生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 222-232.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.02.005
岳航宇1,2( ), 郭成久1, 苏芳莉1,3,4,5,*(
), 郭成久1, 苏芳莉1,3,4,5,*( ), 魏超1,3,4
), 魏超1,3,4
收稿日期:2023-03-24
出版日期:2025-02-18
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
*苏芳莉。E-mail: sufangli@syau.edu.cn作者简介:岳航宇(1998年生),男,助理工程师,主要研究方向为水土保持与水生态研究。E-mail: yhy872437876@163.com
基金资助:
YUE Hangyu1,2( ), GUO Chengjiu1, SU Fangli1,3,4,5,*(
), GUO Chengjiu1, SU Fangli1,3,4,5,*( ), WEI Chao1,3,4
), WEI Chao1,3,4
Received:2023-03-24
Online:2025-02-18
Published:2025-03-03
摘要:
湿地是重要生态系统,微生物对维持其生态稳定发挥着重要作用。了解辽河口湿地不同植被类型根际土壤微生物群落结构和多样性特征对于揭示该区域植被与土壤的相互作用具有重要科学意义。以辽河口湿地为研究对象,选取芦苇分布区-芦苇根际土壤(D1)、芦苇-盐地碱蓬交错区-芦苇根际土壤(D2)、芦苇-盐地碱蓬交错区-盐地碱蓬根际土壤(D3)、盐地碱蓬分布区-盐地碱蓬根际土壤(D4)以及潮滩沉积物(D5),利用Illumina Miseq PE300高通量测序技术进行16S rRNA基因测序分析不同植被类型根际土壤微生物的多样性和群落结构特征,并探究土壤理化因子与其之间的关系。研究结果表明,1)辽河口湿地根际微生物检测出40门,95纲,184目,311科,528属,888种。2)在门水平上,变形菌门是最优势菌群。3)湿地各采样区域土壤微生物群落多样性分析表明,盐地碱蓬分布区-盐地碱蓬根际土壤微生物群落丰富度和多样性最高。4)冗余分析结果表明,土壤总氮、有机质、氯离子含量是影响土壤微生物群落结构的主要因素。研究成果可从微生态学角度为中国北方滨海湿地生态系统功能的研究和保护提供参考。
中图分类号:
岳航宇, 郭成久, 苏芳莉, 魏超. 辽河口湿地不同植被类型根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 222-232.
YUE Hangyu, GUO Chengjiu, SU Fangli, WEI Chao. Analysis of Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Community Structure and Diversity of Different Vegetation Types in Liaohe Estuary Wetland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(2): 222-232.
| 样品 | pH | w(水分)/% | 氧化还原电位(ORP)/mV | w(NO2−)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(TN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(SOM)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(Cl−)/(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 7.79±0.21a | 24.36±2.35a | 0.91±0.10a | 0.01±0.01a | 236.53±33.47b | 25.86±4.61a | 2.84±0.92a |
| D2 | 7.71±0.34a | 20.11±4.87a | 1.54±0.17a | 0.02±0.01a | 232.04±25.86b | 15.56±2.99b | 3.12±1.27a |
| D3 | 8.09±0.53a | 30.67±1.26a | 1.59±0.05a | 0.02±0.02a | 248.52±99.56b | 16.89±4.11b | 2.84±0.54a |
| D4 | 7.82±0.29a | 24.79±2.92a | 1.37±0.12a | 0.03±0.02a | 939.57±161.56b | 15.17±3.81b | 4.11±0.73a |
| D5 | 7.81±0.15a | 21.22±5.58a | 0.42±0.08a | 0.02±0.01a | 1514.50±203.42a | 15.51±2.63b | 5.86±1.71a |
表1 不同植被类型根际土壤的主要理化性质
Table 1 Main physicochemical properties of rhizosphere soil in different vegetation types
| 样品 | pH | w(水分)/% | 氧化还原电位(ORP)/mV | w(NO2−)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(TN)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(SOM)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(Cl−)/(mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 7.79±0.21a | 24.36±2.35a | 0.91±0.10a | 0.01±0.01a | 236.53±33.47b | 25.86±4.61a | 2.84±0.92a |
| D2 | 7.71±0.34a | 20.11±4.87a | 1.54±0.17a | 0.02±0.01a | 232.04±25.86b | 15.56±2.99b | 3.12±1.27a |
| D3 | 8.09±0.53a | 30.67±1.26a | 1.59±0.05a | 0.02±0.02a | 248.52±99.56b | 16.89±4.11b | 2.84±0.54a |
| D4 | 7.82±0.29a | 24.79±2.92a | 1.37±0.12a | 0.03±0.02a | 939.57±161.56b | 15.17±3.81b | 4.11±0.73a |
| D5 | 7.81±0.15a | 21.22±5.58a | 0.42±0.08a | 0.02±0.01a | 1514.50±203.42a | 15.51±2.63b | 5.86±1.71a |
| 样品 | 操作分类 单元 | Shannon 指数 | Simpson 指数 | ACE 指数 | Chao1 指数 | Coverage 指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 661 | 5.133 | 0.0187 | 730.541 | 724.424 | 0.9969 |
| D2 | 1427 | 6.154 | 0.0058 | 1511.769 | 1528.162 | 0.9944 |
| D3 | 1313 | 5.775 | 0.0134 | 1418.338 | 1426.940 | 0.9938 |
| D4 | 1448 | 6.154 | 0.0053 | 1541.361 | 1580.346 | 0.9938 |
| D5 | 1319 | 5.884 | 0.0086 | 1429.491 | 1447.250 | 0.9937 |
表2 不同植被类型根际土壤样品alpha多样性分析
Table 2 α-diversity of different vegetation types rhizosphere soil
| 样品 | 操作分类 单元 | Shannon 指数 | Simpson 指数 | ACE 指数 | Chao1 指数 | Coverage 指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 661 | 5.133 | 0.0187 | 730.541 | 724.424 | 0.9969 |
| D2 | 1427 | 6.154 | 0.0058 | 1511.769 | 1528.162 | 0.9944 |
| D3 | 1313 | 5.775 | 0.0134 | 1418.338 | 1426.940 | 0.9938 |
| D4 | 1448 | 6.154 | 0.0053 | 1541.361 | 1580.346 | 0.9938 |
| D5 | 1319 | 5.884 | 0.0086 | 1429.491 | 1447.250 | 0.9937 |
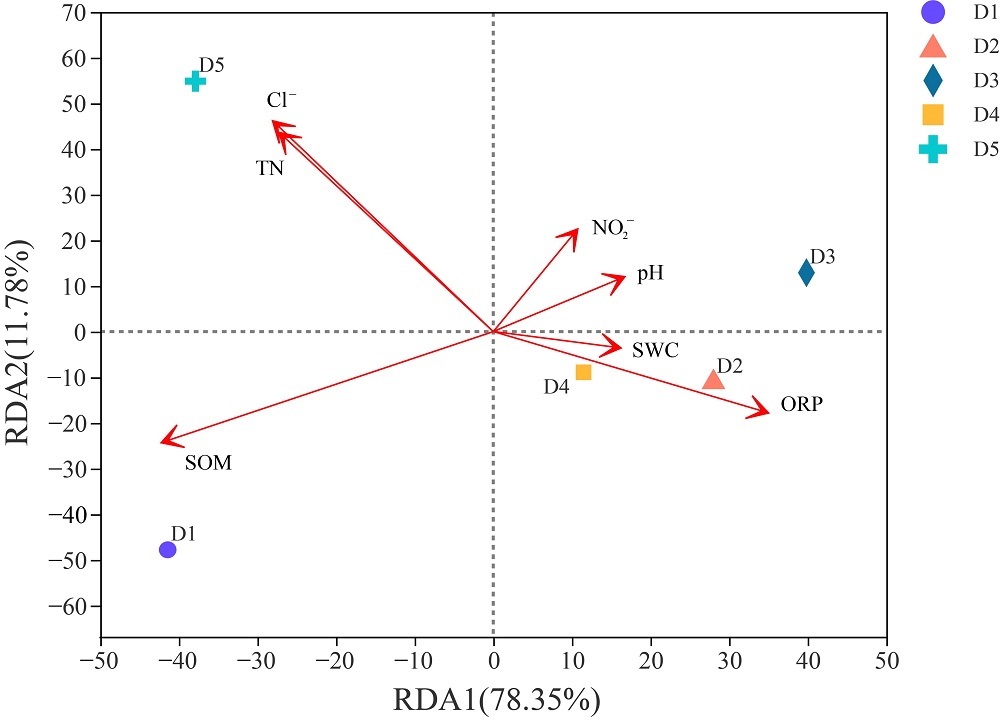
图7 土壤微生物群落结构与土壤环境因子关系的冗余分析
Figure 7 Redundancy analysis of the relationship between soil microbial community structure and soil environmental factors on phylum level
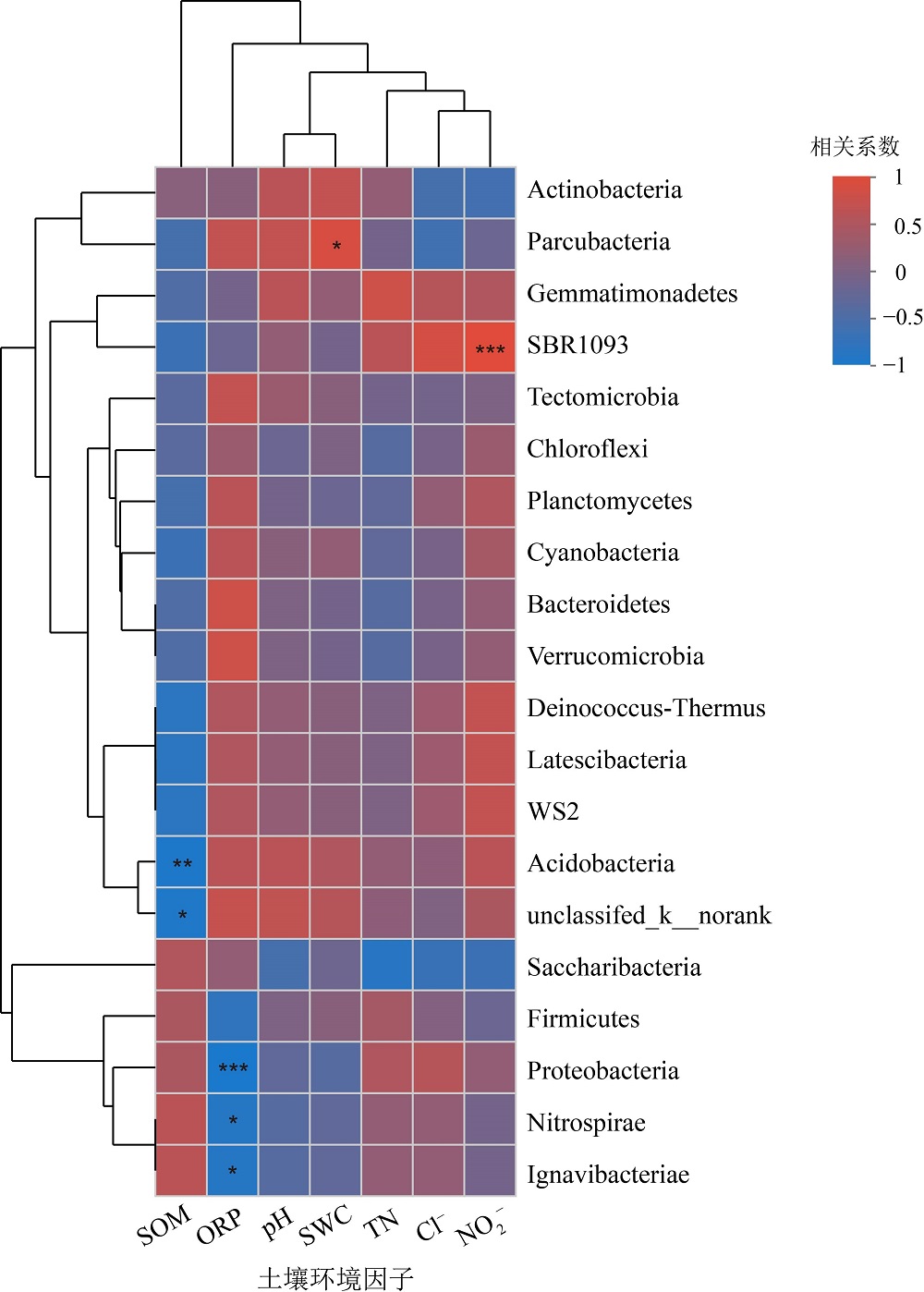
图8 不同植被类型根际土壤微生物门水平群落结构与土壤环境因子相关性分析 “*”表示0.01≤p<0.05;“**”表示0.001≤p<0.01;“***”表示p<0.001
Figure 8 Correlation analysis between soil microbial community structure and soil environmental factors in rhizosphere soil of different vegetation types on phylum level
| [1] | ALAM M Z, BAKI BHUIYAN M A, ABDULLAH H M, et al., 2021. Changes of land use and land cover with the diversity of fishes, aquatic plants, and bird’s species at wetland ecosystem[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2021: 7533119. |
| [2] | AN J X, LIU C, WANG Q, et al., 2019. Soil bacterial community structure in Chinese wetlands[J]. Geoderma, 337(2): 290-299. |
| [3] | SAN MIGUEL A, ROY J, GURY J, et al., 2014. Effects of organochlorines on microbial diversity and community structure in Phragmites australis rhizosphere[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98: 4257-4266. |
| [4] | CHAPARRO J, BADRI D, VIVANCO J, 2013. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development[J]. The International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal, 8: 790-803. |
| [5] | CHEN T, HU W G, HE S B, et al., 2021a. Diversity and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in rhizosphere soil of four plant groups in Ebinur Lake Wetland[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 67(4): 271-280. |
| [6] | CHEN L, WANG Z W, DU S, et al., 2021b. Antimicrobial activity and functional genes of Actinobacteria from coastal wetland[J]. Current Microbiology, 78: 3058-3067. |
| [7] |
COSTELLO E K, SCHMIDT S K, 2006. Microbial diversity in alpine tundra wet meadow soil: Novel Chloroflexi from a cold, water-saturated environment[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 8(8): 1471-1486.
PMID |
| [8] | DAI T J, ZHANG Y, TANG Y S, et al., 2016. Identifying the key taxonomic categories that characterize microbial community diversity using full-scale classification: A case study of microbial communities in the sediments of Hangzhou Bay[J]. Federation of European Microbiological Societies Microbiology Ecology, 92(10): fiw150. |
| [9] | HUANG W, CHEN X, WANG K, et al., 2019. Comparison among the microbial communities in the lake, lake wetland, and estuary sediments of a plain river network[J]. Microbiology Open, 8(2): e00644. |
| [10] | KIRCHMAN D L, 2008. Microbial ecology of the oceans[M]. Second Edition. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: 45-90. |
| [45] | 赵美训, 丁杨, 于蒙, 2017. 中国边缘海沉积有机质来源及其碳汇意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 47(9): 70-76. |
| ZHAO M X, DING Y, YU M et al., 2017. Sources of sedimentary organic matter in China marginal sea surface sediments and implications of carbon sink[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 47(9): 70-76. | |
| [11] | LIM J M, KIM S J, HAMADA M, et al., 2014. Oryzihumus terrae sp. nov., isolated from soil and emended description of the genus Oryzihumus[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 64(Part 7): 2395-2399. |
| [12] | LIU F D, MO X, KONG W J, et al., 2020. Soil bacterial diversity, structure, and function of Suaeda salsa in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils in various habitats in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 740: 140-144. |
| [13] | MITRA D, MONDAL R, KHOSHRU B, et al., 2022. Actinobacteria- enhanced plant growth, nutrient acquisition, and crop protection: Advances in soil, plant, and microbial multifactorial interactions[J]. Pedosphere, 32(1): 149-170. |
| [14] | NARSING RAO M P, LUO Z H, DONG Z Y, et al., 2022. Metagenomic analysis further extends the role of Chloroflexi in fundamental biogeochemical cycles[J]. Environmental Research, 209: 112888. |
| [15] | ODEDISHEMI AJIBADE F, WANG H C, GUADIE A, et al., 2021. Total nitrogen removal in biochar amended non-aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands for secondary wastewater effluent with low C/N ratio: Microbial community structure and dissolved organic carbon release conditions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 322: 124430. |
| [16] | WEI C, SU F L, YUE H Y, et al., 2024. Spatial distribution characteristics of denitrification functional genes and the environmental drivers in Liaohe Estuary Wetland[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(1): 1064-1078. |
| [17] | WU Y N, XU N, WANG H, et al., 2021. Variations in the diversity of the soil microbial community and structure under various categories of degraded wetland in Sanjiang Plain, northeastern China[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 32: 2143-2156. |
| [18] | YIN X B, WANG W T, WANG A H, et al., 2022. Microbial community structure and metabolic potential in the coastal sediments around the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 816(2): 151582. |
| [19] | 陈登稳, 王孝国, 胡文革, 等, 2012. 艾比湖湿地氨氧化细菌数量空间分布及其与土壤环境相关性分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 39(3): 334-343. |
| CHEN D W, WANG X G, HU W G, et al., 2012. Correlation analysis between the distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and soil environment in Ebinur Lake Wetland[J]. Microbiology China, 39(3): 334-343. | |
| [20] | 洪志锋, 张旎晨, 阿丹, 等, 2022. 共代谢作用下芦苇根际细菌多样性与群落组成[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(4): 1812-1818. |
| HONG Z F, ZHANG N C, A D, et al., 2022. Bacterial diversity and community composition in the Phragmites australis rhizosphere by cometabolism[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(4): 1812-1818. | |
| [21] | 黄俊杰, 陆雅海, 2022. 土壤拟杆菌与梭菌分解多糖类有机物质的研究进展与展望[J]. 微生物学通报, 49(3): 1147-1157. |
| HUANG J J, LU Y H, 2022. Decomposition of soil polymeric organic matter by Bacteroidetes and Clostridia: Progress and perspectives[J]. Microbiology China, 49(3): 1147-1157. | |
| [22] | 李金业, 陈庆锋, 李青, 等, 2021. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地微生物多样性及其驱动因子[J]. 生态学报, 41(15): 6103-6114. |
| LI J Y, CHEN Q F, LI Q, et al., 2021. Analysis of microbial diversity and driving factors in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(15): 6103-6114. | |
| [23] | 李善家, 王福祥, 从文倩, 等, 2022. 河西走廊荒漠土壤微生物群落结构及环境响应[J]. 土壤学报, 59(6): 1718-1728. |
| LI S J, WANG F X, CONG W Q, et al., 2022. Microbial community structure and environmental response of desert soil in Hexi Corridor[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 59(6): 1718-1728. | |
| [24] | 林少颖, 陈桂香, 刘旭阳, 等, 2020. 互花米草入侵对河口湿地土壤细菌群落结构及多样性影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(8): 3001-3012. |
| LIN S Y, CHEN G X, LIU X Y, et al., 2020. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil bacterial community structure and diversity in estuarine wetland[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(8): 3001-3012. | |
| [25] | 么秀颖, 闫丹丹, 戚丽萍, 等, 2022. 中国湿地生态系统碳库对环境变化的响应分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(1): 111-120. |
| YAO X Y, YAN D D, QI L P, et al., 2022. Responses of wetland ecosystem carbon pools to multiple environmental change drivers in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(1): 111-120. | |
| [26] | 孟妍君, 秦鹏, 2020. 珠江三角洲滨海湿地土壤微生物群落多样性与养分的耦合关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 27(6): 77-84. |
| MENG Y J, QIN P, 2020. Coupling relationship between microbial community diversity and soilnutrients in different wetlands in coastal area of Pearl River Delta[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(6): 77-84. | |
| [27] | 裴希超, 许艳丽, 魏巍, 2009. 湿地生态系统土壤微生物研究进展[J]. 湿地科学, 7(2): 181-186. |
| PEI X C, XU Y L, WEI W, 2020. A review on soil microorganisms in wetland ecosystem[J]. Wetland Science, 7(2): 181-186. | |
| [28] | 钱凤魁, 周阳, 李婉宁, 等, 2021. 辽河口翅碱蓬湿地退化区土壤理化性质及生态阈值分析[J]. 土壤通报, 52(5): 1085-1094. |
| QIAN F K, ZHOU W, LI W N, et al., 2021. Soil characteristics in wetland degradation areas and soil threshold calculation for Suaeda Salsa growth in Liaohe Estuary Wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 52(5): 1085-1094. | |
| [29] | 沈琦, 郝雅荞, 徐潇航, 等, 2020. 基于高通量测序技术的盐地碱蓬根际细菌群落多样性分析[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 43(5): 671-677. |
| SHEN Q, HAO Y Q, XU X H, et al., 2020. Analysis of rhizosphere bacterial diversity in Suaeda glauca Bunge based on high-throughput sequencing[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 43(5): 671-677. | |
| [30] | 孙建平, 刘雅辉, 左永梅, 等, 2020. 盐地碱蓬根际土壤细菌群落结构及其功能[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 28(10): 1618-1629. |
| SUN J P, LIU Y H, ZUO Y M, et al., 2020. The bacterial community structure and function of Suaeda salsa rhizosphere soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 28(10): 1618-1629. | |
| [31] | 唐旖, 2021. 九龙江口及台湾海峡沉积物中细菌和古菌群落结构分析[D]. 上海: 上海大学. |
| TANG Y, 2021. Community structure analysis of bacteriaand archaea in sediments of the Jiulong River Estuary and the Taiwan Strait[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University. | |
| [32] | 汪仲琼, 王为东, 祝贵兵, 等, 2011. 人工和天然湿地芦苇根际土壤细菌群落结构多样性的比较[J]. 生态学报, 31(16): 4489-4498. |
| WANG Z Q, WANG W D, ZHU G B, et al., 2011. A comparative study on the diversity of rhizospheric bacteria community structure in constructed wetland and natural wetland with reed domination[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(16): 4489-4498. | |
| [33] | 王露莹, 孙慧珍, 杨雪 2022. 松花江下游滨岸带典型植被根际土壤细菌群落结构与功能多样性[J]. 环境科学, 43(4): 2182-2191. |
| WANG L Y, SUN H Z, YANG X, et al., 2022. Structure and functional diversity of bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of typical vegetation in the riparian zone along the downstream of Songhua River[J]. Environmental Science, 43(4): 2182-2191. | |
| [34] | 王娜, 高婕, 魏静, 等, 2019. 三江平原湿地开垦对土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(5): 2375-2381. |
| WANG N, GAO J, WEI J, et al., 2019. Effects of wetland reclamation on soil microbial community structure in the Sanjiang Plain[J]. Environmental Science, 40(5): 2375-2381. | |
| [35] | 王婷, 焦健, 李朝周, 等, 2021. 不同生境芦苇根际土壤性质与根系生理的比较研究[J]. 中国草地学报, 43(4): 78-86. |
| WANG T, JIAO J, LI C Z, et al., 2021. Comparative study on rhizosphere soil properties and root physiology of reedin different habitats[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 43(4): 78-86. | |
| [36] | 王巍琦, 李变变, 张军, 等, 2019. 干旱区不同类型盐碱土壤细菌群落多样性[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(5): 1202-1211. |
| WANG W Q, LI B B, ZHANG J, et al., 2019. Diversity of bacterium communities in saline or alkaline soil in arid area[J]. Arid Zone Research, 36(5): 1202-1211. | |
| [37] | 吴胜男, 王晓锋, 刘婷婷, 等, 2022. 基于CiteSpace的湿地恢复研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 42(3): 1224-1239. |
| WU S N, WANG X F, LIU T T, et al., 2022. The research progress of wetland restoration based on CiteSpace[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(3): 1224-1239. | |
| [38] | 武晓倩, 范保硕, 滕叶文, 等, 2022. 白洋淀流域河岸带草本植物群落分布特征与土壤环境因子的关系[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 28(6): 1608-1614. |
| WU X Q, FAN B S, TENG Y W, et al., 2022. Relationship between herbaceous community distribution and soil environmental factors in the riparian zone of the Baiyangdian River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 28(6): 1608-1614. | |
| [39] | 鲜文东, 张潇橦, 李文均, 2020. 绿弯菌的研究现状及展望[J]. 微生物学报, 60(9): 1801-1820. |
| XIAN W D, ZHANG X T, LI W J, 2020. Research status and prospect on bacterial phylum Chloroflexi[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 60(9): 1801-1820. | |
| [40] | 杨阳, 陈克龙, 章妮, 等, 2022. 青海湖流域高寒湿地土壤微生物群落对不同降水梯度的响应[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 28(2): 290-299. |
| YANG Y, CHEN K L, ZHANG N, et al., 2022. Responses of soil microbial community to different precipitation gradients in the alpine wetlands of Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 28(2): 290-299. | |
| [41] | 张甘霖, 龚子同, 2012. 土壤调查实验室分析方法[M]. 北京: 北京出版社: 38-116. |
| ZHANG G L, GONG Z T, 2012. Methods for laboratory analysis of soil investigation[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 38-116. | |
| [42] | 张攀, 谢先军, 黎清华, 等, 2022. 东寨港红树林沉积物中微生物群落结构特征及其对环境的响应[J]. 地球科学, 47(3): 1122-1135. |
| ZHANG P, XIE X J, LI Q H, et al., 2022. Microbial community structure and its response to environment in mangrove sediments of Dongzhai Port[J]. Earth Science, 47(3): 1122-1135. | |
| [43] | 张鑫磊, 金锐, 杨镇, 等, 2019. 长江口崇明东滩湿地微生物群落结构研究[J]. 土壤通报, 50(5): 1178-1184. |
| ZHANG X L, JIN R, YANG Z, et al., 2019. Microbial community structure in the Chongming Eastern Wetland of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 50(5): 1178-1184. | |
| [44] | 赵华显, 阎冰, 徐悦, 等, 2020. 北部湾红树林沉积物中微生物群落结构的时空变化分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 39(5): 2161-2169. |
| ZHAO H X, YAN B, XUE X, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal analysis of microbial community structure in the mangrove sediments in Beibu Gulf[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 39(5): 2161-2169. |
| [1] | 孙煜佳, 陆梅, 赵旭燕, 冯峻, 刘国庆, 郭础鸟, 王明柳, 黄敏超, 陈志明. 纳帕海高寒退化草甸土壤细菌群落结构对氮添加的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 233-246. |
| [2] | 许铭宇, 俞龙生. 农林废弃有机材料对离子型稀土矿尾砂的土壤改良效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 126-134. |
| [3] | 杨可明, 彭里顺, 张燕海, 谷新茹, 陈新阳, 江克贵. 淮北矿区多种类型植被地上生物量反演研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1027-1035. |
| [4] | 张京磊, 王国良, 吴波, 贾春林, 张进红, 周圆, 马冰. 滨海盐碱地苜蓿-小黑麦轮作对土壤细菌和真菌群落多样性与网络结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1048-1062. |
| [5] | 李成阳, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 蔡敏, 许瑞瑶, 陈秀宇, 丁佳音, 许秋云, 彭飞. 长江源区北麓河流域退化高寒草甸植物群落特征和土壤特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. |
| [6] | 蒋云峰, 严婷, 刘俊男, 马丙增, 王海萌, 窦笑萌. 黑土区农田中型土壤动物群落对免耕玉米秸秆覆盖频率的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 699-707. |
| [7] | 陈弘杰, 廖洪凯, 龙健, 赵雨鑫, 湛凯翔, 冉泰山, 杨国梅. 强还原土壤灭菌对土壤原生生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 539-547. |
| [8] | 何杰, 李宗明, 杨正宇, 沈健林, 刘国平, 吴金水. 牛粪化肥配施对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 573-584. |
| [9] | 罗庆, 何清, 吴慧秋, 寇力月, 方旭, 张鑫雨, 李缘, 柴育廷, 张瑞生, 代文举. 辽河口湿地土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 333-340. |
| [10] | 宋江琴, 尹亚丽, 赵文, 刘燕, 随奇奇, 火久艳, 郑文贤, 李世雄. 青海高原黑土滩退化草地土壤微生物群落空间分异特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1696-1707. |
| [11] | 张传光, 沈艳, 张珊珊, 李玉文, 陈剑, 杨文忠. 原生与迁地毛枝五针松根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1544-1553. |
| [12] | 马媛, 田路露, 吕杰, 柳沛, 张旭, 李二阳, 张清航. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林土壤微生物群落及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [13] | 李晴, 张梦悦, 于明乔, 李小璇, 常明, 陈立斌, 丁森. 东莞城市河流大型底栖动物群落结构及影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 101-110. |
| [14] | 李勋, 张艳, 宋思梦, 周扬, 张健. 西南地区马尾松与乡土阔叶树种凋落叶混合分解过程中的细菌群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 12-27. |
| [15] | 李佳婧, 梁咏亮, 李静尧, 李小伟, 杨君珑. 基于叶片功能性状的贺兰山西坡植物生态策略分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 45-53. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
