生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 158-165.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.017
崔远远1( ), 张征云2, 刘鹏1, 张运春1, 张桥英3,*(
), 张征云2, 刘鹏1, 张运春1, 张桥英3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-18
出版日期:2023-01-18
发布日期:2023-04-06
通讯作者:
*张桥英(1976年生),女,教授,主要从事植物生态与生物地理研究。E-mail: qiaoyingzhang@163.com作者简介:崔远远(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物对环境污染物的响应机制。E-mail: 2978996593@qq.com
基金资助:
CUI Yuanyuan1( ), ZHANG Zhengyun2, LIU Peng1, ZHANG Yunchun1, ZHANG Qiaoying3,*(
), ZHANG Zhengyun2, LIU Peng1, ZHANG Yunchun1, ZHANG Qiaoying3,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-18
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
摘要:
根系是植物适应环境条件的重要器官,分形维数是快速准确的评估根系形态特征的有效方法,尤其是在胁迫下评估植物根系对水分和养分吸收及植物生长贡献分析具有重要意义。为探讨重金属镉及聚乙烯微塑料对小白菜根系生长的影响,采用盆栽实验,研究了不同添加质量分数下(镉:0、10、20 mg·kg-1;聚乙烯:0、18、36 g·kg-1)两种污染物对小白菜根系形态的影响。运用根系分析仪的图像分析系统来研究受镉和聚乙烯胁迫90 d的小白菜的根系形态。采用分形分析的方法对小白菜根系进行描述,并确定镉和聚乙烯的添加对根系的分形维数的影响。结果表明,镉和聚乙烯添加会促进根系的分生能力,增加根系的分形维数,同时在不同浓度的镉和聚乙烯胁迫下,小白菜会形成不同的根系构型。在低浓度胁迫下,小白菜通过增加根系比表面积,减小根平均直径和根体积,促进细根发育来适应胁迫环境。在高浓度胁迫下,小白菜通过增加根长、根表面积、比表面积和比根长,增加根尖数,减小根平均直径,促进细根发育来适应胁迫环境。镉和聚乙烯胁迫影响小白菜根系的分形能力,使得分形维数介于1.55—1.70之间变化。镉浓度对分形维数有显著影响,而聚乙烯对分形维数的影响差异性不显著。基本根系形态与分形维数的变化呈正相关,且分形维数对根直径和根体积的影响更大。该研究揭示了在重金属和微塑料胁迫下,植物会通过构建不同的根系构型来适应土壤环境;实验结果还间接证明了微塑料对重金属有一定的吸附作用。
中图分类号:
崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165.
CUI Yuanyuan, ZHANG Zhengyun, LIU Peng, ZHANG Yunchun, ZHANG Qiaoying. Morphological Characteristics and Fractal Dimension of Brassia chinensis Root System under Cadmium and Polyethylene Microplastic Stress[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 158-165.
| 镉质量分数/ (mg·kg-1) | 聚乙烯 质量分数/ (g·kg-1) | 根长 l/mm | 根平均 直径 d/mm | 根表面积A/mm2 | 根体积V/mm3 | 根生物量 B/g | 根尖数 N | 比根长 ls/(mm·g-1) | 比表面积 As/ (mm²·g-1) | 根尖密度RTD/mm-1 | 根组织密度RTID/ (g·mm-3) | 根细度 RFN/ (mm·mm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 470.423± 151.299b | 0.923± 0.161a | 126.255± 28.945b | 2.791± 0.476a | 0.380± 0.104a | 1016± 272c | 1240.921± 292.995b | 337.058± 46.026c | 2.236± 0.365b | 0.135± 0.019b | 168.760± 50.095d |
| 18 | 484.349± 154.629b | 0.833± 0.106b | 121.934± 25.110b | 2.516± 0.352a | 0.333± 0.047b | 1130± 372c | 1457.507± 445.624b | 366.730± 60.795c | 2.328± 0.056a | 0.132± 0.004b | 1457.507± 445.624c | |
| 36 | 362.895± 72.393c | 0.950± 0.114a | 105.027± 12.455c | 2.469± 0.220a | 0.314± 0.026b | 722± 96d | 1152.090± 188.300b | 334.382± 23.023c | 2.026± 0.209b | 0.127± 0.009b | 1152.090± 188.300d | |
| 10 | 0 | 291.120± 57.192c | 0.954± 0.133a | 86.570± 12.538c | 2.174± 0.535b | 0.230± 0.058c | 670± 115d | 2340.990± 392.969b | 390.924± 67.661c | 2.321± 0.208a | 0.106± 0.014b | 1340.990± 392.969d |
| 18 | 488.987± 128.297b | 0.643± 0.097c | 99.345± 34.485c | 1.658± 0.750b | 0.287± 0.034b | 1240± 256b | 1692.470± 365.558b | 340.011± 93.271c | 2.614± 0.382a | 0.213± 0.093a | 1692.470± 365.558a | |
| 36 | 452.949± 152.111b | 0.794± 0.126b | 107.485± 25.632c | 2.087± 0.341b | 0.257± 0.090c | 919± 348c | 1804.568± 314.035b | 447.948± 85.895b | 2.029± 0.254b | 0.120± 0.033b | 1804.568± 314.035c | |
| 20 | 0 | 367.651± 126.272c | 0.896± 0.148a | 97.280± 27.700c | 2.092± 0.573b | 0.242± 0.062c | 844± 335c | 1482.841± 319.768b | 402.769± 85.024b | 2.231± 0.240b | 0.120± 0.027b | 1482.841± 319.768d |
| 18 | 630.235± 162.527b | 0.711± 0.079b | 134.427± 23.784b | 2.309± 0.249a | 0.244± 0.039c | 1616± 322a | 2634.514± 688.160a | 561.687± 109.915a | 2.618± 0.304a | 0.106± 0.014b | 2634.514± 688.160b | |
| 36 | 832.475± 262.402a | 0.666± 0.077c | 169.235± 38.329a | 2.820± 0.466a | 0.337± 0.070b | 1669± 595a | 2518.831± 796.660a | 511.231± 111.584a | 1.978± 0.109b | 0.119± 0.012b | 2518.831± 796.660b |
表1 不同胁迫浓度对小白菜根系结构形状的影响
Table 1 Changes in root traits of Brassica chinensis under different stress concentrations
| 镉质量分数/ (mg·kg-1) | 聚乙烯 质量分数/ (g·kg-1) | 根长 l/mm | 根平均 直径 d/mm | 根表面积A/mm2 | 根体积V/mm3 | 根生物量 B/g | 根尖数 N | 比根长 ls/(mm·g-1) | 比表面积 As/ (mm²·g-1) | 根尖密度RTD/mm-1 | 根组织密度RTID/ (g·mm-3) | 根细度 RFN/ (mm·mm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 470.423± 151.299b | 0.923± 0.161a | 126.255± 28.945b | 2.791± 0.476a | 0.380± 0.104a | 1016± 272c | 1240.921± 292.995b | 337.058± 46.026c | 2.236± 0.365b | 0.135± 0.019b | 168.760± 50.095d |
| 18 | 484.349± 154.629b | 0.833± 0.106b | 121.934± 25.110b | 2.516± 0.352a | 0.333± 0.047b | 1130± 372c | 1457.507± 445.624b | 366.730± 60.795c | 2.328± 0.056a | 0.132± 0.004b | 1457.507± 445.624c | |
| 36 | 362.895± 72.393c | 0.950± 0.114a | 105.027± 12.455c | 2.469± 0.220a | 0.314± 0.026b | 722± 96d | 1152.090± 188.300b | 334.382± 23.023c | 2.026± 0.209b | 0.127± 0.009b | 1152.090± 188.300d | |
| 10 | 0 | 291.120± 57.192c | 0.954± 0.133a | 86.570± 12.538c | 2.174± 0.535b | 0.230± 0.058c | 670± 115d | 2340.990± 392.969b | 390.924± 67.661c | 2.321± 0.208a | 0.106± 0.014b | 1340.990± 392.969d |
| 18 | 488.987± 128.297b | 0.643± 0.097c | 99.345± 34.485c | 1.658± 0.750b | 0.287± 0.034b | 1240± 256b | 1692.470± 365.558b | 340.011± 93.271c | 2.614± 0.382a | 0.213± 0.093a | 1692.470± 365.558a | |
| 36 | 452.949± 152.111b | 0.794± 0.126b | 107.485± 25.632c | 2.087± 0.341b | 0.257± 0.090c | 919± 348c | 1804.568± 314.035b | 447.948± 85.895b | 2.029± 0.254b | 0.120± 0.033b | 1804.568± 314.035c | |
| 20 | 0 | 367.651± 126.272c | 0.896± 0.148a | 97.280± 27.700c | 2.092± 0.573b | 0.242± 0.062c | 844± 335c | 1482.841± 319.768b | 402.769± 85.024b | 2.231± 0.240b | 0.120± 0.027b | 1482.841± 319.768d |
| 18 | 630.235± 162.527b | 0.711± 0.079b | 134.427± 23.784b | 2.309± 0.249a | 0.244± 0.039c | 1616± 322a | 2634.514± 688.160a | 561.687± 109.915a | 2.618± 0.304a | 0.106± 0.014b | 2634.514± 688.160b | |
| 36 | 832.475± 262.402a | 0.666± 0.077c | 169.235± 38.329a | 2.820± 0.466a | 0.337± 0.070b | 1669± 595a | 2518.831± 796.660a | 511.231± 111.584a | 1.978± 0.109b | 0.119± 0.012b | 2518.831± 796.660b |
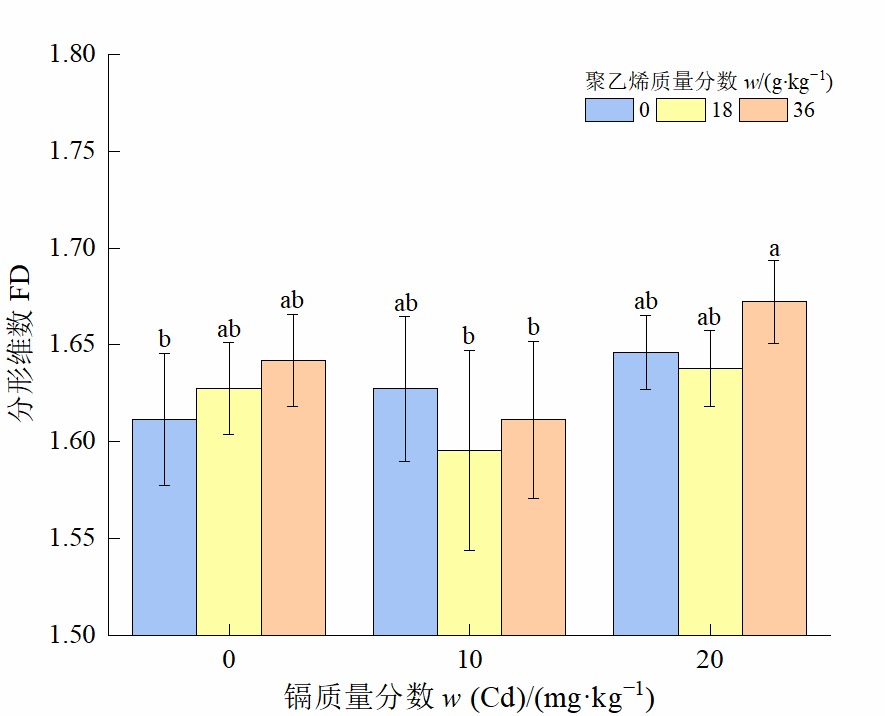
图1 不同质量分数镉和聚乙烯胁迫下小白菜分形维数 图中数据为平均值±标准误,n=5;不同字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 Fractal dimension of Brassica chinensis under different concentrations of cadmium and polyethylene stress
| [1] |
BANDOW N, WILL V, WACHTENDORF V, et al., 2017. Contaminant release from aged microplastic[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 14(6): 394-405.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHUN H C, LEE S, CHOI Y D, et al., 2021. Effects of drought stress on root morphology and spatial distribution of soybean and adzuki bean[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 20(10): 2639-2651.
DOI |
| [3] |
COMAS L H, EISSENSTAT D M, 2004. Linking fine root traits to maximum potential growth rate among 11 mature temperate tree species[J]. Functional Ecology, 18(3): 388-397.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
COSTA C, DWYER L M, DUTILLEUL P, et al., 2003. Morphology and fractal dimension of root systems of maize hybrids bearing the leafy trait[J]. Canadian Journal of Botany, 81(7): 706-713.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DANNOWSKI M, BLOCK A, 2005. Fractal geometry and root system structures of heterogeneous plant communities[J]. Plant and Soil, 272(1-2): 61-76.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FERNÁNDEZ-MARTÍNEZ M, SÁNCHZE-GRANERO M A, 2014. Fractal dimension for fractal structures[J]. Topology and its Applications, 163: 93-111.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HENKE M, SARLIKIOTI V, KURTH W, et al., 2014. Exploring root developmental plasticity to nitrogen with a three-dimensional architectural model[J]. Plant and Soil, 385(1-2): 49-62.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
KHALID N, AQEEL M, NOMAN A, 2020. Microplastics could be a threat to plants in terrestrial systems directly or indirectly[J]. Environmental Pollution, 267: 115653.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MOONEY K A, HALITSCHKE R, KESSLER A, et al., 2010. Evolutionary trade-offs in plants mediate the strength of trophic cascades[J]. Science, 327(5973): 1642-1644.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
RISTOVA D, BUSCH W, 2014. Natural variation of root traits: from development to nutrient uptake[J]. Plant Physiology, 166(2): 518-527.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
ROGERS E D, BENFEY P N, 2015. Regulation of plant root system architecture: Implications for crop advancement[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 32: 93-98.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
TURNER A, HOLMES L A, 2015. Adsorption of trace metals by microplastic pellets in fresh water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 12(5): 600-610.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WAHL S, RYSER P, 2000. Root tissue structure is linked to ecological strategies of grasses[J]. New Phytologist, 148(3): 459-471.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
ZHANG J, WANG J M, CHEN J Y, et al., 2019. Soil moisture determines horizontal and vertical root extension in the perennial grass Lolium perenne L. growing in Karst soil[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10: 00629.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 鲍广灵, 杨庆波, 陶荣浩, 等, 2022. 铜陵市义安区蔬菜产地镉污染调查与评价[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 34(3): 40-44. |
| BAO G L, YANG Q B, TAO R H, et al, 2022. Investigation and evaluation of cadmium pollution in vegetable growing areas in Yi’an district, Tongling City[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environment Monitoring, 34(3): 40-44. | |
| [16] | 陈吉虎, 余新晓, 有祥亮, 等, 2006. 不同水分条件下银叶椴根系的分形特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 4(2): 71-74. |
| CHEN J H, YU X Q, YOU X L, et al., 2006. Fractal characteristics of Tilia tomentosa’s root system under different water conditions[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 4(2): 71-74. | |
| [17] |
陈丽丽, 田爽, 鲁伟丹, 等, 2022. 镉胁迫对3种植物生长及镉吸收和积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 59(4): 1009-1015.
DOI |
| CHEN L L, TIAN S, LU W D, et al., 2022. Effects of cadmium stress on growth in three plants and cadmium uptake and its accumulation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science, 59(4): 1009-1015. | |
| [18] | 黄东华, 麦淑华, 仇曙, 等, 2022. 镉对堇叶碎米荠生长生理特性的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 61(5): 87-90. |
| HUANG D H, MAI S H, QIU S, et al., 2022. Effects of cadmium on growth and physiological characteristics of Cardamine violifolia[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 61(5): 87-90. | |
| [19] | 嵇晓雷, 2010. 分形理论应用于植物根系形态分布的研究进展及其应用前景[J]. 安徽农业科学, 38(25): 13693-13694. |
| JI X L, 2010. Research progress and application prospect of morphology distribution of plants root with fractal theory[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 38(25):13693-13694. | |
| [20] | 雷晓婷, 雷金银, 周丽娜, 等, 2020. 微塑料对农田土壤质量的影响研究现状与分析[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 61(2): 26-28. |
| LEI X T, LEI J Y, ZHOU L N, et al., 2020. Status and analysis of study on effects of microplastics on farmland soil quality[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 61(2): 26-28. | |
| [21] | 李贞霞, 李庆飞, 李瑞静, 等, 2020. 黄瓜幼苗对微塑料和镉污染的生理响应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(5): 973-981. |
| LI Z X, LI Q F, LI R J, et al., 2020. Physiological response of cucumber seedlings to microplastics and cadmium[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(5): 973-981. | |
| [22] | 连加攀, 沈玫玫, 刘维涛, 2019. 微塑料对小麦种子发芽及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(4): 737-745. |
| LIAN J P, SHEN M M, LIU W T, 2019. Effects of microplastics on wheat seed germination and seedling growth[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(4): 737-745. | |
| [23] | 廖成章, 余翔华, 2001. 分形理论在植物根系结构研究中的应用[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 23(2): 192-196. |
| LIAO C Z, YU X H, 2001. Application of fractal theory on studies of the root structure of Plant[J]. Acta Agriculture Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 23(2): 192-196. | |
| [24] | 廖苑辰, 娜孜依古丽·加合甫别克, 李梅, 等, 2019. 微塑料对小麦生长及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(10): 4661-4667. |
| LIAO Y C, NAZYGUL J, LI M, et al., 2019. Effects of microplastics on the growth, physiology, and biochemical characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Environmental Science, 40(10): 4661-4667. | |
| [25] |
刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 等, 2022. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(6): 1263-1271.
DOI URL |
| LIU X H, LIU L Q Q, LI M, et al., 2022. Effects of polyethylene microplastics with different particle sizes on seed germination and seedling growth of maize and cucumber[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(6): 1263-1271. | |
| [26] |
刘晓宇, 郭月峰, 姚云峰, 等, 2021. 砒砂岩区不同留茬高度及坡向下沙棘根系分形特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 100-107.
DOI URL |
| LIU X Y, GUO Y F, YAO Y F, et al., 2021. Fractal features of Hippophae rhamnoides roots under different stubble height and slopes in soft sandstone area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1): 100-107. | |
| [27] | 骆永明, 周倩, 章海波, 等, 2018. 重视土壤中微塑料污染研究防范生态与食物链风险[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(10): 1021-1030. |
| LUO Y M, ZHOU Q, ZHANG H B, et al., 2018. Pay attention to research on microplastic pollution in soil for prevention of ecological and food chain risks[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control Strategy of Microplastics, 33(10): 1021-1030. | |
| [28] | 马雄忠, 王新平, 2020. 阿拉善高原2种荒漠植物根系构型及生态适应性特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(17): 6001-6008. |
| MA X Z, WANG X P, 2020. Root architecture and adaptive strategy of two desert plants in the Alxa Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(17): 6001-6008. | |
| [29] | 倪薇, 霍常富, 王朋, 2014. 落叶松 (Larix) 细根形态特征沿纬度梯度的可塑性[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(9): 2322-2329. |
| NI W, HUO C F, WANG P, 2014. Morphological plasticity of fine root traits in Larix plantations across a latitude gradient[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(9): 2322-2329. | |
| [30] | 乔海涛, 2009. 苹果砧木幼苗根系构型及根区土壤生物学特性研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学: 73. |
| QIAO H T, 2009. Studies on root architecture and biological characteristics of rhizosphere in apple stock[D]. Tai’an: Shangdong Agricultural University: 73. | |
| [31] | 乔海涛, 杨洪强, 申为宝, 等, 2010. 平邑甜茶根系形态构型对氯化镉处理的响应[J]. 林业科学, 46(1): 56-60. |
| QIAO H T, YANG H Q, SHEN W B, et al., 2010. Responses of root morphology and architecture in Malus hupehensis var. pingyiensis seedlings to cadmium chloride[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 46(1): 56-60. | |
| [32] |
曲梦雪, 宋杰, 孙菁, 等, 2022. 镉胁迫对不同耐镉型玉米品种苗期根系生长的影响[J]. 作物学报, 48(11): 2945-2952.
DOI |
| QU M X, SONG J, SUN J, et al., 2022. Effects of cadmium stress on root growth of maize (Zea mays L.) varieties with different cadmium-tolerant at seedling stage[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 48(11): 2945-2952. | |
| [33] | 任永哲, 徐艳花, 丁锦平, 等, 2011. 非生物因素调控植物根系发育可塑性的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(9): 34-38. |
| REN Y Z, XU Y H, DING J P, et al., 2011, Regulation of abiotic factors on the plasticity of plant root development[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(9): 34-38. | |
| [34] | 单立山, 李毅, 董秋莲, 等, 2012. 红砂根系构型对干旱的生态适应[J]. 中国沙漠, 32(5): 1283-1290. |
| SHAN L S, LI Y, DONG Q L, et al., 2012. Ecological adaptation of Reaumuria Soongorica root system architecture to arid environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 32(5): 1283-1290. | |
| [35] |
宋清华, 赵成章, 史元春, 等, 2015. 高寒草地甘肃臭草根系分形结构的坡向差异性[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(8): 816-824.
DOI |
|
SONG Q H, ZHAO C Z, SHI Y C, et al., 2015. Fractal root system of Melica przewalskyi along different aspect in degraded grassland[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(8): 816-824.
DOI URL |
|
| [36] | 孙垦, 华宇峰, 王镇岳, 2022. 工业废水重金属污染与健康风险评价研究[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报 (自然科学版), 43(3): 99-108. |
| SUN K, HUA Y F, WANG Z Y, 2022. Research progress on heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of the industrial wastewater[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 43(3): 99-108. | |
| [37] | 汪堃, 南丽丽, 郭全恩, 等, 2022. 干旱胁迫对不同根型苜蓿根系构型的影响[J]. 生态学报, 42(20): 1-9. |
| WANG K, NAN L L, GUO Q E, et al., 2022. Effects of drought stress on root architecture of different root- type alfalfa[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(20): 1-9 | |
| [38] | 王艺霖, 周玫, 李苹, 等. 根系形态可塑性决定黄栌幼苗在瘠薄土壤中的适应对策[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(06):60-69. |
| WANG Y L, ZHOU M, LI P, et al., 2017. Root morphological plasticity determing the adaptive strategies of Cotinus coggygria seedlings in barren soil environment. | |
| [39] | 魏畅, 焦秋娟, 柳海涛, 等, 2022. 镉暴露条件下玉米生长及根系构型分级特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 31(3): 101-113. |
| WEI C, JIAO Q J, LIU H T, et al., 2022. Physiological effects of different Cd concentration on maize root architecture and classification[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 31(3): 101-113. | |
| [40] | 席佳锐, 吴玲玲, 付融冰, 等, 2021. 土壤环境中锑的生物毒性评价方法比较[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 33(2): 9-13. |
| XI J R, WU L L, FU R B, et al., 2021. Comparison of biotoxicity evaluation methods of antimony in soil environment[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environment Monitoring, 33(2): 9-13 | |
| [41] | 闫励, 杨方社, 李怀恩, 等, 2019. 砒砂岩区不同立地下沙棘根系分形特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 36(2): 467-473. |
| YAN L, YANG F D, LI H E, et al., 2019. Fractal features of Hippophae rhamnoides roots under different site conditions in soft sandstone area[J]. Arid Zone Research, 36(2): 467-473. | |
| [42] | 郑伟, 陈敬仁, 2020. 微塑料在土壤环境中的研究进展[J]. 污染防治技术, 33(3): 4-6. |
| ZHENG W, CHEN J R, 2020. Research progress of microplastics in soil environment[J]. Pollution Control Technology, 33(3): 4-6. | |
| [43] | 郑文俊, 李腾, 张振涛, 2020. 微塑料对水体中重金属吸附机理的研究[J]. 云南化工, 47(2): 40-41, 44. |
| ZHENG W J, LI T, ZHANG Z T, 2020. Adsorption mechanism of heavy metals in water by microplastics[J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 47(2): 40-41, 44. | |
| [44] | 左华丽, 2015. 尾矿库植物根系发育的分形特征及对植物铀分布的影响[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学: 59. |
| ZUO H L, 2015. The fractal characteristic of plant root system and it’s influence on uranium distribution in plant from tailings[D]. Hengyang: University of South China: 59. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [3] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [4] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [5] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [6] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [7] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [8] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [9] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [10] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [11] | 文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 李富荣, 杜瑞英, 黄永东, 李蕾, 王富华. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [12] | 秦坤, 王志康, 王章鸿, 杨成, 刘杰刚, 沈德魁. 木质素-聚乙烯共热解生物炭对Cd(II)的吸附性能[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 344-353. |
| [13] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [14] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [15] | 高歌, 葛晓改, 周君刚, 周本智, 李正才, 杨南. 施氮和干旱对杉木和青冈幼苗生物量及根系形态的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2292-2301. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
