生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1944-1952.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.012
纪晟莹1( ), 李杰2,3, 李鑫1, 陶禹1, 陈娟1,*(
), 李杰2,3, 李鑫1, 陶禹1, 陈娟1,*( ), 王晓玉2,3,*
), 王晓玉2,3,*
收稿日期:2024-08-17
出版日期:2024-12-18
发布日期:2024-12-31
通讯作者:
*王晓玉。E-mail: xiao_yu_100@163.com;作者简介:纪晟莹(1992年生),女,助理研究员,硕士,主要研究方向为蔬菜栽培与农业环境。E-mail: 19495403@qq.com
基金资助:
JI Shengying1( ), LI Jie2,3, LI Xin1, TAO Yu1, CHEN Juan1,*(
), LI Jie2,3, LI Xin1, TAO Yu1, CHEN Juan1,*( ), WANG Xiaoyu2,3,*
), WANG Xiaoyu2,3,*
Received:2024-08-17
Online:2024-12-18
Published:2024-12-31
摘要:
当前耕地土壤镉(Cd)污染严峻,公众通过食用蔬菜摄入镉的风险增加,但针对瓜类蔬菜在不同污染土壤及基因型下的镉富集特性研究尚不足。为探究不同种类及品种的瓜类在不同环境条件下对镉的吸收积累特性,并评估环境因子与基因型对蔬菜镉含量的综合影响,通过在湘江流域选择12个典型镉污染特征区域,采取多点-多瓜类/品种田间试验方法结合土壤镉含量、土壤性质与蔬菜镉累积对应采样分析,采用相关性分析、逐步线性回归分析和多种模型的物种敏感性分布(SSD)分析等方法分析环境因子与蔬菜镉含量、生物富集系数(BCF)的关系及安全阈值。结果显示:1)环境因子对瓜类蔬菜镉含量的影响显著高于基因型,环境、品种和环境品种互作共解析了瓜类蔬菜镉含量和BCF的94.05%和84.03%,其中环境的贡献率分别为62.90%和36.67%;2)瓜类蔬菜镉含量与土壤总镉、有效态镉显著正相关(r=0.721,p≤0.01;r=0.737,p≤0.01),与pH值呈显著负相关(r= −0.390,p≤0.01);土壤有效态镉与pH值是主要的环境影响因素,可以解释瓜类蔬菜镉含量变异的60.80%;3)瓜类蔬菜整体超标风险较低,但不同瓜类品种的镉富集能力存在显著差异,板栗南瓜(Cucurbita moschata)品种V5表现出较高敏感性,蜜本南瓜品种V6表现出低敏感性;4)基于Burr III type分布模型,估算了保障95%瓜类蔬菜安全生长的土壤镉含量阈值,其阈值为1.316 mg∙kg−1。该研究可为镉污染土壤中的瓜类蔬菜种植提供科学的品种选择和风险控制指导。
中图分类号:
纪晟莹, 李杰, 李鑫, 陶禹, 陈娟, 王晓玉. 环境与基因型互作对瓜类蔬菜镉积累的影响及产地土壤安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1944-1952.
JI Shengying, LI Jie, LI Xin, TAO Yu, CHEN Juan, WANG Xiaoyu. Research on the Interaction of Environmental Factors and Genotypes on Cadmium Accumulation in Cucurbit Vegetables and the Soil Safe Threshold[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(12): 1944-1952.
| 种类 | 蔬菜编号 | 品种名 | 商品名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 冬瓜 | V1 | 黑皮冬瓜 | 兴蔬墨地龙 |
| V2 | 粉皮冬瓜 | 兴蔬粉地龙 | |
| 丝瓜 | V3 | 中熟长绿丝瓜 | 兴蔬新美佳 |
| V4 | 极早熟绿丝瓜 | 兴蔬早佳 | |
| 南瓜 | V5 | 板栗南瓜 | 金优红板栗 |
| V6 | 蜜本南瓜 | 兴蔬大果蜜本 |
表1 瓜类蔬菜种类、品种、商品名及编号分类
Table 1 Category, varieties, trade names and numbers of cucurbit vegetables
| 种类 | 蔬菜编号 | 品种名 | 商品名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 冬瓜 | V1 | 黑皮冬瓜 | 兴蔬墨地龙 |
| V2 | 粉皮冬瓜 | 兴蔬粉地龙 | |
| 丝瓜 | V3 | 中熟长绿丝瓜 | 兴蔬新美佳 |
| V4 | 极早熟绿丝瓜 | 兴蔬早佳 | |
| 南瓜 | V5 | 板栗南瓜 | 金优红板栗 |
| V6 | 蜜本南瓜 | 兴蔬大果蜜本 |
| 试验点 | 编号 | w(总镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效态镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株洲市 | S1 | 2.55±0.07aA | 1.85±0.03aA | 35.18±1.60deDEF | 4.90±0.07cCD |
| S3 | 1.95±0.05cC | 1.43±0.03bB | 33.39±0.39efEF | 4.59±0.07defDEF | |
| S8 | 0.63±0.04fF | 0.42±0.04efgEF | 19.75±1.08hH | 5.30±0.10bB | |
| S11 | 0.59±0.01fF | 0.32±0.01gFG | 37.69±0.62cdCD | 5.72±0.11aA | |
| S12 | 0.91±0.05eE | 0.50±0.02eE | 35.09±0.66deDEF | 5.60±0.09aAB | |
| 湘潭市 | S2 | 2.25±0.06bB | 1.44±0.05bB | 36.31±0.97cdeCDE | 4.54±0.06efEF |
| S4 | 1.29±0.03dD | 0.91±0.03cC | 31.32±1.03fF | 4.74±0.13cdeCDEF | |
| S5 | 1.42±0.06dD | 0.82±0.07cCD | 24.48±0.90gG | 4.83±0.08cdCDE | |
| S6 | 0.60±0.03fF | 0.38±0.01fgEF | 52.39±1.31aA | 4.46±0.05fF | |
| S7 | 0.99±0.07eE | 0.70±0.05dD | 38.67±0.75cCD | 4.95±0.03cC | |
| S9 | 0.62±0.05fF | 0.48±0.04efE | 39.28±1.02cC | 5.59±0.09aAB | |
| 长沙市 | S10 | 0.40±0.01gG | 0.20±0.00hG | 43.48±1.11bB | 4.12±0.06gG |
| 中国土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—2018) | |||||
| 风险筛选值 | 0.3 | ‒ | ‒ | pH≤5.5 | |
| 0.3 | ‒ | ‒ | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | ||
| 风险管制值 | 1.5 | ‒ | ‒ | pH≤5.5 | |
| 2.0 | ‒ | ‒ | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | ||
表2 各试验点的土壤理化性质、镉质量分数及标准值情况
Table 2 Soil physical and chemical properties, cadmium content and standard value of test sites
| 试验点 | 编号 | w(总镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有效态镉)/(mg∙kg−1) | w(有机质)/(g∙kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株洲市 | S1 | 2.55±0.07aA | 1.85±0.03aA | 35.18±1.60deDEF | 4.90±0.07cCD |
| S3 | 1.95±0.05cC | 1.43±0.03bB | 33.39±0.39efEF | 4.59±0.07defDEF | |
| S8 | 0.63±0.04fF | 0.42±0.04efgEF | 19.75±1.08hH | 5.30±0.10bB | |
| S11 | 0.59±0.01fF | 0.32±0.01gFG | 37.69±0.62cdCD | 5.72±0.11aA | |
| S12 | 0.91±0.05eE | 0.50±0.02eE | 35.09±0.66deDEF | 5.60±0.09aAB | |
| 湘潭市 | S2 | 2.25±0.06bB | 1.44±0.05bB | 36.31±0.97cdeCDE | 4.54±0.06efEF |
| S4 | 1.29±0.03dD | 0.91±0.03cC | 31.32±1.03fF | 4.74±0.13cdeCDEF | |
| S5 | 1.42±0.06dD | 0.82±0.07cCD | 24.48±0.90gG | 4.83±0.08cdCDE | |
| S6 | 0.60±0.03fF | 0.38±0.01fgEF | 52.39±1.31aA | 4.46±0.05fF | |
| S7 | 0.99±0.07eE | 0.70±0.05dD | 38.67±0.75cCD | 4.95±0.03cC | |
| S9 | 0.62±0.05fF | 0.48±0.04efE | 39.28±1.02cC | 5.59±0.09aAB | |
| 长沙市 | S10 | 0.40±0.01gG | 0.20±0.00hG | 43.48±1.11bB | 4.12±0.06gG |
| 中国土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—2018) | |||||
| 风险筛选值 | 0.3 | ‒ | ‒ | pH≤5.5 | |
| 0.3 | ‒ | ‒ | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | ||
| 风险管制值 | 1.5 | ‒ | ‒ | pH≤5.5 | |
| 2.0 | ‒ | ‒ | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | ||
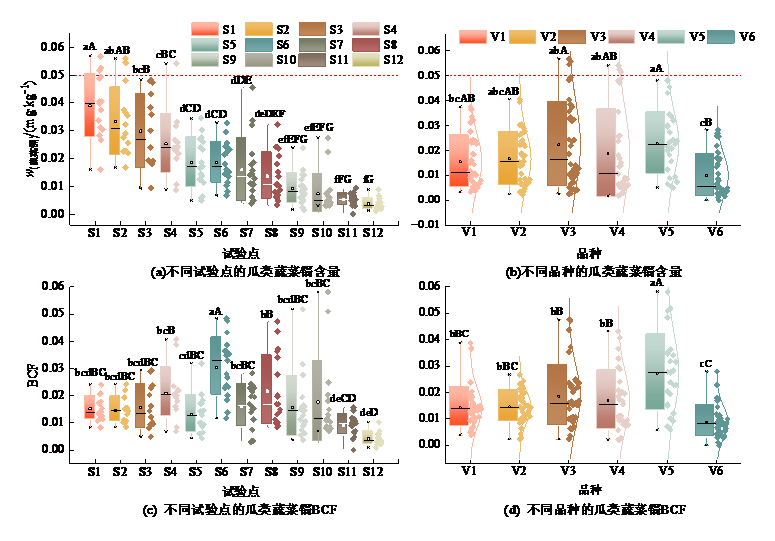
图1 不同试验点及品种的瓜类蔬菜镉质量分数和生物富集系数分布 w为平均值±标准误差(试验点n=18,品种n=36)
Figure 1 Distribution of cadmium content and BCF of cucurbit vegetables in different test sites and varieties
| 评价因素 | 差异来源 | SF | df | F | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜镉含量 | 环境 | 0.0234 | 11 | 101.05** | 62.90% |
| 品种 | 0.0055 | 5 | 52.35** | 14.81% | |
| 环境×品种 | 0.0061 | 54 | 5.35** | 16.34% | |
| BCF | 环境 | 0.0085 | 11 | 35.11** | 36.67% |
| 品种 | 0.0047 | 5 | 42.74** | 20.30% | |
| 环境×品种 | 0.0063 | 54 | 5.28** | 27.06% |
表3 影响瓜类蔬菜镉累积的多因素方差分析
Table 3 Multivariate variance analysis of cadmium accumulation in cucurbit vegetables
| 评价因素 | 差异来源 | SF | df | F | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蔬菜镉含量 | 环境 | 0.0234 | 11 | 101.05** | 62.90% |
| 品种 | 0.0055 | 5 | 52.35** | 14.81% | |
| 环境×品种 | 0.0061 | 54 | 5.35** | 16.34% | |
| BCF | 环境 | 0.0085 | 11 | 35.11** | 36.67% |
| 品种 | 0.0047 | 5 | 42.74** | 20.30% | |
| 环境×品种 | 0.0063 | 54 | 5.28** | 27.06% |
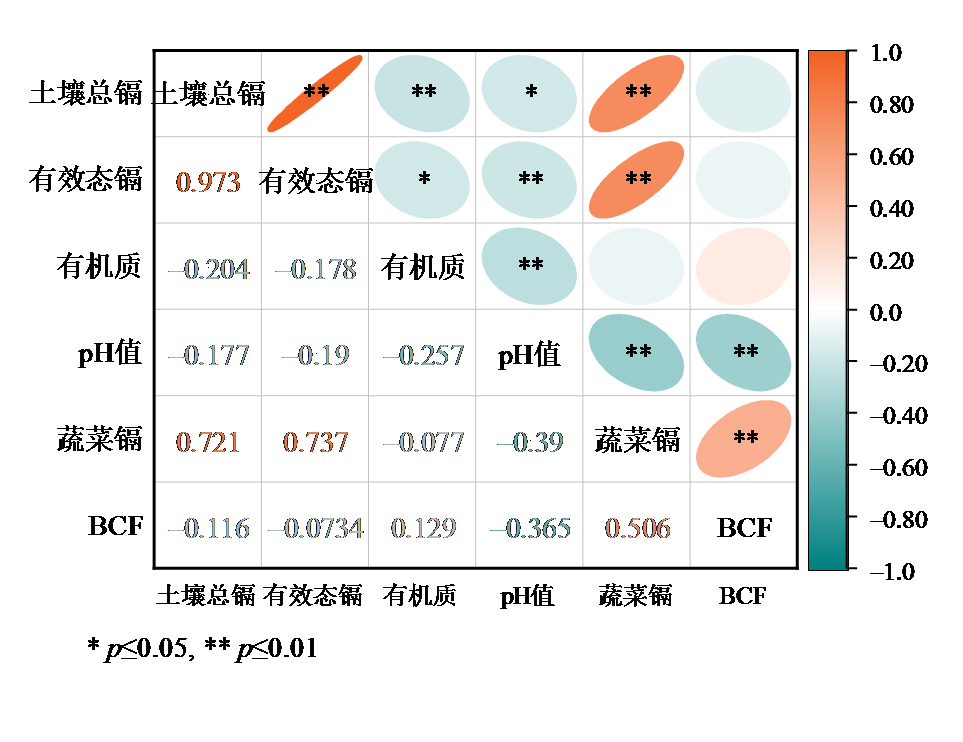
图2 土壤环境变量因子与瓜类蔬菜镉含量、BCF的Pearson相关性分析
Figure 2 Pearson correlation analysis of soil environmental factors with cadmium content and BCF of cucurbit vegetables
| [1] |
AL MAMUN S, CHANSON G, BENYAS E, et al., 2016. Municipal composts reduce the transfer of Cd from soil to vegetables[J]. Environmental Pollution, 213: 8-15.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
CHAUDRI A, MCGRATH S, GIBBS P, et al., 2007. Cadmium availability to wheat grain in soils treated with sewage sludge or metal salts[J]. Chemosphere, 66(8): 1415-1423.
PMID |
| [3] | CHI Y H, LI F B, TAM N F, et al., 2018. Variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations and screening for stable low-accumulating rice cultivars from multi-environment trials[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 643: 1314-1324. |
| [4] | DING C F, ZHANG T L, WANG X X, et al., 2013. Prediction model for cadmium transfer from soil to carrot (Daucus carota L.) and its application to derive soil thresholds for food safety[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(43): 10273-10282. |
| [5] |
DOABI S A, KARAMI M, AFYUNI M, et al., 2018. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 163: 153-164.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | DUAN G L, SHAO G S, TANG Z, et al., 2017. Genotypic and environmental variations in grain cadmium and arsenic concentrations among a panel of high yielding rice cultivars[J]. Rice, 10(1): 9. |
| [7] | GAO J T, YE X X, WANG X Y, et al., 2021. Derivation and validation of thresholds of cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury and arsenic for safe rice production in paddy soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 220: 112404. |
| [8] |
YANG J X, GUO H T, MA Y B, et al., 2010. Genotypic variations in the accumulation of Cd exhibited by different vegetables[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(8): 1246-1252.
PMID |
| [9] | KORSMAN J C, SCHIPPER A M, HENDRIKS A J, 2016. Dietary toxicity thresholds and ecological risks for birds and mammals based on species sensitivity distributions[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(19): 10644-10652. |
| [10] | KWIATKOWSKA-MALINA J, 2018. Functions of organic matter in polluted soils: The effect of organic amendments on phytoavailability of heavy metals[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 123: 542-545. |
| [11] |
LIANG Z F, DING Q, WEI D P, et al., 2013. Major controlling factors and predictions for cadmium transfer from the soil into spinach plants[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 93: 180-185.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | LU J H, YANG X P, MENG X C, et al., 2017. Predicting cadmium safety thresholds in soils based on cadmium uptake by Chinese cabbage[J]. Pedosphere, 27(3): 475-481. |
| [13] |
MI B B, LIU F, XIE L L, et al., 2019. Evaluation of the uptake capacities of heavy metals in Chinese cabbage[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171: 511-517.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | MU D M, ZHENG S N, LIN D S, et al., 2023. Derivation and validation of soil cadmium thresholds for the safe farmland production of vegetables in high geological background area[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 873: 162171. |
| [15] |
NIU Z G, DU L, LI J F, et al., 2018. Ecological risk assessment of microcystin-LR in the upstream section of the Haihe River based on a species sensitivity distribution model[J]. Chemosphere, 193: 403-411.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | SUN T, HU Y N, WANG Z Y, et al., 2022. A tissue atlas of cadmium accumulation and the correlation with thiol-containing chelates in zucchini provide insights into cadmium partitioning and food safety[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 421: 126756. |
| [17] | WANG Y F, SU Y, LU S G, 2020. Predicting accumulation of Cd in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and soil threshold concentration of Cd for rice safe production[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 738: 139805. |
| [18] |
WHEELER J R, GRIST E P M, LEUNG K M Y, et al., 2002. Species sensitivity distributions: Data and model choice[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 45(1-12): 192-202.
PMID |
| [19] |
XIAO W D, YE X Z, ZHANG Q, et al., 2018. Evaluation of cadmium transfer from soil to leafy vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer models, and indication of soil threshold contents[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 164: 355-362.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | XU F L, LI Y L, WANG Y, et al., 2015. Key issues for the development and application of the species sensitivity distribution (SSD) model for ecological risk assessment[J]. Ecological Indicators, 54: 227-237. |
| [21] | XU M Q, YANG L Y, CHEN Y L, et al., 2022. Selection of rice and maize varieties with low cadmium accumulation and derivation of soil environmental thresholds in karst[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 247: 114244. |
| [22] | YANG Y, LI Y L, CHEN W P, et al., 2020. Dynamic interactions between soil cadmium and zinc affect cadmium phytoavailability to rice and wheat: Regional investigation and risk modeling[J]. Environmental Pollution, 267: 115613. |
| [23] | YUE X M, SONG J X, FANG B, et al., 2021. BcNRAMP1 promotes the absorption of cadmium and manganese in Arabidopsis[J]. Chemosphere, 283: 131113. |
| [24] |
ZHANG F, PENG D, LIU L, et al., 2022. Cultivar-dependent rhizobacteria community and cadmium accumulation in rice: Effects on cadmium availability in soils and iron-plaque formation[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 116: 90-102.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | ZHAO F J, MA Y, ZHU Y G, et al., 2015. Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(2): 750-759. |
| [26] |
ZHONG T Y, XUE D W, ZHAO L M, et al., 2018. Concentration of heavy metals in vegetables and potential health risk assessment in China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40: 313-322.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | ZHOU H, YANG W T, ZHOU X, et al., 2016. Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetable species planted in contaminated soils and the health risk assessment[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(3): 289. |
| [28] |
ZHU H H, CHEN C, XU C, et al., 2016. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 219: 99-106.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | 柴冠群, 蔡景行, 吴道明, 等, 2023. 十一个辣椒品种的镉富集和转运能力比较[J]. 南方农业, 17(9): 56-60, 74. |
| CHAI G Q, CAI J X, WU D M, et al., 2023. Comparison of Cd enrichment and transport ability among 11 pepper varieties[J]. South China Agriculture, 17(9): 56-60, 74. | |
| [30] | 高广贤, 刘义强, 杨波, 等, 2023. 化肥减量配施有机肥对盐碱地土壤性状及镉形态的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (1): 30-38. |
| GAO G X, LIU Y Q, YANG B, et al., 2023. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer on soil properties and cadmium forms in saline alkali soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (1): 30-38. | |
| [31] | 和君强, 刘代欢, 邓林, 等, 2017. 农田土壤镉生物有效性及暴露评估研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 12(6): 69-82. |
| HE J Q, LIU D H, DENG L, et al., 2017. Progress in the bioavailability and exposure assessment of cadmium in farmland soil[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 12(6): 69-82. | |
| [32] | 黄贞慧, 2015. 微量元素铅镉的检测及临床意义分析[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 25(3): 43-44. |
| HUANG C H, 2015. Detection and clinical significance analysis of the trace element lead-cadmium[J]. Shenzhen Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 25(3): 43-44. | |
| [33] | 甲卡拉铁, 喻华, 冯文强, 等, 2009. 淹水条件下不同氮磷钾肥对土壤pH和镉有效性的影响研究[J]. 环境科学, 30(11): 3414-3421. |
| JIA K L T, YU H, FENG W Q, et al., 2009. Effect of different N, P and K fertilizers on soil pH and available Cd under waterlogged conditions[J]. Environmental Science, 30(11): 3414-3421. | |
| [34] | 李沛轩, 钟理, 郭蕊, 2021. 重金属镉致心血管疾病的潜在机制及治疗对策[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 51(9): 1241-1253. |
| LI P X, ZHONG L, GUO R, 2021. Potential mechanism and treatment of heavy metal cadmium-induced cardiovascular disease[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 51(9): 1241-1253. | |
| [35] | 李学德, 花日茂, 岳永德, 等, 2004. 合肥市蔬菜中铬、铅、镉和铜污染现状评价[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 31(2): 143-147. |
| LI X D, HUA R M, YUE Y D, et al., 2004. Evaluation on Contamination of Cr, Pb, Cd and Cu in Vegetables of Hefei Region[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 31(2): 143-147. | |
| [36] | 廖敏, 黄昌勇, 谢正苗, 1999. pH对镉在土水系统中的迁移和形态的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 19(1): 83-88. |
| LIAO M, HUANG C Y, XIE Z M, 1999. Effects of pH on the migration and morphology of cadmium in soil-water system[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 19(1): 83-88. | |
| [37] |
柳赛花, 纪雄辉, 谢运河, 等, 2021. 基于GGE双标图和BLUP分析筛选镉砷同步低累积水稻品种[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(2): 405-411.
DOI |
| LIU S H, JI X H, XIE Y H, et al., 2021. Screening of cadmium and arsenic synchronous low-accumulating rice cultivars based on GGE double plot and BLUP analysis[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(2): 405-411. | |
| [38] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Methods for soil agricultural chemical analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [39] | 彭佳师, 王娅婷, 王梦琦, 等, 2024. 植物重金属镉积累调控机制及其应用研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 60(2): 185-210. |
| PENG J S, WANG Y T, WANG M Y, et al., 2024. Research and regulation of cadmium uptake, transport and accumulation in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 60(2): 185-210. | |
| [40] | 史明易, 王祖伟, 王嘉宝, 等, 2020. 基于富集系数对蔬菜地土壤重金属的安全阈值研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 34(2): 130-134. |
| SHI M Y, WANG Z W, WANG J B, et al., 2020. Study on safety threshold of heavy metals in vegetable soils based on bioaccumulation factor[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 34(2): 130-134. | |
| [41] | 谭璐璐, 2023. 父代镉暴露对子代肝脏糖脂代谢的影响及其机制[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学. |
| TAN L L, 2023. Effect and its mechanisms of paternal cadmium exposure on hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in offspring[D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University. | |
| [42] | 文典, 刘香香, 王其枫, 等, 2012. 菜薹(菜心)对土壤中重金属的富集特征及产地土壤安全临界值[J]. 中国蔬菜, 262(12): 83-90. |
| WEN D, LIU X X, WANG Q F, et al., 2012. Heavy metal accumulation characteristics and environmental critical values in flowering cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) var. utilis Tsen et Lee) production area for food security[J]. China Vegetables, 262(12): 83-90. | |
| [43] |
文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 等, 2022. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(3): 603-609.
DOI |
|
WEN D, ZHAO P H, CHEN C G, et al., 2022. Study on safety threshold of soil cadmium in the vegetable producing areas of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 31(3): 603-609.
DOI |
|
| [44] | 谢运河, 田发祥, 张凤, 等, 2024. 水稻镉砷累积的基因型和环境互作效应分析[J/OL]. 农业环境科学学报, 1-15[2024-07-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20240514.1020.002.html. |
| XIE Y H, TIAN F X, ZHANG F, et al., 2024. Responses of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice to cultivar-environment interactions[J/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 1-15 [2024-07-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20240514.1020.002.html. | |
| [45] | 徐亚平, 刘凤枝, 蔡彦明, 等, 2005. 土壤中铅镉有效态提取剂的选择[J]. 农业环境与发展, 22(4): 46-48. |
| XU Y P, LIU F Z, CAI Y M, et al., 2005. Selection of effective extractants for Pb and Cd in soil[J]. Agricultural Environment and Development, 22(4): 46-48. | |
| [46] | 杨菲, 吴琦, 季辉, 等, 2011. 土壤重金属Pb和Cd在小白菜中的富集特征及产地环境安全临界值[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(13): 194-198. |
| YANG F, WU Q, JI H, et al., 2011. Soil Pb and Cd accumulation characteristics of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) and their environmental critical values in pakchoi production area for food security[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(13): 194-198. | |
| [47] | 俞果, 陈梦华, 蒋萍萍, 等, 2019. 黄瓜吸收积累镉的品种差异研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 45(5): 99-102. |
| YU G, CHEN M H, JIANG P P, et al., 2019. Cadmium absorption and accumulation of different cucumber cultivars[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 45(5): 99-102. | |
| [48] | 张丙春, 王磊, 范丽霞, 等, 2015. 铅、镉在蔬菜中的累积特性及对蔬菜生长的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(10): 2873-2878. |
| ZHANG B C, WANG L, FAN L X, et al., 2015. Accumulation characteristics of lead and cadmium in vegetables and their effects on the growth of vegetables[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(10): 2873-2878. | |
| [49] | 章明奎, 郑顺安, 王丽平, 2007. 土壤中颗粒状有机质对重金属的吸附作用[J]. 土壤通报, 38(6): 1100-1104. |
| ZHANG M K, ZHENG S A, WANG L P, 2007. Adsorption of heavy metals by soil particulate organic matter[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 38(6): 1100-1104. | |
| [50] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2016. 土壤和沉积物12种金属元素的测定王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法: HJ 803—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-19. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Soil and sediment-Determination of aqua regia extracts of 12 metal elements Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: HJ 803—2016 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group: 1-19. | |
| [51] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2024. 2023中国生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. [2024-06-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202406/P020240604551536165161.pdf. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2024. China's ecological environment bulletin 2023[EB/OL]. [2024-06-05]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202406/P020240604551536165161.pdf. | |
| [52] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局,, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行): GB 15618—2018 [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团: 1-4. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (Trial): GB 15618—2018 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group: 1-4. | |
| [53] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 自然资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[EB/OL]. [2014-04-17]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201404/W020140417558995804588.pdf. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China, 2014. National soil pollution survey bulletin[EB/OL]. [2014-04-17]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201404/W020140417558995804588.pdf. | |
| [54] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局, 2022. 食品安全国家标准食品中污染物限量: GB 2762—2022 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-18. |
| The National Health Commission, State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China, 2022. National food safety standard Limits of contaminants in foods: GB 2762—2022 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-18. | |
| [55] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 2016. 食品安全国家标准食品中多元素的测定:GB 5009. 268—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-14 |
| The National Health Commission, National Medical Products Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. National standards for food safety Determination of multielement in food: GB 5009. 268—2016 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-14. |
| [1] | 李林峰, 徐梓盛, 陈勇, 李奇, 林晓扬, 李义纯. 施硅水平对水稻根表铁膜和体内Cd累积分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 781-790. |
| [2] | 张腾云, 王静, 高健磊, 葛文静, 王宗耀, 韩龙. 碱性农田土壤冬小麦不同生育期镉的迁移转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 450-459. |
| [3] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [4] | 官国庆, 黄紫琳, 江龙飞, 罗春玲. 伴矿景天对重金属-多环芳烃复合污染土壤有机污染物消减及微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1931-1943. |
| [5] | 范婉仪, 涂晨, 王顺扬, 吴昕优, 李烜桢, 骆永明. 不同品种烟草对轻度污染耕地土壤中镉的累积特征与减量修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524. |
| [6] | 王丽华, 王磊, 许端平, 薛杨. 煤胶体对重金属铜与镉的吸附特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [7] | 李治梅, 安娅, 李梅, 王室苹, 秦好丽. 巯基/铁基功能化蒙脱土对土壤镉的钝化行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312. |
| [8] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [9] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [10] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [11] | 陈桂红. 硫和硅掺杂生物炭对镉污染土壤的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1854-1860. |
| [12] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [13] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [14] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [15] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
