生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 723-731.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.010
邓晓1,2,3( ), 武春媛1,2, 杨桂生1,2, 李怡1,2, 李勤奋1,2,3,*(
), 武春媛1,2, 杨桂生1,2, 李怡1,2, 李勤奋1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-14
出版日期:2022-04-18
发布日期:2022-06-22
通讯作者:
*李勤奋(1974年生),女,研究员,博士,研究方向为热带生态循环农业。E-mail: qinfenli2005@163.com作者简介:邓晓(1976年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究方向为土壤保育与非耕地利用。E-mail: dx0928@foxmail.com
基金资助:
DENG Xiao1,2,3( ), WU Chunyuan1,2, YANG Guisheng1,2, LI Yi1,2, LI Qinfen1,2,3,*(
), WU Chunyuan1,2, YANG Guisheng1,2, LI Yi1,2, LI Qinfen1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-01-14
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
摘要:
选用椰壳生物炭为改良材料,海南滨海盐渍土壤为改良对象,设置5种不同椰壳生物炭与滨海土壤体积比处理,分别为0?20、1?20、2?20、3?20和4?20,采用盆栽试验种植空心菜(Ipomoea aquatica Forsskal),研究椰壳生物炭不同施用量对滨海土壤的改良效果。结果表明,(1)添加1?20—4?20椰壳生物炭后,土壤pH得到明显改善,由酸性变为中性;土壤有机质、全N、有效P和速效K含量得到显著提高,分别提高了42.4%—153%、32.1%—36.7%、35.0%—44.6%和70.0%—220%(P <0.01);空心菜的生长得到明显促进,平均每株叶片数、单株鲜重和地下部根重分别增加19.7%—29.6%、43.2%—59.7%和81.3%—119%(P<0.05)。(2)添加2?20—4?20椰壳生物炭后,土壤过氧化氢酶活性显著提高21.3%—71.1%(P<0.01);土壤盐度显著下降6.83%—14.9%(P<0.05)。(3)添加1?20—3?20椰壳生物炭提高了土壤细菌多样性和丰富度并优化了细菌群落结构,ACE、Chao1和Shannon指数分别提高了6.50%—14.4%、3.50%—11.9% 和3.34%—3.56%;与碳氮循环能力相关的芽单胞菌科(Gemmatimonadaceae)和亚硝化单胞菌科(Nitrosomonadaceae)的丰度分别提高了44.3%—67.2%和229%—243%。(4)RDA冗余分析结果表明,椰壳生物炭能通过提高土壤养分含量、优化微生物群落结构、提高细菌多样性和过氧化氢酶活性来降低土壤盐度。综上,添加体积比为2?20—3?20的椰壳生物炭可显著降低滨海土壤盐分、改善土壤pH、提高土壤养分含量、增强土壤酶活性和提高微生物多样性并优化其群落结构,更有利于作物的生长。
中图分类号:
邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731.
DENG Xiao, WU Chunyuan, YANG Guisheng, LI Yi, LI Qinfen. Improvement Effect of Coconut-shell Biochar on Coastal Soil in Hainan[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 723-731.
| 处理 Treatments | 叶片数 Leaf number | 单株鲜重 Fresh weight per plant/ (g∙plant-1) | 单株根重Underground weight/ (g∙plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0꞉20 1꞉20 2꞉20 3꞉20 4꞉20 | 7.10±0.31cB 8.50±0.22bA 8.60±0.20abA 8.90±0.41abA 9.20±0.23abA | 1.60±0.12bB 2.52±0.49aAB 2.66±0.23aAB 2.81±0.24aA 2.71±0.44aA | 0.16±0.02cC 0.29±0.08bB 0.33±0.01aA 0.35±0.03aA 0.34±0.03aA |
表1 椰壳生物炭对空心菜生长的影响
Table 1 Effects of coconut shell biochar on growth of water spinach
| 处理 Treatments | 叶片数 Leaf number | 单株鲜重 Fresh weight per plant/ (g∙plant-1) | 单株根重Underground weight/ (g∙plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0꞉20 1꞉20 2꞉20 3꞉20 4꞉20 | 7.10±0.31cB 8.50±0.22bA 8.60±0.20abA 8.90±0.41abA 9.20±0.23abA | 1.60±0.12bB 2.52±0.49aAB 2.66±0.23aAB 2.81±0.24aA 2.71±0.44aA | 0.16±0.02cC 0.29±0.08bB 0.33±0.01aA 0.35±0.03aA 0.34±0.03aA |
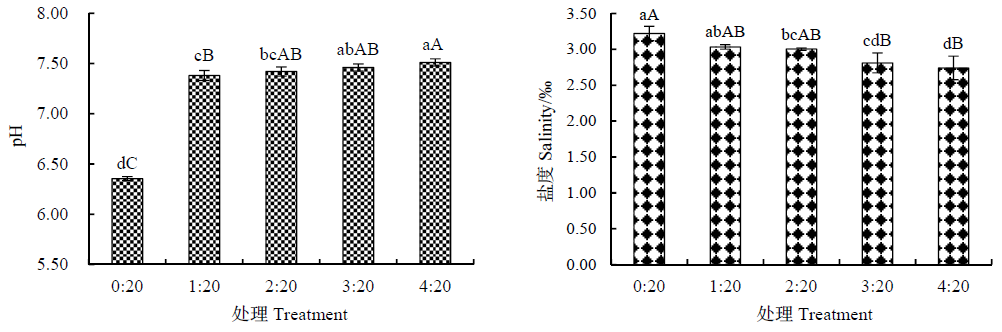
图1 椰壳生物炭对滨海土壤pH和盐分的影响 (1)图中不同处理间的不同小写和大写字母分别表示对应数值在P<0.05和P<0.01水平上存在显著性差异,下同;(2)0?20、1?20、2?20、3?20和4?20分别表示椰壳生物炭与滨海盐渍土壤的体积比。下同
Figure 1 Effects of the coconut-shell biochar on pH and salinity in coastal soil (1) Different lowercase and uppercase letters in the figure represent significant differences of P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively, the same below. (2) 0?20, 1?20, 2?20, 3?20 and 4?20 respectively represent the volume ratio of coconut-shell biochar and coastal soil. The same below
| 处理 Treatment | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0꞉20 1꞉20 2꞉20 3꞉20 4꞉20 | 1335.5 1422.3 1453.5 1528.2 1440.0 | 1386.2 1434.7 1472.6 1550.5 1451.0 | 8.566 8.871 8.740 8.852 8.599 |
表2 椰壳生物炭对滨海土壤细菌Alpha多样性指数的影响
Table 2 Effects of the coconut-shell biochar on bacterial Alpha diversity indices in coastal soil
| 处理 Treatment | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0꞉20 1꞉20 2꞉20 3꞉20 4꞉20 | 1335.5 1422.3 1453.5 1528.2 1440.0 | 1386.2 1434.7 1472.6 1550.5 1451.0 | 8.566 8.871 8.740 8.852 8.599 |
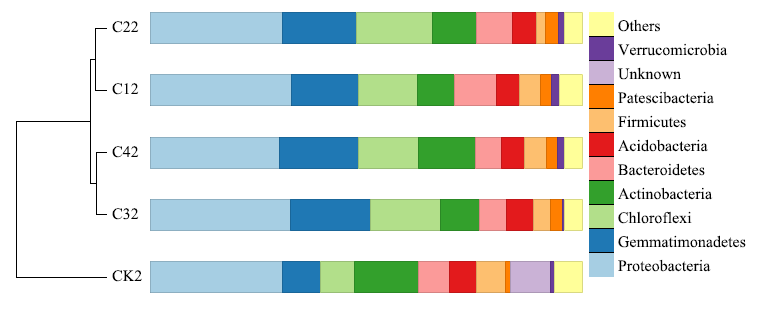
图4 门水平上的细菌相对丰度聚类树(非加权距离法) 图中CK2,C12,C22,C32和C42分别表示椰壳生物炭与滨海土壤体积比为0?20,1?20,2?20,3?20 和 4?20的处理收获空心菜后的土壤样品。下同
Figure 4 Cluster tree of relative abundance of bacteria at phylum level (unweighted distance method) CK2, C12, C22, C32 and C42 in the figure represent the soil samples of water spinach harvest treated with coconut-shell biochar and coastal soil volume ratios of 0:20, 1:20, 2:20, 3:20 and 4:20, respectively. The same below
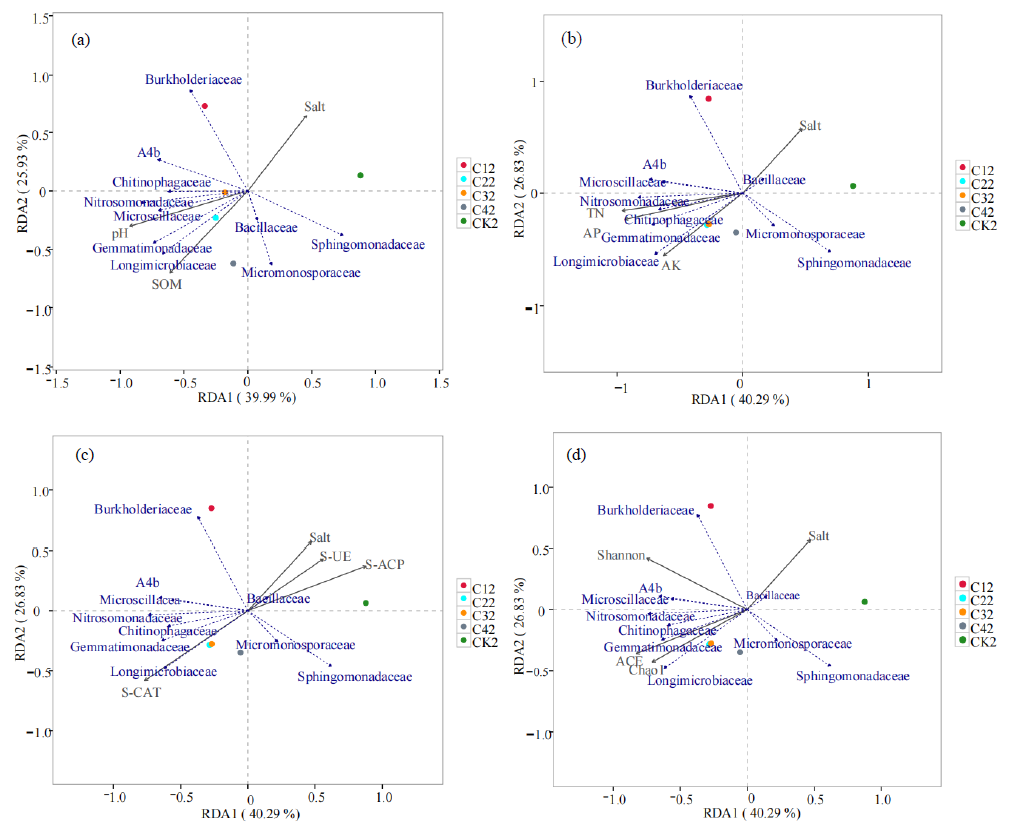
图6 土壤细菌群落结构与环境因子的RDA分析 图中Salt、SOM、TN、AP、AK、S-UE、S-ACP和S-CAT分别表示土壤盐分、有机质、全氮、有效磷、速效钾、土壤脲酶、酸性磷酸酶和过氧化氢酶
Figure 6 RDA analysis between soil bacterial community and environmental factors Salt, SOM, TN, AP, AK, S-UE, S-ACP and S-CAT in the figure represent soil salinity, organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, soil urease, acid phosphatase and catalase, respectively
| [1] |
AMELOOT N, GRABER E R, VERHEIJEN F G A, et al., 2013. Interactions between biochar stability and soil organisms: Review and research needs[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 64(4): 379-390.
DOI URL |
| [2] | CZIMCZIK C I, MASIELLO C A, 2007. Controls on black carbon storage in soils[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 21(3): 113. |
| [3] |
LASHARI M S, YE Y X, JI H S, et al., 2015. Biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution alleviated salt stress and improved leaf bioactivity of maize in a saline soil from central China: A 2-year field experiment[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 95(6): 1321-1327.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LEHMANN J, DA SILVA J P, STEINER C, et al., 2003. Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological anthrosol and a ferralsol of the central Amazon basin: Fertiliser, manure and charcoal amendments[J]. Plant and Soils, 249: 343-357. |
| [5] |
LEHMANN J, RILLIG M C, THIES J, et al., 2011. Biochar effects on soil biota-A review[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 43(9): 1812-1836.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LIU Y, ZHU J R, YE C Y, et al., 2018. Effects of biochar application on the abundance and community composition of denitrifying bacteria in a reclaimed soil from coal mining subsidence area[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 625: 1218-1224.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MIDDELBURG J J, NIEUWENHUIZE J, VAN BREUGEL P, 1999. Black carbon in marine sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 65: 245-252.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MIZUTA K, MATSUMOTO T, HATATE Y, et al., 2004. Removal of nitrate-nitrogen from drinking water using bamboo powder charcoal[J]. Bioresource Technology, 95(3): 255-257
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SHEN P J, ZHANG LM, GUO J F, et al., 2010. Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in northeast China[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 46: 119-124.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TAN L, WANG F, LIANG M M, et al., 2019. Antibiotic resistance genes attenuated with salt accumulation in saline soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 374: 35-42.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WARNOCK D D, MUMMEY D L, MCBRIDE B, et al., 2010. Influences of non-herbaceous biochar on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal abundances in roots and soils: Results from growth-chamber and field experiments[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 46(3): 450-456.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WU Y Y, LIU R C, ZHAO Y G, et al., 2009. Spatial and seasonal variation of salt ions under the influence of halophytes, in a coastal flat in eastern China[J]. Environmental Geology, 57(7): 1501-1508.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHENG J F, CHEN J H, PAN G X, et al., 2016. Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from southwest China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 571: 206-217.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 曹雨桐, 佘冬立, 2017. 施用生物炭和聚丙烯酰胺对海涂围垦区盐碱土水力性质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(11): 3684-3690. |
| CAO Y T, SHE D L, 2017. Effects of biochar and PAM application on saline soil hydraulic properties of coastal reclamation region[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(11): 3684-3690. | |
| [15] | 高敬尧, 王宏燕, 许毛毛, 等, 2016. 生物炭施入对农田土壤及作物生长影响的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 44(10): 10-15. |
| GAO J R, WANG H Y, XU M M, et al., 2016. Research progress on effects of biochar application on soil and crop growth in farmland[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 44(10): 10-15. | |
| [16] | 耿泽铭, 2013. 施用生物有机肥对盐渍土改良效果及玉米产量的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. |
| GENG Z M, 2013. Use bio organic fertilizer on saline soil improvement effect and corn yield[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. | |
| [17] | 顾美英, 葛春辉, 马海刚, 等, 2016. 生物炭对新疆沙土微生物区系及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 34(4): 225-230. |
| GU M Y, GE C H, MA H G, et al., 2016. Effects of biochar application amount on microbial flora and soil enzyme activities in sandy soil of Xinjiang[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 34(4): 225-230. | |
| [18] | 郭伟, 陈红霞, 张庆忠, 等, 2011. 华北高产农田施用生物质炭对耕层土壤总氮和碱解氮含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(3): 425-428. |
| GUO W, CHEN H X, ZHANG Q Z, et al., 2011. Effects of biochar application on total nitrogen and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content in the topsoil of the high-yield cropland in north China Plain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(3): 425-428. | |
| [19] | 何秀峰, 赵丰云, 于坤, 等, 2020. 生物炭对葡萄幼苗根际土壤养分、酶活性及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6): 19-26. |
| HE X F, ZHAO F Y, YU K, et al., 2020. Effect of biochar on nutrient, enzyme activities and microbial diversity of rhizosphere soil of grape seedlings[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (6): 19-26. | |
| [20] | 刘玉学, 刘微, 吴伟祥, 等, 2009. 土壤生物质炭环境行为与环境效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 20(4): 977-982. |
| LIU Y X, LIU W, WU W X, et al., 2009. Environmental behavior and effect of biomass-derived black carbon in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(4): 977-982. | |
| [21] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Analytical methods of soil and agro-chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [22] | 马晨, 马履一, 刘太祥, 等, 2010. 盐碱地改良利用技术研宄进展[J]. 世界林业研宄, 23(2): 28-32. |
| MA C, MA L Y, LIU T X, et al., 2010. Research progress on saline land improvement technology[J]. World Forestry Research, 23(2): 28-32. | |
| [23] | 彭碧媛, 康蒙蒙, 江璇, 等, 2017. 椰壳生物炭对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能研究[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 35(11): 31-34. |
| PENG B Y, KANG M M, JIANG X, et al., 2017. Adsorption of Cr (Ⅵ) on coconut shell biochar in water[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 35(11): 31-34. | |
| [24] | 蒲胜海, 卡拉巴耶夫∙努尔金, 王新勇, 等, 2014. 暗管排盐对吉尔吉斯坦楚河盆地盐碱地的改良效应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 51(11): 2144-2149. |
| PU S H, KARABAYEV N, WANG X Y, et al., 2014. The effect of subsurface pipe drainage systems on improving saline-alkali land in Chu Valley Basin, Kyrgyzstan[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 51(11): 2144-2149. | |
| [25] | 宋玥言, 袁再健, 黄斌, 等, 2021. 生物炭对红壤团聚体吸附Cd的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2402-2410. |
| SONG Y Y, YUAN Z J, HUANG B, et al., 2021. Studies on the influence of biochar on the adsorption of cd onto red soil aggregates[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2402-2410. | |
| [26] | 唐光木, 葛春辉, 徐万里, 等, 2011. 施用生物黑炭对新疆灰漠土肥力与玉米生长的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(9): 1797-1802. |
| TANG G M, GE C H, XU W L, et al., 2011. Effect of applying biochar on the quality of grey desert soil and maize cropping in Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(9): 1797-1802. | |
| [27] | 王荧, 郭航, 李娟, 等, 2019. “改排为蓄”和"覆沙改良”整治前后盐碱地微观结构研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 38(S1): 75-78. |
| WANG Y, GUO H, LI J, et al., 2019. Influence of different soil organic reconstruction methods on microstructure of saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 38(S1): 75-78. | |
| [28] | 王涵, 2018. 不同有机物料对滨海盐碱土改良效果的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学. |
| WANG H, 2018. Research on the improvement effect of different organic materials on coastal saline soil[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University. | |
| [29] | 王卫民, 张保全, 程昌合, 等, 2018. 根区穴施生物炭对烤烟生长及养分吸收的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 57(3): 32-35. |
| WANG W M, ZHANG B Q, CHENG C H, et al., 2018. Effects of biochar with hole application on growth and nutrient uptake of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 57(3): 32-35. | |
| [30] | 王向辉, 杨雪, 王闯, 等, 2020. 改性椰壳生物炭对甲基橙的吸附效果与机制[J]. 科学技术与工程, 20(27): 11371-11377. |
| WANG X H, YANG X, WANG C, et al., 2020. Effects and mechanisms of methyl orange removal from aqueous solutions with modified coconut shell biochar[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(27): 11371-11377. | |
| [31] | 王亚琢, 周翔, 修磊, 等, 2021. 高铁酸钾改性生物炭的制备及其对水体中Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2380-2386. |
| WANG Y Z, ZHOU X, XIU L, et al., 2021. Preparation of K2FeO4 modified biochar and its adsorption characteristics for Cd(Ⅱ) in aqueous solution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2380-2386. | |
| [32] | 王宇超, 王得祥, 2012. 盐胁迫对木本滨藜叶绿素合成及净光合速率的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 28(10): 151-158. |
| WANG Y C, WANG D X, 2012. Effects of salt stress on chlorophyll content and net photosynthetic rate of woody saltbush[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(10): 151-158. | |
| [33] | 王宇佳, 2017. 亚硝化过程控制与厌氧氨氧化工艺运行及其微生物特性[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学. |
| WANG Y J, 2017. Nitritation process control and anammox process performance and their microbial characteristics[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University. | |
| [34] | 魏永霞, 刘志凯, 冯鼎锐, 等, 2016. 生物炭对草甸黑土物理性质及雨后水分动态变化的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 47(8): 201-207. |
| WEI Y X, LIU Z K, FENG D R, et al., 2016. Influences of biochar on physical properties of meadow black soil and dynamic changes of soil water after individual rainfall[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 47(8): 201-207. | |
| [35] | 夏阳, 2015. 生物炭对滨海盐碱植物生长及根际土壤环境的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| XIA Y, 2015. Impact of biochar-rhizosphere system on plant growth by affecting soil nutrient availability and microbial community in Coastal saline soil[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. | |
| [36] | 徐家伊, 胡朝月, 杨雅晗, 等, 2019. 生物炭对水溶液中四环素的吸附效果研究[J]. 高师理科学刊, 39(5): 43-46, 71. |
| XU J Y, HU Z Y, YANG Y H, et al., 2019. Study on the adsorption effect of tetracycline on biochar in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Science of Teachers' College and University, 39(5): 43-46, 71. | |
| [37] | 张济世, 于波涛, 张金凤, 等, 2017. 不同改良剂对滨海盐渍土土壤理化性质和小麦生长的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(3): 704-711. |
| ZHANG J S, YU B T, ZHANG J F, et al., 2017. Effects of different amendments on soil physical and chemical properties and wheat growth in a coastal saline soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 23(3): 704-711. | |
| [38] | 张凌云, 赵庚星, 2006. 盐碱土壤修复材料对滨海盐渍土理化性质的影响研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 13(1): 32-34. |
| ZHANG L Y, ZHAO G X, 2006. Study on the effect of saline soil restoration material on physical and chemical properties of the coastal saline soil[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(1): 32-34. | |
| [39] | 张太平, 肖嘉慧, 胡凤洁, 2021. 生物炭固定化微生物技术在去除水中污染物的应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(5): 1084-1093. |
| ZHANG T P, XIAO J H, HU F J, 2021. Research progress in the removal of contaminants from water by immobilized microorganisms combined with biochar[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 1084-1093. | |
| [40] | 赵永敢, 李玉义, 胡小龙, 等, 2013. 地膜覆盖结合秸秆深埋对土壤水盐动态影响的微区试验[J]. 土壤学报, 50(6): 1129-1137. |
| ZHAO Y G, LI Y Y, HU X L, et al., 2013. Effects of plastic mulching and deep burial of straw on dynamics of soil water and salt in micro-plot field cultivation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 50(6): 1129-1137. | |
| [41] | 郑慧芬, 吴红慧, 翁伯琦, 等, 2019. 施用生物炭提高酸性红壤茶园土壤的微生物特性及酶活性[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, (2): 68-74. |
| ZHENG H F, WU H H, WENG B Q, et al., 2019. Improved soil microbial characteristics and enzyme activities with wheat straw biochar addition to an acid tea plantation in red soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, (2): 68-74. | |
| [42] | 周琦, 藕志强, 饶鑫, 等, 2020. 椰子果皮废弃物的高值化利用现状及发展趋势[J]. 广州化工, 48(18): 16-19. |
| ZHOU Q, OU Z Q, RAO X, et al., 2020. Status and development trend of higher value utilization of coconut waste husk[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 48(18): 16-19. |
| [1] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [4] | 代德敏, 蒋旭升, 刘杰, 王路洋, 陈诗奇, 韩庆坤. 3种有机改良剂对铅锌矿尾砂适生性改善的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 784-793. |
| [5] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [6] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [7] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [8] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [9] | 花莉, 成涛之, 梁智勇. 固定化混合菌对陕北黄土地区石油污染土壤的修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [10] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [11] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [12] | 宋秀丽, 黄瑞龙, 柯彩杰, 黄蔚, 章武, 陶波. 不同种植方式对连作土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [13] | 梁嘉伟, 余炜敏, 姚钰玲, 胡绮琪, 陆丹绵, 王荣萍, 廖新荣, 黄赛花. 生物有机肥对土壤质量及蔬菜产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 497-503. |
| [14] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [15] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
