生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1301-1312.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.013
收稿日期:2023-04-11
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
* 秦好丽。E-mail: hollyqin@126.com作者简介:李治梅(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事土壤重金属钝化材料。E-mail: 1639129523@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Zhimei( ), AN Ya, LI Mei, WANG Shiping, QIN Haoli*(
), AN Ya, LI Mei, WANG Shiping, QIN Haoli*( )
)
Received:2023-04-11
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
土壤镉(Cd)的迁移和富集严重威胁国家粮食安全和损害人体健康。通过整合有机/无机改性方法制备了新型的巯基/铁基复合功能化蒙脱土(SH-Fe-Mont),用于Cd的高效去除和钝化。利用FTIR、XRD、BET、SEM及XPS等表征手段证实了钝化剂被成功制备,且在没有改变蒙脱土(Mont)基本层状结构的基础上拥有丰富的孔隙结构及更大的比表面积。通过系列水溶液吸附实验和土壤有效态Cd及赋存形态变化考察钝化剂对重金属Cd的去除率和钝化效果。等温吸附实验结果证明在293-323 K温度范围内,钝化剂吸附行为均符合Langmuir模型。在303 K时,SH-Fe-Mont和单改性的铁基功能化蒙脱土(Fe-Mont)的理论最大饱和吸附量分别为55.3、42.7 mg·g-1,分别是Mont的46.9、36.2倍。吸附动力学实验的结果显示,初始质量浓度分别为20、50、100 mg·L-1时,钝化剂对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附过程均符合伪二级模型,更快的吸附动力学使SH-Fe-Mont在40 min内达到吸附平衡(Mont:80 min;Fe-Mont:50 min)。更重要的是,SH-Fe-Mont对Cd的去除率超过99.0%(Cd的初始质量浓度20 mg·L-1)。酸雨模拟实验证明了SH-Fe-Mont对镉吸附后的高稳定性,仅有0.31%的镉解吸和0.22 mg·kg-1的镉浸出,远低于原始Mont(41.2%,11.7 mg·kg-1)和Fe-Mont(4.58%,1.67 mg·kg-1)。利用XPS研究了SH-Fe-Mont对镉的吸附机制,结果表明,Cd能被SH-Fe-Mont以一种复杂的络合状态-S-Cd和FeOOCd+固化。与对照组相比,施加2% SH-Fe-Mont后有效态镉含量降低71.2%,且活性高的可交换态和碳酸盐结合态之和由83.8%降低至47.4%,而稳定性较强的铁锰氧化结合态、有机结合态和残渣态之和由16.2%增加至52.6%,从而有效降低了镉的生物活性,进而减弱土壤中镉迁移的风险。该研究结果可为土壤和水中镉污染的钝化修复提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
李治梅, 安娅, 李梅, 王室苹, 秦好丽. 巯基/铁基功能化蒙脱土对土壤镉的钝化行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312.
LI Zhimei, AN Ya, LI Mei, WANG Shiping, QIN Haoli. Study on Passivation Behavior for Cadmium with Sulfhydryl/iron-based Functionalized Montmorillonite in Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312.
| 提取步骤 | 提取试剂 | 提取形态 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 氯化镁 (1 mol·L-1) | 可交换态 |
| 2 | 乙酸钠和醋酸 (1 mol·L-1) | 碳酸盐结合态 |
| 3 | 盐酸羟胺 (0.04 mol·L-1) 和20%醋酸 | 铁锰氧化结合态 |
| 4 | 硝酸 (0.02 mol·L-1) 和30%过氧化氢 | 有机结合态 |
| 5 | 硝酸、过氧化氢和氢氟酸 | 残渣态 |
表1 Tessier法重金属提取步骤
Table 1 Tessier process for extraction of heavy metals
| 提取步骤 | 提取试剂 | 提取形态 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 氯化镁 (1 mol·L-1) | 可交换态 |
| 2 | 乙酸钠和醋酸 (1 mol·L-1) | 碳酸盐结合态 |
| 3 | 盐酸羟胺 (0.04 mol·L-1) 和20%醋酸 | 铁锰氧化结合态 |
| 4 | 硝酸 (0.02 mol·L-1) 和30%过氧化氢 | 有机结合态 |
| 5 | 硝酸、过氧化氢和氢氟酸 | 残渣态 |
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 总孔体积/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mont | 46.6 | 6.96 | 0.11 |
| Fe-Mont | 71.5 | 7.67 | 0.14 |
| SH-Fe-Mont | 169 | 4.95 | 0.24 |
表2 不同钝化剂的比表面积和孔径分布
Table 2 The surface area and pore size distribution of different passivators
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 总孔体积/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mont | 46.6 | 6.96 | 0.11 |
| Fe-Mont | 71.5 | 7.67 | 0.14 |
| SH-Fe-Mont | 169 | 4.95 | 0.24 |
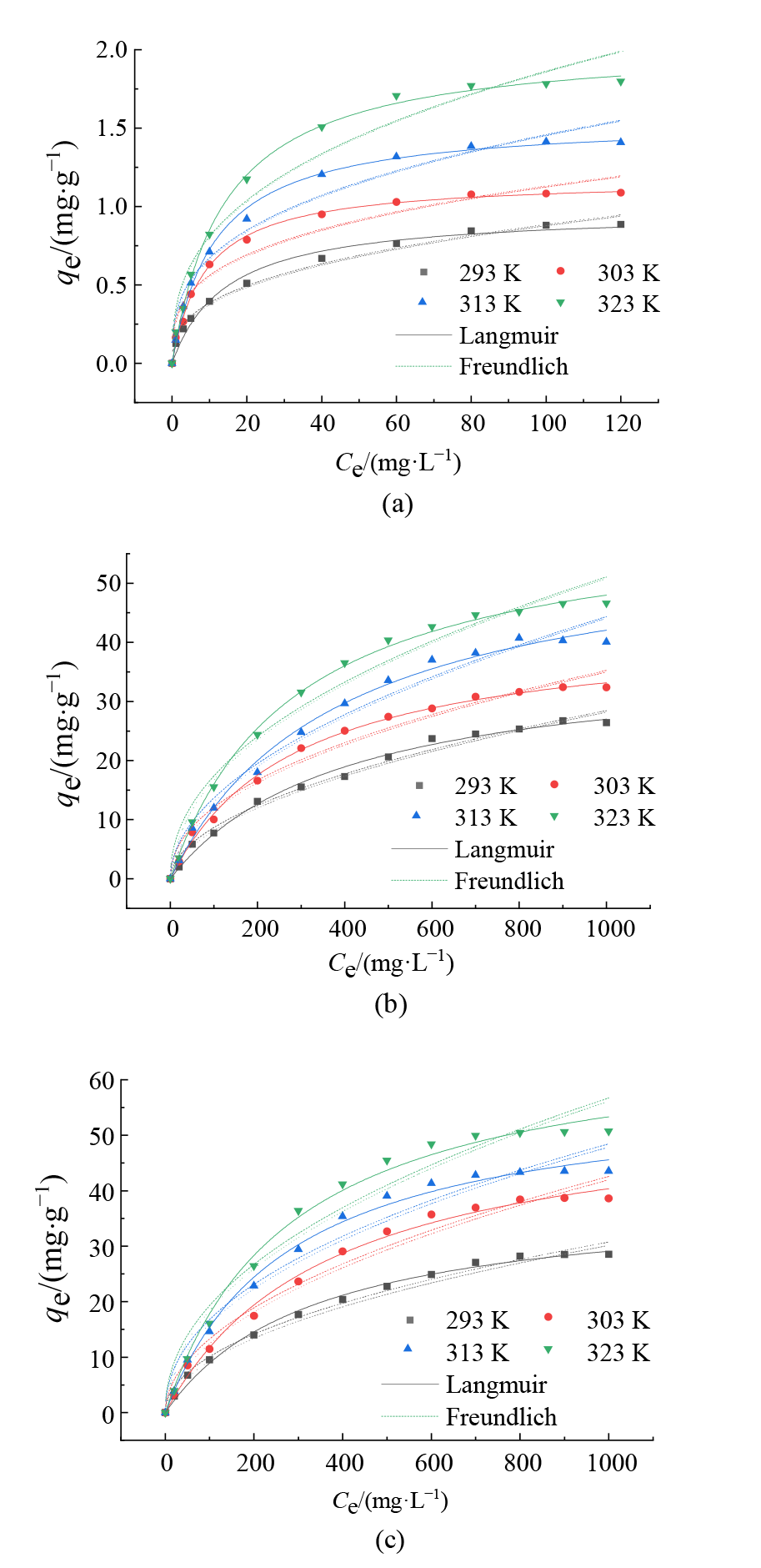
图4 不同钝化剂对Cd(II)的吸附等温线 (a)Mont对Cd(II)的吸附等温线;(b)Fe-Mont对Cd(II)的吸附等温线;(c)SH-Fe-Mont对Cd(II)的吸附等温线
Figure 4 Adsorption isotherms of different passivators on Cd(II)
| 样品 | 温度/ K | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/ (mg·g-1) | KL/ (L·mg-1) | r2 | KF/ (L·g-1) | n | r2 | |||
| Mont | 293 | 0.97 | 0.069 | 0.980 | 0.167 | 0.362 | 0.988 | |
| 303 | 1.18 | 0.112 | 0.996 | 0.278 | 0.305 | 0.939 | ||
| 313 | 1.56 | 0.088 | 0.995 | 0.314 | 0.336 | 0.956 | ||
| 323 | 2.05 | 0.071 | 0.997 | 0.351 | 0.363 | 0.952 | ||
| Fe-Mont | 293 | 37.7 | 0.003 | 0.990 | 0.806 | 0.516 | 0.983 | |
| 303 | 42.7 | 0.003 | 0.996 | 1.422 | 0.465 | 0.970 | ||
| 313 | 58.1 | 0.003 | 0.992 | 1.230 | 0.511 | 0.972 | ||
| 323 | 61.6 | 0.004 | 0.998 | 2.021 | 0.468 | 0.963 | ||
| SH-Fe-Mont | 293 | 38.8 | 0.003 | 0.992 | 1.088 | 0.484 | 0.986 | |
| 303 | 55.3 | 0.003 | 0.991 | 1.297 | 0.505 | 0.971 | ||
| 313 | 58.2 | 0.004 | 0.993 | 2.017 | 0.460 | 0.956 | ||
| 323 | 68.5 | 0.004 | 0.992 | 2.239 | 0.468 | 0.947 | ||
表3 Cd(II)在不同钝化剂上的吸附等温线参数
Table 3 Adsorption isotherm parameters of different passivators on Cd(II)
| 样品 | 温度/ K | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/ (mg·g-1) | KL/ (L·mg-1) | r2 | KF/ (L·g-1) | n | r2 | |||
| Mont | 293 | 0.97 | 0.069 | 0.980 | 0.167 | 0.362 | 0.988 | |
| 303 | 1.18 | 0.112 | 0.996 | 0.278 | 0.305 | 0.939 | ||
| 313 | 1.56 | 0.088 | 0.995 | 0.314 | 0.336 | 0.956 | ||
| 323 | 2.05 | 0.071 | 0.997 | 0.351 | 0.363 | 0.952 | ||
| Fe-Mont | 293 | 37.7 | 0.003 | 0.990 | 0.806 | 0.516 | 0.983 | |
| 303 | 42.7 | 0.003 | 0.996 | 1.422 | 0.465 | 0.970 | ||
| 313 | 58.1 | 0.003 | 0.992 | 1.230 | 0.511 | 0.972 | ||
| 323 | 61.6 | 0.004 | 0.998 | 2.021 | 0.468 | 0.963 | ||
| SH-Fe-Mont | 293 | 38.8 | 0.003 | 0.992 | 1.088 | 0.484 | 0.986 | |
| 303 | 55.3 | 0.003 | 0.991 | 1.297 | 0.505 | 0.971 | ||
| 313 | 58.2 | 0.004 | 0.993 | 2.017 | 0.460 | 0.956 | ||
| 323 | 68.5 | 0.004 | 0.992 | 2.239 | 0.468 | 0.947 | ||
| 钝化剂 | 温度/K | pH | 时间/h | qe/(mg·g-1) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巯基改性海泡石 | 298 | 8.0 | 24 | 8.87 | 符云聪等, |
| 十二烷基二甲基 甜菜碱改性蛭石 | 298 | 5.5 | 4 | 19.72 | Yang et al., |
| 巯基改性凹凸棒石 | 298 | 6.5 | 2 | 22.71 | Fu et al., |
| 羟基铁柱撑蒙脱石 | 298 | 5.0 | - | 25.7 | Wu et al., |
| 生物炭负载 纳米级零价铁 | 298 | 5.5 | 2 | 33.8 | Yang et al., |
| 两性表面活性剂 活化蒙脱土 | 303 | 5.0 | - | 41.73 | Liu et al., |
| 石墨烯类生物炭 负载纳米零价铁 | 298 | 7.0 | 2 | 46.4 | Liu et al., |
表4 其他报道的钝化剂对Cd(Ⅱ)吸附能力对比
Table 4 Comparison of other reported passivators on Cd(II) adsorption capacity
| 钝化剂 | 温度/K | pH | 时间/h | qe/(mg·g-1) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 巯基改性海泡石 | 298 | 8.0 | 24 | 8.87 | 符云聪等, |
| 十二烷基二甲基 甜菜碱改性蛭石 | 298 | 5.5 | 4 | 19.72 | Yang et al., |
| 巯基改性凹凸棒石 | 298 | 6.5 | 2 | 22.71 | Fu et al., |
| 羟基铁柱撑蒙脱石 | 298 | 5.0 | - | 25.7 | Wu et al., |
| 生物炭负载 纳米级零价铁 | 298 | 5.5 | 2 | 33.8 | Yang et al., |
| 两性表面活性剂 活化蒙脱土 | 303 | 5.0 | - | 41.73 | Liu et al., |
| 石墨烯类生物炭 负载纳米零价铁 | 298 | 7.0 | 2 | 46.4 | Liu et al., |
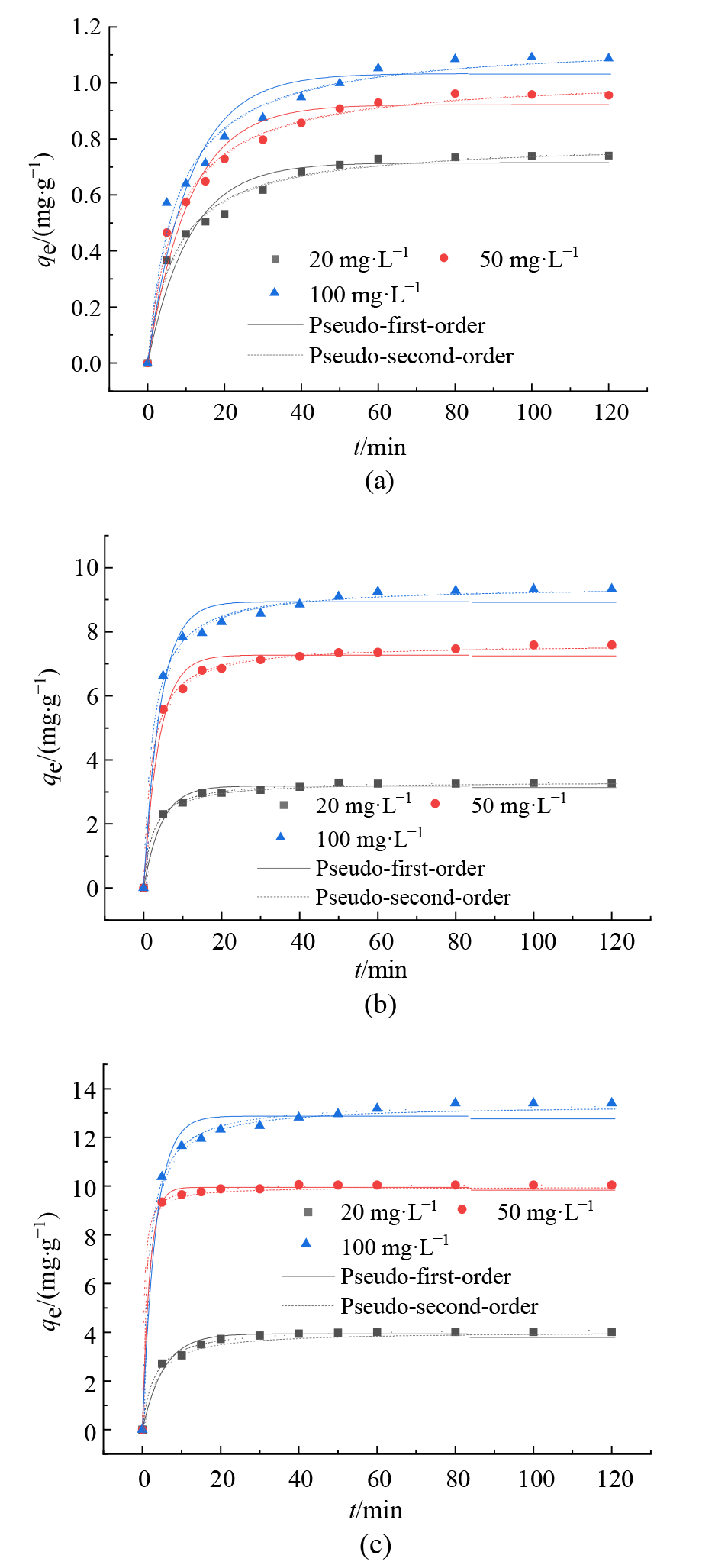
图5 不同钝化剂对Cd(II)的吸附动力学曲线 (a)Cd(II)对反应时间作图(Mont);(b)Cd(II)对反应时间作图(Fe-Mont);(c)Cd(II)对反应时间作图(SH-Fe-Mont)
Figure 5 Adsorption kinetics of different passivators on Cd(II)
| 样品 | 浓度/ (mg·L-1) | 伪一级动力学 | 伪二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg·g-1) | k1 | r2 | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2 | r2 | |||
| Mont | 20 | 0.72 | 0.092 | 0.958 | 0.79 | 0.171 | 0.988 | |
| 50 | 0.92 | 0.092 | 0.965 | 1.03 | 0.129 | 0.992 | ||
| 100 | 1.03 | 0.092 | 0.940 | 1.15 | 0.118 | 0.981 | ||
| Fe-Mont | 20 | 3.19 | 0.221 | 0.984 | 3.36 | 0.125 | 0.998 | |
| 50 | 7.27 | 0.252 | 0.983 | 7.64 | 0.066 | 0.999 | ||
| 100 | 8.94 | 0.236 | 0.977 | 9.45 | 0.046 | 0.997 | ||
| SH-Fe-Mont | 20 | 3.94 | 0.185 | 0.982 | 4.18 | 0.082 | 0.996 | |
| 50 | 9.96 | 0.548 | 0.998 | 10.1 | 0.238 | 0.999 | ||
| 100 | 12.9 | 0.298 | 0.984 | 13.4 | 0.047 | 0.998 | ||
表5 不同钝化剂对Cd(II)的吸附动力学参数
Table 5 Adsorption kinetic parameters of different passivators on Cd(II)
| 样品 | 浓度/ (mg·L-1) | 伪一级动力学 | 伪二级动力学 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg·g-1) | k1 | r2 | qe/(mg·g-1) | k2 | r2 | |||
| Mont | 20 | 0.72 | 0.092 | 0.958 | 0.79 | 0.171 | 0.988 | |
| 50 | 0.92 | 0.092 | 0.965 | 1.03 | 0.129 | 0.992 | ||
| 100 | 1.03 | 0.092 | 0.940 | 1.15 | 0.118 | 0.981 | ||
| Fe-Mont | 20 | 3.19 | 0.221 | 0.984 | 3.36 | 0.125 | 0.998 | |
| 50 | 7.27 | 0.252 | 0.983 | 7.64 | 0.066 | 0.999 | ||
| 100 | 8.94 | 0.236 | 0.977 | 9.45 | 0.046 | 0.997 | ||
| SH-Fe-Mont | 20 | 3.94 | 0.185 | 0.982 | 4.18 | 0.082 | 0.996 | |
| 50 | 9.96 | 0.548 | 0.998 | 10.1 | 0.238 | 0.999 | ||
| 100 | 12.9 | 0.298 | 0.984 | 13.4 | 0.047 | 0.998 | ||
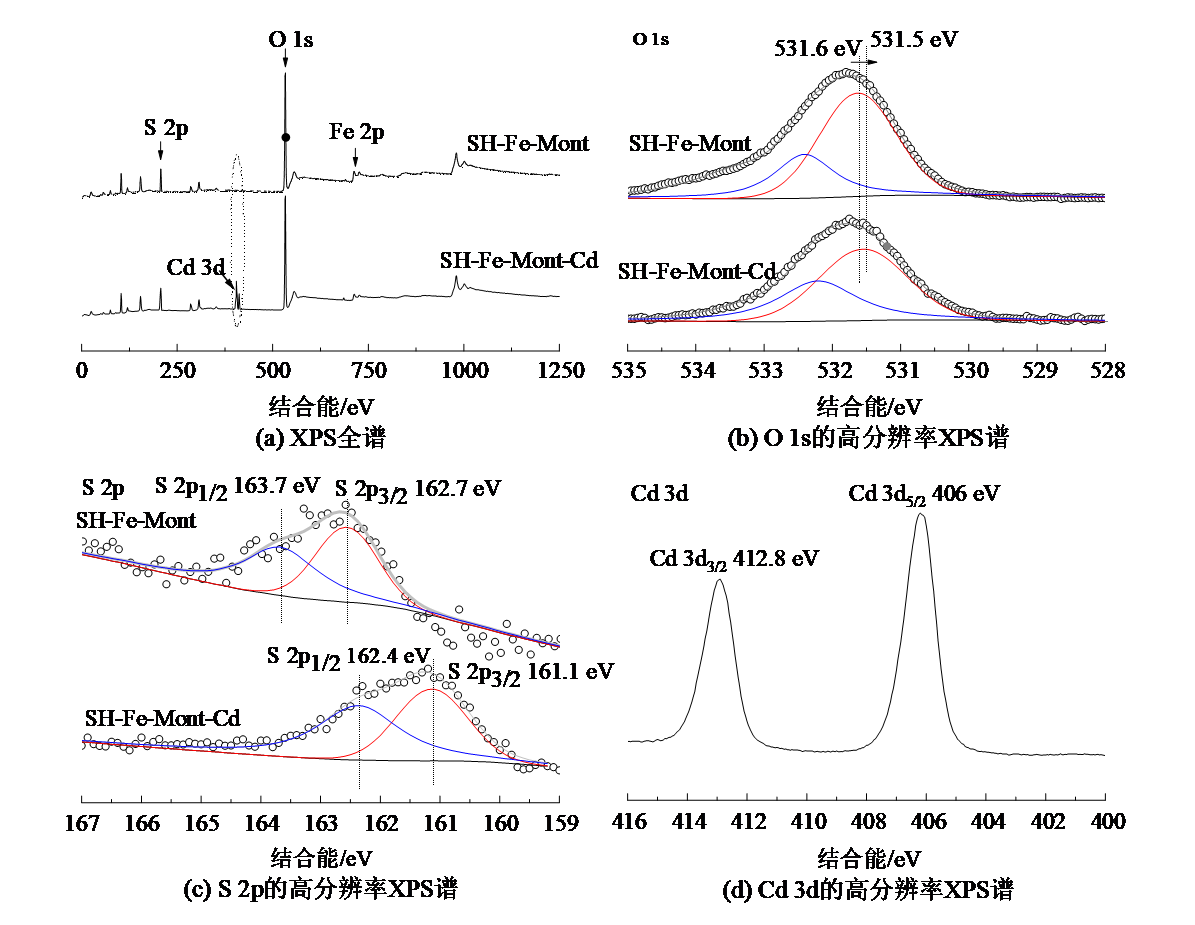
图9 SH-Fe-Mont吸附Cd(II)前后XPS全谱;O 1s、S 2p和Cd 3d的高分辨率XPS谱
Figure 9 XPS survey spectra; high-resolution XPS spectra of O 1s, N 1s, and S 2p of SH-Fe-Mont before and after adsorption of Cd(II)
| [1] |
CHEN D M, CHEN J, LUAN X L, et al., 2011. Characterization of anion-cationic surfactants modified montmorillonite and its application for the removal of methyl orange[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171(3): 1150-1158.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN M, XU P, ZENG G M, et al., 2015. Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: Applications, microbes and future research needs[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 33(6): 745-755.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN Y N, LIU Y H, LI Y P, et al., 2020. Functional wastepaper-montmorillonite composite aerogel for Cd2+ adsorption[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27: 38644-38653.
DOI |
| [4] |
CHOUDARY B M, SHOBHA RANI S, NARENDER N, 1993. Asymmetric oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides by chiral titanium pillared montmorillonite catalyst[J]. Catalysis Letters, 19: 299-307.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CUI H, QIAN Y, LI Q, et al., 2012. Adsorption of aqueous Hg (II) by a polyaniline/attapulgite composite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 211-212: 216-223.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DO NASCIMENTO F H, DE SOUZA COSTA D M, MASINI J C, 2016. Evaluation of thiol-modified vermiculite for removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solutions[J]. Applied Clay Science, 124-125: 227-235.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DU H H, CHEN W L, CAI P, et al., 2016. Cd (II) sorption on montmorillonite-humic acid-bacteria composites[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 19499.
DOI |
| [8] |
ELSHERBINY A S, EL-HEFNAWY M E, GEMEAY A H, 2018. Adsorption efficiency of polyaspartate-montmorillonite composite towards the removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 26: 411-422.
DOI URL |
| [9] | FANG X, BAO P F, XU C Y, et al., 2000. Preparation and hot stability pillared montmorillonite by Fe-Al, Cr-Al hydroxyl[J]. Geology of Zhejiang, 16(2): 66-70. |
| [10] |
FU C, ZHU X P, DONG X, et al., 2021. Study of adsorption property and mechanism of lead (II) and cadmium (II) onto sulfhydryl modified attapulgite[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 14(2): 102960.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GIRI D D, JHA J M, TIWARI A K, et al., 2021. Java plum and amaltash seed biomass based bio-adsorbents for synthetic wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 280: 116890.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GUIMARÃES A DE M F, CIMINELLI V S T, VASCONCELOS W L, 2009. Smectite organofunctionalized with thiol groups for adsorption of heavy metal ions[J]. Applied Clay Science, 42(3-4): 410-414.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HADJLTAIEF H B, SDIRI A, LTAIEF W, et al., 2018. Efficient removal of cadmium and 2-chlorophenol in aqueous systems by natural clay: Adsorption and photo-Fenton degradation processes[J]. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 21(3-4): 253-262.
DOI URL |
| [14] | HAN J, XU Y M, LIANG X F, et al., 2014. Sorption stability and mechanism exploration of palygorskite as immobilization agent for Cd in polluted soil[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225(10): 1-13. |
| [15] |
HUA R, LI Z K, 2014. Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 249: 189-200.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HUSIN N F D C, HARUN F W, JUMAL J, et al., 2015. Preparation and Physicochemical Properties of Metal Complexes Immobilized on Montmorillonite K10 (MMT K10)[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering Research, 1(5): 8-13. |
| [17] |
KAHKHA M R R, KAYKHAII M, KAHKHA B R, et al., 2020. Simultaneous removal of heavy metals from wastewater using modified sodium montmorillonite nanoclay[J]. Analytical Sciences, 36(9): 1039-1043.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
LAN J R, ZHANG S S, DONG Y Q, et al., 2021. Stabilization and passivation of multiple heavy metals in soil facilitating by pinecone-based biochar: Mechanisms and microbial community evolution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 420: 126588.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI S Z, WU P X, 2010. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate modified iron pillared montmorillonite and its application for the removal of aqueous Cu (II) and Co (II)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1-3): 62-70.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIANG X F, LI N, HE L Z, et al., 2019. Inhibition of Cd accumulation in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in alkaline soil using mercapto-modified attapulgite[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 688: 818-826.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LIANG X F, QIN X, HUANG Q Q, et al., 2017. Mercapto functionalized sepiolite: A novel and efficient immobilization agent for cadmium polluted soil[J]. RSC Advances, 7(63): 39955-39961.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LIU C M, WU P X, ZHU Y J, et al., 2016. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd2+ and BPA on amphoteric surfactant activated montmorillonite[J]. Chemosphere, 144: 1026-1032.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU K, LI F B, CUI J H, et al., 2020. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) by graphene-like biochar-supported zero-valent iron from irrigation waters under aerobic conditions: Synergistic effects and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 395: 122623.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LOMBI E, HAMON R E, MCGRATH S P, et al., 2003. Lability of Cd, Cu, and Zn in polluted soils treated with lime, beringite, and red mud and identification of a non-labile colloidal fraction of metals using isotopic techniques[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(5): 979-984.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MIAO Y H, PENG W J, CAO Y J, et al., 2021. Facile preparation of sulfhydryl modified montmorillonite nanosheets hydrogel and its enhancement for Pb (II) adsorption[J]. Chemosphere, 280, 130727.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
MITTAL A, AHMAD R, HASAN I, 2016. Biosorption of Pb2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ ions from aqueous solutions by L-cystein-modified montmorillonite-immobilized alginate nanocomposite[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(38): 17790-17807.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ORDINARTSEV D, PECHISHCHEVA N, ESTEMIROVA S K, et al., 2022. Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by modified montmorillonite in combination with zero-valent iron[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 208: 105813.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
PAN X H, FU L X, WANG H, et al., 2021. Synthesis of novel sulfydryl-functionalized chelating adsorbent and its application for selective adsorption of Ag(I) under high acid[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 271: 118778.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
QU C C, MA M K, CHEN W L, et al., 2018. Modeling of Cd adsorption to goethite-bacteria composites[J]. Chemosphere, 193: 943-950.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
TAN J Q, LI Y T, XIA L, et al., 2022. Enhancement of Cd(II) Adsorption on Microalgae-Montmorillonite Composite[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47(6): 6715-6727.
DOI |
| [31] |
TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G, BISSON M, 1979. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7): 844-851.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
TRAN L, WU P X, ZHU Y J, et al., 2015. Comparative study of Hg (II) adsorption by thiol-and hydroxyl-containing bifunctional montmorillonite and vermiculite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 356: 91-101.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG L W, LI X R, TSANG D C, et al., 2020. Green remediation of Cd and Hg contaminated soil using humic acid modified montmorillonite: Immobilization performance under accelerated ageing conditions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 387: 122005.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG Y, HE T R, YIN D L, et al., 2020. Modified clay mineral: A method for the remediation of the mercury-polluted paddy soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 204: 111121.
DOI URL |
| [35] | WANG Z L, CHEN Y F, ZHANG L Y, et al., 2020. Step-scheme CdS/TiO2 nanocomposite hollow microsphere with enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 56: 143-150. |
| [36] |
WU P X, WU W M, LI S Z, et al., 2009. Removal of Cd2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption using Fe-montmorillonite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1-3): 824-830.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
WU P X, ZHANG Q, DAI Y P, et al., 2011. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solutions on humic acid modified Ca-montmorillonite[J]. Geoderma, 164(3-4): 215-219.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
XIE S, WANG L, XU Y M, et al., 2020. Performance and mechanisms of immobilization remediation for Cd contaminated water and soil by hydroxy ferric combined acid-base modified sepiolite (HyFe/ABsep)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 740: 140009.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
YANG S S, HUANG Z Y, Li C Q, et al., 2020. Individual and simultaneous adsorption of tetracycline and cadmium by dodecyl dimethyl betaine modified vermiculite[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 602(11): 125171.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
YANG D, WANG L, LI Z T, et al., 2020. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II) and As(III) by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems[J]. Science of the Total Environment 708: 134823.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZENG H H, WANG L, ZHANG D, et al., 2019. Amido-functionalized carboxymethyl chitosan/montmorillonite composite for highly efficient and cost-effective mercury removal from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 554: 479-487.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
ZHAO S, FENG C H, HUANG X N, et al., 2012. Role of uniform pore structure and high positive charges in the arsenate adsorption performance of Al13-modified montmorillonite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 203-204: 317-325.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
ZHU S, XIA M Z, CHU Y T, et al., 2019. Adsorption and desorption of Pb(II) on l-lysine modified montmorillonite and the simulation of interlayer structure[J]. Applied Clay Science, 169: 40-47.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ZOTIADIS V, ARGYRAKI A, THEOLOGOU E, 2012. Pilot-scale application of attapulgitic clay for stabilization of toxic elements in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 138(5): 633-637.
DOI URL |
| [45] | 曹心德, 魏晓欣, 代革联, 等, 2011. 土壤重金属复合污染及其化学钝化修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 5(7): 1441-1453. |
| CAO X D, WEI X X, DAI G L, et al., 2011. Combined pollution of multiple heavy metals and their chemical immobilization in contaminated soils: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 5(7): 1441-1453. | |
| [46] | 杜全洪, 张延明, 邢旭鹏, 等, 2022. 钝化石灰的研发与应用[J]. 河北冶金 (9): 43-46. |
| DU Q H, ZHANG Y M, XING X P, et al., 2022. Development and application of passivated lime[J]. Hebei Metallurgy (9): 43-46. | |
| [47] | 方旋, 鲍佩芳, 徐传云, 等, 2000. 羟基Fe-Al, Cr-Al柱撑蒙脱石的制备及热稳定性研究[J]. 浙江地质, 16(2): 66-70. |
| FANG X, BAO P F, XU C Y, et al., 2000. Preparation and hot stability pillared montmorillonite by Fe-Al, Cr-Al hydroxyl[J]. Geology of Zhejiang, 16(2): 66-70. | |
| [48] | 符云聪, 赵瑰施, 张义, 等, 2018. 巯基改性海泡石的制备及其吸附除镉性能[J]. 净水技术, 37(8): 72-77. |
| FU Y C, ZHAO G S, ZHANG Y, et al., 2018. Preparation of sulphydryl modified sepiolite and adsorption property for cadmium removal[J]. Water Purification Technology, 37(8): 72-77. | |
| [49] | 郝红英, 何孟常, 林春野, 2007. 采用XPS研究镉在蒙脱石表面的吸附机理[J]. 环境化学, 26(6): 798-800. |
| HAO H Y, HE M C, LIN C Y, 2007. An xps study of the adsorption m echan ism of cadm ium on montm or illonite[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 26(6): 798-800. | |
| [50] | 李丽, 刘中, 宁阳, 等, 2017. 不同类型粘土矿物对镉吸附与解吸行为的研究[J]. 山西农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 37(1): 60-66. |
| LI L, LIU Z, NING Y, et al., 2017. Study on cadmium adsorption-desorption behavior of different clay minerals[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 37(1): 60-66. | |
| [51] | 李平, 王兴祥, 郎漫, 等, 2012. 改良剂对Cu、Cd污染土壤重金属形态转化的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 32(7): 1241-1249. |
| LI P, WANG X X, LANG M, et al., 2012. Effects of amendments on the fraction transform of heavy metals in soil contaminated by copper and cadmium[J]. China Environmental Science, 32(7): 1241-1249. | |
| [52] | 梁亚琴, 张淑萍, 李慧, 等, 2018. 改性蒙脱土去除水中重金属离子研究新进展[J]. 化工进展, 37(8): 3179-3187. |
| LIANG Y Q, ZHANG S P, LI H, et al., 2018. Progress in development of modified montmorillonite for adsorption of heavy metal ions[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 37(8): 3179-3187. | |
| [53] | 孙长顺, 金奇庭, 秦莉红, 等, 2007. EDTA络合铜在无机柱撑膨润土上的吸附研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 1(9): 131-135. |
| SUN C S, JIN Q T, QIN L H, et al., 2007. Study on adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) onto pillared bentonites in the presence of EDTA[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1(9): 131-135. | |
| [54] | 陶玲, 仝云龙, 余方可, 等, 2022. 碱改性凹凸棒石对土壤中镉化学形态及环境风险的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 41(1): 109-119. |
| TAO L, TONG Y L, YU F K, et al., 2022. Chemical speciation and environmental risk of Cd in soil stabilized with alkali-modified attapulgite[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 41(1): 109-119. | |
| [55] | 王乐杭, 俞栋, 王玉婷, 等, 2021. 重金属污染土壤修复技术及其修复实践[J]. 资源节约与环保 (4): 46-47. |
| WANG L H, YU D, WANG Y T, et al., 2021. Remediation technology of heavy metal contaminated Soil and its remediation practice[J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection (4): 46-47. | |
| [56] | 王学锋, 尚菲, 马鑫, 等, 2013a. pH和腐植酸对Cd, Cr在土壤中形态分布的影响[J]. 河南师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 41(5): 101-105. |
| WANG X F, SHANG F, MA X, et al., 2013a. Effects of pH and humic acid on the form distribution of cadmium, chromium in the soil[J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 41(5): 101-105. | |
| [57] | 王学锋, 尚菲, 马鑫, 等, 2013b. pH和腐植酸对镉、镍、锌在土壤中的形态分布及其生物活性的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 13(27): 8082-8086. |
| WANG X F, SHANG F, MA X, et al., 2013b. pH and humic acid effect on the form distribution of cadmium, nickel, zinc in the soil and biological activity[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 13(27): 8082-8086. | |
| [58] | 辛勤, 罗孟飞, 2009. 现代催化研究方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| XIN Q, LUO M F, 2009. Modern Catalysis Research Methods[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [59] | 杨建斌, 2006. 羟基铁柱撑膨润土的制备及对EDTA-Cu的吸附特性研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学. |
| YANG J B, 2006. The hydroxyl iron pole supports the bentonite the preparation and to the EDTA-Cu adsorption characteristic researcl[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology. | |
| [60] | 张功领, 刘长风, 张晓宇, 等, 2018. 土壤中重金属形态研究[J]. 吉林农业 (23): 87-88. |
| ZHANG G L, LIU C F, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2018. Study on the forms of heavy metals in soil[J]. Agriculture of Jilin (23): 87-88. | |
| [61] | 张欣, 范仲学, 郭笃发, 等, 2011. 3种微生物制剂对轻度镉污染土壤中菠菜生长的影响[J]. 天津农业科学, 17(1): 81-83. |
| ZHANG X, FAN Z X, GUO D F, et al., 2011. Effects of microorganisms on the growth of spinach under Cd stress[J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 17(1): 81-83. | |
| [62] | 赵保林, 那平, 刘剑锋, 2006. 改性蒙脱土的研究进展[J]. 化学工业与工程, 23(5): 453-457. |
| ZHAO B L, NA P, LIU J F, 2006. Progress in modification of montmorillonites[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 23(5): 453-457. | |
| [63] | 赵秋香, 黄晓纯, 李媛媛, 等, 2014. 蒙脱石-OR-SH复合体修复剂对重金属污染土壤中Cd的钝化效果[J]. 环境化学, 33(11): 1871-1877. |
| ZHAO Q X, HUANG X C, LI Y Y, et al., 2014. A smectite-OR-SH compound for reducing cadmium uptake by pakchoi in contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 33(11): 1871-1877. | |
| [64] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部和国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国环境保护部和国土资源部. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China MEP, Ministry of Land and Resources of China MLR, 2014. National Soil Pollution Investigation Bulletin[R]. Beijing: MEP, MLR. |
| [1] | 王丽华, 王磊, 许端平, 薛杨. 煤胶体对重金属铜与镉的吸附特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [2] | 李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [3] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [4] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [5] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [6] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [7] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [8] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [9] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [10] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [11] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [12] | 文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 李富荣, 杜瑞英, 黄永东, 李蕾, 王富华. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [13] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [14] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [15] | 秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
