生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 80-89.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.009
黄伟佳1,2,3( ), 刘春1, 刘岳4, 黄斌2,3, 李定强2,3, 袁再健2,3,*(
), 刘春1, 刘岳4, 黄斌2,3, 李定强2,3, 袁再健2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-10
出版日期:2023-01-18
发布日期:2023-04-06
通讯作者:
*袁再健(1976年生),男,教授,博士,主要从事水土保持、面源污染与生态水文等方面的研究。E-mail: zjyuan@soil.gd.cn作者简介:黄伟佳(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为土壤碳循环。E-mail: 976652113@qq.com
基金资助:
HUANG Weijia1,2,3( ), LIU Chun1, LIU Yue4, HUANG Bin2,3, LI Dingqiang2,3, YUAN Zaijian2,3,*(
), LIU Chun1, LIU Yue4, HUANG Bin2,3, LI Dingqiang2,3, YUAN Zaijian2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-10
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
摘要:
土壤生态化学计量比是表征土壤养分需求与限制的重要指标。为了探究不同海拔梯度土壤生态化学计量特征,选择南岭山地不同海拔土壤为研究对象,分层采集不同海拔0—60 cm土壤,通过测定土壤基本理化性质、微生物生物量碳氮磷和土壤酶活性,分析南岭不同海拔梯度山地土壤养分、微生物生物量碳氮磷、酶活性及其生态化学计量比特征及影响因素。研究结果表明:(1)土壤有机碳(TOC)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)、微生物量氮(MBN)、微生物量磷(MBP)含量和β-葡萄糖苷酶(BG)活性在中高海拔处高于低海拔处,而微生物量碳(MBC)含量、N-乙酰-β-氨基葡萄糖苷酶(NAG)和酸性磷酸酶(AP)活性沿海拔呈现波动变化,其中MBC含量,NAG和AP活性分别在402、809和402 m处到达最高;(2)土壤w(C)/w(N)、w(MBC)/w(MBN)、w(MBC)/w(MBP)、w(MBN)/w(MBP)、NAG:AP均在809 m处最高,土壤w(C)/w(P)、w(N)/w(P)、BG:AP均在1364 m处最高,土壤BG:NAG在1536 m处最高;(3)土壤含水率、TOC、TN分别解释了土壤各化学计量比的25.0%、17.9%、13.6%。其中,含水率与w(N)/w(P)显著正相关(P<0.05),与BG:NAG极显著正相关(P<0.01),与w(MBC)/w(MBP)、NAG:AP极显著负相关(P<0.01),与w(MBN)/w(MBP)显著负相关(P<0.05);TOC与w(C)/w(P)、w(N)/w(P)、BG:AP极显著正相关(P<0.01);TN与w(N)/w(P)极显著正相关(P<0.01),与w(C)/w(P)、BG:NAG、BG:AP显著正相关(P<0.05),与w(C)/w(N)显著负相关(P<0.05)。南岭山地土壤养分、微生物量、酶活性化学计量比有明显的海拔梯度变化特征,土壤理化性质对土壤化学计量比具有重要的影响,对于深入研究南岭山地土壤养分平衡状况和限制因素具有重要的意义。
中图分类号:
黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89.
HUANG Weijia, LIU Chun, LIU Yue, HUANG Bin, LI Dingqiang, YUAN Zaijian. Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors at Different Elevations in Nanling Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 80-89.
| 样地 | 海拔/m | 坡向 | 坡度/(°) | 经纬度 | 土壤类型 | 植被类型 | 优势植被 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 402 | SW | 8 | 112°47′23.49″E, 24°50′21.82″N | 山地红壤 | 沟谷常绿阔叶林 | 广东润楠 Machiluskwangtungensis、石栎 Lithocarpusglaber、鹿角锥 Castanopsislamontii、 赤楠 Syzygiumbuxifolium |
| S2 | 809 | NE | 15 | 112°44′28.47″E, 24°55′28.46″N | 山地红壤 | 沟谷常绿阔叶林 | 广东润楠 Machiluskwangtungensis、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca、罗浮锥 Castanopsisfabri、 小叶青冈Cyclobalanopsismyrsinifolia |
| S3 | 1184 | NE | 10 | 113°0′19.08″E, 24°56′8.79″N | 山地黄壤 | 山地常绿阔叶林 | 鹿角锥 Castanopsislamontii、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca、千年桐 Verniciamontana、罗浮锥 Castanopsisfabri、甜槠 Castanopsiseyrei |
| S4 | 1364 | NE | 15 | 113°1′20.83″E, 24°53′50.52″N | 山地黄壤 | 针阔混交林 | 广东松 PinusKwangtungensis、荷木 Schimasuperba、马尾松 Pinusmassoniana、甜槠 Castanopsiseyrei、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca |
| S5 | 1536 | SW | 5 | 112°58′12.27″E, 24°55′22.30″N | 山地草甸土 | 山顶草甸 | 五节芒 Miscanthusfloridulus |
| S6 | 1653 | SE | 8 | 112°59′8.22″E, 24°55′48.56″N | 山地黄壤 | 山顶矮林 | 野茉莉 Styrax japonicus、少花桂 Cinnamomum pauciflorum、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca |
表1 南岭研究区域样地基本概况
Table 1 The basic situation of the sample plot in Nanling research area
| 样地 | 海拔/m | 坡向 | 坡度/(°) | 经纬度 | 土壤类型 | 植被类型 | 优势植被 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 402 | SW | 8 | 112°47′23.49″E, 24°50′21.82″N | 山地红壤 | 沟谷常绿阔叶林 | 广东润楠 Machiluskwangtungensis、石栎 Lithocarpusglaber、鹿角锥 Castanopsislamontii、 赤楠 Syzygiumbuxifolium |
| S2 | 809 | NE | 15 | 112°44′28.47″E, 24°55′28.46″N | 山地红壤 | 沟谷常绿阔叶林 | 广东润楠 Machiluskwangtungensis、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca、罗浮锥 Castanopsisfabri、 小叶青冈Cyclobalanopsismyrsinifolia |
| S3 | 1184 | NE | 10 | 113°0′19.08″E, 24°56′8.79″N | 山地黄壤 | 山地常绿阔叶林 | 鹿角锥 Castanopsislamontii、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca、千年桐 Verniciamontana、罗浮锥 Castanopsisfabri、甜槠 Castanopsiseyrei |
| S4 | 1364 | NE | 15 | 113°1′20.83″E, 24°53′50.52″N | 山地黄壤 | 针阔混交林 | 广东松 PinusKwangtungensis、荷木 Schimasuperba、马尾松 Pinusmassoniana、甜槠 Castanopsiseyrei、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca |
| S5 | 1536 | SW | 5 | 112°58′12.27″E, 24°55′22.30″N | 山地草甸土 | 山顶草甸 | 五节芒 Miscanthusfloridulus |
| S6 | 1653 | SE | 8 | 112°59′8.22″E, 24°55′48.56″N | 山地黄壤 | 山顶矮林 | 野茉莉 Styrax japonicus、少花桂 Cinnamomum pauciflorum、青冈 Cyclobalanopsisglauca |
| 采样点 | 深度/cm | pH | 容重/(g·cm-3) | 含水率/% | w(有机碳)/(g·kg-1) | w(总氮)/(g·kg-1) | w(总磷)/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0-20 | 4.15±0.06bBC | 0.94±0.15aA | 38.64±2.79aABC | 36.12±7.85aD | 2.58±0.57aC | 0.32±0.04aB |
| 20-40 | 4.31±0.08abB | 1.15±0.16aAB | 34.45±0.39aCD | 24.15±6.09abC | 1.51±0.52bC | 0.29±0.01aA | |
| 40-60 | 4.40±0.10aC | 1.21±0.07aB | 32.07±3.63aC | 17.89±6.38bBC | 1.02±0.32bCD | 0.23±0.02bAB | |
| S2 | 0-20 | 4.68±0.09aA | 0.70±0.01bAB | 33.14±1.83aC | 44.13±8.88aCD | 2.04±0.19aC | 0.20±0.03aC |
| 20-40 | 4.73±0.13aA | 1.39±0.10aA | 30.25±0.03aD | 13.11±4.12bD | 0.35±0.16bD | 0.18±0.06aBC | |
| 40-60 | 4.80±0.04aA | 1.44±0.12aA | 32.85±3.38aC | 8.83±1.17bC | 0.19±0.05bE | 0.17±0.10aBC | |
| S3 | 0-20 | 4.22±0.17bBC | 0.81±0.05bAB | 37.78±3.55aBC | 71.07±14.75aB | 3.63±0.44aB | 0.31±0.02aBC |
| 20-40 | 4.62±0.17aA | 0.99±0.10abB | 42.65±9.17aABC | 49.16±3.53bA | 2.31±0.60bB | 0.25±0.06abAB | |
| 40-60 | 4.68±0.21aAB | 1.25±0.10aAB | 42.22±1.98aABC | 36.79±8.27bA | 1.73±0.52bB | 0.20±0.04bBC | |
| S4 | 0-20 | 3.86±0.11bD | 0.56±0.15bB | 49.85±4.92aA | 104.87±9.93aA | 4.24±0.23aAB | 0.21±0.02aC |
| 20-40 | 4.48±0.18aAB | 1.02±0.11aB | 48.78±10.33aAB | 37.90±3.43bB | 1.66±0.25bBC | 0.15±0.02bC | |
| 40-60 | 4.55±0.17aBC | 1.14±0.03aB | 43.82±4.72aAB | 22.53±5.35cB | 0.92±0.24cD | 0.13±0.02bC | |
| S5 | 0-20 | 4.31±0.29bB | 0.69±0.13bAB | 46.66±8.62aAB | 65.66±3.44aB | 4.53±0.52aA | 0.47±0.12aA |
| 20-40 | 4.62±0.16abA | 0.95 ± 0.07abB | 53.97±0.23aA | 45.96±3.31bA | 3.11±0.17bA | 0.32±0.04bA | |
| 40-60 | 4.73±0.08aAB | 1.06±0.02aB | 54.55±2.15aA | 33.17±6.26cA | 2.49±0.38bA | 0.29±0.01bA | |
| S6 | 0-20 | 4.01±0.04bCD | 0.96±0.14aA | 35.89±0.64aBC | 58.31±4.74aBC | 3.87±0.42aAB | 0.3±0.00aBC |
| 20-40 | 4.26±0.10aB | 1.19±0.12aAB | 38.28±0.86aBCD | 29.31±4.41bC | 2.08±0.37bBC | 0.19±0.01bBC | |
| 40-60 | 4.36±0.06aC | 1.11±0.09aB | 39.72±7.42aBC | 21.20±1.95cB | 1.57±0.24bBC | 0.16±0.03bBC |
表2 不同海拔土壤基本理化性质
Table 2 Basic physical and chemical properties of soil at different elevations
| 采样点 | 深度/cm | pH | 容重/(g·cm-3) | 含水率/% | w(有机碳)/(g·kg-1) | w(总氮)/(g·kg-1) | w(总磷)/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0-20 | 4.15±0.06bBC | 0.94±0.15aA | 38.64±2.79aABC | 36.12±7.85aD | 2.58±0.57aC | 0.32±0.04aB |
| 20-40 | 4.31±0.08abB | 1.15±0.16aAB | 34.45±0.39aCD | 24.15±6.09abC | 1.51±0.52bC | 0.29±0.01aA | |
| 40-60 | 4.40±0.10aC | 1.21±0.07aB | 32.07±3.63aC | 17.89±6.38bBC | 1.02±0.32bCD | 0.23±0.02bAB | |
| S2 | 0-20 | 4.68±0.09aA | 0.70±0.01bAB | 33.14±1.83aC | 44.13±8.88aCD | 2.04±0.19aC | 0.20±0.03aC |
| 20-40 | 4.73±0.13aA | 1.39±0.10aA | 30.25±0.03aD | 13.11±4.12bD | 0.35±0.16bD | 0.18±0.06aBC | |
| 40-60 | 4.80±0.04aA | 1.44±0.12aA | 32.85±3.38aC | 8.83±1.17bC | 0.19±0.05bE | 0.17±0.10aBC | |
| S3 | 0-20 | 4.22±0.17bBC | 0.81±0.05bAB | 37.78±3.55aBC | 71.07±14.75aB | 3.63±0.44aB | 0.31±0.02aBC |
| 20-40 | 4.62±0.17aA | 0.99±0.10abB | 42.65±9.17aABC | 49.16±3.53bA | 2.31±0.60bB | 0.25±0.06abAB | |
| 40-60 | 4.68±0.21aAB | 1.25±0.10aAB | 42.22±1.98aABC | 36.79±8.27bA | 1.73±0.52bB | 0.20±0.04bBC | |
| S4 | 0-20 | 3.86±0.11bD | 0.56±0.15bB | 49.85±4.92aA | 104.87±9.93aA | 4.24±0.23aAB | 0.21±0.02aC |
| 20-40 | 4.48±0.18aAB | 1.02±0.11aB | 48.78±10.33aAB | 37.90±3.43bB | 1.66±0.25bBC | 0.15±0.02bC | |
| 40-60 | 4.55±0.17aBC | 1.14±0.03aB | 43.82±4.72aAB | 22.53±5.35cB | 0.92±0.24cD | 0.13±0.02bC | |
| S5 | 0-20 | 4.31±0.29bB | 0.69±0.13bAB | 46.66±8.62aAB | 65.66±3.44aB | 4.53±0.52aA | 0.47±0.12aA |
| 20-40 | 4.62±0.16abA | 0.95 ± 0.07abB | 53.97±0.23aA | 45.96±3.31bA | 3.11±0.17bA | 0.32±0.04bA | |
| 40-60 | 4.73±0.08aAB | 1.06±0.02aB | 54.55±2.15aA | 33.17±6.26cA | 2.49±0.38bA | 0.29±0.01bA | |
| S6 | 0-20 | 4.01±0.04bCD | 0.96±0.14aA | 35.89±0.64aBC | 58.31±4.74aBC | 3.87±0.42aAB | 0.3±0.00aBC |
| 20-40 | 4.26±0.10aB | 1.19±0.12aAB | 38.28±0.86aBCD | 29.31±4.41bC | 2.08±0.37bBC | 0.19±0.01bBC | |
| 40-60 | 4.36±0.06aC | 1.11±0.09aB | 39.72±7.42aBC | 21.20±1.95cB | 1.57±0.24bBC | 0.16±0.03bBC |
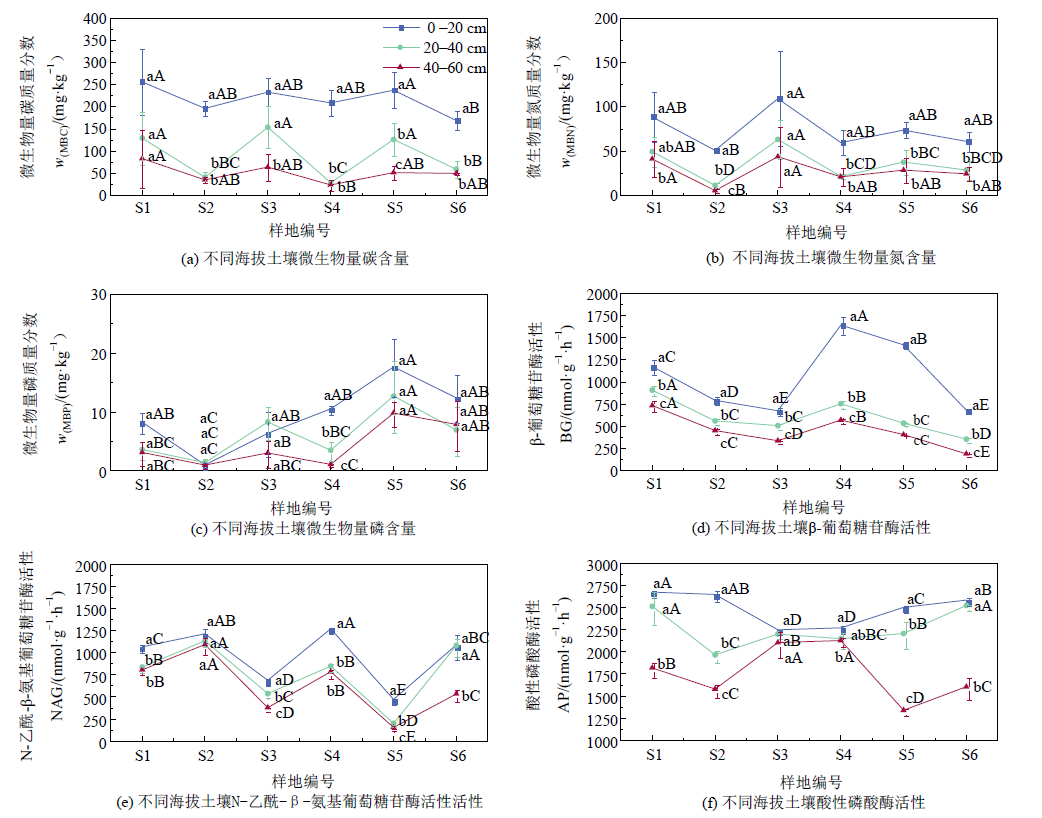
图2 不同海拔土壤微生物量碳、氮、磷含量和酶活性 平均值±标准差,n=3。不同大写字母表示同一深度,不同海拔间差异显著,不同小写字母表示同一海拔,不同深度间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 2 Soil microbial biomass C, N, P and enzyme activity at different elevations
| 化学计量比 stoichiometric ratio | pH | 容重 soil bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | 含水率 Soil moisture content/% | 有机碳 w(TOC)/ (g·kg-1) | 总氮 w(TN)/ (g·kg-1) | 总磷 w(TP)/ (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(C)/w(N) | 0.421 | 0.387 | -0.35 | -0.203 | -0.532* | -0.524* |
| w(C)/w(P) | -0.524* | -0.701** | 0.405 | 0.846** | 0.564* | -0.101 |
| w(N)/w(P) | -0.677** | -0.802** | 0.513* | 0.879** | 0.793** | 0.155 |
| w(MBC)/w(MBN) | 0.12 | -0.048 | -0.244 | 0.09 | 0.054 | 0.199 |
| w(MBC)/w(MBP) | 0.162 | -0.094 | -0.627** | -0.021 | -0.201 | -0.084 |
| w(MBN)/w(MBP) | 0.082 | -0.109 | -0.543* | -0.018 | -0.194 | -0.163 |
| BG:NAG | 0.038 | -0.435 | 0.712** | 0.357 | 0.560* | 0.755** |
| BG:AP | -0.502* | -0.595** | 0.217 | 0.599** | 0.476* | 0.393 |
| NAG:AP | -0.14 | 0.236 | -0.631** | -0.159 | -0.401 | -0.518* |
表3 土壤化学计量比与基本理化性质的相关性分析结果
Table 3 Results of correlation analysis between soil stoichiometric ratio and basic physical and chemical properties
| 化学计量比 stoichiometric ratio | pH | 容重 soil bulk density/ (g·cm-3) | 含水率 Soil moisture content/% | 有机碳 w(TOC)/ (g·kg-1) | 总氮 w(TN)/ (g·kg-1) | 总磷 w(TP)/ (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(C)/w(N) | 0.421 | 0.387 | -0.35 | -0.203 | -0.532* | -0.524* |
| w(C)/w(P) | -0.524* | -0.701** | 0.405 | 0.846** | 0.564* | -0.101 |
| w(N)/w(P) | -0.677** | -0.802** | 0.513* | 0.879** | 0.793** | 0.155 |
| w(MBC)/w(MBN) | 0.12 | -0.048 | -0.244 | 0.09 | 0.054 | 0.199 |
| w(MBC)/w(MBP) | 0.162 | -0.094 | -0.627** | -0.021 | -0.201 | -0.084 |
| w(MBN)/w(MBP) | 0.082 | -0.109 | -0.543* | -0.018 | -0.194 | -0.163 |
| BG:NAG | 0.038 | -0.435 | 0.712** | 0.357 | 0.560* | 0.755** |
| BG:AP | -0.502* | -0.595** | 0.217 | 0.599** | 0.476* | 0.393 |
| NAG:AP | -0.14 | 0.236 | -0.631** | -0.159 | -0.401 | -0.518* |
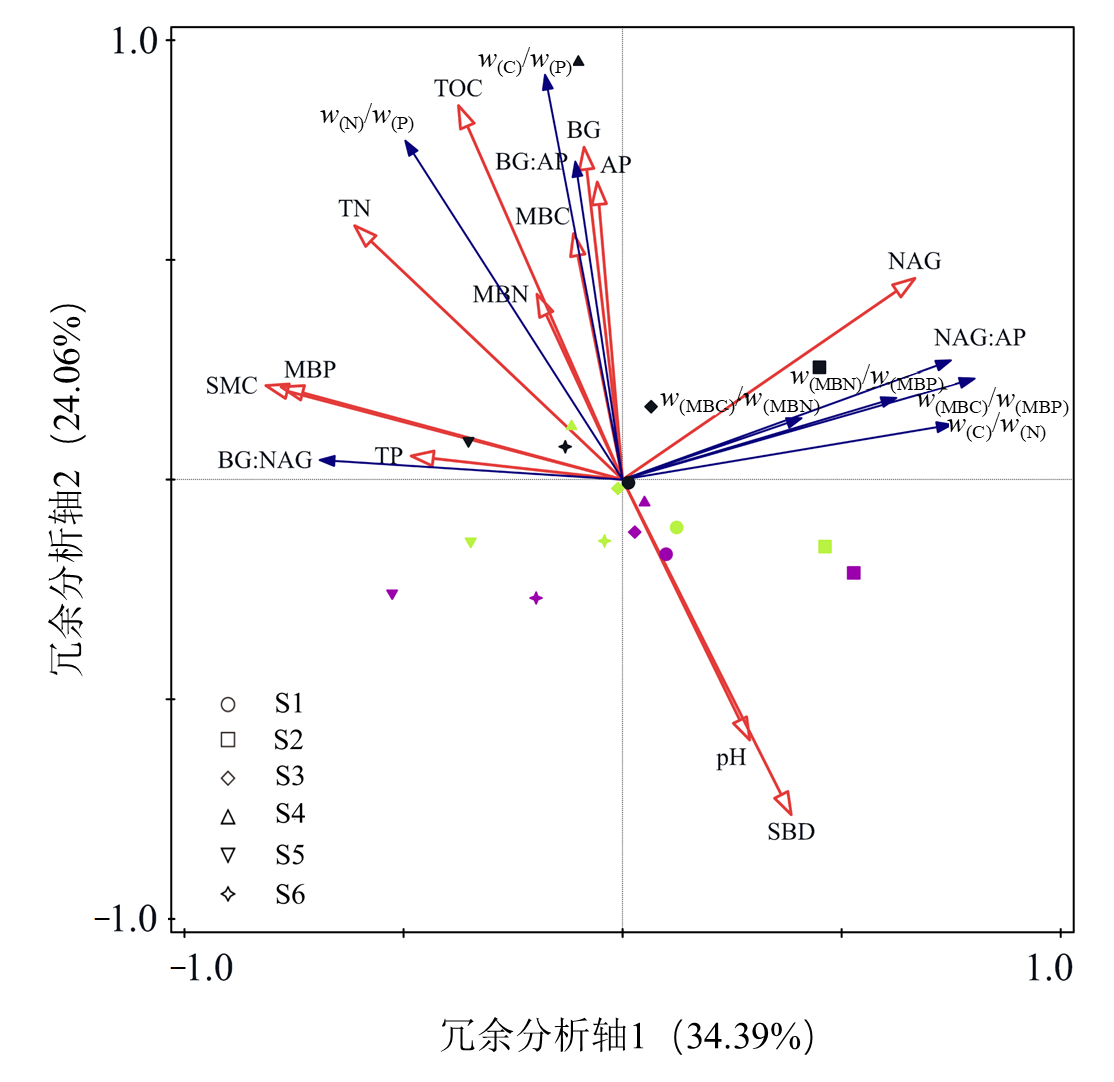
图4 土壤理化性质、微生物量、酶活性及其化学计量比的冗余分析结果 图中pH、SBD、SMC、TOC、TN、TP、MBC、MBN、MBP、BG、NAG和AP分别代表土壤pH值、容重、含水率、有机碳、总氮、总磷、微生物量碳、微生物量氮、微生物量磷、β-葡萄糖苷酶、N-乙酰-β-氨基葡萄糖苷酶和酸性磷酸酶。黑色样点表示0—20 cm土层;绿色样点表示20—40 cm土层;紫色样点表示40—60 cm土层
Figure 4 Results of redundant analysis of soil physicochemical properties, microbial biomass, enzyme activity and stoichiometric ratio
| [1] |
BAI X J, ZENG Q C, FAKHER A, et al., 2018. Characteristics of soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen under different vegetation zones on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Arid Land Research and Management, 32(4): 438-454.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BANGROO S A, NAJAR G R, RASOOL A, 2017. Effect of altitude and aspect on soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Himalayan Mawer Forest Range[J]. Catena, 158: 63-68.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BING H J, WU Y H, ZHOU J, et al., 2016. Stoichiometric variation of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soils and its implication for nutrient limitation in alpine ecosystem of Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(2): 405-416.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BROOKES P C, POWLSON D S, JENKINSON D S, 1982. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 14(4): 319-329.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CAO R Y, YANG W Q, CHANG C H, et al., 2021. Differential seasonal changes in soil enzyme activity along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine-gorge region[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 166: 104078.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ČAPEK P, STARKE R, HOFMOCKEL K S, et al., 2019. Apparent temperature sensitivity of soil respiration can result from temperature driven changes in microbial biomass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 135: 286-293.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CARRINO-KYKER S R, KLUBER L A, PETERSEN S M, et al., 2016. Mycorrhizal fungal communities respond to experimental elevation of soil pH and P availability in temperate hardwood forests[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 92(3): fiw024.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HE Q Q, WU Y H, BING H J, et al., 2020. Vegetation type rather than climate modulates the variation in soil enzyme activities and stoichiometry in subalpine forests in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geoderma, 374: 114424.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HEUCK C, WEIG A, SPOHN M, 2015. Soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 85: 119-129.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MENG L, QU F Z, BI X L, et al., 2021. Elemental stoichiometry (C, N, P) of soil in the Yellow River Delta nature reserve: Understanding N and P status of soil in the coastal estuary[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 751: 141737.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
QIU L P, ZHANG Q, ZHU H S, et al., 2021. Erosion reduces soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality[J]. The ISME Journal, 15(8): 2474-2489.
DOI |
| [12] |
SHEN R C, XU M, LI R Q, et al., 2015. Spatial variability of soil microbial biomass and its relationships with edaphic, vegetational and climatic factors in the Three-River Headwaters region on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 95:191-203.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SINGH J S, RAGHUBANSHI A S, SINGH R S, et al., 1989. Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna[J]. Nature, 338(6215): 499-500.
DOI |
| [14] |
SINSABAUGH R L, LAUBER C L, WEINTRAUB M N, et al., 2008. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale[J]. Ecology Letters, 11(11): 1252-1264.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
SINSABAUGH R L, HILL B H, FOLLSTAD SHAH J J, 2009. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment[J]. Nature, 462(7274): 795-798.
DOI |
| [16] |
TIAN L M, ZHAO L, WU X D, et al., 2018. Soil moisture and texture primarily control the soil nutrient stoichiometry across the Tibetan grassland[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 622-623: 192-202.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
VANCE E D, BROOKES P C, JENKINSON D S, 1987. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 19(6): 703-707.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG R Z, DORODNIKOV M, YANG S, et al., 2015. Responses of enzymatic activities within soil aggregates to 9-year nitrogen and water addition in a semi-arid grassland[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 81: 159-167.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WANG Y, REN Z, MA P P, et al., 2020. Effects of grassland degradation on ecological stoichiometry of soil ecosystems on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 722: 137910.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WARING B G, WEINTRAUB S R, SINSABAUGH R L, 2014. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils[J]. Biogeochemistry, 117(1): 101-113.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
XU Z W, YU G R, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2017. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect in eastern China (NSTEC)[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 104: 152-163.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
XU Z W, ZHANG T Y, WANG S Z, et al., 2020. Soil pH and C/N ratio determines spatial variations in soil microbial communities and enzymatic activities of the agricultural ecosystems in Northeast China: Jilin Province case[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 155: 103629.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG A L, LI X Y, WU S X, et al., 2021. Spatial pattern of C:N:P stoichiometry characteristics of alpine grassland in the Altunshan Nature Reserve at North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Catena, 207: 105691.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG Y, LI C, WANG M L, 2019. Linkages of C: N: P stoichiometry between soil and leaf and their response to climatic factors along altitudinal gradients[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(4): 1820-1829.
DOI |
| [25] | 陈涛, 张宏达, 1994. 南岭植物区系地理学研究——Ⅰ.植物区系的组成和特点[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2(1): 10-23. |
| CHEN T, ZHANG H D, 1994. The floristic geography of Nanling mountain range, China: Ⅰ. floristic composition and characteristics[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2(1): 10-23. | |
| [26] |
邓娇娇, 朱文旭, 周永斌, 等, 2018. 不同土地利用模式对辽东山区土壤微生物群落多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(7): 2269-2276.
DOI |
| DENG J J, ZHU W X, ZHOU Y B, et al., 2018. Effects of different land use patterns on the soil microbial community diversity in montane region of eastern Liaoning Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(7): 2269-2276. | |
| [27] | 董廷发, 2021. 不同海拔云南松林土壤养分及其生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(3): 672-679. |
| DONG T F, 2021. Soil nutrients and their ecological stoichiometry of Pinus yunnanensis forest along an elevation gradient[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(3): 672-679. | |
| [28] | 冯德枫, 包维楷, 2017. 土壤碳氮磷化学计量比时空格局及影响因素研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 23(2): 400-408. |
| FENG D F, BAO W K, 2017. Review of the temporal and spatial patterns of soil C:N:P stoichiometry and its driving factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 23(2): 400-408. | |
| [29] |
贺金生, 韩兴国, 2010. 生态化学计量学:探索从个体到生态系统的统一化理论[J]. 植物生态学报, 34(1): 2-6.
DOI |
| HE J S, HAN X G, 2010. Ecological stoichiometry: Searching for unifying principles from individuals to ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(1): 2-6. | |
| [30] | 黄斌, 王泉泉, 李定强, 等, 2022. 南岭山地土壤有机碳及组分海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 土壤通报, 53(2): 374-383. |
| HUANG B, WANG Q Q, LI D Q, et al., 2022. Variation characteristics of organic carbon and fractions in soils along the altitude gradient in Nanling Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 53(2): 374-383. | |
| [31] | 贾培龙, 安韶山, 李程程, 等, 2020. 黄土高原森林带土壤养分和微生物量及其生态化学计量变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(1): 315-321. |
| JIA P L, AN S S, LI C C, et al., 2020. Dynamics of soil nutrients and their ecological stoichiometry characteristics under different longitudes in the east-west forest belt of the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water conservation, 34(1): 315-321. | |
| [32] | 李新星, 刘桂民, 吴小丽, 等, 2020. 马衔山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(3): 758-765. |
| LI X X, LIU G M, WU X L, et al., 2020. Elevational distribution of soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and their ecological stoichiometry on Maxian Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(3): 758-765. | |
| [33] |
林惠瑛, 周嘉聪, 曾泉鑫, 等, 2022. 土壤酶计量揭示了武夷山黄山松林土壤微生物沿海拔梯度的碳磷限制变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(1): 33-41.
DOI |
| LIN H Y, ZHOU J C, ZENG Q X, et al., 2022. Soil enzyme stoichiometry revealed the changes of soil microbial carbon and phosphorus limitation along an elevational gradient in a Pinus taiwanensis forest of Wuyi Mountains, Southeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33(1): 33-41. | |
| [34] |
刘秉儒, 2010. 贺兰山东坡典型植物群落土壤微生物量碳、氮沿海拔梯度的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(4): 883-888.
DOI URL |
| LIU B R, 2010. Changes in soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen under typical plant communies along an altitudinal gradient in east side of Helan Mountain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(4): 883-888. | |
| [35] | 刘敏, 苏志尧, 2010. 广东低山林下土壤理化特征分析[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 30(2): 36-40, 59. |
| LIU M, SU Z Y, 2010. Soil physicochemical regime analysis of low hills under forest in Guangdong province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 30(2): 36-40, 59. | |
| [36] |
卢建男, 刘凯军, 王瑞雄, 等, 2022. 中国荒漠植物-土壤系统生态化学计量学研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 42(2): 173-182.
DOI |
|
LU J N, LIU K J, WANG R X, et al., 2022. Research advances in stoichiometry of desert plant-soil system in China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 42(2): 173-182.
DOI |
|
| [37] | 孙德斌, 栗云召, 于君宝, 等, 2022. 黄河三角洲湿地不同植被类型下土壤营养元素空间分布及其生态化学计量学特征[J]. 环境科学, 43(6): 3241-3252. |
| SUN D B, LI Y Z, YU J B, et al., 2022. Spatial Distribution and eco-stoichiometric characteristics of soil nutrient elements under different vegetation types in the Yellow River Delta Wetland[J]. Environmental Science, 43(6): 3241-3252. | |
| [38] |
唐立涛, 刘丹, 罗雪萍, 等, 2019. 青海省森林土壤磷储量及其分布格局[J]. 植物生态学报, 43(12): 1091-1103.
DOI |
|
TANG L T, LIU D, LUO X P, et al., 2019. Forest soil phosphorus stocks and distribution patterns in Qinghai, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43(12): 1091-1103.
DOI URL |
|
| [39] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞, 2008. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学报, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R, 2008. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| [40] | 温美丽, 杨龙, 王钧, 等, 2018. 南岭森林的土壤保持功能[J]. 林业与环境科学, 34(2): 123-130. |
| WEN M L, YANG L, WANG J, et al., 2018. Soil Retention Function of Forest in NanLing Mountain[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 34(2): 123-130. | |
| [41] |
吴昊, 邹梦茹, 王思芊, 等, 2019. 秦岭松栎林土壤生态化学计量特征及其对海拔梯度的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(12): 2323-2331.
DOI URL |
| WU H, ZOU M R, WANG S Q, et al., 2019. Eco-stoichiometry characteristics of soil within pine and oak mixed forest and theirs responses to elevation gradient in Qinling Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(12): 2323-2331. | |
| [42] | 许淼平, 任成杰, 张伟, 等, 2018. 土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷与土壤酶化学计量对气候变化的响应机制[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(7): 2445-2454. |
| XU M P, REN C J, ZHANG W, et al., 2018. Responses mechanism of C:N:P stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass and soil enzymes to climate change[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(7): 2445-2454. | |
| [43] | 薛立, 邝立刚, 陈红跃, 等, 2003. 不同林分土壤养分、微生物与酶活性的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 40(2): 280-285. |
| XUE L, KUANG L G, CHEN H Y, et al., 2003. Soil nutrients, microorganisms and enzyme activities of different stands[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 40(2): 280-285. | |
| [44] | 张剑, 宿力, 王利平, 等, 2019. 植被盖度对土壤碳、氮、磷生态化学计量比的影响——以敦煌阳关湿地为例[J]. 生态学报, 39(2): 580-589. |
| ZHANG J, SU L, WANG L P, et al., 2019. The effect of vegetation cover on ecological stoichiometric ratios of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus: A case study of the Dunhuang Yangguan wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(2): 580-589. | |
| [45] | 张星星, 杨柳明, 陈忠, 等, 2018. 中亚热带不同母质和森林类型土壤生态酶化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(16): 5828-5836. |
| ZHANG X X, YANG L M, CHEN Z, et al., 2018. Patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry on types of forest soils form different parent materials in subtropical areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(16): 5828-5836. | |
| [46] | 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等, 2013. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
|
ZHU Q L, XING X Y, ZHANG H, et al., 2013. Soil ecological stoichiometry under different vegetation area on loess hilly-gully region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4674-4682.
DOI URL |
|
| [47] | 宗天韵, 周玮莹, 周平, 2019. 南岭山地1968到2015年降雨的时空变化特征研究[J]. 生态科学, 38(2): 182-190. |
| ZONG T Y, ZHOU W Y, ZHOU P, 2019. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation of rainfall in 1968-2015 in Nanling[J]. Ecological Science, 38(2): 182-190. |
| [1] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [4] | 代德敏, 蒋旭升, 刘杰, 王路洋, 陈诗奇, 韩庆坤. 3种有机改良剂对铅锌矿尾砂适生性改善的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 784-793. |
| [5] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [6] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [7] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [8] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [9] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [10] | 韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 荒漠草原凋落物分解过程中降水量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812. |
| [11] | 刘展航, 张树岩, 侯玉平, 朱书玉, 王立冬, 施欣悦, 李培广, 韩广轩, 谢宝华. 互花米草入侵对黄河口湿地土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369. |
| [12] | 曹晓云, 祝存兄, 陈国茜, 孙树娇, 赵慧芳, 朱文彬, 周秉荣. 2000—2021年柴达木盆地地表绿度变化及地形分异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1080-1090. |
| [13] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [14] | 喻阳华, 吴银菇, 宋燕平, 李一彤. 不同林龄顶坛花椒林地土壤微生物浓度与生物量化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [15] | 孙建波, 畅文军, 李文彬, 张世清, 李春强, 彭明. 香蕉不同生育期根际微生物生物量及土壤酶活的变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1169-1174. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
