生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 1313-1324.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.07.014
李振国( ), 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇*(
), 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-06
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
* 郑新宇。E-mail: zhengxinyu0621@sina.com作者简介:李振国(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物生态学。E-mail: 2446273211@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Zhenguo( ), HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu*(
), HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu*( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-09-27
摘要:
超富集植物修复是目前研究较多且具有良好发展前景的重金属污染土壤治理技术。然而,采用超富集植物对重金属污染土壤进行修复时,生物量大幅下降成为其难以大面积推广应用的难点。以超富集植物紫苏(Perilla frutescens)为材料,采用水培实验,研究竹醋液(BV)对不同Cd胁迫水平下紫苏生长以及Cd富集变化的响应,评估了BV对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应以及提高植物修复效率的可行性。结果表明,在Cd质量浓度为4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1的处理下,外施BV显著增加了紫苏的总干重(36.8%和20.6%),叶酚酸(93.6%和30.9%)和类黄酮质量分数(80.0%和31.9%),以及根酚酸质量分数(25.3%和31.2%)。根类黄酮质量分数在4 mg·L-1 Cd处理下增加了34.7%,而在8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下无显著差异;外施BV处理下,根系POD酶活性在4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下分别增加了64.2%和65.1%。叶和根系APX酶活性在8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下分别提高414.1%和76.0%。总体上,在4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd质量浓度处理下,外施BV显著提高了植株地上部(16.5%和21.4%)和地下部(14.0%和62.8%)Cd质量分数,使植株Cd富集量分别提高了69.3%和55.7%。主成分分析表明,喷施BV可以改善植物酶与非酶抗氧化系统,增加了4 mg·L-1 Cd处理下植物的环境适应性,而对8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下植物的生理损伤影响较小。相关性分析表明,根系镉含量与根系酚酸呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。综上所述,BV通过提高紫苏POD和APX酶活性,增加类黄酮和酚酸类物质含量,缓解Cd对紫苏的损伤,促进Cd胁迫下植物生长,从而提高植物Cd富集效率。研究结果可为植物修复Cd污染土壤治理技术的推广提供理论基础。
中图分类号:
李振国, 郝星雨, 贺甜莲, 景蕊, 荣成, 顾承真, 郑新宇. 竹醋液对紫苏镉毒的缓解效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324.
LI Zhenguo, HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu. Study on the Alleviating Effect of Bamboo Vinegar on Cadmium Toxicity of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt.[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324.
| 类别 | 序号 | 有机物名称 | 相对含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酚类 | 1 | 苯酚 | 12.355 |
| 2 | 愈创木酚 | 7.817 | |
| 3 | 对甲酚 | 5.758 | |
| 4 | 4-乙基苯酚 | 4.880 | |
| 5 | 2-甲基苯酚 | 4.049 | |
| 6 | 2, 4-二甲基苯酚 | 1.609 | |
| 7 | 麦芽酚 | 1.066 | |
| 8 | 2, 6-二甲氧基苯酚 | 3.361 | |
| 9 | 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 | 1.660 | |
| 小计 | 42.554 | ||
| 酯类 | 10 | 乙酸甲酯 | 9.553 |
| 11 | 4-羟基丁酸乙酰酯 | 2.008 | |
| 12 | 丙酸甲酯 | 0.733 | |
| 小计 | 12.293 | ||
| 酸类 | 13 | 丙酸 | 6.659 |
| 14 | 丁酸 | 2.526 | |
| 15 | 乙酸 | 0.898 | |
| 小计 | 10.083 | ||
| 酮类 | 16 | 2-环戊烯酮 | 1.934 |
| 17 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.492 | |
| 18 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.388 | |
| 19 | 2, 3-二甲基-2-环戊烯酮 | 1.188 | |
| 20 | 3-甲基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 | 1.115 | |
| 21 | 1-羟基-2-丁酮 | 1.078 | |
| 22 | 环戊酮 | 0.699 | |
| 23 | 2, 5-二氢-3, 5-二甲基呋喃酮 | 0.682 | |
| 小计 | 9.576 | ||
| 醛类 | 24 | 3-糠醛 | 6.791 |
| 25 | 5-甲基呋喃醛 | 0.822 | |
| 小计 | 7.613 | ||
| 醇类 | 26 | 丝氨醇 | 0.830 |
| 27 | 1, 3-二氧杂烷-2-甲醇 | 0.709 | |
| 小计 | 1.539 | ||
| 其它 | 28 | 2-呋喃甲酰乙腈 | 3.340 |
| 29 | 丁酸酐 | 2.953 | |
| 30 | 3-羟基-4-甲氧基甲苯 | 2.822 | |
| 31 | 丙酸酐 | 2.129 | |
| 32 | 2-乙酰基呋喃 | 2.104 | |
| 33 | 异丁酸酐 | 2.061 | |
| 34 | 吡啶 | 0.934 | |
| 小计 | 16.342 |
表1 竹醋液中有机物的组成及其相对含量
Table 1 Composition and relative content of organic matter in bamboo vinegar
| 类别 | 序号 | 有机物名称 | 相对含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酚类 | 1 | 苯酚 | 12.355 |
| 2 | 愈创木酚 | 7.817 | |
| 3 | 对甲酚 | 5.758 | |
| 4 | 4-乙基苯酚 | 4.880 | |
| 5 | 2-甲基苯酚 | 4.049 | |
| 6 | 2, 4-二甲基苯酚 | 1.609 | |
| 7 | 麦芽酚 | 1.066 | |
| 8 | 2, 6-二甲氧基苯酚 | 3.361 | |
| 9 | 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 | 1.660 | |
| 小计 | 42.554 | ||
| 酯类 | 10 | 乙酸甲酯 | 9.553 |
| 11 | 4-羟基丁酸乙酰酯 | 2.008 | |
| 12 | 丙酸甲酯 | 0.733 | |
| 小计 | 12.293 | ||
| 酸类 | 13 | 丙酸 | 6.659 |
| 14 | 丁酸 | 2.526 | |
| 15 | 乙酸 | 0.898 | |
| 小计 | 10.083 | ||
| 酮类 | 16 | 2-环戊烯酮 | 1.934 |
| 17 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.492 | |
| 18 | 甲基环戊烯醇酮 | 1.388 | |
| 19 | 2, 3-二甲基-2-环戊烯酮 | 1.188 | |
| 20 | 3-甲基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 | 1.115 | |
| 21 | 1-羟基-2-丁酮 | 1.078 | |
| 22 | 环戊酮 | 0.699 | |
| 23 | 2, 5-二氢-3, 5-二甲基呋喃酮 | 0.682 | |
| 小计 | 9.576 | ||
| 醛类 | 24 | 3-糠醛 | 6.791 |
| 25 | 5-甲基呋喃醛 | 0.822 | |
| 小计 | 7.613 | ||
| 醇类 | 26 | 丝氨醇 | 0.830 |
| 27 | 1, 3-二氧杂烷-2-甲醇 | 0.709 | |
| 小计 | 1.539 | ||
| 其它 | 28 | 2-呋喃甲酰乙腈 | 3.340 |
| 29 | 丁酸酐 | 2.953 | |
| 30 | 3-羟基-4-甲氧基甲苯 | 2.822 | |
| 31 | 丙酸酐 | 2.129 | |
| 32 | 2-乙酰基呋喃 | 2.104 | |
| 33 | 异丁酸酐 | 2.061 | |
| 34 | 吡啶 | 0.934 | |
| 小计 | 16.342 |
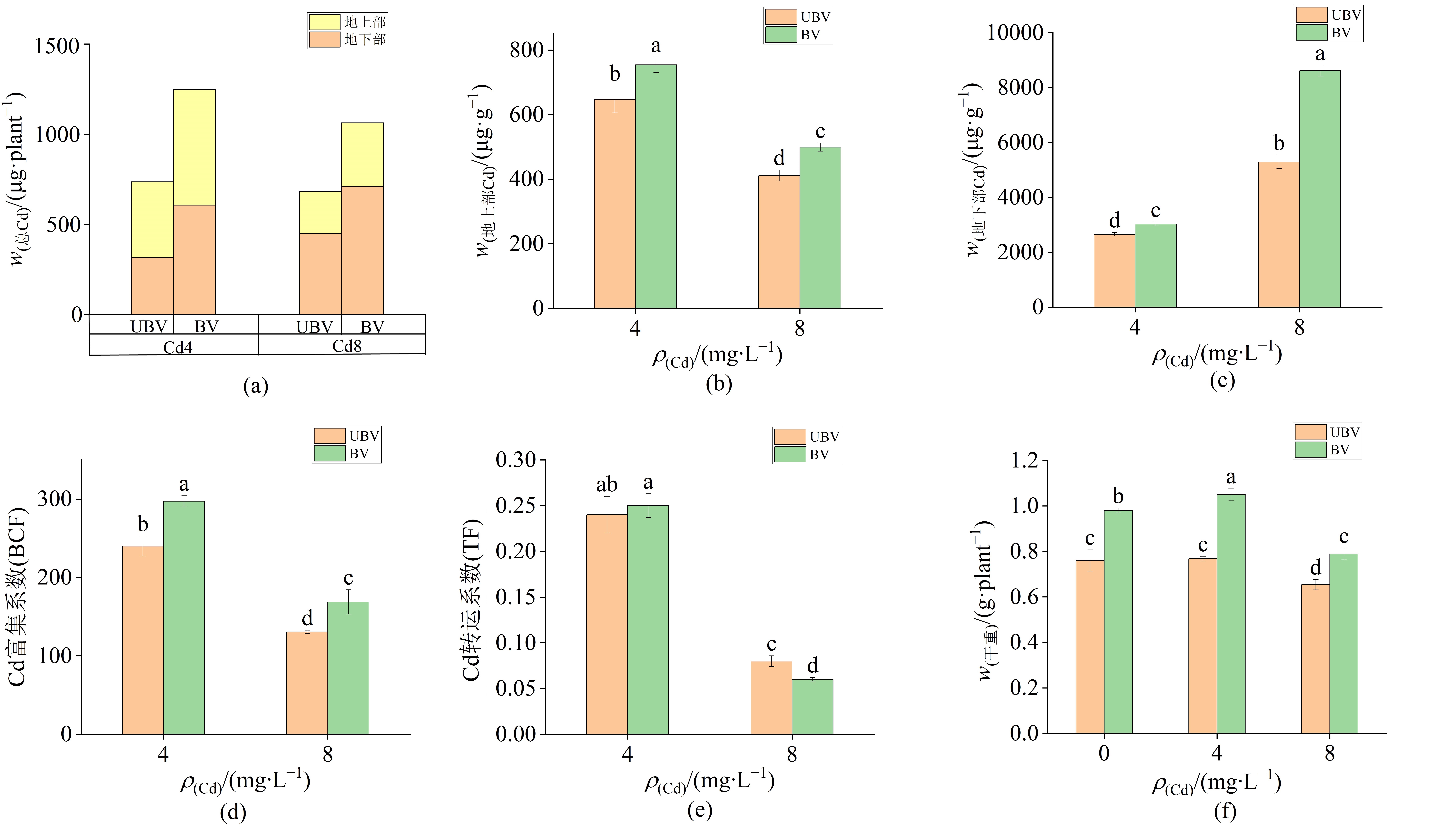
图1 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd浓度处理下,紫苏的单株总Cd富集量(a)、Cd含量(b-地上部、c-地下部)、BCF(d)、TF(e)和干重(f)的影响 不同字母代表处理之间有显著性差异(P<0.05),n=3。下同
Figure 1 Effects of BV spray on total Cd enrichment (a), Cd content (b-aboveground part, c-underground part), BCF(d), TF(e) and dry weight (f) of Perilla frutescens per plant at 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations
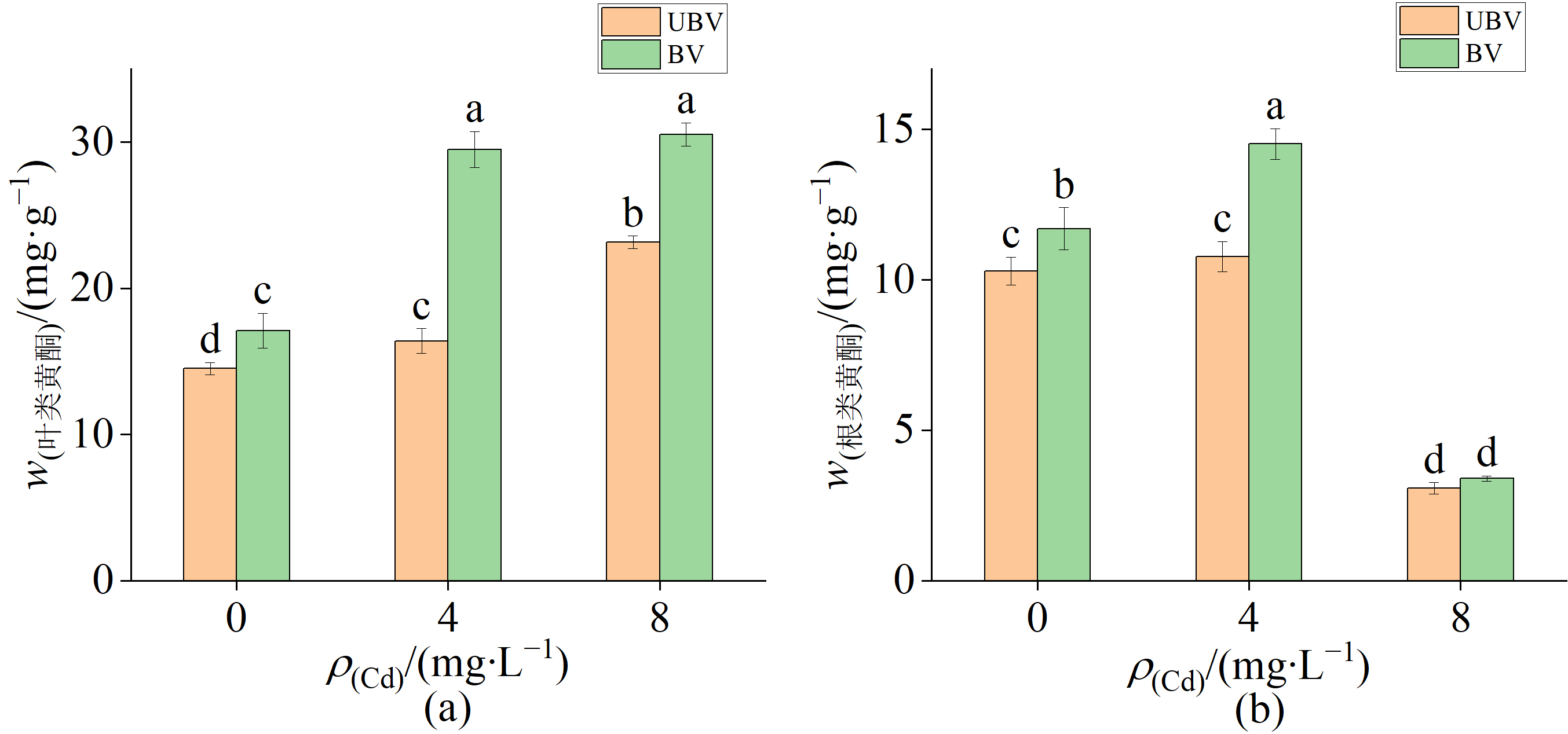
图2 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理紫苏的类黄酮含量(a-叶、b-根)的影响
Figure 2 Effects of BV spray on flavonoid content (a-leaves, b-root) of Perilla frutescens treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
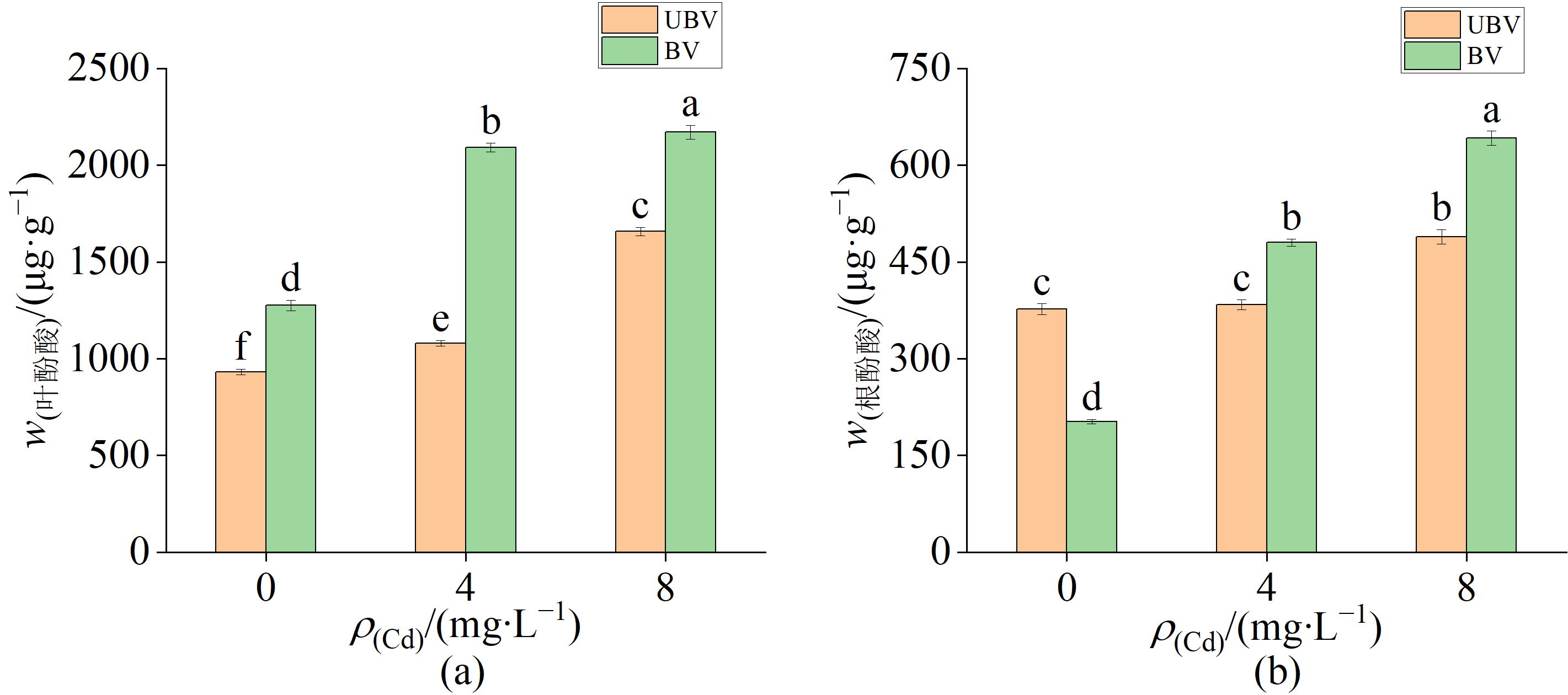
图3 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理紫苏的总酚酸含量(a-叶、b-根)
Figure 3 Total phenolic acid content (a-leaves, b-root) of Perilla frutescens treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd by spraying BV
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 0.382±0.003e | 5.677±0.072e | 2.986±0.153d | 2.886±0.153d | 3.161±0.216e | 3.182±0.149e | 28.165±1.530e | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 1.139±0.090d | 6.481±0.276d | 4.346±0.056bc | 4.246±0.056bc | 6.955±0.089d | 5.903±0.272c | 42.562±1.351d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 1.335±0.074c | 15.312±0.449a | 4.223±0.244c | 4.123±0.244c | 21.807±1.066c | 8.889±0.060a | 64.548±0.233b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 1.162±0.062d | 7.335±0.287c | 4.552±0.228b | 4.452±0.228b | 8.252±0.430d | 4.388±0.247d | 49.928±1.542c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 2.032±0.061b | 12.934±0.471b | 6.864±0.222a | 6.764±0.222a | 30.141±0.427b | 9.324±0.713a | 102.311±2.176a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 2.287±0.053a | 14.983±0.384a | 4.316±0.109bc | 4.216±0.109bc | 36.999±2.756a | 6.642±0.365b | 106.422±5.729a | ||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(迷迭香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
| UBVCd0 | 3.981±0.023d | 263.144±10.848e | 6.509±0.186e | 189.759±10.632e | 116.656±9.937d | 0.715±0.076cd | 627.204±11.565d | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 4.869±0.112c | 313.408±2.736d | 5.986±0.226e | 187.760±3.292e | 69.065±5.968e | 0.934±0.125b | 653.656±3.716d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 5.546±0.056b | 383.415±13.20c | 11.709±0.160c | 373.038±34.147c | 131.269±5.271cd | 1.158±0.059a | 1026.372±37.713b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 4.570±0.034c | 305.021±6.124d | 9.601±0.409d | 276.238±33.507d | 188.393±13.377b | 0.692±0.077d | 864.585±55.811c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 7.590±0.093a | 507.493±2.122a | 35.527±1.393a | 510.685±32.380b | 311.672±20.646a | 0.651±0.036d | 1543.987±22.459a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 8.085±0.673a | 456.245±3.651b | 27.788±0.852b | 721.729±56.173a | 146.704±15.716c | 0.899±0.183bc | 1537.315±58.656a | ||||
表2 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下紫苏叶中可溶性酚酸含量影响
Table 2 Effects of BV spray on soluble phenolic acid content in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 0.382±0.003e | 5.677±0.072e | 2.986±0.153d | 2.886±0.153d | 3.161±0.216e | 3.182±0.149e | 28.165±1.530e | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 1.139±0.090d | 6.481±0.276d | 4.346±0.056bc | 4.246±0.056bc | 6.955±0.089d | 5.903±0.272c | 42.562±1.351d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 1.335±0.074c | 15.312±0.449a | 4.223±0.244c | 4.123±0.244c | 21.807±1.066c | 8.889±0.060a | 64.548±0.233b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 1.162±0.062d | 7.335±0.287c | 4.552±0.228b | 4.452±0.228b | 8.252±0.430d | 4.388±0.247d | 49.928±1.542c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 2.032±0.061b | 12.934±0.471b | 6.864±0.222a | 6.764±0.222a | 30.141±0.427b | 9.324±0.713a | 102.311±2.176a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 2.287±0.053a | 14.983±0.384a | 4.316±0.109bc | 4.216±0.109bc | 36.999±2.756a | 6.642±0.365b | 106.422±5.729a | ||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(迷迭香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | ||||
| UBVCd0 | 3.981±0.023d | 263.144±10.848e | 6.509±0.186e | 189.759±10.632e | 116.656±9.937d | 0.715±0.076cd | 627.204±11.565d | ||||
| UBVCd4 | 4.869±0.112c | 313.408±2.736d | 5.986±0.226e | 187.760±3.292e | 69.065±5.968e | 0.934±0.125b | 653.656±3.716d | ||||
| UBVCd8 | 5.546±0.056b | 383.415±13.20c | 11.709±0.160c | 373.038±34.147c | 131.269±5.271cd | 1.158±0.059a | 1026.372±37.713b | ||||
| BVCd0 | 4.570±0.034c | 305.021±6.124d | 9.601±0.409d | 276.238±33.507d | 188.393±13.377b | 0.692±0.077d | 864.585±55.811c | ||||
| BVCd4 | 7.590±0.093a | 507.493±2.122a | 35.527±1.393a | 510.685±32.380b | 311.672±20.646a | 0.651±0.036d | 1543.987±22.459a | ||||
| BVCd8 | 8.085±0.673a | 456.245±3.651b | 27.788±0.852b | 721.729±56.173a | 146.704±15.716c | 0.899±0.183bc | 1537.315±58.656a | ||||
| 处理 | w(原儿茶酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/ (μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/ (μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/ (μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 1.298±0.106d | 8.838±0.382bc | 2.638±0.890d | 8.397±0.090c | 1.832±0.043c | 3.070±0.132cd | 1.550±0.044c | 35.280±2.434de | 62.905±2.326de |
| UBVCd4 | 1.617±0.063c | 7.201±0.541c | 3.635±0.196c | 8.222±0.397c | 2.801±0.197b | 3.616±0.189c | 1.375±0.187c | 48.347±3.909cd | 76.814±5.244d |
| UBVCd8 | 2.170±0.082b | 8.804±0.383c | 3.813±0.467c | 7.701±0.044cd | 4.004±0.079a | 10.122±0.94a | 1.915±0.226b | 87.692±2.777b | 126.221±3.034b |
| BVCd0 | 1.124±0.012d | 8.708±0.044c | 3.167±0.147cd | 6.943±0.281d | 1.497±0.052d | 2.747±0.077d | 0.999±0.018d | 32.941±1.231e | 58.127±1.392e |
| BVCd4 | 2.481±0.156a | 11.000±0.564b | 4.989±0.169b | 15.078±0.098b | 2.587±0.150b | 4.866±0.191b | 2.294±0.160a | 57.956±11.319c | 101.250±11.836c |
| BVCd8 | 2.588±0.145a | 16.310±2.822a | 8.356±0.552a | 19.640±1.081a | 2.741±0.289b | 10.120±0.531a | 1.528±0.132c | 161.020±15.377a | 222.304±18.065a |
表3 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下紫苏根中可溶性酚酸含量影响
Table 3 Effects of BV spray on soluble phenolic acid content in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1and 8 mg·L-1
| 处理 | w(原儿茶酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/ (μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/ (μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/ (μg·g-1) | w(可溶性酚酸总量)/ (μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 1.298±0.106d | 8.838±0.382bc | 2.638±0.890d | 8.397±0.090c | 1.832±0.043c | 3.070±0.132cd | 1.550±0.044c | 35.280±2.434de | 62.905±2.326de |
| UBVCd4 | 1.617±0.063c | 7.201±0.541c | 3.635±0.196c | 8.222±0.397c | 2.801±0.197b | 3.616±0.189c | 1.375±0.187c | 48.347±3.909cd | 76.814±5.244d |
| UBVCd8 | 2.170±0.082b | 8.804±0.383c | 3.813±0.467c | 7.701±0.044cd | 4.004±0.079a | 10.122±0.94a | 1.915±0.226b | 87.692±2.777b | 126.221±3.034b |
| BVCd0 | 1.124±0.012d | 8.708±0.044c | 3.167±0.147cd | 6.943±0.281d | 1.497±0.052d | 2.747±0.077d | 0.999±0.018d | 32.941±1.231e | 58.127±1.392e |
| BVCd4 | 2.481±0.156a | 11.000±0.564b | 4.989±0.169b | 15.078±0.098b | 2.587±0.150b | 4.866±0.191b | 2.294±0.160a | 57.956±11.319c | 101.250±11.836c |
| BVCd8 | 2.588±0.145a | 16.310±2.822a | 8.356±0.552a | 19.640±1.081a | 2.741±0.289b | 10.120±0.531a | 1.528±0.132c | 161.020±15.377a | 222.304±18.065a |
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 9.003±0.120e | 6.553±0.594c | 40.243±3.678d | 17.673±1.119c | 70.49±5.606d | 4.553±1.070c | 1.617±0.369c | ||||||
| UBVCd4 | 14.889±1.406c | 6.650±1.139c | 58.672±5.292c | 25.354±2.544ab | 108.304±9.917c | 9.740±0.418b | 1.841±0.580bc | ||||||
| UBVCd8 | 25.129±1.036a | 21.782±0.384a | 79.683±2.735b | 23.987±2.876ab | 232.859±9.919a | 14.326±1.363a | 3.244±0.178a | ||||||
| BVCd0 | 12.037±1.65ed | 7.995±1.194c | 72.711±12.36bc | 26.130±3.010ab | 97.994±7.402c | 15.198±1.881a | 2.765±0.440ab | ||||||
| BVCd4 | 15.279±1.103c | 15.064±2.179b | 71.719±11.071bc | 27.222±3.409a | 184.715±9.089b | 10.817±1.712b | 3.449±0.908a | ||||||
| BVCd8 | 19.362±1.782b | 19.96±1.748a | 96.241±12.735a | 20.473±5.517bc | 238.688±13.239a | 9.218±1.851b | 2.989±0.490a | ||||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | |||||||
| UBVCd0 | 102.688±8.512b | 29.736±2.366c | 8.534±1.105c | 12.415±1.064e | 0.462±0.029a | 303.967±18.260d | |||||||
| UBVCd4 | 128.925±5.770a | 38.532±4.058ab | 12.953±1.367ab | 20.458±6.179d | 0.430±0.012a | 426.749±27.125c | |||||||
| UBVCd8 | 128.984±5.305a | 40.642±3.690a | 12.131±1.838bc | 47.992±2.369a | 0.472±0.009a | 631.232±6.895a | |||||||
| BVCd0 | 100.916±6.369b | 34.231±4.161abc | 16.349±1.889a | 23.801±2.414d | 0.448±0.059a | 410.574±21.036c | |||||||
| BVCd4 | 136.678±7.821a | 33.420±4.389bc | 15.354±3.112ab | 33.071±5.194c | 0.497±0.072a | 547.285±29.026b | |||||||
| BVCd8 | 136.867±5.834a | 35.282±3.925abc | 11.858±2.500bc | 41.406±1.942b | 0.501±0.023a | 632.852±11.174a | |||||||
表4 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下紫苏叶中结合态酚酸含量影响
Table 4 Effects of BV spray on the content of bound phenolic acid in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 9.003±0.120e | 6.553±0.594c | 40.243±3.678d | 17.673±1.119c | 70.49±5.606d | 4.553±1.070c | 1.617±0.369c | ||||||
| UBVCd4 | 14.889±1.406c | 6.650±1.139c | 58.672±5.292c | 25.354±2.544ab | 108.304±9.917c | 9.740±0.418b | 1.841±0.580bc | ||||||
| UBVCd8 | 25.129±1.036a | 21.782±0.384a | 79.683±2.735b | 23.987±2.876ab | 232.859±9.919a | 14.326±1.363a | 3.244±0.178a | ||||||
| BVCd0 | 12.037±1.65ed | 7.995±1.194c | 72.711±12.36bc | 26.130±3.010ab | 97.994±7.402c | 15.198±1.881a | 2.765±0.440ab | ||||||
| BVCd4 | 15.279±1.103c | 15.064±2.179b | 71.719±11.071bc | 27.222±3.409a | 184.715±9.089b | 10.817±1.712b | 3.449±0.908a | ||||||
| BVCd8 | 19.362±1.782b | 19.96±1.748a | 96.241±12.735a | 20.473±5.517bc | 238.688±13.239a | 9.218±1.851b | 2.989±0.490a | ||||||
| 处理 | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(异绿原酸A)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(肉桂酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) | |||||||
| UBVCd0 | 102.688±8.512b | 29.736±2.366c | 8.534±1.105c | 12.415±1.064e | 0.462±0.029a | 303.967±18.260d | |||||||
| UBVCd4 | 128.925±5.770a | 38.532±4.058ab | 12.953±1.367ab | 20.458±6.179d | 0.430±0.012a | 426.749±27.125c | |||||||
| UBVCd8 | 128.984±5.305a | 40.642±3.690a | 12.131±1.838bc | 47.992±2.369a | 0.472±0.009a | 631.232±6.895a | |||||||
| BVCd0 | 100.916±6.369b | 34.231±4.161abc | 16.349±1.889a | 23.801±2.414d | 0.448±0.059a | 410.574±21.036c | |||||||
| BVCd4 | 136.678±7.821a | 33.420±4.389bc | 15.354±3.112ab | 33.071±5.194c | 0.497±0.072a | 547.285±29.026b | |||||||
| BVCd8 | 136.867±5.834a | 35.282±3.925abc | 11.858±2.500bc | 41.406±1.942b | 0.501±0.023a | 632.852±11.174a | |||||||
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 17.250±0.929c | 5.803±0.225cd | 81.084±2.491d | 20.161±1.743b | 99.211±5.046d | 43.651±1.774b |
| UBVCd4 | 21.336±0.301b | 6.244±1.386c | 85.943±4.110d | 22.302±2.821b | 87.819±1.000e | 54.415±1.888a |
| UBVCd8 | 24.277±0.708a | 7.858±1.615c | 112.827±5.593b | 23.935±0.397b | 114.76±6.562c | 45.310±2.816b |
| BVCd0 | 10.884±1.263d | 3.642±0.119d | 49.619±4.044e | 15.324±1.765c | 31.780±1.050f | 6.837±0.482c |
| BVCd4 | 20.553±1.631b | 11.849±1.683b | 100.625±3.652c | 28.541±0.621a | 130.723±5.51b | 41.544±6.112b |
| BVCd8 | 21.328±0.314b | 14.855±1.433a | 125.270±5.268a | 28.738±4.003a | 175.552±3.89a | 11.794±0.619c |
| 处理 | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) |
| UBVCd0 | 0.884±0.256c | 12.773±0.892c | 18.703±2.131a | 1.055±0.010bc | 13.013±1.362a | 313.589±6.187c |
| UBVCd4 | 1.414±0.244b | 7.511±0.571d | 11.826±2.452bc | 1.067±0.106bc | 6.640±0.559c | 306.518±11.417c |
| UBVCd8 | 1.641±0.090b | 13.555±0.968c | 11.426±2.988c | 1.005±0.033c | 6.358±0.082c | 362.953±10.921b |
| BVCd0 | 0.631±0.138c | 4.233±0.161e | 10.041±0.749c | 0.549±0.002d | 10.951±0.161b | 144.491±1.959d |
| BVCd4 | 1.479±0.154b | 16.831±0.966b | 12.252±2.288bc | 1.130±0.025b | 6.989±0.720c | 372.517±7.308b |
| BVCd8 | 2.257±0.193a | 19.824±1.303a | 15.445±1.206ab | 1.739±0.084a | 6.119±0.720c | 422.922±3.679a |
表5 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd处理下紫苏根中结合态酚酸含量影响
Table 5 Effects of BV spray on the content of binding phenolic acid in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd
| 处理 | w(没食子酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(原儿茶酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(绿原酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对羟基苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(咖啡酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(丁香酸)/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBVCd0 | 17.250±0.929c | 5.803±0.225cd | 81.084±2.491d | 20.161±1.743b | 99.211±5.046d | 43.651±1.774b |
| UBVCd4 | 21.336±0.301b | 6.244±1.386c | 85.943±4.110d | 22.302±2.821b | 87.819±1.000e | 54.415±1.888a |
| UBVCd8 | 24.277±0.708a | 7.858±1.615c | 112.827±5.593b | 23.935±0.397b | 114.76±6.562c | 45.310±2.816b |
| BVCd0 | 10.884±1.263d | 3.642±0.119d | 49.619±4.044e | 15.324±1.765c | 31.780±1.050f | 6.837±0.482c |
| BVCd4 | 20.553±1.631b | 11.849±1.683b | 100.625±3.652c | 28.541±0.621a | 130.723±5.51b | 41.544±6.112b |
| BVCd8 | 21.328±0.314b | 14.855±1.433a | 125.270±5.268a | 28.738±4.003a | 175.552±3.89a | 11.794±0.619c |
| 处理 | w(香兰素)/(μg·g-1) | w(阿魏酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(对香豆酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(香豆素)/(μg·g-1) | w(苯甲酸)/(μg·g-1) | w(结合态酚酸总量)/(μg·g-1) |
| UBVCd0 | 0.884±0.256c | 12.773±0.892c | 18.703±2.131a | 1.055±0.010bc | 13.013±1.362a | 313.589±6.187c |
| UBVCd4 | 1.414±0.244b | 7.511±0.571d | 11.826±2.452bc | 1.067±0.106bc | 6.640±0.559c | 306.518±11.417c |
| UBVCd8 | 1.641±0.090b | 13.555±0.968c | 11.426±2.988c | 1.005±0.033c | 6.358±0.082c | 362.953±10.921b |
| BVCd0 | 0.631±0.138c | 4.233±0.161e | 10.041±0.749c | 0.549±0.002d | 10.951±0.161b | 144.491±1.959d |
| BVCd4 | 1.479±0.154b | 16.831±0.966b | 12.252±2.288bc | 1.130±0.025b | 6.989±0.720c | 372.517±7.308b |
| BVCd8 | 2.257±0.193a | 19.824±1.303a | 15.445±1.206ab | 1.739±0.084a | 6.119±0.720c | 422.922±3.679a |

图4 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd浓度处理下紫苏叶中PDD活性(a)、CAT活性(b)、SOD活性(c)、APX活性(d)和MDA含量(e)的影响
Figure 4 Effects of BV spray on PDD activity (a), CAT activity (b), SOD activity (c), APX activity (d) and MDA content (e) in Perilla frutescens leaves treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations

图5 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd浓度处理下紫苏根中PDD活性(a)、CAT活性(b)、SOD活性(c)、APX活性(d)和MDA含量(e)的影响
Figure 5 Effects of BV spray on PDD activity (a), CAT activity (b), SOD activity (c), APX activity (d) and MDA content (e) in Perilla frutescens root treated with 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations
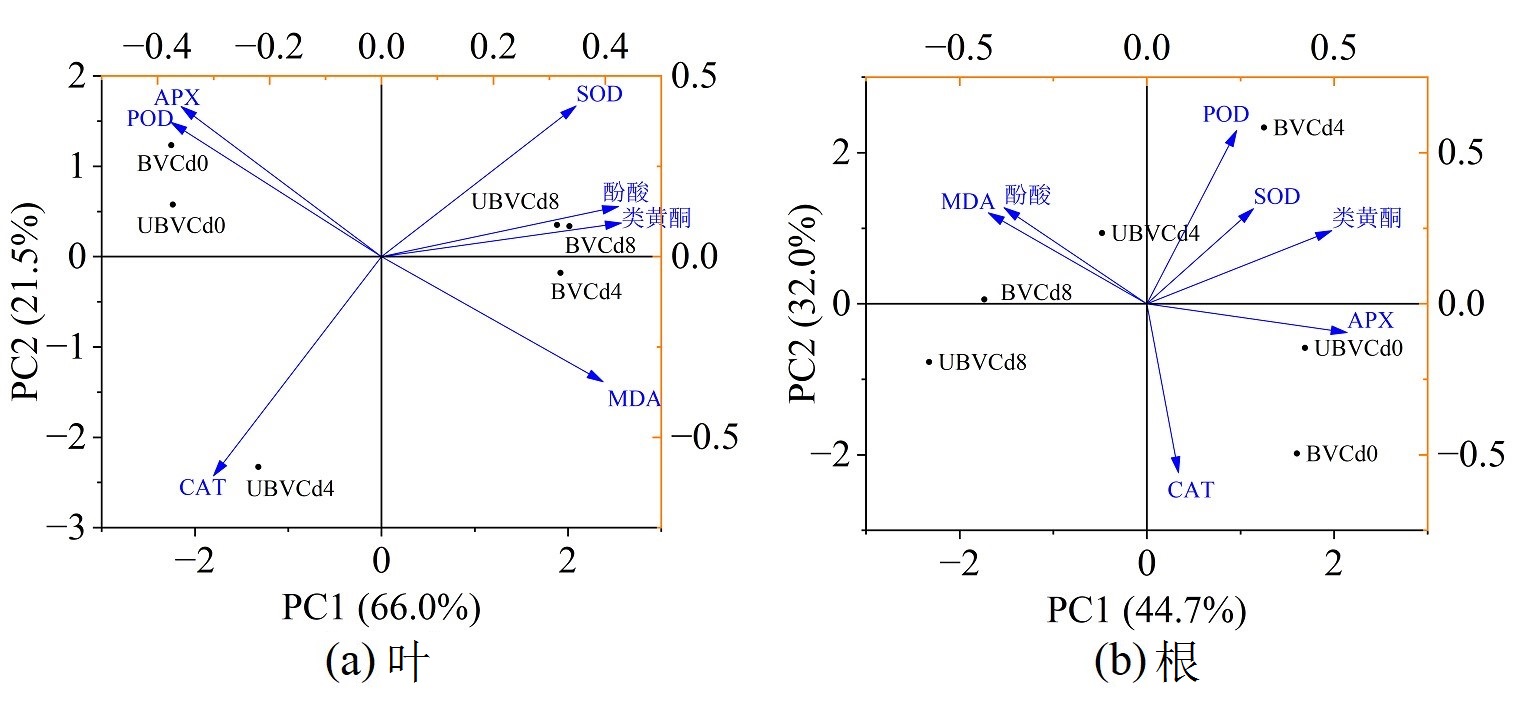
图6 喷施BV对0、4 mg·L-1和8 mg·L-1 Cd浓度处理下紫苏酶系统和非酶系统的主成分分析(PCA)得分图
Figure 6 Principal component analysis (PCA) scores of enzymatic and non-enzymatic systems of Perilla frutescens at 0, 4 mg·L-1 and 8 mg·L-1 Cd concentrations treated with BV

图7 采用皮尔逊相关系数来确定紫苏根和叶中重金属与酚酸和类黄酮含量之间的关系 红色表示正相关,蓝色表示负相关,数字表示皮尔逊指数。颜色越深,相关性越强
Figure 7 Pearson correlation coefficient was used to determine the relationship between heavy metals and phenolic acids and flavonoids contents in Perilla frutescens roots and leaves
| [1] |
BHAT S A, BASHIR O, UL HAQ S A, et al., 2022. Phytoremediation of heavy metals in soil and water: An eco-friendly, sustainable and multidisciplinary approach[J]. Chemosphere, 303(Part 1): 134788.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN S, LIN R Y, LU H L, et al., 2020. Effects of phenolic acids on free radical scavenging and heavy metal bioavailability in kandelia obovata under cadmium and zinc stress[J]. Chemosphere, 249: 126341.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHOUDHURY F K, RIVERO R M, BLUMWALD E, et al., 2017. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination[J]. The Plant Journal, 90(5): 856-867.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
DAS P, SAMANTARAY S, ROUT G R, 1997. Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 98(1): 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
DE ASCENSAO A R, DUBERY I A, 2003. Soluble and wall-bound phenolics and phenolic polymers in Musa acuminata roots exposed to elicitors from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense[J]. Phytochemistry, 63(6): 679-686.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DOU H J, NIU G H, GU M M, et al., 2018. Responses of sweet basil to different daily light integrals in photosynthesis, morphology, yield, and nutritional quality[J]. HortScience, 53(4): 496-503.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FERRER J L, AUSTIN M B, STEWART C J R., et al., 2008. Structure and function of enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 46(3): 356-370.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
GE J, TIAN S K, YU H Y, et al., 2021. Exogenous application of Mn significantly increased Cd accumulation in the Cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii[J]. Environmental Pollution, 278: 116837.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HAGNER M, RÄTY M, NIKAMA J, et al., 2021. Slow pyrolysis liquid in reducing NH3 emissions from cattle slurry-Impacts on plant growth and soil organisms[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 784: 147139.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HAN R, DAI H P, SKUZA L, et al., 2021. Comparative study on different organic acids for promoting Solanum nigrum L. hyperaccumulation of Cd and Pb from the contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 278: 130446.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
IRTELLI B, NAVARI-IZZO F, 2006. Influence of sodium nitrilotriacetate (NTA) and citric acid on phenolic and organic acids in Brassica juncea grown in excess of cadmium[J]. Chemosphere, 65(8): 1348-1354.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KANG Y C, LIU J X, YANG L, et al., 2022. Foliar application of flavonoids (rutin) regulates phytoremediation efficiency of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. by altering the permeability of cell membranes and immobilizing excess Cd in the cell wall[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425: 127875.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KOVÁCIK J, KLEJDUS B, 2008. Dynamics of phenolic acids and lignin accumulation in metal-treated Matricaria chamomilla roots[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 27(3): 605-615.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KÜPPER H, MIJOVILOVICH A, MEYER-KLAUCKE W, et al., 2004. Tissue- and age-dependent differences in the complexation of cadmium and zinc in the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges ecotype) revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy[J]. Plant Physiology, 134(2): 748-757.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LASHARI M S, LIU Y M, LI L Q, et al., 2013. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain[J]. Field Crops Research, 144: 113-118.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU X Y, MAO Y, ZHANG X, et al., 2019. Effects of PASP/NTA and TS on the phytoremediation of pyrene-nickel contaminated soil by Bidens pilosa L[J]. Chemosphere, 237: 124502.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LÜ Q X, XIAO Q T, GUO Y R, et al., 2022. Pollution monitoring, risk assessment and target remediation of heavy metals in rice from a five-year investigation in western Fujian region, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424(2): 127551.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MARTINEZ V, MESTRE T C, RUBIO F, et al., 2016. Accumulation of flavonols over hydroxycinnamic acids favors oxidative damage protection under abiotic stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7: 838.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
NIGGEWEG R, MICHAEL A J, MARTIN C, 2004. Engineering plants with increased levels of the antioxidant chlorogenic acid[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 22(6): 746-754.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | PAN B G, MO H Q, WANG W, et al., 2021. Regulating effects of silicon on Cd-accumulation and stress-resistant responding in rice seedling[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(3): 1096-1104. |
| [21] |
RAI P K, LEE S S, ZHANG M, et al., 2019. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management[J]. Environment International, 125: 365-385.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
RAZAL R A, ELLIS S, SINGH S, et al., 1996. Nitrogen recycling in phenylpropanoid metabolism[J]. Phytochemistry, 41(1): 31-35.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SAIDI I, GUESMI F, KHARBECH O, et al., 2021. Gallic acid improves the antioxidant ability against cadmium toxicity: Impact on leaf lipid composition of sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seedlings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 210: 111906.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SGHERRI C, COSI E, NAVARI-IZZO F, 2003. Phenols and antioxidative status of Raphanus sativus grown in copper excess[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 118(1): 21-28.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SHARMA A, SHAHZAD B, REHMAN A, et al., 2019. Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress[J]. Molecules, 24(13): 2452.
DOI URL |
| [26] | SIVARAM A K, LOGESHWARAN P, ABINANDAN S, et al., 2022. Cyto-genotoxicity evaluation of pyroligneous acid using Allium cepa assay[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering vol, 57(10): 852-857. |
| [27] |
SUN H J, FENG Y F, XUE L H, et al., 2020. Responses of ammonia volatilization from rice paddy soil to application of wood vinegar alone or combined with biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 242: 125247.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
TIAN S K, LU L L, LABAVITCH J, et al., 2011. Cellular sequestration of cadmium in the hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii[J]. Plant Physiology, 157(4): 1914-1925.
DOI URL |
| [29] | VASCONCELOS M T, AZENHA M, DE FREITAS V, 1999. Role of polyphenols in copper complexation in red wines[J]. Ournal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47(7): 2791-2796. |
| [30] |
WANG X S, FU H L, GONG F Y, et al., 2020. Lignin side chain region participates in Cd detoxification related to the cultivar-dependent Cd accumulation in Brassica chinensis L[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 392: 122264.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WIN KT, TOYOTA, MOTOBAYASHI T, et al., 2009. Suppression of ammonia volatilization from a paddy soil fertilized with anaerobically digested cattle slurry by wood vinegar application and floodwater management (vol 55, pg 190, 2009)[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 55(1): 190-202.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
XIAO Q T, WANG Y J, LÜ Q X, et al., 2020. Responses of glutathione and phytochelatins biosysthesis in a cadmium accumulator of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. under cadmium contaminated conditions[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 201: 110805.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YU H, QIU J F, MA L J, et al., 2017. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L. (Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 108(Part B): 375-391.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
YUAN X H, XUE N D, HAN Z G, 2021. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 101: 217-226.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ZHANG X F, XIA H P, LI Z A, et al., 2011. Identification of a new potential Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum by soil seed bank-metal concentration gradient method[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189(1-2): 414-419.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
ZHU K M, GU S C, LIU J H, et al., 2021. Wood vinegar as a complex growth regulator promotes the growth, yield, and quality of rapeseed[J]. Agronomy, 11(3): 510.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 李忠光, 龚明, 2008. 愈创木酚法测定植物过氧化物酶活性的改进[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 44(2): 323-324. |
| LI Z G, GONG M, 2008. Improvement of guaiacol method for determination of plant peroxidase activity[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 44(2): 323-324. | |
| [38] | 林琳, 旦增卓嘎, 吴玲玲, 2022. 铅、镉单一及复合胁迫对生菜幼苗抗氧化酶及亚细胞结构的毒性效应[J]. 生态毒理学报, 17(2): 337-348. |
| LIN L, DAN Z Z G, WU L L, 2022. Toxic effects of lead and cadmium on antioxidant enzymes and subcellular structure of lettuce seedlings[J]. Journal of Ecotoxicology, 17(2): 337-348. | |
| [39] |
谭新中, 彭喜旭, 胡耀军, 等, 2010. 镍处理下水稻酚酸和酚多聚物含量的变化与白叶枯病诱导抗性的关系[J]. 中国水稻科学, 24(4): 438-442.
DOI |
| TAN X Z, PENG X X, HU Y J, et al., 2010. Relationship between changes of phenolic acid and phenolic polymer contents in rice and induced resistance to bacterial blight under nickel treatment[J]. China Rice Science, 24(4): 438-442. | |
| [40] | 汪敦飞, 郑新宇, 肖清铁, 等, 2019. 铜绿假单胞菌对镉胁迫苗期水稻根系活力及叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(8): 2767-2774. |
| WANG D F, ZHENG X Y, XIAO Q T, et al., 2019. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on root activity and leaf physiological characteristics of rice under cadmium stress at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(8): 2767-2774. | |
| [41] | 吴苗苗, 2022. 木醋液/黑麦草联合对土壤重金属Cd的修复效果研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. |
| WU M M, 2022. Study on the remediation effect of wood vinegar/ryegrass combination on heavy metal Cd in soil[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. | |
| [42] | 肖清铁, 郑新宇, 韩永明, 等, 2018. 不同栽培措施对紫苏镉富集能力的影响[J]. 福建农业学报, 33(7): 724-731. |
| XIAO Q T, ZHENG X Y, HAN Y M, et al., 2018. Effects of different cultivation measures on cadmium enrichment ability of Perilla frutescens[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture, 33(7): 724-731. | |
| [43] | 谢惠玲, 陈爱萍, 张凤英, 等, 2011. 紫苏对不同浓度镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 19(3): 672-675. |
| XIE H L, CHEN A P, ZHANG F Y, et al., 2011. Physiological response of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. to cadimium[J]. Journal of China Ecological Agriculture, 19(3): 672-675. | |
| [44] | 杨春燕, 2020. 不同品种龙葵对重金属镉的富集能力与耐性机理研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学. |
| YANG C Y, 2020. Study on the enrichment ability and tolerance mechanism of different varieties of Solanum nigrum to heavy metal cadmium[D]. Xian: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology. | |
| [45] | 张宏, 李文珠, 张文标, 等, 2014. 两种精制竹醋液组分及含量的分析比较[J]. 竹子研究汇刊, 33(3): 32-37. |
| ZHANG H, LI W Z, ZHANG W B, et al., 2014. Analysis and comparison of components and contents of two refined bamboo vinegars[J]. Journal of Bamboo Rresearch, 33(3): 32-37. | |
| [46] | 张洪, 黄建韶, 赵东海, 2006. 紫苏营养成分的研究[J]. 湖南文理学院学报(自然科学版), 18(1): 49-52. |
| ZHANG H, HUANG J S, ZHAO D H, 2006. Study on nutritional components of Perilla frutescens[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Arts and Science (Natural Science Edition), 18(1): 49-52. | |
| [47] | 郑梅琴, 魏燕霞, 林瑞余, 2018. 不同紫苏挥发油化学成分分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 57(24): 143-146. |
| ZHENG M Q, WEI Y X, LIN R Y, 2018. Analysis of chemical constituents of volatile oil from different Perilla frutescens[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 57(24): 143-146. | |
| [48] | 郑新宇, 叶仁杰, 何印波, 等, 2013. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱测定化感水稻根系分泌的酚酸类化合物[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 35(2): 219-224. |
| ZHENG X Y, YE R J, HE Y B, et al., 2013. Determination of phenolic acids secreted by allelopathic rice roots by solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Science Edition), 35(2): 219-224. |
| [1] | 王丽华, 王磊, 许端平, 薛杨. 煤胶体对重金属铜与镉的吸附特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1293-1300. |
| [2] | 李治梅, 安娅, 李梅, 王室苹, 秦好丽. 巯基/铁基功能化蒙脱土对土壤镉的钝化行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(7): 1301-1312. |
| [3] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [4] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [5] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [6] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [7] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [8] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [9] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [10] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [11] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [12] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [13] | 文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 李富荣, 杜瑞英, 黄永东, 李蕾, 王富华. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [14] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [15] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
