生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 1590-1598.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.08.011
樊珂宇1,2( ), 高原2,3,4,5, 赖子尼2,3,4,5, 曾艳艺2,3,4,5, 刘乾甫2,3,4,5, 李海燕2,3,4,5, 麦永湛2,3,4,5, 杨婉玲2,3,4,5, 魏敬欣2,6, 孙金辉1,*(
), 高原2,3,4,5, 赖子尼2,3,4,5, 曾艳艺2,3,4,5, 刘乾甫2,3,4,5, 李海燕2,3,4,5, 麦永湛2,3,4,5, 杨婉玲2,3,4,5, 魏敬欣2,6, 孙金辉1,*( ), 王超2,3,4,5,*(
), 王超2,3,4,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-01
出版日期:2022-08-18
发布日期:2022-10-10
通讯作者:
王超,E-mail: chaowang@prfri.ac.cn作者简介:樊珂宇(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事水环境微塑料污染研究。E-mail: fanky0526@163.com
基金资助:
FAN Keyu1,2( ), GAO Yuan2,3,4,5, LAI Zini2,3,4,5, ZENG Yanyi2,3,4,5, LIU Qianfu2,3,4,5, LI Haiyan2,3,4,5, MAI Yongzhan2,3,4,5, YANG Wanling2,3,4,5, WEI Jingxin2,6, SUN Jinhui1,*(
), GAO Yuan2,3,4,5, LAI Zini2,3,4,5, ZENG Yanyi2,3,4,5, LIU Qianfu2,3,4,5, LI Haiyan2,3,4,5, MAI Yongzhan2,3,4,5, YANG Wanling2,3,4,5, WEI Jingxin2,6, SUN Jinhui1,*( ), WANG Chao2,3,4,5,*(
), WANG Chao2,3,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-01
Online:2022-08-18
Published:2022-10-10
摘要:
近年来,微塑料作为一种新型污染物在水环境中的污染受到越来越多的关注,已经成为一个新兴的全球性环境问题。为了解珠三角河网水域常见野生鱼类中微塑料的污染特征,选取8种野生淡水鱼为研究对象,分析其鳃部和肠道中微塑料的丰度、粒径、形态、颜色和组成成分。结果表明,在所有鱼体中共检测出60个微塑料,平均每条鱼摄入了1.6个微塑料,鳃部的平均丰度为 (0.638±1.276) items∙g-1,肠道的平均丰度为 (0.256±0.326) items∙g-1,鳃部的平均丰度大于肠道的平均丰度。通过对鱼类微塑料的丰度与鱼的体长、体质量的相关性分析表明,鱼类微塑料的丰度与鱼的体长、体质量相关性较弱。本次实验检测出的微塑料粒径多大于100 μm,主要为碎片状,颜色主要为黑色和灰色,检测的聚合物类型主要为聚乙烯和聚丙烯。中上层鱼类摄入的微塑料大多为颗粒状,分析其来源可能为个人护理及化妆品内添加的塑料微珠,通过生活污水排入到环境中,从而被摄食。底层鱼类摄入的多为碎片状,分析其来源可能是固体废物,经过风化和光解沉入水底,从而被底层鱼类所摄食。泥鳅(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)的平均微塑料摄入量最高,鳃和肠道中微塑料含量最高的鱼类均来自左滩采样点。上述研究结果有助于了解珠三角河网野生淡水鱼类群体的微塑料污染现状,可为水生态风险评估提供参考。
中图分类号:
樊珂宇, 高原, 赖子尼, 曾艳艺, 刘乾甫, 李海燕, 麦永湛, 杨婉玲, 魏敬欣, 孙金辉, 王超. 珠三角河网鱼类微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598.
FAN Keyu, GAO Yuan, LAI Zini, ZENG Yanyi, LIU Qianfu, LI Haiyan, MAI Yongzhan, YANG Wanling, WEI Jingxin, SUN Jinhui, WANG Chao. Characteristics of Microplastic Pollution in Fish in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598.
| 种类 Species | 体质量 Body mass/g | 体长 Length/cm | 样品总数 Total number of samples/ind | 栖息水层 Inhabits the water layer | 食性 Feeding habits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鳙 Aristichthys nobilis | 2900.9 | 60.0 | 1 | 中上层 | 滤食性 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 223.4±93.6 | 16.6±35.4 | 3 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
| 麦瑞加拉鲮 Cirrhinus mrigala | 978.8±266.4 | 40.3±24.9 | 3 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
| 罗非鱼 Oreochromis mossambicus | 311.7 | 25.0 | 1 | 中下层 | 杂食性 |
| 鲢 Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 1061.1±64.6 | 40.5±5.0 | 2 | 表层 | 滤食性 |
| 海南鲌 Culter recurviceps | 805.6±46.6 | 47.5±5.0 | 2 | 中上层 | 杂食性 |
| 广东鲂 Megalobrama terminalis | 272.8±18.1 | 26.2±9.3 | 5 | 中下层 | 杂食性 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 7.6±1.1 | 11.3±0.6 | 20 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
表1 珠三角河网鱼类基本信息
Table 1 Basic informations of fishes in the Pearl River Delta
| 种类 Species | 体质量 Body mass/g | 体长 Length/cm | 样品总数 Total number of samples/ind | 栖息水层 Inhabits the water layer | 食性 Feeding habits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鳙 Aristichthys nobilis | 2900.9 | 60.0 | 1 | 中上层 | 滤食性 |
| 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 223.4±93.6 | 16.6±35.4 | 3 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
| 麦瑞加拉鲮 Cirrhinus mrigala | 978.8±266.4 | 40.3±24.9 | 3 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
| 罗非鱼 Oreochromis mossambicus | 311.7 | 25.0 | 1 | 中下层 | 杂食性 |
| 鲢 Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 1061.1±64.6 | 40.5±5.0 | 2 | 表层 | 滤食性 |
| 海南鲌 Culter recurviceps | 805.6±46.6 | 47.5±5.0 | 2 | 中上层 | 杂食性 |
| 广东鲂 Megalobrama terminalis | 272.8±18.1 | 26.2±9.3 | 5 | 中下层 | 杂食性 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 7.6±1.1 | 11.3±0.6 | 20 | 底层 | 杂食性 |
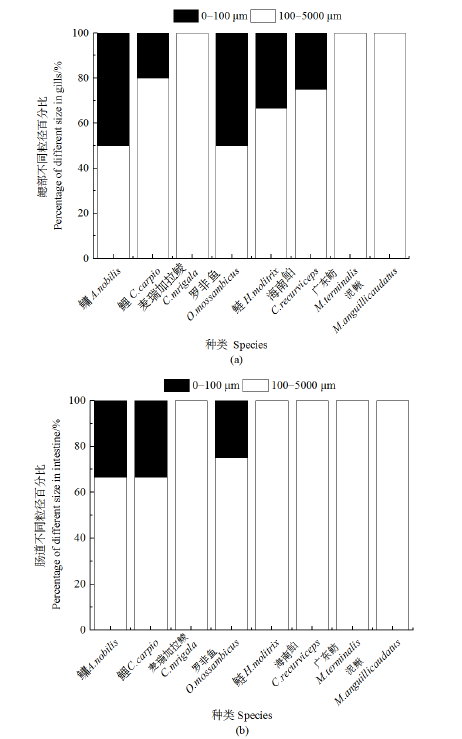
图3 微塑料粒径分布 (a)鳃部不同粒径百分比;(b)肠道不同粒径百分比
Figure 3 Size distribution of microplastics (a) Percentage of different size in gill; (b) Percentage of different size in intestine
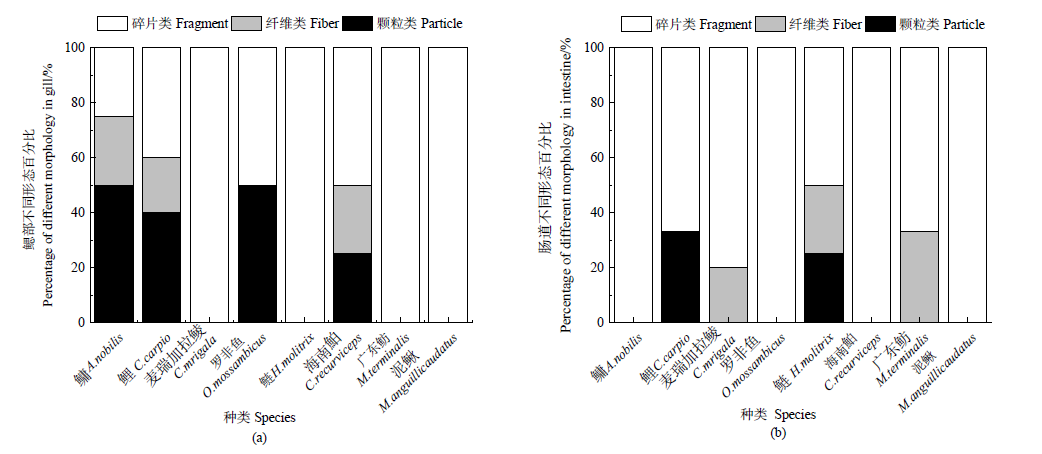
图4 微塑料形态分布 (a)鳃部不同形态百分比;(b)肠道不同形态百分比
Figure 4 Morphology distribution of microplastic (a) Percentage of different morphology in gill; (b) Percentage of different morphology in intestine
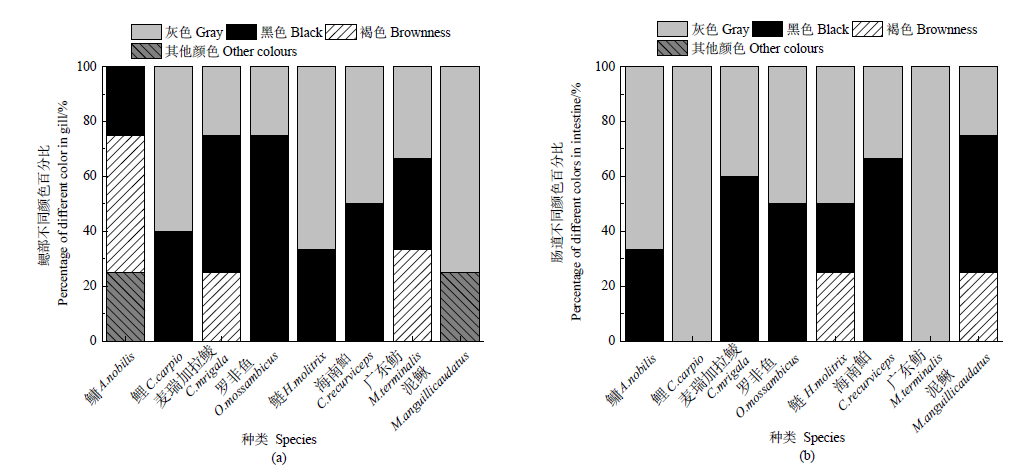
图5 微塑料颜色分布 (a)鳃部不同颜色百分比;(b)肠道不同颜色百分比
Figure 5 Color distribution of microplastics (a) Percentage of different color in gill; (b) Percentage of different colors in intestine
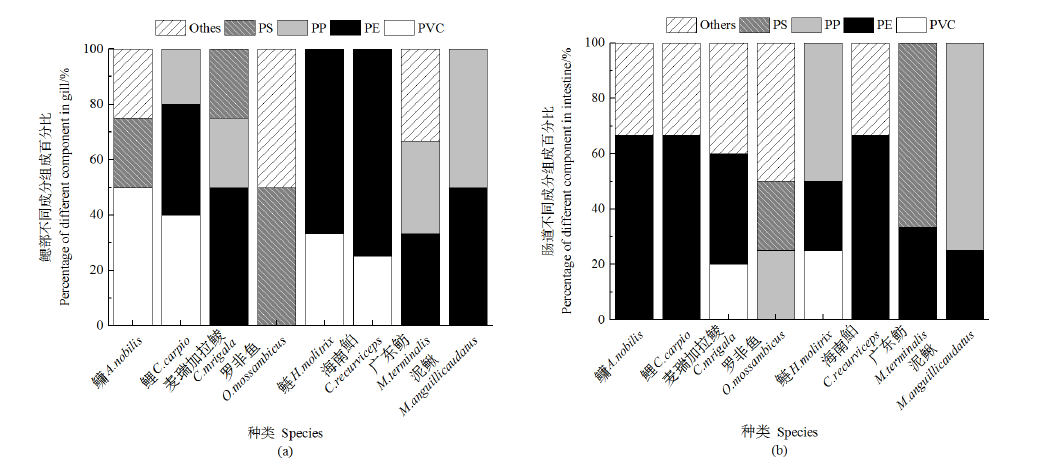
图8 微塑料化学成分类型组成分布 (a)鳃部不同成分组成百分比;(b)肠道不同成分组成百分比
Figure 8 Chemical composition distribution of microplastics (a) Percentage of different component in gill; (b) Percentage of different component in intestine
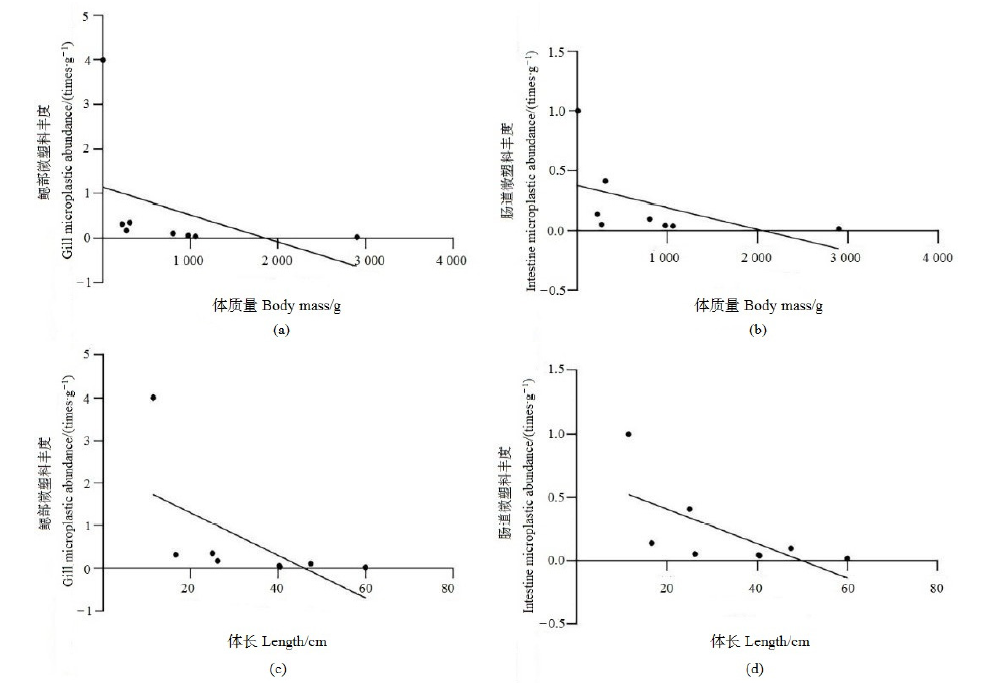
图9 鱼体中鳃部微塑料丰度和肠道微塑料丰度与鱼的体质量、体长的相关性
Figure 9 Correlation between the abundance of microplastics in gill and intestine and the body weight and length of fish
| 国家 Country | 地区 Region | 微塑料检出率 Microplastic detection rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | 三峡大坝 | 25.7 (Zhang et al., |
| 葡萄牙 Portugal | 蒙德古河口 | 38.0 (Bessa, |
| 英法 Britain and France | 英吉利海峡 | 36.5 (Lusher et al., |
| 日本 Japan | 东京湾 | 77.0 (Tanaka et al., |
表2 国内外地区野生鱼体内微塑料检出率
Table 2 Detection rate of microplastics in wild fish at home and abroad
| 国家 Country | 地区 Region | 微塑料检出率 Microplastic detection rate/% |
|---|---|---|
| 中国 China | 三峡大坝 | 25.7 (Zhang et al., |
| 葡萄牙 Portugal | 蒙德古河口 | 38.0 (Bessa, |
| 英法 Britain and France | 英吉利海峡 | 36.5 (Lusher et al., |
| 日本 Japan | 东京湾 | 77.0 (Tanaka et al., |
| [1] |
BALDWIN A K, CORSI S R, MASON S A, 2016. Plastic debris in 29 great lakes tributaries: Relations to watershed attributes and hydrology[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(19): 10377-10385.
PMID |
| [2] |
BELLAS J, MARTÍNEZ-ARMENTAL J, MARTÍNEZ-CÁMARA A, et al., 2016. Ingestion of microplastics by demersalfish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 109: 55-60.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BESSA F, BARRÍA P, NETO J M, et al., 2018. Occurrence of microplastics in commercial fish from a natural estuarine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 128: 575-584.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al., 2011. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(12): 2588-2597.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al., 2011. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(12): 2588-2597.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
DESFORGES J P W, GALBRAITH M, DANGERFIELD N, et al., 2014. Widespread dis-tribution of microplastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 79(1-2): 94-99.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DO SUL J A I, COSTA M F, 2014. The present and future of microplastic pollution in the marine environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 185: 352-364.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
ERIKSEN M, LEBRETON L C M, CARSON H S, et al., 2014. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea[J]. PLoS ONE, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111913.
DOI |
| [9] |
ERIKSEN M, MASON S, WILSON S, et al., 2013. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 77(s1-2): 177-182.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
FIRDAUS M, TRIHADININGRUM Y, LESTARI P, 2019. Microplastic pollution in the sediment of Jagir Estuary, Surabaya City, Indonesia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110790.
DOI |
| [11] |
FOEKEMA E M, GRUIJTERC D, MERGIA M T, et al., 2013. Plastic in North Sea fish[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(15): 8818-8824.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
FOSSI M C, COPPOLA D, BAINI M, et al., 2014. Large filter feeding marine organisms as indicators of microplastic in the pelagic environment: The case studies of the Mediterranean basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus)[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 100: 17-24.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L, 2017. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advance, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1700782.
DOI |
| [14] |
GÜVEN O, GOKDAG K, JOVSNOVIC B, et al., 2017. Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish[J]. Environmental Pollution, 223: 286-294.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
JAMBECK J R, GEYER R, WILCOX C, et al., 2015. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean[J]. Science, 347(6223): 768-771.
DOI URL |
| [16] | KASAMESIRI P, THAIMUANGPHOL W, 2020. Microplastics ingestion by freshwater fish in the Chi River Thailand[J]. International Journal of GEOMATE, 18(67): 114-119. |
| [17] |
KLEIN S, WORCH E, KNEPPER T P, 2015. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in river shore sediments of the rhine-main area in Germany[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(10): 6070-6076.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LAVERS J L, BOND A L, 2017. Exceptional and rapid accumulation of anthropogenic debris on one of the world's most remote and pristine islands[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(23): 6052-6055.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LAW K L, MORÉT-FERGUSON S, MAXIMENKO N A, et al., 2010. Plastic accumulation in the north Atlantic subtropical gyre[J]. Science, 329(5996): 1185-1188.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
LAW K L, THOMPHON R C, 2014. Microplastics in the seas[J]. Science, 345(6193): 144-145.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LEBRETON L C M, ZWET J V D, DAMSTEEG J W, et al., 2017. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans[J]. Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15611.
DOI |
| [22] |
LEI K, QIAO F, LIU Q, et al., 2017. Microplastics releasing from personal care and cosmetic products in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 123(1-2): 122-126.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
LI W C, TSE H F, FOK L, 2016. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 566-567: 333-349.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LUSHER A L, MCHUGH M, THOMPSON R C, 2013. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 67(1-2): 94-99.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
MCGORAN A R, CLARK P F, MORRITT D, 2017. Presence of microplastic in the digestive tracts of european flounder, Platichthys flesus, and european smelt, Osmerus eperlanus, from the River Thames[J]. Environmental Pollution, 220(Part A): 744-751.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MCGORAN A R, PHILLIP R C, CLARK P F, et al., 2018. Ingestion of plastic by fish: A comparison of Thames Estuary and Firth of Clyde populations[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 137: 12-23.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
MORGANA S, GHIGLIOTTI L, ESTEVEZ-CALVAR N, et al., 2018. Microplastics in the Arctic: A case study with sub-surface water and fish samples off Northeast Greenland[J]. Environmental Pollution, 242: 1078-1086.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
NADALM A, ALOMAR C, DEUDERO S, 2016. High levels of microplastic ingestion by the semipelagicfish bogue Boops boops (L.) around the Balearic Islands[J]. Environmental Pollution. 214: 517-523.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
PARK C H, KANG Y K, IM S S, 2004. Biodegradability of cellulose fabrics[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 94(1): 248-253.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
PELLINI G, GOMIERO A, FORTIBUONI T, et al., 2018. Characterization of microplastic litter in the gastrointestinal tract of Solea solea from the Adriatic Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 234: 943-952
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ROCHMAN C M, HOH E, KUROBE T, et al., 2013. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress[J]. Scientific Reports, 3(1): 3263.
DOI URL |
| [32] | ROCHMAN C M, TAHIR A, WILLIAMS S L, et al., 2015. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: plastic debris and fibers from textiles infish and bivalves sold for human consumption[J]. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 1-10. |
| [33] |
SU L, XUE Y G, LI L Y, et al., 2016. Microplastics in Taihu Lake, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 216: 711-719.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | TALLEY T S, VENUTI N, WHELAN R, 2020. Natural history matters: Plastics in estuarine fish and sediments at the mouth of an urban watershed[J]. PLoS ONE, 15(3): e0229777. |
| [35] |
TANAKA K, TAKADA H, 2016. Microplastic fragments and microbeads in digestive tracts of planktivorous fish from urban coastal waters[J]. Scientific reports, 6(1): 34351.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
TEREPOCKI A K, BRUSH A T, KLEINE L U, et al., 2017. Size and dynamics of microplastic in gastrointestinal tracts of Northern Fulmars (Fulmarus glacialis) and Sooty Shearwaters (Ardenna grisea)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 116(1-2): 143-150.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
VALENTE T, SBRANA A, SCACCO U, et al., 2019. Exploring microplastic ingestion by three deep-water elasmobranch species: A case study from the Tyrrhenian Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 253: 342-350.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
WOOTTON N, FERREIRA M, REIS-SANTOS P, et al., 2021. A comparison of microplastic in fish from Australia and Fiji[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, DOI: 10.3389/fmars.2021.690991.
DOI |
| [39] |
WU F Z, WANG Y J, LEUNG J Y S, et al., 2020. Accumulation of microplastics in typical commercial aquatic species: A case study at a productive aquaculture site in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135432.
DOI |
| [40] |
YUAN W K, LIU X N, WANG W F, et al., 2019. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments, and wildfish from Poyang Lake, China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 170: 180-187.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZHANG K, XIONG X, HU H, et al., 2017. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastic pollution in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 51(7): 3794-3801.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
ZHENG K, FAN Y J, ZHU Z W, et al., 2019. Occurrence and species-specific distribution of plastic debris in wild freshwater fish from the Pearl River Catchment, China[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 38(7): 1504-1513.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | 李文华, 简敏菲, 余厚平, 等, 2020. 鄱阳湖流域饶河龙口入湖段优势淡水鱼类对微塑料及重金属污染物的生物累积[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(2): 357-369. |
| LI W H, JIAN M F, YU H P, et al., 2020. Bioaccumulation of microplastics and heavy metal pollutants by dominant freshwater fish in the Longkou inlet of Raohe River in the Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Lake Science, 32(2): 357-369. | |
| [44] | 刘思琪, 唐文乔, 2022. 上海主要河流鱼类体内的微塑料污染研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 31(06):1324-1333. |
| LIU S Q, TANG W Q, 2021. Investigation on Microplastic Pollution of the Fish in Main Rivers of Shanghai[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze River Basin, 31(06):1324-1333. | |
| [45] | 孙凯, 2021. 全球海洋塑料污染问题及治理对策[J]. 国家治理, (15): 44-48. |
| SU K, 2021. Global marine plastic pollution problems and countermeasures[J]. State Governance, (15): 44-48. | |
| [46] | 王骥, 张广文, 2007. 辽宁海洋渔政工作手册[M]. 沈阳: 辽宁人民出版社: 73-111. |
| WANG J, ZHANG G W, 2007. Liaoning marine fishery administration work manual[M]. Shenyang: Liaoning People’s Publishing House: 73-111. | |
| [47] | 徐华林, 2016. 福田红树林保护区潮间带动物图谱[M]. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社: 72. |
| XU H L, 2016. Intertidal fauna map of Futian Mangrove Reserve[M]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press: 72. | |
| [48] | 赵肖, 何蕾, 赵文静, 等, 2021. 珠江口典型生活污水处理厂微塑料处理与排放研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 43(3): 359-363. |
| ZHAO X, HE L, ZHAO W J, et al., 2021. Research on microplastics treatment and discharge in typical domestic sewage treatment plants in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 43(3): 359-363. | |
| [49] | 郑可, 2019. 珠江流域野生淡水鱼类中塑料及有机磷塑料添加剂污染[D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学: 25-40. |
| ZHENG K, 2019. Plastic Debris and organophosphorus additives in wild freshwater fish of the Pearl River Catchment[D]. Guangzhou: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 25-40. |
| [1] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [2] | 王默雷, 李智慧, 陈来国, 郭送军, 刘明, 王硕, 陆海涛. 城市垃圾焚烧厂烟气及周边土壤中多溴联苯醚的污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1582-1589. |
| [3] | 朱丽, 闫怀忠, 孙友敏, 范晶, 刘光辉, 张桂芹. 山东典型重工业区降尘污染特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1393-1399. |
| [4] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [5] | 谢晨敏, 隆楚月, 黎大宁, 朱春友, 彭先芝, 孙毓鑫, 罗孝俊, 张黎, 麦碧娴. 南海永兴岛和东岛土壤中微塑料和卤代阻燃剂的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1008-1014. |
| [6] | 陈雪泉, 孔彬, 兰青, 余志铨, 谢银斯, 黄俊毅. 胶黏剂生产行业VOCs组分特征及臭氧生成潜势分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 750-758. |
| [7] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| [8] | 刘娣, 苏超, 张红, 秦冠宇. 典型煤炭产业聚集区土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 391-399. |
| [9] | 陈赋秋雪, 唐思琪, 袁昊, 马子轩, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 刘颖. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对典型农作物种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392. |
| [10] | 谢洁芬, 章家恩, 危晖, 刘自强, 陈璇. 土壤中微塑料复合污染研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2431-2440. |
| [11] | 姜晶, 阮呈杰, 陈霄宇, 吴仪, 汪永创. 微塑料模拟老化及其对污染物吸附行为影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2263-2274. |
| [12] | 雷雅杰, 李雪, 常春艳, 毛雪飞. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对水中汞离子的吸附研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2048-2057. |
| [13] | 李圣增, 郝赛梅, 谭路遥, 张怀成, 徐标, 谷树茂, 潘光, 王淑妍, 闫怀忠, 张桂芹. 济南市PM2.5中二次组分的时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 100-109. |
| [14] | 王飞, 赵颖. 太原市污灌区农田土壤中多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [15] | 强承魁, 曹丹, 赵虎, 张明, 丁永辉, 关滢, 张光琴, 沈文妍, 秦越华. 土壤-油用牡丹系统重金属含量及生态健康风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1286-1292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
