生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1831-1841.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.007
所属专题: 生物多样性专题汇编
收稿日期:2020-02-09
出版日期:2021-09-18
发布日期:2021-12-08
通讯作者:
*E-mail: xcy@nxu.edu.cn作者简介:贾晨波(1994年生),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为微生物资源开发与利用。E-mail: jcb101003@163.com
基金资助:
JIA Chenbo( ), GUO Yang, MA Chenglian, SU Jianyu, XU Chunyan(
), GUO Yang, MA Chenglian, SU Jianyu, XU Chunyan( )
)
Received:2020-02-09
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
摘要:
根腐病严重制约着枸杞产业的发展,而土壤微生物多样性和物种组成的变化与植株根腐病的发生有密切的关系,因此了解宁夏枸杞根腐病发生与根表、根际和根围土壤微生物群落结构的关系十分必要。应用Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术对枸杞健康株和根腐病患病株的根表、根际及根围土壤中16S rDNA V3+V4区和ITS1片段进行测序,将结果质控后比对相关数据库进行注释和分析。真菌群落中丰度最高的门和属分别是子囊菌门(Ascomycota)和镰刀菌属(Fusarium),细菌群落中优势门依次为放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi),节杆菌属(Arthrobacter)是丰度最高且在根表的丰度显著高于根际和根围土壤,根表、根际和根围3个部位的优势物种组成和占比均不相同。健康株根表的真菌群落丰富度、多样性及均匀度指数均高于患病株(P<0.05),而二者的细菌群落α多样性指数无显著差异。功能预测也同样表明健康株和患病株之间的土壤细菌群落功能差异较小,真菌群落中镰刀菌属的功能丰度较高,其在患病株根表和根际的丰度均大于健康株。综上,枸杞健康株和患病株之间,各样品中真菌群落多样性的差异比细菌群落大,二者根表真菌的差异最显著,患病株根表和根际的镰刀菌属的占比和功能丰度最大。该研究分别从土壤真菌和细菌两个角度阐述了宁杞1号枸杞健康株和根腐病患病株的土壤微生物群落和功能的差异,对宁夏枸杞根腐病的认识具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
贾晨波, 郭洋, 马成莲, 苏建宇, 徐春燕. 宁杞1号枸杞健康株与根腐病患病株的土壤微生物群落和功能差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1831-1841.
JIA Chenbo, GUO Yang, MA Chenglian, SU Jianyu, XU Chunyan. Difference on Soil Microbial Community and Function of Healthy and Diseased Plants of Lycium barbarum Ningqi-1[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1831-1841.
| 样品 Samples | Sobs指数 Sobs index | Shannoneven指数 Shannoneven index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌 Fungi | 根表 Rhizoplane | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 486.33±18.77a | 0.63±0.35b | 3.87±0.20a | 0.99 |
| 411.00±1.00bc | 0.54±0.03c | 3.33±0.09b | 0.99 | |||
| 根际 Rhizosphere | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 502.50±49.74a | 0.66±0.01ab | 4.13±0.14a | 0.99 | |
| 438.00±7.00b | 0.64±0.03b | 3.93±0.19a | 0.99 | |||
| 根围 Root zone | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 387.33±15.04bc | 0.69±0.18a | 3.93±0.33a | 0.99 | |
| 400.00±15.04c | 0.57±0.01c | 3.37±0.17b | 0.99 | |||
| 细菌 Bacteria | 根表 Rhizoplane | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2170.67±142.00bc | 0.72±0.06b | 5.81±0.07b | 0.96 |
| 1998.67±223.72c | 0.69±0.09b | 5.68±0.02b | 0.97 | |||
| 根际 Rhizosphere | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2601.33±110.25a | 0.82±0.03a | 6.41±0.24a | 0.96 | |
| 2568.33±180.07a | 0.82±0.01a | 6.40±0.14a | 0.96 | |||
| 根围 Root zone | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2387.33±31.01ab | 0.81±0.01a | 6.28±0.04a | 0.96 | |
| 2439.33±272.79ab | 0.80±0.01a | 6.26±0.16a | 0.96 | |||
表1 微生物群落的Alpha多样性指数
Table 1 Alpha diversity index of the microbial communities
| 样品 Samples | Sobs指数 Sobs index | Shannoneven指数 Shannoneven index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | 覆盖度 Coverage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 真菌 Fungi | 根表 Rhizoplane | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 486.33±18.77a | 0.63±0.35b | 3.87±0.20a | 0.99 |
| 411.00±1.00bc | 0.54±0.03c | 3.33±0.09b | 0.99 | |||
| 根际 Rhizosphere | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 502.50±49.74a | 0.66±0.01ab | 4.13±0.14a | 0.99 | |
| 438.00±7.00b | 0.64±0.03b | 3.93±0.19a | 0.99 | |||
| 根围 Root zone | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 387.33±15.04bc | 0.69±0.18a | 3.93±0.33a | 0.99 | |
| 400.00±15.04c | 0.57±0.01c | 3.37±0.17b | 0.99 | |||
| 细菌 Bacteria | 根表 Rhizoplane | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2170.67±142.00bc | 0.72±0.06b | 5.81±0.07b | 0.96 |
| 1998.67±223.72c | 0.69±0.09b | 5.68±0.02b | 0.97 | |||
| 根际 Rhizosphere | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2601.33±110.25a | 0.82±0.03a | 6.41±0.24a | 0.96 | |
| 2568.33±180.07a | 0.82±0.01a | 6.40±0.14a | 0.96 | |||
| 根围 Root zone | 患病株 Diseased 健康株 Healthy | 2387.33±31.01ab | 0.81±0.01a | 6.28±0.04a | 0.96 | |
| 2439.33±272.79ab | 0.80±0.01a | 6.26±0.16a | 0.96 | |||
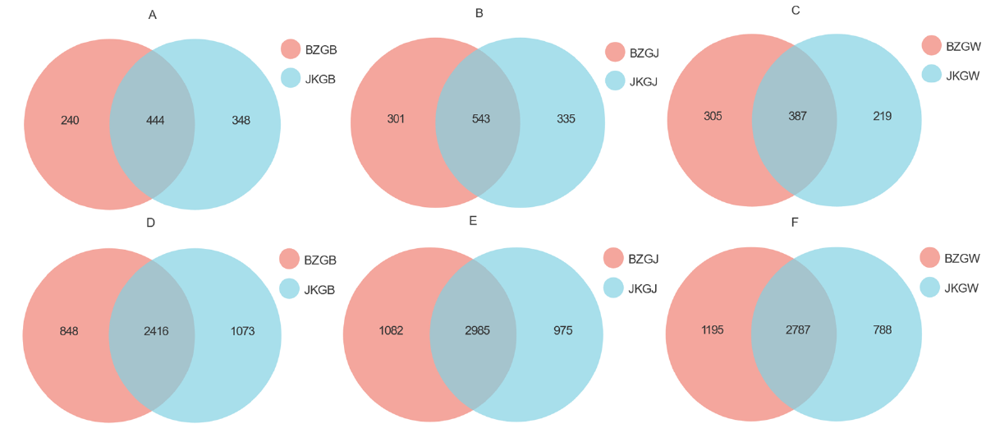
图1 基于OTU水平的Venn图 为根表真菌,图B为根际真菌,图C为根围真菌;图D为根表细菌,图E为根际细菌,图F为根围细菌
图A Venn diagram based on OTU levels is the rhizoplane fungi, Figure B is the rhizosphere fungi, Figure C is the root zone fungi; Figure D is the rhizoplane bacteria, Figure E is the rhizosphere bacteria, Figure F is the root zone bacteria
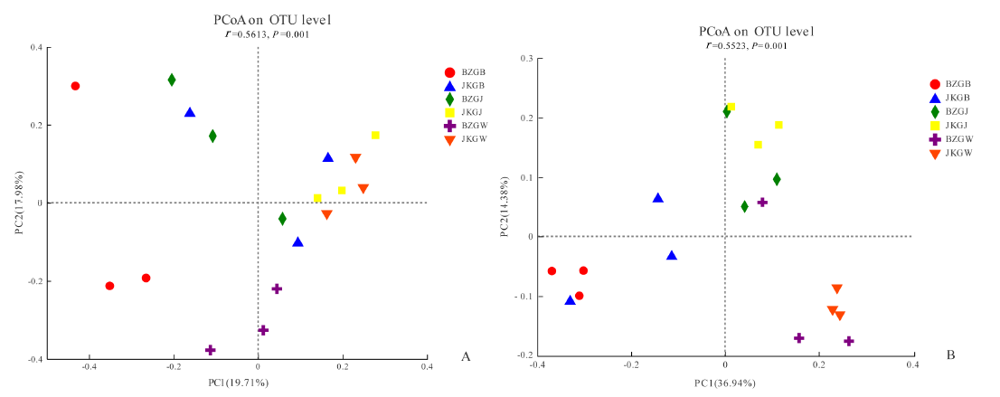
图2 真菌和细菌OTU水平的PCoA分析 PcoA(Principal co-ordinates analysis)图中的PC坐标轴是对样本组成差异的解释度值
Fig. 2 PCoA analysis of OTU levels in fungi and bacteria The PC coordinate axis in the PcoA (Principal co-ordinates analysis) graph is the explanatory value of the difference in sample composition

图5 属水平的LDA判别结果图 横坐标中小写字母c、o、f、g为分类水平,分别代表纲、目、科和属水平
Fig. 5 LDA discriminant result chart of genus level The lowercase letters c, o, f, and g in the abscissa represent the classification level, representing the class, order, family and genus levels respectively
| [1] |
ARIAS M M, LEANDRO L F, MUNKVOLD G P, 2013. Aggressiveness of Fusarium species and impact of root infection on growth and yield of soybeans[J]. Phytopathology, 103(8): 822-832.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAKKER M G, GLOVER J D, MAI J G, et al., 2010. Plant community effects on the diversity and pathogen suppressive activity of soil streptomycetes[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 46(1): 35-42.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BERTRAND H, NALIN R, BALLY R, et al., 2001. Isolation and identification of the most efficient plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with canola (Brassica napus)[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 33(2): 152-156.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHITTEM K, MATHEW F M, GREGOIRE M, et al., 2015. Identification and characterization of Fusarium spp. associated with root rots of field pea in North Dakota[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 143(4): 641-649.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CARIDDI C, MINCUZZI A, SCHENA L, et al., 2018. First report of collar and root rot caused by Phytophthora nicotianae on Lycium barbarum[J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 100(2): 361.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAN L, ZHOU X, ZHAO Y T, et al., 2020. First report of Plectosphaerella plurivora causing root rot disease in Panax notoginseng in China[J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 168(7-8): 375-379.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JEANNOTTER R, NAKANO H A, ARNAUD M, et al., 2005. Negative feedback on a perennial crop: Fusarium crown and root rot of asparagus is related to changes in soil microbial community structure[J]. Plant and Soil, 268(1): 75-87.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI F, CHEN L, REDMILE-GORDON M, et al., 2018. Mortierella Elongata's roles in organic agriculture and crop growth promotion in a mineral soil[J]. Land Degradation and Development, 29(6): 1642-1651.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI M J, PAN X X, LIU Z B, et al., 2020. First report of root rot caused by Fusarium equiseti on ginseng (Panax ginseng ) in China[J]. Plant Disease, DOI: 10.1094/PDIS-12-19-2640-PDN.
DOI |
| [10] |
NYANDORO R, CHANG K F, HWANG S F, et al., 2019. Management of root rot of soybean in Alberta with fungicide seed treatments and genetic resistance[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 99(4): 499-509.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NA X F, YU H L, WANG P, et al., 2019. Vegetation biomass and soil moisture coregulate bacterial community succession under altered precipitation regimes in a desert steppe in northwestern China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107520.
DOI |
| [12] |
PEAY K G, GARBELOTTO M, BRUNS T D, 2010. Evidence of dispersal limitation in soil microorganisms: Isolation reduces species richness on mycorrhizal tree islands[J]. Ecology, 91(12): 3631-3640.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SONG X B, CUI Y P, PENG A T, et al., 2020. First report of brown spot disease in Psidium guajava caused by Alternaria tenuissima in China[J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 102(12): 1309.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SHI S J, RICHARDSON A E, O'CALLAGHAN M, et al., 2011. Effects of selected root exudate components on soil bacterial communities[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 77(3): 600-610.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
VIVES-PERIS V, DE OLLAS C, GOMEZ-CADENAS A, et al., 2020. Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 39(1): 3-17.
DOI URL |
| [16] | WANG J, SHEN J, WU Y, et al., 2013. Phylogenetic beta diversity in bacterial assemblages across ecosystems: Deterministic versus stochastic processes[J]. The ISME Journal: Multidisciplinary Journal of Microbial Ecology, 7(7): 1310-1321. |
| [17] | WANG R Y, ZHAO X, HAO H T, et al., 2015. First Report of Arthrocladiella mougeotii causing powdery mildew on Goji berry (Lycium barbarum) in Ningxia, China[J]. Plant Disease, 99(9): 1283. |
| [18] |
WU Z X, HAO Z P, ZENG Y, et al., 2015. Molecular characterization of microbial communities in the rhizosphere soils and roots of diseased and healthy Panax notoginseng[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 108(5): 1059-1074.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YLVA L, TIM S, RASMUS K, et al., 2011. 454-sequencing reveals stochastic local reassembly and high disturbance tolerance within arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities[J]. Journal of Ecology, 100(1): 151-160.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈伶俐, 2015. 柴达木地区枸杞根腐病病原菌生物学特性及药剂防治研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学. |
| CHEN L L, 2015. Biological characteristics of pathogens causing Wolf berry root rot and fungicides controlling experiment[D]. Xining: Qinghai university. | |
| [21] | 陈姗姗, 罗秀媚, 杨星勇, 2018. 重庆市石柱县黄连根腐病病原菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 植物保护学报, 45(6): 255-256. |
| CHEN S S, LUO X M, YANG X Y, 2018. Isolation and identification of Coptis chinensis root rot pathogen in Shizhu county, Chongqing city[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 45(6): 255-256. | |
| [22] | 崔云龙, 姬金红, 衣海青, 1995. 短小芽孢杆菌D82对小麦根腐病原菌拮抗的研究[J]. 中国生物防治 (3): 114-118. |
| CUI Y L, JI J H, YI H Q, 1995. Antagonistic effect of Bacillus pumilus D82 on wheat root rot pathogens[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control (3): 114-118. | |
| [23] | 高芬, 吴元华, 2008. 链格孢属 (Alternaria) 真菌病害的生物防治研究进展[J]. 植物保护, 34(3): 1-6. |
| GAO F, WU Y H, 2008. Progresses in the biocontrol of plant diseases caused by Alternaria[J]. Plant Protection, 34(3): 1-6. | |
| [24] | 郭梅, 周亚男, 肖倩, 等, 2019. 大白菜腐霉根腐病的病原[J]. 菌物学报, 38(6): 761-767. |
| GUO M, ZHOU Y N, XIAO Q, et al., 2019. The pathogen causing Pythium root rot of Chinese cabbage[J]. Mycosystema, 38(6): 761-767. | |
| [25] | 郭瑞英, 陈清, 李晓林, 2005. 土壤微生物--抑病性与土壤健康[J]. 中国蔬菜 (S1): 78-82. |
| GUO R Y, CHEN Q, LI X L, 2005. Soil microbial-disease inhibition and soil health[J]. China Vegetables (S1): 78-82. | |
| [26] | 贾倩, 周星, 顾沛雯, 2014. 宁夏枸杞炭疽病病原菌的分子鉴定[J]. 北方园艺 (10): 88-91. |
| JIA Q, ZHOU X, GU P W, 2014. Molecular biology identification of Colletotnchum gloeosprioides from Lycium barbarum L. in Ningxia[J]. Northern Horticulture (10): 88-91. | |
| [27] | 蒋景龙, 余妙, 李丽, 等, 2018. 西洋参根腐病发生与根际土壤细菌群落结构变化关系研究[J]. 中草药, 49(18): 4399-4407. |
| JIANG J L, YU M, LI L, et al., 2018. Relationship between occurrence of root-rot and changes of bacterial community structure in rhizosphere soil of Panax quinquefolius[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 49(18): 4399-4407. | |
| [28] | 雷蕾, 李剑萍, 马力文, 等, 2020. 宁夏中宁县枸杞精细化气候区划[J]. 经济林研究, 38(3): 104-111. |
| LEI L, LI J P, MA L W, et al., 2020. A precise climate division of Lycium barbarum in Zhongning county, Ningxia[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 38(3): 104-111. | |
| [29] | 李晖, 李国英, 付建红, 等, 1998. 新疆枸杞烂根病病原的鉴定[J]. 植物保护学报, 25(3): 253-257. |
| LI H, LI G Y, FU J H, et al., 1998. Identification of the root rot pathogen of Lycium barbarum in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 25(3): 253-257. | |
| [30] | 李捷, 冯丽丹, 王有科, 等, 2017. 甘肃枸杞镰孢菌根腐病病原鉴定及优势病原菌生物学特性[J]. 干旱区研究, 34(5): 1093-1100. |
| LI J, FENG L D, WANG Y K, et al., 2017. Identification and biological characteristics of dominant pathogens of Lycium bararum root rot in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 34(5): 1093-1100. | |
| [31] | 刘振荣, 1980. 枸杞枯萎病研究初报[J]. 青海农林科技 (3): 43-45. |
| LIU Z R, 1980. Preliminary report on the study of wilt disease of Lycium barbarum[J]. Science and Technology of Qinghai Agriculture and Forestry (3): 43-45. | |
| [32] | 卢圣鄂, 肖波, 任风鸣, 等, 2021. 基于Illumina Miseq分析黄精根腐病根际土壤真菌群落结构及多样性[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 23(1): 13-19. |
| LU S E, XIAO B, REN F M, et al., 2021. Fungal community structure and diversity of rhizosphere soil of Polygonatum sibiricum with root-rot analyzed by Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 23(1): 13-19. | |
| [33] | 宋旭红, 王钰, 李隆云, 等, 2017. 石柱黄连根腐病根际土壤细菌微生态研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 42(7): 1304-1311. |
| SONG Y H, WANG Y, LI L Y, et al., 2017. Research on bacteria microecology in root rot rhizosphere soil of Coptis chinensis produced in Shizhu city[J]. 42(7): 1304-1311. | |
| [34] | 闫欢, 高芬, 王梦亮, 等, 2020. 黄芪根腐病病株和健株根围微生物菌群变化分析[J]. 植物保护, 46(4): 48-54. |
| YAN H, GAO F, WANG M L, et al., 2020. Changes of microbial community in root zone soil of Astragalus membranaceus suffering from root rot disease[J]. Plant Protection, 46(4): 48-54. | |
| [35] | 杨波, 郭成瑾, 王喜刚, 等, 2019. 新疆马铃薯镰刀菌根腐病发生危害调查及病原菌鉴定[J]. 西北农业学报, 28(12): 2069-2077. |
| YANG B, GUO C J, WANG X G, et al., 2019. Investigation and pathogen identification of potato root rot caused by Fusarium in Xinjiang[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 28(12): 2069-2077. | |
| [36] | 杨剑锋, 张园园, 王娜, 等, 2020. 苜蓿根腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及苜蓿品种的抗性评价[J]. 中国草地学报, 42(3): 52-60. |
| YANG J F, ZHANG Y Y, WANG N, et al., 2020. Isolation and identification of pathogens causing root rot disease in alfalfa and the evaluation of resistant ability of alfalfa varieties to Fusarium equiseti and F. tricinctum[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 42(3): 52-60. | |
| [37] | 杨盼, 翟亚萍, 赵祥, 等, 2020. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌互作对苜蓿根际土壤细菌群落结构的影响及PICRUSt功能预测分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 47(11): 3868-3879. |
| YANG P, ZHAI Y P, ZHAO X, et al., 2020. Effect of interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobium on Medicago sativa rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure and PICRUSt functional prediction[J]. Microbiology China, 47(11): 3868-3879. | |
| [38] | 余金阳, 黄潇慧, 帅正彬, 等, 2020. 四川彭州大蒜根腐病发病土壤细菌与真菌群落结构[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 26(4): 928-935. |
| YU J Y, HUANG X H, SHUAI Z B, et al., 2020. The community structure of bacteria and fungi in soils with root rot diseased garlic plants in Pengzhou, Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 26(4): 928-935. | |
| [39] | 岳苑, 徐娟, 赵飞, 等, 2019. 宁夏地区枸杞所携带真菌的分子鉴定[J]. 现代食品科技, 35(10): 102-109. |
| YUE Y, XU J, ZHAO F, et al., 2019. Molecular identification of fungi carried by Lycium barbarum from Ningxia[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology. 35(10): 102-109. | |
| [40] | 王彩霞, 李兴红, 魏艳敏, 等, 2019. 引起葡萄叶斑病的链格孢种类的初步鉴定[J]. 植物保护学报, 46(1): 175-183. |
| WANG C X, LI X H, WEI Y M, et al., 2019. Identification of Alternaria species causing leaf spots in grapes[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 46(1): 175-183. | |
| [41] | 王国珍, 鲁占魁, 1994. 宁夏枸杞根腐病病原的研究[J]. 微生物学通报, 21(6):330-332. |
| WANG G Z, LU Z K, 1994. Study on the pathogen of lycium barbarum root rot in Ningxia[J]. Microbiology China, 21(6): 330-332. | |
| [42] | 伍晓丽, 王钰, 刘飞, 等, 2020. 黄连根腐病镰刀菌属病原真菌鉴定[J]. 中国中药杂志, 45(6): 1323-1328. |
| WU X L, WANG Y, LIU F, et al., 2020. Identification of Coptis chinensis root rot disease pathogenic Fusarium spp. Fungi[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 45(6): 1323-1328. | |
| [43] | 周园园, 吴治然, 贡长怡, 等, 2019. 茶树链格孢叶斑病的病原鉴定[J]. 植物保护, 45(6): 145-148, 155. |
| ZHOU Y Y, WU Z R, GONG C Y, et al., 2019. Identification of Alternaria alternata causing leaf spot disease of camellia sinensis[J]. Plant Protection, 45(6): 145-148, 155. |
| [1] | 侯晖, 颜培轩, 谢沁宓, 赵宏亮, 庞丹波, 陈林, 李学斌, 胡杨, 梁咏亮, 倪细炉. 贺兰山蒙古扁桃灌丛根际土壤AM真菌群落多样性特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [3] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [4] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [5] | 寇祝, 卿纯, 袁昌果, 李平. 西藏东北部热泉水中硫氧化菌的多样性及分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [6] | 胡芳, 刘聚涛, 温春云, 韩柳, 文慧. 抚河流域浮游植物群落结构特征及其水生态状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [7] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [8] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [9] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [10] | 花莉, 成涛之, 梁智勇. 固定化混合菌对陕北黄土地区石油污染土壤的修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [11] | 朱奕豪, 李青梅, 刘晓丽, 李娜, 宋凤玲, 陈为峰. 不同土地整治类型新增耕地土壤微生物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [12] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [13] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [14] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [15] | 杨贤房, 陈朝, 郑林, 万智巍, 陈永林, 王远东. 稀土矿区不同土地利用类型土壤细菌群落特征及网络分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 793-801. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
