生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 233-246.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.02.006
孙煜佳1( ), 陆梅1,*(
), 陆梅1,*( ), 赵旭燕2, 冯峻3, 刘国庆1, 郭础鸟1, 王明柳1, 黄敏超1, 陈志明2
), 赵旭燕2, 冯峻3, 刘国庆1, 郭础鸟1, 王明柳1, 黄敏超1, 陈志明2
收稿日期:2024-07-16
出版日期:2025-02-18
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
*陆梅。E-mail: lumeizx@126.com作者简介:孙煜佳(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事湿地生态研究。E-mail: sunyujiade@163.com
基金资助:
SUN Yujia1( ), LU Mei1,*(
), LU Mei1,*( ), ZHAO Xuyan2, FENG Jun3, LIU Guoqing1, GUO Chuxiao1, WANG Mingliu1, HUANG Minchao1, CHEN Zhiming2
), ZHAO Xuyan2, FENG Jun3, LIU Guoqing1, GUO Chuxiao1, WANG Mingliu1, HUANG Minchao1, CHEN Zhiming2
Received:2024-07-16
Online:2025-02-18
Published:2025-03-03
摘要: 为探明土壤细菌群落对氮沉降增加的响应机制,以纳帕海高寒退化草甸云雾薹草(Carex nubigena)群落土壤为研究对象,野外设置对照(0 g·m−2·a−1)、低氮(5 g·m−2·a−1)、中氮(10 g·m−2·a−1)和高氮(15 g·m−2·a−1)等4种氮添加量的模拟试验,采用高通量测序测定土壤细菌群落组成及多样性,分析氮添加下植物和土壤环境变化对细菌群落的影响特征。结果表明,1)氮添加显著影响土壤细菌门属水平群落组成。随氮量增加,酸杆菌门、放线菌门、甲烷氧化菌门、芽单胞菌门、硝化螺旋菌门相对丰度先增后减;变形菌门、厚壁菌门相对丰度增加;绿弯菌门、粘菌门、拟杆菌门、疣微菌门相对丰度降低;在属水平上,酸杆菌属、芽单胞杆菌属、Vicinamibacter、RB41先增后减,微球菌属、黄杆菌属先减后增,Candidatus Solibacter增加。2)氮添加显著影响植物与土壤环境。随氮添加量增加,地上生物量增加而植物多样性降低;土壤速效钾、全氮、有机质、速效氮含量增加,全钾、pH降低;全磷、速效磷呈先减后增趋势。3)氮添加下植物变化通过影响土壤养分而间接调控土壤细菌,土壤环境变化则直接影响细菌群落。结论:氮添加主要通过改变植物多样性、土壤pH和土壤养分含量,直接或间接对土壤细菌产生影响。
中图分类号:
孙煜佳, 陆梅, 赵旭燕, 冯峻, 刘国庆, 郭础鸟, 王明柳, 黄敏超, 陈志明. 纳帕海高寒退化草甸土壤细菌群落结构对氮添加的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 233-246.
SUN Yujia, LU Mei, ZHAO Xuyan, FENG Jun, LIU Guoqing, GUO Chuxiao, WANG Mingliu, HUANG Minchao, CHEN Zhiming. Response of Soil Bacterial Community Structure to Nitrogen Addition in Degraded Napahai Alpine Meadow[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(2): 233-246.
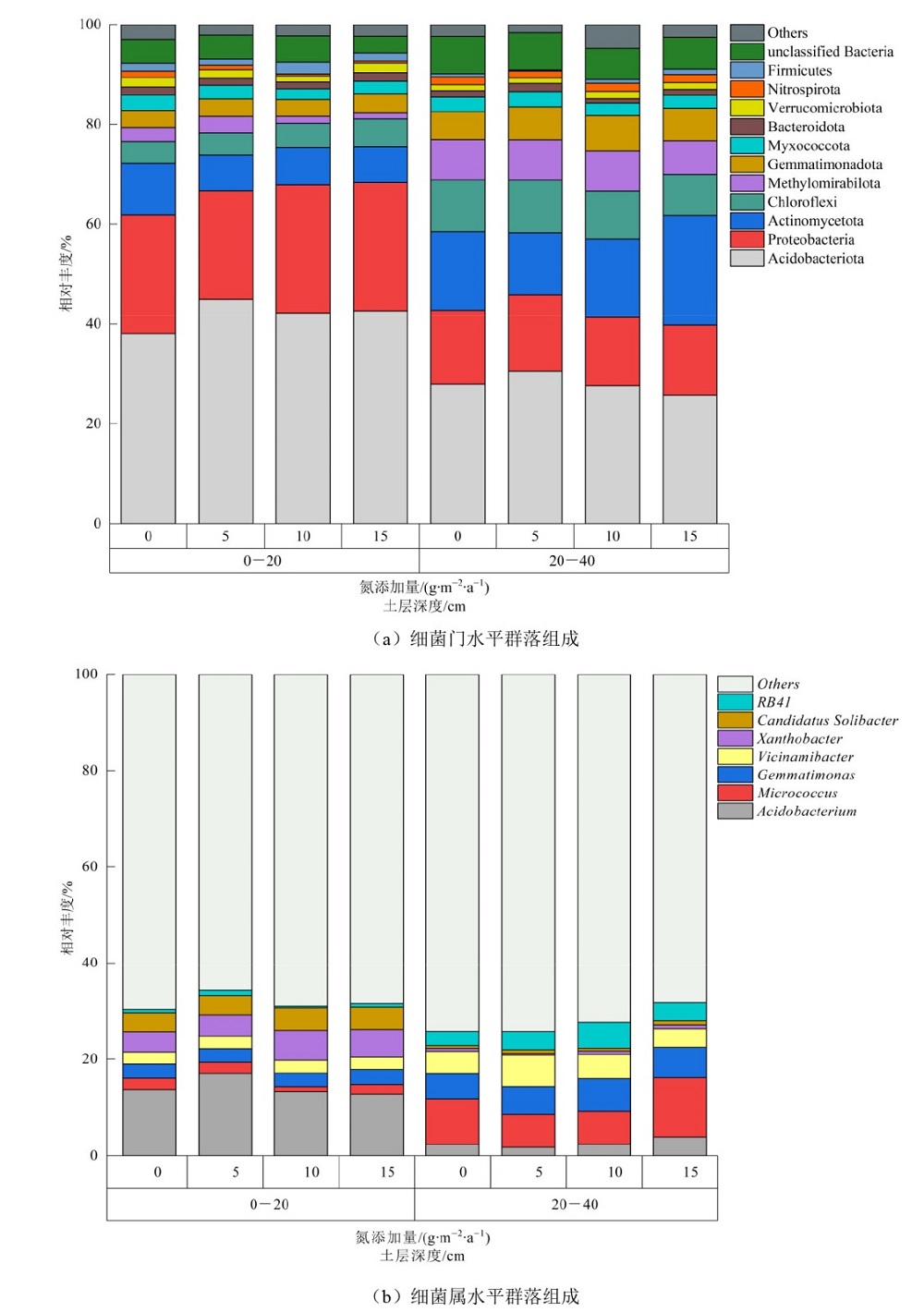
图1 氮添加对高寒退化草甸土壤细菌门属水平群落组成的影响
Figure 1 Effect of nitrogen addition on phylum-genus level of soil bacterial community composition in degraded plateau meadow
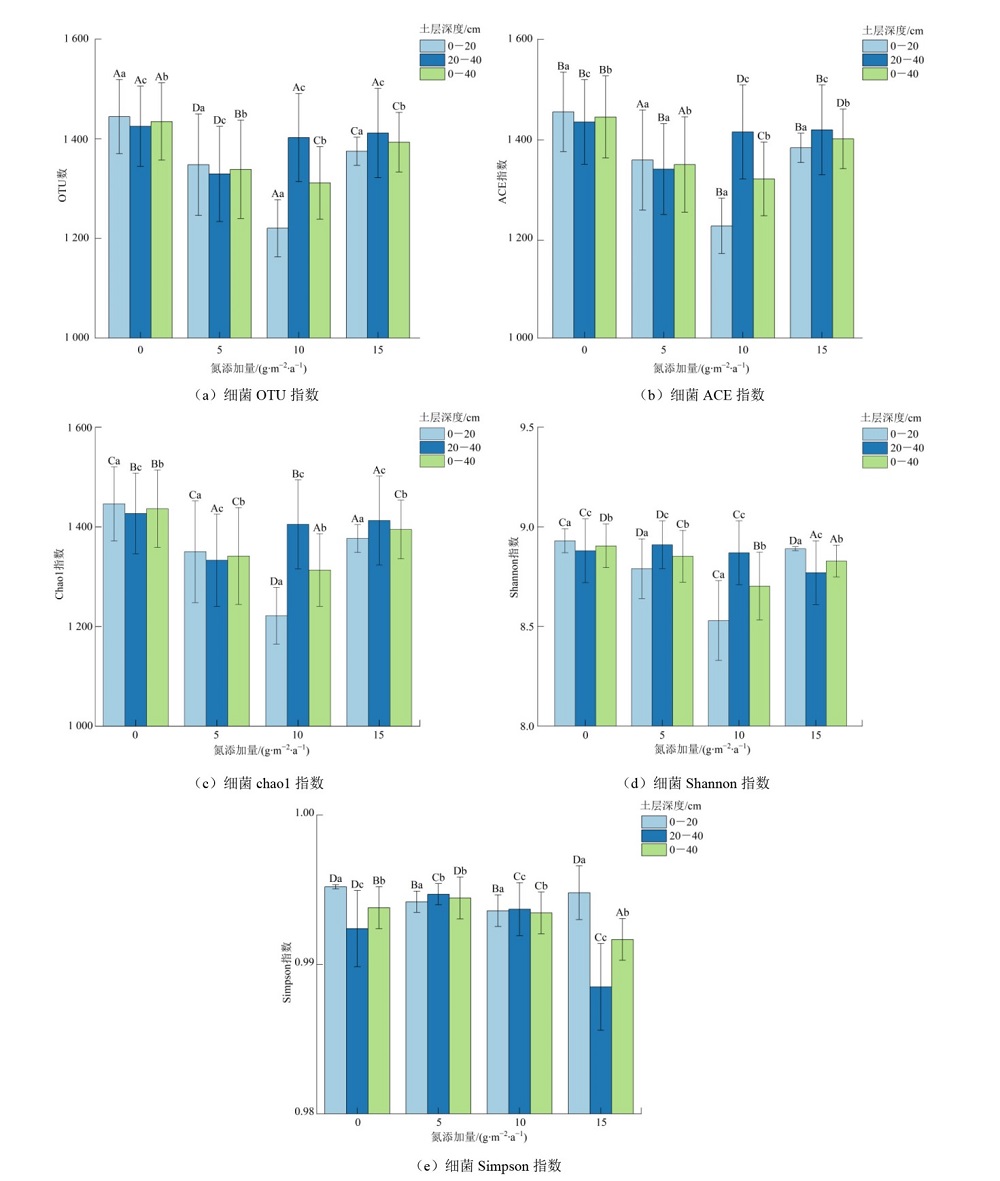
图2 氮添加对高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的影响 不同大写字母表示同一土层不同处理间差异显著,不同小写字母表示同一处理不同土层间差异显著(p<0.05)。下同
Figure 2 Effect of nitrogen addition on soil bacterial diversity in degraded plateau meadow
| 土层/cm | 指标 | 氮添加量/(g·m−2·a−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | ||
| 0-20 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.87±0.00Ba | 0.94±0.03Aa | 0.96±0.02Aa | 0.80±0.004Ca |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 33.46±1.04Ca | 38.34±0.35Ba | 62.53±1.07Aa | 34.24±0.11Ca | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.63±0.04Ba | 0.61±0.083Aa | 0.83±0.293AaCa | 0.79±0.16Ca | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.73±2.69Ca | 15.30±2.47Ba | 15.14±3.823Aa | 14.98±0.28Ca | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 16.88±3.45Aa | 10.62±8.82Ba | 12.64±7.94Ba | 14.26±10.28Ca | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 28.78±7.31Ca | 30.37±7.96Ca | 31.95±7.27Ba | 32.65±2.24Aa | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 215.07±40.83Aa | 250.74±39.16Aa | 299.17±39.85Ba | 263.91±224.07Ca | |
| pH | 7.11±0.033Aa | 6.08±0.01BaAa | 5.40±0.01Ba | 5.23±0.01Ca | |
| 20-40 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.56±0.004Bc | 0.58±0.003Ac | 0.57±0.01Ac | 0.54±0.02Cc |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 16.75±0.47Bc | 17.58±0.52ABc | 17.52±0.94ABc | 17.99±0.08Ac | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.57±0.19Ac | 0.57±0.36Bc | 0.37±0.01Cc | 0.59±0.25Dc | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.74±1.62Dc | 15.31±1.69Ac | 15.14±1.06Bc | 15.00±1.52Dc | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 8.77±5.24Ac | 8.43±4.40Cc | 19.77±9.23Cc | 18.99±10.04Bc | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 19.53±10.79 | 19.12±13.47Ac | 17.59±2.63Bc | 20.59±0.12Cc | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 61.58±17.58Cc | 128.60±41.68Bc | 86.93±36.14 | 80.78±17.25Ac | |
| pH | 7.18±0.01Aa | 6.81±0.01BCa | 6.85±0.07ABa | 6.47±0.37Ca | |
| 0-40 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.71±0.00Bb | 0.76±0.01Ab | 0.76±0.02Ab | 0.67±0.01Cb |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 25.10±0.48Db | 27.96±0.09Bb | 40.03±0.61Ab | 26.11±0.10Cb | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.60±0.13Bb | 0.59±0.24Ab | 0.61±0.31Db | 0.69±0.22Cb | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.73±5.04Ab | 15.30±1.92Bb | 15.14±3.41Db | 14.99±1.82Cb | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 12.82±4.91Bb | 9.53±7.50Ab | 16.89±8.01Db | 19.04±9.14Cb | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 24.15±9.68Cb | 24.75±11.66Db | 24.77±9.26Bb | 26.62±6.76Ab | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 138.32±18.03Bb | 189.67±18.07Ab | 193.05±10.19Cb | 172.34±21.95 | |
| pH | 7.15±0.02Aab | 6.44±0.01Bb | 6.12±0.04Cb | 5.85±0.19Db | |
表1 氮添加对高寒退化草甸土壤理化性质的影响
Table 1 Effect of nitrogen addition on soil physicochemical properties in degraded plateau meadow
| 土层/cm | 指标 | 氮添加量/(g·m−2·a−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | ||
| 0-20 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.87±0.00Ba | 0.94±0.03Aa | 0.96±0.02Aa | 0.80±0.004Ca |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 33.46±1.04Ca | 38.34±0.35Ba | 62.53±1.07Aa | 34.24±0.11Ca | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.63±0.04Ba | 0.61±0.083Aa | 0.83±0.293AaCa | 0.79±0.16Ca | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.73±2.69Ca | 15.30±2.47Ba | 15.14±3.823Aa | 14.98±0.28Ca | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 16.88±3.45Aa | 10.62±8.82Ba | 12.64±7.94Ba | 14.26±10.28Ca | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 28.78±7.31Ca | 30.37±7.96Ca | 31.95±7.27Ba | 32.65±2.24Aa | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 215.07±40.83Aa | 250.74±39.16Aa | 299.17±39.85Ba | 263.91±224.07Ca | |
| pH | 7.11±0.033Aa | 6.08±0.01BaAa | 5.40±0.01Ba | 5.23±0.01Ca | |
| 20-40 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.56±0.004Bc | 0.58±0.003Ac | 0.57±0.01Ac | 0.54±0.02Cc |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 16.75±0.47Bc | 17.58±0.52ABc | 17.52±0.94ABc | 17.99±0.08Ac | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.57±0.19Ac | 0.57±0.36Bc | 0.37±0.01Cc | 0.59±0.25Dc | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.74±1.62Dc | 15.31±1.69Ac | 15.14±1.06Bc | 15.00±1.52Dc | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 8.77±5.24Ac | 8.43±4.40Cc | 19.77±9.23Cc | 18.99±10.04Bc | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 19.53±10.79 | 19.12±13.47Ac | 17.59±2.63Bc | 20.59±0.12Cc | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 61.58±17.58Cc | 128.60±41.68Bc | 86.93±36.14 | 80.78±17.25Ac | |
| pH | 7.18±0.01Aa | 6.81±0.01BCa | 6.85±0.07ABa | 6.47±0.37Ca | |
| 0-40 | w(全氮)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.71±0.00Bb | 0.76±0.01Ab | 0.76±0.02Ab | 0.67±0.01Cb |
| w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | 25.10±0.48Db | 27.96±0.09Bb | 40.03±0.61Ab | 26.11±0.10Cb | |
| w(全磷)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.60±0.13Bb | 0.59±0.24Ab | 0.61±0.31Db | 0.69±0.22Cb | |
| w(全钾)/(g∙kg−1) | 15.73±5.04Ab | 15.30±1.92Bb | 15.14±3.41Db | 14.99±1.82Cb | |
| w(速效磷)/(mg∙kg−1) | 12.82±4.91Bb | 9.53±7.50Ab | 16.89±8.01Db | 19.04±9.14Cb | |
| w(速效钾)/(mg∙kg−1) | 24.15±9.68Cb | 24.75±11.66Db | 24.77±9.26Bb | 26.62±6.76Ab | |
| w(速效氮)/(mg∙kg−1) | 138.32±18.03Bb | 189.67±18.07Ab | 193.05±10.19Cb | 172.34±21.95 | |
| pH | 7.15±0.02Aab | 6.44±0.01Bb | 6.12±0.04Cb | 5.85±0.19Db | |
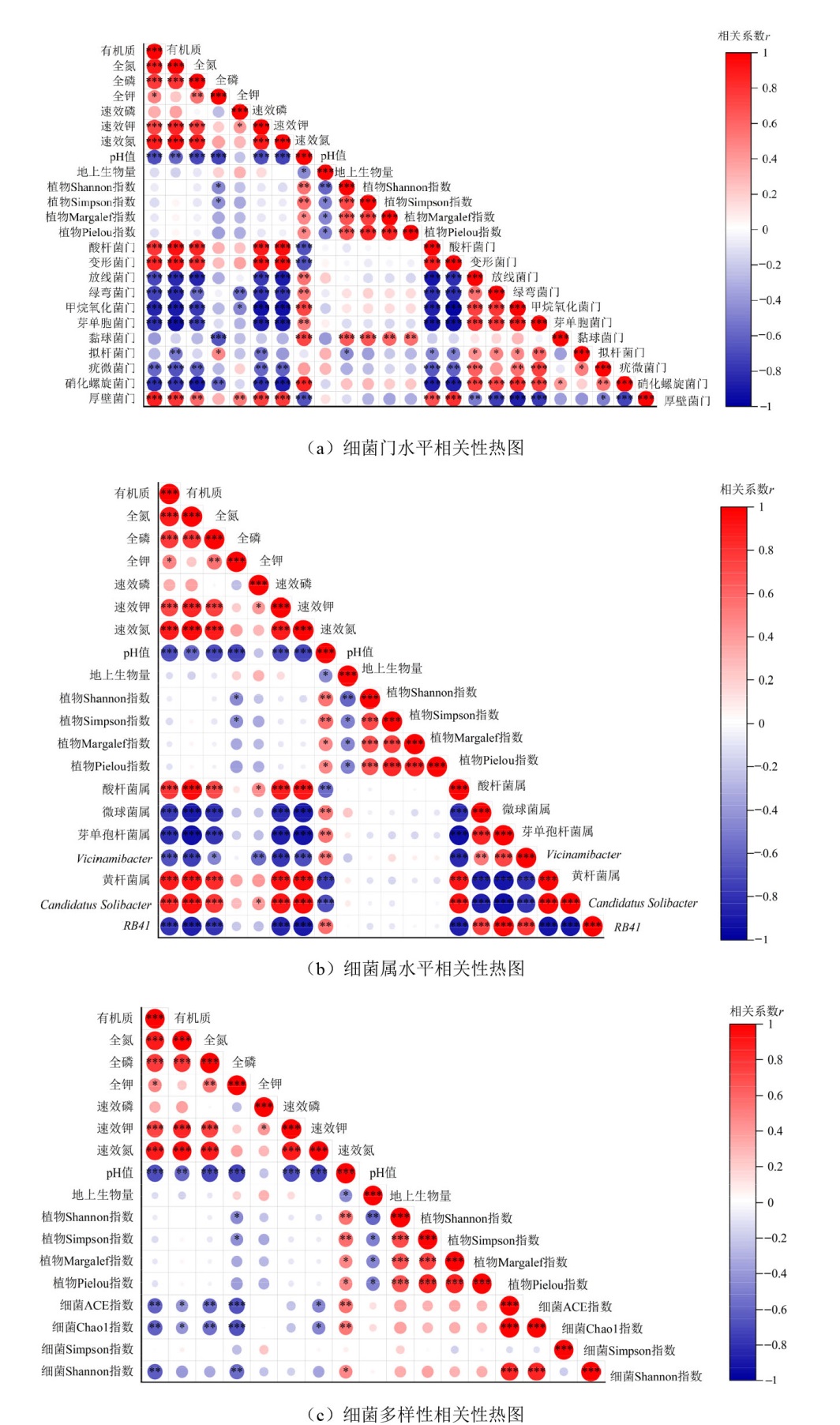
图4 氮添加下细菌相对丰度/多样性与植物、土壤环境因子间的相关性热图 图中红色和蓝色分别表示正相关和负相关;圆圈的大小和颜色深浅表示相关度。*表示p<0.05;**表示p<0.01;***表示p<0.001;不带“*”的表示p≥0.05
Figure 4 Heat map showing the association of bacterial relative abundance and diversity with plants and soil environmental factors under nitrogen addition
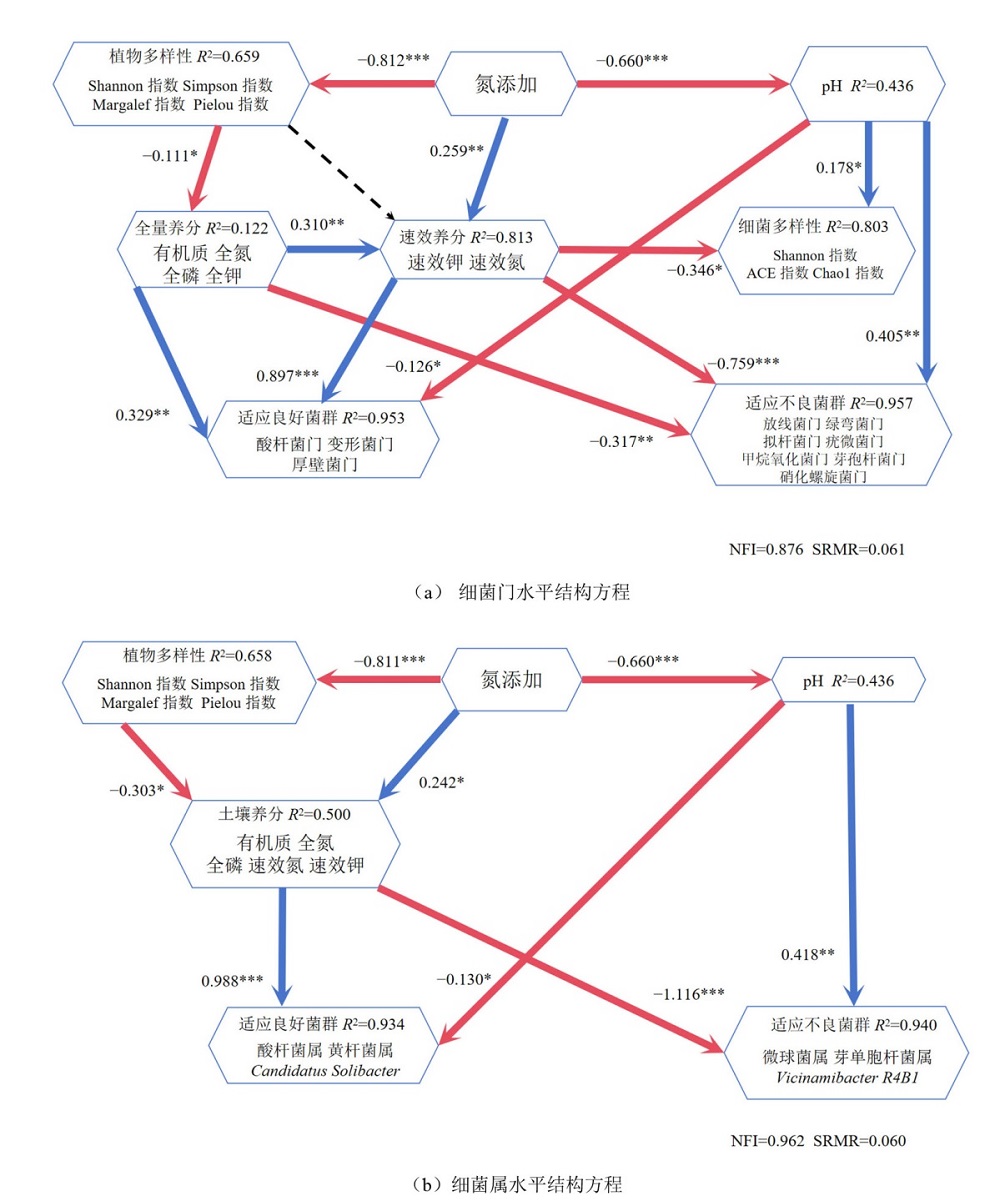
图5 氮添加下植物/土壤环境变化对细菌群落组成及多样性影响的偏最小二乘法结构方程模型分析 单向箭头表示有联系的方向,蓝色实线和红色实线分别表示正、负关系,黑色虚线表示关系不显著,线上黑色数字为路径系数。R2表示模型对变量的解释度;*表示p<0.05,**表示p<0.01,***表示p<0.001
Figure 5 Partial least square structural equation model analysis on the effects of plant and soil environment changes on bacteria under nitrogen addition
| [1] | BAHRAM M, HILDEBRAND F, FORSLUND S K, et al., 2018. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome[J]. Nature, 560(7717): 233-237. |
| [2] | CHEN Q Y, YUAN Y L, HU Y L, et al., 2021. Excessive nitrogen addition accelerates N assimilation and P utilization by enhancing organic carbon decomposition in a Tibetan alpine steppe[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 764: 142848. |
| [3] | CORSTANJE R, REDDY K R, PRENGER J P, et al., 2007. Soil microbial eco-physiological response to nutrient enrichment in a sub-tropical wetland[J]. Ecological Indicators, 7(2):277-289. |
| [4] | EILERS K G, LAUBER C L, KNIGHT R, et al., 2010. Shifts in bacterial community structure associated with inputs of low molecular weight carbon compounds to soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(6): 896-903. |
| [5] |
FIERER N, 2017. Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 15: 579-590.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | FIERER N, LAUBER C L, RAMIREZ K S, et al., 2011. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients[J]. The Isme Journal, 6(5): 1007-1017. |
| [7] |
GALLOWAY J N, TOWNSEND A R, ERISMAN J W, et al., 2008. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions[J]. Science, 320(5878): 889-892.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | HAIR J F, RISHER J J, SARSTEDT M, et al., 2019. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM[J]. European Business Review, 31(1): 2-24. |
| [9] | HARPOLE W S, SULLIVAN L L, LIND E M, et al., 2016. Addition of multiple limiting resources reduces grassland diversity[J]. Nature, 1537(7618): 93-96. |
| [10] | KHALIL M I, RAHMAN M S, SCHMIDHALTER U, et al., 2007. Nitrogen fertilizer-induced mineralization of soil organic C and N in six contrasting soils of Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 170(2): 210-218. |
| [11] | KUYPERS M M M, MARCHANT H K, KARTAl B, et al., 2018. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network[J]. Nature reviews, 16(5): 263-276. |
| [12] | LIU L F, TIAN J Q, WANG H J, et al., 2023. Stable oxic-anoxic transitional interface is beneficial to retard soil carbon loss in drained peatland[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 181: 109024. |
| [13] | LUO Z M, LIU J X, CHAI B F, et al., 2020. Soil bacterial community response and nitrogen cycling variations associated with subalpine meadow degradation on the loess plateau China[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 86(9): e00180-20. |
| [14] | REICHSTEIN M, REY A, FREIBAUER A, et al., 2003. Modeling temporal and large-scale spatial variability of soil respiration from soil water availability, temperature and vegetation productivity indices[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 17(4): 1104. |
| [15] | SIKORSKI J, BAUMGARTNER V, BIRKHOFER K, et al., 2022. The evolution of ecological diversity in Acidobacteriota[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13(5): 715637. |
| [16] | PAREDES S H, LEBEIS S L, 2016. Giving back to the community: Microbial mechanisms of plant-soil interactions[J]. Functional Ecology, 30(7): 1043-1052. |
| [17] |
PROBER S M, LEFF J W, BATES S T, et al., 2015. Plant diversity predicts beta but not alpha diversity of soil microbes across grasslands worldwide[J]. Ecology Letters, 18(1): 85-95.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | WANG Y S, LI C N, KOU Y P, et al., 2017. Soil pH is a major driver of soil diazotrophic community assembly in Qinghai-Tibet alpine meadows[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 115: 547-555. |
| [19] | XU D H, FANG X W, ZHANG R Y, et al., 2016. Influences of nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon addition on plant productivity and species richness in an alpine meadow[J]. AoB PLANTS, 7(7): 19-34. |
| [20] | ZHANG T A, CHEN H Y H, RUAN H H, et al., 2018. Global negative effects of nitrogen deposition on soil microbes[J]. The Isme Journal, 12(7): 1817-1825. |
| [21] | ZHANG R J, TIAN X R, XIANG Q J, et al., 2022. Response of soil microbial community structure and function to different altitudes in arid valley in Panzhihua, China[J]. BMC Microbiology, 22: 1-11. |
| [22] |
ZONG N, SHI P, SONG M, et al., 2016. Nitrogen critical loads for an alpine meadow ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Management, 57: 531-542.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 2-37. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Methods of soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 2-37. | |
| [24] | 曹子铖, 程淑兰, 方华军, 等, 2020. 温带针阔叶林土壤有机碳动态和微生物群落结构对有机氮添加的响应特征[J]. 土壤学报, 57(4): 963-974. |
| CAO Z C, CHENG S L, FANG H J, et al., 2020. Responses of soil organic carbon dynamics and microbial community structure to organic nitrogen fertilization in the temperate needle-broad leaved mixed forest[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 57(4): 963-974. | |
| [25] |
付伟, 武慧, 赵爱花, 等, 2020. 陆地生态系统氮沉降的生态效应:研究进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 44(5): 475-493.
DOI |
| FU W, WU H, ZHAO A H, et al., 2020. Ecological impacts of nitrogen deposition on terrestrial ecosystems: Research progresses and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44(5): 475-493. | |
| [26] | 胡启良, 杨滨娟, 刘宁, 等, 2022. 绿肥混播下不同施氮量对水稻产量、土壤碳氮和微生物群落的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 41(6): 16-26. |
| HU Q L, YANG B J, LIU N, et al., 2022. Effects of application rates of nitrogen on rice yield, carbon and nitrogen, microbial community in soil under mixed sowing of green manure[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 41(6): 16-26. | |
| [27] | 胡洋, 丛孟菲, 陈末, 等, 2022. 氮添加对巴音布鲁克高寒湿地土壤微生物量和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 42(13): 5328-5339. |
| HU Y, CONG M F, CHEN M, et al., 2022. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activity in Bayinbuluk alpine wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(13): 5328-5339. | |
| [28] | 刘灿然, 马克平, 1998. 生物群落多样性的测度方法VI: 与多样性测度有关的统计问题[J]. 生物多样性, 6(3): 229-239. |
| LIU C R, MA K P, 1998. Measurement of biotic community diversity VI: The statistical aspects of diversity measures[J]. Chinese Biodiversity, 6(3): 229-239. | |
| [29] |
刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张海芳, 等, 2019. 氮添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 28(9): 23-32.
DOI |
| LIU H M, YANG D L, ZNANG H F, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen addition on the soil bacterial community structure of Stipa baicalensis steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 28(9): 23-32. | |
| [30] | 刘红梅, 张海芳, 皇甫超河, 等, 2017. 长期氮添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤微生物群落多样性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 36(4): 709-717. |
| LIU H M, ZHANG H F, HUANGFU C H, et al., 2017. Effects of different long-term nitrogen addition on soil microbial diversity of Stipa baicalensis steppe in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 36(4): 709-717. | |
| [31] | 刘伟, 程积民, 高阳, 等, 2012. 黄土高原草地土壤有机碳分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 49(1): 68-76. |
| LIU W, CHENG J M, GAO Y, et al., 2012. Soil organic carbon distribution and its influencing factors in grassland on the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 49(1): 68-76. | |
| [32] |
刘艳, 陈梦娇, 郭童童, 等, 2023. 多梯度氮磷添加对高寒退化草甸植物群落生物量与氮磷含量的影响[J]. 草地学报, 31(3): 751-759.
DOI |
|
LIU Y, CHEN M J, GUO T T, et al., 2023. Effects of Multi-gradient Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Biomass and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Content of Alpine Meadow Plant Community[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 31(3): 751-759.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 刘株秀, 2023. 东北均腐土剖面微生物群落分布和功能特征分析[D]. 长春市: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所): 1-89. |
| LIU Z X, 2023. Distribution and functional characteristics of microbial communities in Isohumosol profiles in Northeast China[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences): 1-89. | |
| [34] | 陆梅, 2018. 纳帕海湿地退化对土壤微生物群落结构及多样性的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 1-207. |
| LU M, 2018. Effects of wetlands degradation on structure and biodiversity of soil microbial community in Napahai plateau wetlands[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 1-207. | |
| [35] | 吕博, 丁亮, 过聪, 等, 2024. 复合微生物肥对棉田土壤养分及根际细菌群落的影响[J/OL]. 作物杂志: 1-10.1-10 [2024-07-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1808.S.20240220.0946.003.html. |
| LÜ B, DING L, GUO C, et al., 2024. Effect of compound microbial fertilizer on soil nutrients and inter-root bacterial communities in cotton fields[J/OL]. Crops: 1-10.1-10 [2024-07-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1808.S.20240220.0946.003.html. | |
| [36] | 吕晶花, 李聪, 杨志东, 等, 2023a. 纳帕海高原湿地土壤微生物群落对土地利用方式改变的响应[J]. 土壤通报, 54(3): 682-694. |
| LÜ J H, LI C, YANG Z D, et al., 2023. Responses of soil microbial communities to land use changes in the Napahai plateau wetlands[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 54(3): 682-694. | |
| [37] | 吕晶花, 赵旭燕, 陆梅, 等, 2023b. 氮沉降下纳帕海草甸植被与土壤变化对微生物生物量碳氮的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 34(6): 1525-1532. |
| LÜ J H, ZHAO X Y, LU M, et al., 2023. Effects of vegetation and soil changes on microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in the Napahai meadow under N deposition[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 34(6): 1525-1532. | |
| [38] | 潘禹, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 等, 2021. 模拟N沉降对滇中亚高山典型森林凋落物分解及土壤微生物的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 34(3): 88-97. |
| PAN Y, SONG Y L, WANG K Q, et al., 2021. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on litter decomposition and soil microorganisms of typical subalpine forests in central Yunnan, China[J]. Forestry Research, 34(3): 88-97. | |
| [39] |
孙官发, 陆梅, 闪昇阳, 等, 2024. 短期氮沉降对纳帕海高寒退化疏花早熟禾草甸土壤呼吸干湿季变化的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 35(2): 390-398.
DOI |
| SUN G F, LU M, SHAN S Y, et al., 2024. Effect of short-term nitrogen deposition on dry-wet seasonal variation of soil respiration in degraded Poa pratensis alpine meadow of the Napahai, Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35(2): 390-398. | |
| [40] |
孙建波, 畅文军, 李文彬, 等, 2022. 香蕉不同生育期根际微生物生物量及土壤酶活的变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1169-1174.
DOI |
| SUN J B, CHANG W J, LI W B, et al., 2022. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil at different growing stages of banana[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(6): 1169-1174. | |
| [41] | 童永尚, 张春平, 俞旸, 等, 2024. 多年生高寒栽培草地土壤微生物学特性对短期氮添加的响应[J/OL]. 环境科学, 1-13[2024-07-15]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202312228. |
| TONG Y S, ZNANG C P, YU Y, et al., 2024. Response of Microbiological Properties to Short-term Nitrogen Addition in Perennial Alpine Cultivated Grassland[J/OL]. Environmental Science, 1-13 [2024-07-15]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202312228. | |
| [42] | 图纳热, 红梅, 闫瑾, 等, 2023. 降水变化和氮沉降对荒漠草原土壤细菌群落结构及酶活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 42(2): 403-413. |
| TU N R, HONG M, YAN J, et al., 2023. Effects of precipitation change and nitrogen deposition on soil bacterial community structure and enzyme activities in desert steppe[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 42(2): 403-413. | |
| [43] | 王长庭, 王根绪, 李香真, 等, 2017. 氮肥添加对高寒藏嵩草 (Kobresia tibetica) 沼泽化草甸和土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(2): 405-415. |
| WANG C T, WANG G X, LI X Z, et al., 2017. Effects of N addition on the plant and soil microbial community in alpine Kobresia tibetica meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(2): 405-415. | |
| [44] | 王金双, 2018. 氮沉降背景下枯落物对松嫩草地微生物群落的作用[D]. 长春市: 东北师范大学: 1-54. |
| WANG J S, 2018. Effects of nitrogen and litter input on microbial community in Songnen Grassland[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University: 1-54. | |
| [45] |
王燚, 李文珊, 展鹏飞, 等, 2024. 若尔盖高原泥炭沼泽土壤微生物空间分布[J]. 应用生态学报, 35(6): 1705-1715.
DOI |
|
WANG Y, LI W S, ZHAN P F, et al., 2024. Spatial distribution of soil microorganisms in the Zoige Plateau peatland, Southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 35(6): 1705-1715.
DOI |
|
| [46] |
吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄, 2014. 根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 38(3): 298-310.
DOI |
| WU L K, LIN X M, LIN W X, 2014. Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38(3): 298-310. | |
| [47] | 姚继周, 2016. 水杉人工林细根生产和周转及对氮沉降的响应[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学: 1-51. |
| YAO J Z, 2016. Fine root production and turnover and the response to nitrogen deposition in Metasequoia glyptostroboides plantation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University: 1-51. | |
| [48] | 曾红丽, 白炜, 房佳辰, 等, 2022. 氮添加对青藏高原高寒沼泽草甸土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 3(8): 1035-1045. |
| ZENG H L, BAI W, FANG J C, et al., 2022. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil bacterial community in alpine marsh meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 3(8): 1035-1045. | |
| [49] | 张昊, 姜娜, 樊林染, 等, 2024. 长期养分添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 44(3): 1130-1139. |
| ZHANG H, JIANG N, FAN L R, et al., 2024. Effects of long-term nutrient addition on microbi ial community in soil of Stipa baicalensis steppe in the Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Ecology, 44(3): 1130-1139. | |
| [50] | 张晓黎, 孙向阳, 安宝晟, 等, 2024. 拉萨河流域不同生态系统类型土壤微生物群落结构特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 43(6): 1728-1737. |
| ZHANG X L, SUN X Y, AN B S, et al., 2024. Characterization of soil microbial community structure in different ecosystem types in the Lhasa River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 43(6): 1728-1737. | |
| [51] | 张紫薇, 陈召莹, 张甜娜, 等, 2022. 岗南水库沉积物好氧反硝化菌群落时空分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 43(1): 314-328. |
| ZHANG Z W, CHEN Z Y, ZHANG T N, et al., 2022. Spatial and temporal distribution of aerobic denitrification bacterial community in sediments of Gangnan Reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 43(1): 314-328. | |
| [52] |
朱锦福, 黄瑞灵, 董志强, 等, 2022. 青海湖高寒湿地土壤细菌群落对氮添加的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1101-1109.
DOI |
| ZHU J F, HUANG R L, DONG Z Q, et al., 2022. Response of the soil bacterial community to nitrogen addition in alpine wetland of Qinghai Lake[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(6): 1101-1109. | |
| [53] | 朱小梅, 邢锦城, 洪立洲, 等, 2024. 不同施氮处理下黑麦草翻压还田对滩涂盐渍土碳氮与细菌群落结构的影响[J/OL]. 浙江农业学报, 1-11 [2024-11-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1151.S.20241017.1102.006.html. |
| ZHU X M, XING J C, HONG L Z, et al., 2024. Effects of overturning Lolium perenne under different nitrogen rates on carbon, nitrogen and bacterial community structure in saline soil of coastal area[J/OL]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 1-11 [2024-11-14]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/33.1151.S.20241017.1102.006.html. | |
| [54] | 周艳翔, 吕茂奎, 谢锦升, 等, 2013. 深层土壤有机碳的来源、特征与稳定性[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 8(1): 48-55. |
| ZHOU Y X, LÜ M K, XIE J S, et al., 2013. Sources, characteristics and stability of organic carbon in deep soil[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 8(1): 48-55. | |
| [55] |
宗宁, 段呈, 耿守保, 等, 2018. 增温施氮对高寒退化草甸生产力及生物量分配的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(1): 59-67.
DOI |
|
ZONG N, DUAN C, GENG S B, et al., 2018. Effects of warming and nitrogen addition on community production and biomass allocation in an alpine meadow[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(1): 59-67.
DOI |
| [1] | 岳航宇, 郭成久, 苏芳莉, 魏超. 辽河口湿地不同植被类型根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(2): 222-232. |
| [2] | 朱乐洋, 张西哲, 陶江, 王秀, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮添加对色季拉山急尖长苞冷杉林土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1384-1396. |
| [3] | 张京磊, 王国良, 吴波, 贾春林, 张进红, 周圆, 马冰. 滨海盐碱地苜蓿-小黑麦轮作对土壤细菌和真菌群落多样性与网络结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1048-1062. |
| [4] | 李成阳, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 蔡敏, 许瑞瑶, 陈秀宇, 丁佳音, 许秋云, 彭飞. 长江源区北麓河流域退化高寒草甸植物群落特征和土壤特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071. |
| [5] | 王梓晗, 吕世杰, 王忠武, 刘红梅. 放牧强度对优势种群重要值和物种多样性及其二者典型关系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 869-876. |
| [6] | 关玉亮, 甘先华, 殷祚云, 黄钰辉, 陶玉柱, 李宽, 张卫强, 邓彩琼, 曾祥尧, 黄芳芳. 南岭自然保护区不同海拔梯度植物多样性分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 877-887. |
| [7] | 王俊伟, 陈永豪, 曾哲飞, 陈孟焱, 拉琼. 西藏拉萨市入侵植物曼陀罗群落物种多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(6): 900-907. |
| [8] | 蒋云峰, 严婷, 刘俊男, 马丙增, 王海萌, 窦笑萌. 黑土区农田中型土壤动物群落对免耕玉米秸秆覆盖频率的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 699-707. |
| [9] | 卿彩霞, 陈圣宾, 邓杰文, 邓惺位, 李喆, 邱鹭. 生境数量和生境质量以及气象因子对成都市粪食性金龟物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 708-719. |
| [10] | 黄倩, 朱时应, 李天顺, 李明燕, 索南措, 普布. 西藏热振国家森林公园土壤原生动物群落沿海拔分布格局及其与环境因子的关联特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 499-508. |
| [11] | 卫玺玺, 晁鑫艳, 郑景明, 唐可欣, 万龙, 周金星. 贺兰山东、西侧典型植物群落物种多样性差异及其影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 520-530. |
| [12] | 陈弘杰, 廖洪凯, 龙健, 赵雨鑫, 湛凯翔, 冉泰山, 杨国梅. 强还原土壤灭菌对土壤原生生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 539-547. |
| [13] | 丁昊, 李长鑫, 丁静, 兰昊. n-damo细菌在不同生态环境中的遗传多样性和潜在功能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 202-211. |
| [14] | 崔盼盼, 于洋, 曲波, 苏芳莉. 封育对退化河岸草地植物多样性和植被景观的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1708-1716. |
| [15] | 陈会玲, 勾蒙蒙, 刘常富, 雷蕾, 胡建文, 朱粟锋, 斛如媛, 肖文发. 鄂中丘陵区不同林龄马尾松人工林林下植物多样性与土壤理化性质关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1525-1533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
