生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 126-134.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.01.014
收稿日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2025-01-18
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
* 俞龙生。E-mail: sysulss@163.com作者简介:许铭宇(1991年生),男,高级工程师,主要从事植被生态恢复和土地复垦。E-mail: xmy4200@126.com
基金资助:
XU Mingyu1( ), YU Longsheng2,*(
), YU Longsheng2,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-20
Online:2025-01-18
Published:2025-01-21
摘要:
离子型稀土矿区生物生境破碎、土壤贫瘠,生态系统自然恢复困难,使用农林废弃资源有机材料进行土壤改良是稀土尾砂土壤低成本高效修复的手段之一。为探究农林废弃有机材料对稀土矿土壤改良的生态效应,以离子型稀土矿尾砂作为研究对象,选用油茶果壳、花生壳、松果壳、玉米秸秆和园林植物落叶等作为农林废弃有机材料,进行了单施试验,分析其对稀土矿土壤理化性质的改良效果,并通过16S rDNA基因测序分析了各处理组的土壤微生物多样性和群落结构。结果表明:利用油茶果壳、花生壳、松果壳、玉米秸秆和落叶重构矿区土壤具有可行性,均可显著改善土壤环境质量,增加土壤肥力;施加落叶对土壤pH值的调控效果较为明显,土壤pH为7.32,较对照组高38.52%;施加改良材料后土壤有机质含量均显著高于对照组(p<0.05),油茶果壳对土壤有机质改良效果优于其他处理组,质量分数均值为132.28 g·kg−1,较对照组提高了2962.04%;玉米秸秆对稀土矿尾砂土壤改良的综合效果最佳,其土壤全氮、全磷、全钾、碱解氮和有效磷含量分别提高了971.43%、150%、9.46%、961.64%和7765.32%。不同农林废弃有机材料显著改变了土壤细菌群落结构和多样性,各处理门水平优势细菌群落组成基本相似,第一优势微生物为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)。该研究结果可为稀土矿区土壤有机质富集及农林废弃物资源化利用提供技术参考。
中图分类号:
许铭宇, 俞龙生. 农林废弃有机材料对离子型稀土矿尾砂的土壤改良效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(1): 126-134.
XU Mingyu, YU Longsheng. Soil Improvement Effect of Agricultural and Forestry Waste Organic Materials on Ionic Rare Earth Mine Tailing[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2025, 34(1): 126-134.
| 供试材料 | pH | 电导率/ (μS·cm−1) | w(SOM)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TN)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TP)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TK)/ (g·kg−1) | w(AN)/ (mg·kg−1) | w(AP)/ (mg·kg−1) | w(AK)/ (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尾砂土壤 | 4.36 | 120.85 | 1.68 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 32.13 | 2.97 | 0.99 | 25.83 |
| 油茶果壳 | 4.70 | 1540 | 627.62 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 16.90 | 201.00 | 6.00 | 1590.00 |
| 花生壳 | 6.25 | 1027 | 644.41 | 2.17 | 1.10 | 4.96 | 741.00 | 3.02 | 4870.00 |
| 玉米秸秆 | 6.37 | 2200 | 516.69 | 3.05 | 5.55 | 22.50 | 410.00 | 2740.00 | 2190.00 |
| 松果 | 5.41 | 152.9 | 675.45 | 1.37 | 0.51 | 1.13 | 664.00 | 3.00 | 1110.00 |
| 园林植物落叶 | 7.91 | 1553 | 549.19 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 11.90 | 348.00 | 5.00 | 10900.00 |
表1 供试材料理化性质背景值
Table 1 The background values of physical and chemical properties of the tested materials
| 供试材料 | pH | 电导率/ (μS·cm−1) | w(SOM)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TN)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TP)/ (g·kg−1) | w(TK)/ (g·kg−1) | w(AN)/ (mg·kg−1) | w(AP)/ (mg·kg−1) | w(AK)/ (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 尾砂土壤 | 4.36 | 120.85 | 1.68 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 32.13 | 2.97 | 0.99 | 25.83 |
| 油茶果壳 | 4.70 | 1540 | 627.62 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 16.90 | 201.00 | 6.00 | 1590.00 |
| 花生壳 | 6.25 | 1027 | 644.41 | 2.17 | 1.10 | 4.96 | 741.00 | 3.02 | 4870.00 |
| 玉米秸秆 | 6.37 | 2200 | 516.69 | 3.05 | 5.55 | 22.50 | 410.00 | 2740.00 | 2190.00 |
| 松果 | 5.41 | 152.9 | 675.45 | 1.37 | 0.51 | 1.13 | 664.00 | 3.00 | 1110.00 |
| 园林植物落叶 | 7.91 | 1553 | 549.19 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 11.90 | 348.00 | 5.00 | 10900.00 |
| 供试材料 | 编号 | 处理 |
|---|---|---|
| 稀土矿尾砂土壤 | CK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤 |
| 油茶果壳 | YCGK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg油茶果壳 |
| 花生壳 | HSK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg花生壳 |
| 玉米秸秆 | YMJG | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg玉米秸秆 |
| 松果壳 | SG | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg松果壳 |
| 园林植物落叶 | LY | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.35 kg落叶 |
表2 试验设计方案
Table 2 Test design scheme
| 供试材料 | 编号 | 处理 |
|---|---|---|
| 稀土矿尾砂土壤 | CK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤 |
| 油茶果壳 | YCGK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg油茶果壳 |
| 花生壳 | HSK | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg花生壳 |
| 玉米秸秆 | YMJG | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg玉米秸秆 |
| 松果壳 | SG | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.15 kg松果壳 |
| 园林植物落叶 | LY | 1.5 kg稀土矿尾砂土壤+0.35 kg落叶 |
| 指标 | pH | 电导率 | 有机质 | 全氮 | 全磷 | 全钾 | 碱解氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | ||||||||
| 电导率 | 0.867*1) | 1.000 | |||||||
| 有机质 | 0.095 | −0.27 | 1.000 | ||||||
| 全氮 | 0.909* | 0.68 | 0.432 | 1.000 | |||||
| 全磷 | 0.614 | 0.848* | −0.303 | 0.522 | 1.000 | ||||
| 全钾 | 0.46 | 0.753 | −0.467 | 0.335 | 0.684 | 1.000 | |||
| 碱解氮 | 0.866* | 0.768 | 0.242 | 0.934**2) | 0.77 | 0.447 | 1.000 | ||
| 有效磷 | 0.534 | 0.79 | −0.334 | 0.433 | 0.990** | 0.605 | 0.708 | 1.000 | |
| 速效钾 | 0.484 | 0.576 | 0.343 | 0.586 | 0.488 | 0.595 | 0.569 | 0.409 | 1.000 |
表3 土壤各理化指标Pearson相关性分析
Table 3 Pearson correlation analysis of soil physical and chemical indices
| 指标 | pH | 电导率 | 有机质 | 全氮 | 全磷 | 全钾 | 碱解氮 | 有效磷 | 速效钾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | ||||||||
| 电导率 | 0.867*1) | 1.000 | |||||||
| 有机质 | 0.095 | −0.27 | 1.000 | ||||||
| 全氮 | 0.909* | 0.68 | 0.432 | 1.000 | |||||
| 全磷 | 0.614 | 0.848* | −0.303 | 0.522 | 1.000 | ||||
| 全钾 | 0.46 | 0.753 | −0.467 | 0.335 | 0.684 | 1.000 | |||
| 碱解氮 | 0.866* | 0.768 | 0.242 | 0.934**2) | 0.77 | 0.447 | 1.000 | ||
| 有效磷 | 0.534 | 0.79 | −0.334 | 0.433 | 0.990** | 0.605 | 0.708 | 1.000 | |
| 速效钾 | 0.484 | 0.576 | 0.343 | 0.586 | 0.488 | 0.595 | 0.569 | 0.409 | 1.000 |
| 处理 | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 | Richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.04±0.98b | 0.16±0.15a | 834.18±217.21c | 649.53±205.55b | 647.67±206.45b |
| YCGK | 3.79±0.95b | 0.14±0.10ab | 1338.83±316.54bc | 1130.83±310.74b | 1130.00±311.04b |
| HSK | 5.75±0.10a | 0.01±0.001b | 3031.82±109.66a | 2687.50±145.74a | 2687.00±145.91a |
| YMJG | 5.46±0.26a | 0.02±0.008ab | 3300.95±314.89a | 2920.30±332.97a | 2920.00±333.06a |
| SG | 4.00±0.18b | 0.05±0.008ab | 1563.76±85.67b | 1255.33±99.22b | 1254.33±99.50b |
| LY | 5.54±0.22a | 0.02±0.005b | 3128.41±776.41a | 2802.07±855.20a | 2801.67±855.61a |
表4 不同处理细菌α多样性分析
Table 4 Analysis of α diversity of bacteria under different treatments
| 处理 | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 | Richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.04±0.98b | 0.16±0.15a | 834.18±217.21c | 649.53±205.55b | 647.67±206.45b |
| YCGK | 3.79±0.95b | 0.14±0.10ab | 1338.83±316.54bc | 1130.83±310.74b | 1130.00±311.04b |
| HSK | 5.75±0.10a | 0.01±0.001b | 3031.82±109.66a | 2687.50±145.74a | 2687.00±145.91a |
| YMJG | 5.46±0.26a | 0.02±0.008ab | 3300.95±314.89a | 2920.30±332.97a | 2920.00±333.06a |
| SG | 4.00±0.18b | 0.05±0.008ab | 1563.76±85.67b | 1255.33±99.22b | 1254.33±99.50b |
| LY | 5.54±0.22a | 0.02±0.005b | 3128.41±776.41a | 2802.07±855.20a | 2801.67±855.61a |
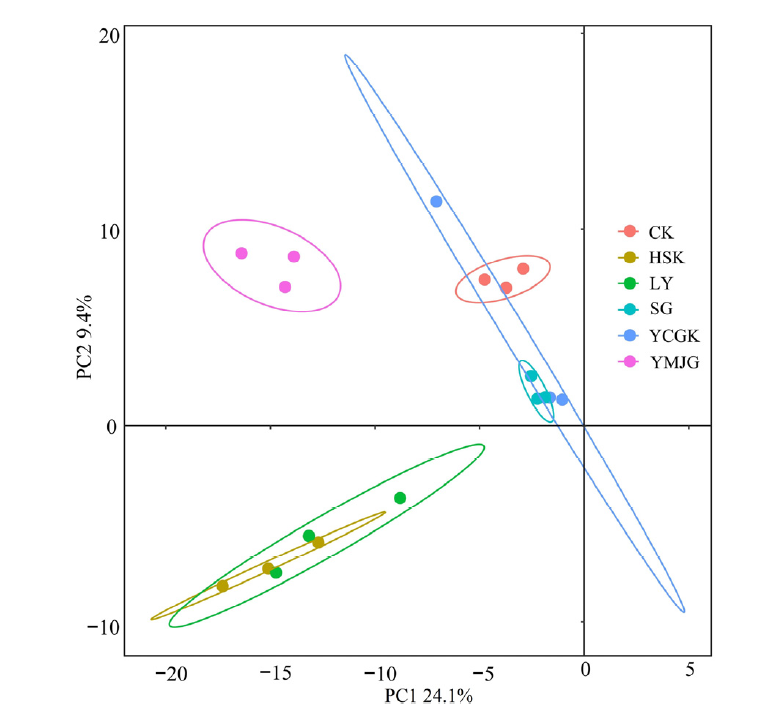
图6 土壤细菌群落β多样性分析 横坐标(x)表示第一主成分,百分比则表示第一主成分对样品差异的贡献值;纵坐标(y)表示第二主成分,百分比表示第二主成分对样品差异的贡献值。不同颜色的点代表不同分组的样本
Figure 6 Analysis of the β diversity in soil bacterial communities
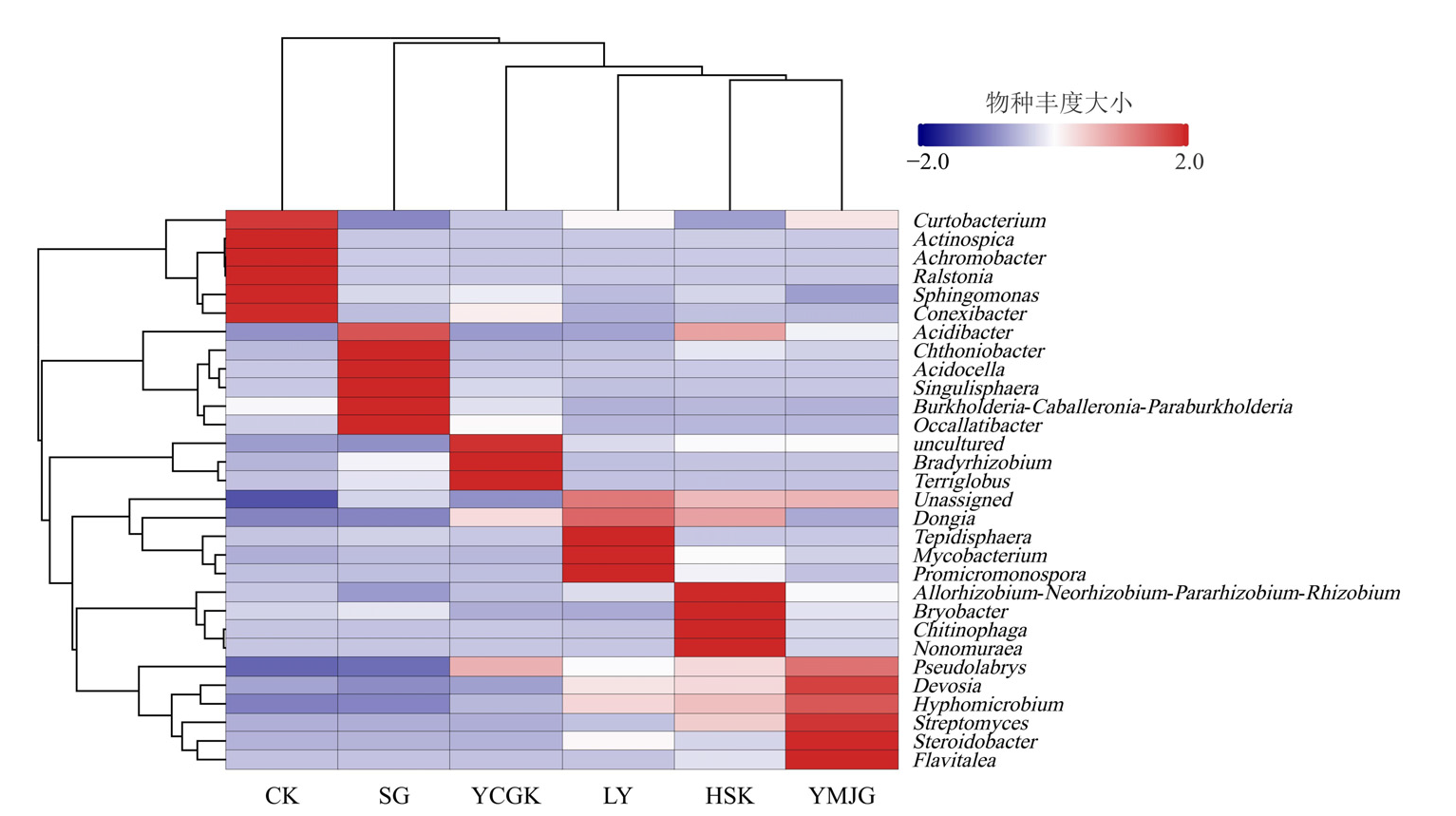
图7 不同处理在属分类水平上的物种丰度聚类热图 蓝色代表物种的相对丰度低,红色代表物种的相对丰度高
Figure 7 Species abundance clustering heat map of different treatments at the genus classification level
| [1] | CUI J W, YANG B G, ZHANG M L, et al., 2023. Investigating the effects of organic amendments on soil microbial composition and its linkage to soil organic carbon: A global meta-analysis[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 894:164899. |
| [2] | GUO M N, ZHONG X, LIU W S, et al., 2022. Biogeochemical dynamics of nutrients and rare earth elements (REEs) during natural succession from biocrusts to pioneer plants in REE mine tailings in southern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 828:154361. |
| [3] | HAMANAKA A, SASAOKA T, SHIMADA H, et al., 2022. Amelioration of acidic soil using fly Ash for Mine Revegetation in Post-Mining Land[J]. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 9(3):201-206. |
| [4] | MENG X Y, ZHAO H B, ZHAO Y, et al., 2023. Heap leaching of ion adsorption rare earth ores and REEs recovery from leachate with lixiviant regeneration[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 898:165417. |
| [5] | LI Q, CHANG J J, LI L F, et al., 2024. Soil amendments alter cadmium distribution and bacterial communitystructure in paddy soils[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 924:171399. |
| [6] | WORLANYO A S, LI J F, 2021. Evaluating the environmental and economic impact of mining for post-mined land restoration and land-use: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 279:111623. |
| [7] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:22-114. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:22-114. | |
| [8] | 毕银丽, 郭晨, 王坤, 2020. 煤矿区复垦土壤的生物改良研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 48(4):52-59. |
| BI Y L, GUO C, WANG K, 2020. Research progress on bioimprovement of reclaimed soil in coal mine area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 48(4):52-59. | |
| [9] | 陈敏, 张大超, 朱清江, 等, 2017. 离子型稀土矿山废弃地生态修复研究进展[J]. 中国稀土学报, 35(4):461-468. |
| CHEN M, ZHANG D C, ZHU Q J, et al., 2017. Ionic Rare Earth Mine of Abandoned Land of Ecological Restoration of Research Progress[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earth, 35(4):461-468. | |
| [10] | 陈莺燕, 刘文深, 丁铿博, 等, 2018. 有机改良剂及生物炭对离子型稀土矿尾砂地生态修复的改良探究[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(12):4769-4778. |
| CHEN Y Y, LIU W S, DING K B, et al., 2018. Study on the improvement of ecological restoration of Ion-type rare earth tailings by organic amendments and biochar[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 38(12):4769-4778. | |
| [11] | 程胜, 林龙勇, 李俊春, 等, 2024. 离子吸附型稀土矿区生态环境问题与土壤修复技术研究进展[J]. 地球化学, 53(1):17-29. |
| CHENG S, LIN L Y, LI J C, et al., 2024. Research progress on Eco-environmental problems and soil remediation technologies of ion-adsorption type rare earth mining areas[J]. GEOCHIMICA, 53(1):17-29. | |
| [12] | 贺燕子, 田芷源, 马瑞, 等, 2023. 保水保肥材料对废弃离子型稀土矿区尾砂土壤理化性质及皇竹草生长的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 37(2):267-274. |
| HE Y Z, TIAN Z Y, MA R, et al., 2023. Effects of water and fertilizer retaining materials on soil physical and chemical properties of tailings in abandoned Ion-type rare earth mining area and growth of Imperial bamboo grass[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(2):267-274. | |
| [13] |
姜勇, 张勇勇, 李天鹏, 等, 2022. 玉米秸秆还田和有机配施提高黑土酸中和容量[J]. 地理学报, 77(7):1701-1712.
DOI |
|
JIANG Y, ZHANG Y Y, LI T P, et al., 2022. Increasing acid neutralization capacity of black soil by corn straw returning and organic application[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(7):1701-1712.
DOI |
|
| [14] | 孔令健, 张琳, 任杰, 等, 2024. 高寒矿区环境材料混施下土壤改良及工程应用研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 52(S1):1-13. |
| KONG L J, ZHANG L, REN J, et al., 2024. Study on soil improvement and engineering application under mixed application of environmental materials in alpine mining area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 52(S1):1-13. | |
| [15] | 李江遐, 关强, 黄伏森, 等, 2014. 不同改良剂对矿区土壤重金属有效性及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(6):211-215. |
| LI J X, GUAN Q, HUANG F S, et al., 2014. Effects of different amendments on soil heavy metal availability and soil enzyme activity in mining area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(6):211-215. | |
| [16] |
李依临, 尚海丽, 温欣, 等, 2022. 多源废弃物配施对矿区土壤的改良效应[J]. 北方农业学报, 50(4):74-82.
DOI |
| LI Y L, SHANG H L, WEN X, et al., 2022. Effect of mixed application of multi-source wastes on soil improvement in mining area[J]. Acta Agriculturae Sinica of North China, 50(4):74-82. | |
| [17] | 刘文深, 刘畅, 王志威, 等, 2015. 离子型稀土矿尾砂地植被恢复障碍因子研究[J]. 土壤学报, 52(4):879-887. |
| LIU W S, LIU C, WANG Z W, et al., 2015. Study on obstacle factors of vegetation restoration in ion-type rare earth mine tailings[J]. Acta Edologica Sinica, 52(4):879-887. | |
| [18] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社:146-195. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods for Agricultural chemical Analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press:146-195. | |
| [19] | 荣颖, 王淳, 孙光林, 等, 2022. 不同重构土壤材料配比的土壤改良和苜蓿生长效应研究[J]. 金属矿山, 552(6):197-204. |
| RONG Y, WANG C, SUN G L, et al., 2022. Study on effects of soil improvement and alfalfa growth with different ratios of reconstructed soil materials[J]. Metal Mine, 552(6):197-204. | |
| [20] | 汪江萍, 邓扬悟, 黄金, 等, 2021. 人工BSCs对稀土尾砂理化性质及抗蚀性的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1):327-334. |
| WANG J P, DENG Y W, HUANG J, et al., 2021. Effects of artificial BSCs on physicochemical properties and corrosion resistance of rare earth tailings[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(1):327-334. | |
| [21] | 杨海婷, 祁文俊, 高超前, 等, 2024. 园林绿化废弃物有机肥养分释放特征及对油松生长的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 30(6):1173-1184. |
| YANG H T, QI W J, GAO C Q, et al., 2024. Characteristics of nutrient release from garden greening waste organic fertilizer and its Effects on growth of Pinus tabulaeformis[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 30(6):1173-1184. | |
| [22] | 杨侨, 赵龙, 侯红, 等, 2018. 土壤改良剂对赣南废弃稀土尾矿的改良效应[J]. 应用化工, 47(2):211-214. |
| YANG Q, ZHAO L, HOU H, et al., 2018. Improvement effect of soil conditioner on waste rare earth tailings in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 47(2):211-214. | |
| [23] | 杨阳, 钟瑞林, 王有霖, 等, 2023. 钙矾石法去除离子型稀土矿尾水中硫酸根研究[J]. 河北环境工程学院学报, 33(1):79-83. |
| YANG Y, ZHONG R L, WANG Y L, et al., 2023. Study on removal of sulfate from tailing water of ion-type rare earth ores by ettringite process[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, 33(1):79-83. | |
| [24] |
于方明, 袁月, 曾梦, 等, 2024. 氮源添加对重金属污染土壤氨氧化微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 33(5):771-780.
DOI |
| YU F M, YUAN Y, ZENG M, et al., 2024. Variations on the ammonia oxidizers under different nitrogen fertilization regimes in heavy metal-contaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecological Environment, 33(5):771-780. | |
| [25] | 悦飞雪, 李继伟, 王艳芳, 等, 2019. 生物炭和AM真菌提高矿区土壤养分有效性的机理[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(8):1325-1334. |
| YUE F X, LI J W, WANG Y F, et al., 2019. Mechanism of biochar and AM fungi to improve soil nutrient availability in mining area[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Journal, 25(8):1325-1334. | |
| [26] | 张朔, 秦磊, 王观石, 等, 2023. 离子吸附型稀土无铵开采现状[J]. 稀土, 44(6):123-134. |
| ZHANG S, QIN L WANG G S, et al., 2023. Status of ammonium-free mining of ion-adsorbed rare earth[J]. Rare Earth, 44(6):123-134. | |
| [27] | 赵鹏, 史兴萍, 尚卿, 等, 2023. 矿区复垦地土壤改良研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 40(1):1-14. |
| ZHAO P, SHI X P, SHANG Q, et al., 2023. Research progress on soil improvement of reclamation land in mining area[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 40(1):1-14. | |
| [28] | 周丹, 罗才贵, 苏佳, 等, 2014. 离子型稀土矿区土壤生态恢复[J]. 金属矿山, 460(10):103-109. |
| ZHOU D, LUO C G, SU J, et al., 2014. Soil ecological restoration in ion-type rare earth mining area[J]. Metal Mine, 460(10):103-109. |
| [1] | 张京磊, 王国良, 吴波, 贾春林, 张进红, 周圆, 马冰. 滨海盐碱地苜蓿-小黑麦轮作对土壤细菌和真菌群落多样性与网络结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1048-1062. |
| [2] | 李多美, 孔涛, 陈曦, 高明夫, 高熙梣, 曾泽宇, 保佳慧. 古龙酸母液混制肥和草席覆盖措施对新疆旱区牧草生长和土壤养分含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 548-559. |
| [3] | 何杰, 李宗明, 杨正宇, 沈健林, 刘国平, 吴金水. 牛粪化肥配施对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(4): 573-584. |
| [4] | 宋江琴, 尹亚丽, 赵文, 刘燕, 随奇奇, 火久艳, 郑文贤, 李世雄. 青海高原黑土滩退化草地土壤微生物群落空间分异特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(11): 1696-1707. |
| [5] | 张传光, 沈艳, 张珊珊, 李玉文, 陈剑, 杨文忠. 原生与迁地毛枝五针松根际土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1544-1553. |
| [6] | 马媛, 田路露, 吕杰, 柳沛, 张旭, 李二阳, 张清航. 天山北坡雪岭云杉森林土壤微生物群落及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-11. |
| [7] | 唐志伟, 翁颖, 朱夏童, 蔡洪梅, 代雯慈, 王捧娜, 郑宝强, 李金才, 陈翔. 秸秆还田下中国农田土壤微生物生物量碳变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [8] | 李航, 陈金平, 丁兆华, 舒洋, 魏江生, 赵鹏武, 周梅, 王宇轩, 梁驰昊, 张轶超. 火干扰对兴安落叶松林土壤氮组分及土壤中氮循环功能基因的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1563-1573. |
| [9] | 刘晗, 王萍, 孙鲁沅, 秦文婧, 陈晓芬, 陈金, 周国朋, 梁婷, 刘佳, 李燕丽. 种植冬绿肥对红壤幼龄橘园土壤微生物量碳、氮和酶活的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1623-1631. |
| [10] | 陈懂懂, 霍莉莉, 赵亮, 陈昕, 舒敏, 贺福全, 张煜坤, 张莉, 李奇. 青海高寒草地水热因子对土壤微生物生物量碳、氮空间变异的贡献——基于增强回归树模型[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| [11] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [12] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [13] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [14] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [15] | 秦佳琪, 肖指柔, 明安刚, 朱豪, 滕金倩, 梁泽丽, 陶怡, 覃林. 针阔人工混交林及其纯林对土壤微生物碳循环功能基因丰度的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1719-1731. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
