生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2244-2250.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.11.015
吴慧1( ), 吴程龙1, 张仕颖1,2, 夏运生1,2,*(
), 吴程龙1, 张仕颖1,2, 夏运生1,2,*( ), 张乃明1,2, 普绍才1
), 张乃明1,2, 普绍才1
收稿日期:2021-04-29
出版日期:2021-11-18
发布日期:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
* 夏运生,教授,E-mail: yshengxia@163.com作者简介:吴慧(1997年生),女,硕士研究生。E-mail: 1364765752@qq.com
基金资助:
WU Hui1( ), WU Chenglong1, ZHANG Shiying1,2, XIA Yunsheng1,2,*(
), WU Chenglong1, ZHANG Shiying1,2, XIA Yunsheng1,2,*( ), ZHANG Naiming1,2, PU Shaocai1
), ZHANG Naiming1,2, PU Shaocai1
Received:2021-04-29
Online:2021-11-18
Published:2021-12-29
摘要:
为研究有机-无机改良剂配施对锡尾矿的改良效果,采用室内培养试验,设置添加米糠(RB)5%、蘑菇渣(MR)5%、不同水平的钙镁磷肥[0% (P0)、1% (P1)、2% (P2)] 3种改良剂,研究不同改良剂组合处理对锡尾矿pH值、有机质、速效养分、重金属含量及优势改良剂组合对黑麦草(Lolium perenne L.)生长的影响。结果表明,添加改良剂的锡尾矿pH、碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾、有机质含量均显著增加。其中,MR+P2处理下pH、速效磷和速效钾含量最高,增幅分别为123.7%、4837%和136%;RB+P2处理下碱解氮和有机质含量最高,增幅分别为2425%和752%。锡尾矿中Cu、Pb、Cd、As均超过土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—1995),Cu、Cd、As含量超过三级标准,Pb含量超过一级标准。施入改良剂均显著降低有效态Cu、Pb、Cd、As含量,降幅分别为36.6%—64.6%、63.2%—82.5%、67.2%—70.3%、21.3%—66%,MR+P2对重金属有效态含量影响最明显。添加优势改良剂组合均显著增加黑麦草生物量。综上,米糠、蘑菇渣、钙镁磷肥协同配施均有助于锡尾矿基质的改良,MR+P2处理尾矿改良效果较好、植物生物量大。本研究结果可为酸性尾矿基质改良及先锋草本植物修复提供技术参考。
中图分类号:
吴慧, 吴程龙, 张仕颖, 夏运生, 张乃明, 普绍才. 施用有机-无机改良剂对锡尾矿化学属性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2244-2250.
WU Hui, WU Chenglong, ZHANG Shiying, XIA Yunsheng, ZHANG Naiming, PU Shaocai. Effects of Applying Organic-inorganic Modifiers on the Chemical Properties of Tin Tailings[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2244-2250.
| 重金属形态 Heavy metal speciation | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cd | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全量 Total amount/(mg∙kg-1) | 514 | 0.50 | 163 | 1.5 | 36.1 |
| 有效态 Effective state/(mg∙kg-1) | 17.09 | 0.33 | 1.66 | 0.64 | 0.47 |
表1 供试尾矿重金属质量分数
Table 1 Mass fraction of heavy metals in test tailings
| 重金属形态 Heavy metal speciation | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cd | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全量 Total amount/(mg∙kg-1) | 514 | 0.50 | 163 | 1.5 | 36.1 |
| 有效态 Effective state/(mg∙kg-1) | 17.09 | 0.33 | 1.66 | 0.64 | 0.47 |
| 改良剂Improver | pH | w(OM)/ % | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 米糠 Rice bran | 5.8 | 52.1 | 22.6 | 10.6 | 15.2 |
| 蘑菇渣 Mmushroom residue | 8.5 | 32.4 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 18.9 |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | 8.6 | — | — | 66.5 | — |
表2 供试改良剂酸碱度、养分状况
Table 2 Table 2 pH value and contents of the tested amendments
| 改良剂Improver | pH | w(OM)/ % | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 米糠 Rice bran | 5.8 | 52.1 | 22.6 | 10.6 | 15.2 |
| 蘑菇渣 Mmushroom residue | 8.5 | 32.4 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 18.9 |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | 8.6 | — | — | 66.5 | — |
| 改良剂 Improver | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Ni | Pb | Cd | As | |
| 米糠 Rice bran | 27.7 | 4.5 | 6.1 | 0.15 | 0.62 |
| 蘑菇渣 Mushroom residue | 49 | 24 | 25.6 | 0.29 | 1.63 |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | 22.5 | 16 | 23.3 | 0.14 | 9.47 |
表3 供试改良剂重金属含量状况
Table 3 Heavy metal contents of the tested amendments
| 改良剂 Improver | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Ni | Pb | Cd | As | |
| 米糠 Rice bran | 27.7 | 4.5 | 6.1 | 0.15 | 0.62 |
| 蘑菇渣 Mushroom residue | 49 | 24 | 25.6 | 0.29 | 1.63 |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | 22.5 | 16 | 23.3 | 0.14 | 9.47 |
| 指标 Index | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Cd | Ni | Pb | As | |
| 全量 Total amount | 514 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 163 | 36.1 |
| GB I | 35 | 0.2 | 40 | 35 | 15 |
| GB II | 50 | 0.3 | 40 | 250 | 20 |
| GB III | 400 | 1 | 200 | 500 | 30 |
表4 锡尾矿重金属全量质量分数
Table 4 Total content of heavy metals in tin tailings
| 指标 Index | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Cd | Ni | Pb | As | |
| 全量 Total amount | 514 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 163 | 36.1 |
| GB I | 35 | 0.2 | 40 | 35 | 15 |
| GB II | 50 | 0.3 | 40 | 250 | 20 |
| GB III | 400 | 1 | 200 | 500 | 30 |
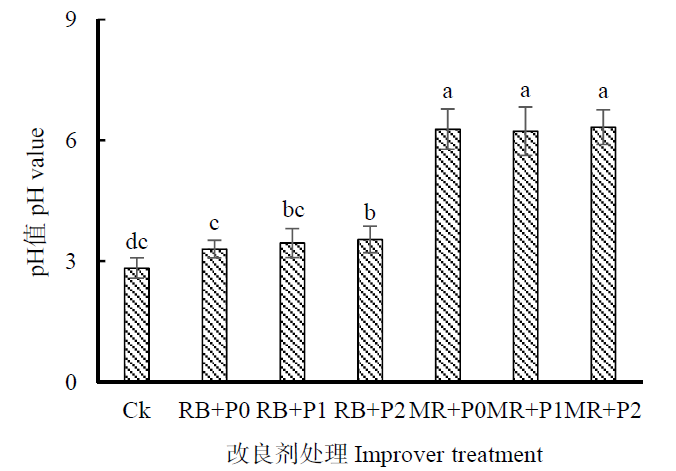
图1 施用不同改良剂对锡尾矿酸碱度的影响 图中标注的不同字母表示存在显著差异性(P<0.05),CK:不添加改良剂;RB+P0:5%米糠+0%钙镁磷肥;RB+P1:5%米糠+1%钙镁磷肥;RB+P2:5%米糠+2%钙镁磷肥;MR+P0:5%蘑菇渣+0%钙镁磷肥;MR+P1:5%蘑菇渣+1%钙镁磷肥;MR+P2:5%蘑菇渣+2%钙镁磷肥,下同
Fig. 1 pH values of different treatments The different letters marked in the figure indicate significant differences (P<0.05), CK: no improver; RB+P0: 5% rice bran +0% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; RB+P1: 5% rice bran+1% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; RB+P2: 5% rice bran+2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; MR+P0: 5% mushroom residue+0% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; MR+P1: 5% mushroom residue+1% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer; MR+P2: 5% mushroom residue+2% calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, the same below
| 改良剂处理 Improver treatment | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCl-Cu | HCl-Ni | DTPA-Pb | DTPA-Cd | NaH2PO3-As | |
| CK | 17.09±0.12a | 0.33±0.03e | 1.66±0.06a | 0.64±0.04a | 0.47±0.02a |
| RB+P0 | 10.83±0.04b | 0.38±0.03de | 0.61±0.01b | 0.20±0.02b | 0.37±0.01b |
| RB+P1 | 10.22±0.15bc | 0.59±0.03ab | 0.53±0.02c | 0.20±0.01b | 0.26±0.01c |
| RB+P2 | 9.86±0.09c | 0.62±0.02a | 0.36±0.02de | 0.20±0.02b | 0.18±0.00d |
| MR+P0 | 7.03±0.58d | 0.45±0.03cd | 0.42±0.02d | 0.21±0.02b | 0.36±0.01b |
| MR+P1 | 6.02±0.07e | 0.48±0.02c | 0.35±0.02de | 0.19±0.01b | 0.25±0.00c |
| MR+P2 | 6.05±0.09e | 0.52±0.02bc | 0.29±0.01e | 0.19±0.01b | 0.16±0.01d |
| 有机改良剂 Organic modifier | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| 有机改良剂×钙镁磷肥 Organic modifier×calcium magnesium phosphate | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS |
表5 施用不同改良处理对锡尾矿重金属含量的影响
Table 5 Heavy metal contention in tin tailings of different treatments
| 改良剂处理 Improver treatment | w/(mg∙kg-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCl-Cu | HCl-Ni | DTPA-Pb | DTPA-Cd | NaH2PO3-As | |
| CK | 17.09±0.12a | 0.33±0.03e | 1.66±0.06a | 0.64±0.04a | 0.47±0.02a |
| RB+P0 | 10.83±0.04b | 0.38±0.03de | 0.61±0.01b | 0.20±0.02b | 0.37±0.01b |
| RB+P1 | 10.22±0.15bc | 0.59±0.03ab | 0.53±0.02c | 0.20±0.01b | 0.26±0.01c |
| RB+P2 | 9.86±0.09c | 0.62±0.02a | 0.36±0.02de | 0.20±0.02b | 0.18±0.00d |
| MR+P0 | 7.03±0.58d | 0.45±0.03cd | 0.42±0.02d | 0.21±0.02b | 0.36±0.01b |
| MR+P1 | 6.02±0.07e | 0.48±0.02c | 0.35±0.02de | 0.19±0.01b | 0.25±0.00c |
| MR+P2 | 6.05±0.09e | 0.52±0.02bc | 0.29±0.01e | 0.19±0.01b | 0.16±0.01d |
| 有机改良剂 Organic modifier | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** |
| 钙镁磷肥 Calcium magnesium phosphate | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| 有机改良剂×钙镁磷肥 Organic modifier×calcium magnesium phosphate | NS | ** | NS | NS | NS |
| [1] |
ALVARENGAl P, GONALVES A P, FERNANDES R M, et al., 2009. Organic residues as immobilizing agents in aided phytostabilization: (I) Effects on soil chemical characteristics.[J]. Chemosphere, 74(10): 1292-1300.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, THANGARAJAN R, et al., 2014. Remediation of heavy metal (loid)s contaminated soils: To mobilize or to immobilize[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 266: 141-166.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHANG C S, SUNG J M, 2004. Nutrient uptake and yield responses of peanuts and rice to lime and fused magnesium phosphate in an acid soil[J]. Field Crops Research, 89(2-3): 319-325.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CHEN G Q, ZENG G M, XIANG T U, et al., 2005. A novel biosorbent; characterization of the spent mushroom compost and its application for removal of heavy metals[J]. J Environ, 17(5): 756-760. |
| [5] |
CHIU K K, YE Z H, WONG M H, 2006. Growth of Vetiveria zizanioides and Phragmities australis on Pb/Zn and Cu mine tailings amended with manure compost and sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 97: 158-170.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
STUMBEA D, CHICO M M, NICA V, 2019. Effects of waste deposit geometry on the mineralogical and geochemical composition of mine tailings[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 368: 496-505.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LEE S H, JI W H, LEE W S, et al., 2014. Influence of amendments and aided phytostabilization on metal availability and mobility in Pb/Zn mine tailings[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 139: 15-21.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI Z Y, YANG S X, PENG X Z, et al., 2018. Field comparison of the effectiveness of agricultural and nonagricultural organic wastes for aided phytostabilization of a Pb-Zn mine tailings pond in Hunan Province, China[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 20(12): 1264-1273.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI X K, KANG J X, 2021. Status and Measures of Preventing and Controlling Environmental Risks in Tailing Impoundment[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/621/1/012148.
DOI |
| [10] | RODRÍGUEZ L, GÓMEZ R, SÁNCHEZ V, et al., 2016. Chemical and plant tests to assess the viability of amendments to reduce metal availability in mine soils and tailings[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 23(7): 46-54. |
| [11] |
UDEIGWE T K, EZE P N, TEBOH J M, et al., 2011. Application, chemistry, and environmental implications of contaminant-immobilization amendments on agricultural soil and water quality[J]. Environment International, 37(1): 258-267.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 81-83. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. ThirdEdition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 81-83. | |
| [13] | 曹心德, 魏晓欣, 代革联, 等, 2011. 土壤重金属复合污染及其化学钝化修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 5(7): 1441-1453. |
| CAO X D, WEI X X, DAI G L, et al., 2011. Combined pollution of multiple heavy metals and their chemical immobilization in contaminated soil: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 5(7): 1441-1453. | |
| [14] | 陈甲斌, 2013. 尾矿资源调查评价与综合利用政策研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| CHEN J B, 2013. Investigation and evaluation of tailings resources and policy research on comprehensive utilization[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. | |
| [15] | 丁苏苏, 李凯华, 黄珏瑛, 等, 2020. 含磷材料修复铅、镉污染农田土壤效果及影响因素研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 42(7): 929-936. |
| DING S S, LI K H, HUANG Y Y, et al., 2020. Research progress on the effects of phosphorus-containing materials in remediation of lead and cadmium contaminated farmland soils and influencing factors[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 42(7): 929-936. | |
| [16] | 胡清秀, 卫智涛, 王洪媛, 2011. 双孢蘑菇渣菌堆肥及其肥效的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(9): 1902-1909. |
| HU Q X, WEI Z T, WANG H Y, 2011. Study on Agaricus bisporus slag fungus compost and its fertilizer efficiency[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(9): 1902-1909. | |
| [17] | 李如艳, 崔红标, 刘笑生, 等, 2018. 模拟酸雨对磷酸二氢钾钝化污染土壤Cu、Cd、Pb和P释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 12(1): 227-234. |
| LI R Y, CUI H B, LIU X S, et al., 2018. The effect of simulated acid rain on the release of Cu, Cd, Pb and P from polluted soil by potassium dihydrogen phosphate[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 12(1): 227-234. | |
| [18] | 刘新梅, 田剑, 张昊, 等, 2021. 改良剂对复垦土壤团聚体组成及有机碳含量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(1): 326-333, 355. |
| LIU X M, TIAN J, ZHANG H, et al., 2021. Effects of amendments on aggregate composition and organic carbon content of reclaimed soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(1): 326-333, 355. | |
| [19] | 舒冉君, 2018. 米糠与氧化钙、过磷酸钙联用钝化重金属铅镉污染土壤[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学. |
| SU R J, 2018. Rice bran combined with calcium oxide and calcium superphosphate to passivate heavy metal lead and cadmium contaminated soil[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong University of Technology. | |
| [20] | 汪吉东, 张永春, 俞美香, 等, 2007. 不同有机无机肥配合施用对土壤活性有机质含量及pH值的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 23(6): 573-578. |
| WANG J D, ZHANG Y C, YU X M, 2007. Effect of combined application of different organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil active organic matter content and pH value[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 23(6): 573-578. | |
| [21] | 卫智涛, 周国英, 胡清秀, 2010. 食用菌菌渣利用研究现状[J]. 中国食用菌, 29(5): 3-6. |
| WEI Z T, ZHOU G Y, HU Q X, 2010. Research status of the utilization of edible mushroom residues[J]. Edible Fungi of China, 29(5): 3-6. | |
| [22] | 吴清清, 马军伟, 姜丽娜, 等, 2010. 鸡粪和垃圾有机肥对苋菜生长及土壤重金属积累的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 29(7): 1302-1309. |
| WU Q Q, MA J W, JIANG L N, et al., 2010. Effect of poultry and household garbage manure on the growth of Aamaranth tricolor L. and heavy metal accumulation in soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 29(7): 1302-1309. | |
| [23] | 卫智涛, 周国英, 胡清秀, 2010. 食用菌菌渣利用研究现状[J]. 中国食用菌, 29(5): 3-6, 11. |
| WEI Z T, ZHOU G Y, HU Q X, 2010. Current status of research on utilization of edible fungus residue[J]. Edible Fungi of China, 29(5): 3-6, 11. | |
| [24] | 孙清斌, 尹春芹, 邓金锋, 等, 2019. 施用外源物对尾矿土壤种植胡枝子修复效应初探[J]. 土壤, 51(5): 986-994. |
| SUN Q B, YING C Q, DENG J F, et al., 2019. Preliminary Study on the Effect of Exogenous Materials on the Remediation of Planting Lespedeza in Tailing Soil[J]. Soils, 51(5): 986-994. | |
| [25] | 邢金峰, 仓龙, 任静华, 2019. 重金属污染农田土壤化学钝化修复的稳定性研究进展[J]. 土壤, 51(2): 224-234. |
| XING J F, CANG L, REN J H, 2019. Research progress on stability of chemical passivation remediation of heavy metal contaminated farmland soil[J]. Soils, 51(2): 224-234. | |
| [26] | 于广明, 宋传旺, 潘永战, 等, 2014. 尾矿坝安全研究的国外新进展及我国的现状和发展态势[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 33(S1): 3238-3248. |
| YU G M, SONG C W, PANG Y Z, et al., 2014. New foreign developments of tailings dam safety research and my country's current situation and development trend[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 33(S1): 3238-3248. | |
| [27] | 王正刚, 周望岩, 李永飞, 2008. 稻米及其副产品深加工技术[J]. 粮食加工, 33(4): 26-28. |
| WANG Z G, ZHOU W Y, LI Y F, 2008. Deep processing technology of rice and its by-products[J]. Grain Processing, 33(4): 26-28. | |
| [28] | 周相玉, 冯文强, 秦鱼生, 等, 2012. 镁、锰、活性炭和石灰对土壤pH及镉有效性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 26(6): 199-203, 208. |
| ZHOU X Y, FENG W Q, QIN Y S, et al., 2012. Effects of magnesium, manganese, activated carbon and lime on soil pH and cadmium availability[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(6): 199-203, 208. | |
| [29] | 张晓君, 杨胜香, 段纯, 等, 2014. 蘑菇渣作为改良剂对铅锌尾矿改良效果研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(3): 526-531. |
| ZHANG X J, YANG S X, DUAN C, et al., 2014. Study on the effect of mushroom residue as a modifier on the improvement of lead-zinc tailings[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(3): 526-531. | |
| [30] | 邹富桢, 2016. 无机-有机混合改良剂对酸性多金属污染土壤的修复效应[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学. |
| ZHOU F Z, 2016. The remediation effect of inorganic-organic mixed amendment on acidic polymetallic contaminated soil[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University. | |
| [31] | 周武先, 何银生, 朱盈徽, 等, 2019. 生石灰和钙镁磷肥对酸化川党参土壤的改良效果[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(9): 3224-3232. |
| ZHOU W S, HE Y S, ZHU Y W, et al., 2019. Effect of quicklime and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer on soil improvement of acidified codonopsis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(9): 3224-3232. | |
| [32] | 张文彦, 杨晓帆, 李琛, 2021. 云南2种色稻米糠营养成分及储存品质分析[J]. 粮食与饲料工业 (1): 23-26. |
| ZHANG W Y, YANG X F, LI C, 2021. Analysis of nutrient composition and storage quality of two kinds of color rice bran in Yunnan[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry (1): 23-26. |
| [1] | 张兴旺, 谢艳萍, 吴晓敏, 李垚, 肖书平. 福建省明溪县极小种群野生植物喜树种群结构与动态特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1037-1044. |
| [2] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [3] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [4] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [5] | 代德敏, 蒋旭升, 刘杰, 王路洋, 陈诗奇, 韩庆坤. 3种有机改良剂对铅锌矿尾砂适生性改善的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 784-793. |
| [6] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [7] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [8] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [9] | 徐晨, 裴顺祥, 吴莎, 郭慧, 马淑敏, 吴迪, 章尧想, 法蕾. 北京九龙山不同林型林间大气主要BVOCs组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 245-255. |
| [10] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [11] | 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻, 李永斌, 郭丽芳, 焦念元. 尾矿先锋植物根际溶磷菌的分离鉴定与其促生研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [12] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [13] | 刘桢迪, 宋艳宇, 王宪伟, 谭稳稳, 张豪, 高晋丽, 高思齐, 杜宇. 冻土区泥炭地植物生长及碳氮特征对模拟增温的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1765-1772. |
| [14] | 肖以华, 付志高, 许涵, 史欣, 唐海明, 陈步峰. 城市化对珠江三角洲不同功能群植物叶片功能性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1783-1793. |
| [15] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
