生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1249-1259.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.016
蔡杨1,2( ), 李伟1,2,*, 左雪燕1,2, 崔丽娟1,2, 雷茵茹1,2, 赵欣胜1,2, 翟夏杰1,2, 李晶1,2, 潘旭1,2
), 李伟1,2,*, 左雪燕1,2, 崔丽娟1,2, 雷茵茹1,2, 赵欣胜1,2, 翟夏杰1,2, 李晶1,2, 潘旭1,2
收稿日期:2020-11-24
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
*作者简介:蔡杨(1994年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事湿地生态恢复研究。E-mail: caiy9160@163.com
基金资助:
CAI Yang1,2( ), LI Wei1,2,*, ZUO Xueyan1,2, CUI Lijuan1,2, LEI Yinru1,2, ZHAO Xinsheng1,2, ZHAI Xiajie1,2, LI Jing1,2, PAN Xu1,2
), LI Wei1,2,*, ZUO Xueyan1,2, CUI Lijuan1,2, LEI Yinru1,2, ZHAO Xinsheng1,2, ZHAI Xiajie1,2, LI Jing1,2, PAN Xu1,2
Received:2020-11-24
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
多环芳烃(PAHs)是一类具有致癌、致畸和致突变作用的环境污染物,研究盐城滨海湿地土壤中PAHs的分布特征、来源以及环境因子对其分布的影响,可揭示盐城滨海湿地的污染现状,并为PAHs污染区域修复提供理论依据,进而为我国滨海湿地的生态修复与保护提供科学参考。2019年8月,分别采集研究区域内4种优势植被(互花米草Spartina alterniflora、海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter、白茅Imperata cylindrica和盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa)覆盖下的表层土壤(0—20 cm)样本21个,并测定PAHs的质量分数。结果显示,(1)盐城滨海湿地土壤中16种多环芳烃(∑16PAHs)的检出率为100%,质量分数范围为227—884 ng∙g-1,均值为479 ng∙g-1,其中7种致癌多环芳烃(∑7PAHs)质量分数范围为79.8—553 ng∙g-1,均值为286 ng∙g-1。研究区内21个点位中,有4个点位处于中度污染水平,其余点位均为轻度污染。不同植被覆盖下土壤中4种PAHs单体质量分数及总质量分数存在显著差异。(2)采用特征比值法和主成分分析法对研究区内土壤PAHs来源进行解析发现,PAHs主要来源于燃烧过程。(3)针对环境因素和PAHs的相关性分析得出,萘(Nap)、芴(Flu)和?(Chr)与土壤含水率(SWC)呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05);Chr和二苯并[a, h]蒽(DahA)与土壤有机质(SOM)呈极显著正相关关系(P<0.01);苊烯(Acy)与土壤粘粒呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05)。通过偏相关性分析发现,剔除土壤粒径这一因素后,SOM和SWC与PAHs的相关性显著减弱。剔除植被密度(VD)或土壤pH的影响后,减轻了SOM与PAHs关系的显著程度,而增加了SWC与PAHs的相关性。
中图分类号:
蔡杨, 李伟, 左雪燕, 崔丽娟, 雷茵茹, 赵欣胜, 翟夏杰, 李晶, 潘旭. 盐城滨海湿地土壤多环芳烃分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1249-1259.
CAI Yang, LI Wei, ZUO Xueyan, CUI Lijuan, LEI Yinru, ZHAO Xinsheng, ZHAI Xiajie, LI Jing, PAN Xu. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PAHs in Yancheng Coastal Wetland Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1249-1259.
| 单体种类 Type | 缩写 Abbreviation | 环数 Ring | 分子式 Molecular formula | 结构式 Structural formula | 分子质量 Molecular weight | 致癌性 Carcinogenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萘 | Nap | 2 | C10H8 | 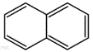 | 128 | |
| 苊烯 | Acy | 3 | C12H8 | 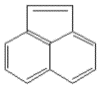 | 152 | |
| 苊 | Ace | 3 | C12H10 | 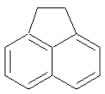 | 154 | |
| 芴 | Flu | 3 | C13H10 | 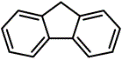 | 166 | |
| 蒽 | Ant | 3 | C14H10 | 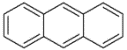 | 178 | |
| 菲 | Phe | 3 | C14H10 | 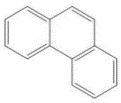 | 178 | |
| 荧蒽 | Flt | 4 | C16H10 | 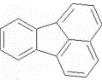 | 202 | |
| 芘 | Pyr | 4 | C16H10 | 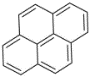 | 202 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 | BaA | 4 | C18H12 | 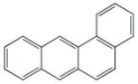 | 228 | √ |
| 䓛 | Chr | 4 | C18H12 | 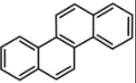 | 228 | √ |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽 | BbF | 5 | C20H12 | 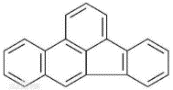 | 252 | √ |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽 | BkF | 5 | C20H12 | 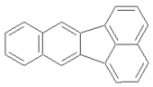 | 252 | √ |
| 苯并[a]芘 | BaP | 5 | C20H12 | 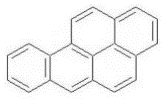 | 252 | √ |
| 二苯并[a, h]蒽 | DahA | 5 | C22H14 | 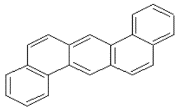 | 278 | √ |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 | IcdP | 6 | C22H12 | 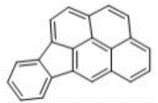 | 276 | √ |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 | BghiP | 6 | C22H12 | 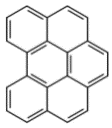 | 276 |
表1 EPA所列16种优先控制PAHs
Table 1 Table 1 16 priority PAHs listed in EPA
| 单体种类 Type | 缩写 Abbreviation | 环数 Ring | 分子式 Molecular formula | 结构式 Structural formula | 分子质量 Molecular weight | 致癌性 Carcinogenicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 萘 | Nap | 2 | C10H8 |  | 128 | |
| 苊烯 | Acy | 3 | C12H8 |  | 152 | |
| 苊 | Ace | 3 | C12H10 |  | 154 | |
| 芴 | Flu | 3 | C13H10 |  | 166 | |
| 蒽 | Ant | 3 | C14H10 |  | 178 | |
| 菲 | Phe | 3 | C14H10 |  | 178 | |
| 荧蒽 | Flt | 4 | C16H10 |  | 202 | |
| 芘 | Pyr | 4 | C16H10 |  | 202 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 | BaA | 4 | C18H12 |  | 228 | √ |
| 䓛 | Chr | 4 | C18H12 |  | 228 | √ |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽 | BbF | 5 | C20H12 |  | 252 | √ |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽 | BkF | 5 | C20H12 |  | 252 | √ |
| 苯并[a]芘 | BaP | 5 | C20H12 |  | 252 | √ |
| 二苯并[a, h]蒽 | DahA | 5 | C22H14 |  | 278 | √ |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 | IcdP | 6 | C22H12 |  | 276 | √ |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 | BghiP | 6 | C22H12 |  | 276 |
| 采样点 Sample sites | 植被 Vegetation | 植被覆盖度 Coverage/% | 土壤类型 Soil type |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 23 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S2 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 84 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S3 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 43 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S4 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 27 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S5 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 33 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S6 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 76 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S7 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 39 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S8 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 66 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S9 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 36 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S10 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 43 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S11 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 30 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S12 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 37 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S13 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 58 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S14 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 54 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S15 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 21 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S16 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 89 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S17 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 62 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S18 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 83 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S19 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 68 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S20 | 盐地碱蓬(Suaeda salsa | 25 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S21 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 78 | 粘土Clay loam |
表2 样点植被土壤基本概况
Table 2 Basic situation of vegetation and soil in sample sites
| 采样点 Sample sites | 植被 Vegetation | 植被覆盖度 Coverage/% | 土壤类型 Soil type |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 23 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S2 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 84 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S3 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 43 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S4 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 27 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S5 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 33 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S6 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 76 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S7 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 39 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S8 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 66 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S9 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 36 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S10 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 43 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S11 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 30 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S12 | 海三稜藨草Scirpus×mariqueter | 37 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S13 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 58 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S14 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 54 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S15 | 盐地碱蓬Suaeda salsa | 21 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S16 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 89 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S17 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 62 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S18 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 83 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S19 | 白茅Imperata cylindrica | 68 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S20 | 盐地碱蓬(Suaeda salsa | 25 | 砂土Sandy soil |
| S21 | 互花米草Spartina alterniflora | 78 | 粘土Clay loam |
| 单体种类 Type | 海三稜藨草 Scirpus× mariqueter | 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 盐地碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 4.98±1.13B 2) | 9.89±4.72A | 8.58±1.43A | 6.34±2.41AB |
| Acy | 7.75±2.16A | 10.2±9.08A | 11.6±4.64A | 6.54±1.35A |
| Ace | 9.15±6.75A | 16.4±9.93A | 8.20±3.47A | 7.61±3.67A |
| Flu | 9.49±3.00A | 17.3±6.45A | 11.2±2.36A | 11.0±5.67A |
| Ant | 13.9±3.33A | 19.5±5.90A | 17.5±6.07A | 14.4±5.02A |
| Phe | 16.0±12.4A | 26.3±6.27A | 26.6±17.8A | 32.3±15.6A |
| Flt | 12.6±6.51B | 42.1±32.6A | 17.5±8.97B | 15.6±3.65B |
| Pyr | 32.0±17.9A | 77.7±84.3A | 127±119A | 23.6±7.08A |
| BaA | 6.08±0.796A | 19.4±13.9A | 50.1±54.3A | 10.3±5.81A |
| Chr | 6.65±1.75A | 12.4±3.81A | 9.26±5.67A | 8.56±5.00A |
| BbF | 9.73±5.05A | 9.14±6.34A | 9.16±4.54A | 5.18±0.953A |
| BkF | 30.1±11.7B | 171±90.3A | 122±102AB | 181±92.6A |
| BaP | 17.0±11.0A | 19.5±9.34A | 12.6±3.47A | 22.2±6.86A |
| DahA | 26.3±18.6B | 103±78.7A | 26.4±10.6B | 77.2±45.5AB |
| IcdP | 37.1±25.9A | 72.0±25.9A | 58.9±40.7A | 46.4±40.9A |
| BghiP | 28.6±7.86A | 29.8±7.88A | 27.2±5.01A | 24.9±8.33A |
| ∑16PAHs | 267±21.3C | 655±178A | 544±57.3AB | 493±81.1B |
表3 不同植被覆盖下土壤中PAHs质量分数1)
Table 3 PAHs concentration in soil under different vegetation cover
| 单体种类 Type | 海三稜藨草 Scirpus× mariqueter | 互花米草 Spartina alterniflora | 盐地碱蓬 Suaeda salsa | 白茅 Imperata cylindrica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 4.98±1.13B 2) | 9.89±4.72A | 8.58±1.43A | 6.34±2.41AB |
| Acy | 7.75±2.16A | 10.2±9.08A | 11.6±4.64A | 6.54±1.35A |
| Ace | 9.15±6.75A | 16.4±9.93A | 8.20±3.47A | 7.61±3.67A |
| Flu | 9.49±3.00A | 17.3±6.45A | 11.2±2.36A | 11.0±5.67A |
| Ant | 13.9±3.33A | 19.5±5.90A | 17.5±6.07A | 14.4±5.02A |
| Phe | 16.0±12.4A | 26.3±6.27A | 26.6±17.8A | 32.3±15.6A |
| Flt | 12.6±6.51B | 42.1±32.6A | 17.5±8.97B | 15.6±3.65B |
| Pyr | 32.0±17.9A | 77.7±84.3A | 127±119A | 23.6±7.08A |
| BaA | 6.08±0.796A | 19.4±13.9A | 50.1±54.3A | 10.3±5.81A |
| Chr | 6.65±1.75A | 12.4±3.81A | 9.26±5.67A | 8.56±5.00A |
| BbF | 9.73±5.05A | 9.14±6.34A | 9.16±4.54A | 5.18±0.953A |
| BkF | 30.1±11.7B | 171±90.3A | 122±102AB | 181±92.6A |
| BaP | 17.0±11.0A | 19.5±9.34A | 12.6±3.47A | 22.2±6.86A |
| DahA | 26.3±18.6B | 103±78.7A | 26.4±10.6B | 77.2±45.5AB |
| IcdP | 37.1±25.9A | 72.0±25.9A | 58.9±40.7A | 46.4±40.9A |
| BghiP | 28.6±7.86A | 29.8±7.88A | 27.2±5.01A | 24.9±8.33A |
| ∑16PAHs | 267±21.3C | 655±178A | 544±57.3AB | 493±81.1B |
| 特征比值 Characteristic ratio | 热解源 Combustion | 石油源 Petroleum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 石油燃烧 Petroleum combustion | 生物质、煤燃烧 Biomass & coal combustion | ||
| Ant/(Ant+Phe) | >0.1 | <0.1 | |
| Flt/(Flt+Pyr) | >0.4 | <0.4 | |
| BaA/(BaA+Chr) | 0.2‒0.35 | >0.35 | <0.2 |
| IcdP/(IcdP+BghiP) | 0.2‒0.5 | >0.5 | <0.2 |
表4 PAHs同分异构体特征比值大小及对应来源
Table 4 Isomer ratios and corresponding sources of PAHs
| 特征比值 Characteristic ratio | 热解源 Combustion | 石油源 Petroleum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 石油燃烧 Petroleum combustion | 生物质、煤燃烧 Biomass & coal combustion | ||
| Ant/(Ant+Phe) | >0.1 | <0.1 | |
| Flt/(Flt+Pyr) | >0.4 | <0.4 | |
| BaA/(BaA+Chr) | 0.2‒0.35 | >0.35 | <0.2 |
| IcdP/(IcdP+BghiP) | 0.2‒0.5 | >0.5 | <0.2 |
| 单体种类 Type | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.381 | -0.0624 | 0.205 |
| Acy | 0.327 | -0.0522 | -0.245 |
| Ace | 0.310 | -0.0382 | 0.202 |
| Flu | 0.373 | 0.119 | 0.173 |
| Ant | 0.284 | 0.239 | 0.0480 |
| Phe | 0.0640 | 0.312 | -0.289 |
| Flt | 0.373 | -0.0183 | -0.0182 |
| Pyr | 0.202 | -0.423 | 0.198 |
| BaA | 0.100 | -0.397 | 0.252 |
| Chr | 0.268 | 0.301 | -0.0799 |
| BbF | 0.216 | -0.231 | -0.352 |
| BkF | 0.0425 | 0.361 | 0.250 |
| BaP | -0.0224 | 0.307 | 0.246 |
| DahA | 0.153 | 0.191 | 0.352 |
| IcdP | 0.235 | 0.139 | -0.498 |
| BghiP | 0.196 | -0.251 | -0.115 |
| 方差贡献率 Percentage of variance/% | 33.3 | 19.6 | 9.93 |
表5 主成分分析矩阵
Table 5 Principal component analysis matrix
| 单体种类 Type | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | 0.381 | -0.0624 | 0.205 |
| Acy | 0.327 | -0.0522 | -0.245 |
| Ace | 0.310 | -0.0382 | 0.202 |
| Flu | 0.373 | 0.119 | 0.173 |
| Ant | 0.284 | 0.239 | 0.0480 |
| Phe | 0.0640 | 0.312 | -0.289 |
| Flt | 0.373 | -0.0183 | -0.0182 |
| Pyr | 0.202 | -0.423 | 0.198 |
| BaA | 0.100 | -0.397 | 0.252 |
| Chr | 0.268 | 0.301 | -0.0799 |
| BbF | 0.216 | -0.231 | -0.352 |
| BkF | 0.0425 | 0.361 | 0.250 |
| BaP | -0.0224 | 0.307 | 0.246 |
| DahA | 0.153 | 0.191 | 0.352 |
| IcdP | 0.235 | 0.139 | -0.498 |
| BghiP | 0.196 | -0.251 | -0.115 |
| 方差贡献率 Percentage of variance/% | 33.3 | 19.6 | 9.93 |
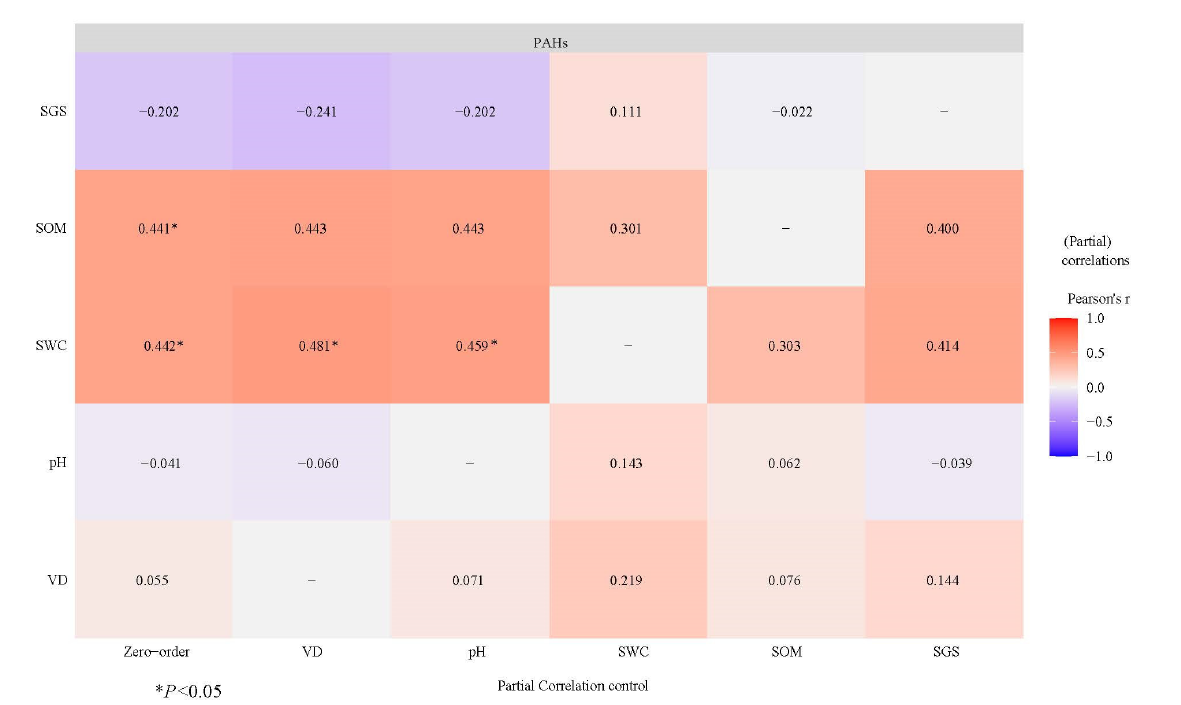
图7 ∑16PAHs与5个变量的偏相关关系 SGS代表土壤粒径,通过sand、clay、silt进行主成分分析提取PC1表示(PC1的解释率为97.68%)
Fig. 7 Partial correlations (Pearson's r) between ∑16PAHs and the five variables SGS stands for soil particle size, and PC1 is extracted by principal component analysis of sand, clay, and silt (the explanation rate of PC1 is 97.68%)
| 研究区Study area | PAHs种数PAHs number | 质量分数Concentration | 参考文献Renference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盐城滨海湿地Yancheng coastal wetlands | 16 | 227‒884 ng∙g-1 | 本文This study |
| 辽河口Liaohe estuary | 16 | 235‒374 ng∙g-1 | Li et al., |
| 崇明岛Chongming Island | 16 | 47.97‒1.67×103 ng∙g-1 | 锁玉栋, |
| 汕头红树林Mangrove wetlands in Shantou, South China | 16 | 79.1‒853 ng∙g-1 | Cai et al., |
| 爱丁堡湾(爱琴海)Edremit Bay (Aegean Sea) | 18 | 0.650‒175 ng∙g-1 | Darilmaz et al., |
| 印度申达本红树林湿地Sundarban Mangrove Wetland, India | 19 | 9.40‒4.22×103 ng∙g-1 | Santosh et al., |
表6 国内外不同研究区域PAHs质量分数比较
Table 6 Comparison of PAHs in different research areas at home and abroad
| 研究区Study area | PAHs种数PAHs number | 质量分数Concentration | 参考文献Renference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盐城滨海湿地Yancheng coastal wetlands | 16 | 227‒884 ng∙g-1 | 本文This study |
| 辽河口Liaohe estuary | 16 | 235‒374 ng∙g-1 | Li et al., |
| 崇明岛Chongming Island | 16 | 47.97‒1.67×103 ng∙g-1 | 锁玉栋, |
| 汕头红树林Mangrove wetlands in Shantou, South China | 16 | 79.1‒853 ng∙g-1 | Cai et al., |
| 爱丁堡湾(爱琴海)Edremit Bay (Aegean Sea) | 18 | 0.650‒175 ng∙g-1 | Darilmaz et al., |
| 印度申达本红树林湿地Sundarban Mangrove Wetland, India | 19 | 9.40‒4.22×103 ng∙g-1 | Santosh et al., |
| [1] |
ABBASI S, KESHAVARZI B, MOORE F, et al., 2019. Geochemistry and environmental effects of potentially toxic elements, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and microplastics in coastal sediments of the Persian Gulf[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(15): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AICHNER B, BUSSIAN B, LEHNIK-HABRINK P, et al., 2013. Levels and spatial distribution of persistent organic pollutants in the environment: a case study of german forest soils[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(22): 12703-12714.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BUCHELI T D, BLUM F, DESAULES A, et al., 2004. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, black carbon, and molecular markers in soils of Switzerland[J]. Chemosphere, 56(11): 1061-1076.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CAI Y M, WU J D, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2019. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of mangrove wetlands in Shantou, South China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 205: 106332.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CULOTTA L, STEFANO C D, GIANGUZZA A, et al., 2006. The PAH composition of surface sediments from Stagnone coastal lagoon, Marsala (Italy)[J]. Marine Chemistry, 99(1-4): 117-127.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DARILMAZ E, ALYURUK H, KONTAS A, et al., 2019. Distributions and Sources of PAHs and OCPs in Surficial Sediments of Edremit Bay (Aegean Sea)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(2): 237-248.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DAVIS E M, WALKER T R, ADAMS M, et al., 2019. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in small craft harbor (SCH) surficial sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 691: 528-537.
DOI URL |
| [8] | DUVAL M M, FRIEDLANDER S K, 1981. Source resolution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the los angeles atmosphere: Application of a CMB with first-order decay[J]. USEPA Report EPA-600/2-81-161 Washington, DC US Government Printing Office. |
| [9] | EDWARDS N T, 1983. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Terrestrial Environment: a review[J]. Journal of Environment Quality, 12(4): 427-441. |
| [10] | FERNÁNDEZ-LUQUEÑO F, VALENZUELA-ENCINAS C, MARSCH R, et al., 2011. Microbial communities to mitigate contamination of PAHs in soil-possibilities and challenges: a review[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 18(1): 12-30. |
| [11] |
GAN S, LAU E V, NG H K, 2009. Remediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2-3): 532-549.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
HELLOU J, STELLER S, ZITKO V, et al., 2002. Distribution of PACs in surficial sediments and bioavailability to mussels, Mytilus edulis of Halifax harbour[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 53(4): 357-379.
DOI URL |
| [13] | IARC, 2010. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol. 92. Some Non-Heterocyclic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Some Related Exposures[M]. Lyon: IARC. |
| [14] |
JAFARABADI A R, BAKHTIARI A R, YAGHOOBI Z, et al., 2019. Distributions and compositional patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their derivatives in three edible fishes from Kharg coral Island, Persian Gulf, Iran[J]. Chemosphere, 215(1): 835-845.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JENKINS B M, JONES A D, TURN S Q, et al., 1996. Emission factors for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from biomass burning[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(8): 2462-2469.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JEON H D, OH S Y, 2019. Distribution, toxicity, and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils in Ulsan, South Korea[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(7): 409-421.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KANNAN K, JOHNSON B, YOHN S S, et al., 2005. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments from Michigan Inland Lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(13): 4700-4706.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KHALILI N, SCHEFF P A, HOLSEN T M, 1995. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 29(4): 533-542.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LARSEN R K, BAKER J E, 2003. Source Apportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Urban Atmosphere: A Comparison of Three Methods[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(9): 1873-1881.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LI G L, LANG Y H, YANG W, et al., 2014. Source contributions of PAHs and toxicity in reed wetland soils of Liaohe estuary using a CMB-TEQ method[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 490: 199-204.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LIU N, ZHANG D L, CEN K, et al., 2018. Influence of Anthropogenic Activities on the Temporal and Spatial Variation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the sediments of Jiangsu Coastal Zone, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 170(6): 11-20.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MA B, HE Y, CHEN H H, et al., 2010. Dissipation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the rhizosphere: synthesis through meta-analysis[J]. Environmental Pollution, 158(3): 855-861.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
MALISZEWSKA-KORDYBACH B, 1996. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils in Poland: Preliminary proposals for criteria to evaluate the level of soil contamination[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 11(1-2): 121-127.
DOI URL |
| [24] | MALISZEWSKA-KORDYBACH B, 1998. The relationship between the properties of soils and the content of PAHs on the example of agricultural soils from Lublin district[J]. Archives of Environmental Protection, 24: 79-91. |
| [25] |
NAM J J, THOMAS G O, JAWARD F, et al., 2008. PAHs in background soils from Western Europe: Influence of atmospheric deposition and soil organic matter[J]. Chemosphere, 70(9): 1596-1602.
DOI URL |
| [26] | PAZI I, GONUL L T, KUCUKSEZGIN F, 2019. Sources and Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic and Aliphatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments Collected near Aquaculture Sites from Eastern Aegean Coast[J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2019.1645708. |
| [27] |
QU C K, ALBANESE S, LIMA A, et al., 2019. The occurrence of OCPs, PCBs, and PAHs in the soil, air, and bulk deposition of the Naples metropolitan area, southern Italy: implications for sources and environmental processes[J]. Environment International, 124: 89-97.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SAMANTA S K, SINGH O V, JAIN R K, 2002. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: environmental pollution and bioremediation[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 20(6): 243-248.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SANTOSH K S, ANDREA B, MOUSUMI C, et al., 2012. Distribution and Ecosystem Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Core Sediments of Sundarban Mangrove Wetland, India[J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 32(1): 1-26.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SIMCIK M F, EISENREICH S J, LIOY P J, 1999. Source apportionment and source/sink relationships of PAHs in the coastal atmosphere of Chicago and Lake Michigan[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 33(30): 5071-5079.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SIMPSON C D, MOSI A A, CULLEN W R, et al., 1996. Composition and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination in surficial marine sediments from Kitimat Harbor, Canada[J]. The science of the Total Environment, 181(3): 265-78.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SUN H W, LI J G, 2005. Availability of pyrene in unaged and aged soils to earthworm uptake, butanol extraction and SFE[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 166(1): 353-365.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
TRAPIDO M, 1999. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Estonian soil: contamination and profiles[J]. Environmental Pollution, 105(1): 67-74.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG X T, MIAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al., 2013. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils of the megacity Shanghai: occurrence, source apportionment and potential human health risk[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 447: 80-89.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YANG W, LANG Y H, BAI J, et al., 2015. Quantitative evaluation of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic potential for PAHs in coastal wetland soils of China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 74: 117-124.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YANG Z Y, SHAH K, CREVIER C, et al., 2018. Occurrence, source and ecological assessment of petroleum related hydrocarbons in intertidal marine sediments of the Bay of Fundy, New Brunswick, Canada[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133(8): 799-807.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YAO Y, MENG X Z, WU C C, et al., 2016. Tracking human footprints in Antarctica through passive sampling of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in inland lakes[J]. Environmental Pollution, 213: 412-419.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
YUNKER M B, MACDONALD R W, VINGAZAN R, et al., 2002. PAHs in the Fraiser river basin: a critical appraisal of PAHs ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 33(4): 489-515.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHANG H B, LUO Y M, WONG M H, et al., 2006. Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils[J]. Environmental Pollution 141(1): 107-114.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHAO X G, JIN H Y, JI Z Q, et al., 2019. PAES and PAHs in the surface sediments of the East China Sea: Occurrence, distribution and influence factors[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 703: 134763.
DOI URL |
| [41] | 陈丽琼, 2010. 比重计法测定土壤颗粒组成的研究[J]. 环境科学导刊, 29(4): 99-101. |
| CHEN L Q, 2010. Research on Structure of Soil Particle by Hydro meter Method[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 29(4): 99-101. | |
| [42] | 刘娜, 2017. 人类活动影响下江苏省典型海岸带多环芳烃分布特征研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学. |
| LIU N, 2017. Study on the Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments of Anthropogenic Activities influenced in Jiangsu coast Abstract[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University. | |
| [43] | 倪妮, 宋洋, 王芳, 等, 2016. 多环芳烃污染土壤生物联合强化修复研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 53(3): 561-571. |
| NI N, SONNG Y, WANG F, et al., 2016. Research progress of bio-intensified bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(3): 561-571. | |
| [44] | 孙玉川, 沈立成, 袁道先, 2014. 表层岩溶泉水中多环芳烃污染特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 35(6): 2091-2098. |
| SUN Y C, SHEN L C, YUAN D X, 2014. Contamination and Source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Epikarst Spring Water[J]. Environmental Science, 35(6): 2091-2098. | |
| [45] | 锁玉栋, 2020. 崇明岛表层土壤持久性有机污染物分布、来源及风险评价[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| SUO Y Z, 2020. Distribution, source and risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants in topsoil of Chongming Island[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University. | |
| [46] | 杨国义, 张天彬, 高淑涛, 等, 2007. 珠江三角洲典型区域农业土壤中多环芳烃的含量分布特征及其污染来源[J]. 环境科学, 28(10): 2350-2354. |
| YANG G Y, ZHANG T B, GAO S T, et al., 2007. Distribution characteristics and pollution sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in agricultural soils in the typical region of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Environmental Science, 28(10): 2350-2354. | |
| [47] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2016. 土壤和沉积物多环芳烃的测定气相色谱-质谱法: HJ 805—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China, 2016. Soil and Sediment Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon by Gas chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method: HJ 805—2016 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [48] | 朱鸣鹤, 方飚雄, 庞艳华, 等, 2010. 海三稜藨草 (Scirpus mariqueter) 根系低分子量有机酸对根际沉积物重金属生物有效性的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(4): 583-589. |
| ZHU M H, FANG B X, PANG Y H, et al., 2010. Effects of low molecular weight organic acids of root exudates on heavy metal bioavailability around Scirpus mariqueter rhizosphere sediments[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 41(4): 583-589. |
| [1] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [2] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [3] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [4] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [5] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [6] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [7] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [8] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [9] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [10] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [11] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [12] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [13] | 王钊, 张曼胤, 胡宇坤, 刘魏魏, 张苗苗. 盐度对典型滨海湿地沉积物汞甲基化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [14] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [15] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
