生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1516-1524.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.017
范婉仪1,2( ), 涂晨1,2, 王顺扬1, 吴昕优1,2, 李烜桢3, 骆永明1,2,*
), 涂晨1,2, 王顺扬1, 吴昕优1,2, 李烜桢3, 骆永明1,2,*
收稿日期:2023-01-17
出版日期:2023-08-18
发布日期:2023-11-08
通讯作者:
*骆永明。作者简介:范婉仪(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为重金属污染土壤的植物修复。E-mail: fanwanyi@issas.ac.cn
基金资助:
FAN Wanyi1,2( ), TU Chen1,2, WANG Shunyang1, WU Xinyou1,2, LI Xuanzhen3, LUO Yongming1,2,*
), TU Chen1,2, WANG Shunyang1, WU Xinyou1,2, LI Xuanzhen3, LUO Yongming1,2,*
Received:2023-01-17
Online:2023-08-18
Published:2023-11-08
摘要:
烟草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)具有生物量大、适应性强、栽培面积广、栽种技术成熟等特点,对镉污染土壤可能具有较大的植物修复潜力。为了比较轻度镉(Cd)污染土壤上不同品种烟草对镉的积累能力和减量修复潜力,以烟草品种云烟87和K326为研究对象,采用盆栽试验比较了两种烟草在台州(铁聚水耕人为土,Cd 0.83 mg?kg-1)和徐州(砂姜钙积潮湿变性土,Cd 0.76 mg?kg-1)两种不同类型镉轻度污染土壤上的生长状况和镉累积特征,以及烟草收获后土壤中有效态Cd(CaCl2和NH4OAc提取态)和总Cd的质量分数变化,评估了2种烟草对轻度Cd染土壤的减量修复潜力。结果表明,种植50 d后,同一品种在台州土壤中的株高、根和茎干质量显著高于徐州土壤,但同一土壤上生长的两种烟草之间在株高、地上部鲜质量和干质量等指标方面均无显著性差异。在2种土壤上,烟草K326的叶片中Cd质量分数(15.1-25.3 mg?kg-1)均显著高于云烟87(11.7-20.7 mg?kg-1),但2种烟草的根和茎中的Cd质量分数无显著性差异。2种烟草的地上部生物富集系数和地下部向地上部转移系数均大于1;在徐州土壤上,云烟87和K326的地上部生物富集系数分别高达23.09和28.16,茎向叶转移系数则分别达到3.18和3.40。种植云烟87和K326可显著降低土壤中CaCl2提取态和NH4OAc提取态Cd质量分数,从而显著降低土壤中有效态Cd和总Cd质量分数。烟草K326的Cd吸取总量(285.0-310.2 μg?pot-1)显著高于云烟87(254.8-261.2 μg?pot-1),移除烟草植株后,云烟87和K326对土壤总Cd的去除率最高分别可达8.4%和9.4%。云烟87和K326可作为高积累性作物,对轻度污染耕地土壤具有较大的Cd减量修复潜力。
中图分类号:
范婉仪, 涂晨, 王顺扬, 吴昕优, 李烜桢, 骆永明. 不同品种烟草对轻度污染耕地土壤中镉的累积特征与减量修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524.
FAN Wanyi, TU Chen, WANG Shunyang, WU Xinyou, LI Xuanzhen, LUO Yongming. Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics and Pollution Reduction Potential of Different Tobacco Species in Lightly Contaminated Farmland Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524.
| 项目 | 台州土 | 徐州土 |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤类型 | 铁聚水耕人为土 | 砂姜钙积潮湿变性土 |
| 土壤pH | 5.60 | 5.08 |
| 黏粒质量分数/% | 11.7 | 11.5 |
| 粉粒质量分数/% | 67.1 | 70.2 |
| 砂粒质量分数/% | 21.2 | 18.3 |
| 阳离子交换量/(cmol∙kg-1) | 7.52 | 15.23 |
| 有机质质量分数/(g∙kg-1) | 44.03 | 22.09 |
| 总氮质量分数/(g∙kg-1) | 2.99 | 1.24 |
| 速效磷质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 34.84 | 42.21 |
| 速效钾质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 70.25 | 102.55 |
| 总镉质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.83 | 0.76 |
表1 供试土壤主要理化性质
Table 1 The main physico-chemical properties of the two soils tested
| 项目 | 台州土 | 徐州土 |
|---|---|---|
| 土壤类型 | 铁聚水耕人为土 | 砂姜钙积潮湿变性土 |
| 土壤pH | 5.60 | 5.08 |
| 黏粒质量分数/% | 11.7 | 11.5 |
| 粉粒质量分数/% | 67.1 | 70.2 |
| 砂粒质量分数/% | 21.2 | 18.3 |
| 阳离子交换量/(cmol∙kg-1) | 7.52 | 15.23 |
| 有机质质量分数/(g∙kg-1) | 44.03 | 22.09 |
| 总氮质量分数/(g∙kg-1) | 2.99 | 1.24 |
| 速效磷质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 34.84 | 42.21 |
| 速效钾质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 70.25 | 102.55 |
| 总镉质量分数/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.83 | 0.76 |
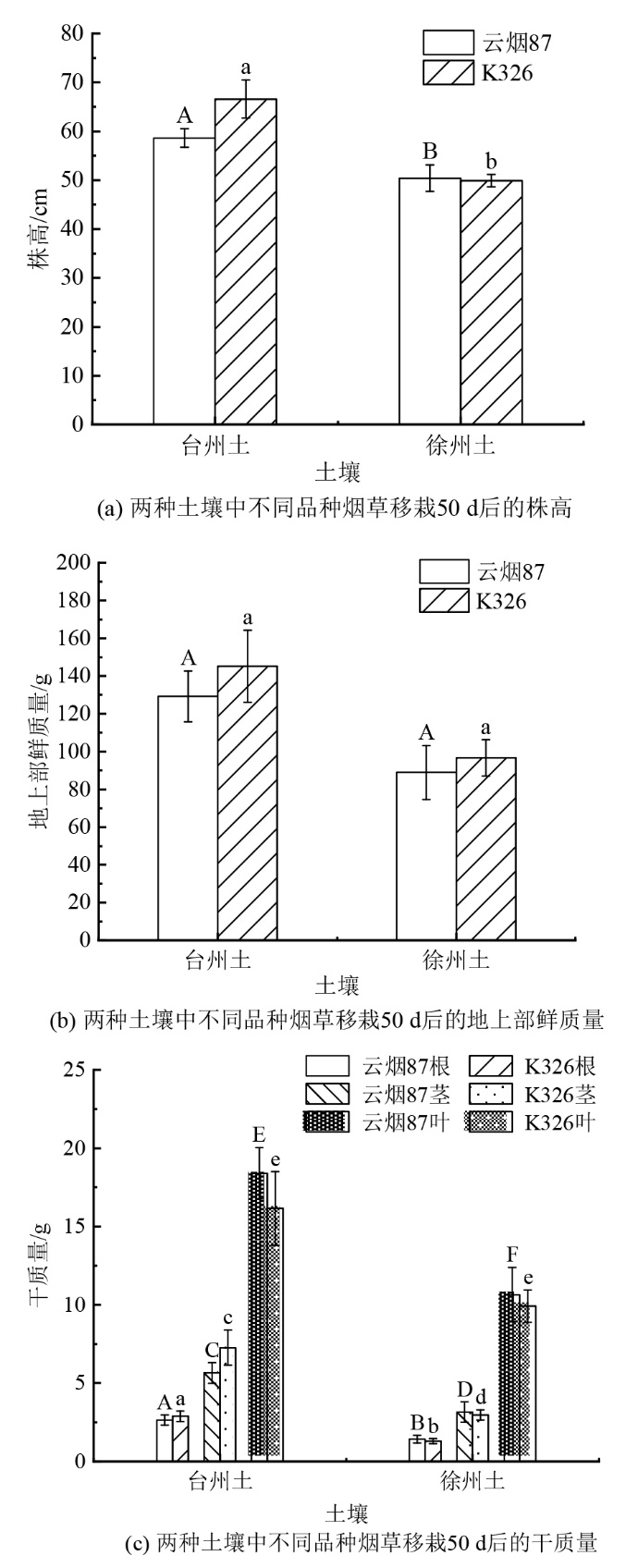
图1 两种土壤中不同品种烟草移栽50 d后的生长状况 同一颜色直方柱上方不同大/小写字母表示显著性差异(P<0.05);样品重复数n=4。下同
Figure 1 The growth of different tobacco species after transplantation for 50 days in two soils
| 土壤 | 烟草品种 | VBCF(root) | VBCF(shoot) | VTF(root-shoot) | VTF(root-stem) | VTF(stem-leaf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 台州土 | 云烟87 | 8.94 | 12.03 | 1.37 | 0.60 | 2.67 |
| K326 | 8.28 | 14.82 | 1.90 | 0.93 | 2.48 | |
| 徐州土 | 云烟87 | 9.08 | 23.09 | 2.54 | 0.95 | 3.18 |
| K326 | 10.16 | 28.16 | 3.13 | 1.10 | 3.40 |
表2 不同品种烟草的生物富集系数和转移系数
Table 2 Bioaccumulation factors (BCF) and transfer factor (TF) of different tobacco species
| 土壤 | 烟草品种 | VBCF(root) | VBCF(shoot) | VTF(root-shoot) | VTF(root-stem) | VTF(stem-leaf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 台州土 | 云烟87 | 8.94 | 12.03 | 1.37 | 0.60 | 2.67 |
| K326 | 8.28 | 14.82 | 1.90 | 0.93 | 2.48 | |
| 徐州土 | 云烟87 | 9.08 | 23.09 | 2.54 | 0.95 | 3.18 |
| K326 | 10.16 | 28.16 | 3.13 | 1.10 | 3.40 |
| 土壤 | 烟草品种 | 植物Cd吸取量/(µg∙pot-1) | Cd去除率/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 | 茎 | 叶 | 整株 | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | 整株 | |||
| 台州土 | 云烟87 | 19.8±2.7 | 25.0±2.7 | 216.5±24.5 | 261.2±28.3 | 0.6±0.1 | 0.8±0.1 | 6.5±0.7 | 7.9±0.9 | |
| K326 | 19.6±2.7 | 45.0±8.2 | 245.6±44.6 | 310.2±49.2 | 0.6±0.1 | 1.4±0.2 | 7.4±1.3 | 9.3±1.5 | ||
| 徐州土 | 云烟87 | 9.9±1.7 | 20.8±4.5 | 224.1±40.6 | 254.8±46.7 | 0.3±0.1 | 0.7±0.1 | 7.4±1.3 | 8.4±1.5 | |
| K326 | 9.3±0.9 | 23.1±2.4 | 252.6±31.9 | 285.0±30.3 | 0.3±0.0 | 0.8±0.1 | 8.3±1.0 | 9.4±1.0 | ||
表3 两种土壤上不同品种烟草各部位的Cd吸取量和Cd去除率
Table 3 Plant uptake and Cd removal rate by different parts of tobacco species in two soils
| 土壤 | 烟草品种 | 植物Cd吸取量/(µg∙pot-1) | Cd去除率/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 | 茎 | 叶 | 整株 | 根 | 茎 | 叶 | 整株 | |||
| 台州土 | 云烟87 | 19.8±2.7 | 25.0±2.7 | 216.5±24.5 | 261.2±28.3 | 0.6±0.1 | 0.8±0.1 | 6.5±0.7 | 7.9±0.9 | |
| K326 | 19.6±2.7 | 45.0±8.2 | 245.6±44.6 | 310.2±49.2 | 0.6±0.1 | 1.4±0.2 | 7.4±1.3 | 9.3±1.5 | ||
| 徐州土 | 云烟87 | 9.9±1.7 | 20.8±4.5 | 224.1±40.6 | 254.8±46.7 | 0.3±0.1 | 0.7±0.1 | 7.4±1.3 | 8.4±1.5 | |
| K326 | 9.3±0.9 | 23.1±2.4 | 252.6±31.9 | 285.0±30.3 | 0.3±0.0 | 0.8±0.1 | 8.3±1.0 | 9.4±1.0 | ||
| [1] | ADAMU C A, MULCHI C L, BELL P F, 1989. Relationships between soil pH, clay, organic matter and CEC and heavy metal concentrations in soils and tobacco[J]. Tobacco Science, 33: 96-100. |
| [2] |
BAKE A J M, 1981. Accumulators and excluders-Strategies in the response of plants to heavy metal[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 3(1-4): 643-654.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN L H, YANG W J, YANG Y, et al., 2022. Three-season rotation of chicory-tobacco-peanut with high biomass and bioconcentration factors effectively remediates cadmium-contaminated farmland[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(43): 64822-64831.
DOI |
| [4] |
DUPLAY J, SEMHI K, ERRAIS E, et al., 2014. Copper, zinc, lead and cadmium bioavailability and retention in vineyard soils (Rouffach, France): The impact of cultural practices[J]. Geoderma, 230-231: 318-328.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
JIA H F, YIN Z R, XUAN D D, et al., 2022. Mutation of NtNRAMP3 improves cadmium tolerance and its accumulation in tobacco leaves by regulating the subcellular distribution of cadmium[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 432: 128701.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HUANG W X, ZHANG D M, CAO Y Q, et al., 2021. Differential cadmium translocation and accumulation between Nicotiana tabacum L. and Nicotiana rustica L. by transcriptome combined with chemical form analyses[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208: 111412.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KELLER C, HAMMER D, KAYSER A, et al., 2003. Root development and heavy metal phytoextraction efficiency: Comparison of different plant species in the field[J]. Plant and Soil, 249: 67-81.
DOI URL |
| [8] | KING L D, 1988. Effect of selected soil properties on cadmium content of tobacco[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 17(2): 251-255. |
| [9] |
LI J T, GURAJALA H K, WU L H, et al., 2018. Hyperaccumulator plants from China: A synthesis of the current state of knowledge[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(21): 11980-11994.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU H W, WANG H Y, ZHANG Y, et al., 2019. Comparison of heavy metal accumulation and cadmium phytoextraction rates among ten leading tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) cultivars in China[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(7): 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LU Y G, MA J, TENG Y, et al., 2018. Effect of silicon on growth, physiology, and cadmium translocation of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) in cadmium-contaminated soil[J]. Pedosphere, 28(4): 680-689.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
RASCIO N, NAVARI-IZZO F, 2011. Heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants: how and why do they do it? And what makes them so interesting?[J]. Plant Science, 180(2): 169-181.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
RAURET G, 1998. Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment[J]. Talanta, 46(3): 449-455.
PMID |
| [14] |
SUN X, LI Z, WU L H, et al., 2019. Root-induced soil acidification and cadmium mobilization in the rhizosphere of Sedum plumbizincicola: Evidence from a high-resolution imaging study[J]. Plant and Soil, 436(1): 267-282.
DOI |
| [15] |
TSADILAS C D, KARAIVAZOGLOU N A, TSOTSOLIS N C, et al., 2005. Cadmium uptake by tobacco as affected by liming, N form, and year of cultivation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 134(2): 239-246.
PMID |
| [16] |
WANG P, CHEN H P, KOPITTKE M P, et al., 2019. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety[J]. Environmental Pollution, 249: 1038-1048.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
YANG F W, ZHANG H B, WANG Y, et al., 2021. The role of antioxidant mechanism in photosynthesis under heavy metals Cd or Zn exposure in tobacco leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Interactions, 16(1): 354-366.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YANG Y, GE Y C, TU P F, et al., 2019. Phytoextraction of Cd from a contaminated soil by tobacco and safe use of its metal-enriched biomass[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 363: 385-393.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
ZHANG M K, LIU Z Y, WANG H, et al., 2010. Use of single extraction methods to predict bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils to rice[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 41(7): 820-31.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 柏佳, 谭长银, 曹雪莹, 等, 2020. 3种有机酸对伴矿景天修复效率及土壤微生物数量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(2): 318-324. |
| BAI J, TAN C Y, CAO X Y, et al., 2020. Effect of three organic acids on the remediation efficiency of Sedum plumbizincicola and soil microbial quality[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(2): 318-324. | |
| [21] | 曹晨亮, 2015. 烟草镉的健康风险评价和消减技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院: 3. |
| CAO C L, 2015. Studies on health risk assessment and reduction techniques of cadmium in tobacco[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences:3. | |
| [22] | 陈洁宜, 刘广波, 崔金立, 等, 2019. 广东大宝山矿区土壤植物体系重金属迁移过程及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 40(12): 5629-5639. |
|
CHEN J Y, LIU G B, CUI J L, et al., 2019. Mobilization of heavy metals in a soil-plant system and risk assessment in the Dabaoshan mine area, Guangdong Province, China[J]. Environmental Science, 40(12): 5629-5639.
DOI URL |
|
| [23] | 党锋, 江荣风, 夏立江, 2006. Cd Zn处理对烤烟生长和烟株Cd含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 26(2):713-717. |
| DANG F, JIANG R F, XIA L J. Effects of cadmium and zinc on growth and cadmium concentration of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 26(2): 713-717. | |
| [24] | 国家烟草专卖局, 2010. 烟草农艺性状调查测量方法: YC/T 142—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 4. |
| State Tobacco Monopoly Administration, 2010. Investigating and measuring methods of agronomical character of tobacco: YC/T 142—2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 4. | |
| [25] | 贺远, 刘海伟, 石屹, 等, 2015. 镉在烟草中的积累分配及其对烟草生长的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 36(2): 99-104. |
| HE Y, LIU H W, SHI Y, et al., 2015. Effects of cadmium on the growth of tobacco and the characteristics of cadmium accumulation by tobacco[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 36(2): 99-104. | |
| [26] | 黄标, 潘剑君, 2017. 中国土系志∙江苏卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 277. |
| HUANG B, PAN J J, 2017. Soil Series of China Jiangsu[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 277. | |
| [27] | 孔祥方, 魏树和, 赵继蓉, 等, 2021. 旺盛期烟草对镉富集敏感性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(10): 4872-4877. |
| KONG X F, WEI S H, ZHAO J R, et al., 2018. Sensitivity of Nicotiana tabacum L. accumulating cadmium at its vigorous growth stage[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(10): 4872-4877. | |
| [28] | 雷丽萍, 刘彬, 陈世宝, 等, 2015. 不同烟草对Cd吸收的敏感性分布及烟草中Cd的结合形态[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(10): 1858-1864. |
| LEI L P, LIU B, CHEN S B, et al., 2015. Cd-phytotoxicity species sensitivity distributions and root cd forms of different tobacco cultivars[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(10): 1858-1864. | |
| [29] | 李海涛, 杨柳, 方丽, 等, 2022. 茶园土壤有效态镉的提取方法[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(1): 75-83. |
| LI H T, YANG L, FANG L, et al., 2022. Extraction method of available cadmium in tea garden soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(1): 75-83. | |
| [30] | 陆颖昭, 李龙, 李德贵, 2021. 高值化烟草提取物的应用研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 49(22): 14-17. |
| LU Y Z, LI L, LI D G, et al., 2021. Research progress on application of high value tobacco extract[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 49(22): 14-17. | |
| [31] | 李晓锋, 丁豪杰, 苏奇倩, 等, 2022. 降低烟草吸收土壤镉的钝化技术及其机理研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 12(3): 893-904. |
| LI X F, DING H J, SU Q Q, et al., 2022. Research progress on passivation technologies and their mechanism of reducing soil cadmium uptake by tobacco[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(3): 893-904. | |
| [32] | 刘登璐, 李廷轩, 余海英, 等, 2016. 不同烟草材料镉积累差异评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(11): 2067-2076. |
| LIU D L, LI T X, YU H Y, et al., 2016. Evaluation of differential cadmium accumulation ability in different tobacco species[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(11): 2067-2076. | |
| [33] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 1999. Analysis Methods for Soil Agricultural Chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [34] | 罗杰, 昂依娜, 董清, 等, 2020. 烤烟新品种云烟116在兴义烟区的适应性研究[J]. 作物研究, 34(6): 531-536. |
| LUO J, ANG Y N, DONG Q, et al., 2020. Study on the adaptability of a new flue-cured tobacco variet Yunyan 116 in Xingyi tobacco growing area[J]. Crop Research, 34(6): 531-536. | |
| [35] | 麻万诸, 章明奎, 2017. 中国土系志∙浙江卷[M]. 北京:科学出版社: 191. |
| MA W Z, ZHANG M K, 2017. Soil Series of China Zhejiang[M]. Beijing:Science Press: 191. | |
| [36] | 邵玉祥, 杨忠芳, 王磊, 等, 2021. 广西南流江流域土壤-水稻系统Cd生物有效性及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 35(3): 625-636. |
| SHAO Y X, YANG Z H, WANG L R, et al., 2021. Cadmium bioavailability and influencing factors of soil-rice system in nanliujiang catchment of Guangxi[J]. Modern Geology, 35(3): 625-636 | |
| [37] | 王存龙, 曾宪东, 刘华峰, 等, 2015. 烟台市土壤环境质量现状及重金属元素分布迁移规律[J]. 中国地质, 42(1): 317-330. |
| WANG C L, ZENG X D, LIU H F, et al., 2015. The present situation of soil environmental quality and the distribution and migration regularity of heavy metals in soil of Yantai[J]. Geology in China, 42(1): 317-330. | |
| [38] | 王浩朴, 胡丽, 冯莲莲, 等, 2017. 石灰、硅酸钠和羟基磷灰石对烟草吸收镉的影响[J]. 热带作物学报, 38(8): 1434-1440. |
| WANG H P, HU L, FENG L L, et al., 2017. Effects of slaked lime, sodium silicate and hydroxyapatite on cadmium accumulation in tobacco plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 38(8): 1434-1440. | |
| [39] | 汪洁, 沈丽波, 李柱, 等, 2014. 氮肥形态对伴矿景天生长和锌镉吸收性的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(11): 2118-2124. |
| WANG J, SHEN L B, LI Z, et al., 2014. Effects of nitrogen forms on growth and Zn/Cd uptake of Sedum plumbizincicola[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(11): 2118-2124. | |
| [40] | 王敏捷, 盛光遥, 王锐, 2021. 土壤重金属污染修复植物处置技术进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 38(2): 151-159. |
| WANG M J, SHENG G Y, WANG R, 2021. Progress in disposal technologies for plants polluted with heavy metals after phytoextraction[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 38(2): 151-159. | |
| [41] | 王卫, 梁振飞, 李菊梅, 等, 2014. 土壤性质对烟草中镉富集的影响及预测模型研究[J]. 土壤, 46(1): 178-183. |
| WANG W, LIANG Z F, LI J M, et al., 2014. Studies on effects of soil properties on cd accumulation in tobacco and prediction model[J]. Soil, 46(1): 178-183. | |
| [42] | 吴仁杰, 陈银萍, 曹雯婕, 等, 2021. 营养元素与螯合剂强化植物修复重金属污染土壤研究进展[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (5): 328-337. |
| WU R J, CHEN Y P, CAO W J, et al., 2021. Research advances in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil strengthened by chelating agents and nutrient elements[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (5): 328-337. | |
| [43] | 武文飞, 南忠仁, 王胜利, 等, 2013. 绿洲土Cd、Pb、Zn、Ni复合污染下重金属的形态特征和生物有效性[J]. 生态学报, 33(2): 619-630. |
|
WU W F, NAN Z R, WANG S L, et al., 2013. Fractionation character and bioavailability of Cd, Pb, Zn and Ni combined pollution in oasis soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(2): 619-630.
DOI URL |
|
| [44] | 杨远, 邓飞跃, 肖立青, 等, 2013. 湿法消解-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定烟叶中22种元素[J]. 中国烟草学报, 19(3): 11-17. |
| YANG Y, DENG F Y, XIAO L Q, et al., 2013. Determination of 22 elements in leaf tobacco by ICP-AES using wet-digestion sample preparation[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 19(3): 11-17. | |
| [45] | 易蔓, 韦慧琴, 胡梦坤, 等, 2016. 氮素形态对烟草根际镉的有效性及镉吸收的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 10(2): 941-947. |
| YI M, WEI H Q, HU M K, et al., 2016. Effects of nitrogen forms on bioavailability of cadmium in rhizosphere and its uptake by tobacco[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 10(2): 941-947. | |
| [46] | 余浩, 王幽静, 宋睿, 等, 2018. 不同品种烟草对Cd的富集及根际有机酸的分泌特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(9): 1827-1832. |
| YU H, WANG Y J, SONG R, et al., 2018. Bioaccumulation of Cd in different varieties of tobacco and their rhizosphere organic acid secretion characteristics[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(9): 1827-1832. | |
| [47] | 杨勇, 王巍, 江荣风, 等, 2009. 超累积植物与高生物量植物提取镉效率的比较[J]. 生态学报, 29(5): 2732-2737. |
| YANG Y, WANG W, JIANG R F, et al., 2009. Comparison of phytoextraction efficiency of Cd with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens and three high biomass species[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(5): 2732-2737. | |
| [48] | 章明奎, 方利平, 周翠, 2006. 污染土壤重金属的生物有效性和移动性评价: 四种方法比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 17(8): 1501-1504. |
| ZHANG M K, FANG L P, ZHOU C, 2006. Evaluation of heavy metals bioavailability and mobility in polluted soils: A comparison of four methods.[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(8): 1501-1504. |
| [1] | 王丽华, 王磊, 许端平, 薛杨. 煤胶体对重金属铜与镉的吸附特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [2] | 李治梅, 安娅, 李梅, 王室苹, 秦好丽. 巯基/铁基功能化蒙脱土对土壤镉的钝化行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312. |
| [3] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [4] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [5] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [6] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [8] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [9] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [10] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [11] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [12] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [13] | 文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 李富荣, 杜瑞英, 黄永东, 李蕾, 王富华. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [14] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [15] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
