生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1996-2006.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.010
吴炜龙1( ), 陈艺杰1, 卫婷1, 杨贵琼1, 阳长洪1, 甄珍1, 蔺中2,*(
), 陈艺杰1, 卫婷1, 杨贵琼1, 阳长洪1, 甄珍1, 蔺中2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-24
出版日期:2023-11-18
发布日期:2024-01-17
通讯作者:
* 蔺中,E-mail: 50234029@qq.com作者简介:吴炜龙(2000年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为从事土壤污染修复研究。E-mail: 2830632924@qq.com
基金资助:
WU Weilong1( ), CHEN Yijie1, WEI Ting1, YANG Guiqiong1, YANG Changhong1, ZHEN Zhen1, LIN Zhong2,*(
), CHEN Yijie1, WEI Ting1, YANG Guiqiong1, YANG Changhong1, ZHEN Zhen1, LIN Zhong2,*( )
)
Received:2023-07-24
Online:2023-11-18
Published:2024-01-17
摘要:
滨海盐碱地是中国重要的耕地资源,而人类活动等加重了滨海盐碱地的多环芳烃(PAHs)污染。微生物降解是去除土壤PAHs污染的重要手段。外源微生物的低环境适应性限制了其实际应用,诱导强化土著微生物原位修复具有重要意义。以较难降解的三环芳烃-蒽为多环芳烃代表,湛江市轻度滨海盐碱土为污染研究对象,赤子爱胜蚓(Eisenia foetida)为受试生物,设置4组处理(灭菌对照,SS;灭菌土壤加蚯蚓,SE;自然对照,OS;自然土壤加蚯蚓,OE)。比较不同时间段各处理土壤中蒽的降解效率、理化性质和培养结束时土壤微生物群落结构,明确蚯蚓对粤西地区滨海农田土壤蒽降解的强化效果、降解功能微生物种群和关键环境因子的贡献率。结果表明:蚯蚓能够影响滨海盐碱土壤中蒽的降解,并且加速其降解。在OS中蒽降解率为40.7%,而SS中蒽的降解率仅为17.7%。土壤中蒽的降解以生物降解为主(23.0%),而不是非生物降解(17.7%)。OE处理的降解效率最高为62.1%,SE处理的降解效率为50.4%。蚯蚓强化非生物降解和肠道菌群作用共同的效果(32.7%)高于蚯蚓强化土著微生物降解的效果(21.4%)。同时,蚯蚓影响了土壤中微生物的丰度,提高了假单胞菌科(Pseudomonadaceae)、伯克氏菌科(Burkholderiaceae)和气单胞菌科(Aeromonadaceae)等降解微生物的丰度。相关性网络分析表明,蒽的残留浓度与伯克氏菌科、气单胞菌科、鞘脂单胞菌和黄杆菌(Flavobacteriaceae)为显著负相关,而与pH、有机质为显著正相关,说明蚯蚓能够通过影响pH、有机质和土壤中的微生物,加速滨海盐碱土壤中蒽的降解。
中图分类号:
吴炜龙, 陈艺杰, 卫婷, 杨贵琼, 阳长洪, 甄珍, 蔺中. 蚯蚓驱动的滨海盐碱农田土壤中多环芳烃生物降解的机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1996-2006.
WU Weilong, CHEN Yijie, WEI Ting, YANG Guiqiong, YANG Changhong, ZHEN Zhen, LIN Zhong. Mechanisms of Earthworm-driven Biodegradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Coastal Saline Agricultural Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1996-2006.
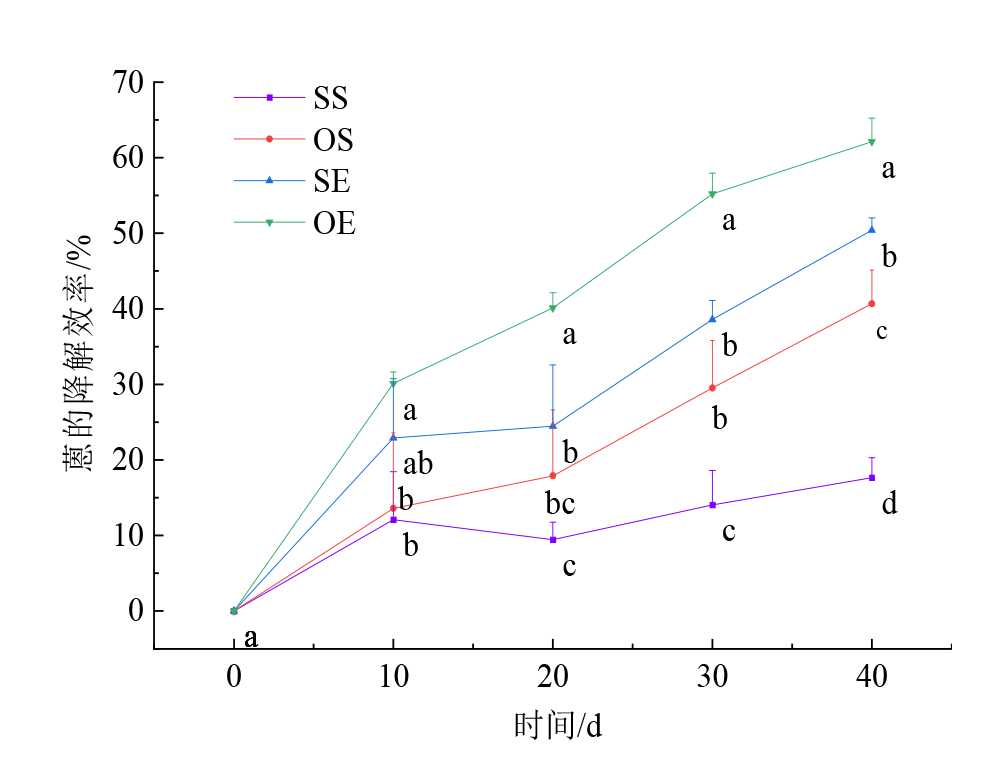
图1 不同处理蒽降解效率随时间的变化 数据是3个重复的平均值±标准差(n=3),不同字母表示同一时间不同处理之间的差异(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 Variation of anthracene degradation efficiency with time for different treatments
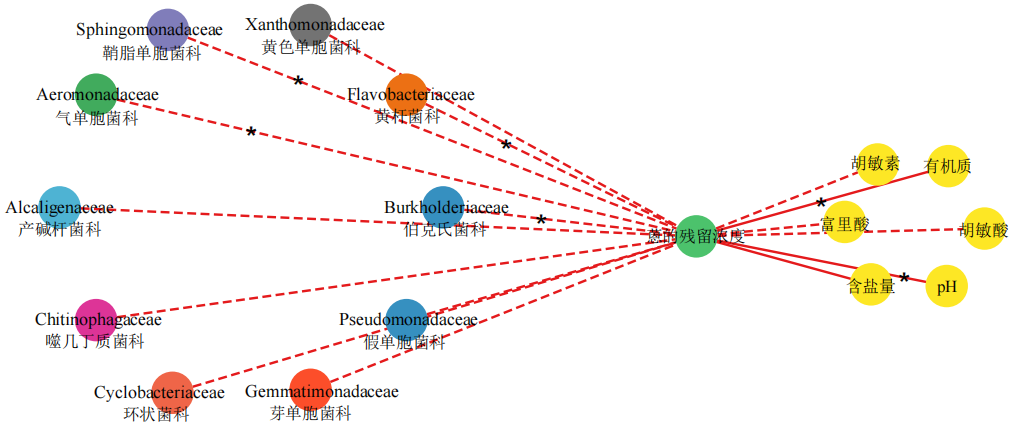
图4 环境因子、土壤微生物与蒽的残留浓度间的网络分析图 实线表示正相关,虚线为负相关。*表示P<0.05
Figure 4 Network analysis diagram of the residual concentration of anthracene among environmental factors, soil microorganisms
| [1] |
BOLAN S, PADHYE L P, MULLIGAN C N, et al., 2023. Surfactant-enhanced mobilization of persistent organic pollutants: Potential for soil and sediment remediation and unintended consequences[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 443(Part A): 130189.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN W S, XIAN W X, HE G Y, et al., 2023. Occurrence and spatiotemporal distribution of PAHs and OPAHs in urban agricultural soils from Guangzhou City, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 254: 114767.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DAI C M, HAN Y M, DUAN Y P, et al., 2022. Review on the contamination and remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal soil and sediments[J]. Environmental Research, 205: 112423.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FERNáNDEZ-LUQUEñO F, MARSCH R, ESPINOSA-VICTORIA D, et al., 2008. Remediation of PAHs in a saline-alkaline soil amended with wastewater sludge and the effect on dynamics of C and N[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 402(1): 18-28.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HAWLICZEK A, NOTA B, CENIJN P, et al., 2012. Developmental toxicity and endocrine disrupting potency of 4-azapyrene, benzo[b]fluorene and retene in the zebrafish Danio rerio[J]. Reproductive Toxicology, 33(2): 213-23.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
HERNÁNDEZ-VEGA J C, CADY B, KAYANJA G, et al., 2017. Detoxification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Arabidopsis thaliana involves a putative flavonol synthase[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321: 268-80.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAO Y Q, ZHAO L X, SUN Y, et al., 2018. Enhancement effect of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) on acetochlor biodegradation in soil and possible mechanisms[J]. Environ Pollution, 242(Part A): 728-737.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JACQUES R J S, OKEKE B C, BENTO F M, et al., 2008. Microbial consortium bioaugmentation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil[J]. Bioresource Technology, 99(7): 2637-43.
PMID |
| [9] |
KäSTNER M, BREUER-JAMMALI M, MAHRO B, 1998. Impact of inoculation protocols, salinity, and pH on the degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and survival of PAH-degrading bacteria introduced into soil[J]. Appl Environ Microbiology, 64(1): 359-362.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KARIYAWASAM T, DORAN G S, HOWITT J A, et al., 2022. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in soils and sediments: Sustainable approaches for extraction and remediation[J]. Chemosphere, 291(Part 3): 132981.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KIM Y H, FREEMAN J P, MOODY J D, et al., 2005. Effects of pH on the degradation of phenanthrene and pyrene by Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1[J]. Appl Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67(2): 275-285.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KELSEY J W, KOTTLER B D, ALEXANDER M, 1997. Selective chemical extractants to predict bioavailability of soil-aged organic chemicals[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(1): 214-7.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KALBITZ K, KAISER K, BARGHOLZ J, et al., 2006. Lignin degradation controls the production of dissolved organic matter in decomposing foliar litter[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 57(4): 504-16.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI C H, ZHOU H W, WONG Y S, et al., 2009. Vertical distribution and anaerobic biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove sediments in Hong Kong, South China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 407(21): 5772-5779.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIN Z, BAI J, ZHEN Z, et al., 2016a. Enhancing pentachlorophenol degradation by vermicomposting associated bioremediation[J]. Ecological Engineering, 87: 288-294.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIN Z, ZHEN Z, LUO S W, et al., 2021. Effects of two ecological earthworm species on tetracycline degradation performance, pathway and bacterial community structure in laterite soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412: 125212.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIN Z, ZHEN Z, WU Z H, et al., 2016b. The impact on the soil microbial community and enzyme activity of two earthworm species during the bioremediation of pentachlorophenol-contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 301: 35-45.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIN Z, ZHEN Z, REN L, et al., 2018. Effects of two ecological earthworm species on atrazine degradation performance and bacterial community structure in red soil[J]. Chemosphere, 196: 467-75.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
LU X Y, ZHANG T, FANG H H, 2011. Bacteria-mediated PAH degradation in soil and sediment[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89(5): 1357-71.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LUO S W, REN L, WU W J, et al., 2022. Impacts of earthworm casts on atrazine catabolism and bacterial community structure in laterite soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425: 127778.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MA W C, VAN KLEUNEN A, IMMERZEEL J, et al., 1998. Bioaccumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by earthworms: Assessment of equilibrium partitioning theory in in situ studies and water experiments[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17(9): 1730-1737.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MOSCOSO F, DEIVE F J, LONGO M A, et al., 2012. Technoeconomic assessment of phenanthrene degradation by Pseudomonas stutzeri CECT 930 in a batch bioreactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 104: 81-9.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
NZILA A, 2018. Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under anaerobic conditions: Overview of studies, proposed pathways and future perspectives[J]. Environmental Pollution, 239: 788-802.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
OO A N, IWAI C B, SAENJAN P, 2015. Soil properties and maize growth in saline and nonsaline soils using cassava-industrial waste compost and vermicompost with or without earthworms[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 26(3): 300-310.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
PRAMANIK P, GHOSH G K, CHUNG Y R, 2010. Changes in nutrient content, enzymatic activities and microbial properties of lateritic soil due to application of different vermicomposts: A comparative study of ergosterol and chitin to determine fungal biomass in soil[J]. Soil Use and Management, 26(4): 508-515.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SINGH A, KARMEGAM N, SINGH G S, et al., 2020. Earthworms and vermicompost: An eco-friendly approach for repaying nature’s debt[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(6): 1617-1642.
DOI |
| [27] |
SHI R G, LI X H, YANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Contamination and human health risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface soils from Tianjin coastal new region, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268(Part B): 115938.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
TIAN H F, LI C Q, WANG Z, et al., 2023. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation mechanisms in methods using activated persulfate: Radical and non-radical pathways[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 473: 145319.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG S X, LI X J, LIU W, et al., 2012. Degradation of pyrene by immobilized microorganisms in saline-alkaline soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1662-1669.
PMID |
| [30] |
XU C B, DONG D B, MENG X L, et al., 2013. Photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on soil surfaces under UV irradiation[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(3): 569-575.
PMID |
| [31] |
XIANG C G, ZHANG P J, PAN G X, et al., 2006. Changes in diversity, protein content, and amino acid composition of earthworms from a paddy soil under different long-term fertilizations in the Tai Lake Region, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(6): 1667-1673.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
YADAV A, GARG V K, 2011. Industrial wastes and sludges management by vermicomposting[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 10(3): 243-76.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YANG W, LANG Y-H, BAI J, et al., 2015. Quantitative evaluation of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic potential for PAHs in coastal wetland soils of China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 74: 117-124.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHAO F Y, ZHANG Y Y, LI Z J, et al., 2020. Vermicompost improves microbial functions of soil with continuous tomato cropping in a greenhouse[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(1): 380-391.
DOI |
| [35] |
ZHANG H Y, QIAN W, WU L, et al., 2022. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) derived from biomass pyrolysis: Biochar-derived DOC versus smoke-derived DOC, and their differences from natural DOC[J]. Chemosphere, 302: 134869.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHAO L R, ZHAO Z K, ZHANG J B, et al., 2023. Seasonal variation, spatial distribution, and sources of PAHs in surface seawater from Zhanjiang bay influenced by land-based inputs[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 188: 106028.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHU L, LIU J B, ZHOU J Y, et al., 2022. The overlooked toxicity of environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) induced by anthracene transformation to earthworms (Eisenia fetida)[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 853: 158571.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 25-35. |
| BAO S D, 2002. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 25-35. | |
| [39] |
蔡杨, 李伟, 左雪燕, 等, 2021. 盐城滨海湿地土壤多环芳烃分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(6): 1249-1259.
DOI |
| CAI Y, LI W, ZUO X Y, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of PAHs in Yancheng coastal wetland soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences. 30(6): 1249-1259. | |
| [40] | 丁家琪, 罗丽娟, 栾天罡, 2023. 海洋多环芳烃及其衍生物的污染特征和来源分析[J]. 环境化学, 42(3): 893-903. |
| DING J Q, LUO L J, LUUAN T G, 2023. Characteristics and source analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives in marine environment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 42(3): 893-903. | |
| [41] | 代军帅, 左小虎, 王明霞, 等, 2018. 硝酸盐对土壤反硝化活性及蒽厌氧降解的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(1):422-429. |
| DAI J S, ZUO X H, WANG M X, et al., 2018. Effect of nitrate amendment on soil denitrification activity and Anthracene anaerobic degradation[J]. Environmental Science, 39(1): 422-429. | |
| [42] | 黄兴如, 张彩文, 张瑞杰, 等, 2016. 多环芳烃降解菌的筛选、鉴定及降解特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 43(5): 965-973. |
| HUANG X R, ZHANG C W, ZHANG R J, et al., 2016. Isolation, identification and degrading properties of PAHs-degrading bacteria[J]. Microbiology China, 43(5): 965-973. | |
| [43] | 胡炎, 杨帆, 杨宁, 等, 2023. 盐碱地资源分析及利用研究展望[J]. 土壤通报, 54(2): 489-494. |
| HU Y, YANG F, YANG N, et al., 2023. Analysis and prospects of saline-alkali land in China from the perspective of utilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 54(2): 489-494. | |
| [44] | 井永苹, 2013. 土壤动物 (线虫、蚯蚓) 对污染土壤多环芳烃去除的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学: 39-40. |
| JING Y P, 2013. Effects of soil fauna (nematodes and earthworms) on the removal of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from contaminated soil[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University: 39-40. | |
| [45] | 蒋绪洋, 2022. 人工促进自然衰减技术降解土壤中的多环芳烃[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学: 8-11. |
| JIANG X Y, 2022. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil by artificial natural attenuation technology[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology: 8-11. | |
| [46] | 罗舒文, 甄珍, 李文清, 等, 2020. 两种生态型蚯蚓对四环素污染土壤中酶活性和细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(2): 321-330. |
| LUO S W, ZHEN Z, LI W Q, et al., 2020. Ecological effects of two earthworms on the enzymic activity and bacterial community structure in tetracycline-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(2): 321-330. | |
| [47] | 潘政, 郝月崎, 赵丽霞, 等, 2020. 蚯蚓在有机污染土壤生物修复中的作用机理与应用[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(9): 3108-3117. |
|
PAN Z, HAO Y Q, ZHAO L X, et al., 2020. Mechanism and application of earthworm in bioremediation of soil contaminated with organic pollutants: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(9): 3108-3117.
DOI |
|
| [48] | 潘声旺, 2009. 多环芳烃污染土壤的生态修复研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学: 99-101. |
| PAN S W, 2009. Phytoremediation of contaminated soils with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its ecologically enhanced techniques[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University: 99-101. | |
| [49] | 孙池涛, 张俊鹏, 冯棣, 等, 2018. 滨海盐碱农田排水沟土壤水盐分布特征研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电 (8): 19-21. |
| SUN C T, ZHANG J P, FENG D, et al., 2018. Research on the characteristics of water and salt distribution in a coastal saline field drainage ditch[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower (8): 19-21. | |
| [50] | 史志明, 2014. 菲在蚯蚓体内的分布及其对蚯蚓抗氧化防御体系的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学: 35-36. |
| SHI Z M, 2014. Distribution of phenanthrene in earthworms and Its effects on the anti-oxidant defence system of earthworm[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University: 35-36. | |
| [51] | 牛东玲, 王启基, 2002. 盐碱地治理研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 33(6): 449-455. |
| NIU D L, WANG Q J, 2002. Research progress on saline-alkali field control[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 33(6): 449-455. | |
| [52] | 宋兴良, 王江涛, 张哲, 2010. 多环芳烃蒽高效降解菌的筛选及其降解中间产物分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 29(6): 815-818. |
| SONG X L, WANG J T, ZHANG Z, 2010. Selection of microorganisms of degraded anthracene and analysis of its middle products[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 29(6): 815-818. | |
| [53] | 王佳丽, 黄贤金, 钟太洋, 等, 2011. 盐碱地可持续利用研究综述[J]. 地理学报, 66(5): 673-684. |
|
WANG J L, HUANG X J, ZHONG T Y, et al., 2011. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 66(5): 673-684.
DOI |
|
| [54] | 吴文良, 乔玉辉, 徐芹, 等, 2001. 华北盐渍化改造区农田蚯蚓生态学研究——以河北省曲周县为例[J]. 生态学报, 21(7): 1109-1113. |
| WU W L, QIAO Y H, XU Q, et al., 2001. An ecological study on earthworm in farmland of salinity transforming area in north China plain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21(7): 1109-1113. | |
| [55] | 王庆洲, 徐立新, 杨梅玉, 等, 2013. 蚯蚓与有机质分解的激发效应关系研究进展[J]. 农机化研究, 35(12): 5-9. |
| WANG Q Z, XU L X, YANG M Y, et al., 2013. Research progress on the relationship between earthworm and priming effect of organic matter mineralization[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 35(12): 5-9. | |
| [56] | 伍玉鹏, 吕丽媛, 毕艳孟, 等, 2013. 接种蚯蚓对盐碱土养分、土壤生物及植被的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 18(4): 45-51. |
| WU Y P, LÜ L Y, BI Y M, et al., 2013. Effects of earthworm inoculation on saline-alkali soil nutrient, soil organisms and plant cultivation[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 18(4): 45-51. | |
| [57] | 袁向华, 周艳玲, 宋清姿, 等, 2017. 蚯蚓吞食过程中土壤理化性质与放线菌多样性的变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 37(4): 1199-1210. |
| YUAN X H, ZHOU Y L, SONG Q Z, et al., 2017. Variations of soil physical-chemical properties and the diversity of actinomycetes during the process of swallowing of earthworms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(4): 1199-1210. | |
| [58] | 杨真, 王宝山, 2015. 中国盐渍土资源现状及改良利用对策[J]. 山东农业科学, 47(4): 125-130. |
| YANG Z, WANG B S, 2015. Present status of saline soil resources and countermeasures for improvement and utilization in China[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 47(4): 125-130. | |
| [59] | 于英钗, 王冲, 孙梦实, 等, 2019. 蚯蚓-菌根互作对滨海盐碱土的改良作用[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 24(5): 123-129. |
| YU Y C, WANG C, SUN M S, et al., 2019. Meliorative effect of earthworm-mycorrhiza interaction on coastal saline soil[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 24(5): 123-129. | |
| [60] | 姚炎红, 王明霞, 左小虎, 等, 2016. 典型油田多环芳烃污染对土壤反硝化微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 环境科学, 37(12): 4750-4759. |
| YAO Y H, WANG X M, ZUO X H, et al., 2016. Effects of PAHs pollution on the community structure of denitrifiers in a typical oilfield[J]. Environmental Science, 37(12): 4750-4759. | |
| [61] |
闫双堆, 刘利军, 曹燕篆, 等, 2021. 3株多环芳烃高效降解菌株的分离鉴定及降解特性[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(12): 4439-4446.
DOI |
| YAN S D, LIU L J, CAO Y Z, et al., 2021. Isolation, identification, and degradation characteristics of three effective PAHs degradation strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(12): 4439-4446. | |
| [62] | 于瑶瑶, 韩伟, 王莹莹, 2015. 一株蒽降解细菌的分离及降解特性研究[J]. 微生物学通报, 42(12): 2321-2329. |
| YU Y Y, HAN W, WANG Y Y, 2015. Isolation and characterization of an anthracene degradation bacterial strain[J]. Microbiology China, 42(12): 2321-2329. | |
| [63] | 中国标准出版社, 2007. 环境监测方法标准汇编: 土壤环境与固体废物[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社:434-437. |
| Standards Press of China, 2007. Compilation of standards for environmental monitoring methods: Soil environment and solid waste[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China:434-437. | |
| [64] | 钟茂生, 姜林, 夏天翔, 等, 2012. 基于土壤中多环芳烃解吸特性的生物修复效果评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 32(3): 726-730. |
| ZHONG M S, JIANG L, XIA T X, et al., 2012. Evaluation of effectiveness of bioremediation based on PAHs desorption characteristics in soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32(3): 726-730. | |
| [65] | 张涛, 李素艳, 孙向阳, 等, 2017. 磷石膏、红糖等对蚯蚓改良滨海盐土的促进作用[J]. 土壤学报, 54(1): 255-264. |
| ZHANG T, LI S Y, SUN X Y, et al., 2017. Effect of amendments of phosphogypsum and brown sugar on earthworms ameliorating coastal saline soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54(1): 255-264. | |
| [66] | 张与真, 李香兰, 黄福珍, 1981. 蚯蚓对土壤腐殖质含量和组成的影响[J]. 土壤, 13(6): 225-227. |
| ZHANG Y Z, LI X L, HUANG F Z, 1981. Effects of earthworm on soil humus content and composition[J]. Soils, 13(6): 225-227. |
| [1] | 姜懿珊, 孙迎韬, 张干, 罗春玲. 中国不同气候类型森林土壤微生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1355-1364. |
| [2] | 梁川, 杨艳芳, 俞姗姗, 周利, 张经纬, 张秀娟. 围网与围塘养鱼下沉积物微生物量和群落结构特征差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1487-1495. |
| [3] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [4] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [5] | 李成涛, 吴婉晴, 陈晨, 张勇, 张凯. 可生物降解PBAT微塑料对土壤理化性质及上海青生理指标的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1964-1977. |
| [6] | 梁川, 杨艳芳, 俞姗姗, 周利, 张经纬, 张秀娟. 围网与围塘养鱼下沉积物微生物量和群落结构特征差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810. |
| [7] | 李璇, 钱秀雯, 黄娟, 王鸣宇, 肖君. 纳米氧化镍暴露下人工湿地运行性能及微生物群落的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1833-1841. |
| [8] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [9] | 吉冰静, 刘艺, 吴杨, 高淑涛, 曾祥英, 于志强. 长江口及邻近东海沉积物中多环芳烃和含氧多环芳烃的分布特征、来源及生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408. |
| [10] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| [11] | 张楷悦, 刘增辉, 王颜昊, 王敬宽, 崔德杰, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲自然保护区土壤PAHs的风险评估和空间特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2198-2205. |
| [12] | 王飞, 赵颖. 太原市污灌区农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [13] | 刘秉儒. 土壤微生物呼吸热适应性与微生物群落及多样性对全球气候变化响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 181-186. |
| [14] | 吴洁婷, 赵若帆, 包红旭, 张营, 赵磊, 许琪, 陈忠林, 徐丽丽, 张驰, 许海萍, 马放. 鼠李糖脂强化多环芳烃微生物修复的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 205-214. |
| [15] | 蔡杨, 李伟, 左雪燕, 崔丽娟, 雷茵茹, 赵欣胜, 翟夏杰, 李晶, 潘旭. 盐城滨海湿地土壤多环芳烃分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1249-1259. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
