生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 2048-2057.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.013
收稿日期:2022-05-22
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*毛雪飞(1983年生),男,研究员,博士,研究方向为农产品与环境质量安全。E-mail: mxf08@163.com, maoxuefei@caas.cn作者简介:雷雅杰(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为农产品质量与安全。
基金资助:
LEI Yajie, LI Xue, CHANG Chunyan, MAO Xuefei*( )
)
Received:2022-05-22
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
微塑料(MPs)和重金属汞(Hg)之间的相互作用会对水环境及水生生物产生潜在危害,目前尚缺乏水环境中MPs对Hg吸附行为的系统研究。利用直接进样测汞仪、场发射扫描电镜-能谱仪和傅里叶变换红外光谱仪等手段,研究不同吸附时间、溶液pH、离子强度、PS-MPs粒径、环境温度等条件下PS-MPs对Hg2+的吸附行为以及相关的物化参数,探究环境中广泛存在的聚苯乙烯微塑料(PS-MPs)与水环境中Hg2+之间的相互作用,评价PS-MPs和Hg的环境行为。结果表明,平均粒径为60 μm的PS-MPs能在数分钟内快速吸附Hg2+,在4 h内达到吸附平衡;PS-MPs对Hg2+的吸附动力学符合准二级动力学模型,吸附等温线遵循Freundlich模型。其对Hg2+的最大吸附量为291.03 ng·mg-1,在此范围内溶液中Hg2+含量越高,PS-MPs的吸附量越大。吸附过程存在多个吸附阶段且以非线性多分子层吸附机制为主,结合能谱和红外光谱结果证明了PS-MPs与Hg2+的吸附过程主要包括静电、范德华力和化学络合吸附作用。另外,该研究还发现当溶液pH为7.0时,PS-MPs对100 ng·g-1 Hg2+的平衡吸附量最大,约为41.51 ng·mg-1;温度越高,粒径更小的PS-MPs对Hg2+的平衡吸附量大;溶液中离子强度越高,Hg2+吸附量降低。该论文为实际环境中PS-MPs和重金属Hg的混合污染治理提供了一定的理论参考,今后还需进一步研究PS-MPs和Hg结合对水生生物的生物效应。
中图分类号:
雷雅杰, 李雪, 常春艳, 毛雪飞. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对水中汞离子的吸附研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2048-2057.
LEI Yajie, LI Xue, CHANG Chunyan, MAO Xuefei. Adsorption of Mercury Ions in Water by Polystyrene Microplastics[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2048-2057.
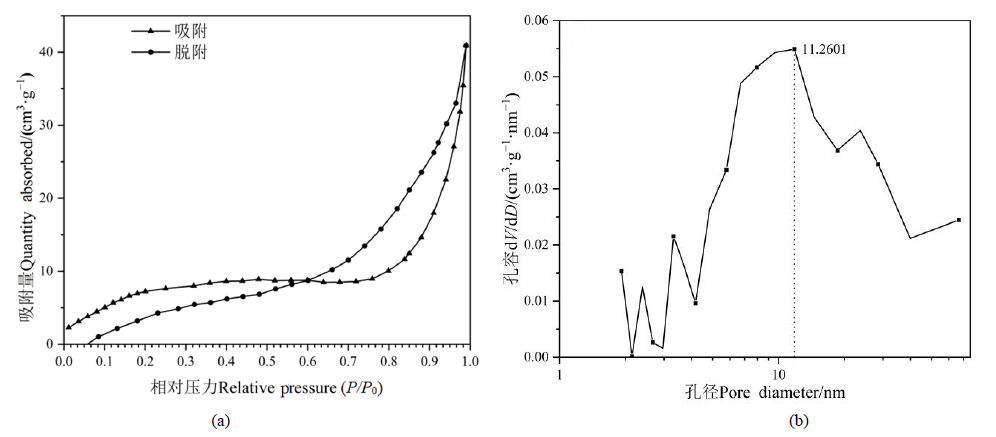
图1 不同N2相对压力下的吸附和解吸附曲线(a)和不同孔径下的孔容(b)
Figure 1 Adsorption and desorption curves under different N2 relative pressures (a) and pore volume under different pore diameters (b)
| 准一级动力学模型Pesudo-first order kinetic model | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second order kinetic mode | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe/(ng·mg-1) | k1/min-1 | R12 | Qe/(ng·mg-1) | k2/(g·ng-1·min-1) | R22 | |
| 31.540 | 0.027 | 0.955 | 33.184 | 0.00117 | 0.967 | |
表1 PS-MPs吸附Hg2+的吸附动力学拟合参数
Table 1 Fitting parameters of adsorption kinetics of Hg2+ on PS-MPs
| 准一级动力学模型Pesudo-first order kinetic model | 准二级动力学模型 Pseudo-second order kinetic mode | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe/(ng·mg-1) | k1/min-1 | R12 | Qe/(ng·mg-1) | k2/(g·ng-1·min-1) | R22 | |
| 31.540 | 0.027 | 0.955 | 33.184 | 0.00117 | 0.967 | |
| Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax/(ng·mg-1) | KL/(L·ng-1) | R12 | Kf/(mL3·g-1) | n | R22 | |
| 291.03 | 0.00115 | 0.945 | 496.80 | 0.0866 | 0.952 | |
表2 PS-MPs吸附Hg2+的吸附等温线参数
Table 2 Adsorption isotherm parameters for the adsorption of Hg2+ by PS-MPs
| Langmuir模型 Langmuir model | Freundlich模型 Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax/(ng·mg-1) | KL/(L·ng-1) | R12 | Kf/(mL3·g-1) | n | R22 | |
| 291.03 | 0.00115 | 0.945 | 496.80 | 0.0866 | 0.952 | |
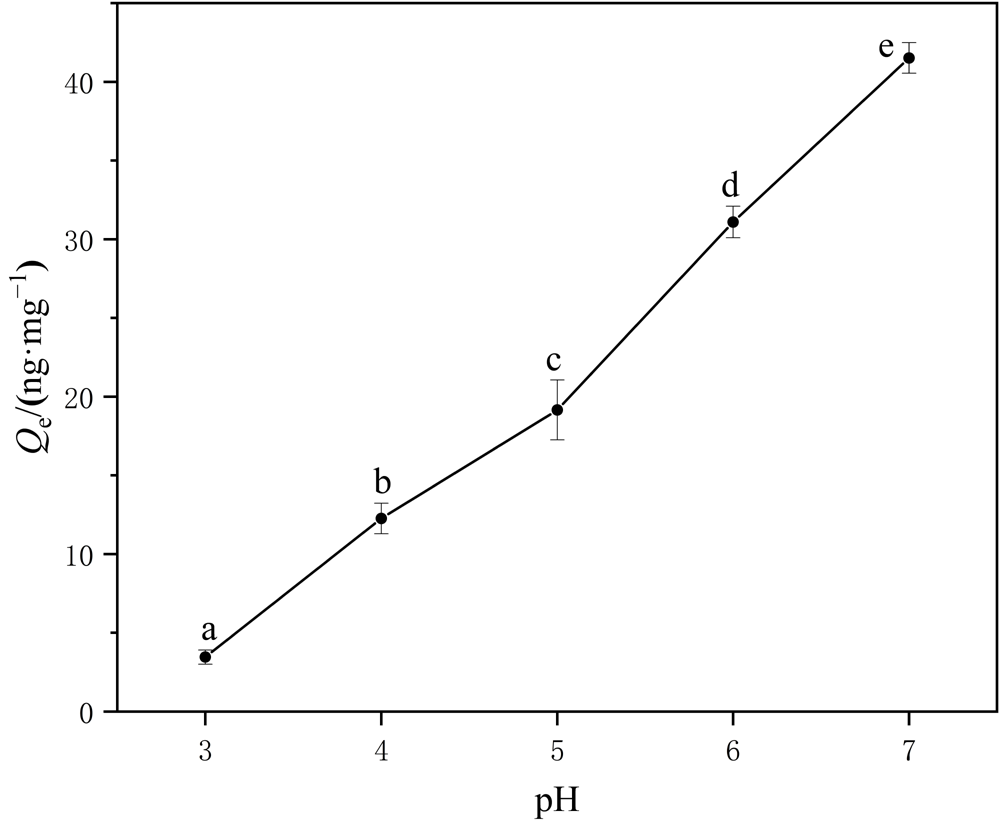
图8 PS-MPs在不同pH条件下对Hg2+的吸附 不同字母(a、b、c、d、e)代表不同pH条件下之间吸附量的显著差异(P<0.05)
Figure 8 Adsorption of Hg2+ by PS-MPs under different pH values The different letters (a, b, c, d and e) are significantly different for adsorption levels among different pH values
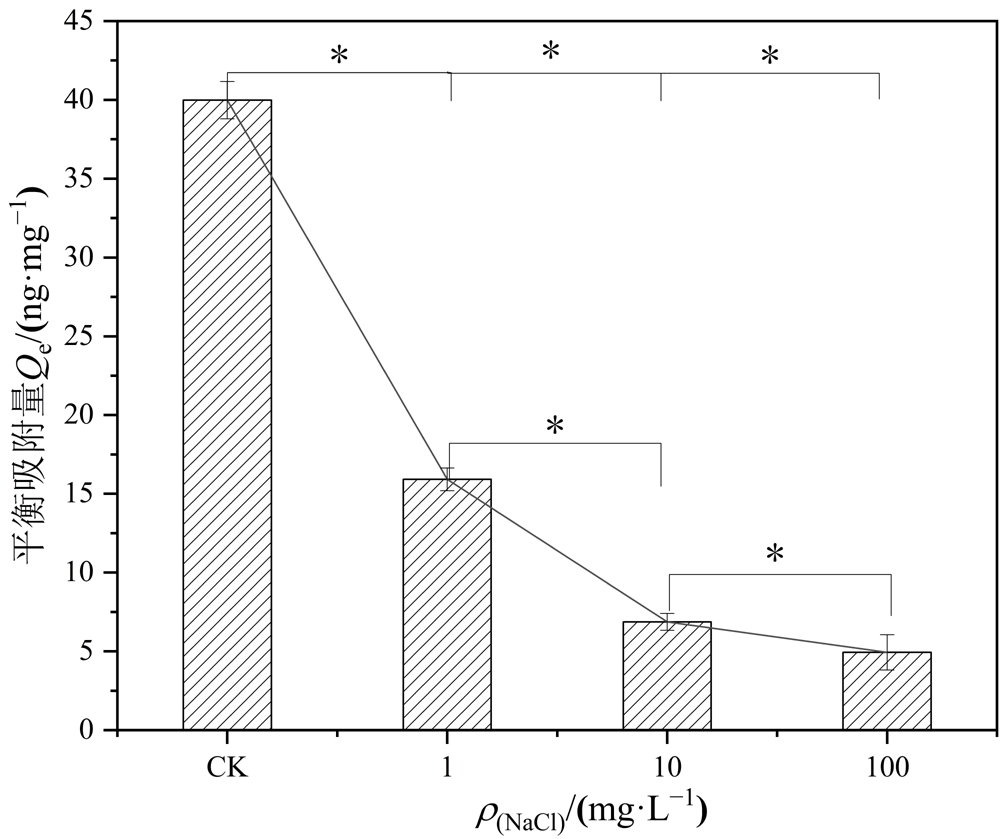
图9 PS-MPs在不同离子强度条件下对Hg2+的吸附 “*”代表不同离子强度之间吸附量的显著差异(P<0.05)
Figure 9 Adsorption of Hg2+ by PS-MPs under different ionic levels between adsorption levels and different ionic levels “*” are significantly different (P<0.05)
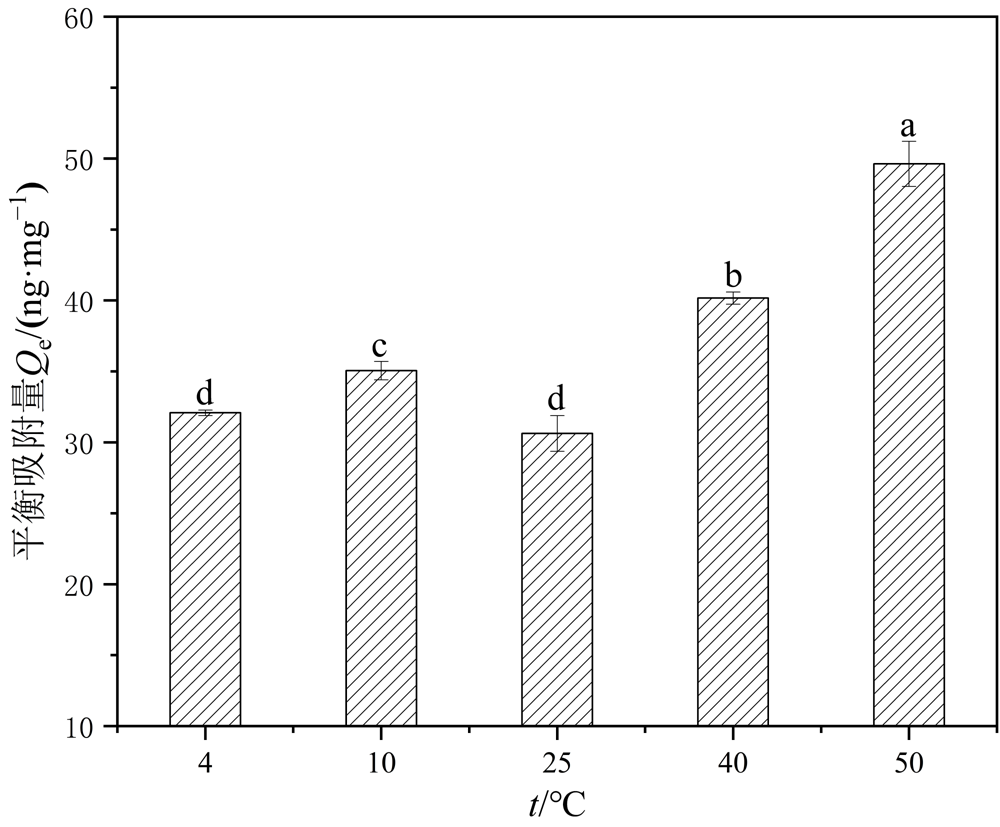
图10 PS-MPs在不同温度情况下对Hg2+的吸附 不同字母(a、b、c、d)代表不同温度下吸附量的显著差异(P<0.05)
Figure 10 Adsorption of Hg2+ by PS-MPs at different temperatures The different letters (a, b, c and d) are significantly different for adsorption levels among different temperatures
| 元素 Elements | 60 μm PS-MPs | 400 nm PS-MPs | 60 μm PS-MPs-Hg2+ | 400 nm PS-MPs-Hg2+ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均质量数Weight | 平均原子数Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | ||||
| C K | 91.038% | 93.299% | 0.434% | 93.586% | 95.381% | 0.470% | 95.974% | 97.627% | 0.499% | 95.807% | 97.521% | 0.490% | |||
| O K | 8.688% | 6.684% | 0.495% | 6.004% | 4.594% | 0.512% | 3.028% | 2.313% | 0.478% | 3.162% | 2.416% | 0.471% | |||
| Hg L | 0.274% | 0.017% | 0.494% | 0.410% | 0.025% | 0.727% | 0.998% | 0.061% | 0.887% | 1.031% | 0.063% | 0.830% | |||
表3 PS-MPs吸附Hg2+前后的平均质量数和平均原子数
Table 3 Average mass number and average atom number before and after adsorption of Hg2+ by PS-MPs
| 元素 Elements | 60 μm PS-MPs | 400 nm PS-MPs | 60 μm PS-MPs-Hg2+ | 400 nm PS-MPs-Hg2+ | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均质量数Weight | 平均原子数Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | 平均质量数 Weight | 平均原子数 Atomic | 误差 Error | ||||
| C K | 91.038% | 93.299% | 0.434% | 93.586% | 95.381% | 0.470% | 95.974% | 97.627% | 0.499% | 95.807% | 97.521% | 0.490% | |||
| O K | 8.688% | 6.684% | 0.495% | 6.004% | 4.594% | 0.512% | 3.028% | 2.313% | 0.478% | 3.162% | 2.416% | 0.471% | |||
| Hg L | 0.274% | 0.017% | 0.494% | 0.410% | 0.025% | 0.727% | 0.998% | 0.061% | 0.887% | 1.031% | 0.063% | 0.830% | |||
| [1] |
BARUS B S, CHEN K, CAI M G, et al., 2021. Heavy metal adsorption and release on polystyrene particles at various salinities[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8: 671802-671815.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN C, WEI F, YE L, et al., 2022. Adsorption of Cu2+ by UV aged polystyrene in aqueous solution[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 232: 113292-113298.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
COSTA J P D, SANTOS P S M, DUARTE A C, et al., 2016. (Nano) plastics in the environment-sources, fates and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 566-567(1): 15-26.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CÓZAR A, ECHEVARRÍA F, GONZÁLEZ-GORDILLO J I, et al., 2014. Plastic debris in the open ocean[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 111(28): 10239-10244. |
| [5] |
DONG Y M, GAO M L, SONG Z G, et al., 2020. As(III) adsorption onto different-sized polystyrene microplastic particles and its mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 239: 124792-124802.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FANG S, YU W S, LI C L, et al., 2019. Adsorption behavior of three triazole fungicides on polystyrene microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 691(15): 1119-1126.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GAO F L, LI J X, SUN C J, et al., 2019. Study on the capability and characteristics of heavy metals enriched on microplastics in marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 144(7): 61-67.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GODOY V, BLAZQUEZ G, CALERO M, et al., 2019. The potential of microplastics as carriers of metals[J]. Enviromental Pollution, 255(3): 113363-113374.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HOLMES L A, TURNER A, THOMPSON R C, 2012. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment[J]. Environment Pollution, 160: 42-48.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HOLMES L A, TURNER A, THOMPSON R C, 2014. Interactions between trace metals and plastic production pellets under estuarine conditions[J]. Marine Chemistry, 167(12): 25-32.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HU J Q, YANG S Z, GUO L, et al., 2017. Microscopic investigation on the adsorption of lubrication oil on microplastics[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 227: 351-355.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
JÄRUP L, 2003. Hazards of heavy metal contamination[J]. British Medical Bulletin, 68: 167-182.
PMID |
| [13] |
LANG M F, YU X Q, LIU J H, et al., 2020. Fenton aging significantly affects the heavy metal adsorption capacity of polystyrene microplastics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 722: 137762-137770.
DOI URL |
| [14] | LANGSTON W J, BEBIANNO M J, 1998. Metal metabolism in aquatic environments[M]. Boston: Springer-Verlag:1-449. |
| [15] |
LAW K L, THOMPSON R C, 2014. Microplastics in the seas[J]. Science, 345(6193): 144-145.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI J, ZHANG K N, ZHANG H, 2018. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics[J]. Environmental Pollution, 237(6): 460-467.
DOI URL |
| [17] | LI Y H, ZHANG Y, SU F, et al., 2022. Adsorption behaviour of microplastics on the heavy metal Cr(VI) before and after ageing[J]. Chemosphere, Chemosphere, 302: 134865-134873. |
| [18] |
LIN Z K L, HU Y W, YUAN Y J, et al., 2021. Comparative analysis of kinetics and mechanisms for Pb(II) sorption onto three kinds of microplastics[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208: 111451-111458.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU G Z, ZHU Z L, YANG Y X, et al., 2019. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater[J]. Environmental Pollution, 246(3): 26-33.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LU S H, ZHU K R, SONG W C, et al., 2018. Impact of water chemistry on surface charge and aggregation of polystyrene microspheres suspensions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 630: 951-959.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MA Y N, HUANG A N, CAO S Q, et al., 2016. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water[J]. Environmental Pollution, 219: 166-173.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | MASON S A, GARNEAU D, SUTTON R, et al., 2016. Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent[J]. Environtal Pollution, 218: 1045-1054. |
| [23] | MEAD J, 1981. A comparison of the langmuir, freundlich and temkin equations to describe phosphate adsorption properties of soils[J]. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 19(3): 333-342. |
| [24] |
NANTHAMATHEE C, DECHATIWONGSE P, 2021. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of neutral dye removal from water using zirconium metal-organic framework analogues[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 258: 123924-123939.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
NAQASH N, PRAKASH S, KAPOOR D, et al., 2020. Interaction of freshwater microplastics with biota and heavy metals: a review[J]. Environment Chemistry Letters, 18(6): 1813-1824.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
NAUGHTON M M, JAMES R O, 1974. Adsorption of aqueous mercury (II) complexes at the oxide/water interface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 47(2): 431-440.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
NG E L, LWANGA E H, ELDRIDGE S M, et al., 2018. An overview of microplastic and nanoplastic pollution in agroecosystems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 627: 1377-1388.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
QIAO R X, LU K, DENG Y F, et al., 2019. Combined effects of polystyrene microplastics and natural organic matter on the accumulation and toxicity of copper in zebrafish[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 682: 128-137.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
RAHMAN M M, MUTTAKIN M, PAL A, et al., 2019. A statistical approach to determine optimal models for IUPAC-classified adsorption isotherms[J]. Energies, 12(23): 4565-4598.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
RISHER J F, ROSA C T D, 2007. Inorganic: The other mercury[J]. Journal of Environmental Health, 70(4): 9-16.
PMID |
| [31] |
SAHA S, BAKER G L, 2015. Substituent effects in surface-initiated ATRP of substituted styrenes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 359: 911-916.
DOI URL |
| [32] | SING K S W, EVERETT D H, HAUL R A W, et al., 1985. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity[J]. Pure & Applied Chemistry, 57(4): 603-619. |
| [33] |
TANG S, LIN L J, WANG X S, et al., 2021. Interfacial interactions between collected nylon microplastics and three divalent metal ions (Cu(II), Ni(II), Zn(II)) in aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403: 123548-123558.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
THOMPSON R C, OLSEN Y, MITCHELL R P, et al., 2004. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic?[J]. Science, 304(5672): 838.
PMID |
| [35] |
TONCÓN-LEAL C F, VILLARROEL-ROCHA J, SILVA M T P, et al., 2021. Characterization of mesoporous region by the scanning of the hysteresis loop in adsorption-desorption isotherms[J]. Adsorption, 27(7): 1109-1122.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG C H, JIAN Z, XING B S, 2021. Environmental source, fate, and toxicity of microplastics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 407: 124357-124373.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
WANG J, LIU X H, LIU G N, et al., 2019. Size effect of polystyrene microplastics on sorption of phenanthrene and nitrobenzene[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 173(3): 331-338.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WRIGHT S L, THOMPSON R C, GALLOWAY T S, 2013. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review[J]. Environment Pollution, 178: 483-492.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WRIGHT S L, KELLY F J, 2017. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue?[J]. Environmental Science &Technology, 51(12): 6634-6647.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
XIA M D, CHEN Z X, LI Y, et al., 2019. Removal of Hg(ii) in aqueous solutions through physical and chemical adsorption principles[J]. RSC Advances, 9(36): 20941-20953.
DOI URL |
| [41] | YIN Y J, ALLEN H E, LI Y M, et al., 1996. Adsorption of mercury(II) by soil: Effects of pH, chloride, and organic matter[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25(4): 837-844. |
| [42] |
YIN Y Y, GUO X T, PENG D, 2018. Iron and manganese oxides modified maize straw to remove tylosin from aqueous solutions[J]. Chemosphere, 205(8): 156-165.
DOI URL |
| [43] | YU A Q, SUN X, TANG S, et al., 2021. Adsorption mechanism of cadmium on polystyrene microplastics containing hexabromocyclododecane[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 24: 102036-102046. |
| [44] | YU R M, SHI Y Z, YANG D Z, et al., 2017. Graphene oxide/chitosan aerogel microspheres with honeycomb-cobweb and radially oriented microchannel structures for broad-spectrum and rapid adsorption of water contaminants[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(26): 21809-21819. |
| [45] |
YUAN W K, ZHOU Y F, CHEN Y L, et al., 2020. Toxicological effects of microplastics and heavy metals on the Daphnia magna[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 746: 141254-141263.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHOU Z Q, SUN YR, WANG Y Y, et al., 2022. Adsorption behavior of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) on aged microplastics in antibiotics-heavy metals coexisting system[J]. Chemosphere, 291(1): 132794-132801.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 杨宏旻, 曹晏, 潘伟平, 2006. 吸附剂的汞吸附特性实验[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 12(6): 5-10. |
| YANG H M, CAO Y, PAN W P, 2006. Experimental investigation on elemental mercury adsorption characteristics of sorbents[J]. Journal of Combustion Sciense and Technology, 12(6): 5-10. | |
| [48] | 国家环境保护局, 1996. 污水综合排放标准: GB 8978—1996[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 1996. Integrated wastewater discharge standard: GB 8978—1996[M]. Beijing: China Quality and Standards Publishing & Media Co., Ltd. |
| [1] | 杨宇, 邓仁健, 隆佩, 黄中杰, 任伯帜, 王政华. 砷氧化菌Pseudomonas sp. AO-1的分离鉴定及其对As(Ⅲ)的氧化性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [2] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [3] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [4] | 汤家喜, 向彪, 李玉, 谭婷, 朱永乐, 甘建平. 硅藻土对水中氟化物的吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 335-343. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
