生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 1140-1148.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.06.016
收稿日期:2023-01-14
出版日期:2023-06-18
发布日期:2023-09-01
通讯作者:
*E-mail: weiwei@rcees.ac.cn作者简介:王琳(1997年生),女,博士研究生,研究方向为生态水文。E-mail: linwang2019_st@rcees.ac.cn
基金资助:
WANG Lin1,2( ), WEI Wei1,2,3,*(
), WEI Wei1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-01-14
Online:2023-06-18
Published:2023-09-01
摘要:
陕北黄土高原沟壑区作为全国重点水土流失区和退耕还林还草核心区,探究县域尺度生态系统服务的时空变化特征、驱动因素和权衡关系对于生态系统的可持续管理更有针对性和现实性。基于RUSLE、CASA和InVEST模型,分析了陕北志丹县2000—2018年土壤保持、碳固存和水源供给3种生态系统服务的时空变化,并运用地理探测器和偏相关分析研究了生态系统服务的驱动因子和权衡关系。结果表明:2000—2018年,志丹县土壤保持、碳固存(以C计)和水源供给都呈现增加趋势,分别增加了199 t·hm-2·a-1、426 g·m-2·a-1和122 mm。地形、气候和植被生长状况等自然因素对生态系统服务空间异质性的影响强于土地利用类型等人为因素,并且多因子的交互作用对生态系统服务的影响大于单一因子。影响土壤保持服务空间异质性最主要的因子是坡度,其次是NDVI,碳固存服务空间异质性受降雨、NDVI和土壤类型等因素的综合影响,水源供给服务空间异质性的主要驱动因素是降雨和土地利用类型。志丹县土壤保持和碳固存、土壤保持和水源供给以及碳固存和水源供给之间的关系整体上分别表现为弱协同、弱协同和协同作用,并在空间上具有异质性。该研究有助于进一步了解不同生态系统服务间的复杂关系及其驱动因子差异,可为黄土高原县域生态系统管理和可持续发展提供参考。
中图分类号:
王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148.
WANG Lin, WEI Wei. Characteristics and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services Changes in A Typical County of the Loess Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148.
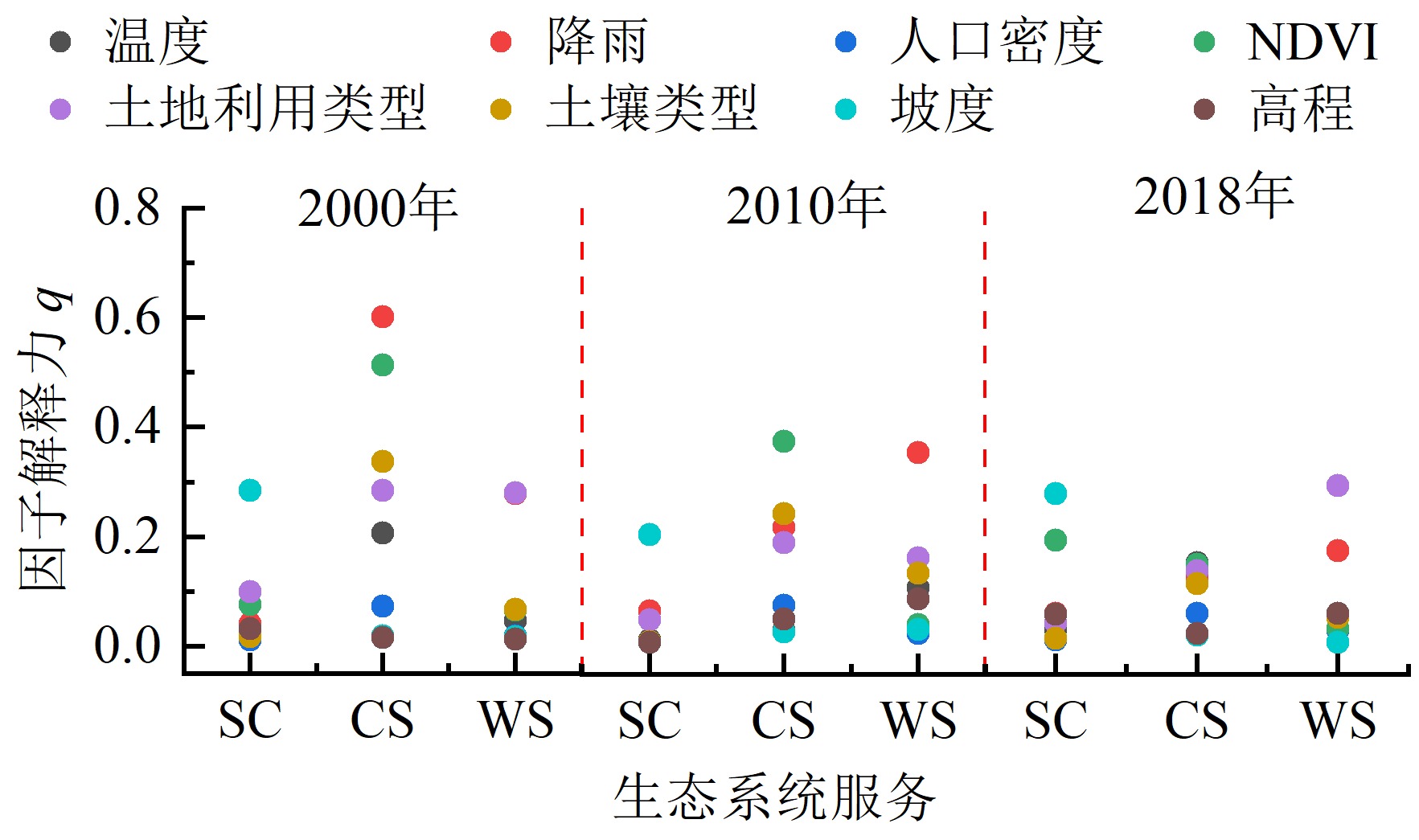
图3 2000—2018年各驱动因子对志丹县生态系统服务的影响程度 SC表示土壤保持(t·hm-2·a-1);CS表示碳固存(以C计,g·m-2·a-1);WS表示水源供给(mm)
Figure 3 Impacts of driving factors on ecosystem services in Zhidan County from 2000 to 2018
| [1] |
BAI Y, OCHUODHO T O, YANG J, 2019. Impact of land use and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Kentucky, USA[J]. Ecological Indicators, 102(6141): 51-64.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BEJAGAM V, SHARMA A, 2022. Impact of climatic changes and anthropogenic activities on ecosystem net primary productivity in India during 2001-2019[J]. Ecological Informatics, 70: 101732.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FALLOON P, JONES C D, CERRI C E, et al., 2007. Climate change and its impact on soil and vegetation carbon storage in Kenya, Jordan, India and Brazil[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 122(1): 114-124.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FU B J, WANG S, SU C H, et al., 2013. Linking ecosystem processes and ecosystem services[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 5(1): 4-10.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GAO J B, ZUO L Y, 2021. Revealing ecosystem services relationships and their driving factors for five basins of Beijing[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 31: 111-129.
DOI |
| [6] |
HAO R F, YU D Y, WU J G, 2017. Relationship between paired ecosystem services in the grassland and agro-pastoral transitional zone of China using the constraint line method[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 240: 171-181.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HE C J, SHAO H Y, XIAN W, 2022. Spatiotemporal variation and driving forces analysis of eeco-system service vvalues: A case study of Sichuan Province, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14): 8595.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI J, ZHOU Z X, 2016. Natural and human impacts on ecosystem services in Guanzhong-Tianshui economic region of China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23: 6803-6815.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU L L, ZHANG H B, GAO Y, et al., 2019. Hotspot identification and interaction analyses of the provisioning of multiple ecosystem services: Case study of Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 107: 105566.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MEHRI A, SALMANMAHINY A, TABRIZI A R M, et al., 2018. Investigation of likely effects of land use planning on reduction of soil erosion rate in river basins: Case study of the Gharesoo River Basin[J]. Catena, 167: 116-129.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG L J, GONG J W, MA S, et al., 2022a. Ecosystem service supply-demand and socioecological drivers at different spatial scales in Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 140(7713): 109058.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG T F, GONG Z W, 2022d. Evaluation and analysis of water conservation function of ecosystem in Shaanxi Province in China based on “Grain for Green” Projects[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(55):83878-83896.
DOI |
| [13] |
WANG X J, LIU G X, LIN D R, et al., 2022c. Water yield service influence by climate and land use change based on InVEST model in the monsoon hilly watershed in south China[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 13(1): 2024-2048.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG X Z, WU J Z, LIU Y L, et al., 2022b. Driving factors of ecosystem services and their spatiotemporal change assessment based on land use types in the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 311: 114835.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG Y X, WANG H M, LIU G, et al., 2022e. Factors driving water yield ecosystem services in the Yellow River Economic Belt, China: Spatial heterogeneity and spatial spillover perspectives[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 317: 115477.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WEI X D, YANG J, LUO P P, et al., 2022. Assessment of the variation and influencing factors of vegetation NPP and carbon sink capacity under different natural conditions[J]. Ecological Indicators, 138(2): 108834.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XIANG M S, WANG C J, TAN Y X, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of carbon storage in the western Sichuan Plateau[J]. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 8114.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
XU T Y, NIU X, WANG B, 2022. The Grain for Green Project in contiguous poverty-stricken regions of China: A nature-based solution[J]. Sustainability, 14(13): 7755.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XU X B, YANG G S, TAN Y, et al., 2018. Ecosystem services trade-offs and determinants in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2015[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 634: 1601-1614.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YAN K, WANG W F, LI Y H, et al., 2022. Identifying priority conservation areas based on ecosystem services change driven by Natural Forest Protection Project in Qinghai province, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 362: 132453.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YANG P, WANG N A, ZHAO L Q, et al., 2022b. Responses of grassland ecosystem carbon fluxes to precipitation and their environmental factors in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(8): 75805-75821.
DOI |
| [22] |
YANG Z, ZHAN J Y, WANG C, et al., 2022a. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between sustainable development and ecosystem services in Shanxi Province, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 836: 155625.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YU L X, LIU Y, LIU T X, et al., 2020. Impact of recent vegetation greening on temperature and precipitation over China[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 295: 108197.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZEN M, CANDIAGO S, SCHIRPKE U, et al., 2019. Upscaling ecosystem service maps to administrative levels: Beyond scale mismatches[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 660: 1565-1575.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAI D C, GAO X Z, LI B L, et al., 2022. Driving climatic factors at critical plant developmental stages for Qinghai-Tibet Plateau alpine grassland productivity[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(7): 1564.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHANG D, HUANG Q X, HE C Y, et al., 2019. Planning urban landscape to maintain key ecosystem services in a rapidly urbanizing area: A scenario analysis in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 96(Part 1): 559-571.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHAO W, YU X B, JIAO C C, et al., 2021b. Increased association between climate change and vegetation index variation promotes the coupling of dominant factors and vegetation growth[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 767: 144669.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHAO Y H, LIU L, KANG S Z, et al., 2021a. Quantitative analysis of factors influencing spatial distribution of soil erosion based on geo-detector model under diverse geomorphological types[J]. Land, 10(6): 604-604.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 陈春谛, 2022. 基于文献计量分析的生态系统服务研究: 从理论研究到实践应用[J]. 生态学报, 42(14): 6030-6039. |
| CHEN C D, 2022. Research on ecosystem services based on bibliometric analysis: from theoretical research to practical application[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(14): 6030-6039. | |
| [30] | 陈玉福, 董鸣, 2003. 生态学系统的空间异质性[J]. 生态学报, 23(2): 346-352. |
| CHEN Y F, DONG M, 2003. Spatial heterogeneity in ecological systems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(2): 346-352. | |
| [31] |
邓楚雄, 刘俊宇, 李忠武, 等, 2019. 近20年国内外生态系统服务研究回顾与解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(10): 2119-2128.
DOI |
| DENG C X, LIU J N, LI Z W, et al., 2019. Review and analysis of ecosystem services research between domestic and foreign in recent 20 years[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(10): 2119-2128. | |
| [32] |
丁倩, 张弛, 2021. 基于地理探测器的中国陆地生态系统土壤有机碳空间异质性影响因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(1): 19-28.
DOI |
| DING Q, ZHANG C, 2021. Influential factors analysis for spatial heterogeneity of soil organic carbon in Chinese terrestrial ecosystem with geographical detector[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(1): 19-28. | |
| [33] |
傅伯杰, 于丹丹, 2016. 生态系统服务权衡与集成方法[J]. 资源科学, 38(1): 1-9.
DOI |
| FU B J, YU D D, 2016. Trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services[J]. Resoirces Science, 38(1): 1-9. | |
| [34] |
黄欣, 彭双云, 王哲, 等, 2022. 基于地理探测器的云南省生态系统产水服务的空间异质性及驱动因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(10): 2813-2821.
DOI |
| HUANG X, PENG S Y, WANG Z, et al., 2022. Spatial heterogeneity and driving factors of ecosystem water production services in Yunnan Province, China based on Geodetector[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Applied Ecology, 33(10): 2813-2821. | |
| [35] | 李理, 赵芳, 朱连奇, 等, 2021. 淇河流域生态系统服务权衡及空间分异机制的地理探测[J]. 生态学报, 41(19): 7568-7578. |
| LI L, ZHAO F, ZHU L Q, et al., 2021. Geographical detection of ecosystem services trade-offs and their spatial variation mechanism in Qihe River Basin[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(19): 7568-7578. | |
| [36] | 林隆超, 王晓飞, 刘延平, 等, 2022. 退耕还林工程背景下延安植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候的响应[J]. 陕西气象 (4): 1-6. |
| LI L C, WANG X F, LIU Y P, et al., 2022. Temporal and spatial changes of vegetation cover and its response to climate in Yan’an under the background of Farmland Conversion Project[J]. Meteorology of Shaanxi (4): 1-6. | |
| [37] | 刘婷, 周自翔, 朱青, 等, 2021. 延河流域生态系统土壤保持服务时空变化[J]. 水土保持研究, 28(1): 93-100. |
| LI T, ZHOU Z X, ZHU Q, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial changes of ecosystem soil conservation services in Yanhe River Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(1): 93-100. | |
| [38] | 李扬子, 宋敏, 胡灿, 2021. 耕地资源的关键性生态系统服务识别——以差别化耕地保护政策目标为导向[J]. 农业技术经济 (10): 121-133. |
| LI Y Z, SONG M, HU C, 2021. Identification of key ecosystem services of farmland[J]. Agro-technical Economy (10): 121-133. | |
| [39] | 刘海龙, 唐飞, 丁娅楠, 等, 2022. 山西省县域高质量发展与生态系统服务耦合的时空演变特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 39(4): 1234-1245. |
| LIU H L, TANG F, DING Y N, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal evolution of coupling high-quality development and ecosystem services in counties of Shanxi Province[J]. Arid Zone Research, 39(4): 1234-1245. | |
| [40] |
卢乔倩, 江涛, 柳丹丽, 等, 2020. 中国不同植被覆盖类型NDVI对气温和降水的响应特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(1): 23-34.
DOI |
| LU Q Q, JIANG T, LIU D L, et al., 2020. The response characteristics of NDVI with different vegetation cover types to ttemperature and precipitation in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(1): 23-34. | |
| [41] | 马传功, 陈建军, 郭先华, 等, 2016. 坡耕地不同种植模式对农田水土保持效应及土壤养分流失的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 33(1): 72-79. |
| MA C G, CHEN J J, GUO X H, et al., 2016. Effects of differernt cropping patterns on soil and water conservation benefits and soil nutrients loss on sloping land[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 33(1): 72-79. | |
| [42] | 宁静, 石东伟, 周思宇, 等, 2022. 宾县生态系统服务时空格局及权衡协同关系[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(5): 293-300. |
| NING J, SHI D W, ZHOU S Y, et al., 2022. Spatial and temporal patterns of ecosystem services in Bin County[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(5): 293-300. | |
| [43] | 裴渊杰, 罗漫雅, 赵永华, 等, 2022. 多尺度生态系统服务权衡与协同关系——以延安市为例[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(7): 1351-1360. |
| PEI Y J, LUO M Y, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2022. Multi-scale ecosystem service Tradeoff and synergistic relationship: A case study of Yan’an City[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(7): 1351-1360. | |
| [44] |
钱彩云, 巩杰, 张金茜, 等, 2018. 甘肃白龙江流域生态系统服务变化及权衡与协同关系[J]. 地理学报, 73(5): 868-879.
DOI |
| QIAN C Y, GONG J, ZHANG J Q, et al., 2018. Ecosystem service changes, tradeoffs and synergies in Bailong River Basin, Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 73(5): 868-879. | |
| [45] | 邵明, 董宇翔, 林辰松, 2020. 基于GWR模型的成渝城市群生态系统服务时空演变及驱动因素研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 42(11): 118-129. |
| SHAO M, DONG Y X, LIN C S, 2020. Spatial and temporal evolution of ecosystem services and its driving factors in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration based on GWR Model[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 42(11): 118-129. | |
| [46] | 孙思琦, 陈永喆, 王聪, 等, 2022. 华北地区生态保护与恢复的水资源效应研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 24(5): 97-106. |
| SUN S Q, CHEN Y Z, WANG C, et al., 2022. Water resource effectiveness of vegetation conservation and restoration in north China[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 24(5): 97-106. | |
| [47] | 唐志雄, 周自翔, 白继洲, 等, 2023. 泾河流域生态系统服务权衡/协同关系的尺度异质性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 30(4): 318-326. |
| TANG Z X, ZHOU Z X, BAI J Z, et al., 2023. Scale seterogeneity of ecosystem service trade-offs/synergies in the Jinghe River Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(4): 318-326. | |
| [48] |
王鹏涛, 张立伟, 李英杰, 等, 2017. 汉江上游生态系统服务权衡与协同关系时空特征[J]. 地理学报, 72(11): 2064-2078.
DOI |
| WANG P T, ZHANG L W, LI Y J, et al., 2017. Spatial and temporal characteristics of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in upper Hanjiang River[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(11): 2064-2078. | |
| [49] |
王钊, 李登科, 2018. 2000-2015年陕西植被净初级生产力时空分布特征及其驱动因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(6): 1876-1884.
DOI |
|
WANG Z, LI D K, 2018. Spatial and temporal distribution of net primary productivity of vegetation and its driving factors in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2015[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(6): 1876-1884.
DOI |
|
| [50] | 汪宙峰, 贺相綦, 王成武, 2022. 基于地理探测器与SVM的冰湖溃决预测研究——以喜马拉雅山地区为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 31(6): 220-228. |
| WANG Z F, HE X Q, WANG C W, 2022. Prediction of glacial lake outburst floods based on geodetector and SVM: A case study of the Himalayan region[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 31(6): 220-228. | |
| [51] | 夏楚瑜, 国淏, 赵晶, 等, 2023. 京津冀地区生态系统服务对城镇化的多空间尺度动态响应[J]. 生态学报, 43(7): 2756-2769. |
| XIA C Y, GUO H, ZHAO J, et al., 2023. Dynamic response of ecosystem services to urbanization at muti-spatial scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(7): 2756-2769. | |
| [52] | 许小明, 张晓萍, 何亮, 等, 2022. 黄土丘陵区不同恢复植被类型的固碳特征[J]. 环境科学, 43(11): 5263-5273. |
|
XU X M, ZHANG X P, HE L, et al., 2022. Carbon sequestration characteristics of different restored vegetation types in loess hilly region[J]. Environmental Science, 43(11): 5263-5273.
DOI URL |
|
| [53] |
杨艳, 周德成, 宫兆宁, 等, 2022. 基于植被生产力的黄土高原地区生态脆弱性及其控制因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(10): 1951-1958.
DOI |
| YANG Y, ZHOU D C, GONG Z N, et al., 2022. Ecological vulnerability and its drivers of the Loess Plateau based on vegetation productivity[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(10): 1951-1958. | |
| [54] |
叶璇, 康帅直, 赵永华, 等, 2022. 陕北黄土高原植被恢复与生态系统服务的时空关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(10): 2760-2768.
DOI |
| YE X, KANG S Z, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2022. The relationship between vegetation restoration and ecosystem services in Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33(10): 2760-2768. | |
| [55] | 余玉洋, 李晶, 周自翔, 等, 2022. 基于贝叶斯网络的生态系统服务空间格局优化——以泾河流域为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(4): 1268-1280. |
| YU Y Y, LI J, ZHOU Z X, et al., 2022. Spatial pattern optimization of ecosystem services based on Bayesian networks: A case study of Jinghe River Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography, 45(4): 1268-1280. | |
| [56] |
张静静, 朱文博, 朱连奇, 等, 2020. 伏牛山地区森林生态系统服务权衡/协同效应多尺度分析[J]. 地理学报, 75(5): 975-988.
DOI |
| ZHANG J J, ZHU W B, ZHU L Q, et al., 2020. Multi-scale analysis of forest ecosystem service trade-offs/synergies in Funiu Mountain region[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(5): 975-988. | |
| [57] | 赵清贺, 冀晓玉, 徐珊珊, 等, 2018. 河岸植被对坡面径流侵蚀产沙的阻控效果[J]. 农业工程学报, 34(13): 170-178. |
| ZHAO Q H, JI X Y, XU S S, et al., 2018. Effect of riparian vegetation on sediment yield by slope runoff erosion[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 34(13): 170-178. | |
| [58] |
左丽媛, 高江波, 2020. 基于地理探测器的喀斯特植被NPP定量归因[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(4): 686-694.
DOI |
| ZUO L Y, GAO J B, 2020. Quantitative attribution analysis of NPP in karst peak cluster depression based on geographical detector[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(4): 686-694. |
| [1] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [2] | 许静, 廖星凯, 甘崎旭, 周茅先. 基于MSPA与电路理论的黄河流域甘肃段生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 805-813. |
| [3] | 张平江, 党国锋. 基于MCR模型与蚁群算法的洮河流域生态安全格局构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 481-491. |
| [4] | 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225. |
| [5] | 朱锦维, 柯新利, 何利杰, 周婷, 王青, 任妍钰. 基于价值链理论的生态产品价值实现机制理论解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 421-428. |
| [6] | 付蓉, 武新梅, 陈斌. 城市地表温度空间分异及驱动因子差异性分析——以合肥市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 110-122. |
| [7] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [8] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| [9] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| [10] | 李梦华, 韩颖娟, 赵慧, 王云霞. 基于地理探测器的宁夏植被覆盖度时空变化特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1317-1325. |
| [11] | 李美娇, 何凡能, 赵彩杉, 杨帆. 全球历史LUCC数据集新疆地区耕地数据可靠性评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1215-1224. |
| [12] | 刘香华, 王秀明, 刘谞承, 张音波, 刘飘. 基于外溢生态系统服务价值的广东省生态补偿机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1024-1031. |
| [13] | 张恒宇, 孙树臣, 吴元芝, 安娟, 宋红丽. 黄土高原不同植被密度条件下土壤水、碳、氮分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 875-884. |
| [14] | 高思琦, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 聂桐, 郭欣伟, 党素珍, 李心宇, 李昊洋. 黄河源植被覆盖度变化及空间分布自然驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 429-439. |
| [15] | 赵锐, 詹梨苹, 周亮, 张军科. 地理探测联合地理加权岭回归的PM2.5驱动因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 307-317. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
