生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 781-790.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.05.011
李林峰1,2,3( ), 徐梓盛1,2,3, 陈勇1,2,3, 李奇1,2,3, 林晓扬1,2,3, 李义纯1,2,3,*(
), 徐梓盛1,2,3, 陈勇1,2,3, 李奇1,2,3, 林晓扬1,2,3, 李义纯1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-06
出版日期:2024-05-18
发布日期:2024-06-27
通讯作者:
* 李义纯。E-mail: yichunli@gdaas.cn作者简介:李林峰(1986年生),男,副研究员,博士,研究方向为农田重金属污染防治。E-mail: lilinfeng@gdaas.cn
基金资助:
LI Linfeng1,2,3( ), XU Zisheng1,2,3, CHEN Yong1,2,3, LI Qi1,2,3, LIN Xiaoyang1,2,3, LI Yichun1,2,3,*(
), XU Zisheng1,2,3, CHEN Yong1,2,3, LI Qi1,2,3, LIN Xiaoyang1,2,3, LI Yichun1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-06
Online:2024-05-18
Published:2024-06-27
摘要:
稻田镉(Cd)污染治理是中国当前亟需解决的重大科学问题;根表铁膜是水稻根系吸收Cd的重要屏障,施硅(Si)调控水稻根系抗氧化酶和乙烯合成酶活性影响根表铁膜对Cd的吸附,并改变水稻体内Cd的累积和分布,但不同施Si水平对水稻根表铁膜和体内Cd累积分布的影响尚未完全清楚。采用水稻盆栽试验,探讨高、低两种施Si水平条件下,水稻成熟期不同组织器官中Cd的含量、分布规律和水稻体内Cd的转运能力,以及抽穗期根表铁膜的Cd含量、形貌特征与根系抗氧化酶和乙烯合成酶基因的表达,试图揭示不同施Si水平对水稻根表铁膜Cd吸附和体内Cd累积分布的影响。结果表明,施Si会减少成熟期水稻茎中Cd的含量,增大根系中Cd的分布比例,而高Si水平(0.66 g∙kg−1)还会进一步降低茎节和糙米中Cd的含量和分布比例,抑制根系转运Cd至糙米的能力。此外,施Si可以增强抽穗期水稻根系超氧化物歧化酶基因(OsSOD-Cu/Zn和OsSOD-Fe)、过氧化氢酶基因(OsCATa和OsCATb)以及乙烯合成酶基因(OsACS1)的表达,高Si水平(0.66 g∙kg−1)能够显著增加根表铁膜中的DCB-Fe和DCB-Cd含量,增大根表铁膜的表面粗糙度,并且进一步增强根系OsSOD-Fe和OsACS1的表达。研究结果证实施Si水平是影响水稻根表铁膜和体内Cd累积分布的关键因素,高水平Si能够更显著地促进水稻根系抗氧化酶基因的表达,增强铁膜形成及其对Cd的吸附,并且抑制根系Cd向糙米的转运和茎节中Cd的分布,从而降低糙米中Cd的累积。该研究成果可为解决中国稻田Cd污染治理难题提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
李林峰, 徐梓盛, 陈勇, 李奇, 林晓扬, 李义纯. 施硅水平对水稻根表铁膜和体内Cd累积分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(5): 781-790.
LI Linfeng, XU Zisheng, CHEN Yong, LI Qi, LIN Xiaoyang, LI Yichun. The Impact of Silicon Application Levels on the Iron Plaque of Rice Roots and the Accumulation and Distribution of Cadmium Within the Plant[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(5): 781-790.
| 功能基因 | 基因登录号 | 引物序列 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抗氧化酶基因 | OsSOD-Cu/Zn | LOC_Os07g46990 | F: CTGTGACGGGAAGTGTCTCTG |
| R: GGCGGTTCTCATCTTGTGG | |||
| OsSOD-Fe | LOC_Os06g05110 | F: AAGCATACAACAACGGCAACC | |
| R: TCTTCAAGACAAGCCAAACCC | |||
| OsAPX1 | LOC_Os03g17690 | F: CTGATGCTACCAAGGGTTCTG | |
| R: AAGGTCCCTCAAAACCAGATC | |||
| OsAPX3 | LOC_Os04g14680 | F: GGATTTGATGGTGCCTGGAC | |
| R: ATAGCGGCGGAATGTAGGAT | |||
| OsCATa | LOC_Os02g02400 | F: CAAGGGCTTCTTCGAGTGC | |
| R: GTGGAGAAGCGGACGATGA | |||
| OsCATb | LOC_Os06g51150 | F: GGCATCCCACTCAACTACAGG | |
| R: CTGCAATAGAATCAGTCAAGTCCTT | |||
| 乙烯合成酶基因 | OsACS1 | LOC_Os03g51740 | F: ACTCGTCCTACTTCCTGGGG |
| R: GGTTCTTCTCCAGCCACTCC | |||
| OsACS2 | LOC_Os04g48850 | F: CACCACCACCACCTCAGC | |
| R: GACGTAGTAAGGCGCAGCAT | |||
表1 功能基因及其引物序列
Table 1 Primers for qPCR analysis of the functional genes
| 功能基因 | 基因登录号 | 引物序列 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抗氧化酶基因 | OsSOD-Cu/Zn | LOC_Os07g46990 | F: CTGTGACGGGAAGTGTCTCTG |
| R: GGCGGTTCTCATCTTGTGG | |||
| OsSOD-Fe | LOC_Os06g05110 | F: AAGCATACAACAACGGCAACC | |
| R: TCTTCAAGACAAGCCAAACCC | |||
| OsAPX1 | LOC_Os03g17690 | F: CTGATGCTACCAAGGGTTCTG | |
| R: AAGGTCCCTCAAAACCAGATC | |||
| OsAPX3 | LOC_Os04g14680 | F: GGATTTGATGGTGCCTGGAC | |
| R: ATAGCGGCGGAATGTAGGAT | |||
| OsCATa | LOC_Os02g02400 | F: CAAGGGCTTCTTCGAGTGC | |
| R: GTGGAGAAGCGGACGATGA | |||
| OsCATb | LOC_Os06g51150 | F: GGCATCCCACTCAACTACAGG | |
| R: CTGCAATAGAATCAGTCAAGTCCTT | |||
| 乙烯合成酶基因 | OsACS1 | LOC_Os03g51740 | F: ACTCGTCCTACTTCCTGGGG |
| R: GGTTCTTCTCCAGCCACTCC | |||
| OsACS2 | LOC_Os04g48850 | F: CACCACCACCACCTCAGC | |
| R: GACGTAGTAAGGCGCAGCAT | |||
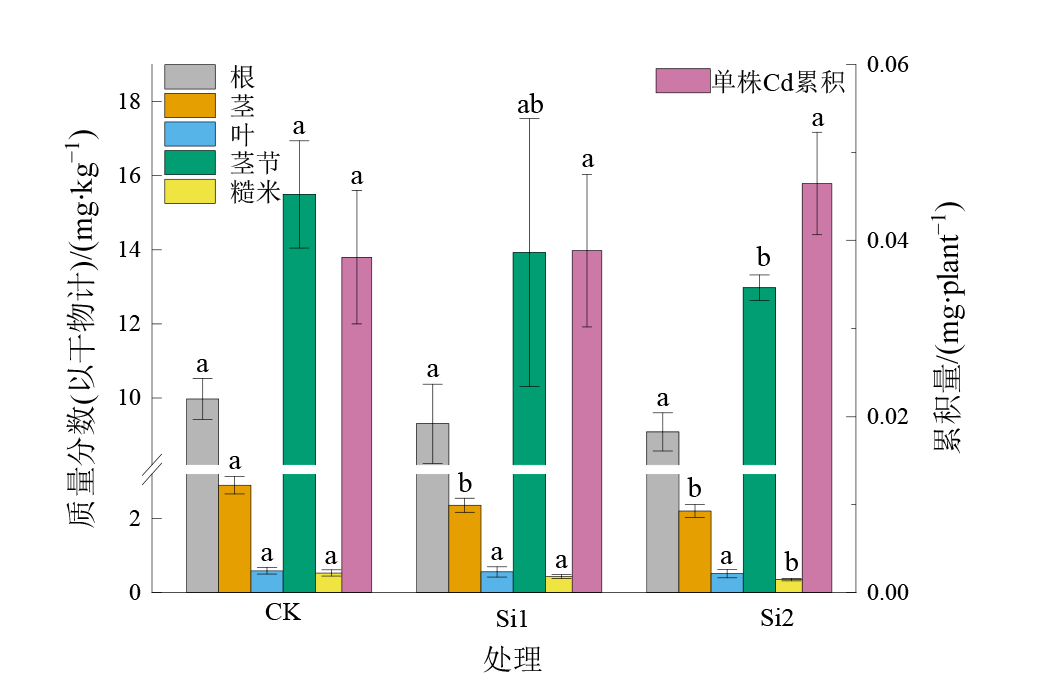
图1 水稻成熟期不同组织器官中Cd的含量与Cd单株累积量 不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(p<0.05),n=3
Figure 1 The content of Cd in different tissues and the total Cd accumulation per plant in rice at the mature stage
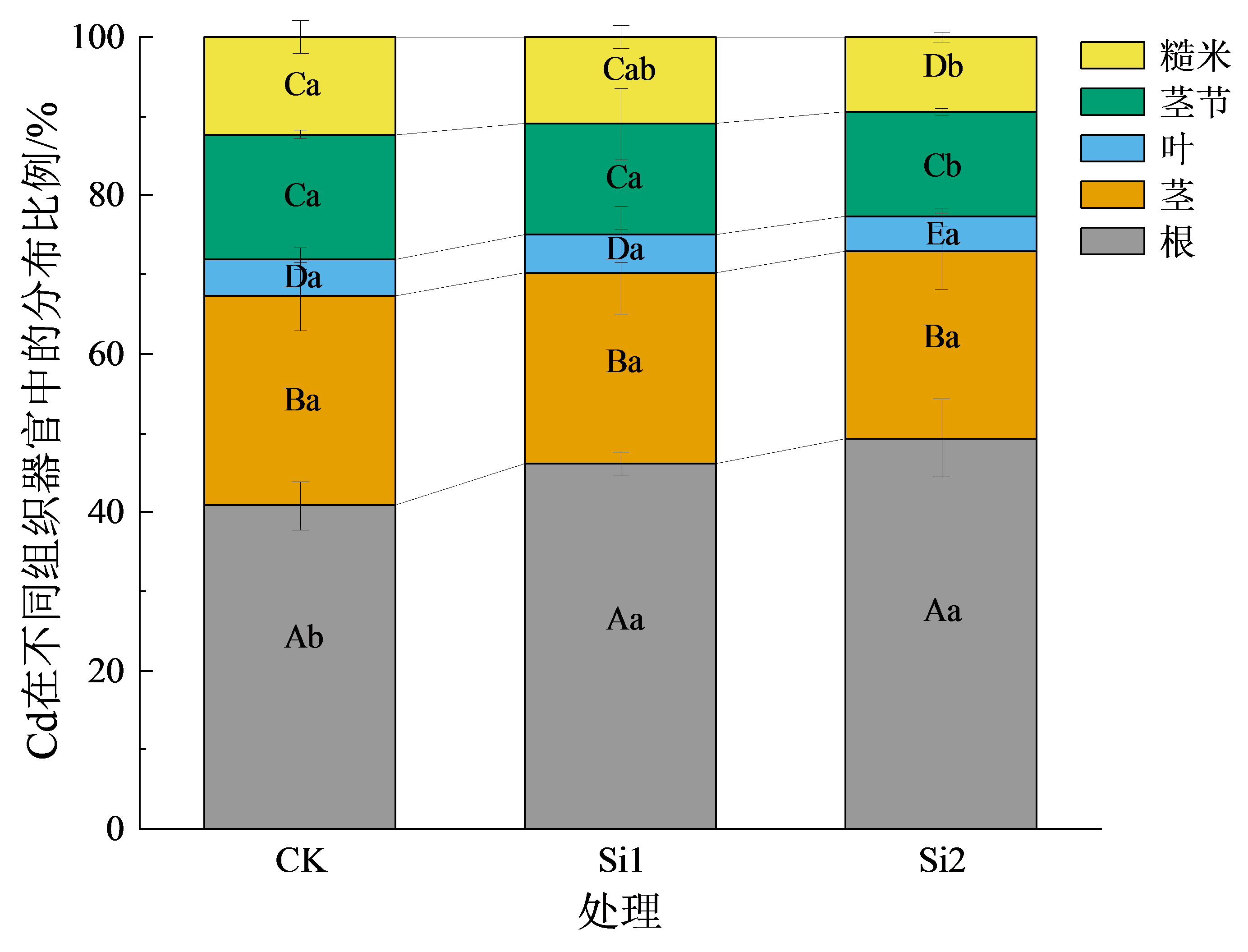
图2 水稻成熟期不同组织器官中Cd的分布比例 不同大写字母表示同一处理中不同组织器官之间差异显著(p<0.05),n=3;不同小写字母表示相同组织器官不同处理之间差异显著(p<0.05),n=3
Figure 2 Distribution ratio of Cd in different tissues of rice at the mature stage
| [1] | AMARAL D C, LOPES G, GUILHERME L R, et al., 2017. A new approach to sampling intact Fe plaque reveals Si-induced changes in Fe mineral composition and shoot As in rice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(1): 38-45. |
| [2] | BHOOMIKA K, PYNGROPE S, DUBEY R S, 2013. Differential responses of antioxidant enzymes to aluminum toxicity in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars with marked presence and elevated activity of Fe SOD and enhanced activities of Mn SOD and catalase in aluminum tolerant cultivar[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 71: 235-252. |
| [3] | CAI Y X, PAN B G, LIU B Q, et al., 2022. The Cd sequestration effects of rice roots affected by different Si management in Cd-contaminated paddy soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 849: 157718. |
| [4] | CHEN R, ZHANG C B, ZHAO Y L, et al., 2018. Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(3): 2361-2368. |
| [5] |
CLEMENS S, AARTS M G M, THOMINE S, et al., 2013. Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 18(2): 92-99.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
COSKUN D, DESHMUKH R, SONAH H, et al., 2019. The controversies of silicon's role in plant biology[J]. New Phytologist, 221(1): 67-85.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | DOELSCH E, ROSE J R, MASION A, et al., 2000. Speciation and crystal chemistry of iron(III) chloride hydrolyzed in the presence of SiO4 ligands. 1. An Fe K-edge EXAFS study[J]. Langmuir, 16(10): 4726-4731. |
| [8] |
FAROOQ M A, DETTERBECK A, CLEMENS S, et al., 2016. Silicon-induced reversibility of cadmium toxicity in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67(11): 3573-3585.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | FENDIYA M H, SATRIO R D, PRATAMI M P, et al., 2021. Analysis of Superoxide Dismutase (OsSOD) gene expression using qRT-PCR, its morphophysiological characters and path analysis in rice variety IR64 under aluminum stress[J]. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 26(4): 546-554 |
| [10] |
FLECK A T, NYE T, REPENNING C, et al., 2011. Silicon enhances suberization and lignification in roots of rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62(6): 2001-2011.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | FLECK A T, SCHULZE S, HINRICHS M, et al., 2015. Silicon promotes exodermal casparian band formation in Si-accumulating and Si-excluding species by forming phenol complexes[J]. PLoS One, 10(9): e0138555. |
| [12] |
GILL S S, TUTEJA N, 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12): 909-930.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | GONG H J, RANDALL D P, FLOWERS T J, 2006. Silicon deposition in the root reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by reducing bypass flow[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 29(10): 1970-1979. |
| [14] | GUO Y, ZHU C H, GAN L J, et al., 2014. Ethylene is involved in the complete-submergence induced increase in root iron and manganese plaques in Oryza sativa[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 76(3): 259-268. |
| [15] | HUANG G X, DING C F, LI Y S, et al., 2020. Selenium enhances iron plaque formation by elevating the radial oxygen loss of roots to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 398: 122860. |
| [16] | JONES A M, COLLINS R N, ROSE J, et al., 2009. The effect of silica and natural organic matter on the Fe(II)-catalysed transformation and reactivity of Fe(III) minerals[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(15): 4409-4422. |
| [17] | LI L F, LI Y C, WANG Y H, et al., 2021. Si-rich amendment combined with irrigation management to reduce Cd accumulation in brown rice[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 21(4): 3221-3231. |
| [18] | LIMMER M A, MANN J, AMARAL D C, et al., 2018. Silicon-rich amendments in rice paddies: Effects on arsenic uptake and biogeochemistry[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 624: 1360-1368. |
| [19] | LIMMER M A, THOMAS J, SEYFFERTH A L, 2022. The effect of silicon on the kinetics of rice root iron plaque formation[J]. Plant and Soil, 477: 171-181. |
| [20] | LIU S H, JI X H, CHEN Z L, et al., 2023. Silicon facilitated the physical barrier and adsorption of cadmium of iron plaque by changing the biochemical composition to reduce cadmium absorption of rice roots[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 256: 114879. |
| [21] | LIU W J, ZHU Y G, HU Y, et al., 2006. Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque, its accumulation and speciation in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(18): 5730-5736. |
| [22] |
MA J, CAI H M, HE C W, et al., 2015. A hemicellulose-bound form of silicon inhibits cadmium ion uptake in rice (Oryza sativa) cells[J]. New Phytologist, 206(3): 1063-1074.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | MEHRABANJOUBANI P, ABDOLZADEH A, SADEGHIPOUR H R, et al., 2019. Silicon increases cell wall thickening and lignification in rice (Oryza sativa) root tip under excess Fe nutrition[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 44: 264-273. |
| [24] | MENDELSOHN I A, KLEISS B A, WAKELEY J S, 1995. Factors controlling the formation of oxidized root channels: A review[J]. Wetlands, 15: 37-46. |
| [25] | RIAZ M, KAMRAN M, RIZWAN M, et al., 2021. Cadmium uptake and translocation: Selenium and silicon roles in Cd detoxification for the production of low Cd crops: A critical review[J]. Chemosphere, 273: 129690. |
| [26] | RODDA M S, LI G, REID R J, 2011. The timing of grain Cd accumulation in rice plants: The relative importance of remobilisation within the plant and root Cd uptake post-flowering[J]. Plant and Soil, 347(1-2): 105-114. |
| [27] | SAED M A, SOHRABI F, FASIHFAR E et al., 2021. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) as a selection criterion for triticale grain yield under drought stress: A comprehensive study on genomics and expression profiling, bioinformatics, heritability, and phenotypic variability[J]. BioMed Central Plant Biology, 21(1): 1-19. |
| [28] | SCHWERTMANN U, THALMANN H, 1976. The influence of [Fe(II)], [Si], and pH on the formation of lepidocrocite and ferrihydrite during oxidation of aqueous FeCl2 solutions[J]. Clay Minerals, 11(3): 189-200. |
| [29] | SEYFFERTH A L, LIMMER M, WU W D, 2019. Si and water management drives changes in Fe and Mn pools that affect As cycling and uptake in rice[J]. Soil Systems, 3(3): 58. |
| [30] |
SHAO J F, CHE J, YAMAJI N, et al., 2017. Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 68(20): 5641-5651.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
WU C, ZOU Q, XUE S G, et al., 2016. The effect of silicon on iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation in rice genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 212: 27-33.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
YAMAUCHI T, SHIONO K, NAGANO M, et al., 2015. Ethylene biosynthesis is promoted by very-long-chain fatty acids during lysigenous aerenchyma formation in rice roots[J]. Plant Physiology, 169(1): 180-193.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | YANG J C, ZHANG H, ZHANG J H, 2012. Root morphology and physiology in relation to the yield formation of rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 11(6): 920-926. |
| [34] | ZHAN L P, PENG D L, WANG X L, et al., 2018. Priming effect of root-applied silicon on the enhancement of induced resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola in rice[J]. BioMed Central Plant Biology, 18(1): 50. |
| [35] | ZHANG Q, LIU J C, LU H L, et al., 2015. Effects of silicon on growth, root anatomy, radial oxygen loss (ROL) and Fe/Mn plaque of Aegiceras corniculatum (L.) Blanco seedlings exposed to cadmium[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 4: 6-11. |
| [36] | ZHOU J, GAO M, CUI H B, et al., 2021. Influence of silicon and selenium and contribution of the node to cadmium allocation and toxicity in rice[J]. Agricultural Science Technology, 1(5): 550-557. |
| [37] | 曹庭悦, 刘鸣达, 沃惜慧, 等, 2020. 硅、磷配施对水稻镉吸收转运的影响及其机制[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(1): 37-44. |
| CAO T Y, LIU M D, WO X H, et al., 2020. Effects of combined application of silicon and phosphorus on cadmium uptake and transport in rice and its mechanisms[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(1): 37-44. | |
| [38] | 高明霞, 胡正义, 王国栋, 2007. 水稻根表胶膜的浸提及其元素测定方法[J]. 环境化学, 26(3): 331-334. |
| GAO M X, HU Z Y, WANG G D, 2007. The extraction and elemental analysis of iron plaque from the surface of rice roots[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 26(3): 331-334. | |
| [39] | 环境保护部, 国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业, 36(5): 10-11. |
| Department of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources, 2014. National soil pollution survey report[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 36(5): 10-11. | |
| [40] | 李林峰, 文伟发, 徐梓盛, 等, 2023. 施硅对水稻铁膜砷固定和体内砷转运的影响[J]. 环境科学, 44(5): 2899-2907. |
| LI L F, WEN W F, XU Z S, et al., 2023. Effects of silicon application on arsenic sequestration in iron plaque and arsenic translocation in rice[J]. Environmental Science, 44(5): 2899-2907. | |
| [41] | 李天哲, 陈爱婷, 李彩, 等, 2018. 镉胁迫下硅对水稻幼苗生长与生理响应的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(6): 1072-1078. |
| LI T Z, CHEN A T, LI C, et al., 2018. Effects of silicon on growth and physiological responses of rice seedlings under cadmium stress[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(6): 1072-1078. | |
| [42] | 彭鸥, 刘玉玲, 铁柏清, 等, 2019. 施硅对镉胁迫下水稻镉吸收和转运的调控效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 1049-1056. |
| PENG O, LIU Y L, TIE B Q, et al., 2019. Effects of silicon application on cadmium uptake and translocation of rice under cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(4): 1049-1056. | |
| [43] | 生态环境部国家市场监督管理总局, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行): GB15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团: 1-4. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation,2018. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (Trial): GB15618—2018[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group: 1-4. | |
| [44] | 闫国超, 樊小平, 谭礼, 等, 2020. 盐胁迫下添加外源硅提高水稻抗氧化酶活性与钠钾平衡相关基因表达[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(11): 1935-1943. |
| YAN G C, FAN X P, TAN L, et al., 2020. Exogenous silicon effectively enhances salt stress resistance of rice by upregulating antioxidant enzymes activities and expression of genes related to Na/K homeostasis[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(11): 1935-1943. | |
| [45] | 杨旭健, 傅友强, 沈宏, 等, 2014. 水稻根表铁膜及其形成的形态生理及分子机理综述[J]. 生态学杂志, 33(8): 2235-2244. |
| YANG X J, FU Y Q, SHEN H, et al., 2014. A review on iron plaque on rice (Oryza sativa) root surface and the morphology, physiology and molecular biology of its formation mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(8): 2235-2244. | |
| [46] | 汪鹏, 王静, 陈宏坪, 等, 2018. 我国稻田系统镉污染风险与阻控[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(7): 1409-1417. |
| WANG P, WANG J, CHEN H P, et al., 2018. Cadmium risk and mitigation in paddy systems in China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(7): 1409-1417. | |
| [47] | 王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等, 2014. 客观地看待我国耕地土壤环境质量的调查公报中有关问题的讨论和建议[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(8): 1465-1473. |
| WANG Y J, LIU C, ZHOU D M, et al., 2014. A Critical view on the status quo of the farmland soil environmental quality in China: Discussion and suggestion of relevant issues on report on the national general survey of soil contamination[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 33(8): 1465-1473. | |
| [48] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局, |
| The National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2022. National food safety standard Limits of contaminants in foods: GB 2762—2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China:1-18. |
| [1] | 张腾云, 王静, 高健磊, 葛文静, 王宗耀, 韩龙. 碱性农田土壤冬小麦不同生育期镉的迁移转化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 450-459. |
| [2] | 刘楚天, 郭栋栋, 侯磊, 梁启斌, 王艳霞, 施艳婷, 戚艳娥. 营养调控影响滇杨幼苗镉积累的效应模型分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [3] | 王金明, 秦晓波, 万运帆, 周盛, 张志伟. 中国水稻食物系统碳足迹结构组成和地区差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1405-1418. |
| [4] | 范婉仪, 涂晨, 王顺扬, 吴昕优, 李烜桢, 骆永明. 不同品种烟草对轻度污染耕地土壤中镉的累积特征与减量修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524. |
| [5] | 宫亮, 金丹丹, 牛世伟, 王娜, 邹晓锦, 张鑫, 隋世江, 解占军, 韩瑛祚. 辽宁省水稻田固碳减排潜力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1226-1236. |
| [6] | 王丽华, 王磊, 许端平, 薛杨. 煤胶体对重金属铜与镉的吸附特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [7] | 李治梅, 安娅, 李梅, 王室苹, 秦好丽. 巯基/铁基功能化蒙脱土对土壤镉的钝化行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312. |
| [8] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [9] | 黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [10] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [11] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [12] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [13] | 尹浩均, 龙明亮, 刘维, 倪春林, 李芳柏, 吴云当. 溶氧浓度调控嗜水气单胞菌的砷还原:效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [14] | 陈桂红. 硫和硅掺杂生物炭对镉污染土壤的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1854-1860. |
| [15] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
