生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 450-459.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.03.013
张腾云1,2( ), 王静1,2, 高健磊1, 葛文静1,3,*(
), 王静1,2, 高健磊1, 葛文静1,3,*( ), 王宗耀2, 韩龙1
), 王宗耀2, 韩龙1
收稿日期:2024-01-22
出版日期:2024-03-18
发布日期:2024-05-08
通讯作者:
*葛文静,E-mail: gewj2021@zzu.edu.cn作者简介:张腾云(1988年生),女,工程师,主要研究方向土壤污染防治。E-mail: zty0530127@126.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Tengyun1,2( ), WANG Jing1,2, GAO Jianlei1, GE Wenjing1,3,*(
), WANG Jing1,2, GAO Jianlei1, GE Wenjing1,3,*( ), WANG Zongyao2, HAN Long1
), WANG Zongyao2, HAN Long1
Received:2024-01-22
Online:2024-03-18
Published:2024-05-08
摘要:
目前,农田土壤镉污染导致的农业生态环境安全问题引起了极大的关注,然而与酸性土壤相比,针对碱性土壤镉污染导致小麦籽粒镉超标的相关研究进展缓慢。为探明镉在碱性土壤-作物系统中的迁移转化规律,以河南省济源市碱性镉污染农田土壤及冬小麦为例,通过分析小麦不同生育期土壤和小麦植株各器官镉含量的分布变化,阐明了土壤镉随小麦生长发育的富集及迁移转化规律,揭示了根际效应和土壤理化性质对该过程的影响。结果显示:1)随着小麦生长发育,相较于非根际,根际土壤理化性质的变化更为明显,有机质向根际环境的富集趋势显著(P<0.01);2)土壤镉有效态含量在小麦灌浆期明显上升,且在非根际土壤中受有机质正向促进(rBS=0.471,PBS<0.05;rRS=0.544,PRS<0.01),而在根际中被CEC负向抑制(rBS= −0.707,PBS<0.01;rRS= −0.637,PRS<0.01);3)小麦根部对镉的富集能力(RBCF:0.559-1.61)显著高于茎叶(LBCF:0.146-0.584),土壤镉向根部富集主要表现在分蘖期(分蘖期1.61>灌浆期0.600>成熟期0.559),向地上部分迁移转运则集中在灌浆期(灌浆期1.04>分蘖期0.277>成熟期0.260);4)小麦根部对镉的富集能力随根际土壤pH的升高而增强(r=0.690,P<0.05),茎叶对镉的富集能力随根际土壤CEC的升高而降低(r= −0.697,P<0.05)。由此,在碱性土壤镉污染修复治理中,针对性地在镉向小麦富集迁移的关键期(分蘖期、灌浆期)采取阻控措施,调节关键影响因素(土壤有机质、CEC),可控制小麦籽粒镉超标风险。研究结果可为碱性镉污染农田土壤的修复治理及风险防控提供理论基础。
中图分类号:
张腾云, 王静, 高健磊, 葛文静, 王宗耀, 韩龙. 碱性农田土壤冬小麦不同生育期镉的迁移转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 450-459.
ZHANG Tengyun, WANG Jing, GAO Jianlei, GE Wenjing, WANG Zongyao, HAN Long. Study on Cadmium Transfer and Transformation in Winter Wheat at Different Growth Stages in Alkaline Field Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 450-459.
| 土壤理化指标 | 检测结果 |
|---|---|
| pH | 8.38±0.08 |
| w(有机质SOM)/(g∙kg−1) | 11.7±0.153 |
| 阳离子交换量 CEC/(cmol∙kg−1) | 14.9±0.564 |
| w(总钾TK)/(g∙kg−1) | 21.3±0.104 |
| w(总磷TP)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.859±0.0982 |
| w(总氮TN)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.893±0.0956 |
| w(速效钾AK)/(mg∙kg−1) | 193±11.9 |
| w(有效磷AP)/(mg∙kg−1) | 31.5±2.31 |
表1 研究区土壤理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of soil in the study area
| 土壤理化指标 | 检测结果 |
|---|---|
| pH | 8.38±0.08 |
| w(有机质SOM)/(g∙kg−1) | 11.7±0.153 |
| 阳离子交换量 CEC/(cmol∙kg−1) | 14.9±0.564 |
| w(总钾TK)/(g∙kg−1) | 21.3±0.104 |
| w(总磷TP)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.859±0.0982 |
| w(总氮TN)/(g∙kg−1) | 0.893±0.0956 |
| w(速效钾AK)/(mg∙kg−1) | 193±11.9 |
| w(有效磷AP)/(mg∙kg−1) | 31.5±2.31 |
| 检测项目 | 检测标准 |
|---|---|
| 土壤机械组成的测定 | NY/T 1121.3—2006《土壤检测第3部分: 土壤机械组成的测定》 |
| pH | NY/T 1121.2—2006土壤检测第2部分: 土壤pH的测定 |
| 有机质 | DZ/T 0279.27—2016区域地球化学样品分析方法 第27部分: 有机碳量测定 重铬酸钾容量法 |
| 阳离子交换量 | LY/T 1243—1999森林土壤阳离子交换量的测定 |
| 土壤镉 | GB/T 14506.30—2010硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第30部分: 44个元素量测定 |
| 土壤有效镉 | HJ 804—2016土壤8种有效态元素的测定 二乙烯三胺五乙酸浸提-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 |
| 小麦植株、籽粒镉 | GB5009.268—2016食品安全国家标准 食品中多元素的测定 |
表2 检测标准及方法
Table 2 Testing standards and methods
| 检测项目 | 检测标准 |
|---|---|
| 土壤机械组成的测定 | NY/T 1121.3—2006《土壤检测第3部分: 土壤机械组成的测定》 |
| pH | NY/T 1121.2—2006土壤检测第2部分: 土壤pH的测定 |
| 有机质 | DZ/T 0279.27—2016区域地球化学样品分析方法 第27部分: 有机碳量测定 重铬酸钾容量法 |
| 阳离子交换量 | LY/T 1243—1999森林土壤阳离子交换量的测定 |
| 土壤镉 | GB/T 14506.30—2010硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第30部分: 44个元素量测定 |
| 土壤有效镉 | HJ 804—2016土壤8种有效态元素的测定 二乙烯三胺五乙酸浸提-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法 |
| 小麦植株、籽粒镉 | GB5009.268—2016食品安全国家标准 食品中多元素的测定 |
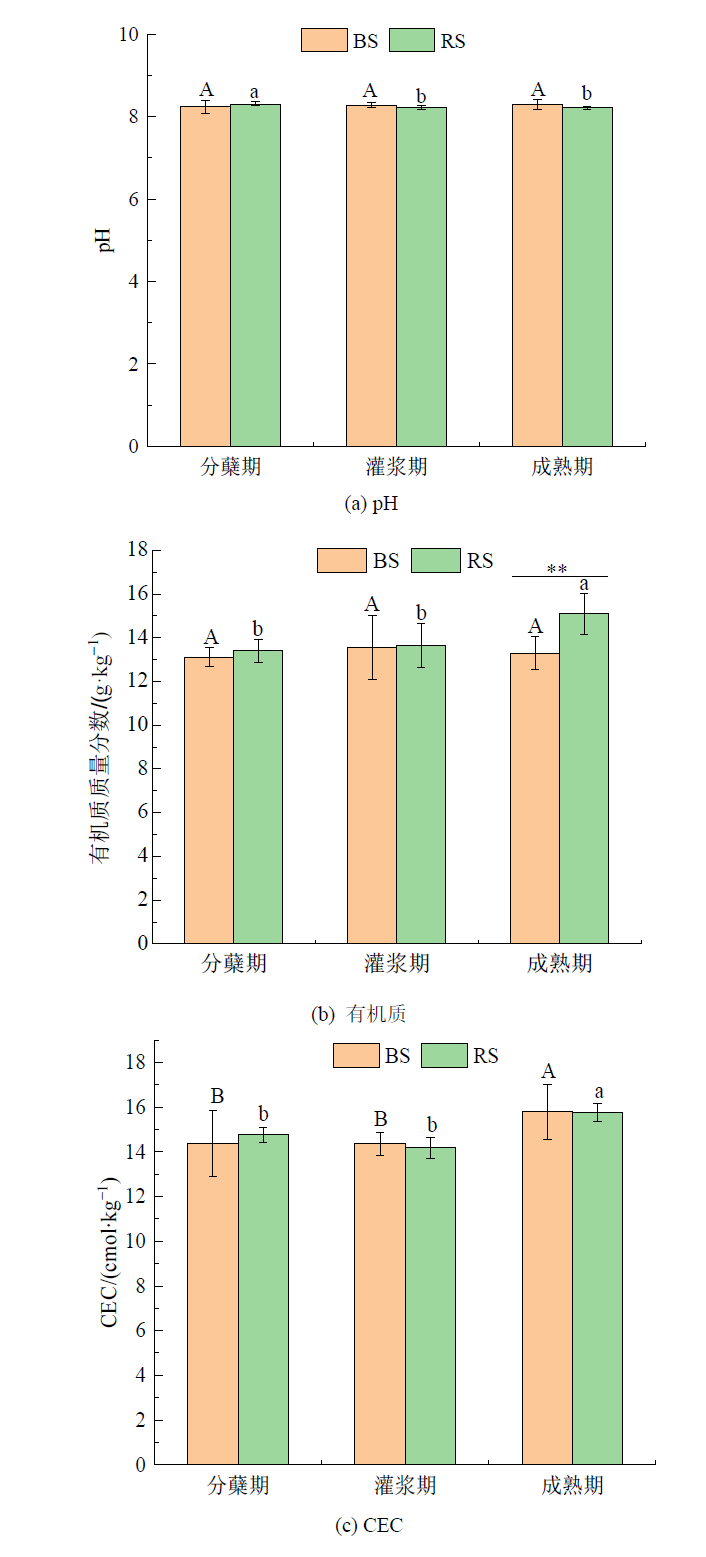
图1 小麦不同生育期非根际与根际土壤理化性质变化 不同大写字母表示非根际pH(a)、有机质(b)、CEC(c)在小麦不同生育期的差异显著性,不同小写字母表示根际pH(a)、有机质(b)、CEC(c)在小麦不同生育期的差异显著性(P<0.05);图中*表示非根际与根际有机质的差异显著性(**P<0.01),n=9
Figure 1 Changes in physical and chemical properties of bulk and rhizosphere soil at different growth stages of wheat
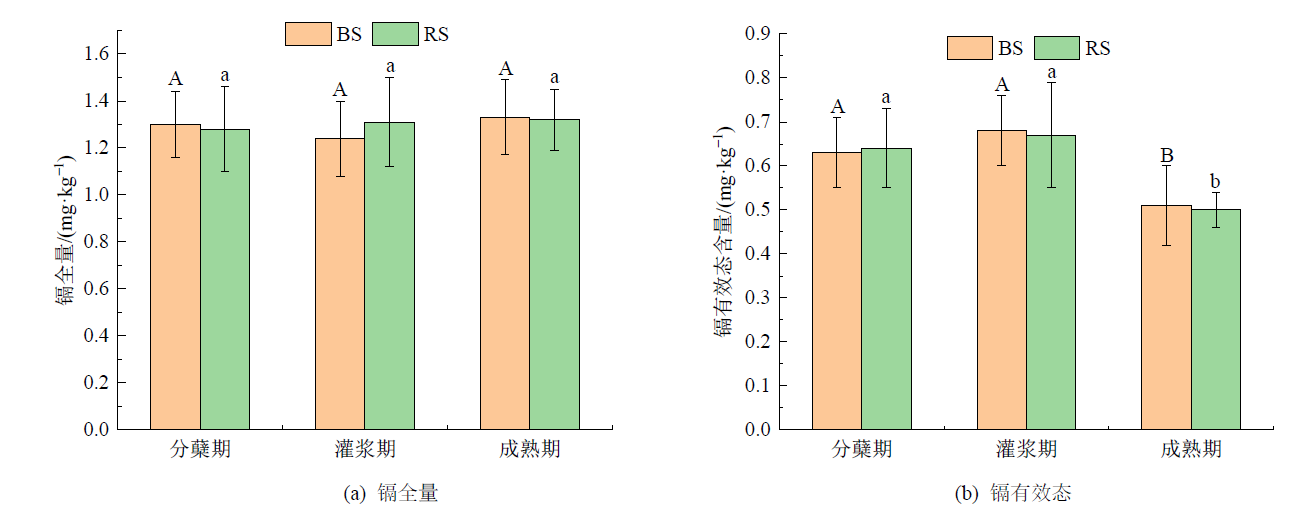
图2 小麦不同生育期土壤镉全量及其有效态含量变化 不同大写字母表示非根际镉全量(a)、镉有效态含量(b)在小麦不同生育期的差异显著性,不同小写字母表示根际镉全量(a)、镉有效态含量(b)在小麦不同生育期的差异显著性(P<0.05),n=9
Figure 2 Changes in total and available cadmium content in soil at different growth stages of wheat
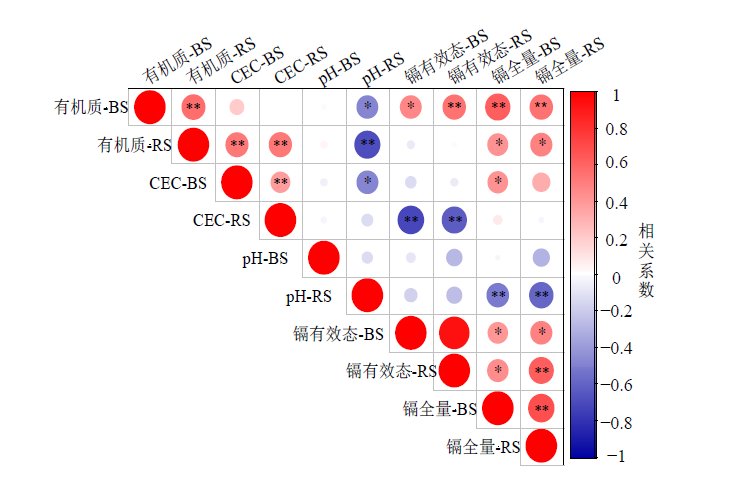
图3 土壤理化性质与镉全量及有效态相关性热点图 图中BS代表非根际土,RS代表根际土;*代表不同处理间差异显著(*P<0.05,**P<0.01),n=27
Figure 3 Hot spot map of correlation between soil physicochemical properties and total and available cadmium levels
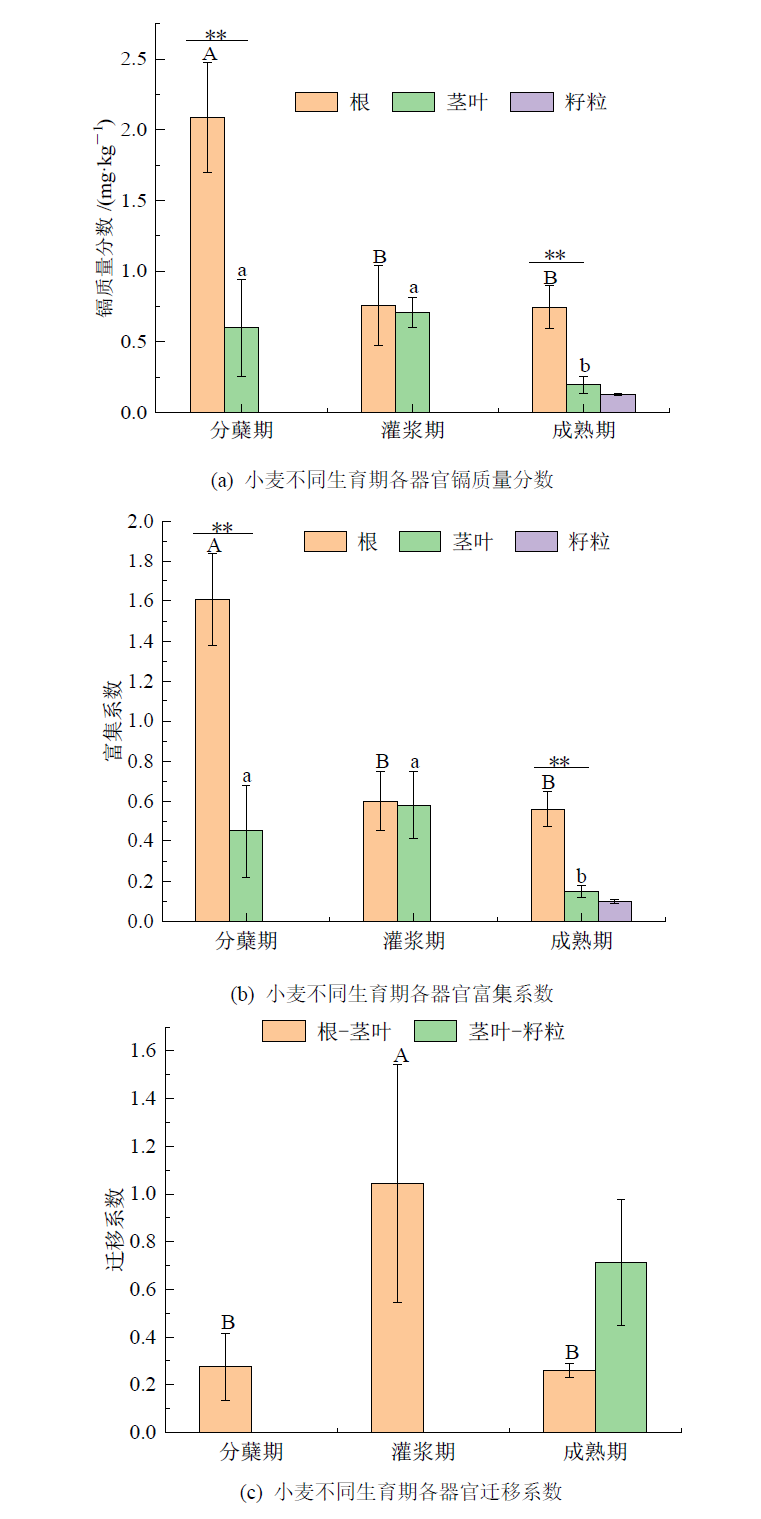
图4 不同生育期小麦植株各器官镉含量及其富集、迁移系数 不同大写字母表示小麦根部镉含量(a)、富集系数(b)、迁移系数(c)在不同生育期的差异显著性,不同小写字母表示小麦茎叶部镉含量(a)、富集系数(b)、迁移系数(c)在不同生育期的差异显著性(P<0.05);图中*表示小麦根部与茎叶部的差异显著性(*P<0.05,**P<0.01),n=9
Figure 4 Cadmium content and its enrichment and migration coefficient in organs of wheat plants at different growth stages
| 土壤理化指标 | 相关系数 | 富集系数BCF | 迁移系数TF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 | 茎叶 | 籽粒 | 根-茎叶 | 茎叶-籽粒 | ||||
| 有机质 | BS | r | 0.016 | −0.010 | −0.599 | −0.192 | −0.946 | |
| RS | r | −0.320 | −0.483 | −0.289 | −0.416 | −0.778 | ||
| CEC | BS | r | −0.333 | -0.346 | −0.977 | −0.334 | −0.686 | |
| RS | r | −0.155 | −0.697* | 0.914 | −0.565 | 0.526 | ||
| PH | BS | r | −0.292 | −0.106 | −0.898 | 0.303 | −0.990 | |
| RS | r | 0.690* | 0.252 | −0.062 | −0.005 | 0.512 | ||
表3 土壤理化理化性质与镉富集迁运系数的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of soil physicochemical properties with cadmium accumulation and migration coefficient
| 土壤理化指标 | 相关系数 | 富集系数BCF | 迁移系数TF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 | 茎叶 | 籽粒 | 根-茎叶 | 茎叶-籽粒 | ||||
| 有机质 | BS | r | 0.016 | −0.010 | −0.599 | −0.192 | −0.946 | |
| RS | r | −0.320 | −0.483 | −0.289 | −0.416 | −0.778 | ||
| CEC | BS | r | −0.333 | -0.346 | −0.977 | −0.334 | −0.686 | |
| RS | r | −0.155 | −0.697* | 0.914 | −0.565 | 0.526 | ||
| PH | BS | r | −0.292 | −0.106 | −0.898 | 0.303 | −0.990 | |
| RS | r | 0.690* | 0.252 | −0.062 | −0.005 | 0.512 | ||
| [1] | BOLAN N S, ADRIANO D C, DURAISAMY P, et al., 2003. Immobilization and phytoavailability of cadmium in variable charge soils. I. Effect of phosphate addition[J]. Plant & Soil, 250(1): 83-94. |
| [2] |
KIM K R, OWENS G, KWON S L, 2010. Influence of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) on rhizosphere soil solution chemistry in long-term contaminated soils: A rhizobox study[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22(1): 98-105.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LI X X, HUANG S, MCBRIDE M B, 2021. Rhizosphere effecton Pb solubility and phytoavailability in Pb-contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268: 115840.
DOI URL |
| [4] | NAFTEL S J, MARTIN R R, MACFIE S M, et al., 2007. An investigation of metals at the soil/root interface using synchrotron radiation analysis[J]. Canadian Journal of Analytical Sciences & Spectroscopy, 52(1): 18-24. |
| [5] | QIN Y, QIANG C, ZHANG M, et al., 2019. Difference analysis of accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in two wheat varieties and their health risk[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 17(8): 2742-2748. |
| [6] |
QIU K Y, XING W Q, SCHECKELl K G, et al., 2016. Temporal and seasonal variations of As, Cd and Pb atmospheric deposition flux in the vicinity of lead smelters in Jiyuan, China[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 7(1): 170-179.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TAO S, LIU W X, CHEN Y J, et al., 2004. Evaluation of factors influencing root-induced changes of copper fractionation in rhizosphere of a calcareous soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 129(1): 5-12.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
XING W Q, ZHANG H Y, SCHECKEL K G, et al., 2016. Heavy metal and metalloid concentrations in components of 25 wheat (Triticum aestivum) varieties in the vicinity of lead smelters in Henan province, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YANG Q Q, LI Z Y, LU X N, et al., 2018. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 642: 690-700.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHAO F J, MA Y B, ZHU Y G, et al., 2015. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(2): 750-759.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 毕春娟, 陈振楼, 郑祥民, 等, 2001. 根际环境重金属地球化学行为及其生物有效性研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 16(3): 387-393. |
| BI C J, CHEN Z L, ZHENG X M, et al., 2001. Research progress on geochemical behavior and bioavailability of heavy metals in rhizosphere environment[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 16(3): 387-393. | |
| [12] | 毕春娟, 陈振楼, 2000. 根际环境重金属研究进展[J]. 福建地理, 15(3): 29-32. |
| BI C J, CHEN Z L, 2000. Research progress of heavy metals in rhizosphere environment[J]. Fujian Geography, 15(3): 29-32. | |
| [13] | 陈思奇, 杨雨薇, 杨其亮, 等, 2020. 国内土壤重金属镉污染修复技术应用现状与展望[J]. 安徽化工, 46(1): 8-12. |
| CHEN S Q, YANG Y W, YANG Q L, et al., 2020. Application status and prospect of remediation technology of soil heavy metal cadmium pollution in China[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 46(1): 8-12. | |
| [14] | 曹丹, 白耀博, 李文红, 2020. 不同施肥处理对土壤质量及小麦吸收镉的影响[J]. 现代农业科技 (9): 1-2. |
| CAO D, BAI Y B, LI W H, 2020. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil quality and cadmium uptake in wheat[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology (9): 1-2. | |
| [15] | 曹秋华, 普绍苹, 徐卫红, 等, 2006. 根际重金属形态与生物有效性研究进展[J]. 广州环境科学, 21(3): 1-4. |
| CAO Q H, PU S P, XU W H, et al., 2006. Research progress on the morphology and bioavailability of heavy metals in rhizosphere[J]. Guangzhou Environmental Science, 21(3): 1-4. | |
| [16] | 陈洁, 王娟, 王怡雯, 等, 2021. 影响不同农作物镉富集系数的土壤因素[J]. 环境科学, 42(4): 2031-2039. |
| CHEN J, WANG J, WANG Y W, et al., 2021. Soil factors affecting cadmium enrichment coefficient of different crops[J]. Environmental Science, 42(4): 2031-2039. | |
| [17] | 陈珊珊, 2011. 土壤-植物系统中Se与重金属Hg、Cd相互关系的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. |
| CHEN S S, 2011. Study on the relationship between Se and heavy metals Hg and Cd in soil-plant system[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. | |
| [18] | 陈有鉴, 陶澎, 邓宝山, 2001. 不同作物根际环境对土壤重金属形态的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 38(1): 54-59. |
| CHEN Y J, TAO P, DENG B S, 2001. Effects of rhizosphere environment of different crops on soil heavy metal forms[J]. Acta Pedol Sinica, 38(1): 54-59. | |
| [19] | 代杰瑞, 郝兴中, 庞绪贵, 等, 2013. 典型土壤环境中重金属元素的形态分布和转化——以山东烟台为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(6): 713-719. |
| DAI J R, HAO X Z, PANG X G, et al., 2013. Morphological distribution and transformation of heavy metal elements in typical soil environment: A case study of Yantai, Shandong Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(6): 713-719. | |
| [20] | 樊霆, 叶文玲, 陈海燕, 等, 2013. 农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(10): 1727-1736. |
| FAN T, YE W L, CHEN H Y, et al., 2013. Study on heavy metal pollution status and remediation technology of farmland soil[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 22(10): 1727-1736. | |
| [21] | 黄晓露, 戴勤, 梁文汇, 等, 2022. 桂西北板栗园区土壤养分含量分析及评价[J]. 西南农业学报, 35(12): 2827-2835. |
| HUANG X L, DAI Q, LIANG W H, et al., 2022. Analysis and evaluation of soil nutrient content in chestnut orchard in northwest Guangxi[J]. Journal of Southwest China Agricultural Sciences, 35(12): 2827-2835. | |
| [22] | 黄亚男, 傅志强, 2018. 水稻根系分泌物对镉吸收、积累影响机理研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 32(3): 244-248, 264. |
| HUANG Y N, FU Z Q, 2018. Research progress on mechanism of influence of rice root exudates on cadmium uptake and accumulation[J]. Crop Research, 32(3): 244-248, 264. | |
| [23] | 黄萍霞, 2007. 不同小麦品种对Cd、Pb的响应和机理研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学. |
| HUANG P X, 2007. Response and mechanism of different wheat varieties to Cd and Pb[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University. | |
| [24] | 景文杰, 全占军, 韩煜, 等, 2022. 重金属污染土壤修复中的根际效应研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 12(1): 153-160. |
| JING W J, QUAN Z J, HAN Y, et al., 2022. Research progress of rhizosphere effect in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(1): 153-160. | |
| [25] |
姜丽娜, 邵云, 李春喜, 等, 2004. 镉在小麦植株体内的吸收、分配和累积规律研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 33(7): 13-17.
DOI |
| JIANG L N, SHAO Y, LI C X, et al., 2004. Study on the absorption, distribution and accumulation of cadmium in wheat plants[J]. Henan Agricultural Sciences, 33(7): 13-17. | |
| [26] | 李华, 刘树庆, 芝彦峰, 等, 2002. 重金属在根际土壤环境中的化学行为的研究进展[J]. 河北环境科学 (1): 39-42. |
| LI H, LIU S Q, ZHI Y F, et al., 2002. Research progress of chemical behavior of heavy metals in rhizosphere soil environment[J]. Hebei Environmental Science (1): 39-42. | |
| [27] | 李娟, 2020. 安全利用类轻中度镉污染农田土壤原位调理修复应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| LI J, 2020. Study on in-situ remediation of farmland soil contaminated by light and moderate cadmium for safe use[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [28] | 李杰, 2022. 白银东大沟某农田土壤重金属污染评价及其修复应用研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| LI J, 2022. Evaluation and remediation of soil heavy metal pollution in Dongdagou, Baiyin[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. | |
| [29] | 李铭红, 李侠, 宋瑞生, 2008. 受污农田中农作物对重金属镉的富集特征研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 16(3): 675-679. |
| LI M H, LI X, SONG R S, 2008. Study on enrichment characteristics of cadmium in crops in polluted farmland[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 16(3): 675-679. | |
| [30] | 李思民, 王豪吉, 朱曦, 等, 2021. 土壤pH和有机质含量对重金属可利用性的影响[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 41(1): 49-55. |
| LI S M, WANG H J, ZHU X, et al., 2021. Effects of soil pH and organic matter content on availability of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 41(1): 49-55. | |
| [31] | 刘娜, 2020. 重金属汞/镉低积累小麦品种筛选及根际微环境研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学. |
| LIU N, 2020. Screening and rhizosphere microenvironment of wheat varieties with low accumulation of heavy metals Mercury/Cadmium[D] Ji’nan: Shandong University. | |
| [32] | 刘仁波, 周富忠, 2021. 不同调理剂组合对酸性土壤改良及稻谷降镉的效果研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 49(20): 93-97, 130. |
| LIU R B. ZHOU F Z, 2019. Effects of different conditioner combinations on acid soil improvement and cadmium reduction of rice[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 49(20): 93-97, 130. | |
| [33] | 骆永明, 2016. 土壤污染特征、 过程与有效性[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 89-92. |
| LUO Y M, 2016. Characteristics, process and effectiveness of Soil pollution[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 89-92. | |
| [34] | 庞荣丽, 王瑞萍, 谢汉忠, 等, 2016. 农业土壤中镉污染现状及污染途径分析[J]. 天津农业科学, 22(12): 87-91. |
| PANG R L, WANG R P, XIE H Z, et al., 2016. Cadmium pollution status and pollution path analysis in agricultural soil[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 22(12): 87-91. | |
| [35] | 秦樊鑫, 魏朝富, 李红梅, 2015. 重金属污染土壤修复技术综述与展望[J]. 环境科学与技术, 38(S2): 199-208. |
| QIN F X, WEI C F, LI H M, 2015. Review and prospect of remediation technologies of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(S2): 199-208. | |
| [36] | 史高玲, 周东美, 余向阳, 等, 2021. 水稻和小麦累积镉和砷的机制与阻控对策[J]. 江苏农业学报, 37(5): 1333-1343. |
| SHI G L, ZHOU D M, YU X Y, et al., 2021. Mechanism of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice and wheat and countermeasures of resistance and control[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 37(5): 1333-1343. | |
| [37] | 施积炎, 陈英旭, 林琦, 等, 2004. 根分泌物与微生物对污染土壤重金属活性的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 24(3): 316-319. |
| SHI J Y, CHEN Y X, LIN Q, et al., 2004. Effects of root exudates and microorganisms on heavy metal activity in contaminated soil[J]. China Environmental Science, 24(3): 316-319. | |
| [38] | 孙芳立, 苏忠亮, 郭庆增, 2019. Cd在小麦不同生育期器官及亚细胞中的分布[J]. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 43(1): 87-93. |
| SUN F L, SU Z L, GUO Q Z, 2019. Distribution of Cd in wheat organs and subcells at different growth stages[J]. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 43(1): 87-93. | |
| [39] | 孙芳立, 张金恒, 孙永红, 等, 2018. 重金属Cd、Cu、Zn在小麦全生育期中的富集规律[J]. 青岛大学学报(自然科学版), 39(5): 34-41. |
| SUN F L, ZHANG J H, SUN Y H, et al., 2018. Enrichment of heavy metals Cd, Cu and Zn during the whole growth period of wheat[J]. Journal of Qingdao University (Natural Science Edition), 39(5): 34-41. | |
| [40] | 汪红霞, 廖文华, 孙伊辰, 等, 2014. 长期施用有机肥和磷肥对潮褐土土壤有机质及腐殖质组成的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6): 39-46. |
| WANG H X, LIAO W H, SUN Y C, et al., 2014. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer and phosphate fertilizer on soil organic matter and humus composition of tidal brown soil[J]. China Soil and Fertilizer (6): 39-46. | |
| [41] | 王蔚华, 2004. 小麦金属元素吸收分配特性及胁迫生理效应研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学. |
| WANG W H, 2004. Study on absorption and distribution characteristics of metal elements and Stress physiological effects of wheat[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University. | |
| [42] | 夏传波, 郑建业, 成学海, 等, 2020. 农用地土壤中7种重金属可提取态的测定[J]. 山东国土资源, 36(3): 59-65. |
| XIA C B, ZHENG J Y, CHENG X H, et al., 2020. Determination of extractable states of 7 heavy metals in agricultural soil[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 36(3): 59-65. | |
| [43] | 徐红宁, 杨居荣, 许嘉琳, 1995. 作物对Cd的吸收与根系阳离子交换容量[J]. 农业环境保护, 14(4): 150-153. |
| XU H N, YANG J R, XU J L, 1995. Cation-exchange capacity of roots and Cd uptake by crops[J]. Agricultural Environmental Protection, 14(4): 150-153. | |
| [44] | 许仙菊, 陈丹艳, 张永春, 等, 2008. 水稻不同生育期重金属污染土壤中镉铅的形态分布[J]. 江苏农业科学 (6): 243-255, 280. |
| XU X J, CHEN D Y, ZHANG Y C, et al., 2008. Distribution of cadmium and lead in soil contaminated by heavy metals at different growth stages of rice[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences (6): 243-255, 280. | |
| [45] | 杨树俊, 韩张雄, 王思远, 等, 2023. 土壤阳离子交换量与有机质、机械组成的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 23(7): 2799-2805. |
| YANG S J, HAN Z X, WANG S Y, et al., 2023. Relationship between cation exchange capacity and organic matter and mechanical composition of soil[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 23(7): 2799-2805. | |
| [46] | 姚澄, 周天宇, 樊广萍, 等, 2024. 不同锌肥对土壤镉有效性及小麦镉吸收转运的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 43(1): 19-29. |
| YAO C, ZHOU T Y, FAN G P, et al., 2024. Effects of different zinc fertilizers on cadmium availability in soil and cadmium uptake and transport in wheat[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 43(1): 19-29. | |
| [47] | 叶俊文, 金耀铭, 李兴杰, 等, 2019. 土壤质地、pH、有机质含量对镉存在形态的影响及其机理研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 37(3): 29-33. |
| YE J W, JI Y M, LI X J, et al., 2019. Effects of soil texture, pH and organic matter content on the existence and morphology of cadmium and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Agricultural Science Edition), 37(3): 29-33. | |
| [48] | 张丙春, 王磊, 孟立红, 等, 2010. 镉胁迫下春小麦中镉的分布、富集及转移规律[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(12): 2521-2524. |
| ZHANG B C, WANG L, MENG L H, et al., 2010 Distribution, enrichment and transfer of cadmium in spring wheat under cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(12): 2521-2524. | |
| [49] | 章飞翔, 陈新友, 董力军, 等, 2023. 酸性土壤背景下不同品种水稻对镉的吸收差异分析[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 50(2): 319-325. |
| ZHANG F X, CHEN X Y, DONG L J, et al., 2023. Analysis of cadmium uptake by different rice varieties in acidic soil[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 50(2): 319-325. | |
| [50] | 张新帅, 钟伟, 湛方栋, 等, 2021. 铅锌矿区周边玉米根系低分子量有机酸、根际土壤镉铅形态与植株镉铅累积特征[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 40(3): 7-14. |
| ZHANG X S, ZHONG W, ZHAN F D, et al., 2021. Characteristics of low molecular weight organic acids in maize roots, cadmium and lead morphology in rhizosphere soil and cadmium and lead accumulation in plants around lead-zinc mining area[J]. Journal of Mountain Agricultural Biology, 40(3): 7-14. | |
| [51] | 赵鲁, 李旭军, 刘安辉, 等, 2013. 大豆和小麦对土壤中镉的吸收与富集研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 29(5): 45-49. |
| ZHAO L, LI X J, LIU A H, et al., 2013 Study on absorption and enrichment of cadmium in soil by soybean and wheat[J]. China Soil and Fertilizer, 29(5): 45-49. | |
| [52] | 赵晶, 2009. 不同氮磷钾肥对土壤镉有效性和小麦吸收镉的影响[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学. |
| ZHAO J, 2009. Effects of different nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on cadmium availability in soil and cadmium uptake in wheat[D] Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University. | |
| [53] |
赵秀娟, 任意, 张淑香, 2017. 25年来褐土区土壤养分演变特征[J]. 核农学报, 31(8): 1647-1655.
DOI |
| ZHAO X J, REN Y, ZHANG S X, 2017. Characteristics of soil nutrient evolution in brown soil region in the past 25 years[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 31(8): 1647-1655. | |
| [54] | 赵中秋, 朱永官, 蔡运龙, 2005. 镉在土壤-植物系统中的迁移转化及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境, 14(2): 282-286. |
| ZHAO Z Q, ZHU Y G, CAI Y L, 2005. Cadmium migration and transformation in soil-plant system and its influencing factors[J]. Ecological Environment, 14(2): 282-286. | |
| [55] | 邹天娥, 丁明军, 张华, 等, 2024. 环鄱阳湖消落区湿地土壤重金属的赋存形态及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(3): 354-364. |
| ZOU T E, DING M J, ZHANG H, et al., 2024. Analysis on the occurrence forms and influencing factors of heavy metals in wetland soil in the water-falling area of the ring Poyang Lake[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 44(3): 354-364. |
| [1] | 罗庆, 何清, 吴慧秋, 寇力月, 方旭, 张鑫雨, 李缘, 柴育廷, 张瑞生, 代文举. 辽河口湿地土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 333-340. |
| [2] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [3] | 宋思梦, 林冬梅, 周恒宇, 罗宗志, 张丽丽, 易超, 林辉, 林兴生, 刘斌, 苏德伟, 郑丹, 余世葵, 林占熺. 种植巨菌草对乌兰布和沙漠植物物种多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [4] | 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 周睿, 王宏生. 黄帚橐吾扩散对高寒草甸土壤理化特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [5] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [6] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [7] | 袁佳宝, 宋艳宇, 刘桢迪, 朱梦圆, 程小峰, 马秀艳, 陈宁, 李晓宇. 松嫩平原芦苇湿地土壤酶活性剖面分布特征及其微生物养分限制指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2141-2153. |
| [8] | 赵蔓, 张晓曼, 杨明洁. 林火干扰对栓皮栎-辽东栎混交林植物多样性与土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1732-1740. |
| [9] | 陈桂红. 硫和硅掺杂生物炭对镉污染土壤的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1854-1860. |
| [10] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [11] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| [12] | 王礼霄, 刘晋仙, 柴宝峰. 华北亚高山土壤细菌群落及氮循环对退耕还草的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [13] | 王磊, 温远光, 周晓果, 朱宏光, 孙冬婧. 尾巨桉与红锥混交对林下植被和土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [14] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [15] | 夏开, 邓鹏飞, 马锐豪, 王斐, 温正宇, 徐小牛. 马尾松次生林转换为湿地松和杉木林对土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
