生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 497-503.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.008
梁嘉伟( ), 余炜敏(
), 余炜敏( ), 姚钰玲, 胡绮琪, 陆丹绵, 王荣萍**(
), 姚钰玲, 胡绮琪, 陆丹绵, 王荣萍**( ), 廖新荣, 黄赛花
), 廖新荣, 黄赛花
收稿日期:2020-04-09
出版日期:2022-03-18
发布日期:2022-05-25
通讯作者:
**王荣萍(1976年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究方向为土壤与植物营养。E-mail: rpwang@soil.gd.cn作者简介:梁嘉伟(1991年生),男,助理工程师,研究方向为土壤与植物营养。E-mail: jwliang@soil.gd.cn;基金资助:
LIANG Jiawei( ), YU Weimin(
), YU Weimin( ), YAO Yuling, HU Qiqi, LU Danmian, WANG Rongping**(
), YAO Yuling, HU Qiqi, LU Danmian, WANG Rongping**( ), LIAO Xinrong, HUANG Saihua
), LIAO Xinrong, HUANG Saihua
Received:2020-04-09
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
摘要:
为了探讨生物有机肥对菜地土壤质量及蔬菜产量的影响,采用田间小区试验,以华南地区代表性瓜类蔬菜白瓜(Cucurbita pepo L.)为试验作物,配施生物有机肥研究了白瓜不同生育期土壤肥力、酶活性、微生物生物量及产量。结果表明,(1)施用生物有机肥能够提高土壤的pH值、碱解氮、速效钾和有效磷的含量。在白瓜清藤期,配施生物有机肥的土壤其pH值、碱解氮、速效钾和有效磷的含量均比农户习惯施肥和无机肥处理均增加10%以上。(2)施用生物有机肥对土壤的酶活性和微生物生物量的含量影响不同。在白瓜苗期,生物有机肥可提高土壤微生物生物量碳含量,与农户习惯施肥和无机肥处理相比分别增加了67.0%和91.8%;在白瓜伸蔓期,生物有机肥可提高微生物量碳含量、蔗糖酶和酸性磷酸酶活性,与农户习惯施肥和无机肥处理相比分别增加了11.8%—33.2%和13.1%—37.4%;在白瓜盛瓜期,生物有机肥可提高微生物生物量碳含量、过氧化氢酶和酸性磷酸酶活性,与农户习惯施肥和无机肥处理相比,分别增加了12.1%—22.7%和19.3%—28.4%;在白瓜清藤期,生物有机肥可增强过氧化氢酶和酸性磷酸酶活性,与农户习惯施肥和无机肥处理相比,分别增加了8.02%—33.5%和20.1%—27.7%。因此,配施生物有机肥对白瓜不同生育期的微生物活性影响不同。(3)生物有机肥对白瓜的增产作用发生在盛瓜期前期,对盛瓜期后期影响很小。综上所述,生物有机肥可提高土壤肥力,增强微生物生物量和酶活性,改良土壤环境,提高白瓜产量。
中图分类号:
梁嘉伟, 余炜敏, 姚钰玲, 胡绮琪, 陆丹绵, 王荣萍, 廖新荣, 黄赛花. 生物有机肥对土壤质量及蔬菜产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 497-503.
LIANG Jiawei, YU Weimin, YAO Yuling, HU Qiqi, LU Danmian, WANG Rongping, LIAO Xinrong, HUANG Saihua. Effects of a Bio-organic Fertilizer on Soil Quality and Vegetable Yield[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 497-503.
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N/ (kg∙hm-2) | 磷P2O5/ (kg∙hm-2) | 钾K2O/ (kg∙hm-2) | 生物有机肥 Bio-organic fertilizer/ (kg∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 135 | 135 | 135 | 0 |
| T2 | 187 | 90 | 120 | 0 |
| T3 | 187 | 90 | 120 | 4500 (曲成闯等, |
表1 养分施入量a
Table 1 Nutrient dosage
| 处理 Treatment | 氮N/ (kg∙hm-2) | 磷P2O5/ (kg∙hm-2) | 钾K2O/ (kg∙hm-2) | 生物有机肥 Bio-organic fertilizer/ (kg∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 135 | 135 | 135 | 0 |
| T2 | 187 | 90 | 120 | 0 |
| T3 | 187 | 90 | 120 | 4500 (曲成闯等, |
| 肥力指标 Soil property | 处理 Treatment | 苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine elongation stage | 盛瓜期 Fruiting stage | 清藤期 Mature stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T1 | 5.22±0.599a | 5.06±0.810a | 4.88±0.630a | 4.56±0.280a |
| T2 | 5.26±0.170a | 5.22±0.0874a | 4.93±0.0757a | 5.01±0.274a | |
| T3 | 5.12±0.342a | 4.97±0.395a | 5.10±0.0721a | 5.33±0.238a | |
| 有机质质量分数 w(organic matter)/(g∙kg-1) | T1 | 24.5±4.84a | 25.9±1.60a | 25.1±1.97a | 23.6±0.617a |
| T2 | 24.3±1.20a | 24.8±1.35a | 21.8±2.40a | 24.7±2.35a | |
| T3 | 24.3±0.700a | 25.9±4.22a | 24.7±1.13a | 25.3±0.373a | |
| 全N质量分数 w(total N)/(g∙kg-1) | T1 | 1.52±0.312a | 1.81±0.0766a | 1.65±0.0956a | 1.52±0.162a |
| T2 | 1.60±0.0506a | 1.65±0.116a | 1.56±0.192a | 1.75±0.0869a | |
| T3 | 1.66±0.128a | 1.67±0.104a | 1.58±0.115a | 1.69±0.0224a | |
| 碱解N质量分数 w(alkali-hydrolyzable N)/ (mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 134±7.24a | 148±5.88a | 155±5.84a | 159±16.6a |
| T2 | 131±6.50a | 144±5.92a | 154±22.1a | 128±5.20a | |
| T3 | 139±4.10a | 152±7.83a | 158±21.6a | 262±29.4a | |
| 速效K质量分数 w(available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 195±0.00a | 228±1.41a | 179±7.74a | 177±23.2a |
| T2 | 205±47.2a | 333±77.8a | 189±51.3a | 101±31.0a | |
| T3 | 249±4.98a | 253±10.6a | 213±30.9a | 381±9. 85a | |
| 有效P质量分数 w(available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 129±19.1a | 123±5.43a | 120±4.16a | 121±9.17a |
| T2 | 122±4.90a | 123±3.61a | 122±4.77a | 125±15.3a | |
| T3 | 131±5.75a | 135±6.50a | 117±3.07a | 130±7.16a |
表2 生物有机肥对白瓜土壤中肥力特征的影响
Table 2 Effects of bio-organic fertilizer application on soil pH and fertility at different growth stages of squash (Cucurbita pepo L.)
| 肥力指标 Soil property | 处理 Treatment | 苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine elongation stage | 盛瓜期 Fruiting stage | 清藤期 Mature stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | T1 | 5.22±0.599a | 5.06±0.810a | 4.88±0.630a | 4.56±0.280a |
| T2 | 5.26±0.170a | 5.22±0.0874a | 4.93±0.0757a | 5.01±0.274a | |
| T3 | 5.12±0.342a | 4.97±0.395a | 5.10±0.0721a | 5.33±0.238a | |
| 有机质质量分数 w(organic matter)/(g∙kg-1) | T1 | 24.5±4.84a | 25.9±1.60a | 25.1±1.97a | 23.6±0.617a |
| T2 | 24.3±1.20a | 24.8±1.35a | 21.8±2.40a | 24.7±2.35a | |
| T3 | 24.3±0.700a | 25.9±4.22a | 24.7±1.13a | 25.3±0.373a | |
| 全N质量分数 w(total N)/(g∙kg-1) | T1 | 1.52±0.312a | 1.81±0.0766a | 1.65±0.0956a | 1.52±0.162a |
| T2 | 1.60±0.0506a | 1.65±0.116a | 1.56±0.192a | 1.75±0.0869a | |
| T3 | 1.66±0.128a | 1.67±0.104a | 1.58±0.115a | 1.69±0.0224a | |
| 碱解N质量分数 w(alkali-hydrolyzable N)/ (mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 134±7.24a | 148±5.88a | 155±5.84a | 159±16.6a |
| T2 | 131±6.50a | 144±5.92a | 154±22.1a | 128±5.20a | |
| T3 | 139±4.10a | 152±7.83a | 158±21.6a | 262±29.4a | |
| 速效K质量分数 w(available K)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 195±0.00a | 228±1.41a | 179±7.74a | 177±23.2a |
| T2 | 205±47.2a | 333±77.8a | 189±51.3a | 101±31.0a | |
| T3 | 249±4.98a | 253±10.6a | 213±30.9a | 381±9. 85a | |
| 有效P质量分数 w(available P)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 129±19.1a | 123±5.43a | 120±4.16a | 121±9.17a |
| T2 | 122±4.90a | 123±3.61a | 122±4.77a | 125±15.3a | |
| T3 | 131±5.75a | 135±6.50a | 117±3.07a | 130±7.16a |
| 微生物性质 Soil biological property | 处理 Treatment | 苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine elongation stage | 盛瓜期 Fruiting stage | 清藤期 Mature stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity (by KMnO4)/ (0.1 mol∙L-1∙g-1∙h-1) | T1 | 0.688±0.0941a | 0.631±0.110a | 0.568±0.0882a | 0.484±0.107a |
| T2 | 0.674±0.0607a | 0.670±0.0250a | 0.526±0.0633a | 0.506±0.132a | |
| T3 | 0.758±0.0346a | 0.622±0.101a | 0.675±0.0523a | 0.646±0.0469a | |
| 酸性磷酸酶活性 Acid phosphatase activity (by phenol)/(µg∙g-1∙h-1) | T1 | 220±16.9a | 338±85.9b | 329±56.7b | 234±38.4a |
| T2 | 209±10.2a | 327±28.2b | 324±18.7b | 210±36.2a | |
| T3 | 217±5.80a | 450±20.9a | 404±37.2a | 253±34.2a | |
| 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity (by Na2S2O3)/ (0.1 mol∙L-1∙kg-1∙h-1) | T1 | 6.03±0.212a | 2.65±0.251a | 2.09±0.0493a | 1.92±0.436a |
| T2 | 4.72±0.191b | 2.62±0.115a | 2.04±0.277a | 2.35±0.665a | |
| T3 | 5.87±0.396a | 2.96±0.515a | 2.24±0.248a | 2.41±0.591a | |
| 脲酶活性 Urease activity (by NH3)/ (mg∙kg-1∙h-1) | T1 | 244±10.4a | 235±1.53a | 207±2.08a | 217±8.96a |
| T2 | 230±8.00a | 215±2.65a | 230±36.8a | 222±2.65a | |
| T3 | 226±6.25a | 216±13.8a | 229±55.2a | 228±4.51a | |
| 微生物生物量碳质量分数 w(Microbial biomass C)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 149±23.2b | 175±36.9b | 121±24.7b | 114±7.09a |
| T2 | 130±22.6b | 195±38.4a | 146±50.9b | 141±32.2b | |
| T3 | 148±17.7a | 203±29.6a | 168±24.8a | 127±7.81a | |
| 微生物生物量氮质量分数 w(Microbial biomass N)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 34.2±9.70b | 28.3±6.01a | 57.9±10.0a | 57.8±0.757a |
| T2 | 59.9±5.70a | 17.5±9.90b | 54.4±4.41a | 57.3±19.7a | |
| T3 | 63.4±4.76a | 15.6±3.78b | 64.9±12.1a | 72.7±4.67a |
表3 生物有机肥对白瓜土壤中酶活性和微生物生物量的影响
Table 3 Effects of bio-organic fertilizer application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass at different growth stages of squash (Cucurbita pepo L.)
| 微生物性质 Soil biological property | 处理 Treatment | 苗期 Seedling stage | 伸蔓期 Vine elongation stage | 盛瓜期 Fruiting stage | 清藤期 Mature stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity (by KMnO4)/ (0.1 mol∙L-1∙g-1∙h-1) | T1 | 0.688±0.0941a | 0.631±0.110a | 0.568±0.0882a | 0.484±0.107a |
| T2 | 0.674±0.0607a | 0.670±0.0250a | 0.526±0.0633a | 0.506±0.132a | |
| T3 | 0.758±0.0346a | 0.622±0.101a | 0.675±0.0523a | 0.646±0.0469a | |
| 酸性磷酸酶活性 Acid phosphatase activity (by phenol)/(µg∙g-1∙h-1) | T1 | 220±16.9a | 338±85.9b | 329±56.7b | 234±38.4a |
| T2 | 209±10.2a | 327±28.2b | 324±18.7b | 210±36.2a | |
| T3 | 217±5.80a | 450±20.9a | 404±37.2a | 253±34.2a | |
| 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity (by Na2S2O3)/ (0.1 mol∙L-1∙kg-1∙h-1) | T1 | 6.03±0.212a | 2.65±0.251a | 2.09±0.0493a | 1.92±0.436a |
| T2 | 4.72±0.191b | 2.62±0.115a | 2.04±0.277a | 2.35±0.665a | |
| T3 | 5.87±0.396a | 2.96±0.515a | 2.24±0.248a | 2.41±0.591a | |
| 脲酶活性 Urease activity (by NH3)/ (mg∙kg-1∙h-1) | T1 | 244±10.4a | 235±1.53a | 207±2.08a | 217±8.96a |
| T2 | 230±8.00a | 215±2.65a | 230±36.8a | 222±2.65a | |
| T3 | 226±6.25a | 216±13.8a | 229±55.2a | 228±4.51a | |
| 微生物生物量碳质量分数 w(Microbial biomass C)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 149±23.2b | 175±36.9b | 121±24.7b | 114±7.09a |
| T2 | 130±22.6b | 195±38.4a | 146±50.9b | 141±32.2b | |
| T3 | 148±17.7a | 203±29.6a | 168±24.8a | 127±7.81a | |
| 微生物生物量氮质量分数 w(Microbial biomass N)/(mg∙kg-1) | T1 | 34.2±9.70b | 28.3±6.01a | 57.9±10.0a | 57.8±0.757a |
| T2 | 59.9±5.70a | 17.5±9.90b | 54.4±4.41a | 57.3±19.7a | |
| T3 | 63.4±4.76a | 15.6±3.78b | 64.9±12.1a | 72.7±4.67a |
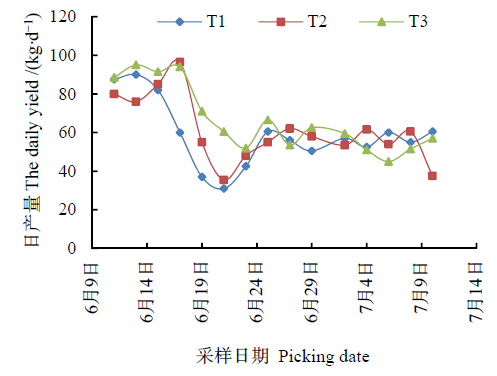
图1 生物有机肥对白瓜日产量的影响 n=5. The same below
Figure 1 Effect of bio-organic fertilizer application on the daily yield of squash (Cucurbita pepo L.) n=5. The same below
| [1] |
EKENLER M, TABATABAI M A, 2003. Effects of liming and tillage systems on microbial biomass and glycosidase in soils[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 39(1): 51-61.
DOI URL |
| [2] | GUO Z, WANG X L, LI Y, 2018. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in different size fraction[J]. Land Development and Engineering Research, 3(12): 62-68. |
| [3] |
LIU L, LI T Y, WEI X H, et al., 2014. Effects of a nutrient additive on the density of functional bacteria and the microbial community structure of bioorganic fertilizer[J]. Bioresource Technology, 172: 328-334.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG N, HE X, ZHANG J, et al., 2014. Suppression of Fusarium wilt of banana with application of bio-organic fertilizers[J]. Pedosphere, 24(5): 613-624.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZHANG Q, ZHOU W, LIANG G Q, et al., 2015. Distribution of soil nutrients, extracellular enzyme activities and microbial communities across particle-size fractions in a long-term fertilizer experiment[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 94: 59-71.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG S S, RAZA W, YANG X M, et al., 2008. Control of Fusarium wilt disease of cucumber plants with the application of a bioorganic fertilizer[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 44: 1073-1080.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 陈会鲜, 曹升, 严华兵, 等, 2019. 增施生物有机肥对食用木薯产量及品质的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 40(3): 417-424. |
| CHEN H X, CAO S, YAN H B, et al., 2019. The effect of increasing bio-organic fertilizer on the yield and quality of edible-cassava[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 40(3): 417-424. | |
| [8] | 崔红标, 田超, 周静, 等, 2011. 纳米羟基磷灰石对重金属污染土壤Cu/Cd形态分布及土壤酶活性影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(5): 874-880. |
| CUI H B, TIAN C, ZHOU J, et al., 2011. The Effects of Nano-scale Hydroxyapatite on the Speciation of Cu and Cd and Enzymatic Activities in Soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(5): 874-880. | |
| [9] | 丁文娟, 曹群, 赵兰凤, 等, 2014. 生物有机肥施用期对香蕉枯萎病及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(8): 1575-1582. |
| DING W J, CAO Q, ZHAO L F, et al., 2014. Effects of biological fertilizer applications on banana wilt disease and soil microorganisms[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(8): 1575-1582. | |
| [10] | 贺文员, 宋清晖, 杨尚霖, 等, 2019. 生物有机肥对水稻土壤酶活性及微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 35(27): 106-113. |
| HE W Y, SONG Q H, YANG S L, et al., 2019. Biological fertilizer: effects on enzyme activity and microbial community structure in rice soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 35(27): 106-113. | |
| [11] | 胡诚, 曹志平, 罗艳蕊, 等, 2007. 长期施用生物有机肥对土壤肥力及微生物生物量碳的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 15(3): 48-51. |
| HU C, CAO Z P, LUO Y R, et al., 2007. Effect of long-term application of microorganismic compost or vermicompost on soil fertility and microbial biomass carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 15(3): 48-51. | |
| [12] | 蒋仁成, 厉志华, 李德民, 1990. 有机肥和无机肥在提高黄潮土肥力中的作用研究[J]. 土壤学报, 27(2): 179-185. |
| JIANG R C, LI Z H, LI D M, 1990. Studies on role of chemical and organic fertilizer in promoting the fertility of yellow fluvo-aquic soils[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 27(2):179-185. | |
| [13] | 林先贵, 2010. 土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| LIN X G, 2010. Principles and methods of soil microbial research[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. | |
| [14] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [15] | 马祥, 贾志锋, 张永超, 等, 2019. 生物有机肥对青海高寒牧区燕麦产量和土壤肥力的影响[J]. 草地学报, 27(6): 1759-1765. |
| MA X, JIA Z F, ZHANG Y C, et al., 2019. Effects of bio-organic fertilizers on oat production and soil fertility in alpine region of Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 27(6): 1759-1765. | |
| [16] | 马晓霞, 王莲莲, 黎青慧, 等, 2012. 长期施肥对玉米生育期土壤微生物量碳氮及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(17): 5502-5511. |
|
MA X X, WANG L L, LI Q H, et al., 2012. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities during maize growing season[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(17): 5502-5511.
DOI URL |
|
| [17] | 曲成闯, 陈效民, 韩召强, 等, 2017. 施用生物有机肥对黄瓜不同生育期土壤肥力特征及酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(6): 279-284. |
| QU C C, CHEN X M, HAN Z Q, et al., 2017. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil fertility and enzymes activities in different growth stages of cucumber[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(6): 279-284. | |
| [18] | 曲成闯, 陈效民, 韩召强, 等, 2018. 生物有机肥对潮土物理性状及微生物量碳、氮的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 38(5): 76-82. |
| QU C C, CHEN X M, HAN Z Q, et al., 2018. Effects of bioorganic fertilizer application on soil Physical properties and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in fluvoaquic soil[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 38(5): 76-82. | |
| [19] | 宋以玲, 于建, 陈士更, 等, 2018. 化肥减量配施生物有机肥对油菜生长及土壤微生物和酶活性影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(1): 352-360. |
| SONG Y L, YU J, CHEN S G, et al., 2018. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with application of bio-organic fertilizer on rape growth, microorganism and enzymes activities in soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(1): 352-360. | |
| [20] | 孙家骏, 付青霞, 谷洁, 等, 2016. 生物有机肥对猕猴桃土壤酶活性和微生物群落的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 27(3): 829-837. |
| SUN J J, FU Q X, GU J, et al., 2016. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activities and microbial community in kiwifruit orchard[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(3): 829-837. | |
| [21] | 孙薇, 钱勋, 付青霞, 等, 2013. 生物有机肥对秦巴山区核桃园土壤微生物群落和酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 19(5): 1224-1233. |
| SUN W, QIAN X, FU Q X, et al., 2013. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer on soil microbial community and enzymes activities in walnut orchards of the Qinling-Bashan region[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 19(5): 1224-1233. | |
| [22] | 田小明, 李俊华, 王成, 等, 2014. 连续3年施用生物有机肥对土壤养分、微生物生物量及酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 46(3): 481-488. |
| TIAN X M, LI J H, WANG C, et al., 2013. Effects of continuous application of bio-organic fertilizer for three years on soil nutrients, microbial biomass and enzyme activity[J]. Soils, 46(3): 481-488. | |
| [23] | 王成, 吕剑, 李静, 等, 2019. 不同生物有机肥用量对韭菜产量、品质及养分利用的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6): 204-211. |
| WANG C, LV J, LI J, et al., 2019. Effects of different biological fertilizer levels on yield, quality and nutrient utilization of Chinese chive[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (6): 204-211. | |
| [24] | 王艳群, 彭正萍, 薛世川, 等, 2005. 过量施肥对设施农田土壤生态环境的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 24(增刊): 81-84. |
| WANG Y Q, PENG Z P, XUE S C, et al., 2005. Effect of excessive fertilization on soil ecological environment in the facility farmland[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 24(Z1): 81-84. | |
| [25] | 张静, 杨江舟, 胡伟, 等, 2012. 生物有机肥对大豆红冠腐病及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(3): 548-554. |
| ZHANG J, YANG J Z, HU W, et al., 2012. Effect of biological organic fertilizer on soybean red crown rot and soil enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(3): 548-554. | |
| [26] | 张敏, 孙宝利, 宋阿琳, 等, 2016. 微生物多样性对土壤氮磷钾转化、酶活性及油菜生长的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(18): 5856-5864. |
| ZHANG M, SUN B L, SONG A L, et al., 2016. Effects of soil microbial diversity on soil NPK transformation, enzyme activities, and canola growth[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(18): 5856-5864. |
| [1] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [2] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [3] | 喻阳华, 吴银菇, 宋燕平, 李一彤. 不同林龄顶坛花椒林地土壤微生物浓度与生物量化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [4] | 孙建波, 畅文军, 李文彬, 张世清, 李春强, 彭明. 香蕉不同生育期根际微生物生物量及土壤酶活的变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1169-1174. |
| [5] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [6] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [8] | 孙战, 王圣洁, 杨锦昌, 魏永成, 林春花, 马海宾. 木麻黄根区土壤理化特性及酶活性与青枯病发生关联分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 70-78. |
| [9] | 丁洪, 余居华, 郑祥洲, 张玉树, 钟云峰. 中国城市污泥应用对作物产量、品质和土壤质量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1933-1942. |
| [10] | 胡瑞, 房焕英, 肖胜生, 段剑, 张杰, 刘洪光, 汤崇军. 南方红壤典型花岗岩侵蚀区主要治理模式的土壤碳汇效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1617-1626. |
| [11] | 李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641. |
| [12] | 陈思, 王灿, 李想, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 祖艳群, 何永美. 不同UV-B辐射增幅对稻田土壤酶活性、活性有机碳含量及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268. |
| [13] | 杨洪炳, 肖以华, 李明, 许涵, 史欣, 郭晓敏. 典型城市森林旱季土壤团聚体稳定性与微生物胞外酶活性耦合关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1976-1989. |
| [14] | 刘红梅, 李睿颖, 高晶晶, 朱平, 路杨, 高洪军, 张贵龙, 张秀芝, 彭畅, 杨殿林. 保护性耕作对土壤团聚体及微生物学特性的影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(6): 1277-1284. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
