生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 556-566.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.013
郝金虎1,2( ), 韦玮1,2,*(
), 韦玮1,2,*( ), 李胜男1,2, 马牧源1,2, 李肖夏1,2, 杨洪国1,2, 姜琦宇1,2, 柴沛东1,2
), 李胜男1,2, 马牧源1,2, 李肖夏1,2, 杨洪国1,2, 姜琦宇1,2, 柴沛东1,2
收稿日期:2022-11-29
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
*韦玮(1972年生),女,副研究员,博士,研究方向为湿地遥感和湿地植物生态。E-mail: weiwei@caf.ac.cn作者简介:郝金虎(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为湿地遥感。E-mail: haojinhu0201@caf.ac.cn
基金资助:
HAO Jinhu1,2( ), WEI Wei1,2,*(
), WEI Wei1,2,*( ), LI Shengnan1,2, MA Muyuan1,2, LI Xiaoxia1,2, YANG Hongguo1,2, JIANG Qiyu1,2, CHAI Peidong1,2
), LI Shengnan1,2, MA Muyuan1,2, LI Xiaoxia1,2, YANG Hongguo1,2, JIANG Qiyu1,2, CHAI Peidong1,2
Received:2022-11-29
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
京津冀地区水资源严重短缺,已成为制约京津冀协同发展的瓶颈。明晰长时序地表水体时空变化特征及其影响因素,对该区域的水资源合理配置及构建协同发展生态安全格局具有重要意义。基于Google Earth Engine(GEE)云平台,综合利用多指数水体检测规则、线性斜率、多元线性回归和偏微分分解等方法,构建了京津冀地表水体高时空分辨率连续变化图谱,揭示了研究区及安固里淖、密云水库、白洋淀和北大港湿地4个典型区的地表水体时空分异规律,厘定了降水量、气温、潜在蒸散发、前一年水体面积、人类生产生活用水和和引水调水等因素对地表水体变化的影响量。结果表明,(1)1985-2021年京津冀地区水体面积整体呈先增加后减少趋势,永久性水体面积净增122.85 km2,季节性水体面积净增1788.95 km2。其中安固里淖和白洋淀水体面积呈减少趋势,密云水库和北大港湿地水体面积呈增加趋势。(2)京津冀地表水体空间分布特征整体表现为东部沿海和中部地区地表水资源较丰富,北部和南部地区相对匮乏,4个典型区水体转换幅度大,具有较强的空间异质性。(3)降水量、前一年水体面积、引水调水(其他因素)对京津冀地表水体变化起正向影响,气温、潜在蒸散发、农业用水、工业用水和生活用水均起负向影响作用,且非气象因素的影响作用整体大于气象因素,其中安固里淖和白洋淀水体面积减少主要受农业用水和水利工程建设等因素的负向影响。
中图分类号:
郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566.
HAO Jinhu, WEI Wei, LI Shengnan, MA Muyuan, LI Xiaoxia, YANG Hongguo, JIANG Qiyu, CHAI Peidong. GEE Based Evaluation of the Spatial-temporal Pattern and Drivers of Long-term Water Body in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 556-566.
| 数据 | 时间范围 | 空间分辨率 | 时间分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat5 TM | 1985-2012年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| Landsat7 ETM+ | 1999-2002年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| Landsat8 OLI | 2013-2021年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| SRTM | - | 30 m | - |
| 降水量、气温、潜在蒸散发 | 1985-2021年 | 0.5°×0.5° | 1 a |
| 农业、工业、生活用水 | 1996-2021年 | - | 1 a |
表1 数据参数介绍
Table 1 All the datasets used in this study
| 数据 | 时间范围 | 空间分辨率 | 时间分辨率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat5 TM | 1985-2012年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| Landsat7 ETM+ | 1999-2002年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| Landsat8 OLI | 2013-2021年 | 30 m | 16 d |
| SRTM | - | 30 m | - |
| 降水量、气温、潜在蒸散发 | 1985-2021年 | 0.5°×0.5° | 1 a |
| 农业、工业、生活用水 | 1996-2021年 | - | 1 a |

图2 1985―2021年京津冀地区Landsat影像有效观测次数的空间分布
Figure 2 Spatial distribution of effective observations of Landsat images in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 1985 to 2021
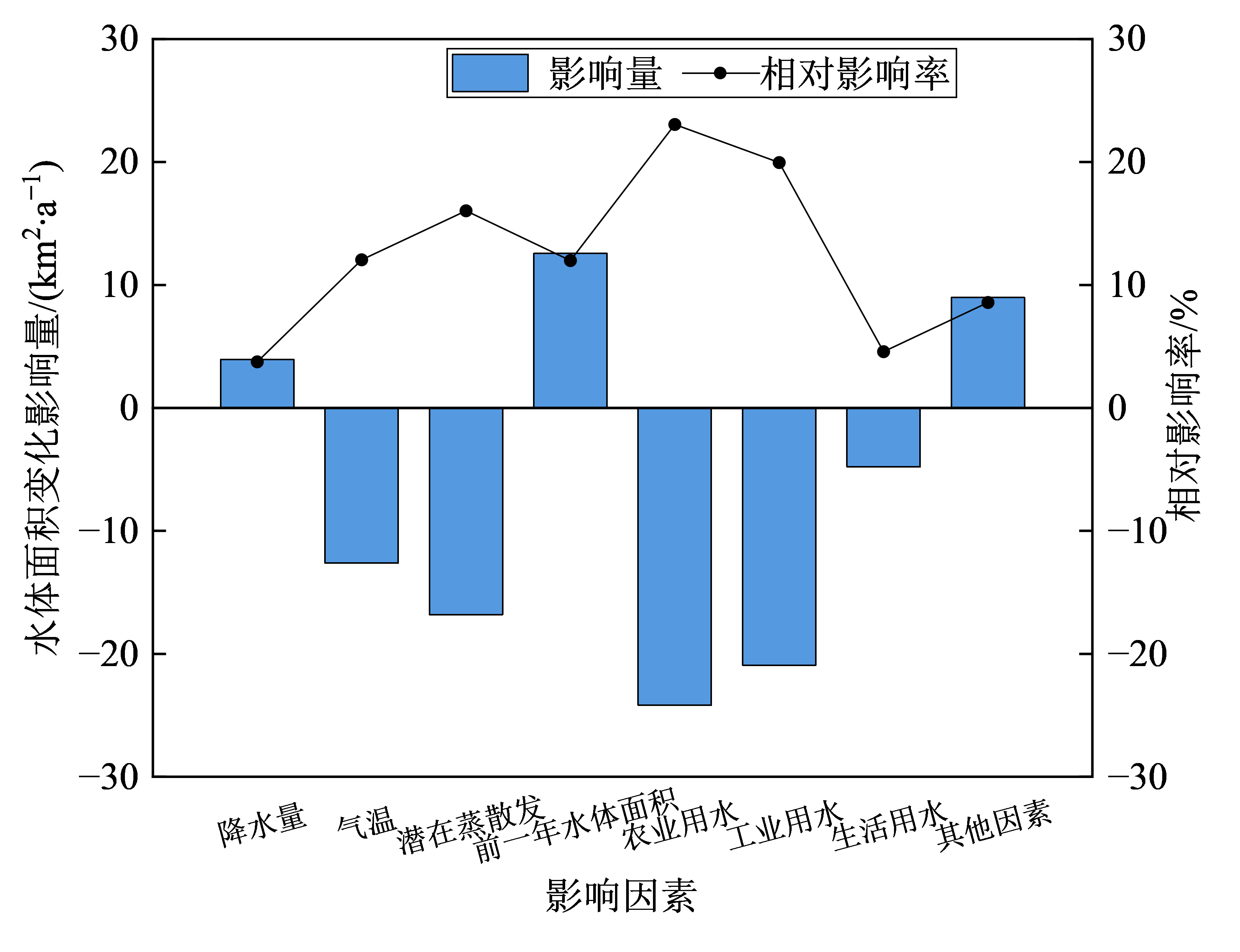
图10 各因素对京津冀地表水体面积变化的影响量和相对影响率
Figure 10 Impacts and relative influence rates of various factors on surface water area change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
| [1] |
DENG X Y, SONG C Q, LIU K, et al., 2020. Remote sensing estimation of catchment-scale reservoir water impoundment in the upper Yellow River and implications for river discharge alteration[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 585: 124791.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DENG Y W, JIANG W G, WU Z F, et al., 2022. Assessing surface water losses and gains under rapid urbanization for SDG 6.6.1 using long-term Landsat imagery in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(4): 881.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAO C, RUAN T, 2018. The influence of climate change and human activities on runoff in the middle reaches of the Huaihe River Basin, China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 28(1): 79-92.
DOI |
| [4] |
HARRIS I, OSBORN T J, JONES P, et al., 2020. Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset[J]. Scientific Data, 7(1): 1-18.
DOI |
| [5] |
HUANG Z, LIU J H, MEI C, et al., 2020. Analysis of driving forces of water demand in Jing-Jin-Ji district in recent years based on water demand field theory[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 63(12): 2593-2605.
DOI |
| [6] |
LI Y, YAO N, CHAU H W, 2017. Influences of removing linear and nonlinear trends from climatic variables on temporal variations of annual reference crop evapotranspiration in Xinjiang, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 592: 680-692.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MUTANGA O, KUMAR L, 2019. Google earth engine applications[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(5): 591.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
OLIPHANT A J, THENKABAIL P S, TELUGUNTLA P, et al., 2019. Mapping cropland extent of Southeast and Northeast Asia using multi-year time-series Landsat 30-m data using a random forest classifier on the Google Earth Engine Cloud[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 81: 110-124.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PEKEL J F, COTTAM A, GORELICK N, et al., 2016. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes[J]. Nature, 540(7633): 418-422.
DOI |
| [10] |
WANG C, JIA M M, CHEN N C, et al., 2018. Long-term surface water dynamics analysis based on Landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine platform: a case study in the middle Yangtze River Basin[J]. Remote Sensing, 10(10): 1635.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG X X, XIAO X M, ZOU Z H, et al., 2020. Gainers and losers of surface and terrestrial water resources in China during 1989-2016[J]. Nature Communications, 11(1): 1-12.
DOI |
| [12] |
WANG X Y, WANG W J, JIANG W G, et al., 2018. Analysis of the dynamic changes of the Baiyangdian Lake surface based on a complex water extraction method[J]. Water, 10(11): 1616.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WICKRAMAGAMAGE P, 2010. Seasonality and spatial pattern of rainfall of Sri Lanka: Exploratory factor analysis[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 30(8): 1235-1245.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG X, LIU L Y, WANG Y J, et al., 2018. A SPECLib-based operational classification approach: a preliminary test on China land cover mapping at 30 m[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 71: 83-94.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHOU Y, DONG J W, XIAO X M, et al., 2017. Open surface water mapping algorithms: A comparison of water-related spectral indices and sensors[J]. Water, 9(4): 256.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 成晨, 傅文学, 胡召玲, 等, 2015. 基于遥感技术的近30年中亚地区主要湖泊变化[J]. 国土资源遥感, 27(1): 146-152. |
| CHENG C, FU W X, HU Z L, et al., 2015. Changes of major lakes in Central Asia over the past 30 years revealed by remote sensing technology[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 27(1): 146-152. | |
| [17] | 崔亚莉, 王亚斌, 邵景力, 等, 2009. 南水北调实施后华北平原地下水调控研究[J]. 资源科学, 31(3): 382-387. |
| CUI Y L, WANG Y B, SHAO J L, et al., 2009. Research on groundwater regulation and recovery in North China Plain after the implementation of south-to-north water transfer[J]. Resources Science, 31(3): 382-387. | |
| [18] | 付颖, 徐新良, 通拉嘎, 等, 2014. 近百年来北京市地表水体时空变化特征及驱动力分析[J]. 资源科学, 36(1): 75-83. |
| FU Y, XU X L, TONG L G, et al., 2014. Spatial-temporal variation and driving forces of surface water in Beijing over one hundred years[J]. Resources Science, 36(1): 75-83. | |
| [19] | 郭旭宁, 郦建强, 李云玲, 等, 2022. 京津冀地区水资源空间均衡评价及调控措施[J]. 水资源保护, 38(1): 62-66, 81. |
| GUO X N, LI J Q, LI Y L, et al., 2022. Water resources spatial equilibrium evaluation and regulation measures in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[J]. Water Resources Protection, 38(1): 62-66, 81. | |
| [20] | 韩会然, 杨成凤, 宋金平, 2015. 北京市土地利用变化特征及驱动机制[J]. 经济地理, 35(5): 148-154, 197. |
| HAN H R, YANG C F, SONG J P, 2015. The spatial-temporal characteristic of land use change in Beijing and its driving mechanism[J]. Economic Geography, 35(5): 148-154, 197. | |
| [21] | 胡云峰, 商令杰, 张千力, 等, 2018. 基于GEE平台的1990年以来北京市土地变化格局及驱动机制分析[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 33(4): 573-583. |
| HU Y F, SHANG L J, ZHANG Q L, et al., 2018. Land change patterns and driving mechanism in Beijing since 1990 based on GEE platform[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33(4): 573-583. | |
| [22] | 焦晨泰, 宋世雄, 黄庆旭, 等, 2021. 基于Google Earth Engine平台的官厅水库流域开放水体动态研究[J]. 北京师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 57(5): 639-647. |
| JIAO C T, SONG S X, HUANG Q X, et al., 2021. Dynamics of open-surface water in Guanting Reservoir basin: A Google Earth Engine platform study[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University, 57(5): 639-647. | |
| [23] |
李崇巍, 王志慧, 汤秋鸿, 等, 2022. 1986―2019年黄河流域地表水体动态变化及其影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 77(5): 1153-1168.
DOI |
|
LI C W, WANG Z H, TANG Q H, et al., 2022. Dynamics of surface water area in the Yellow River Basin and its influencing mechanism during 1986-2019 based on Google Earth Engine[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(5): 1153-1168.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 李强, 刘剑锋, 李小波, 等, 2016. 京津冀土地承载力空间分异特征及协同提升机制研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 32(1): 105-111. |
| LI Q, LIU J F, LI X B, et al., 2016. Study on spatial differentiation characteristic and collaboration enhancement mechanism of land carrying capacity in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Geography and geo-information science, 32(1): 105-111. | |
| [25] | 李英华, 崔保山, 杨志峰, 2004. 白洋淀水文特征变化对湿地生态环境的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 19(1): 62-68. |
|
LI Y H, CUI B S, YANG Z F, 2004. Influence of hydrological characteristic change of Baiyangdian on the ecological environment in wetland[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 19(1): 62-68.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 吕金霞, 蒋卫国, 王文杰, 等, 2018. 近30年来京津冀地区湿地景观变化及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报, 38(12): 4492-4503. |
| LÜ J X, JIANG W G, WANG W J, et al., 2018. Wetland landscape pattern change and its driving forces in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in recent 30 years[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(12): 4492-4503. | |
| [27] | 马振刚, 李黎黎, 艾立志, 2015. 1978―2013年官厅水库面积变化的时空分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 32(3): 428-434. |
| MA Z G, LI L L, AI L Z, 2015. Spatial and temporal analysis of Guanting Reservoir area change from 1978 to 2013[J]. Arid Zone Research, 32(3): 428-434. | |
| [28] |
王利伟, 冯长春, 2016. 转型期京津冀城市群空间扩展格局及其动力机制-基于夜间灯光数据方法[J]. 地理学报, 71(12): 2155-2169.
DOI |
|
WANG L W, FENG C C, 2016. Spatial expansion pattern and its driving dynamics of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region: Based on nighttime light data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 71(12): 2155-2169.
DOI |
|
| [29] | 叶许春, 张奇, 刘健, 等, 2009. 气候变化和人类活动对鄱阳湖流域径流变化的影响研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 31(5): 835-842. |
| YE X C, ZHANG Q, LIU J, et al., 2009. Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff change in Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 31(5): 835-842. | |
| [30] | 张超, 2010. 基于GIS干旱风险评估与区划方法研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学: 1-105. |
| ZHANG C, 2010. Research on drought risk assessment and regionalization based on GIS[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Normal University: 1-105. | |
| [31] | 张恒, 陶胜利, 唐志尧, 等, 2020. 近30年京津冀地区湖泊面积的变化[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 56(2): 324-330. |
| ZHANG H, TAO S L, TANG Z Y, et al., 2020. Lake area changes in Jing-Jin-Ji region in recent 30 years[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 56(2): 324-330. | |
| [32] | 张敏, 宫兆宁, 赵文吉, 等, 2016. 近30年来白洋淀湿地景观格局变化及其驱动机制[J]. 生态学报, 36(15): 4780-4791. |
| ZHAO M, GONG Z N, ZHAO W J, et al., 2016. Landscape pattern change and the driving forces in Baiyangdian wetland from 1984 to 2014[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(15): 4780-4791. | |
| [33] | 张盛, 王铁宇, 张红, 等, 2017. 多元驱动下水生态承载力评价方法与应用——以京津冀地区为例[J]. 生态学报, 37(12): 4159-4168. |
| ZHANG S, WANG T Y, ZHANG H, et al., 2017. Using a multivariate-driven model to evaluate water ecological carrying capacity: Method-building and application in the Beijing-Tianjin-Ji (Hebei Province) region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(12): 4159-4168. | |
| [34] | 朱金峰, 周艺, 王世新, 等, 2019. 1975年―2018年白洋淀湿地变化分析[J]. 遥感学报, 23(5): 971-986. |
| ZHU J F, ZHOU Y, WANG S X, et al., 2019. Analysis of changes of Baiyangdian wetland from 1975 to 2018 based on remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(5): 971-986. | |
| [35] | 祝鹏, 2020. 基于多源遥感数据的京津冀地区地表水体提取方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院: 1-70. |
| ZHU P, 2020. Study on surface water extraction method in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region-based on multi-source remote sensing data[D]. Beijing: China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research: 1-70. | |
| [36] | 周岩, 2021. 基于遥感云计算的典型农牧区水资源变化监测及归因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学: 1-168. |
| ZHOU Y, 2021. Monitoring of water resources changes in typical agricultural and pastoral regions and driver analyses based on remote sensing cloud computing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 1-168. |
| [1] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [2] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [3] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [4] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [5] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [6] | 孙正, 曹亚非, 王德彩, 刘峰, 宋效东, 张甘霖, 吴华勇. 近30年京津冀电镀场地时空演变特征及趋势预测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 183-194. |
| [7] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [8] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [9] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [10] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [11] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [12] | 陈文裕, 夏丽华, 徐国良, 余世钦, 陈行, 陈金凤. 2000—2020年珠江流域NDVI动态变化及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1306-1316. |
| [13] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [14] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 邹佳何, 孟海, 赵晗, 崔雪, 董齐琪. 长白山北坡云冷杉阔叶混交林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 663-669. |
| [15] | 刘沙沙, 陈诺, 杨晓茵. 微塑料对有机污染物的吸附-解吸特性及其复合毒性效应研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 610-620. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
