生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 814-823.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.020
收稿日期:2021-10-08
出版日期:2022-04-18
发布日期:2022-06-22
通讯作者:
*周丹丹,E-mail: 01yongheng@163.com作者简介:赵超凡(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,从事土壤重金属污染修复研究。E-mail: 2361623132@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHAO Chaofan( ), ZHOU Dandan*(
), ZHOU Dandan*( ), SUN Jiancai, QIAN Kunpeng, LI Fangfang
), SUN Jiancai, QIAN Kunpeng, LI Fangfang
Received:2021-10-08
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
摘要:
为研究生物炭中可溶性组分对生物炭吸附重金属的影响,以玉米秸秆和松木屑为原材料,采用限氧升温炭化法,分别于200、400和600 ℃下制备生物炭,并通过批量吸附实验研究生物炭对镉的吸附特性及去除可溶性组分对其吸附Cd2+的影响。研究结果表明,随热解温度升高,生物炭的碳化程度增加,pH值增大,比表面积逐渐增大,含氧官能团数量减少,矿物组分不断富集,溶解性矿物离子K+、Ca2+、Mg2+和PO43-含量降低;去除可溶性组分后生物炭的pH值下降,溶解性矿物离子含量明显降低。LM模型更适合于对松木生物炭和200、400 ℃下制备的玉米秸秆生物炭吸附Cd2+的数据进行拟合,而FM模型更适合于拟合600 ℃下制备的玉米秸秆生物炭对Cd2+的吸附数据。玉米秸秆生物炭对Cd2+的吸附量(29.58—12.21 mg∙g-1)高于松木生物炭(1.72—4.14 mg∙g-1),这与玉米秸秆生物炭中的矿物组分含量明显高于松木生物炭,从而有利于发生共沉淀和离子交换作用有关。去除可溶性组分后,玉米秸秆和松木生物炭对Cd2+的吸附量分别降低25%—42%和15%—40%。共沉淀和离子交换作用是低温生物炭(≤400 ℃)吸附Cd2+的主要机制;而高温生物炭(>400 ℃)吸附Cd2+的主要机制是阳离子-π作用。溶解性矿物离子的含量降低使得Cd2+与生物炭之间的共沉淀和离子交换作用减弱,从而降低生物炭对Cd2+的吸附量。研究结果有助于认识可溶性组分在生物炭对重金属吸附机制中的作用,也将为生物炭在土壤修复中的应用提供科学参考。
中图分类号:
赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823.
ZHAO Chaofan, ZHOU Dandan, SUN Jiancai, QIAN Kunpeng, LI Fangfang. The Effect of Soluble Components on the Adsorption of Cadmium on Biochar[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 814-823.
| 生物炭 Biochar | SBETα/ (m2·g-1) | w(ash)/ % | pH | w/% | Element ratio | w/(mg·kg-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | H/C | O/C | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | PO43- | ||||||
| PC | 7.581 | 1.71 | 5.83 | 47.1 | 6.44 | 64.4 | 1.64 | 1.03 | 744.6 | 848.5 | 103.3 | 96.20 | ||
| PC2 | 6.305 | 1.55 | 5.69 | 50.0 | 6.64 | 64.6 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 1113 | 527.6 | 69.14 | 85.51 | ||
| PC4 | 3.996 | 4.41 | 7.75 | 76.7 | 4.17 | 18.9 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 386.6 | 728.0 | 30.67 | 66.18 | ||
| PC6 | 321.6 | 7.26 | 9.09 | 84.9 | 2.59 | 9.53 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 36.04 | 408.6 | 53.86 | 53.88 | ||
| PC2W | 7.040 | 1.15 | 5.39 | 49.5 | 6.87 | 44.9 | 1.67 | 0.68 | 304.3 | 486.9 | 50.10 | 34.01 | ||
| PC4W | 8.631 | 4.16 | 7.59 | 74.6 | 4.21 | 20.7 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 145.2 | 587.3 | 23.62 | 33.23 | ||
| PC6W | 292.0 | 6.78 | 8.43 | 88.2 | 2.66 | 9.92 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 24.94 | 267.8 | 22.65 | 21.97 | ||
| CS | 7.513 | 8.64 | 9.24 | 38.8 | 5.48 | 40.1 | 1.69 | 0.77 | 3979 | 551.4 | 65.83 | 5165 | ||
| CS2 | 5.486 | 4.34 | 6.55 | 45.7 | 6.11 | 41.9 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 4614 | 178.5 | 453.5 | 3775 | ||
| CS4 | 8.443 | 24.7 | 10.3 | 68.2 | 3.87 | 20.3 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 3225 | 6.274 | 16.93 | 2930 | ||
| CS6 | 15.94 | 31.5 | 10.8 | 61.4 | 2.27 | 14.0 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 1950 | — | 7.219 | 1384 | ||
| CS2W | 5.910 | 2.50 | 6.23 | 48.7 | 6.51 | 43.0 | 1.61 | 0.66 | 4284 | 164.4 | 273.6 | 1632 | ||
| CS4W | 15.31 | 21.8 | 9.18 | 68.7 | 3.53 | 19.8 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 2438 | 3.984 | 16.43 | 993.6 | ||
| CS6W | 19.42 | 27.8 | 10.2 | 52.0 | 2.09 | 13.0 | 0.48 | 0.19 | 1178 | — | 4.294 | 184.1 | ||
表1 生物质及其制备生物炭的物理化学性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of biomass and their biochars
| 生物炭 Biochar | SBETα/ (m2·g-1) | w(ash)/ % | pH | w/% | Element ratio | w/(mg·kg-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | H/C | O/C | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | PO43- | ||||||
| PC | 7.581 | 1.71 | 5.83 | 47.1 | 6.44 | 64.4 | 1.64 | 1.03 | 744.6 | 848.5 | 103.3 | 96.20 | ||
| PC2 | 6.305 | 1.55 | 5.69 | 50.0 | 6.64 | 64.6 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 1113 | 527.6 | 69.14 | 85.51 | ||
| PC4 | 3.996 | 4.41 | 7.75 | 76.7 | 4.17 | 18.9 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 386.6 | 728.0 | 30.67 | 66.18 | ||
| PC6 | 321.6 | 7.26 | 9.09 | 84.9 | 2.59 | 9.53 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 36.04 | 408.6 | 53.86 | 53.88 | ||
| PC2W | 7.040 | 1.15 | 5.39 | 49.5 | 6.87 | 44.9 | 1.67 | 0.68 | 304.3 | 486.9 | 50.10 | 34.01 | ||
| PC4W | 8.631 | 4.16 | 7.59 | 74.6 | 4.21 | 20.7 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 145.2 | 587.3 | 23.62 | 33.23 | ||
| PC6W | 292.0 | 6.78 | 8.43 | 88.2 | 2.66 | 9.92 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 24.94 | 267.8 | 22.65 | 21.97 | ||
| CS | 7.513 | 8.64 | 9.24 | 38.8 | 5.48 | 40.1 | 1.69 | 0.77 | 3979 | 551.4 | 65.83 | 5165 | ||
| CS2 | 5.486 | 4.34 | 6.55 | 45.7 | 6.11 | 41.9 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 4614 | 178.5 | 453.5 | 3775 | ||
| CS4 | 8.443 | 24.7 | 10.3 | 68.2 | 3.87 | 20.3 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 3225 | 6.274 | 16.93 | 2930 | ||
| CS6 | 15.94 | 31.5 | 10.8 | 61.4 | 2.27 | 14.0 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 1950 | — | 7.219 | 1384 | ||
| CS2W | 5.910 | 2.50 | 6.23 | 48.7 | 6.51 | 43.0 | 1.61 | 0.66 | 4284 | 164.4 | 273.6 | 1632 | ||
| CS4W | 15.31 | 21.8 | 9.18 | 68.7 | 3.53 | 19.8 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 2438 | 3.984 | 16.43 | 993.6 | ||
| CS6W | 19.42 | 27.8 | 10.2 | 52.0 | 2.09 | 13.0 | 0.48 | 0.19 | 1178 | — | 4.294 | 184.1 | ||
| FM | LM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Kf | n | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | Qm/ (mg∙g-1) | KL | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | ||
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | |||||||
| PC | 1.68 | 0.57 | 0.96 | 1.68 | 0.62 | 6.26 | 0.38 | 0.97 | 1.73 | 0.50 |
| PC2 | 1.65 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 1.65 | 0.44 | 4.14 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 1.75 | 0.36 |
| PC4 | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.17 | 1.72 | 1.32 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.16 |
| PC6 | 1.15 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 1.12 | 0.23 | 2.29 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 0.21 |
| CS | 1.56 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 1.56 | 0.55 | 6.67 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 1.46 | 0.49 |
| CS2 | 3.98 | 0.46 | 0.97 | 3.98 | 1.06 | 9.58 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 4.28 | 0.85 |
| CS4 | 6.74 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 6.74 | 1.92 | 15.31 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 7.55 | 1.39 |
| CS6 | 6.63 | 0.40 | 0.98 | 6.63 | 1.66 | 12.21 | 1.64 | 0.93 | 7.59 | 1.15 |
表2 LM和FM模型对生物炭吸附Cd2+等温线拟合参数
Table 2 Fit parameters of Cd2+ adsorption isotherm for biochar by LM and FM models
| FM | LM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Kf | n | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | Qm/ (mg∙g-1) | KL | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | ||
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | |||||||
| PC | 1.68 | 0.57 | 0.96 | 1.68 | 0.62 | 6.26 | 0.38 | 0.97 | 1.73 | 0.50 |
| PC2 | 1.65 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 1.65 | 0.44 | 4.14 | 0.73 | 0.98 | 1.75 | 0.36 |
| PC4 | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.17 | 1.72 | 1.32 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.16 |
| PC6 | 1.15 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 1.12 | 0.23 | 2.29 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 0.21 |
| CS | 1.56 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 1.56 | 0.55 | 6.67 | 0.28 | 0.99 | 1.46 | 0.49 |
| CS2 | 3.98 | 0.46 | 0.97 | 3.98 | 1.06 | 9.58 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 4.28 | 0.85 |
| CS4 | 6.74 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 6.74 | 1.92 | 15.31 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 7.55 | 1.39 |
| CS6 | 6.63 | 0.40 | 0.98 | 6.63 | 1.66 | 12.21 | 1.64 | 0.93 | 7.59 | 1.15 |
| FM | LM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Kf | n | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | Qm/ (mg∙g-1) | KL | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | ||
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | |||||||
| PC2W | 0.89 | 0.43 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 2.48 | 0.54 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.21 |
| PC4W | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.12 | 1.37 | 0.41 | 0.97 | 0.40 | 0.11 |
| PC6W | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.96 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 1.94 | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.16 |
| CS2W | 3.32 | 0.37 | 0.95 | 3.32 | 0.77 | 7.15 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 3.56 | 0.65 |
| CS4W | 4.56 | 0.35 | 0.95 | 4.56 | 1.03 | 8.82 | 1.42 | 0.96 | 5.17 | 0.82 |
| CS6W | 4.16 | 0.34 | 0.96 | 4.16 | 0.92 | 7.75 | 1.54 | 0.91 | 4.70 | 0.73 |
表3 LM和FM模型对去除可溶性组分后生物炭吸附Cd2+等温线拟合参数
Table 3 Fit parameters of Cd2+ adsorption isotherm of biochar after the removal of soluble components by LM and FM models
| FM | LM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Kf | n | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | Qm/ (mg∙g-1) | KL | radj2 | Kd/(L∙kg-1) | ||
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 10 | |||||||
| PC2W | 0.89 | 0.43 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 2.48 | 0.54 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.21 |
| PC4W | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.12 | 1.37 | 0.41 | 0.97 | 0.40 | 0.11 |
| PC6W | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.96 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 1.94 | 0.39 | 0.97 | 0.55 | 0.16 |
| CS2W | 3.32 | 0.37 | 0.95 | 3.32 | 0.77 | 7.15 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 3.56 | 0.65 |
| CS4W | 4.56 | 0.35 | 0.95 | 4.56 | 1.03 | 8.82 | 1.42 | 0.96 | 5.17 | 0.82 |
| CS6W | 4.16 | 0.34 | 0.96 | 4.16 | 0.92 | 7.75 | 1.54 | 0.91 | 4.70 | 0.73 |
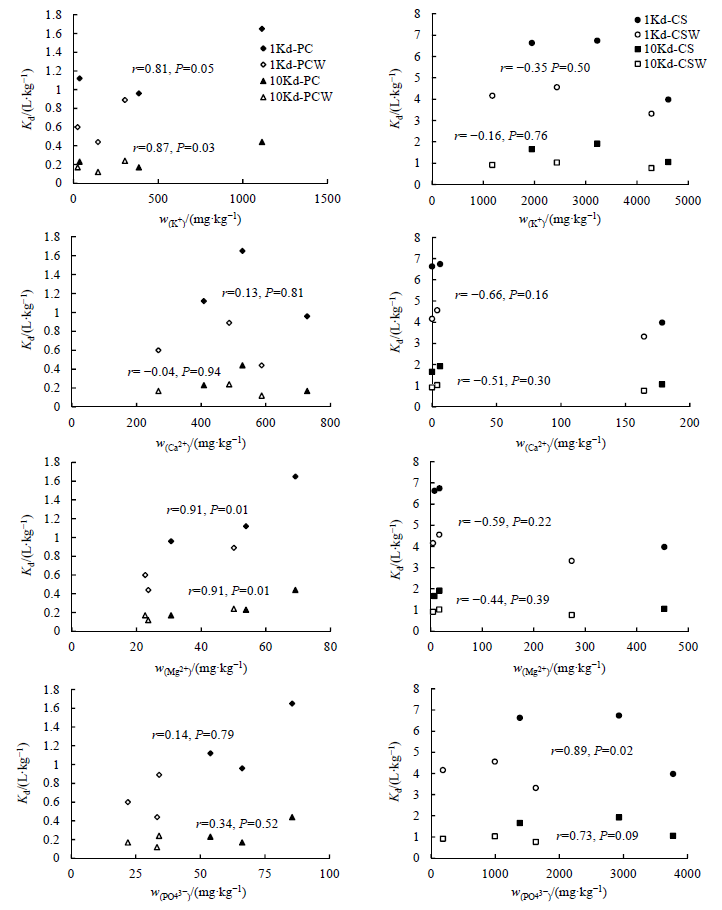
图7 不同Cd2+浓度下K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、PO43-含量与Kd值相关性
Figure 7 The correlation between K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, PO43- and Kd calculated at the concentrations of Cd2+ 1Kd: 1 mg∙L-1 Cd2+; 10Kd: 10 mg∙L-1 Cd2+
| [1] |
CAO X D, HARRIS W, 2010. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 101(14): 5222-5228.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CAO X D, MA L N, GAO B, et al., 2009. Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(9): 3285-3291.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CASE S, MCNAMARA N P, REAY D S, et al., 2013. Can biochar reduce soil greenhouse gas emissions from a Miscanthus bioenergy crop?[J]. Global Change Biology Bioenergy, 6(1): 76-89.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHOUDHARY M, KUMAR R, NEOGI S, 2020. Activated biochar derived from Opuntia ficus-indica for the efficient adsorption of malachite green dye, Cu2+ and Ni2+from water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122441.
DOI |
| [5] |
CUI X Q, FANG S Y, YAO Y Q, et al., 2016. Potential mechanisms of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Canna indica derived biochar[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 562: 517-525.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
EDVALDO, SAGRILO, JEFFERY, et al., 2015. Emission of CO2 from biochar-amended soils and implications for soil organic carbon[J]. Global change biology bioenergy, 7(6):1294-1304.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAN B, ANTHONY J M, KATHRY M, et al., 2022. Modification of naturally abundant resources for remediation of potentially toxic elements: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126755.
DOI |
| [8] | HE Z Q, MAO J D, HONEYCUTT C W, et al., 2009. Characterization of plant-derived water extractable organic matter by multiple spectroscopic techniques[J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 45(6): 609-616. |
| [9] |
HUA Y, ZHENG X B, XUE L H, et al., 2020. Microbial aging of hydrochar as a way to increase cadmium ion adsorption capacity: Process and mechanism[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122708.
DOI |
| [10] |
INYANG M I, GAO B, YAO Y, et al., 2016. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 46(4): 406-403.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KEILUWEIT M, NICO P S, JOHNSON M G, et al., 2010. Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(4): 1247-1253.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KLASSON K T, UCHIMIYA M, LIMA I M, 2014. Uncovering surface area and micropores in almond shell biochars by rainwater wash[J]. Chemosphere, 111: 129-134.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI H B, DONG X L, SILVA E, et al., 2017. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications[J]. Chemosphere, 178: 466-478.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI H, MAHYOUB S, LIAO W J, et al., 2017. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on characteristics and aromatic contaminants adsorption behavior of magnetic biochar derived from pyrolysis oil distillation residue[J]. Bioresource Technology, 223: 20-26.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LU H L, ZHANG W H, YANG Y X, et al., 2012. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar[J]. Water Research, 46(3): 854-862.
DOI URL |
| [16] | MUKOME F, ZHANG X, SILVA L, et al., 2013. Use of chemical and physical characteristics to investigate trends in biochar feedstocks[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 61(9): 2196-2204 |
| [17] |
PENG H B, GAO P, CHU G, et al., 2017. Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars[J]. Environmental Pollution, 229: 846-853.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
PENG Z, SUN H W, LI Y, et al., 2013. Adsorption and catalytic hydrolysis of carbaryl and atrazine on pig manure-derived biochars: Impact of structural properties of biochars[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 244-245: 217-224.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
RAMLOW M, COTRUFO M F, 2018. Woody biochar's greenhouse gas mitigation potential across fertilized and unfertilized agricultural soils and soil moisture regimes[J]. Global Change Biology Bioenergy, 10(2): 108-122.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SAGRILO E, JEFFERY S, HOFFLAND E, et al., 2015. Emission of CO2 from biochar-amended soils and implications for soil organic carbon[J]. Global Change Biology Bioenergy, 7(6): 1294-1304.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
TAN Y H, WAN X R ZHOU T, et al., 2022. Novel Zn-Fe engineered kiwi branch biochar for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424: 127349.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG J W, ZHANG Y S, LIU Z, et al., 2019. Coeffect of air pollution control devices on trace element emissions in an ultralow emission coal-fired power plant[J]. Energy & Fuels, 33: 248-256.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WANG L L, WANG X F, ZOU B, et al., 2011. Preparation of carbon black from rice husk by hydrolysis, carbonization and pyrolysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(17): 8220-8224.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG R Z, HUANG D L, LIU Y G, et al., 2018. Investigating the adsorption behavior and the relative distribution of Cd2+ sorption mechanisms on biochars by different feedstock[J]. Bioresource Technology, 261: 265-271.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG Z Y, LIU G C, ZHENG H, et al., 2015. Investigating the mechanisms of biochar's removal of lead from solution[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.077.
DOI |
| [26] |
WU J W, WANG T, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2019. The distribution of Pb(II)/ Cd(II) adsorption mechanisms on biochars from aqueous solution: Considering the increased oxygen functional groups by HCl treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019. 121859.
DOI |
| [27] | XU X Y, CAO X D, LING Z, et al., 2013. Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 20(1): 358-368. |
| [28] |
YANG X W, CUI C X, ZHENG A Q, et al., 2020. Ultrasonic and microwave assisted organosolv pretreatment of pine wood for producing pyrolytic sugars and phenols[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112921.
DOI |
| [29] |
YIN Y J, IMPELLITTERI C A, YOU S J, et al., 2002. The importance of organic matter distribution and extract soil: Solution ratio on the desorption of heavy metals from soils[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 287(1-2): 107-119.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YU W B, HU J W, YU Y C, et al., 2021. Facile preparation of sulfonated biochar for highly efficient removal of toxic Pb(II) and Cd(II) from wastewater[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/ j.scitotenv.2020.141545.
DOI |
| [31] |
YUAN J H, XU R K, HONG Z, 2011. The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(3): 3488-3497.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHANG C, ZENG G M, HUANG D L, et al., 2019. Biochar for environmental management: Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, contaminant treatment, and potential negative impacts[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 373: 902-922.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHENG X B, MA X G, HUA Y, et al., 2021. Nitric acid-modified hydrochar enhance Cd2+ sorption capacity and reduce the Cd2+ accumulation in rice[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131261.
DOI |
| [34] |
ZHOU D D, SAIKAT G, ZHANG D, et al., 2016. Role of ash content in biochar for copper immobilization[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 33(12): 962-969.
DOI URL |
| [35] | ALBERTO B C, 王航, 吕春欣, 等, 2015. 不同温度下松木生物质炭对阿特拉津的吸附性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(3): 505-510. |
| ALBERTO B C, WANG H, LV C X, et al., 2015. Adsorption properties of pinus derived biochar for atrazine at different temperature[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(3): 505-510 | |
| [36] | 陈再明, 万还, 徐义亮, 等, 2012. 水稻秸秆生物碳对重金属Pb2+的吸附作用及影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 32(4): 769-776. |
| CHEN Z M, WAN H, XU Y L, et al., 2012. Adsorption of Pb2+ by rice straw derived-biochar and its influential factors[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 32(4): 769-776. | |
| [37] | 崔志文, 任艳芳, 王伟, 等, 2020. 碱和磁复合改性小麦秸秆生物炭对水体中镉的吸附特性及机制[J]. 环境科学, 41(7): 3315-3325. |
| CUI Z W, REN Y F, WANG W, et al., 2020. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of cadmium in water by alkali and magnetic composite modified wheat straw biochar[J]. Environmental Science, 41(7): 3315-3325. | |
| [38] | 韩林, 2017. 生物炭和改性生物炭对有机污染物的吸附-转化性能及作用机理[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学. |
| HAN L, 2017. Adsorption-transformation performance and mechanism of organic pollutants on biochar and modified biochar[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. | |
| [39] | 李力, 陆宇超, 刘娅, 等, 2012. 玉米秸秆生物炭对Cd(Ⅱ) 的吸附机理研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(11): 2277-2283. |
| LI L, LU Y C, LIU Y, et al., 2011. Adsorption mechanisms of cadmium(Ⅱ) on biochars derived from corn straw[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(11): 2277-2283. | |
| [40] | 林庆毅, 姜存仓, 张梦阳, 2017. 生物炭老化后理化性质及微观结构的表征[J]. 环境化学, 36(10): 2107-2114. |
| LIN Q Y, JIANG C C, ZHANG M Y, 2017. Characterization of the physical and chemical structures of biochar under simulated aging condition[J]. Environmental Chemistry. 36(10): 2107-2114. | |
| [41] | 王震宇, 刘国成, Monica Xing, 等, 2014. 不同热解温度生物炭对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J]. 环境科学, 35(12): 4735-4744. |
| WANG Z Y, LIU G C, MONICA X, et al., 2014. Adsorption of Cd(Ⅱ) varies with biochars derived at different pyrolysis temperatures[J]. Environmental Science, 35(12): 4735-4744. | |
| [42] |
郑奎, 张士秋, 刘海峰, 等, 2019. 不同处理方式对生物炭吸附Sr(Ⅱ) 的影响机制[J]. 核化学与放射化学, 41(5): 492-502.
DOI |
|
ZHENG K, ZHANG S Q, LIU H F, et al., 2019. Effect of different treatments on Sr(Ⅱ) adsorption on biochar[J]. Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemistry, 41(5): 492-502.
DOI |
|
| [43] | 周丹丹, 吴文卫, 赵婧, 等, 2016. 花生壳和松木屑制备的生物炭对Cu2+的吸附研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(3): 523-530. |
| ZHOU D D, WU W W, ZHAO J, et al., 2016. Study on the adsorption of Cu2+ to biochars produced from peanut shells and pine chips[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(3): 523-530. |
| [1] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [2] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [3] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [4] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [5] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [6] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [7] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [8] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [9] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [10] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [11] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [12] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [13] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [14] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [15] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
