生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1802-1810.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.009
梁川1( ), 杨艳芳2,*(
), 杨艳芳2,*( ), 俞姗姗1, 周利1, 张经纬1, 张秀娟2
), 俞姗姗1, 周利1, 张经纬1, 张秀娟2
收稿日期:2023-02-22
出版日期:2023-10-18
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
*杨艳芳。E-mail: yangyf1977@163.com作者简介:梁川(1996年生),男,硕士,主要研究方向为土壤微生物生态。E-mail: joyecl1015@163.com
基金资助:
LIANG Chuan1( ), YANG Yanfang2,*(
), YANG Yanfang2,*( ), YU Shanshan1, ZHOU Li1, ZHANG Jingwei1, ZHANG Xiujuan2
), YU Shanshan1, ZHOU Li1, ZHANG Jingwei1, ZHANG Xiujuan2
Received:2023-02-22
Online:2023-10-18
Published:2024-01-16
摘要:
沉积物微生物在水产养殖生态系统中起着至关重要的作用。围网和围塘养殖是长江中下游淡水湖泊两种主要渔业养殖模式,而当前对围网和围塘养殖模式下沉积物环境差异及其对微生物群落结构影响的了解甚少。采用磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)方法分析了菜子湖围网和围塘养殖区沉积物微生物量及其群落组成,应用相关性分析和冗余分析(RDA)方法探究养殖区沉积物微生物量和群落结构与沉积物环境因子间联系,并探讨沉积物微生物指标的生态指示意义。结果表明,养殖区沉积物微生物以细菌为主;围网养殖区季节性淹水沉积物微生物总生物量、细菌总生物量、厌氧菌、放线菌和真菌生物量显著高于围塘养殖区;而常年淹水沉积物微生物总生物量、细菌总生物量、各类细菌生物量和真菌生物量均显著性高于围塘养殖区。围网养殖区沉积物真菌生物量相对比例、F/B和Shannon指数显著高于围塘养殖区,其他各类群微生物生物量相对比例和G+/G−在两种养殖模式下差异均不显著。沉积物粉粒、砂粒、有机质、有效磷等理化性质及抗生素类污染状况可能是解释两种养殖模式下沉积物微生物量和群落结构差异的主要环境因子。PLFAs指示下的沉积物微生物量和微生物群落结构均较灵敏地响应了围网和围塘养殖区的沉积物环境差异;同时围网养殖区沉积物生态系统相对于围塘养殖区更稳定。
中图分类号:
梁川, 杨艳芳, 俞姗姗, 周利, 张经纬, 张秀娟. 围网与围塘养鱼下沉积物微生物量和群落结构特征差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810.
LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810.
| 生境 | w(粘粒)/% | w(粉粒)/% | w(砂砾)/% | pH | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性 淹水 | 围网 | 38.71±9.92a | 51.59±5.86ab 1) | 9.70±5.50a | 5.13±0.32c | 79.39±20.10a | 0.68±0.08b | 18.40±9.23a | 2.01±0.62a | 77.00±19.80b |
| 围塘 | 37.69±8.39a | 52.46±4.92a | 9.85±6.95a | 5.54±0.42bc | 62.55±31.00ab | 0.69±0.15b | 19.44±9.00a | 1.76±0.96ab | 108.11±40.23a | |
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 30.30±7.28a | 53.16±6.96a | 16.55±10.83a | 6.01±0.50ab | 64.64±26.34ab | 0.93±0.16a | 17.29±9.98a | 1.56±0.70ab | 63.78±7.38b |
| 围塘 | 35.18±13.52a | 45.75±5.33c | 19.08±14.92a | 6.26±0.39a | 40.85±10.91c | 1.13±0.28a | 22.16±7.04a | 1.03±0.45c | 77.00±18.52b | |
表1 研究区沉积物基本理化性质特征
Table1 Basic physical and chemical properties of sediments in the studied area
| 生境 | w(粘粒)/% | w(粉粒)/% | w(砂砾)/% | pH | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | w(有效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | w(碱解氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性 淹水 | 围网 | 38.71±9.92a | 51.59±5.86ab 1) | 9.70±5.50a | 5.13±0.32c | 79.39±20.10a | 0.68±0.08b | 18.40±9.23a | 2.01±0.62a | 77.00±19.80b |
| 围塘 | 37.69±8.39a | 52.46±4.92a | 9.85±6.95a | 5.54±0.42bc | 62.55±31.00ab | 0.69±0.15b | 19.44±9.00a | 1.76±0.96ab | 108.11±40.23a | |
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 30.30±7.28a | 53.16±6.96a | 16.55±10.83a | 6.01±0.50ab | 64.64±26.34ab | 0.93±0.16a | 17.29±9.98a | 1.56±0.70ab | 63.78±7.38b |
| 围塘 | 35.18±13.52a | 45.75±5.33c | 19.08±14.92a | 6.26±0.39a | 40.85±10.91c | 1.13±0.28a | 22.16±7.04a | 1.03±0.45c | 77.00±18.52b | |
| 生境 | 微生物PLFAs总量/ (nmol∙g−1) | 细菌PLFAs含量/(nmol∙g−1) | 真菌PLFAs含量/ (nmol∙g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+细菌 | G−细菌 | 放线菌 | 厌氧菌 | 总PLFAs | ||||
| 季节性 淹水 | 围网 | 44.56±12.44b | 10.81±3.19b | 12.49±3.48bc | 4.64±0.97a | 0.56±0.19a | 39.44±10.95b | 1.72±0.37b |
| 围塘 | 25.15±10.48c | 6.56±3.01b | 6.83±2.85c | 2.65±1.36b | 0.31±0.18b | 22.60±9.62c | 0.73±0.35c | |
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 93.85±21.86a | 22.14±5.38a | 28.27±10.58a | 4.51±1.10a | 0.72±0.19a | 73.45±20.09a | 4.81±1.22a |
| 围塘 | 45.02±7.51b | 10.79±2.49b | 14.45±3.24b | 2.32±0.37b | 0.28±0.07b | 38.53±6.29bc | 1.83±0.27b | |
表2 研究区不同养殖模式下沉积物微生物PLFAs含量
Table2 The amount of sediment microbial PLFAs under different fish farming models in the studied area
| 生境 | 微生物PLFAs总量/ (nmol∙g−1) | 细菌PLFAs含量/(nmol∙g−1) | 真菌PLFAs含量/ (nmol∙g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+细菌 | G−细菌 | 放线菌 | 厌氧菌 | 总PLFAs | ||||
| 季节性 淹水 | 围网 | 44.56±12.44b | 10.81±3.19b | 12.49±3.48bc | 4.64±0.97a | 0.56±0.19a | 39.44±10.95b | 1.72±0.37b |
| 围塘 | 25.15±10.48c | 6.56±3.01b | 6.83±2.85c | 2.65±1.36b | 0.31±0.18b | 22.60±9.62c | 0.73±0.35c | |
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 93.85±21.86a | 22.14±5.38a | 28.27±10.58a | 4.51±1.10a | 0.72±0.19a | 73.45±20.09a | 4.81±1.22a |
| 围塘 | 45.02±7.51b | 10.79±2.49b | 14.45±3.24b | 2.32±0.37b | 0.28±0.07b | 38.53±6.29bc | 1.83±0.27b | |
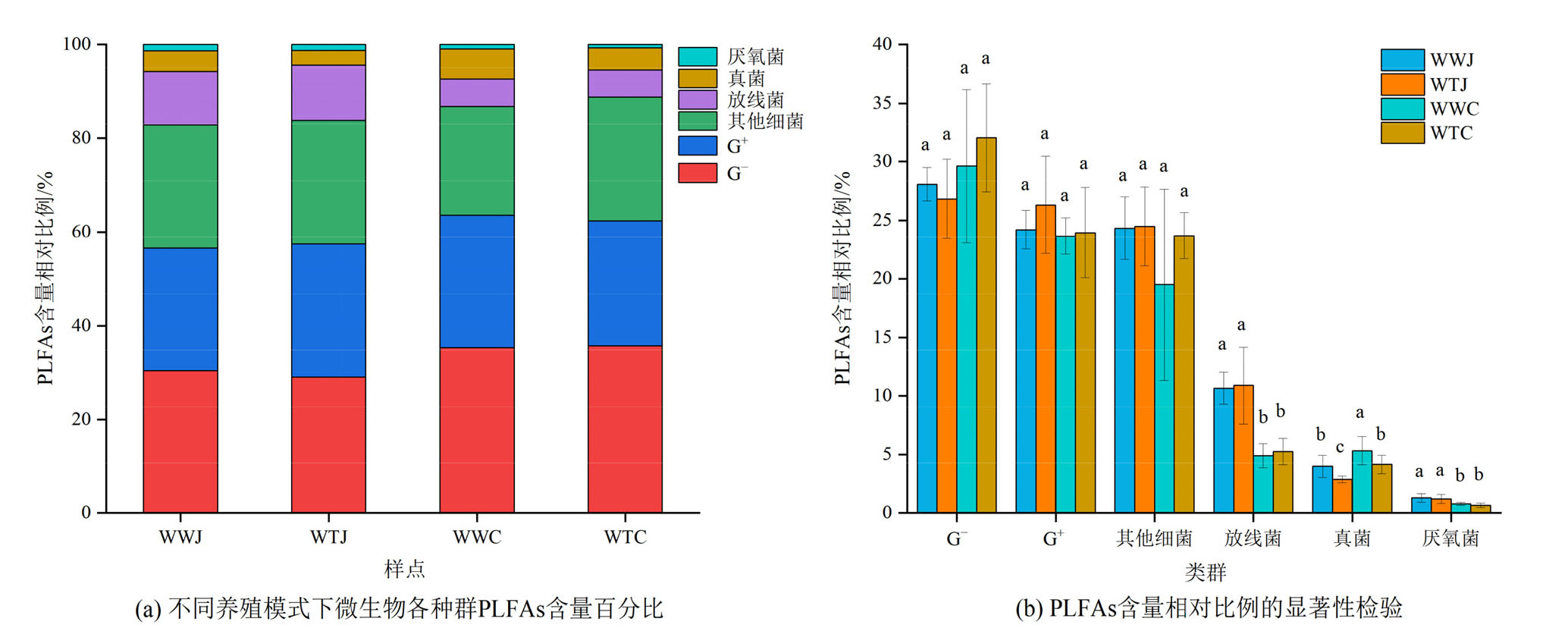
图1 不同养殖模式下微生物各种群PLFAs含量相对比例及其显著性检验 WWJ:围网养殖区季节性淹水沉积物;WTJ:围塘养殖区季节性淹水沉积物;WWC:围网养殖区常年淹水沉积物;WTC:围塘养殖区常年淹水沉积物(不同小写字母表示同一类群微生物PLFAs含量相对比例在不同生境下差异显著,P<0.05;n=9)
Figure 1 Relative proportions of different microbial population PLFAs in total microbial PLFAs under different fish farming models and their significance tests
| 生境 | 菌类比值 | Alpha 多样性指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F/B | G+/G− | Simpson指数 | Shannon指数 | |||
| 季节性淹水 | 围网 | 0.17±0.04b | 0.87±0.09a | 0.06±0.01c | 3.20±0.12a | |
| 围塘 | 0.12±0.03b | 1.01±0.27a | 0.07±0.02bc | 2.91±0.09b | ||
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 0.31±0.18a | 0.86±0.03a | 0.08±0.01ab | 3.08±0.13a | |
| 围塘 | 0.18±0.04b | 0.78±0.25a | 0.09±0.01a | 2.81±0.06b | ||
表3 研究区沉积物菌类比值和微生物多样性指数
Table 3 Ratio of different microbial population and microbial diversity index of sediments in the studied area
| 生境 | 菌类比值 | Alpha 多样性指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F/B | G+/G− | Simpson指数 | Shannon指数 | |||
| 季节性淹水 | 围网 | 0.17±0.04b | 0.87±0.09a | 0.06±0.01c | 3.20±0.12a | |
| 围塘 | 0.12±0.03b | 1.01±0.27a | 0.07±0.02bc | 2.91±0.09b | ||
| 常年 淹水 | 围网 | 0.31±0.18a | 0.86±0.03a | 0.08±0.01ab | 3.08±0.13a | |
| 围塘 | 0.18±0.04b | 0.78±0.25a | 0.09±0.01a | 2.81±0.06b | ||
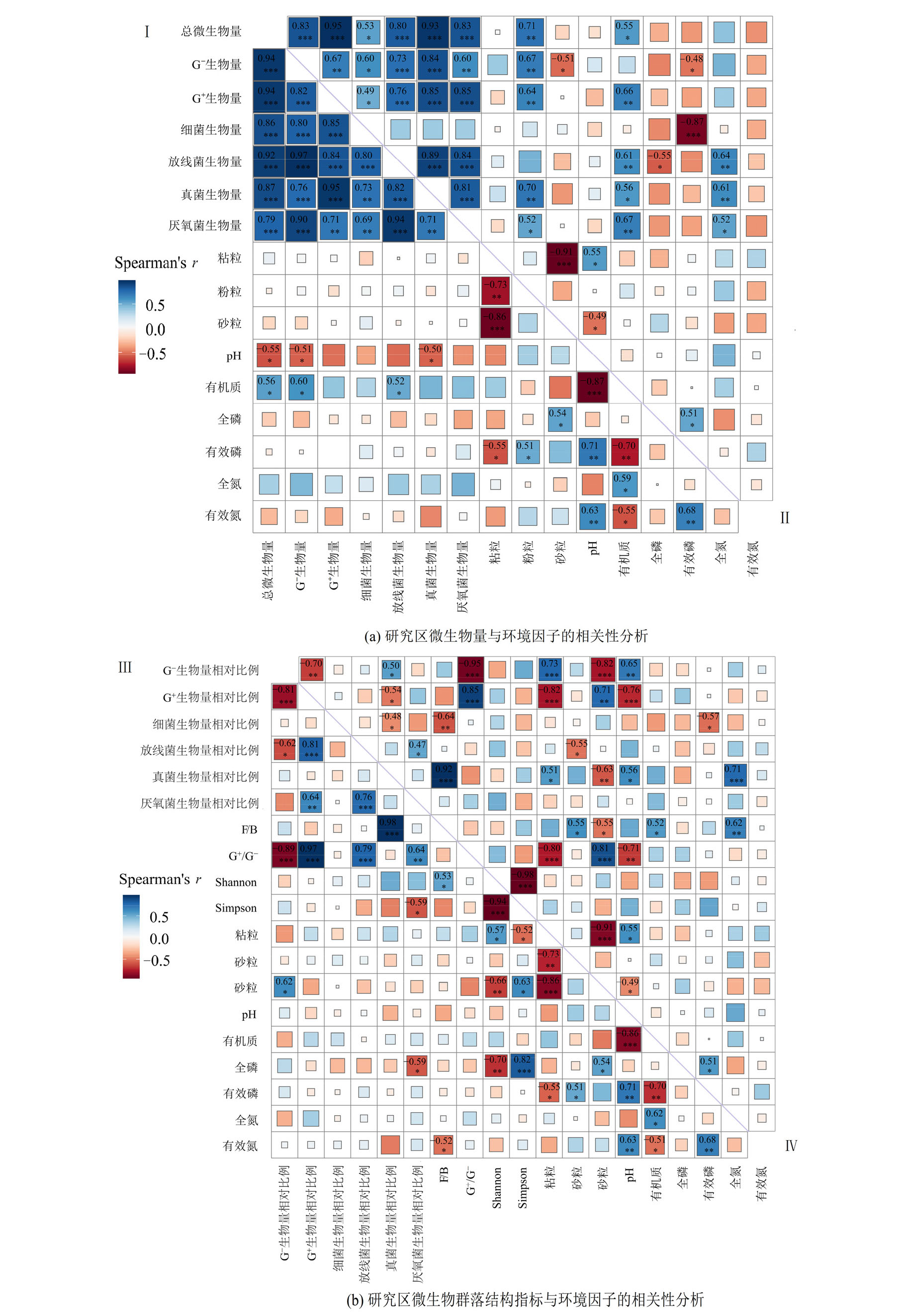
图2 研究区微生物量和群落结构指标与环境因子的相关性分析 沉积物微生物量(Ⅰ季节性淹水;Ⅱ常年淹水)和群落结构指标(Ⅲ季节性淹水;Ⅳ常年淹水)与环境因子的相关性分析(*P<0.5,**P<0.01,n=18)
Figure 2 Correlation analysis of bacterial biomass and community structure indexes with environmental factors in the studied area
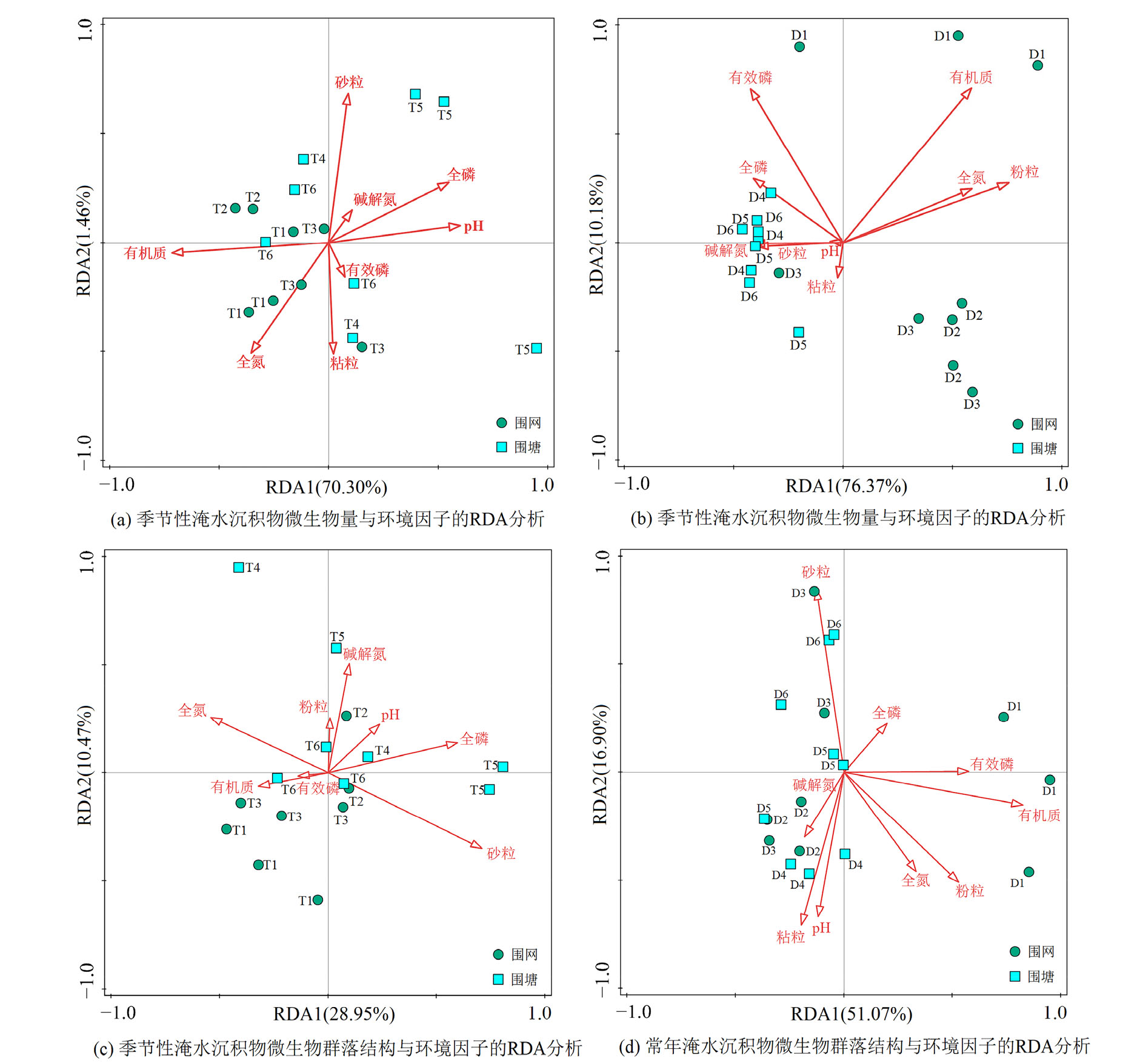
图3 研究区微生物生物量和群落结构指标与环境因子的RDA分析
Figure 3 RDA analysis of microbial biomass and community structure indexes and environmental factors in the studied area
| [1] |
BAHRAM M, HILDEBRAND F, FORSLUND S K, et al., 2018. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome[J]. Nature, 560(7717): 233-237.
DOI |
| [2] |
BOSSIO D A, SCOW K M, 1998. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns[J]. Microbial Ecology, 35(3): 265-278.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
CHELOSSI E, VEZZULLI L, MILANO A, et al., 2003. Antibiotic resistance of benthic bacteria in fish-farm and control sediments of the Western Mediterranean[J]. Aquaculture, 219(1-4): 83-97.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CURD E E, MARTINY J B H, LI H, et al., 2018. Bacterial diversity is positively correlated with soil heterogeneity[J]. Ecosphere, 9(1): 1-16. |
| [5] |
DE MENEZES A B, PRENDERGAST-MILLER M T, POONPATANA P, et al., 2015. C/N ratio drives soil actinobacterial cellobiohydrolase gene diversity[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(9): 3016-3028.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
DE VRIES F T, HOFFLAND E, VAN EEKEREN N, et al., 2006. Fungal/bacterial ratios in grasslands with contrasting nitrogen management[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(8): 2092-2103.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FROSTEGRD A, BTH E, 1996. The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 22(1-2): 59-65.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
INGWERSEN J, POLL C, STRECK T, et al., 2008. Micro-scale modelling of carbon turnover driven by microbial succession at a biogeochemical interface[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(4): 864-878.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
KUCUKSEZGIN F, PAZI I, GONUL L T, et al., 2021. The impact of fish farming on the water column and marine sediments in three coastal regions from eastern Aegean coast[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(23): 29564-29580.
DOI |
| [10] |
LIU Z G, IQBAL M, ZENG Z B, et al., 2020. Comparative analysis of microbial community structure in the ponds with different aquaculture model and fish by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 142: 104101.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MARTENSSON L, OLSSON P A, 2012. Reductions in microbial biomass along disturbance gradients in a semi-natural grassland[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 62: 8-13.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TAMMINEN M, KARKMAN A, CORANDER J, et al., 2011. Differences in bacterial community composition in Baltic Sea sediment in response to fish farming[J]. Aquaculture, 313(1-4): 15-23.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
VEZZULLI L, CHELOSSI E, RICCARDI G, et al., 2002. Bacterial community structure and activity in fish farm sediments of the Ligurian sea (Western Mediterranean)[J]. Aquaculture international, 10(2): 123-141.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU R S S, 1995. The environmental impact of marine fish culture: toward a sustainable future[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4-12): 159-166.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHOU A G, XIE S L, JUNAID M, et al., 2021. First insight into the environmental microbial communities associated with potentially pathogenic strains in pond cultured tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) at various growth stages based on 16S, 18S, and ITS2 rRNA gene amplicons sequencing[J]. Aquaculture, 532: 736007.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHOU J G, WANG Y, LEI Q L, 2020. Using bioinformatics to quantify the variability and diversity of the microbial community structure in pond ecosystems of a subtropical catchment[J]. Current Bioinformatics, 15(10): 1178-1186
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHOU J Z, XIA B C, TREVES D S, et al., 2002. Spatial and resource factors influencing high microbial diversity in soil[J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 68(1): 326-334.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 刘秉儒, 牛宋芳, 张文文, 2019. 荒漠草原区土壤粒径组成对柠条根际土壤微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(24): 9171-9178. |
| LIU B R, NIU S F, ZHANG W W, 2019. Effects of soil particle size on enzyme activities and the amount of soil microorganism in rhizosphere of Caragana korshinskii in desert steppe[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(24): 9171-9178 | |
| [19] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods for agrochemical analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [20] | 裘琼芬, 张德民, 叶仙森, 等, 2013. 象山港网箱养殖对近海沉积物细菌群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(2): 483-491. |
|
QIU Q F, ZHANG D M, YE X S, et al., 2013. The bacterial community of coastal sediments influenced by cage culture in Xiangshan Bay, Zhejiang, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(2): 483-491.
DOI URL |
|
| [21] | 王好才, 夏敏, 刘圣恩, 等, 2021. 若尔盖高原泥炭沼泽湿地土壤细菌群落空间分布及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 41(7): 2663-2675. |
| WANG H C, XIA M, LIU S E, et al., 2021. Spatial distribution and driving mechanism of soil bacterial communities in the wetland of Zoigeplateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(7): 2663-2675. | |
| [22] | 王群艳, 吴小红, 祝贞科, 等, 2016. 土壤质地对自养固碳微生物及其同化碳的影响[J]. 环境科学, 37(10): 3987-3995. |
| WANG Q Y, WU X H, ZHU Z K, et al., 2016. Effects of soil texture on autotrophic CO2 fixation bacterial communities and their CO2 assimilation contents[J]. Environmental Science, 37(10): 3987-3995. | |
| [23] | 吴庆龙, 陈开宁, 高光, 等, 1995. 大水面网围精养对水环境的影响及其对策[J]. 水产学报, 19(4): 343-349. |
| WU Q L, CHEN K N, GAO G, et al., 1995. Effects of pen fish culture on water environment and their countermeasure[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 19(4): 343-349. | |
| [24] | 杨长明, 吴亚琼, 王育来, 等, 2018. 南淝河表层沉积物细菌群落结构特征及驱动因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(9): 3552-3561. |
| YANG C M, WU Y Q, WANG Y L, et al., 2018. Microbial community structure characteristics and its key driving factors in surface sediments along Nanfei River[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(9): 3552-3561. | |
| [25] | 于小彦, 张平究, 张经纬, 等, 2020. 城市河流沉积物微生物量分布和群落结构特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(2): 585-596. |
| YU X Y, ZHANG P J, ZHANG J W, et al., 2020. Characteristics of distribution patterns of microbial biomass and community structures in the sediments from urban river[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(2): 585-596. | |
| [26] | 张广帅, 闫吉顺, 赵全民, 等, 2020. 辽东湾小凌河口湿地土壤微生物群落结构与微生态环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(7): 2283-2291. |
| ZHANG G S, YAN J S, ZHAO Q M, et al., 2020. Relationship between soil microbial community structure and micro-ecological environmental factors in Xiaolinghe estuarine wetland of Liaodong Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(7): 2283-2291. | |
| [27] | 张广帅, 于秀波, 张全军, 等, 2018. 鄱阳湖湿地土壤微生物群落结构沿地下水位梯度分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(11): 3825-3837. |
| ZHANG G S, YU X B, ZHANG Q J, et al., 2018. Variation in the distribution of soil microbial community structure along ground water level gradients in the Poyang Lake Wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 3825-3837. | |
| [28] | 周雅心, 林少颖, 郑毅, 等, 2021. 围垦养殖对中国典型滨海湿地土壤真菌多样性及群落结构影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(7): 2826-2837. |
| ZHOU Y X, LIN S Y, ZHENG Y, et al., 2021. Effects of reclamation aquaculture on soil fungi diversity and community structure of typical coastal wetlands in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(7): 2826-2837. | |
| [29] |
朱义族, 李雅颖, 韩继刚, 等, 2019. 水分条件变化对土壤微生物的影响及其响应机制研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(12): 4323-4332.
DOI |
| ZHU Y Z, LI Y Y, HAN J G, et al., 2019. Effects of changes in water status on soil microbes and their response mechanism: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(12): 4323-4332. | |
| [30] | 卓丽, 王美欢, 石运刚, 等, 2019. 南方典型水源地及水产养殖区抗生素的复合污染特征及生态风险[J]. 生态毒理学报, 14(2): 164-175. |
| ZHUO L, WANG M H, SHI Y G, et al., 2019. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk of antibiotics in surface water of typical drinking water sources and aquaculture in South China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 14(2): 164-175. |
| [1] | 刘晗, 王萍, 孙鲁沅, 秦文婧, 陈晓芬, 陈金, 周国朋, 梁婷, 刘佳, 李燕丽. 种植冬绿肥对红壤幼龄橘园土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1623-1631. |
| [2] | 姜懿珊, 孙迎韬, 张干, 罗春玲. 中国不同气候类型森林土壤微生物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1355-1364. |
| [3] | 梁川, 杨艳芳, 俞姗姗, 周利, 张经纬, 张秀娟. 围网与围塘养鱼下沉积物微生物量和群落结构特征差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1487-1495. |
| [4] | 童永杰, 汪毅, 华玉妹, 赵建伟, 刘广龙, 蒋永参. 有机电子供体影响下硝酸盐和铁对磷转化的驱动作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1263-1274. |
| [5] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [6] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [7] | 张广毅, 张嘉涛, 王晓伟. 湖泊底泥微生物燃料电池中磷形态分布及释放研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 590-598. |
| [8] | 杨奇丽, 窦韦丽, 刘之文, 郭景, 吕刚. 正构烷烃示源的阜新细河河道石油烃类污染特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 599-608. |
| [9] | 何文宣, 李垒, 孙思宇, 李昌, 李久义, 田秀君. 北运河水体、沉积物和鱼类中微塑料的分布特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1901-1912. |
| [10] | 吴炜龙, 陈艺杰, 卫婷, 杨贵琼, 阳长洪, 甄珍, 蔺中. 蚯蚓驱动的滨海盐碱农田土壤中多环芳烃生物降解的机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 1996-2006. |
| [11] | 李璇, 钱秀雯, 黄娟, 王鸣宇, 肖君. 纳米氧化镍暴露下人工湿地运行性能及微生物群落的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1833-1841. |
| [12] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [13] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [14] | 花莉, 成涛之, 梁智勇. 固定化混合菌对陕北黄土地区石油污染土壤的修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1610-1615. |
| [15] | 崔乔, 李宗省, 张百娟, 赵越, 南富森. 冻融作用对土壤可溶性碳氮和微生物量碳氮含量影响的荟萃分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1700-1712. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
