生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2382-2392.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.013
陈赋秋雪1( ), 唐思琪1, 袁昊1, 马子轩1, 陈坦1,2,**(
), 唐思琪1, 袁昊1, 马子轩1, 陈坦1,2,**( ), 杨婷1,2, 张冰1,2, 刘颖1,2
), 杨婷1,2, 张冰1,2, 刘颖1,2
收稿日期:2022-08-02
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
**陈坦,E-mail: chentan05@tsinghua.org.cn作者简介:陈赋秋雪(2001年生),女(布依族),硕士研究生,研究方向为微塑料的环境行为。E-mail: 1301494088@qq.com;第一联系人:*共同第一作者:唐思琪与第一作者同等贡献
基金资助:
CHEN Fuqiuxue1( ), TANG Siqi1, YUAN Hao1, MA Zixuan1, CHEN Tan1,2,**(
), TANG Siqi1, YUAN Hao1, MA Zixuan1, CHEN Tan1,2,**( ), YANG Ting1,2, ZHANG Bing1,2, LIU Ying1,2
), YANG Ting1,2, ZHANG Bing1,2, LIU Ying1,2
Received:2022-08-02
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
微塑料在农业土壤中可直接或间接地影响作物生长,而种子发芽和幼苗生长初期是作物生理毒性的敏感阶段。为认识微塑料对典型农作物的生理毒性,选用5 μm聚苯乙烯微塑料(5 μm-MPs),通过7 d种子发芽试验和33 d土培观测其对中国几种典型农作物种子发芽及幼苗生长的影响。0—100 mg?L?1 5 μm-MPs水培试验结果表明,5 μm-MPs对小麦(Triticum aestivum)、玉米(Zea mays)、谷子(Setaria italica)、花生(Arachis hypogaea)、向日葵(Helianthus annuus)等5种作物种子的平均发芽时间均无显著影响,对小麦、玉米、向日葵、谷子的种子发芽能力和种子活力无显著影响,但花生种子对5 μm-MPs敏感,指标受到显著抑制,且5 μm-MPs质量浓度越大抑制越强。以玉米、小麦、花生为例,0—100 mg?kg?1 5 μm-MPs土培试验结果表明,部分处理5 μm-MPs对3种作物幼苗生长表现出一定的抑制作用。种植15 d时各处理5 μm-MPs均显著抑制小麦幼苗株高,但种植30 d时5 μm-MPs对3种作物幼苗株高均无显著影响。各处理5 μm-MPs对小麦和玉米叶片叶绿素总含量未表现出一致的显著影响趋势,对两者叶片叶绿素a的抑制作用均强于叶绿素b,且可显著诱导小麦、玉米叶片超氧化物歧化酶活性下降,20 mg?kg?1 5 μm-MPs处理与对照组相比分别下降了35.5%和50.6%。含5 μm-MPs土壤的氮含量在种植后显著增加,而小麦、玉米幼苗叶面氮含量在不同生长时期均偏低,抑制植物吸收、转运土壤中的氮元素是5 μm-MPs影响作物幼苗生长的可能机制。
中图分类号:
陈赋秋雪, 唐思琪, 袁昊, 马子轩, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 刘颖. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对典型农作物种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392.
CHEN Fuqiuxue, TANG Siqi, YUAN Hao, MA Zixuan, CHEN Tan, YANG Ting, ZHANG Bing, LIU Ying. Impacts of Polystyrene Microplastics on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Typical Crops[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392.
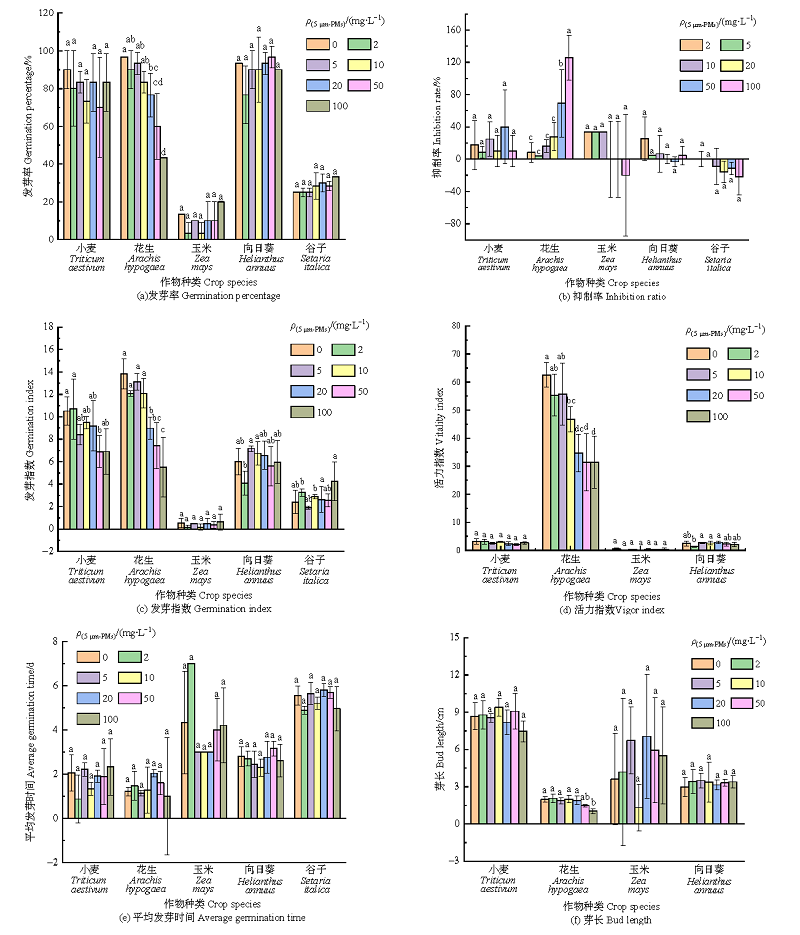
图1 不同质量浓度微塑料暴露下5种作物的发芽情况 图中不同小写字母代表处理间的差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 1 Germination of 5 species of crops exposed to microplastics of different mass concentrations The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05)
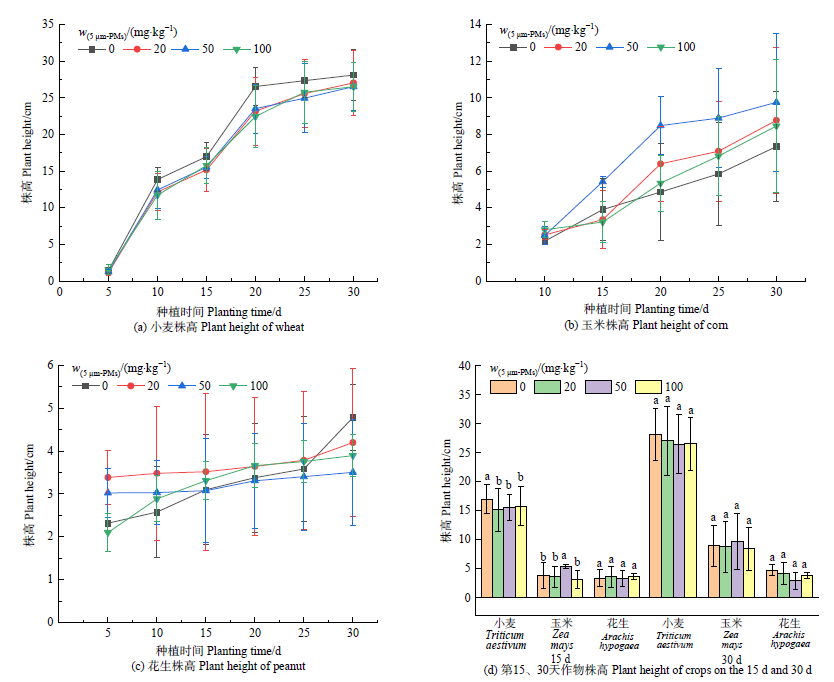
图2 土培不同质量分数微塑料胁迫下小麦、玉米、花生的株高
Figure 2 Plant heights of wheat, corn and peanut under the stress of microplastics with different mass fractions in soil culture
| w(5 μm-PMs)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(Wheat leaf Chl)/(mg∙g−1) | w(Corn leaf Chl)/(mg∙g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla | Chlb | Chla/Chlb | Chla | Chlb | Chla/Chlb | ||
| 0 | 3.97a | 4.91a | 0.81 | 3.17a | 7.02a | 0.45 | |
| 20 | 2.97c | 4.95a | 0.60 | 2.07c | 4.66c | 0.44 | |
| 50 | 3.84ab | 4.89a | 0.79 | 2.26b | 5.37b | 0.42 | |
| 100 | 3.64b | 4.93a | 0.74 | 2.38b | 5.66b | 0.42 | |
表1 土培不同质量分数微塑料胁迫下小麦、玉米叶绿素a、叶绿素b的质量分数
Table 1 Contents of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in wheat and corn under the stress of microplastics with different mass fractions in soil culture
| w(5 μm-PMs)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(Wheat leaf Chl)/(mg∙g−1) | w(Corn leaf Chl)/(mg∙g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla | Chlb | Chla/Chlb | Chla | Chlb | Chla/Chlb | ||
| 0 | 3.97a | 4.91a | 0.81 | 3.17a | 7.02a | 0.45 | |
| 20 | 2.97c | 4.95a | 0.60 | 2.07c | 4.66c | 0.44 | |
| 50 | 3.84ab | 4.89a | 0.79 | 2.26b | 5.37b | 0.42 | |
| 100 | 3.64b | 4.93a | 0.74 | 2.38b | 5.66b | 0.42 | |
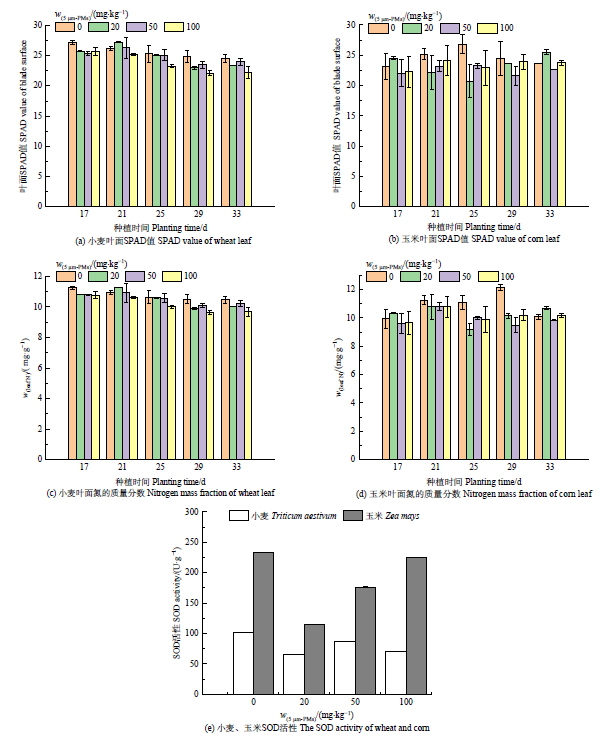
图3 土培不同质量分数微塑料胁迫下小麦、玉米生理指标变化
Figure 3 Changes of physiological indexes of wheat and corn under the stress of microplastics with different mass fractions in soil culture
| 作物种类 Crop species | w(5 μm-PMs)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DTN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DNN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DAN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DON)/(mg∙kg−1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | ||||||
| 小麦 Wheat | 0 | 126.2 | 135.3 | 78.3 | 83.8 | 39.3 | 40.2 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 32.6 | 36.5 | ||||
| 20 | 131.4 | 140.2 | 79.7 | 85.4 | 37.7 | 37.7 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 35.1 | 39.5 | |||||
| 50 | 138.3 | 152.9 | 81.1 | 87.3 | 33.9 | 34.1 | 7.7 | 9.6 | 39.4 | 43.6 | |||||
| 100 | 177.7 | 193.7 | 81.0 | 89. 0 | 32.2 | 32.6 | 8.1 | 10.9 | 40.7 | 45.5 | |||||
| 玉米 Corn | 0 | 104.2 | 114.4 | 105.2 | 117.7 | 35.7 | 36.2 | 9.2 | 10.5 | 60.4 | 71.0 | ||||
| 20 | 106.8 | 123.1 | 105.4 | 119.1 | 30.6 | 29.1 | 10.0 | 11.2 | 64.9 | 78.9 | |||||
| 50 | 102.6 | 128.2 | 105.6 | 122.9 | 24.8 | 22.3 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 69.8 | 88.0 | |||||
| 100 | 129.3 | 164.8 | 107.8 | 120.8 | 23.5 | 21.8 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 72.4 | 85.8 | |||||
| 花生 Peanut | 0 | 129.6 | 140.6 | 90.8 | 102.5 | 41.6 | 41.0 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 33.8 | 45.5 | ||||
| 20 | 136.5 | 153.7 | 92.8 | 105.9 | 38.0 | 37.2 | 16.5 | 18.8 | 38.3 | 49.9 | |||||
| 50 | 157.9 | 176.4 | 95.5 | 109.5 | 33.5 | 30.5 | 17.9 | 21.4 | 44.1 | 57.5 | |||||
| 100 | 199.7 | 224.5 | 95.8 | 106.8 | 32.3 | 29.9 | 18.4 | 21.0 | 45.1 | 56.0 | |||||
表2 培养前后作物土壤中可溶性营养物质的质量分数
Table 2 Mass fractions of some elements in crop soil before and after culture
| 作物种类 Crop species | w(5 μm-PMs)/ (mg∙kg−1) | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DTN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DNN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DAN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(DON)/(mg∙kg−1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | 培养前 Before planting | 培养后 After planting | ||||||
| 小麦 Wheat | 0 | 126.2 | 135.3 | 78.3 | 83.8 | 39.3 | 40.2 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 32.6 | 36.5 | ||||
| 20 | 131.4 | 140.2 | 79.7 | 85.4 | 37.7 | 37.7 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 35.1 | 39.5 | |||||
| 50 | 138.3 | 152.9 | 81.1 | 87.3 | 33.9 | 34.1 | 7.7 | 9.6 | 39.4 | 43.6 | |||||
| 100 | 177.7 | 193.7 | 81.0 | 89. 0 | 32.2 | 32.6 | 8.1 | 10.9 | 40.7 | 45.5 | |||||
| 玉米 Corn | 0 | 104.2 | 114.4 | 105.2 | 117.7 | 35.7 | 36.2 | 9.2 | 10.5 | 60.4 | 71.0 | ||||
| 20 | 106.8 | 123.1 | 105.4 | 119.1 | 30.6 | 29.1 | 10.0 | 11.2 | 64.9 | 78.9 | |||||
| 50 | 102.6 | 128.2 | 105.6 | 122.9 | 24.8 | 22.3 | 11.1 | 12.7 | 69.8 | 88.0 | |||||
| 100 | 129.3 | 164.8 | 107.8 | 120.8 | 23.5 | 21.8 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 72.4 | 85.8 | |||||
| 花生 Peanut | 0 | 129.6 | 140.6 | 90.8 | 102.5 | 41.6 | 41.0 | 15.4 | 15.9 | 33.8 | 45.5 | ||||
| 20 | 136.5 | 153.7 | 92.8 | 105.9 | 38.0 | 37.2 | 16.5 | 18.8 | 38.3 | 49.9 | |||||
| 50 | 157.9 | 176.4 | 95.5 | 109.5 | 33.5 | 30.5 | 17.9 | 21.4 | 44.1 | 57.5 | |||||
| 100 | 199.7 | 224.5 | 95.8 | 106.8 | 32.3 | 29.9 | 18.4 | 21.0 | 45.1 | 56.0 | |||||
| [1] |
ALIMI O S, FARNER B J, Hernandez L M, et al., 2018. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(4): 1704-1724.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BOSKER T, BOUWMAN L J, BRUN N R, et al., 2019. Microplastics accumulate on pores in seed capsule and delay germination and root growth of the terrestrial vascular plant Lepidium sativum[J]. Chemosphere, 226: 774-781.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CHAE Y, KIM D, KIM S W, et al., 2018. Trophic transfer and individual impact of nano-sized polystyrene in a four-species freshwater food chain[J]. Scientific Reports, 8: 1-11. |
| [4] |
COLE M, LINDEQUE P, HALSBAND C, et al., 2011. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(12): 2588-2597.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
DE SOUZA MACHADO A, LAU C W, KLOAS W, et al., 2019. Microplastics can change soil properties and affect plant performance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(10): 6044-6052.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG Y M, GAO M L, SONG Z G, et al., 2020. As (III) adsorption onto different-sized polystyrene microplastic particles and its mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 239: 124792.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
EVANS J R, 1989. Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants[J]. Oecologia, 78(1): 9-19.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FEI Y F, HUANG S Y, ZHANG H B, et al., 2020. Response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities to the accumulation of microplastics in an acid cropped soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 707(C): 135634.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GABRIELA K, ANDREJA Ž G, ALES K, et al., 2017. Impact of polyethylene microbeads on the floating freshwater plant duckweed Lemna minor[J]. Environmental Pollution, 230: 1108-1115.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GONG P, WILKE B-M, et al., 2001. Evaluation and refinement of a continuous seed germination and early seeding growth test for the use in the ecotoxicological assessment of soils[J]. Chemosphere, 44: 491-500.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JIANG X F, CHEN H, LIAO Y C, et al., 2019. Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of polystyrene microplastics on higher plant Vicia faba[J]. Environmental Pollution, 250: 831-838.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KONG X, JIN D C, JIN S L, et al., 2018. Responses of bacterial community to dibutyl phthalate pollution in a soil-veqetable ecosystem[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 353: 142-150.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LAW K L, THOMPSON R C, 2014. Microplastics in the seas[J]. Science, 345(6193): 144-145.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI L Z, LUO Y M, LI R J, et al., 2020. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode[J]. Nature Sustainability, 3(11): 929-937.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIAN J, WU J, XIONG H, et al., 2020. Impact of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385: 121620.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU H F, YANG X M, LIU G B, et al., 2017. Response of soil dissolved organic matter to microplastic addition in Chinese loess soil[J]. Chemosphere, 185: 907-917.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
LIU Q L, CHEN B, WANG Q L, et al., 2009. Carbon nanotubes as molecular transporters for walled plant cells[J]. Nano Letters, 9(3): 1007-1010.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
NIZZETTO L, FUTTER M, LANGAAS S, 2016. Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin?[J] Environmental Science & Technology, 50(20): 10777-10779.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
RICHARD C, THOMPSON, YLVA O, et al., 2004. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic?[J]. Science, 304(5672): 838-838.
PMID |
| [20] | SANDER V, PAULA E, NOEL J, et al., 2019. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on the growth of sediment-rooted macrophytes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 654(C): 1040-1047. |
| [21] |
SHI R Y, LIU W T, LIAN Y H, et al., 2022. Phytotoxicity of polystyrene, polyethylene and polypropylene microplastics on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.)[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 317: 115441-115441.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SJOLLEMA S B, REDONDO-HASSELERHAR P, LESLIE H A, et al., 2016. Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth?[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 170: 259-261.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
TAN W, PERALTA-VIDEA J R, GARDEA-TORRESDEY J L, 2018. Interaction of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with soil components and plants: current knowledge and future research needs: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science: Nano, 5(2): 257-278. 130923.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
VERA B, JASMIN D M, TIM K, et al., 2012. Uptake of fluorescent nano beads into BY2-cells involves clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis[J]. FEBS Letters, 586(20): 3626-3632.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
WAN Y, WU C X, XUE Q, et al., 2019. Effects of plastic contamination on water evaporation and desiccation cracking in soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 654: 576-582.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WARREN C R, ADAMS M A, 2022. Phosphorus affects growth and partitioning of nitrogen to Rubisco in Pinus pinaster [J]. Tree Physiology, 22(1): 11-9.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZANG H D, ZHOU J, MILES R M, et al., 2020. Microplastics in the agroecosystem: Are they an emerging threat to the plant-soil system?[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 148: 107926.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 安菁, 刘欢语, 郑艳, 等, 2021. 土壤微塑料残留对大豆幼苗生长及生理生化特征的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报, 39(1): 41-46, 113. |
| AN J, LIU H Y, ZHENG Y, et al., 2021. Effects of soil microplastic residue on soybean seedlings growth and the physiological and biochemical characteristics[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 39(1): 41-46, 113. | |
| [29] | 陈熹, 马琼, 陶宗娅, 等, 2020. 微塑料对小麦农艺性状及氮素利用效率的影响[J]. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43(5): 664-670. |
| CHEN X, MA Q, TAO Z Y, et al., 2020. Effects of microplastics on agronomic characters and nitrogen utilization efficiency of wheat[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science), 43(5): 664-670. | |
| [30] | 冯雪莹, 孙玉焕, 张书武, 等, 2021. 微塑料对土壤-植物系统的生态效应[J]. 土壤学报, 58(2): 299-313. |
| FENG X Y, SUN Y H, ZHANG S W, et al., 2021. Ecological effects of microplastics on soil-plant systems[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58(2): 299-313. | |
| [31] | 侯军华, 檀文炳, 余红, 等, 2020. 土壤环境中微塑料的污染现状及其影响研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 38(2): 16-27, 15. |
| HOU J H, TAN W B, YU H, et al., 2020. Microplastics in soil ecosystem: A review on sources, fate and ecological impact[J]. Environmental Engineering, 38(2): 16-27, 15. | |
| [32] | 胡桂林, 2019. 微塑料与土壤介质相互作用机制的研究[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学: 1-4. |
| HU G L, 2019. Interaction mechanism between microplastics and soil media[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology: 1-4. | |
| [33] | 纪红, 陈修文, 赵宏利, 等, 2021. 微塑料对高等植物生长发育影响研究进展[J]. 科学技术与工程, 21(18): 7415-7424. |
| JI H, CHEN X W, ZHAO H L, et al., 2021. Research advances of the influence of microplastics on the growth and development of higher plants[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 21(18): 7415-7424. | |
| [34] | 李连祯, 周倩, 尹娜, 等, 2019. 食用蔬菜能吸收和积累微塑料[J]. 科学通报, 64(9): 928-934. |
| LI L Z, ZHOU Q, YIN N, et al., 2019. Uptake and accumulation of microplastics in an edible plant[J]. Scientific Bulletin, 64(9): 928-934. | |
| [35] | 李瑞静, 赵亚菲, 耿佳慧, 等, 2021. 农田土壤微塑料污染及其对植物的影响研究进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(6): 681-688. |
| LI R J, ZHAO Y F, GENG J H, et al., 2021. Research progress of microplastics pollution and its effect on plant ecosystem in farmland[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(6): 681-688. | |
| [36] | 连加攀, 沈玫玫, 刘维涛, 2019. 微塑料对小麦种子发芽及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(4): 737-745. |
| LIAN J P, SHEN M M, LIU W T, 2019. Effects of microplastics on wheat seed germination and seedling growth[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(4): 737-745. | |
| [37] | 廉宇航, 刘维涛, 史瑞滢, 等, 2022. 聚乙烯和聚乳酸微塑料对大豆生长和生理生化及代谢的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(6): 2894-2903. |
| LIAN Y H, LIU W T, SHI R Y, et al., 2022. Impact of polyethylene and polylactic acid microplastics on growth, physio-biochemistry and metabolism in soybean (Glycine max)[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(6): 2894-2903. | |
| [38] | 廖苑辰, 李梅, 王晓琳, 等, 2019. 微塑料对小麦生长及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(10): 4661-4667. |
| LIAO Y C, LI M, WANG X L, et al., 2019. Effects of microplastics on the growth, physiology and biochemical characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Environmental Science, 40(10): 4661-4667. | |
| [39] | 刘玲, 洪婷婷, 胡倩男, 等, 2021. 微塑料与铅复合污染对水稻幼苗根系生长和氧化应激的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 40(12): 2623-2633. |
| LIU L, HONG T T, HU Q N, et al., 2021. Effects of the combination of microplastics and lead pollution on growth and oxidative responses of rice seedlings’ roots[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(12): 2623-2633. | |
| [40] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 等, 2022. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| LIU X H, LIU L Q Q, LI M, et al., 2022. Effects of polyethylene microplastics with different particle sizes on seed germination and seedling growth of maize and cucumber[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(6): 1263-1271. | |
| [41] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵, 2022. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(3): 610-620. |
| LIU S S, CHEN N, YANG X Y, 2022. Research progress on adsorption-desorption characteristics of organic pollutants by microplastics and their combined toxic effects[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(3): 610-620. | |
| [42] | 刘蓥蓥, 张旗, 崔文智, 等, 2019. 聚乙烯微塑料对绿豆发芽的毒性研究[J]. 环境与发展, 31(5): 123-125. |
| LIU Y Y, ZHANG Q, CUI W Z, et al., 2019. Toxicity of polyethylene microplastics to seed germination of mung bean[J]. Environment and Development, 31(5): 123-125. | |
| [43] | 骆永明, 周倩, 章海波, 等, 2018. 重视土壤中微塑料污染研究防范生态与食物链风险[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(10): 1021-1030. |
| LUO Y M, ZHOU Q, ZHANG H B, et al., 2018. Pay attention to research on microplastic pollution in soil for prevention ecological and food chain risks[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33(10): 1021-1030. | |
| [44] | 任欣伟, 唐景春, 于宸, 等, 2018. 土壤微塑料污染及生态效应研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(6): 1045-1058. |
| REN X W, TANG J C, YU C, et al., 2018. Advances in research on the ecological effects of microplastic pollution on soil ecosystems[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(6): 1045-1058. | |
| [45] | 邵媛媛, 张帆, 梁庆霞, 2020. 陆地-海洋生态系统微塑料污染现状研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(10): 2118-2129. |
| SHAO Y Y, ZHANG F, LIANG Q X, 2020. Research on microplastic pollution in terrestrial-marine ecosystems[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(10): 2118-2129. | |
| [46] | 孙晓东, 2019. 不同电荷纳米塑料在拟南芥体内的毒性、吸收和积累[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 24-37. |
| SUN X D, 2019. Phytotoxicty, uptake and accumulation of diferentially charged nanoplastics in Arabidopsis thaliana[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University:24-37. | |
| [47] | 吾兰∙恩特马克, 2021. 外源添加微塑料对土壤性质和玉米生长的影响研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学:20-23. |
| WULAN E, 2021. Study on the effect of adding microplastics on soil properties and corn growth[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University: 20-23. | |
| [48] | 吴佳妮, 杨天志, 连加攀, 等, 2020. 聚苯乙烯纳米塑料 (PSNPs) 对大豆 (Glycine max) 种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(12): 4581-4589. |
| WU J N, YANG T Z, LIAN J P, et al., 2020. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNPs) on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean (Glycine max)[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(12): 4581-4589. | |
| [49] | 谢洁芬, 章家恩, 危晖, 等, 2022. 土壤中微塑料复合污染研究进展与展望[J/OL]. 生态环境学报: 1-10[2022-09-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20220916.1628.004.html. |
| XIE J F, ZHANG J E, WEI H, et al., 2022. Microplastic combined pollution in soil: An overview[J/OL]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences: 1-10 [2022-09-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1661.X.20220916.1628.004.html. | |
| [50] | 谢勇, 王友绍, 2021. 重金属胁迫下4种红树植物幼苗生理响应特征[J/OL]. 热带海洋学报: 1-8[2022-09-27]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1500.P.20211012.1021.002.html. |
| XIE Y, WANG Y S, 2021. Physiological response characteristics of four mangrove plants seedlings under heavy metal stress[J/OL]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography: 1-8 [2022-06-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/44.1500.P.20211012.1021.002.html. | |
| [51] | 徐荣乐, 海热提, 2010. 塑料地膜对小麦种子萌发及幼苗抗氧化酶系统的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(11): 2702-2707. |
| XU R L, HAI R T, 2010. Effects of plastic film on seed germination and the activities of antioxidant enzyme of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(11): 2702-2707. | |
| [52] |
张晨, 简敏菲, 陈宇蒙, 等, 2021. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对黑藻生长及生理生化特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(1): 317-325.
DOI |
|
ZHANG C, JIAN M F, CHEN Y M, et al., 2021. Effects of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) on the growth, physiology, and biochemical characteristics of Hydrilla verticillata[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(1): 317-325.
DOI |
|
| [53] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2009. 水质总有机碳的测定燃烧氧化-非分散红外吸收法: HJ 501—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2009. Water quality—Determination of total organic carbon—Combustion oxidation nondispersive infrared absorption method: HJ 501—2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [54] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2013. 水质总氮的测定流动注射-盐酸萘乙二胺分光光度: HJ 668—2013[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2013. Water quality-Determination of total nitrogen by flow injection analysis (FIA) and N-(1-naphthyl) ethylene diamine dihydrochloride spectrophotometry: HJ 668—2013[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [55] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2014. 肥料硝态氮、铵态氮、酰胺态氮含量的测定: NY/T 1116—2014[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China, 2014. Fertilizers—Determination of nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, amide nitrogen contents: NY/T 1116—2014[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. |
| [1] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [2] | 樊珂宇, 高原, 赖子尼, 曾艳艺, 刘乾甫, 李海燕, 麦永湛, 杨婉玲, 魏敬欣, 孙金辉, 王超. 珠三角河网鱼类微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598. |
| [3] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [4] | 谢晨敏, 隆楚月, 黎大宁, 朱春友, 彭先芝, 孙毓鑫, 罗孝俊, 张黎, 麦碧娴. 南海永兴岛和东岛土壤中微塑料和卤代阻燃剂的分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1008-1014. |
| [5] | 陈碧珊, 郑康慧, 王璟, 叶林海, 宋军霞. 雷州半岛土壤-农作物汞元素含量特征与健康风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 572-582. |
| [6] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| [7] | 谢洁芬, 章家恩, 危晖, 刘自强, 陈璇. 土壤中微塑料复合污染研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2431-2440. |
| [8] | 姜晶, 阮呈杰, 陈霄宇, 吴仪, 汪永创. 微塑料模拟老化及其对污染物吸附行为影响研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2263-2274. |
| [9] | 雷雅杰, 李雪, 常春艳, 毛雪飞. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对水中汞离子的吸附研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2048-2057. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
