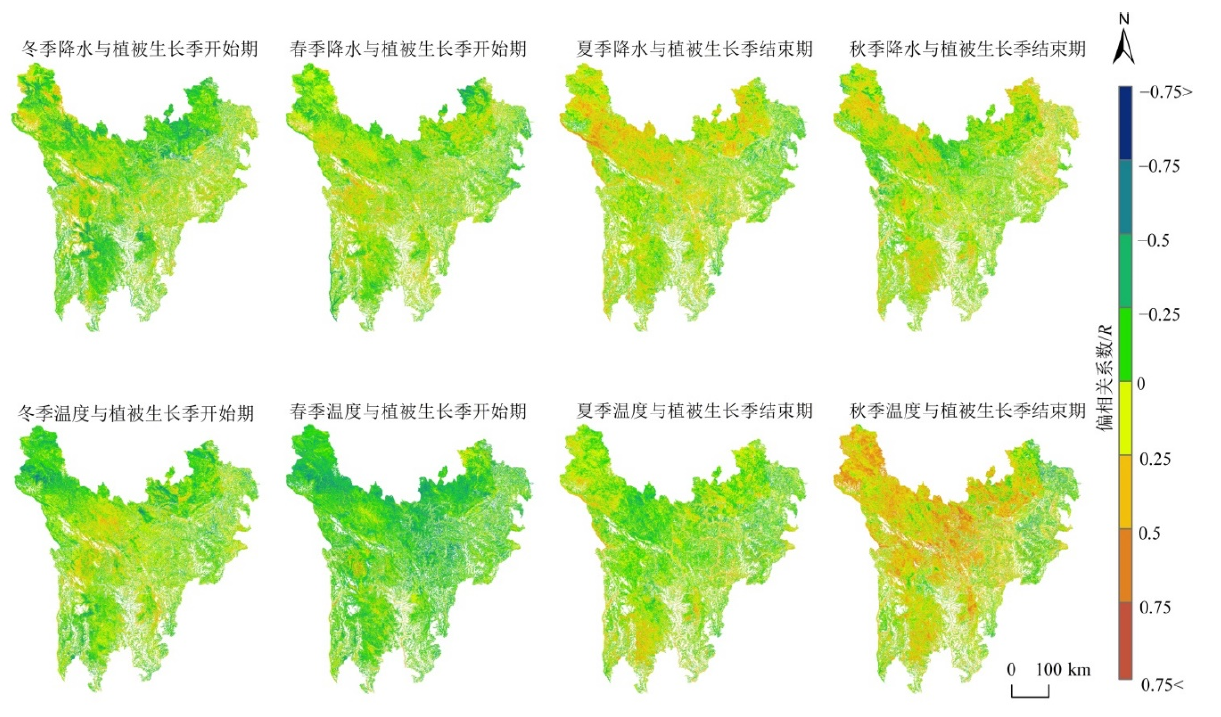
图11 2001—2020年川西高原植被物候与季节性温度、降水的偏相关系数
Figure 11 Partial correlation coefficients of vegetation phenology, seasonal temperature and precipitation in the western Sichuan Plateau from 2001 to 2020
| [1] |
CHEN L, HÄNNINEN H, ROSSI S, et al., 2020. Leaf senescence exhibits stronger climatic responses during warm than during cold autumns[J]. Nature Climate Change, 10(8): 777-780.
DOI URL |
| [2] | CHRISTOPHER B F, VICENTE R B, DAVID J D, et al., 2014. Climate Change 2014:Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [3] |
FRIEDL M A, MCIVER D K, HODGES J C F, et al., 2002. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: algorithms and early results[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(1): 287-302.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FU Y H, ZHAO H F, PIAO S L, et al., 2015. Declining global warming effects on the phenology of spring leaf unfolding[J]. Nature, 526(7571): 104-107.
DOI URL |
| [5] | JONSSON P, EKLUNDH L, 2002. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 40(8): 1824-1832. |
| [6] |
JONSSON P, EKLUNDH L, 2004. TIMESAT-a program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 30(8): 833-845.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU Q, FU Y H, ZENG Z Z, et al., 2016. Temperature, precipitation, and insolation effects on autumn vegetation phenology in temperate China[J]. Global Change Biology, 22(2): 644-655.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU X D, CHEN B D, 2000. Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 20(14): 1729-1742.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PIAO S L, CUI M D, CHEN A P, et al., 2011. Altitude and temperature dependence of the change in the spring vegetation green up data from1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai Xizang Plateau[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(12): 1599-1608.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
RAN Y H, LI X, LU L, et al., 2012. Large-scale land cover mapping with the integration of multi-source information based on the Dempster- Shafer theory[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 26(1-2): 169-191.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SHEN M G, ZHANG G X, CONG N, et al., 2014. Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 189-190: 71-80.
DOI URL |
| [12] | SHI Y, WANG Y, MA Y, et al., 2014. Field-based observations of regional-scale, temporal variation in net primary production in Tibetan alpine grasslands[J]. Biogeosciences, 11(10): 16843-16878. |
| [13] |
WANG H J, WU C Y, CIAIS P, et al., 2020. Overestimation of the effect of climatic warming on spring phenology due to misrepresentation of chilling[J]. Nature Communications, 11(1): 4945.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG X F, XIAO J F, LI X, et al., 2019. No trends in spring and autumn phenology during the global warming hiatus[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
YING H, ZHANG H Y, ZHAO J J, et al., 2020. Effects of spring and summer extreme climate events on the autumn phenology of different vegetation types of Inner Mongolia, China, from 1982 to 2015 [J]. Ecological Indicators, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105974.
DOI |
| [16] | YU H Y, EIKE L, XU J C, et al., 2010. Winter and spring warming result in delayed spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(51): 22151-22156. |
| [17] |
YU H Y, XU J C, ERICK O, et al., 2012. Seasonal Response of Grasslands to Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plos One, 7(11): e49230.
DOI URL |
| [18] | ZHANG G L, ZHANG Y J, DONG J W, et al., 2013. Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011 [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(11): 4309-4314. |
| [19] |
ZHANG W, WANG L C, XIANG F F, et al., 2020. Vegetation dynamics and the relations with climate change at multiple time scales in the Yangtze River and Yellow River Basin, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105892.
DOI |
| [20] |
ZHENG Z T, ZHU W Q, CHEN G S, et al., 2016. Continuous but diverse advancement of spring-summer phenology in response to climate warming across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 223: 194-202.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
曹沛雨, 张雷明, 李胜功, 等, 2016. 植被物候观测与指标提取方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 31(4): 365-376.
DOI |
| CAO P Y, ZHANG L M, LI S G, et al., 2016. Review on vegetation phenology observation and phenological index extraction[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 31(4): 365-376. | |
| [22] | 曹云, 钱永兰, 孙应龙, 等, 2020. 基于MODIS NDVI的西南森林植被时空变化特征及其气候响应分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(5): 857-865. |
| CAO Y, QIAN Y L, SUN Y L, et al., 2020. Spatial-temporal variations of forest vegetation and climatic driving force analysis in southwest China based on MODIS NDVI and climate data[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(5): 857-865 | |
| [23] |
陈效逑, 王林海, 2009. 遥感物候学研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 28(1): 33-40.
DOI |
| CHEN X Q, WANG L H, 2009. Progress in Remote Sensing Phenological Research[J]. Progress in Geography, 28(1): 33-40. | |
| [24] | 程琳琳, 李玉虎, 孙海元, 等, 2019. 京津冀MODIS长时序增强型植被指数拟合重建方法适用性研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 35(11): 148-158. |
| CHENG L L, LI Y H, SUN H Y, et al., 2019. Applicability of fitting and reconstruction method of MODIS long-time enhanced vegetation index in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 35(11): 148-158. | |
| [25] |
丛楠, 沈妙根, 2016. 1982-2009年基于卫星数据的北半球中高纬地区植被春季物候动态及其与气候的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(9): 2737-2746.
DOI |
|
CONG N, SHEN M G, 2016. Variation of satellite-based spring vegetation phenology and the relationship with climate in the Northern Hemisphere over 1982 to 2009 [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(9): 2737-2746.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 丁登, 陈效逑, 2007. 我国遥感植被生长季节的地面检验研究--以温带草原和暖温带落叶阔叶林区为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 22(3): 382-388. |
| DING D, CHEN X Q, 2007. A study on surface validation of the satellite-derived vegetation growing season in China: A case of the temperate steppe area and the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest area[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 22(3): 382-388. | |
| [27] | 范思睿, 范广洲, 董一平, 等, 2011. 青藏高原四季划分方法探讨[J]. 高原山地气象研究, 31(2): 1-11. |
| FAN S R, FAN G Z, DONG Y P, et al., 2011. Research of the seasonal division method on Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research, 31(2): 1-11. | |
| [28] | 何月, 樊高峰, 张小伟, 等, 2013. 浙江省植被物候变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 自然资源学报, 28(2): 220-233. |
| HE Y, FAN G F, ZHANG X W, et al., 2013. Vegetation phenological variation and its response to climate changes in Zhejiang province[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 28(2): 220-233. | |
| [29] | 胡顺石, 黄春晓, 杨斌, 等, 2020. 自适应加权Savitzky-Golay滤波重构MODIS植被指数时间序列[J]. 测绘科学, 45(4): 105-116. |
| HU S S, HUANG C X, YANG B, et al., 2020. Reconstruction of MODIS vegetation index time series by adaptive weighted Savitzky- Golay filter[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 45(4): 105-116. | |
| [30] | 吉珍霞, 裴婷婷, 陈英, 等, 2021. 黄土高原植被物候变化及其对季节性气候变化的响应[J]. 生态学报, 41(16): 1-13. |
|
JI Z X, PEI T T, CHEN Y, et al., 2021. Vegetation phenology change and its response to seasonal climate changes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(16): 1-13.
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 贾文雄, 赵珍, 俎佳星, 等, 2016. 祁连山不同植被类型的物候变化及其对气候的响应[J]. 生态学报, 36(23): 7826-7840. |
| JIA W X, ZHAO Z, ZU J X, et al., 2016. Phenological variation in different vegetation types and their response to climate change in the Qilian Mountains, China, 1982-2014 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(23): 7826-7840. | |
| [32] |
孔冬冬, 张强, 黄文琳, 等, 2017. 1982-2013年青藏高原植被物候变化及气象因素影响[J]. 地理学报, 72(1): 39-52.
DOI |
| KONG D D, ZHANG Q, HUANG W L, et al., 2017. Vegetation phenology change in Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2013 and its related meteorological factors[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(1): 39-52. | |
| [33] | 李荣平, 周广胜, 张慧玲, 2006. 植物物候研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 17(3): 3541-3544. |
| LI R P, ZHOU G S, ZHANG H L, 2006. Research advances in plant phenology[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(3): 3541-3544. | |
| [34] | 刘啸添, 周蕾, 石浩, 等, 2018. 基于多种遥感植被指数、叶绿素荧光与CO2通量数据的温带针阔混交林物候特征对比分析[J]. 生态学报, 38(10): 3482-3494. |
| LIU X T, ZHOU L, SHI H, et al., 2018. Phenological characteristics of temperate coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests based on multiple remote sensing vegetation indices, chlorophyll fluorescence and CO2 flux data[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(10): 3482-3494. | |
| [35] | 卢晨媛, 冯文兰, 王永前, 等, 2021. 不同深度土壤水分同化产品在川西高原的应用[J]. 水土保持通报, 41(1): 173-181. |
| LU C Y, FENG W L, WANG Y Q, et al., 2021. Application of soil moisture assimilation products at different depths in western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 41(1): 173-181. | |
| [36] |
冉有华, 李新, 卢玲, 2009. 基于多源数据融合方法的中国1 km土地覆盖分类制图[J]. 地球科学进展, 24(2): 192-203.
DOI |
| RAN Y H, LI X, LU L, et al., 2009. China land cover classification at 1 km spatial resolution based on a multi-source data fusion approach[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 24(2): 192-203. | |
| [37] | 宋春桥, 游松财, 柯灵红, 等, 2011. 藏北高原植被物候时空动态变化的遥感监测研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 35(8): 853-863. |
|
SONG C Q, YOU S C, KE L H, et al., 2011. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation phenology in the Northern Tibetan Plateau as detected by MODIS remote sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 35(8): 853-863.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 宋歌, 2020. 中国有热带稀树草原吗?[J]. 森林与人类, 40(11): 2. |
| SONG G, 2020. Does China has savanna?[J]. Forest & Humankind, 40(11): 2. | |
| [39] | 王贝贝, 周淑琴, 荆耀栋, 等, 2021. 山西省植被物候时空变化以及地形对物候的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(6): 1839-1848. |
| WANG B B, ZHOU S Q, JING Y D, et al., 2021. Temporal-spatial variations of vegetation phenology and the influence of topography on phenology in Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(6): 1839-1848. | |
| [40] | 王连喜, 陈怀亮, 李琪, 等, 2010. 植物物候与气候研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 30(2): 447-454. |
| WANG L X, CHEN H L, LI Q, et al., 2010. Research advances in plant phenology and climate[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(2): 447-454. | |
| [41] |
王庆莉, 王茹琳, 张利平, 等, 2021. 基于MaxEnt模型的川西高原松茸气候生态适宜性与潜在分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(7): 2525-2533.
DOI |
| WANG Q L, WANG R L, ZHANG L P, et al., 2021. Climatic ecological suitability and potential distribution of Tricholoma matsutake in western Sichuan Plateau, China based on MaxEnt model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(7): 2525-2533. | |
| [42] | 王云川, 2017. 2001-2015年川西高原植被物候时空变化特征及与气候变化的响应研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. |
| WANG Y C, 2017. Spatial-temporal variation and climate response of vegetation phenology in western Sichuan Plateau during 2001-2015 [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. | |
| [43] |
吴伟, 杨飞龄, 王军军, 等, 2021. 基于MODIS时序数据的中国西南地区主要植被生态系统干扰动态监测及分析[J]. 地理研究, 40(5): 1478-1494.
DOI |
| WU W, YANG F L, WANG J J, et al., 2021. Dynamic monitoring and analysis of ecosystem disturbances in major vegetation types based on MODIS time series data in Southwest China[J]. Geographical Research, 40(5): 1478-1494. | |
| [44] | 伍良旭, 王晗, 邵怀勇, 等, 2021. 川西高原植被时空格局及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 水土保持研究, 28(1): 171-178. |
| WU L X, WANG H, SHAO H Y, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal pattern of vegetation and its response to climate change in the western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(1): 171-178. | |
| [45] | 谢宝妮, 秦占飞, 王洋, 等, 2015. 基于遥感的黄土高原植被物候监测及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 农业工程学报, 31(15): 153-160. |
| XIE B N, QIN Z F, WANG Y, et al., 2015. Monitoring vegetation phenology and their response to climate change on Chinese Loess Plateau based on remote sensing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(15): 153-160. | |
| [46] | 徐满厚, 薛娴, 2013. 气候变暖对高寒地区植物生长与物候影响分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 27(3): 137-141. |
| XU M H, XUE X, 2013. Analysis on the effects of climate warming on growth and phenology of alpine plants[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 27(3): 137-141. | |
| [47] | 杨存建, 赵梓健, 任小兰, 等, 2012. 基于遥感和GIS的川西绿被时空变化研究[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 632-640. |
|
YANG C J, ZHAO Z J, REN X L, et al., 2012. The analysis of the green vegetation cover change in western Sichuan based on GIS and Remote sensing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(2): 632-640.
DOI URL |
|
| [48] | 杨琪, 李书恒, 李家豪, 等, 2021. 秦岭森林植被物候及其对气象因子的响应[J]. 干旱区研究, 38(4): 1065-1074. |
| YANG Q, LI S H, LI J H, et al., 2021. Phenology of forest vegetation and its response to climate change in the Qinling Mountains[J]. Arid Zone Research, 38(4): 1065-1074. | |
| [49] | 杨雪梅, 杨太保, 刘海猛, 等, 2016. 气候变暖背景下近30 a北半球植被变化研究综述[J]. 干旱区研究, 33(2): 379-391. |
| YANG X M, YANG T B, LIU H M, et al., 2016. Vegetation Variation in the North Hemisphere under Climate Warming in the Last 30 Years[J]. Arid Zone Research, 33(2): 379-391. | |
| [50] | 袁丽华, 蒋卫国, 申文明, 等, 2013. 2000-2010年黄河流域植被覆盖的时空变化[J]. 生态学报, 33(24): 7798-7806. |
| YUAN L H, JIANG W G, SHEN W M, et al., 2013. The spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2010 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(24): 7798-7806. | |
| [51] | 张婷, 薛东剑, 段金亮, 等, 2021. 2000-2019嘉陵江流域植被覆盖时空变化特征及气候响应分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 30(5): 1110-1120. |
| ZHANG T, XUE D J, DUAN J L, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and climate response analysis of vegetation coverage in Jialing River Basin from 2000 to 2019 [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 30(5): 1110-1120. | |
| [52] | 张艳可, 王金亮, 农兰萍, 等, 2021. 基于MODIS时序数据北回归线(云南段)地区植被物候时空变化及其对气候响应分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(2):274-287. |
| ZHANG Y K, WANG J L, NONG L P, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation phenology and its response to climate in the tropic of cancer (Yunnan section) based on MODIS Time-series Data[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(2): 274-287. | |
| [53] | 郑勇, 杨武年, 刘冲, 等, 2020. 川西高原近20 a植被覆盖变化遥感动态监测及驱动力分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 35(6): 1447-1456. |
| ZHENG Y, YANG W N, LIU C, et al., 2020. Dynamic monitoring and driving force analysis of vegetation cover change in western Sichuan Plateau in recent 20 years[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 35(6): 1447-1456. | |
| [54] | 周稳, 迟永刚, 周蕾, 2021. 基于日光诱导叶绿素荧光的北半球森林物候研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 45(4): 345-354. |
|
ZHOU W, CHI Y G, ZHOU L, 2021. Vegetation phenology in the Northern Hemisphere based on the solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45(4): 345-354.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [3] | 张兴旺, 谢艳萍, 吴晓敏, 李垚, 肖书平. 福建省明溪县极小种群野生植物喜树种群结构与动态特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1037-1044. |
| [4] | 杜彩艳, 杨鹏, 蜂述先, 毛妍婷, 陶琼, 此主拉姆, 彭慧娉, 和建美, 李卫林. 不同生态区维西糯山药品质与生态因子相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1053-1061. |
| [5] | 翁升恒, 张玉琴, 姜冬昕, 潘卫华, 李丽纯, 张方敏. 福建省森林植被NEP时空变化及影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 845-856. |
| [6] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [7] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [8] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [9] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [10] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [11] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [12] | 徐晨, 裴顺祥, 吴莎, 郭慧, 马淑敏, 吴迪, 章尧想, 法蕾. 北京九龙山不同林型林间大气主要BVOCs组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 245-255. |
| [13] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [14] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [15] | 贾志峰, 刘鹏程, 刘宇, 吴博博, 陈丹姿, 张向飞. 气候变化和人类活动对松辽流域植被覆盖的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
