生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1814-1820.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.005
宋贤冲1,2,3( ), 蔡雪梅4, 陈韬4, 潘文1,2, 石媛媛1,2,3, 唐健1,2,3, 曹继钊1,2,3,*(
), 蔡雪梅4, 陈韬4, 潘文1,2, 石媛媛1,2,3, 唐健1,2,3, 曹继钊1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-10-10
出版日期:2021-09-18
发布日期:2021-12-08
通讯作者:
*曹继钊(1972年生),男,教授级高级工程师,研究方向为森林土壤、森林生态、植物营养与测土配方施肥等。E-mail: jizhaocao@126.com作者简介:宋贤冲(1986年生),男,博士,主要研究方向为森林土壤与土壤微生物。E-mail: songxc123@126.com
基金资助:
SONG Xianchong1,2,3( ), CAI Xuemei4, CHEN Tao4, PAN Wen1,2, SHI Yuanyuan1,2,3, TANG Jian1,2,3, CAO Jizhao1,2,3,*(
), CAI Xuemei4, CHEN Tao4, PAN Wen1,2, SHI Yuanyuan1,2,3, TANG Jian1,2,3, CAO Jizhao1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-10-10
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
摘要:
萌芽更新是除植苗更新外桉树人工林再造林的最主要方式,且省时省力、成本低、短期内可取得较高的经济收益。探讨萌芽更新对桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的影响,可以为桉树人工林土壤健康和可持续经营提供理论依据和技术支持。采用时空代换的方法,以桉树新造林、一代萌芽更新林和二代萌芽更新林根际和非根际土壤为研究对象,探究不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤的养分变化特征。结果表明,根际和非根际土壤pH随萌芽代次增加而下降,但不同萌芽代次间根际土壤pH差异不显著(P>0.05),非根际土壤pH差异显著(P=0.015)。土壤有机质随着萌芽代次的增加呈现先下降后上升的趋势,新造林根际和非根际均显著高于一代萌芽林(P=0.001和P=0.026)。随着萌芽代次的增加,根际和非根际土壤中氮元素大体上呈增加的趋势,但不同代次间差异不显著(P>0.05)。不同萌芽代次的根际和非根际土壤磷元素大体上呈先下降后上升的趋势,一代萌芽林根际和非根际土壤磷元素含量均最低,且与新造林之间差异显著(P=0.025,0.015和P=0.037,0.010)。不同萌芽代次之间钾元素含量的变化趋势与磷元素完全相反。不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的主成分分析结果表明,根际土壤前两个主成分的累积贡献率达到86.92%,在主成分1方向,萌芽代次对桉树人工林根际土壤养分的影响主要体现在有机质、磷和钾养分含量等指标;非根际土前两个主成分的累积贡献率达到72.77%,在主成分1方向,萌芽代次对桉树人工林非根际土壤养分的影响主要体现在磷和钾养分含量等指标。综上,土壤有机质和磷、钾元素在评价萌芽更新桉树人工林综合地力中占首要地位,提高多代萌芽更新桉树人工林土壤有机质和磷、钾养分含量对保持桉树人工林土壤健康和可持续经营具有积极的意义。
中图分类号:
宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820.
SONG Xianchong, CAI Xuemei, CHEN Tao, PAN Wen, SHI Yuanyuan, TANG Jian, CAO Jizhao. Variation Characteristics of Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil Nutrient in Successive Eucalyptus Plantation[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820.
| 林分 Stand | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新造林 New afforestation | 4.23±0.06a | 95.54±10.90a | 2.47±0.19a | 1.10±0.18a | 2.94±0.06c | 188.77±11.28a | 6.63±1.62a | 46.60±16.69b |
| 一代萌芽林 First generation coppice plantation | 4.19±0.09a | 51.85±0.71b | 2.56±0.19a | 0.83±0.03b | 14.57±0.13a | 199.39±17.55a | 3.20±0.520b | 74.85±1.85a |
| 二代萌芽林 Second generation coppice plantation | 4.11±0.12a | 63.94±10.65b | 2.66±0.36a | 1.06±0.08a | 7.48±0.27b | 238.33±35.97a | 4.40±1.40ab | 72.40±8.46a |
表1 不同萌芽代次桉树人工林根际土壤养分特征
Table 1 Soil nutrient characteristics of rhizosphere under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 林分 Stand | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新造林 New afforestation | 4.23±0.06a | 95.54±10.90a | 2.47±0.19a | 1.10±0.18a | 2.94±0.06c | 188.77±11.28a | 6.63±1.62a | 46.60±16.69b |
| 一代萌芽林 First generation coppice plantation | 4.19±0.09a | 51.85±0.71b | 2.56±0.19a | 0.83±0.03b | 14.57±0.13a | 199.39±17.55a | 3.20±0.520b | 74.85±1.85a |
| 二代萌芽林 Second generation coppice plantation | 4.11±0.12a | 63.94±10.65b | 2.66±0.36a | 1.06±0.08a | 7.48±0.27b | 238.33±35.97a | 4.40±1.40ab | 72.40±8.46a |
| 林分 Stand | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新造林 New Afforestation | 4.36±0.12a | 57.51±2.50a | 2.17±0.34a | 1.02±0.17a | 2.98±0.41c | 136.87±53.35a | 7.13±1.53a | 55.33±10.01b |
| 一代萌芽林 First Generation Coppice Plantation | 4.24±0.11ab | 48.62±3.93b | 2.40±0.11a | 0.80±0.01b | 14.30±1.22a | 183.96±6.62a | 3.65±1.25b | 80.35±3.45a |
| 二代萌芽林 Second Generation Coppice Plantation | 4.06±0.10b | 53.20±4.40ab | 2.21±0.08a | 0.99±0.02ab | 6.85±0.53b | 179.72±19.04a | 3.20±0.10b | 45.77±9.48b |
表2 不同萌芽代次桉树人工林非根际土壤养分特征
Table 2 Soil nutrient characteristics of non-rhizosphere under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 林分 Stand | pH | w(OM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TP)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TK)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新造林 New Afforestation | 4.36±0.12a | 57.51±2.50a | 2.17±0.34a | 1.02±0.17a | 2.98±0.41c | 136.87±53.35a | 7.13±1.53a | 55.33±10.01b |
| 一代萌芽林 First Generation Coppice Plantation | 4.24±0.11ab | 48.62±3.93b | 2.40±0.11a | 0.80±0.01b | 14.30±1.22a | 183.96±6.62a | 3.65±1.25b | 80.35±3.45a |
| 二代萌芽林 Second Generation Coppice Plantation | 4.06±0.10b | 53.20±4.40ab | 2.21±0.08a | 0.99±0.02ab | 6.85±0.53b | 179.72±19.04a | 3.20±0.10b | 45.77±9.48b |
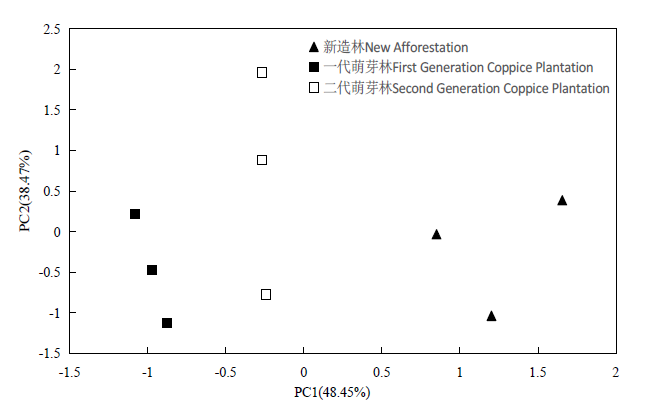
图1 不同萌芽代次桉树人工林根际土壤养分的主成分分析
Fig. 1 Principal component analysis of nutrient characteristics of rhizosphere soil under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 主成分 Principal Component | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 水解性氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | 0.388 | 0.958 | -0.242 | 0.731 | -0.926 | -0.303 | 0.870 | -0.713 |
| 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | -0.794 | 0.194 | 0.923 | 0.588 | -0.169 | 0.911 | 0.402 | 0.440 |
表3 根际土壤养分的载荷因子
Table 3 Loading factors of principal components of soil nutrient characteristics of rhizosphere under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 主成分 Principal Component | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 水解性氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | 0.388 | 0.958 | -0.242 | 0.731 | -0.926 | -0.303 | 0.870 | -0.713 |
| 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | -0.794 | 0.194 | 0.923 | 0.588 | -0.169 | 0.911 | 0.402 | 0.440 |
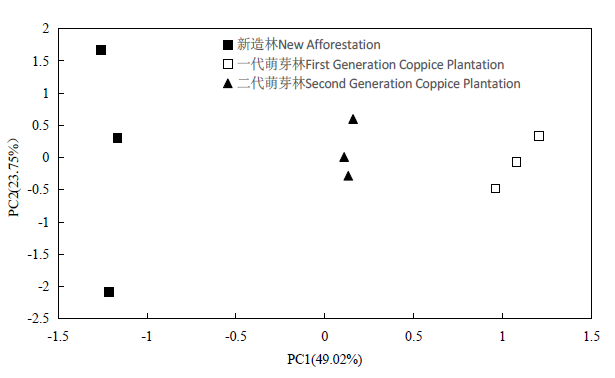
图2 不同萌芽代次桉树人工林非根际土壤养分的主成分分析
Fig. 2 Principal component analysis of nutrient characteristics of non-rhizosphere soil under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 主成分 Principal Component | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 水解性氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | -0.419 | -0.321 | 0.466 | -0.680 | 0.956 | 0.593 | -0.827 | 0.760 |
| 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | 0.152 | 0.419 | 0.834 | 0.608 | 0.028 | 0.727 | 0.257 | 0.201 |
表4 非根际土壤养分的载荷因子
Table 4 Loading factors of principal components of nutrient characteristics of non-rhizosphere soil under coppice regenerated Eucalyptus plantation
| 主成分 Principal Component | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 全钾 Total potassium | 水解性氮 Available nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal Component 1 | -0.419 | -0.321 | 0.466 | -0.680 | 0.956 | 0.593 | -0.827 | 0.760 |
| 主成分2 Principal Component 2 | 0.152 | 0.419 | 0.834 | 0.608 | 0.028 | 0.727 | 0.257 | 0.201 |
| [1] |
SUN H, WANG Q X, LIU N, et al., 2017. Effects of different leaf litters on the physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in Panax ginseng growing soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 111: 17-24.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WEN Y G, YE D, CHEN F, et al., 2010. The changes of understory plant diversity in continuous cropping system of Eucalyptus plantations, South China[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 15(4): 252-258.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHU L Y, WANG X H, CHEN F F, et al., 2019. Effects of the successive planting of Eucalyptus urophylla on soil bacterial and fungal community structure, diversity, microbial biomass, and enzyme activity[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 30(6): 636-646.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 陈灿灿, 马红亮, 高人, 等, 2021. 施氮与凋落物去除影响下中亚热带阔叶林土壤氮素矿化潜势和硝化潜势研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 503-511. |
| CHEN C C, MA H L, GAO R, et al., 2021. Study on the potential of nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in mid-subtropical broad-leaved forest soil already treated with nitrogen addition and litter removal[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 503-511. | |
| [5] | 陈立新, 段文标, 乔璐, 2011. 落叶松人工林根际与非根际土壤养分特征及酸度研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(3): 131-135. |
| CHEN L X, DUAN W B, QIAO L, 2011. Study on nutriention characteristics and acidity in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils in Larch plantations[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(3): 503-511. | |
| [6] | 段文军, 王金叶, 2013. 广西喀斯特和红壤地区桉树人工林土壤理化性质对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(4): 595-597. |
| DUAN W J, WANG J Y, 2013. Comparative study on the physical and chemical properties of eucalyptus plantation soil in Guangxi Karst and red soil area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(4): 595-597. | |
| [7] | 吉艳芝, 冯万忠, 陈立新, 等, 2008. 落叶松混交林根际与非根际土壤养分、微生物和酶活性特征[J]. 生态环境, 17(1): 339-343. |
| JI Y Z, FENG W Z, CHEN L X, et al., 2008. Soil nutrition, microorganisms and enzyme activity of the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of mixed plantation of Larix[J]. Ecology and Environment, 17(1): 339-343. | |
| [8] | 李宝福, 张金文, 赖彦斌, 等, 1999. 巨尾桉根际与非根际土壤酶活性的研究[J]. 福建林业科技 (S1): 17-20. |
| LI B F, ZHANG J W, LAI Y B, et al., 1999. Soil enzyme activity of the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of Eucalyptus grandis×E. urophylla plantations[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology (S1): 17-20. | |
| [9] | 李朝婷, 周晓果, 温远光, 等, 2019. 桉树高代次连栽对林下植物、土壤肥力和酶活性的影响[J]. 广西科学, 26(2): 176-187. |
| LI C T, ZHOU X G, WEN Y G, et al., 2019. Effects of high-generation ratations of Eucalyptus on under-growth, soil fertility and enzyme activities[J]. Guangxi Sciences and Technology, 26(2): 176-187. | |
| [10] | 李明臣, 2007. 桉树林取代马尾松疏林后群落组成结构与土壤理化性质的变化[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| LI M C, 2007. Effects of Eucalyptus plantation replacing open Pinus massoniana forest on community compositions and soil physical- chemical proprieties[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [11] | 李远航, 2016. 连栽桉树人工林土壤磷素形态变化及吸附-解吸特征[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| LI Y H, 2016. Characteristics of soil phosphorus forms and adsorption-desorption in continuous planting of Eucalyptus plantation[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [12] | 廖观荣, 林书蓉, 李淑仪, 等, 2002. 雷州半岛桉树人工林地力退化的现状和特征[J]. 土壤与环境, 11(1): 25-28. |
| LIAO G R, LIN S R, LI S Y, et al., 2002. The current status and characteristics of land capacity degeneration of eucalyptus plantation in Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 11(1): 25-28. | |
| [13] | 令狐荣云, 余炜敏, 王荣萍, 等, 2017. 铁还原菌Shewanella oneidensis MR-1对铁磷复合物中铁、磷释放规律的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(10): 1704-1709. |
| LINGHU R Y, YU W M, WANG R P, et al., 2017. Effects of iron-reducing bacterium strain Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 on the release of iron and phosphorus from iron/phosphorus compounds[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(10): 1704-1709. | |
| [14] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学出版社. |
| LU R K, 1999. Method for soil agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [15] | 梅杰, 周国英, 2011. 不同林龄马尾松林根际与非根际土壤微生物、酶活性及养分特征[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 31(4): 46-49. |
| MEI J, ZHOU G Y, 2011. Study of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere microbial, enzyme activity and nutrient element content of soil in different stand ages Pinus massoniana forest[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 31(4): 46-49. | |
| [16] | 明安刚, 温远光, 朱宏光, 等, 2009. 连栽对桉树人工林土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 广西林业科学, 38(1): 26-30. |
| MING A G, WEN Y G, ZHU H G, et al., 2009. Effects of continuous cropping on content of soil nutriention in Eucalyptus plantations[J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 38(1): 26-30. | |
| [17] | 宋贤冲, 杨中宁, 曹继钊, 等, 2014. 萌芽更新对桉树根际土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 桉树科技, 31(3): 36-40. |
| SONG X C, YANG Z N, CAO J Z, et al., 2014. Effect of sprout regeneration on the microbial functional diversity in rhizosphere soil of Eucalyptus [J]. Eucalypt Science and Technology, 31(3): 36-40. | |
| [18] | 宋贤冲, 项东云, 郭丽梅, 等, 2016. 猫儿山森林土壤养分的空间变化特征[J]. 森林与环境学报, 36(3): 349-354. |
| SONG X C, XIANG D Y, GUO L M, et al., 2014. Spatial variation pattern of soil nutrients in forests of Maoer mountain[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 36(3): 349-354. | |
| [19] | 孙启武, 杨承栋, 焦如珍, 2003. 连栽杉木人工林土壤肥力变化的主分量分析[J]. 林业科学研究, 16(6): 689-693. |
| SUN Q W, YANG C D, JIAO R Z, 2003. PCA on the soil degradation of the successive Chinese fir plantation[J]. Forest Research, 16(6): 689-693. | |
| [20] | 童琪, 陈玫婷, 龙菁琦, 等, 2019. 不同龄组南酸枣根际与非根际土壤养分特征研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 39(12): 108-113. |
| TONG Q, CHEN M T, LONG J Q, et al., 2019. Research on soil nutrient characteristics at rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere for different age groups of Choerospondias axillarist[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 39(12): 108-113. | |
| [21] | 王劲松, 2017. 两种不同更新方式巨尾桉生长及效益研究[J]. 桉树科技, 34(4): 37-41. |
| WANG J S, 2017. Study on growth and economic benefits of two different regeneration methods of Eucalyptus grandis×E. urophylla[J]. Eucalypt Science and Technology, 34(4): 37-41. | |
| [22] | 项东云, 2000. 华南地区桉树人工林生态问题的评价[J]. 广西林业科学, 29(2): 57-64, 86. |
| XIANG D Y, 2000. Evaluation of ecological problems of Eucalyptus plantation in South China[J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 29(2): 57-64, 86. | |
| [23] | 杨卫星, 庞赞松, 银彬吾, 等, 2018. 桂西南2种更新方式尾巨桉人工林生长特性的比较[J]. 广西林业科学, 47(1): 47-51. |
| YANG W X, PANG Z S, YIN B W, et al., 2018. Comparison on growth characteristics in two regeneration patterns of Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis plantation in Southwest Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Forestry Science, 47(1): 47-51. | |
| [24] | 杨玉盛, 何宗明, 邹双全, 等, 1998. 格氏栲天然林与人工林根际土壤微生物及其生化特性的研究[J]. 生态学报, 18(2): 3-5. |
| YANG Y S, HE Z M, ZOU S Q, et al., 1998. A study on the soil microbes and biochemistry of rhizospheric and total soil in natural forest and plantation of Castanopsis kauakamii[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 18(2): 3-5. | |
| [25] | 杨远彪, 吕成群, 黄宝灵, 等, 2008. 连栽桉树人工林土壤微生物和酶活性的分析[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 36(12): 10-12. |
| YANG Y B, LV C Q, HUANG B L, et al., 2008. Soil microbes and enzymes in Eucalyptus plantations under different rotations of continuously planting[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 36(12): 10-12. | |
| [26] | 杨章旗, 2019. 广西桉树人工林引种发展历程与可持续发展研究[J]. 广西科学, 26(4): 355-361. |
| YANG Z Q, 2019. Development history and sustainable development of Eucalyptus plantations introduction in Guangxi[J]. Guangxi Sciences and Technology, 26(4): 355-361. | |
| [27] | 叶绍明, 温远光, 张慧东, 2010. 连栽桉树人工林土壤理化性质的主分量分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 30(5): 104-108. |
| YE S M, WEN Y G, ZHANG H D, 2010. Principal component analysis of soil physical and chemical properties in successive Eucalyptus plantation[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(5): 104-108. | |
| [28] | 尤业明, 陈永康, 朱宏光, 等, 2019. 桉树人工林更新方式对林下植物功能群的影响[J]. 广西植物, 39(1): 126-135. |
| YOU Y M, CHEN Y K, ZHU H G, et al., 2019. Effects of different regeneration modes on understory plant functional group in Eucalyptus plantation[J]. Guihaia, 39(1): 126-135. | |
| [29] | 余雪标, 白先权, 徐大平, 等, 1999. 不同连栽代次桉树人工林的养分循环[J]. 热带作物学报, 20(3): 3-5. |
| YU X B, BAI X Q, XU D P, et al., 1999a. Nutrient cycle of Eucalyptus plantation with different continuous-planting rotations[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 20(3): 3-5. | |
| [30] | 占丽平, 李小坤, 鲁剑巍, 等, 2012. 土壤钾素运移的影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, 44(4): 548-553. |
| ZHAN L P, LI X K, LU J W, et al., 2012. Research advances on influence factors of soil potassium movement[J]. Soils, 44(4): 548-553. | |
| [31] | 张昌顺, 李昆, 2005. 人工林地力的衰退与维护研究综述[J]. 世界林业研究, 18(1): 17-21. |
| ZHANG C S, LI K, 2005. Advance in research on soil degradation and soil improvement of timber plantations[J]. World Forestry Research, 18(1): 17-21. | |
| [32] | 张学利, 杨树军, 张百习, 等, 2005. 不同林龄樟子松根际与非根际土壤的对比[J]. 福建林学院学报, 25(1): 80-84. |
| ZHANG X L, YANG S J, ZHANG B X, et al., 2005. Comparative research on rhizosphere soil and non-rhizosphere soil properties in different stand age of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica sand-fixation forest[J]. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 25(1): 80-84. | |
| [33] | 张义凡, 陈林, 李学斌, 等, 2017. 不同荒漠草原植被根际与非根际土壤养分及碳库管理指数特征[J]. 草业学报, 26(8): 24-34. |
| ZHANG Y F, CHEN L, LI X B, et al., 2017. Soil nutrients and carbon management indexes in the rhizosphere versus non-rhizosphere area of different plant species in desert grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 26(8): 24-34. | |
| [34] | 朱祖祥, 1983. 土壤学[M]. 北京: 农业出版社: 55-57. |
| ZHU Z X, 1983. Soil science[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Publishing House: 55-57. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [4] | 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻, 李永斌, 郭丽芳, 焦念元. 尾矿先锋植物根际溶磷菌的分离鉴定与其促生研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [5] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [6] | 喻阳华, 吴银菇, 宋燕平, 李一彤. 不同林龄顶坛花椒林地土壤微生物浓度与生物量化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [7] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [8] | 赵隽宇, 黄小芮, 石媛媛, 宋贤冲, 覃祚玉, 唐健. 南亚热带多代连栽桉树人工林根际土壤FTIR特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 688-694. |
| [9] | 梁蕾, 马秀枝, 韩晓荣, 李长生, 张志杰. 模拟增温下凋落物对大青山油松人工林土壤温室气体通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [10] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [11] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [12] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [13] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [14] | 肖军, 雷蕾, 曾立雄, 李肇晨, 马成功, 肖文发. 不同经营模式对华北油松人工林碳储量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2134-2142. |
| [15] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
