生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 299-308.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.02.010
盛美君( ), 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚*(
), 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚*( ), 修伟明*(
), 修伟明*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-12
出版日期:2023-02-18
发布日期:2023-05-11
通讯作者:
李刚(1981年生),男,副研究员,主要从事农田土壤质量提升与健康培育研究。E-mail: ligang20032002@126.com作者简介:盛美君(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事健康土壤培育的生物学机制研究。E-mail: shengmeijun1218@163.com
基金资助:
SHENG Meijun( ), LI Shengjun, YANG Xinyue, WANG Rui, LI Jie, LI Gang*(
), LI Shengjun, YANG Xinyue, WANG Rui, LI Jie, LI Gang*( ), XIU Weiming*(
), XIU Weiming*( )
)
Received:2022-12-12
Online:2023-02-18
Published:2023-05-11
摘要:
集约化农业引发的负面效应已成为亟需解决的全球性问题。土壤酶是指示农田土壤质量变化的重要生物学指标,为探究土壤酶活性对农田土地利用强度调整的响应及其驱动因子,设置高土地利用强度(玉米-小麦轮作,MW)、中土地利用强度(临时草地-小麦,GW和玉米-临时草地,MG)和低土地利用强度(多年生草地,PG)共4个处理,在玉米拔节期、扬花期和成熟期采集土壤样品,测定土壤脱氢酶(Dehydrogenase,DHA)、纤维素酶(Cellulose,CL)、脲酶(Urease,UE)和碱性磷酸酶(Alkaine phosphatase,ALP)活性,分析其时间动态变化特征,并耦合土壤理化性质解析其驱动力。结果表明,土地利用强度降低后,土壤pH值下降,而有机质(Soil organic matter,SOM)和全氮(Total nitrogen,TN)含量上升;随着作物生长期的推进,土壤CL与UE活性整体呈现下降趋势,而ALP活性整体呈现上升趋势,土壤DHA未呈现有规律的变化;土地利用强度的降低增加了土壤DHA及ALP活性,而降低了CL与UE活性。相关分析结果表明,土壤CL和UE活性均与pH显著正相关(P<0.05),而ALP活性与pH呈极显著负相关关系(P<0.01);土壤UE活性与含水量(Soil moisture,SM)极显著负相关(P<0.01);CL活性与有效磷(Available phosphorus,AP)显著负相关(P<0.05),与铵态氮极显著负相关(P<0.01)。随机森林分析(Random forest analysis,RFA)结果表明,研究中所选定的土壤理化性质对ALP活性的解释度最高(44.66%)。冗余分析(Redundancy analysis,RDA)结果表明,pH、SM和铵态氮是土壤酶活性的关键调控因子,共同驱动土壤酶活性的变化。研究结果可为华北潮土区土地利用强度调整与保护性耕作措施的提出及优化提供基础数据支撑和理论依据。
中图分类号:
盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308.
SHENG Meijun, LI Shengjun, YANG Xinyue, WANG Rui, LI Jie, LI Gang, XIU Weiming. Changes of Soil Enzyme Activities in Cropland with Different Land Use Intensities in Fluvo-aquic Soil Area, North China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 299-308.
| 生长时期 | 处理 | pH值 | 含水量/% | w(有机质)/ (g·kg-1) | w(全氮)/ (g·kg-1) | w(全磷)/ (g·kg-1) | w(铵态氮)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(硝态氮)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(速效磷)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 | MW | 8.64±0.06Aa | 20.20±1.59Ba | 18.44±1.13Aa | 1.48±0.07Aa | 0.77±0.07Aa | 3.20±0.28Ba | 18.70±4.05Ba | 23.01±5.74Aa |
| GW | 8.33±0.03Ab | 17.11±3.36Bab | 20.50±1.68Aa | 1.55±0.08Aa | 0.77±0.04Aa | 2.47±0.30Bbc | 7.02±0.90Bc | 23.29±2.46Aa | |
| MG | 8.51±0.05Aa | 17.97±3.65Bab | 19.54±1.97Ba | 1.50±0.06ABa | 0.73±0.03Bab | 2.35±0.16Bc | 14.40±0.79Bb | 21.82±0.80Aa | |
| PG | 7.82±0.07Bc | 15.68±2.46Cb | 19.80±1.07Aa | 1.54±0.05Aa | 0.67±0.03Bb | 2.77±0.14Cb | 5.41±1.30Bc | 17.02±0.63Ba | |
| 扬花期 | MW | 8.14±0.19Bab | 21.02±1.13Ba | 19.96±1.45Aa | 1.53±0.10Aa | 0.85±0.02Aa | 8.93±1.47Aa | 7.19±0.73Cb | 27.81±2.49Ab |
| GW | 8.32±0.05Aa | 19.15±0.25Bbc | 20.57±1.02Aa | 1.52±0.04Aa | 0.79±0.01Ab | 8.47±0.24Aa | 10.99±3.67Bb | 19.04±2.17Ac | |
| MG | 8.22±0.08Ba | 18.13±0.37Bc | 21.22±1.18Aa | 1.56±0.10Aa | 0.80±0.04Aab | 10.29±1.27Aa | 21.74±4.35Aa | 37.62±1.86Aa | |
| PG | 7.99±0.07Ab | 19.40±0.62Bb | 21.59±1.54Aa | 1.55±0.01Aa | 0.69±0.01Bc | 9.45±1.28Aa | 13.57±7.96Aab | 18.79±0.82Bc | |
| 成熟期 | MW | 7.99±0.07Ba | 23.37±1.02Ab | 19.88±2.31Aa | 1.52±0.04Aa | 0.83±0.07Aa | 8.65±0.39Aa | 39.43±0.87Aa | 27.28±3.18Ab |
| GW | 7.95±0.08Ba | 24.13±0.33Ab | 20.60±1.44Aa | 1.45±0.01Aa | 0.77±0.07Aa | 8.16±0.93Aa | 11.20±0.65Ac | 19.82±3.58Ab | |
| MG | 7.96±0.05Ca | 26.21±0.33Aa | 19.53±1.11ABa | 1.36±0.10Ba | 0.75±0.03ABa | 8.74±1.01Aa | 9.51±0.28Bc | 24.02±8.56Ab | |
| PG | 7.75±0.04Cb | 24.99±1.49Aa | 21.71±1.57Aa | 1.84±0.42Aa | 0.75±0.03Aa | 7.50±0.45Ba | 14.66±2.90Ab | 37.00±3.08Aa |
表1 土地利用强度调整对土壤理化性质的影响
Table 1 Effects of land use intensity manipulation on soil physical and chemical properties
| 生长时期 | 处理 | pH值 | 含水量/% | w(有机质)/ (g·kg-1) | w(全氮)/ (g·kg-1) | w(全磷)/ (g·kg-1) | w(铵态氮)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(硝态氮)/ (mg·kg-1) | w(速效磷)/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拔节期 | MW | 8.64±0.06Aa | 20.20±1.59Ba | 18.44±1.13Aa | 1.48±0.07Aa | 0.77±0.07Aa | 3.20±0.28Ba | 18.70±4.05Ba | 23.01±5.74Aa |
| GW | 8.33±0.03Ab | 17.11±3.36Bab | 20.50±1.68Aa | 1.55±0.08Aa | 0.77±0.04Aa | 2.47±0.30Bbc | 7.02±0.90Bc | 23.29±2.46Aa | |
| MG | 8.51±0.05Aa | 17.97±3.65Bab | 19.54±1.97Ba | 1.50±0.06ABa | 0.73±0.03Bab | 2.35±0.16Bc | 14.40±0.79Bb | 21.82±0.80Aa | |
| PG | 7.82±0.07Bc | 15.68±2.46Cb | 19.80±1.07Aa | 1.54±0.05Aa | 0.67±0.03Bb | 2.77±0.14Cb | 5.41±1.30Bc | 17.02±0.63Ba | |
| 扬花期 | MW | 8.14±0.19Bab | 21.02±1.13Ba | 19.96±1.45Aa | 1.53±0.10Aa | 0.85±0.02Aa | 8.93±1.47Aa | 7.19±0.73Cb | 27.81±2.49Ab |
| GW | 8.32±0.05Aa | 19.15±0.25Bbc | 20.57±1.02Aa | 1.52±0.04Aa | 0.79±0.01Ab | 8.47±0.24Aa | 10.99±3.67Bb | 19.04±2.17Ac | |
| MG | 8.22±0.08Ba | 18.13±0.37Bc | 21.22±1.18Aa | 1.56±0.10Aa | 0.80±0.04Aab | 10.29±1.27Aa | 21.74±4.35Aa | 37.62±1.86Aa | |
| PG | 7.99±0.07Ab | 19.40±0.62Bb | 21.59±1.54Aa | 1.55±0.01Aa | 0.69±0.01Bc | 9.45±1.28Aa | 13.57±7.96Aab | 18.79±0.82Bc | |
| 成熟期 | MW | 7.99±0.07Ba | 23.37±1.02Ab | 19.88±2.31Aa | 1.52±0.04Aa | 0.83±0.07Aa | 8.65±0.39Aa | 39.43±0.87Aa | 27.28±3.18Ab |
| GW | 7.95±0.08Ba | 24.13±0.33Ab | 20.60±1.44Aa | 1.45±0.01Aa | 0.77±0.07Aa | 8.16±0.93Aa | 11.20±0.65Ac | 19.82±3.58Ab | |
| MG | 7.96±0.05Ca | 26.21±0.33Aa | 19.53±1.11ABa | 1.36±0.10Ba | 0.75±0.03ABa | 8.74±1.01Aa | 9.51±0.28Bc | 24.02±8.56Ab | |
| PG | 7.75±0.04Cb | 24.99±1.49Aa | 21.71±1.57Aa | 1.84±0.42Aa | 0.75±0.03Aa | 7.50±0.45Ba | 14.66±2.90Ab | 37.00±3.08Aa |
| 因素 | 处理 | 生长时期 | 处理*生长时期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 脱氢酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 纤维素酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 脲酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
表2 土壤酶活性的双因素方差分析
Table 2 Two-factor ANOVA for soil enzyme activities
| 因素 | 处理 | 生长时期 | 处理*生长时期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 脱氢酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 纤维素酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 脲酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | P<0.01** | P<0.01** | P<0.01** |
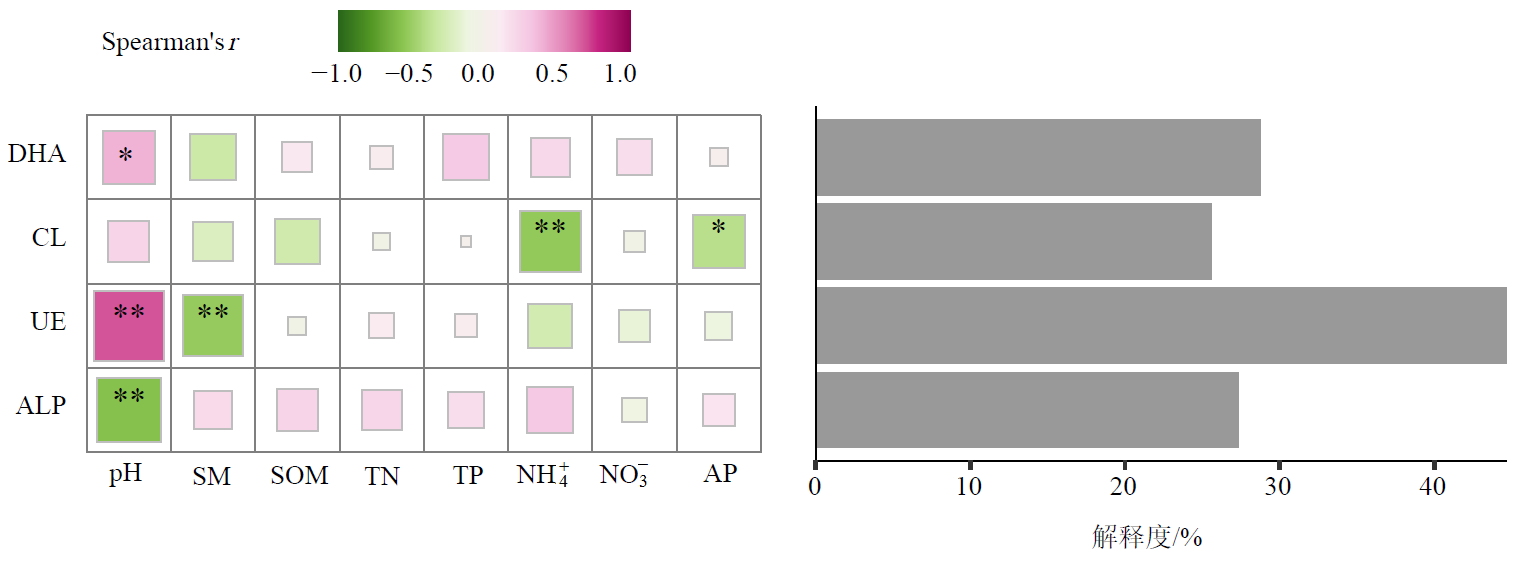
图3 土壤酶活性和土壤理化性质的相关性分析和随机森林分析 红色表示正相关关系,绿色表示负相关关系
Figure 3 Correlation analysis and random forest analysis between soil enzyme activities and edaphic properties
| 因子 | 贡献率/% | R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 63.20 | 0.62 | 0.001** |
| 含水量 | 30.62 | 0.35 | 0.001** |
| 有机质 | -0.95 | 0.05 | 0.404 |
| 全氮 | 2.28 | 0.03 | 0.603 |
| 全磷 | -1.12 | 0.03 | 0.636 |
| 铵态氮 | 8.51 | 0.28 | 0.002** |
| 硝态氮 | 5.10 | 0.07 | 0.276 |
| 速效磷 | -7.63 | 0.04 | 0.485 |
表3 土壤酶活性与土壤理化性质RDA统计学分析
Table 3 Statistics analysis for RDA of soil enzyme activities and edaphic properties
| 因子 | 贡献率/% | R2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 63.20 | 0.62 | 0.001** |
| 含水量 | 30.62 | 0.35 | 0.001** |
| 有机质 | -0.95 | 0.05 | 0.404 |
| 全氮 | 2.28 | 0.03 | 0.603 |
| 全磷 | -1.12 | 0.03 | 0.636 |
| 铵态氮 | 8.51 | 0.28 | 0.002** |
| 硝态氮 | 5.10 | 0.07 | 0.276 |
| 速效磷 | -7.63 | 0.04 | 0.485 |
| [1] |
AKINDE B P, OLAKAYODE A O, OYEDELE D J, et al., 2020. Selected physical and chemical properties of soil under different agricultural land-use types in Ile-Ife, Nigeria[J]. Heliyon, 6(9): e05090.
DOI URL |
| [2] | SINEGANI A A S, SINEGANI M, 2012. The effects of carbonates removal on adsorption, immobilization and activity of cellulase in a calcareous soil[J]. Geoderma, 173-174: 145-151. |
| [3] |
ALLAN E, MANNING P, ALT F, et al., 2015. Land use intensification alters ecosystem multifunctionality via loss of biodiversity and changes to functional Composition[J]. Ecology Letters, 18(8): 834-843.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
BURNS R G, DEFOREST J L, MARXSEN J, et al., 2013. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58: 216-234.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CARVALHO J L N, RAUCCI G S, FRAZÃO L A, et al., 2014. Crop-pasture rotation: A strategy to reduce soil greenhouse gas emissions in the Brazilian Cerrado[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 183: 167-175.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHAMBERLAIN L A, WHITMAN T, ANÉ J-M, et al., 2021. Corn-soybean rotation, tillage, and foliar fungicides: Impacts on yield and soil Fungi[J]. Field Crops Research, 262: 108030.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CHEN J, LUO Y Q, VAN GROENIGEN K J, et al., 2018. A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage[J]. Science Advances, 4(8): eaaq1689. |
| [8] |
CRIQUET S, FERRE E, FARNET A M, et al., 2004. Annual dynamics of phosphatase activities in an evergreen oak litter: Influence of biotic and abiotic Factors[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36(7): 1111-1118.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CUI Y X, MOORHEAD D L, GUO X B, et al., 2021. Stoichiometric models of microbial metabolic limitation in soil systems[J]. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30(11): 2297-2311.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CUI J W, SONG D L, DAI X L, et al., 2021. Effects of Long-term cropping regimes on SOC stability, soil microbial community and enzyme activities in the mollisol region of northeast China[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 164: 103941.
DOI URL |
| [11] | GUNJAL A B, WAGHMODE M S, PATIL N N, et al., 2019. Chapter 9-significance of soil enzymes in agriculture[M]. Smart Bioremediation Technologies. Academic Press: 159-168. |
| [12] |
GUO H, YAO J, CAI M M, et al., 2012. Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity[J]. Chemosphere, 87(11): 1273-1280.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
HOSSEINI M, RAJABI AGEREH S, KHALEDIAN Y, et al., 2017. Comparison of multiple statistical techniques to predict soil phosphorus[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 114: 123-131.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG J C W, RHODES G, HUANG Q W, et al., 2018. Plant growth stages and fertilization regimes drive soil fungal community compositions in a wheat-rice rotation System[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 54(6): 731-742.
DOI |
| [15] | KEHOE L, ROMERO-MUÑOZ A, POLAINA E, et al., 2017. Biodiversity at risk under future cropland expansion and intensification[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1(8): 1129-1135. |
| [16] | KUMAR S, CHAUDHURI S, MAITI S K, 2013. Soil dehydrogenase enzyme activity in natural and mine soil: A review[J]. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research, 13(7): 898-906. |
| [17] |
LE PROVOST G, THIELE J, WESTPHAL C, et al., 2021. Contrasting responses of Above- and belowground diversity to multiple components of land-use intensity[J]. Nature Communications, 12(1): 3918.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Lemaire G, Gastal F, Franzluebbers A, et al., 2015. Grassland-Cropping Rotations: An Avenue for Agricultural Diversification to Reconcile High Production with Environmental Quality[J]. Environmental Management, 56(5): 1065-1077.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | LIU B, XIA H, JIANG C C, et al., 2022. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 841: 156608. |
| [20] |
PANETTIERI M, GUIGUE J, CHEMIDLIN PREVOST-BOURÉ N, et al., 2020. Grassland-cropland rotation cycles in crop-livestock farming systems regulate priming effect potential in soils through modulation of microbial communities, composition of soil organic matter and abiotic soil properties[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 299: 106973.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PANETTIERI M, RUMPEL C, DIGNAC M F, et al., 2017. Does grassland introduction into cropping cycles affect carbon dynamics through changes of allocation of soil organic matter within aggregate fractions?[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 576: 251-263.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PARRAS-ALCÁNTARA L, DÍAZ-JAIMES L, LOZANO-GARCÍA B, 2015. Management effects on soil organic carbon stock in mediterranean open rangelands-treeless grasslands: Management effects on soc stock in mediterranean open rangelands[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 26(1): 22-34.
DOI URL |
| [23] | RIAH-ANGLET W, CUSSET E, CHAUSSOD R, et al., 2021. Introducing grasslands into crop rotations, a way to restore microbiodiversity and soil functions[J]. 11(10): 909. |
| [24] |
ROMDHANE S, SPOR A, BANERJEE S, et al., 2022. Land-use intensification differentially affects bacterial, fungal and protist communities and decreases microbiome network complexity[J]. Environmental Microbiome, 17(1): 1.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | RUMPEL C, CRÈME A, NGO P T, et al., 2015. The impact of grassland management on biogeochemical cycles involving carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 15(2): 353-371. |
| [26] |
SCHLATTER D C, SCHILLINGER W F, BARY A I, et al., 2017. Biosolids and conservation tillage: Impacts on soil fungal communities in dryland wheat-fallow cropping systems[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 115: 556-567.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHAO J L, LAI B, JIANG W, et al., 2019. Diversity and co-occurrence patterns of soil bacterial and fungal communities of chinese cordyceps habitats at Shergyla Mountain, Tibet: Implications for the occurrence[J]. Microorganisms, 7(9): 284.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SHAO T Y, ZHAO J J, LIU A H, et al., 2020. Effects of soil physicochemical properties on microbial communities in different ecological niches in coastal area[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 150: 103486.
DOI URL |
| [29] | SHUKLA G, VARMA A, 2011. Soil Enzymology[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. |
| [30] |
SIMON L M, OBOUR A K, HOLMAN J D, et al., 2022. Long-term cover crop management effects on soil properties in dryland cropping systems[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 328: 107852.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SINSABAUGH R L, LAUBER C L, WEINTRAUB M N, et al., 2008. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale: Stoichiometry of soil enzyme Activity[J]. Ecology Letters, 11(11): 1252-1264.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
SÜNNEMANN M, ALT C, KOSTIN J E, et al., 2021. Low-intensity land-use enhances soil microbial activity, biomass and fungal-to-bacterial ratio in current and future climates[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 58(11): 2614-2625.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG G S, GAO Q, YANG Y F, et al., 2022. Soil enzymes as indicators of soil function: A step toward greater realism in microbial ecological modeling[J]. Global Change Biology, 28(5): 1935-1950.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZABEL F, DELZEIT R, SCHNEIDER J M, et al., 2019. Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1): 2844.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | ZADE S P, KAMDIAND S R, DEOGIRKAR G V, 2010. Soil enzyme : Concepts and relevance in soil health and productivity[J]. Asian Journal of Soil Science, 5: 225-235. |
| [36] |
ZHANG C F, LIN Z L, QUE Y X, et al., 2021. Straw retention efficiently improves fungal communities and functions in the fallow ecosystem[J]. BMC Microbiology, 21(1): 52.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
代红翠, 张慧, 薛艳芳, 等, 2019. 不同耕作和秸秆还田下褐土真菌群落变化特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 52(13): 2280-2294.
DOI |
|
DAI H C, ZHANG H, XUE Y F, et al., 2019. Response of fungal community and function to different tillage and straw returning methods[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52(13): 2280-2294.
DOI |
|
| [38] | 丁夏夏, 2019. 不同土地经营强度对土壤养分及微生物的影响研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. |
| DING X X, 2019. The effect of land management intensification on soil property and microbial community[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University. | |
| [39] | 董齐琪, 王海燕, 杜雪, 等, 2022. 东北低山区典型林分类型土壤脲酶活性特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报: 1-10. |
| DONG Q Q, WANG H Y, DU X, et al., 2022. Characteristics of soil urease activity in typical stand types in low mountainous area of northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology: 1-10. | |
| [40] | 高梦瑶, 2020. 秸秆还田与化肥配施对土壤养分和土壤酶活性的影响[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. |
| GAO M Y, 2020. Effects of straw returning to field and combined application of chemical fertilizer on soil nutrient and soil enzyme activity[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University. | |
| [41] | 胡菏, 吴宪, 赵建宁, 等, 2021. 有机-无机肥配施对麦玉轮作土壤中细菌氮循环功能基因的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(1): 144-154. |
| HU H, WU X, ZHAO J N, et al., 2021. The effects of combined organic and inorganic fertilizer on the bacterial nitrogen cycling functional genes in wheat and maize soils by PICRUSt functional prediction[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(1): 144-154. | |
| [42] |
焦亚鹏, 齐鹏, 王晓娇, 等, 2020. 施氮量对农田土壤有机氮组分及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(12): 2423-2434.
DOI |
|
JIAO Y P, QI P, WANG X J, et al., 2020. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on soil organic nitrogen components and enzyme activities in farmland[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(12): 2423-2434.
DOI |
|
| [43] | 孔云, 张婷, 李刚, 等, 2020. 不同施肥方式下玉米田土壤中小型节肢动物的群落特征及稳定性[J]. 玉米科学, 28(2): 156-162. |
| KONG Y, ZHANG T, LI G, et al., 2020. Soil meso-and micro-arthropods community characteristics and stability in maize soil with different fertilization regimes[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 28(2): 156-162. | |
| [44] | 李胜君, 盛美君, 李刚, 等, 2022. 华北不同利用强度潮土酶生态化学计量特征比较[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(12): 2733-2741. |
| LI S J, SHENG M J, LI G, et al., 2022. Variations in eco-enzymatic stoichiometric characteristics of Fluvo-aquic soil with different use intensities in North China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(12): 2733-2741. | |
| [45] | 陆琴, 李冬琴, 2020. 土壤酶及其生态指示作用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(18): 14-17. |
| LU Q, LI D Q, 2020. Research progress on soil enzymes and their functioning as ecosystem indicators[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(18): 14-17. | |
| [46] |
魏晗梅, 郑粉莉, 赵苗苗, 等, 2022. CO2浓度升高、增温和冬小麦生长对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(11): 2971-2978.
DOI |
| WEI H M, ZHENG F L, ZHAO M M, et al., 2022. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration, temperature increasing and winter wheat growth on soil enzyme activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33(11): 2971-2978. | |
| [47] | 吴宪, 胡菏, 王蕊, 等, 2022. 化肥减量和有机替代对潮土微生物群落分子生态网络的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 59(2): 545-556. |
| WU X, HU H, WANG R, et al., 2022. Effects of reduction of chemical fertilizer and substitution coupled with organic manure on the molecular ecological network of microbial communities in fluvo-aquic soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 59(2): 545-556. | |
| [48] |
徐一兰, 唐海明, 李益锋, 等, 2017. 长期施肥大麦生育期双季稻田土壤微生物和酶活性动态变化特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(13): 12-20.
DOI |
|
XU Y L, TANG H M, LI Y F, et al., 2017. Dynamic change of soil microbe and soil enzyme activities during barley main growth stages under different long-term fertilizer treatments[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(13): 12-20.
DOI |
|
| [49] | 张成君, 师尚礼, 康文娟, 等, 2020. 不同轮作模式土壤酶活性特征及与化学性质的关系[J]. 中国草地学报, 42(5): 92-102. |
| ZHANG C J, SHI S L, KANG W J, et al., 2020. Characteristics of soil enzyme activity and its relationship with chemical properties under different rotation patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 42(5): 92-102. | |
| [50] | 张婷, 孔云, 李刚, 等, 2019. 不同秸秆还田量对华北小麦-玉米体系土壤中小型节肢动物的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(1): 70-75. |
| ZHANG T, KONG Y, LI G, et al., 2020. Effects of straw returning on soil meso- and micro-arthropod community diversity in wheat-maize fields in North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 25(1): 70-75. | |
| [51] | 赵永超, 李晓鹏, 闫一凡, 等, 2018. 激发式秸秆还田对麦季潮土团聚体中酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 50(3): 498-507. |
| ZHAO Y C, LI X P, YAN Y F, et al., 2018. Effects of straw returning via application of organic fertilizer as primer on fluvo-aquic soil enzyme activities in soil aggregates[J]. Soil, 50(3): 498-507. |
| [1] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [2] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [3] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [4] | 李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
