生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 784-793.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.04.016
代德敏1( ), 蒋旭升1, 刘杰1,2,*(
), 蒋旭升1, 刘杰1,2,*( ), 王路洋1, 陈诗奇1, 韩庆坤1
), 王路洋1, 陈诗奇1, 韩庆坤1
收稿日期:2022-08-22
出版日期:2023-04-18
发布日期:2023-07-12
通讯作者:
*刘杰,E-email: liujie@glut.edu.cn作者简介:代德敏(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为矿山环境生态恢复。E-email: 2120200428@glut.edu.cn
基金资助:
DAI Demin1( ), JIANG Xusheng1, LIU Jie1,2,*(
), JIANG Xusheng1, LIU Jie1,2,*( ), WANG Luyang1, CHEN Shiqi1, HAN Qingkun1
), WANG Luyang1, CHEN Shiqi1, HAN Qingkun1
Received:2022-08-22
Online:2023-04-18
Published:2023-07-12
摘要:
铅锌矿尾砂由于肥力低、物理结构差且重金属镉(Cd)铅(Pb)锌(Zn)浓度高,植物难以生长,从而严重制约了尾砂库的生态恢复。利用改良剂改善尾砂的适生性是尾砂库生态恢复的重要方法。通过基质改良试验探究添加不同质量分数(1%、2.5%、5%)的发酵羊粪、污泥和椰壳生物炭对铅锌矿尾砂养分、物理结构的改良效果和对重金属镉铅锌的固定效果,再通过黑麦草(Lolium perenne L.)盆栽试验验证对适生性的改善效果。结果表明,添加改良剂使有效态氮、磷、钾以及有机质分别提高了0.87-9.56、1.87-37.7、1.87-43.7和0.85-7.28倍。添加质量分数为2.5%时,3种改良剂对尾砂的导水性、总孔隙度和持水性的积极影响最为显著,表现为发酵羊粪>生物炭>污泥。此外,3种改良剂显著(P<0.05)降低有效态重金属质量分数,Cd、Pb、Zn分别降低了28.6%-64.6%、30.4%-70.6%、14.4%-45.5%。其中,椰壳生物炭对3种重金属的固定效果最好。添加改良剂显著提高了黑麦草的发芽率、总高度和总干质量分别提高了16.1%-20.3%、10.8%-48.9%和7.55%-19.5%,其中发酵羊粪效果最好。因此,发酵羊粪、污泥和椰壳生物炭可作为改良剂改善铅锌矿尾砂的适生性并促进植物生长。Pearson相关性分析表明,植物地上部分干质量和株高与阳离子交换量和速效钾呈极显著(P<0.01)正相关,与饱和导水率和有效态重金属呈极显著(P<0.01)负相关。植物根干质量和根长均与饱和含水量呈显著正相关,而与1-2 mm的粒径呈显著负相关。该文可为养分贫瘠、物理结构差和高重金属污染尾砂库的植被恢复提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
代德敏, 蒋旭升, 刘杰, 王路洋, 陈诗奇, 韩庆坤. 3种有机改良剂对铅锌矿尾砂适生性改善的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 784-793.
DAI Demin, JIANG Xusheng, LIU Jie, WANG Luyang, CHEN Shiqi, HAN Qingkun. Study on Suitability of Pb/Zn Mine Tailings Using Three Different Organic Amendments[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 784-793.
| 参数 | 铅锌尾砂 | 发酵羊粪 | 污泥 | 生物炭 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.50 | 7.28 | 7.81 | 7.90 |
| 电导率/(mS∙cm−1) | 0.06 | 5.29 | 2.89 | 2.90 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 1.20 | 187 | 132 | 348 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 2.78 | 2280 | 556 | 2512 |
| w(总氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.40 | 6.10 | 39.3 | 3.60 |
| w(总碳)/(g∙kg−1) | 22.1 | 369 | 219 | 754 |
| w(总镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | 18.8 | 0.43 | 0.35 | ND |
| w(总铅)/(mg∙kg−1) | 3425 | 43.8 | 53.1 | 20.6 |
| w(总锌)/(mg∙kg−1) | 3400 | 368 | 964 | 33.7 |
表1 所用试验材料的基本性质
Table 1 Basic properties of the test materials
| 参数 | 铅锌尾砂 | 发酵羊粪 | 污泥 | 生物炭 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.50 | 7.28 | 7.81 | 7.90 |
| 电导率/(mS∙cm−1) | 0.06 | 5.29 | 2.89 | 2.90 |
| w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 1.20 | 187 | 132 | 348 |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 2.78 | 2280 | 556 | 2512 |
| w(总氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.40 | 6.10 | 39.3 | 3.60 |
| w(总碳)/(g∙kg−1) | 22.1 | 369 | 219 | 754 |
| w(总镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | 18.8 | 0.43 | 0.35 | ND |
| w(总铅)/(mg∙kg−1) | 3425 | 43.8 | 53.1 | 20.6 |
| w(总锌)/(mg∙kg−1) | 3400 | 368 | 964 | 33.7 |
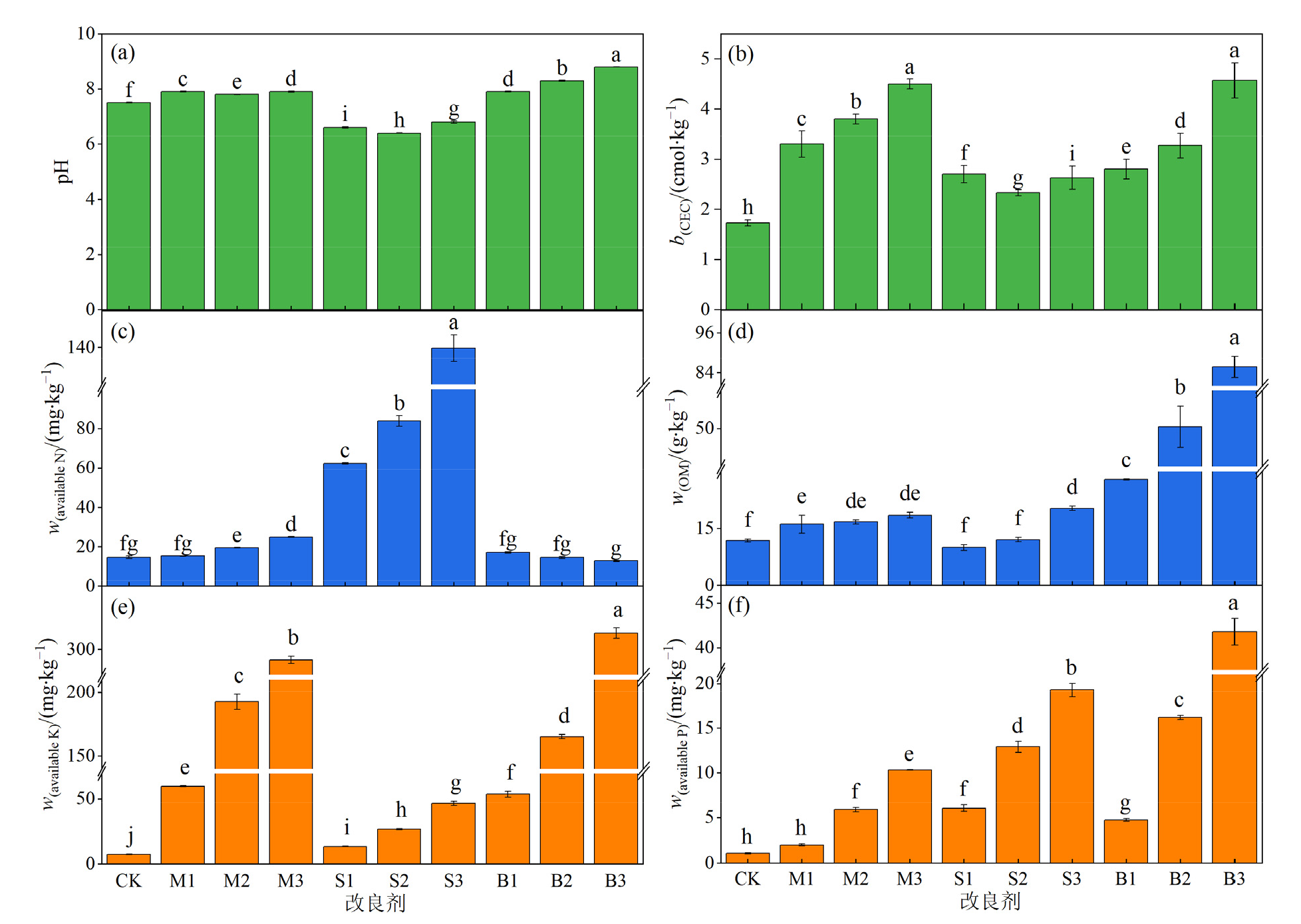
图1 添加不同改良剂对尾砂化学性质的影响 (a) pH vs.改良剂;(b)CEC vs.改良剂; (c)有效氮质量分数vs.改良剂; (d)有机质质量分数vs.改良剂; (e)速效钾质量分数vs.改良剂;(f)有效磷质量分数vs.改良剂 CK表示未添加改良剂的尾砂。M、S和B分别表示添加发酵羊粪、污泥和生物炭,1、2和3分别表示改良剂添加质量分数为1%、2.5%和5%。例如,S2表示添加2.5%的污泥的尾砂样品。不同小写字母表示不同处理样品数值间存在统计学上的显著差异(Duncan,P<0.05,n=3 )
Figure 1 Effect of different amendments on chemical properties of tailing sand
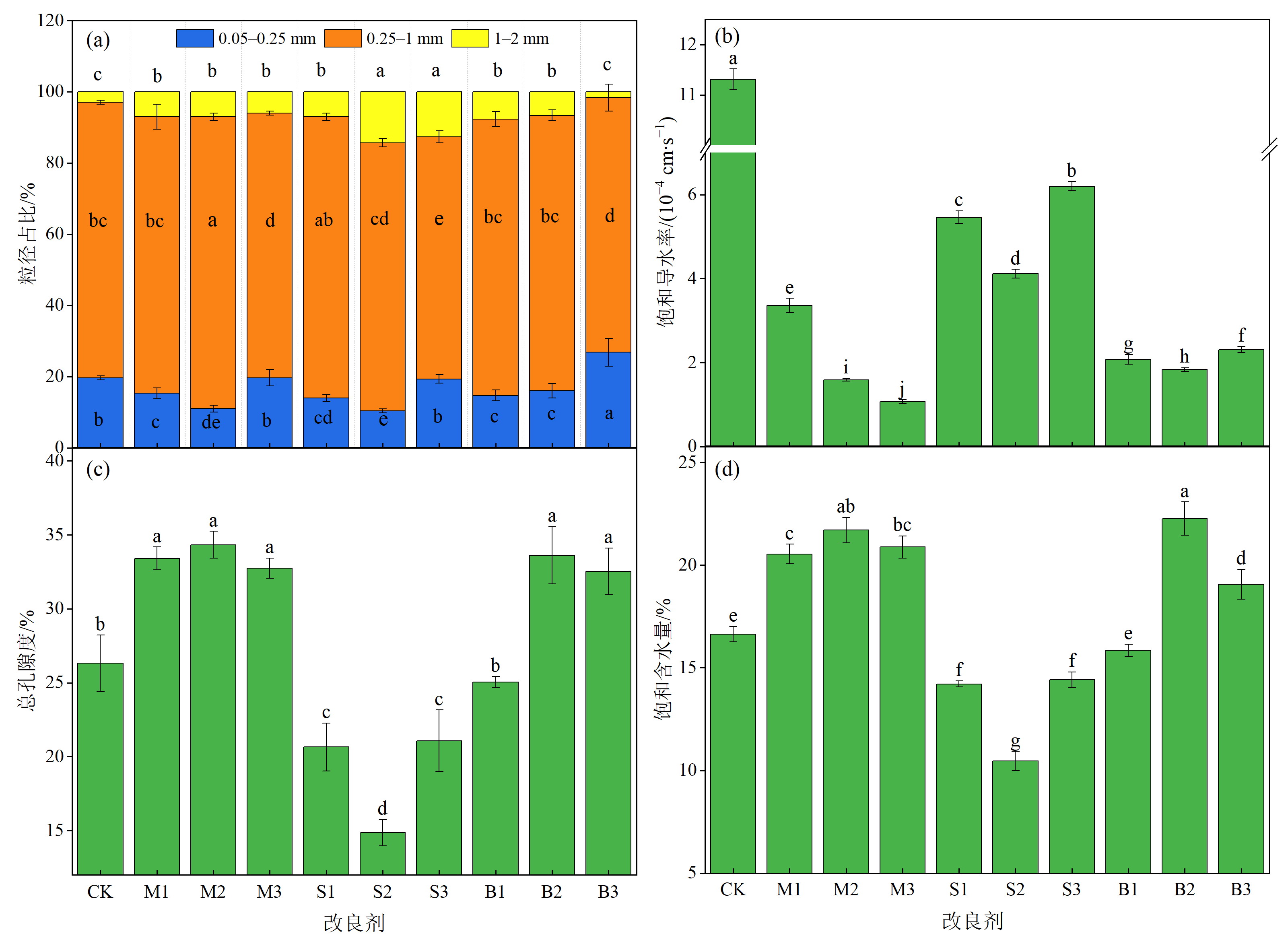
图2 添加不同改良剂对尾砂物理性质的影响(a)粒径占比vs.改良剂;(b)饱和导水率vs.改良剂;(c)总孔隙度vs.改良剂;(d)饱和含水量vs.改良剂
Figure 2 Effect of different amendments on the physical properties of tailing sand
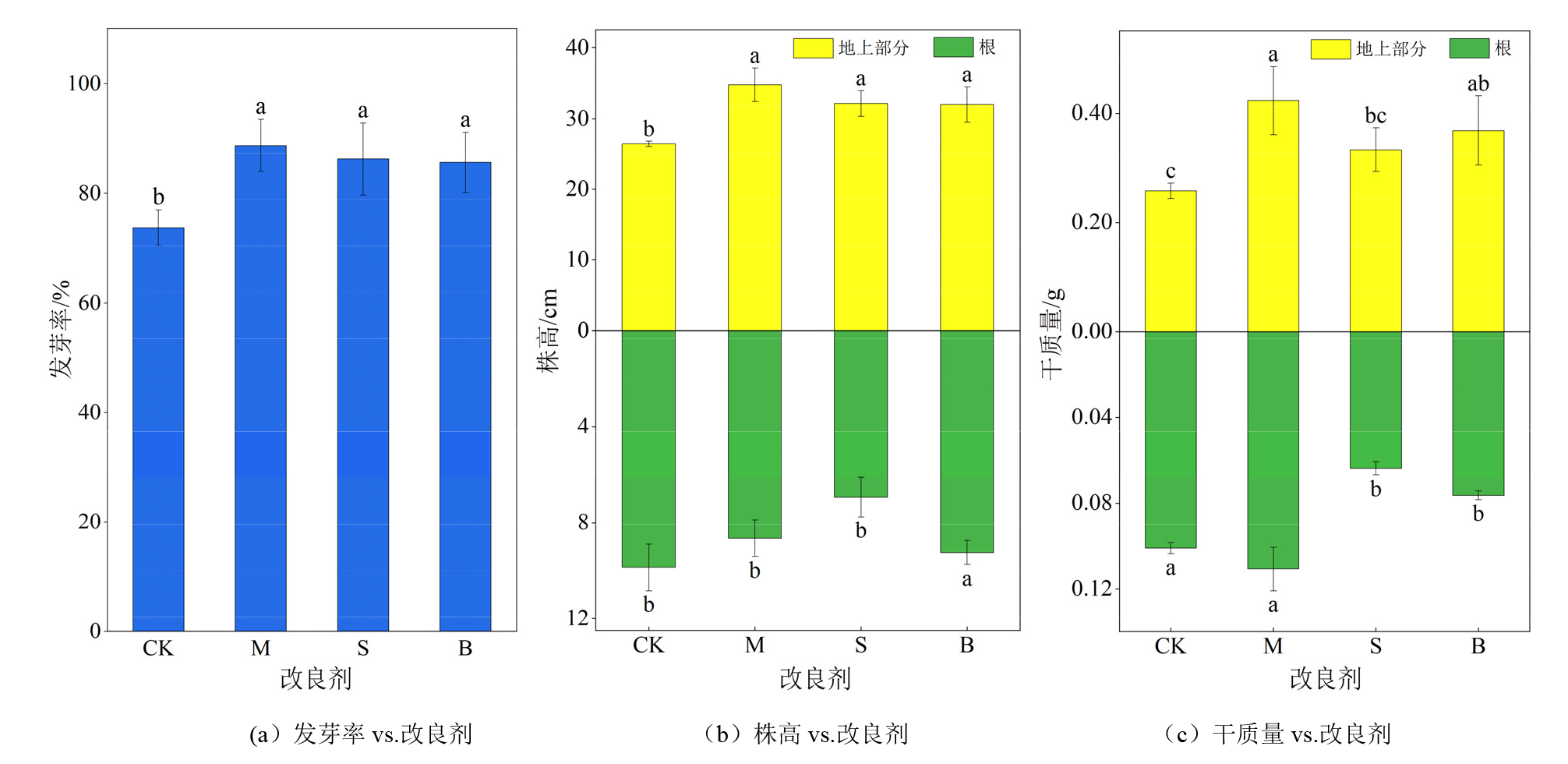
图4 添加不同改良剂对尾砂基质上黑麦草生长的影响 CK表示未添加改良剂的尾砂。M、S和B分别表示添加2.5%发酵羊粪、2.5%污泥和2.5%的生物炭尾砂样品。不同小写字母表示不同处理样品数值间存在统计学上的显著差异(Duncan,P<0.05,n=3)
Figure 4 Effect of different amendments for ryegrass growth on tailing sand substrates
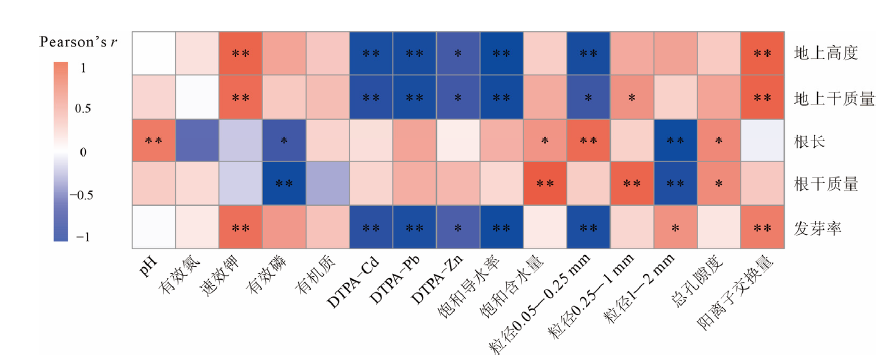
图5 改良尾砂理化指标与植物参数相关性分析 *表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01;色柱颜色深浅表示相关性强弱,蓝色表示负相关,红色表示正相关
Figure 5 Correlation analysis of physical and chemical indicators of tailing sand with plant parameters
| [1] |
AJAYI A E, HORN R, 2016. Modification of chemical and hydrophysical properties of two texturally differentiated soils due to varying magnitudes of added biochar[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 164: 34-44.
DOI URL |
| [2] | AL-LAMI M K, OUSTRIERE N, GONZALES E, et al., 2019. Amendment-assisted revegetation of mine tailings: Improvement of tailings quality and biomass production[J]. Internation Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(5): 425-434. |
| [3] |
AL-LAMI M K, OUSTRIERE N, GONZALES E, et al., 2022. Phytomanagement of Pb/Zn/Cu tailings using biosolids-biochar or -humus combinations: Enhancement of bioenergy crop production, substrate functionality, and ecosystem services[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 836: 155676.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ALVAREZ-ROGEL J, TERCERO-GOMEZ M D C, CONESA H M, et al., 2018. Biochar from sewage sludge and pruning trees reduced porewater Cd, Pb and Zn concentrations in acidic, but not basic, mine soils under hydric conditions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 223: 554-565.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ARLO L, BERETTA A, SZOGI A A, et al., 2022. Biomass production, metal and nutrient content in sorghum plants grown on soils amended with sewage sludge[J]. Heliyon, 8(1): e08658.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHIU K K, YE Z H, WONG M H, 2006. Growth of Vetiveria zizanioides and Phragmities australis on Pb/Zn and Cu mine tailings amended with manure compost and sewage sludge: A greenhouse study[J]. Bioresource Technology, 97(1): 158-170.
DOI URL |
| [7] | DE FIGUEIREDO C C, COSER T R, MOREIRA T N, et al., 2019. Carbon mineralization in a soil amended with sewage sludge-derived biochar[J]. Applied Science-Basel, 9(21): 4481. |
| [8] |
EL RASAFI T, OUKARROUM A, HADDIOUI A, 2021. Response of maize to coniferous tree woods biochar and sheep manure application to contaminated mine soil[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 13: 3917-3927.
DOI |
| [9] |
ELOUEAR Z, BOUHAMED F, BOUJELBEN N, et al., 2016. Application of sheep manure and potassium fertilizer to contaminated soil and its effect on zinc, cadmium and lead accumulation by alfalfa plants[J]. Sustainable Environment Research, 26(3): 131-135.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FU Y T, DE JONGE L W, MOLDRUP P, et al., 2022. Improvements in soil physical properties after long-term manure addition depend on soil and crop type[J]. Geoderma, 425: 116062.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GONZAGA M I S, MACKOWIAK C, DE ALMEIDA A Q, et al., 2018. Positive and negative effects of biochar from coconut husks, orange bagasse and pine wood chips on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and nutrition[J]. Catena, 162: 414-420.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HOUBEN D, EVRARD L, SONNET P, 2013. Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 92(11): 1450-1457.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
HU Y L, MGELWA A S, SINGH A N, et al., 2018. Differential responses of the soil nutrient status, biomass production, and nutrient uptake for three plant species to organic amendments of placer gold mine-tailing soils[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 29(9): 2836-2845.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
IBRAHIM A, HORTON R, 2021. Biochar and compost amendment impacts on soil water and pore size distribution of a loamy sand soil[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 85(4): 1021-1036.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JAYNES W F, ZARTMAN R E, 2005. Origin of tale, iron phosphates, and other minerals in biosolids[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 69(4): 1047-1056.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JIA Y H, LI J, ZENG X B, et al., 2022. The performance and mechanism of cadmium availability mitigation by biochars differ among soils with different pH: Hints for the reasonable choice of passivators[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 312: 114903.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KANG M W, YIBELTAL M, KIM Y H, et al., 2022. Enhancement of soil physical properties and soil water retention with biochar-based soil amendments[J]. Science of Total Environment, 836: 155746.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KHAWKOMOL S, NEAMCHAN R, THONGSAMER T, et al., 2021. Potential of biochar derived from agricultural residues for sustainable management[J]. Sustainability, 13(15): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI J Q, MARSCHNER P, 2019. Phosphorus pools and plant uptake in manure-amended soil[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 19(1): 175-186.
DOI |
| [20] |
LIN H, JIANG X Y, LI B, et al., 2021. Soilless revegetation: An efficient means of improving physicochemical properties and reshaping microbial communities of high-salty gold mine tailings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207: 111246.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LIU C J, LIN H, HE P D, et al., 2022. Peat and bentonite amendments assisted soilless revegetation of oligotrophic and heavy metal contaminated nonferrous metallic tailing[J]. Chemosphere, 287(Part 1): 132101.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LIU C j, LIN H, LI B, et al., 2021. Endophyte Pseudomonas putida enhanced Trifolium repens L. growth and heavy metal uptake: A promising in-situ non-soil cover phytoremediation method of nonferrous metallic tailing[J]. Chemosphere, 272: 129816.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LU J Y, YANG J F, KEITEL C, et al., 2020. Rhizosphere priming effects of Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens depend on phosphorus fertilization and biological nitrogen fixation[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 150: 108005.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
NAVARRO-CANO J A, VERDU M, GOBERNA M, et al., 2018. Trait-based selection of nurse plants to restore ecosystem functions in mine tailings[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 55(3): 1195-1206.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SARATHCHANDRA S S, RENGEL Z, SOLAIMAN Z M, 2022. Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated iron ore tailings by applying compost and growing perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)[J]. Chemosphere, 288(2): 132573.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SONG L, QIAN J Z, ZHANG F W, et al., 2022. An ecological remediation model combining optimal substrate amelioration and native hyperaccumulator colonization in non-ferrous metal tailings pond[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 322: 116141.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
VAN DER SLOOT M, KLEIJN D, DE DEYN G B, et al., 2022. Carbon to nitrogen ratio and quantity of organic amendment interactively affect crop growth and soil mineral N retention[J]. Crop and Environment, 1(3): 161-167.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WANG Z P, SHEN R, JI S B, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar derived from sewage sludge and sewage sludge/cotton stalks on the immobilization and phytoavailability of Pb, Cu, and Zn in sandy loam soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 419: 126468.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
XIE L, VAN ZYL D, 2020. Distinguishing reclamation, revegetation and phytoremediation, and the importance of geochemical processes in the reclamation of sulfidic mine tailings: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 252: 126446.
DOI URL |
| [30] | YAN W C, QU J B, QU Y P, et al., 2022. Effect of biochar addition on mechanism of heavy metal migration and transformation in biogas residue aerobic compost[J]. Fermentation-Basel, 8(10): 523. |
| [31] |
YANG Y H, WU J C, DU Y L, et al., 2022. Effect on soil properties and crop yields to long-term application of superabsorbent polymer and manure[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10: 859434.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZAHEDIFAR M, 2020. Effect of biochar on cadmium fractions in some polluted saline and sodic soils[J]. Environmental Management, 66(6): 1133-1141.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | ZHANG B, ZHANG M Y, ZHOU X X, et al., 2022. Effect of the mineral-microbial complexes on the quality, soil nutrients, and microbial community of tailing substrates for growing potted Rorippa[J]. Microbiology Research, 262: 127084. |
| [34] | 曹秀芹, 刘丰, 柴莲莲, 等, 2022. 污泥与污泥生物炭对比修复铜、镉污染土壤[J]. 应用化工, 51(4): 1036-1041. |
| CAO X Q, LIU F, CHAI L L, et al., 2022. Restoration of Cu and Cd heavy metal contaminated soil by sludge and sludge-derived biochar[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 51(4): 1036-1041. | |
| [35] | 陈奕暄, 邓昭赞, 吴双军, 等, 2021. 速效钾对沟叶结缕草吸收和转运Cd的影响[J]. 北方园艺 (17): 66-74. |
| CHEN Y X, DENG Z Z, WU S J, et al., 2021. Effects of available potassium on cadmium accumulation in Zoysia Matrella[J]. Northern Horticulture (17): 66-74. | |
| [36] |
崔保伟, 刘全永, 秦广利, 等, 2021. 发酵羊粪与松土促根剂配施对土壤理化性状及朝天椒品质和产量的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 36(2): 182-187.
DOI |
|
CUI B W, LIU Q Y, QIN G L, et al., 2021. Effect of combined application of fermented sheep manure and soil loosening and root promoting agent on soil physical and chemical properties yield and quality of red cluster pepper[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 36(2): 182-187.
DOI |
|
| [37] | 黄雷, 张时伟, 任重, 等, 2016. 不同修复材料对铅锌尾砂中DTPA浸提态Pb、Zn、Cu、Cd含量的影响[J]. 环境工程, 34(9): 166-170. |
| HUANG L, ZHANG S W, REN Z, et al., 2016. Effect of different remediation materials on DTPA extractable contents of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in lead-zinc mine tailings[J]. Environmental Engineering, 34(9): 166-170. | |
| [38] | 黄小洋, 邵劲松, 马运涛, 2017. 施用猪粪有机肥对土壤环境质量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 46(11): 60-68. |
| HUANG X Y, SHAO J S, MA Y T, 2017. Effects of the application of pig manure organic fertilizers on soil environment quality[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 46(11): 60-68. | |
| [39] | 李程, 姚义鸣, 李逍逍, 等, 2022. 多环芳烃和镉土壤复合暴露条件下黑麦草的氧化应激指标变化[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(8): 1739-1749. |
| LI C, YAO Y M, LI X X, et al., 2022. Changes of oxidative stress indexes of ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) under compound exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cadmium in soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(8): 1739-1749. | |
| [40] | 刘洁, 孙可, 韩兰芳, 2021. 生物炭对土壤重金属形态及生物有效性影响的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 40(6): 1643-1658. |
| LIU J, SUN K, HAN L F, 2021. Effect of biochar on soil heavy metal speciation and bioavailability: A review[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 40(6): 1643-1658. | |
| [41] | 刘蓉, 邓茂, 李莹莹, 等, 2020. 不同酸碱度土壤阳离子交换量的测定研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 36(1): 125-130. |
| LIU R, DENG M, LI Y Y, et al., 2022. Optimization for the determination of cation exchange capacity in soils with different acidity and alkalinity[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 36(1): 125-130. | |
| [42] | 罗大富, 2018. 市政污泥用于矿区土壤改良的污染风险评估及配比分析[J]. 地球环境学报, 9(1): 101-108. |
| LUO D F, 2018. The pollution risk assessment and matched analysis of municipal sullage being used for soil improvement in mining area[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 9(1): 101-108. | |
| [43] |
马宜林, 吴广海, 申洪涛, 等, 2021. 羊粪有机肥与化肥配施对烤烟生长及土壤肥力特性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 35(10): 2423-2430.
DOI |
|
MA Y L, WU G H, SHEN H T, et al., 2021. Effects of combined application of sheep manure-derived organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer on tobacco growth and soil fertility[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 35(10): 2423-2430.
DOI |
|
| [44] | 彭维新, 杨源通, 冯嘉仪, 等, 2020. 污泥及强化措施对稀土矿区废弃地土壤的改良[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 41(5): 65-72. |
| PENG W X, YANG Y T, FENG J Y, et al., 2020. Improvement of sewage sludge and enhanced measure on soil of rare earth mine wasteland[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 41(5): 65-72. | |
| [45] | 任怀新, 王冬梅, 王慧, 等, 2021. 生物炭对盐碱胁迫下黑麦草和紫花苜蓿光合及抗氧化特征的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 37(17): 116-123. |
| REN H X, WANG D M, WANG H, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar on the photosynthetic and antioxidant characteristics of ryegrass and alfalfa under saline-alkali stress[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 37(17): 116-123. | |
| [46] | 谭川疆, 潘忠图, 罗有发, 等, 2022. 不同改良剂对黔西北锌冶炼区农用地土壤重金属修复效果研究[J]. 地球与环境, 50(4): 575-585. |
| TAN C J, PAN Z T, LUO Y F, et al., 2022. Remediation effect of different amendments on heavy metals in agricultural soil in zinc smelting area of northwest Guizhou[J]. Earth and Environment, 50(4): 575-585. | |
| [47] | 陶晨斌, 竺宇航, 陈建军, 等, 2022. 不同人工植被群落对铅锌矿废弃地径流重金属流失特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 36(1): 375-383. |
| TAO C B, ZHU Y H, CHEN J J, et al., 2022. Effects of different artificial vegetation communities on characterisitics of heavy meatal loss in runoff of lead zinc mine wasteland[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(1): 375-383. | |
| [48] |
吴慧, 吴程龙, 张仕颖, 等, 2021. 施用有机-无机改良剂对锡尾矿化学属性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2244-2250.
DOI URL |
| WU H, WU C L, ZHANG S Y, et al., 2021. Effects of applying organic-inorganic modifiers on the chemical properties of tin tailings[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(11): 2244-2250. | |
| [49] | 殷飞, 王海娟, 李燕燕, 等, 2015. 不同钝化剂对重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(3): 438-448. |
| YIN F, WANG H J, LI Y Y, et al., 2015. Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(3): 438-448. | |
| [50] | 余杭, 潘佳虹, 杨柳生, 等, 2021. 金沙江干热河谷优势草本植物生物量与土壤物理性质的关系[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 27(4): 884-892. |
| YU H, PAN J H, YANG L S, et al., 2021. Relationship between biomass of dominant herbaceous plants and soil physical properties in a dry-hot valley area of the Jinsha River[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 27(4): 884-892. | |
| [51] | 张紫翔, 马龙, 刘廷玺, 等, 2023. 内蒙古典型铅锌矿及其影响区地下水重金属污染生态环境风险评估[EB/OL]. 生态学杂志, 1-13 [2023-04-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20221019.1714.021.html. |
| ZHANG Z X, MA L, LIU T X, et al., 2023. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in groundwater of typical lead-zinc mine and influenced area in Inner Mongolia[EB/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-13 [2023-04-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20221019.1714.021.html |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [4] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [5] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [6] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [7] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [8] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [9] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [10] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [11] | 梅闯, 蔡昆争, 黎紫珊, 徐美丽, 黄飞. 稻秆生物炭对稻田土壤Cd形态转化和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 380-390. |
| [12] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [13] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [14] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [15] | 宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
