生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2403-2413.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.015
秦秦1,2,4( ), 段海芹1,3, 宋科1, 孙丽娟1, 孙雅菲1, 周斌1, 薛永1,*(
), 段海芹1,3, 宋科1, 孙丽娟1, 孙雅菲1, 周斌1, 薛永1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-08
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*薛永,E-mail: exueyong@163.com作者简介:秦秦(1987年生),女,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为农田土壤修复与保育。E-mail: qinqin19870987@126.com
基金资助:
QIN Qin1,2,4( ), DUAN Haiqin1,3, SONG Ke1, SUN Lijuan1, SUN Yafei1, ZHOU Bin1, XUE Yong1,*(
), DUAN Haiqin1,3, SONG Ke1, SUN Lijuan1, SUN Yafei1, ZHOU Bin1, XUE Yong1,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-08
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
土壤团聚体是土壤颗粒的主要存在形式,对重金属在土壤中的富集和生物有效性具有重要影响。施肥方式会影响土壤团聚体的粒径分布和理化特性,但是不同粒径团聚体自身理化特性对重金属富集和赋存化学形态的影响仍缺乏系统研究。选取两种施肥处理(常规施肥和不施肥)的水稳性团聚体颗粒为研究对象,采用平衡等温法研究各粒级团聚体中镉(Cd)的吸附解吸特性和赋存化学形态,探讨施肥-团聚体理化特性-Cd吸附解吸及其赋存化学形态的内在关系。结果表明:相比未施肥处理,常规施肥处理能够显著增加大粒径团聚体(>53 μm)占比及其有机质、游离氧化铁(特别是无定形氧化铁)、全氮、有效磷和速效钾含量。与未施肥处理不同,常规施肥处理原土及各粒径团聚体对Cd2+的吸附解吸过程符合Freundlich方程,可达到非均匀多层吸附,其中2000—250 μm粒径团聚体对Cd2+的吸附、固持能力最强,随着粒径的减小,对Cd2+的吸附、固持能力均降低,主要与其游离氧化铁(特别是无定形氧化铁)、有机质、有效磷及全氮含量呈显著正相关。随着溶液中Cd2+初始浓度的增大,各粒径团聚体对Cd2+的吸附、解吸能力均增加。原土及各粒径团聚体固持Cd2+的化学形态以交换态为主,其中2000—250 μm粒径团聚体交换态Cd占比最低,为66.0%。常规施肥处理使各粒径团聚体中交换态Cd和有机结合态Cd含量显著降低,铁锰氧化物结合态Cd和残渣态Cd含量显著增加。由此可以得出,适当施肥处理能够增加团粒胶结物质含量,有利于大团聚结构生成,提高土壤颗粒对Cd2+的固持能力,促使固持的Cd2+向更稳定的形态转化,降低其生物活性和迁移能力。
中图分类号:
秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413.
QIN Qin, DUAN Haiqin, SONG Ke, SUN Lijuan, SUN Yafei, ZHOU Bin, XUE Yong. Effect of Conventional Fertilization on the Adsorption-desorption Characteristics and Chemical forms of Cadmium in Soil Water-stable Aggregates[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413.
| 处理 Treatment | 有机肥 Organic manure (N-P2O5-K2O) | 尿素 Urea (N) | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate (P2O5) | 硫酸钾 Potassium sulfate (K2O) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 4950 (99-40-114) | 660 (304) | 131 (79) | 330 (172) |
表1 各处理的施肥量
Table 1 Fertilizers application rate relative to each treatment kg?hm?2
| 处理 Treatment | 有机肥 Organic manure (N-P2O5-K2O) | 尿素 Urea (N) | 过磷酸钙 Calcium superphosphate (P2O5) | 硫酸钾 Potassium sulfate (K2O) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 4950 (99-40-114) | 660 (304) | 131 (79) | 330 (172) |
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/ μm | 质量分数 Mass percentage/ % | 有机质 w(Organic matter)/ (g∙kg−1) | 游离氧化铁 w(Free iron oxide)/ (g∙kg−1) | 无定形氧化铁 w(Amorphous iron oxide)/ (g∙kg−1) | 全氮 w(Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg−1) | 有效磷 w(Available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg−1) | 速效钾 w(Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | — | 26.30±0.91ab | 9.02±0.08c | 4.60±0.01b | 1.53±0.02c | 74.75±3.95b | 306.10±5.69c | 6.76±0.02a |
| 2000‒250 | 40.84±0.32c | 29.91±1.06b | 8.83±0.05bc | 4.82±0.06c | 1.67±0.07d | 106.06±2.54c | 242.19±17.13b | 7.53±0.01c | |
| 250‒53 | 34.74±0.66b | 25.79±4.65ab | 8.74±0.01b | 4.71±0.01bc | 1.30±0.01b | 70.36±5.64b | 167.52±25.69a | 7.7±0.01d | |
| <53 | 20.13±0.80a | 21.11±0.62a | 8.43±0.02a | 4.42±0.10a | 1.01±0.02a | 31.08±1.41a | 240.17±14.27b | 7.47±0.03b | |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | — | 14.95±0.06b | 8.92±0.03d | 3.71±0.01c | 1.16±0.01d | 20.10±0.56a | 125.16±2.27b | 6.99±0.03b |
| 2000‒250 | 44.47±0.48c | 16.39±1.54b | 7.61±0.02c | 3.90±0.02d | 0.85±0.01b | 31.87±1.41b | 153.38±5.71c | 7.38±0.01c | |
| 250‒53 | 31.41±1.00b | 12.07±0.42a | 6.50±0.01b | 3.32±0.04b | 0.98±0.02c | 20.10±2.26a | 115.04±8.56b | 7.32±0.02c | |
| <53 | 13.24±0.23a | 9.71±0.81a | 5.62±0.02a | 3.17±0.02a | 0.74±0.04a | 15.52±0.84a | 94.86±8.56a | 6.79±0.01a |
表2 不同施肥处理下原土及各粒径团聚体的理化性质
Table 2 Effects of different fertilization treatments on physicochemical properties of bulk soil and different particle size aggregates
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/ μm | 质量分数 Mass percentage/ % | 有机质 w(Organic matter)/ (g∙kg−1) | 游离氧化铁 w(Free iron oxide)/ (g∙kg−1) | 无定形氧化铁 w(Amorphous iron oxide)/ (g∙kg−1) | 全氮 w(Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg−1) | 有效磷 w(Available phosphorus)/ (mg∙kg−1) | 速效钾 w(Available potassium)/ (mg∙kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | — | 26.30±0.91ab | 9.02±0.08c | 4.60±0.01b | 1.53±0.02c | 74.75±3.95b | 306.10±5.69c | 6.76±0.02a |
| 2000‒250 | 40.84±0.32c | 29.91±1.06b | 8.83±0.05bc | 4.82±0.06c | 1.67±0.07d | 106.06±2.54c | 242.19±17.13b | 7.53±0.01c | |
| 250‒53 | 34.74±0.66b | 25.79±4.65ab | 8.74±0.01b | 4.71±0.01bc | 1.30±0.01b | 70.36±5.64b | 167.52±25.69a | 7.7±0.01d | |
| <53 | 20.13±0.80a | 21.11±0.62a | 8.43±0.02a | 4.42±0.10a | 1.01±0.02a | 31.08±1.41a | 240.17±14.27b | 7.47±0.03b | |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | — | 14.95±0.06b | 8.92±0.03d | 3.71±0.01c | 1.16±0.01d | 20.10±0.56a | 125.16±2.27b | 6.99±0.03b |
| 2000‒250 | 44.47±0.48c | 16.39±1.54b | 7.61±0.02c | 3.90±0.02d | 0.85±0.01b | 31.87±1.41b | 153.38±5.71c | 7.38±0.01c | |
| 250‒53 | 31.41±1.00b | 12.07±0.42a | 6.50±0.01b | 3.32±0.04b | 0.98±0.02c | 20.10±2.26a | 115.04±8.56b | 7.32±0.02c | |
| <53 | 13.24±0.23a | 9.71±0.81a | 5.62±0.02a | 3.17±0.02a | 0.74±0.04a | 15.52±0.84a | 94.86±8.56a | 6.79±0.01a |
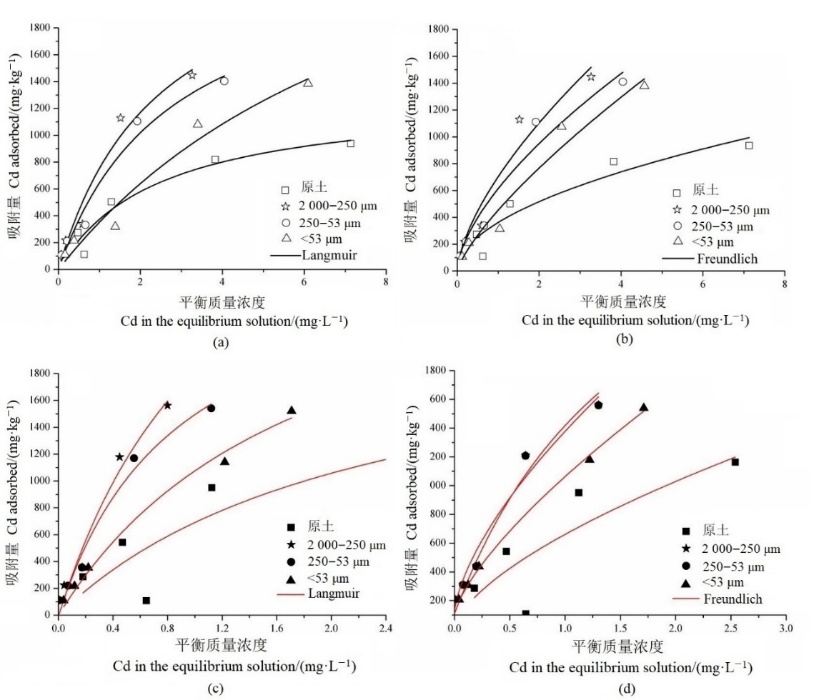
图1 原土及各粒径团聚体对Cd2+的等温吸附曲线 (a)未施肥(Langmuir拟合);(b)未施肥(Freundlich拟合);(c)常规施肥(Langmuir拟合);(d)常规施肥(Freundlich拟合);图中数据为3次重复的平均值(n=3)。下同
Figure 1 Adsorption isotherm of Cd2+ in bulk soil and different particle size aggregates (a) No fertilizer (Langmuir fitted); (b) No fertilizer (Freundlich fitted); (c) Conventional fertilization (Langmuir fitted); (d) Conventional fertilization (Freundlich fitted); Data in the figure are the mean values of three replications (n=3). The same below
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/μm | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qmax | r | KF | n | r | |||
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | 0.441 | 2257.10 | 0.603 | 660.802 | 0.639 | 0.603 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.689 | 4089.67 | 0.958 | 1699.788 | 0.748 | 0.962 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.579 | 3792.11 | 0.974 | 1350.562 | 0.651 | 0.960 | ||
| <53 | 0.545 | 3055.37 | 0.989 | 1020.904 | 0.719 | 0.998 | ||
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | 0.405 | 1290.72 | 0.912 | 361.971 | 0.514 | 0.859 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.406 | 2611.26 | 0.954 | 704.912 | 0.648 | 0.932 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.363 | 2428.97 | 0.966 | 609.095 | 0.634 | 0.944 | ||
| <53 | 0.229 | 2308.04 | 0.954 | 458.056 | 0.752 | 0.948 | ||
表3 原土及不同粒径团聚体对Cd2+的等温吸附方程拟合参数
Table 3 Parameters of isothermal adsorption of Cd2+ in bulk soil and different particle size aggregates
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/μm | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qmax | r | KF | n | r | |||
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | 0.441 | 2257.10 | 0.603 | 660.802 | 0.639 | 0.603 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.689 | 4089.67 | 0.958 | 1699.788 | 0.748 | 0.962 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.579 | 3792.11 | 0.974 | 1350.562 | 0.651 | 0.960 | ||
| <53 | 0.545 | 3055.37 | 0.989 | 1020.904 | 0.719 | 0.998 | ||
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | 0.405 | 1290.72 | 0.912 | 361.971 | 0.514 | 0.859 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.406 | 2611.26 | 0.954 | 704.912 | 0.648 | 0.932 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.363 | 2428.97 | 0.966 | 609.095 | 0.634 | 0.944 | ||
| <53 | 0.229 | 2308.04 | 0.954 | 458.056 | 0.752 | 0.948 | ||
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 游离氧化铁 Free iron oxide | 无定形氧化铁Amorphous iron oxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 0.232 | 0.867* | 0.985** | 0.992** | 0.033 | 0.959** | 0.975** |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 0.823* | 0.933** | 0.294 | 0.986** | 0.989** | 0.979** | 0.967** |
表4 不同粒径团聚体对Cd2+最大吸附量与其理化性质的相关性
Table 4 Correlation analysis between maximum adsorbance of Cd2+ and physicochemical properties of different particle size aggregates
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 游离氧化铁 Free iron oxide | 无定形氧化铁Amorphous iron oxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 0.232 | 0.867* | 0.985** | 0.992** | 0.033 | 0.959** | 0.975** |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 0.823* | 0.933** | 0.294 | 0.986** | 0.989** | 0.979** | 0.967** |
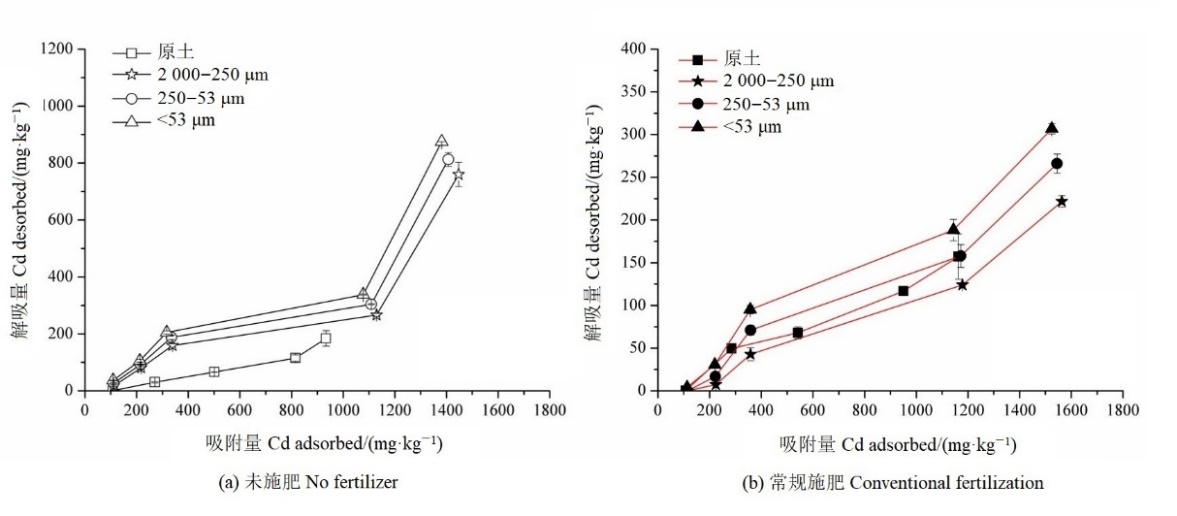
图2 原土及各粒径团聚体对Cd2+解吸量与吸附量的关系
Figure 2 The relationship between Cd2+ desorption and adsorption capacity by bulk soil and different particle size aggregate relative to treatments
| 溶液初始浓度 Initial centration of Cd2+/ (mg∙L−1) | 原土 Bulk soil | 2000‒250 µm | 250‒53 µm | <53 µm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | ||||
| 2 | 0.37 | 1.01 | — | 15.88 | — | 24.32 | 3.54 | 33.87 | |||
| 5 | 17.34 | 11.11 | 3.23 | 37.08 | 7.53 | 42.76 | 13.83 | 47.76 | |||
| 10 | 12.54 | 13.14 | 11.92 | 46.94 | 19.80 | 56.04 | 26.57 | 64.80 | |||
| 20 | 12.29 | 14.11 | 10.52 | 23.58 | 13.47 | 27.44 | 16.46 | 31.36 | |||
| 30 | 13.51 | 19.73 | 14.18 | 52.53 | 17.22 | 57.73 | 20.12 | 63.33 | |||
表5 原土及各粒径团聚体对Cd2+的解吸率
Table 5 Desorption rates of Cd2+ by bulk soil and different particle size aggregates %
| 溶液初始浓度 Initial centration of Cd2+/ (mg∙L−1) | 原土 Bulk soil | 2000‒250 µm | 250‒53 µm | <53 µm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 未施肥 No fertilizer | ||||
| 2 | 0.37 | 1.01 | — | 15.88 | — | 24.32 | 3.54 | 33.87 | |||
| 5 | 17.34 | 11.11 | 3.23 | 37.08 | 7.53 | 42.76 | 13.83 | 47.76 | |||
| 10 | 12.54 | 13.14 | 11.92 | 46.94 | 19.80 | 56.04 | 26.57 | 64.80 | |||
| 20 | 12.29 | 14.11 | 10.52 | 23.58 | 13.47 | 27.44 | 16.46 | 31.36 | |||
| 30 | 13.51 | 19.73 | 14.18 | 52.53 | 17.22 | 57.73 | 20.12 | 63.33 | |||
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/μm | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qmax | r | KF | H | r | |||
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | 0.20 | 371.11 | 0.99 | 62.52 | 1.11 | 0.99 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.28 | 359.92 | 0.93 | 14.55 | 2.54 | 0.96 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.19 | 475.15 | 0.94 | 31.32 | 2.01 | 0.97 | ||
| <53 | 0.14 | 608.64 | 0.96 | 37.71 | 1.63 | 0.99 | ||
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | 0.26 | 332.20 | 0.96 | 51.58 | 2.02 | 0.85 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.020 | 3105.19 | 0.99 | 44.20 | 1.62 | 0.99 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.017 | 3668.98 | 0.99 | 45.29 | 1.64 | 0.99 | ||
| <53 | 0.014 | 4412.69 | 0.99 | 44.61 | 1.37 | 0.99 | ||
表6 原土及不同粒径团聚体对Cd2+的等温解吸方程拟合参数
Table 6 Parameters of isothermal desorption of Cd2+ in bulk soil and different particle size aggregates
| 处理 Treatment | 粒径 Particle size/μm | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | Qmax | r | KF | H | r | |||
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | 原土 | 0.20 | 371.11 | 0.99 | 62.52 | 1.11 | 0.99 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.28 | 359.92 | 0.93 | 14.55 | 2.54 | 0.96 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.19 | 475.15 | 0.94 | 31.32 | 2.01 | 0.97 | ||
| <53 | 0.14 | 608.64 | 0.96 | 37.71 | 1.63 | 0.99 | ||
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | 原土 | 0.26 | 332.20 | 0.96 | 51.58 | 2.02 | 0.85 | |
| 2000‒250 | 0.020 | 3105.19 | 0.99 | 44.20 | 1.62 | 0.99 | ||
| 250‒53 | 0.017 | 3668.98 | 0.99 | 45.29 | 1.64 | 0.99 | ||
| <53 | 0.014 | 4412.69 | 0.99 | 44.61 | 1.37 | 0.99 | ||
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 游离氧化铁 Free iron oxide | 无定形氧化铁 Amorphous iron oxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | −0.102 | −0.815* | −0.992** | −0.978** | −0.054 | −0.935** | −0.944** |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | −0.826* | −0.931** | −0.527 | −0.904** | −0.869* | −0.91** | −0.861** |
表7 不同粒径团聚体对Cd2+解吸量与其理化性质的相关性
Table 7 Correlation analysis between maximum desorption capacity of Cd2+ and physicochemical properties of different particle size aggregates
| 处理 Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium | 游离氧化铁 Free iron oxide | 无定形氧化铁 Amorphous iron oxide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规施肥 Conventional fertilization | −0.102 | −0.815* | −0.992** | −0.978** | −0.054 | −0.935** | −0.944** |
| 未施肥 No fertilizer | −0.826* | −0.931** | −0.527 | −0.904** | −0.869* | −0.91** | −0.861** |
| [1] |
CAMBARDELLA C A, ELLIOTT E T, 1994. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics of soil organic matter fractions from cultivated grassland soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58: 123-130.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GU J F, ZHOU H, TANG H L, et al., 2019. Cadmium and arsenic accumulation during the rice growth period under in situ remediation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171: 451-459.
DOI URL |
| [3] | HE G H, GAO L C, WANG R S, 1994. Studies on solubilization and transformation of species Cu, Pb, Zn and Cr in simulant acid rain[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 5(1): 93-94. |
| [4] |
HUANG B, LI Z W, HUANG J Q, et al., 2014. Adsorption Characteristics of Cu and Zn onto various size fractions of aggregates from red paddy soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 264: 176-183.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
HUANG S, PENG X X, HUANG Q R, et al., 2010. Soil aggregation and organic carbon fractions affected by long-term fertilization in a red soil of subtropical China[J]. Geoderma, 154(3-4): 364-369.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KIRKHAM M B, 2006. Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: Effects of soil factors, hyperaccumulation, and amendments[J]. Geoderma, 137(-12): 19-32.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI Y L, DONG S F, QIAO J C, et al., 2020. Impact of nanominerals on the migration and distribution of cadmium on soil aggregates[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 262: 121355.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LOMBI E, SLETTEN R S, WENZEL W W, 2000. Sequentially extracted arsenic from different size fractions of contaminated soils[J]. Water Air Soil Pollute, 124(34): 319-332. |
| [9] |
LUND U, FOBIAN A, 1991. Pollution of two soils by arsenic, chromium and copper of denmark[J]. Geoderma, 49(1-2): 83-103.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MCLAREN R G, BACKS C A, RATES A W, et al., 1998. Cadmium and cobalt desorption kinetics from soil clays: Effect of sorption period[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 62(2): 332-337.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TESSIER A, 1979. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7): 844-851.
DOI URL |
| [12] | TINKOV A A, AJSUVAKOVA O P, ASETH J, et al., 2018. Mechanism of toxic effects of cadmium on life activities[J]. Journal of Environmental & Occupational Medicine, 35(5): 460-470. |
| [13] |
YUAN X Z, HUANG H J, ZENG G G, et al., 2011. Total concentrations and chemical speciation of heavy metals in liquefaction residues of sewage sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(5): 4104-4110.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | ZHANG M K, KE Z X, 2004. Copper and Zinc enrichment in different size fractions of organic matter from polluted soils[J]. Pedosphere, 14(1): 27-36. |
| [15] | 陈朕, 梁成华, 杜立宇, 等, 2013. 不同粒级土壤团聚体对砷(Ⅴ)的吸附与解吸影响研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 26(3): 1100-1104. |
| CHEN Z, LIANG C H, DU L Y, et al., 2013. Study on effect of different size fraction soil aggregate on adsorption and desorption of As(Ⅴ)[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 26(3): 1100-1104. | |
| [16] | 龚仓, 马玲玲, 成杭新, 等, 2012. 典型农耕区黑土和沼泽土团聚体颗粒中重金属的分布特征解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(9): 1635-1639. |
| GONG C, MA L L, CHENG H X, et al., 2012. Characterization of the particle size fractionation associated heavy metals in typical black and bog arable soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(9): 1635-1639. | |
| [17] | 郭菊花, 陈小云, 刘满强, 等, 2007. 不同施肥处理对红壤性水稻土团聚体的分布及有机碳、氮含量的影响[J]. 土壤, 39(5): 787-793. |
| GUO J H, CHEN X Y, LIU M Q, et al., 2007. Effects of fertilizer management practice on distribution of aggregates and content of organic carbon and nitrogen in red paddy soil[J]. Soils, 39(5): 787-793. | |
| [18] | 贺前锋, 桂娟, 刘代欢, 等, 2016. 淹水稻田中土壤性质的变化及其对土壤镉活性影响的研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(12): 2260-2268. |
| HE Q F, GUI J, LIU D H, et al., 2016. Research progress of soil property’s changes and its impacts on soil cadmium activity in flooded paddy field[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(12): 2260-2268. | |
| [19] | 姜强, 夏建国, 杨奕, 等, 2014. 名山河流域水稻土微团聚体对砷(As5+)的吸附-解吸特性[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(6): 148-154. |
| JIANG Q, XIA J G, YANG Y, et al., 2014. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of As5+ on the paddy soil micro-aggregates in Mingshan watershed[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(6): 148-154. | |
| [20] | 李春玲, 岳钦艳, 李颖, 等, 2009. 锌(Ⅱ)、镉(Ⅱ)在伊利石上的吸附及解吸特征研究[J]. 山东大学学报 (理学版), 44(11): 6-11. |
| LI C L, YUE Q Y, LI Y, et al., 2009. Adsorption and desorption of zinc (Ⅱ) and cadmium (Ⅱ) on illite[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 44(11): 6-11. | |
| [21] | 梁利宝, 冯鹏艳, 许剑敏, 2019. 施肥对采煤塌陷复垦土壤团聚体组成及其碳、氮分布的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 38(7): 45-51. |
| LIANG L B, FENG P Y, XU J M, 2019. Efficacy of fertilization in improving soil aggregation, carbon and nitrogen in soil reclaimed from subsided areas caused by coal mining[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 38(7): 45-51. | |
| [22] | 刘桃妹, 叶伟, 肖亿金, 等, 2021. 椰壳生物炭对多种重金属在广东水稻土中的吸附解吸特性影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 16(4): 342-350. |
| LIU T M, YE W, XIAO Y J, et al., 2021. Adsorption and desorption of several heavy metals in paddy soils in Guangdong Province influenced by coconut shell biochar[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 16(4): 342-350. | |
| [23] | 刘旭, 李庭宇, 安婷婷, 等, 2022. 不同施肥处理黑土覆膜后秸秆碳氮在团聚体中的固存特征[J]. 生态学报, 42(11): 1-12. |
| LIU X, LI T Y, AN T T, et al., 2022. Sequestration characteristics of straw residue carbon and nitrogen in aggregates following plastics film mulching on Mollisols with different fertilization treatments[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(11): 1-12. | |
| [24] | 刘哲, 张扬, 雷娜, 等, 2021. 优化施肥方式对黄土高原新增耕地土壤有机质含量和团聚体特性的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 41(5): 99-106. |
| LIU Z, ZHANG Y, LEI N, et al., 2021. Effects of optimized fertilization treatments on soil aggregate characteristics and organic matter content of newly reclaimed cultivated land in Loess Plateau[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 41(5): 99-106. | |
| [25] | 龙新宪, 倪吾钟, 杨肖娥, 2000. 菜园土壤铜吸附-解吸特性的研究[J]. 农村生态环境, 16(3): 39-41. |
| LONG X X, NI W Z, YANG X E, 2000. Characteristics of Cu adsorption/desorption of vegetable garden soils[J]. Rural Eco-Environment, 16(3): 39-41. | |
| [26] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社:12-193. |
| LU R K, 2000. Analytical methods for soil and agro-chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 12-193. | |
| [27] | 罗谦, 李英菊, 秦樊鑫, 等, 2020. 铅锌矿区周边耕地土壤团聚体重金属污染状况及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(3): 605-614. |
| LUO Q, LI Y J, QIN F X, et al., 2020. Contamination status and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil aggregates of Pb-Zn mining area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(3): 605-614. | |
| [28] | 蒲昌英, 刘昱昊, 2018. 土壤团聚体中重金属及有机质的分布[J]. 科学技术创新, 18(13): 19-20. |
| PU C Y, LIU Y H, 2018. Distribution of heavy metals and organic matters in soil aggregates[J]. Innovation in Science and Technology, 18(13): 19-20. | |
| [29] | 王润珑, 徐应明, 王农, 等, 2018. 天津污灌区菜地土壤团聚体中有机碳和重金属含量特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(11): 4490-4496. |
| WANG R L, XU Y M, WANG N, et al., 2018. Characteristics of organic carbon and heavy metals in aggregates of wastewater irrigation soils of Tianjin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(11): 4490-4496. | |
| [30] | 文勤亮, 郭倩楠, 祝媛, 等, 2014. 南方酸性土壤团聚体对磷的吸附解吸特征及pH值的影响[J]. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报, 31(6): 800-805. |
| WEN Q L, GUO Q N, ZHU Y, et al., 2014. Characteristic of phosphorus adsorption-desorption on southern acid soils and the effect of pH value[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Heilongjiang University, 31(6): 800-805. | |
| [31] | 熊东, 夏建国, 2012. 名山河流域黄壤组分对微团聚体吸附解吸镉的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(11): 2160-2173. |
| XIONG D, XIA J G, 2012. Effect of yellow soil components on adsorption and desorption of cadmium by microaggregates in Mingshan watershed, Sichuan province, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(11): 2160-2173. | |
| [32] | 许海波, 赵道远, 刘培亚, 等, 2013. 磷酸盐对水稻土团聚体不同类型重金属镉、铬(Ⅵ)吸附的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(5): 857-862. |
| XU H B, ZHAO D Y, LIU P Y, et al., 2013. Effect of phosphate on the kinetic of the adsorption of different types of heavy metal: cadmium and chromium by aggregates in paddy soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(5): 857-862. | |
| [33] | 徐温新, 叶正钱, 窦春英, 等, 2008. 西北典型林地和农田土壤锌的吸附-解吸特性研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 22(2): 191-194. |
| XU W X, YE Z Q, DOU C Y, et al., 2008. Zinc adsorption-desorption characteristics of typical forest and farmland soils in Northwest China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(2): 191-194. | |
| [34] | 郁红艳, 阮文权, 杨广龙, 2016. 冶炼厂周边农田土壤水稳性团聚体中镉的分布规律[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(1): 80-85. |
| YU H Y, RUAN W Q, YANG G L, 2016. Distribution of cadmium in soil water-stable aggregates in farmland surrounding a smelter[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(1): 80-85. | |
| [35] | 岳平, 2008. 添加化学改良剂对海南岛砖红壤中铅的化学形态与转化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(5): 1791-1795. |
| YUE P, 2008. Chemical forms and transformations of Pb in Granitic Latosol on Hainan Island through adding chemical amendments[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 27(5): 1797-1795. | |
| [36] | 翟龙波, 章熙锋, 陈靖, 等, 2019. 施肥对坡地土壤团聚体与磷素赋存形态的影响[J]. 西南大学学报 (自然科学版), 41(7): 105-115. |
| ZHAI L B, ZHANG X F, CHEN J, et al., 2019. Effects of fertilization on soil aggregates and phosphorus fractions of sloping upland of purple soil[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 41(7): 105-115. | |
| [37] | 张洪, 赖凡, 吕家恪, 等, 2009. 氮肥对油菜根-土界面镉迁移及镉组分变化特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 23(2): 169-172. |
| ZHANG H, LAI F, LÜ J K, et al., 2009. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on Cd translocation and changes of Cd fractions at soil-root interface of rape[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(2): 169-172. |
| [1] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [2] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [3] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [4] | 樊慧琳, 张佳敏, 李欢, 王艳玲. 坡耕地稻田剖面磷的储存格局与流失风险研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [5] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [6] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [7] | 古琛, 贾志清, 杜波波, 何凌仙子, 李清雪. 中国退化草地生态修复措施综述与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1465-1475. |
| [8] | 刘红梅, 海香, 安克锐, 张海芳, 王慧, 张艳军, 王丽丽, 张贵龙, 杨殿林. 不同施肥措施对华北潮土区玉米田土壤固碳细菌群落结构多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [9] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [10] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| [11] | 苏焱, 全妍红, 宦紫嫣, 姚佳, 苏小娟. 磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 593-602. |
| [12] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| [13] | 丛鑫, 王宇, 李瑶, 何洋洋. 生物炭及氧化石墨烯/生物炭复合材料对水中抗生素吸附性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 326-334. |
| [14] | 汤家喜, 向彪, 李玉, 谭婷, 朱永乐, 甘建平. 硅藻土对水中氟化物的吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 335-343. |
| [15] | 秦坤, 王志康, 王章鸿, 杨成, 刘杰刚, 沈德魁. 木质素-聚乙烯共热解生物炭对Cd(II)的吸附性能[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 344-353. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
