生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 567-578.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.014
收稿日期:2022-06-27
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
*刘安,女,副教授,研究方向为水环境治理及雨水回用研究。E-mail: liuan@szu.edu.cn作者简介:何贝贝(1991年生),女,博士后,主要从事城市水环境中新型污染物研究工作。E-mail: beibei.he@szu.edu.cn
基金资助:
HE Beibei1,2( ), FAN Shanshan2, HONG Nian3, LIU An2,*(
), FAN Shanshan2, HONG Nian3, LIU An2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-27
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
城市雨水作为一种可回用的新兴水源,近年来受到学者们的广泛关注。雨水在储存过程中存在水质变化和细菌复活的可能性,是保障雨水回用安全面临的最大风险因素之一。但目前关于不同储存方式下,雨水水质变化规律的研究仍十分有限。据此,以屋顶雨水为对象,采用大肠杆菌(E. coli)和金黄色葡萄球菌(S. aureus)作为雨水中典型病原微生物代表,探究了屋顶雨水在密封式和开放式两种不同储存方式下水质变化规律和细菌再生情况,以期为保障储存雨水的回用安全提供科学依据和技术指导。研究结果表明,尽管两种储存方式下的雨水水质参数变异性较大,但密封式储存下的雨水由于受外界环境的干扰低,因此水质波动变化较开放式储存小。具体表现为密封式储存条件下,水质指标如UV254、TOC、浊值度及NH4+-N等参数随储存时间的延长呈降低趋势。然而,从细菌复活情况来看,密封式储存下雨水具有更高的细菌复活率,且金黄色葡萄球菌相比大肠杆菌显著复活。因此,为了确保雨水回用安全性,有必要考虑不同储存方式对水质和细菌生长的影响,以及细菌种类对水质变化的影响,以此采取针对性的措施对储存雨水进行再次处理。
中图分类号:
何贝贝, 范珊珊, 洪念, 刘安. 不同储存方式下屋顶雨水水质特性变化规律研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 567-578.
HE Beibei, FAN Shanshan, HONG Nian, LIU An. Variations of Roof Stormwater Quality under Different Storage Types[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 567-578.
| 项目 | 水质指标 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 吸光度 (UV254)/ cm-1 | ρ(NH4+-N )/ (mg·L-1) | 浊度/ NTU | ρ(TOC)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(DO)/ (mg·L-1) | |
| 测定值 | 7.02 | 0.0240 | 0.530 | 0.380 | 2.55 | 7.58 |
表1 屋顶雨水的原始水质情况
Table 1 Roof original stormwater quality
| 项目 | 水质指标 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 吸光度 (UV254)/ cm-1 | ρ(NH4+-N )/ (mg·L-1) | 浊度/ NTU | ρ(TOC)/ (mg·L-1) | ρ(DO)/ (mg·L-1) | |
| 测定值 | 7.02 | 0.0240 | 0.530 | 0.380 | 2.55 | 7.58 |
| 检测指标 | 密封式储存 | 开放式储存 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 包含大肠杆菌的 雨水样品 | 包含金黄色葡萄球菌的雨水样品 | 包含大肠杆菌的 雨水样品 | 包含金黄色葡萄球菌的 雨水样品 | ||
| pH | 6.75 | 6.64 | 7.15 | 7.56 | |
| 吸光度(UV254)/cm-1 | 0.055 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.087 | |
| 浊度/NTU | 1.13 | 1.46 | 2.13 | 3.56 | |
| ρ(NH4+-N )/(mg·L-1) | 1.44 | 2.96 | 1.05 | 2.19 | |
| ρ(TOC)/(mg·L-1) | 4.09 | 6.19 | 6.40 | 9.94 | |
| ρ(DO)/(mg·L-1) | 7.95 | 7.73 | 7.99 | 7.90 | |
| 大肠杆菌菌落总数 E. coli/(CFU·mL-1) | 5.72×104 | - | 9.34×103 | - | |
| 金黄色葡萄球菌菌落总数S. aureus/(CFU·mL-1) | - | 8.68×104 | - | 2.59×104 | |
表2 大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌屋顶雨水样品水质参数比较
Table 2 Comparison of roof stormwater quality parameters including E. coli and S. aureus
| 检测指标 | 密封式储存 | 开放式储存 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 包含大肠杆菌的 雨水样品 | 包含金黄色葡萄球菌的雨水样品 | 包含大肠杆菌的 雨水样品 | 包含金黄色葡萄球菌的 雨水样品 | ||
| pH | 6.75 | 6.64 | 7.15 | 7.56 | |
| 吸光度(UV254)/cm-1 | 0.055 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.087 | |
| 浊度/NTU | 1.13 | 1.46 | 2.13 | 3.56 | |
| ρ(NH4+-N )/(mg·L-1) | 1.44 | 2.96 | 1.05 | 2.19 | |
| ρ(TOC)/(mg·L-1) | 4.09 | 6.19 | 6.40 | 9.94 | |
| ρ(DO)/(mg·L-1) | 7.95 | 7.73 | 7.99 | 7.90 | |
| 大肠杆菌菌落总数 E. coli/(CFU·mL-1) | 5.72×104 | - | 9.34×103 | - | |
| 金黄色葡萄球菌菌落总数S. aureus/(CFU·mL-1) | - | 8.68×104 | - | 2.59×104 | |
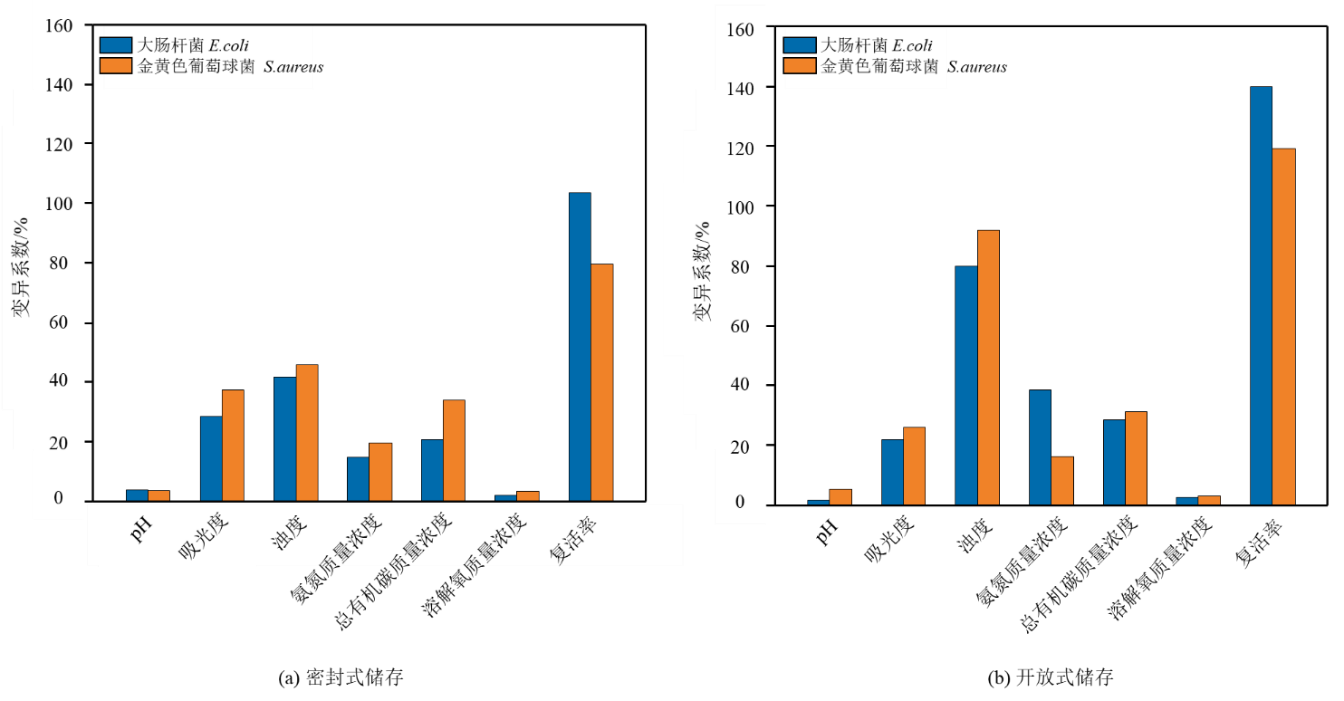
图10 不同储存方式中雨水样品水质参数和细菌复活率变异系数分析
Figure 10 Coefficient of variation (CV) analysis of stormwater quality and bacteria reactivation rate during different storage types
| [1] |
AHUMED W, BRANDES H, GYAWALI P, et al., 2014. Opportunistic pathogens in roof-captured rainwater samples, determined using quantitative PCR[J]. Water Research, 53: 361-369.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
AMIN M T, KIM T I, AMIN M N, et al., 2013. Effects of catchment, first-flush, storage conditions, and time on microbial quality in rainwater harvesting systems[J]. Water Environment Research, 85(12): 2317-2329.
PMID |
| [3] |
BEI E, LIAO X B, MENG X T, et al., 2016. Identification of nitrosamine precursors from urban drainage during storm events: A case study in southern China[J]. Chemosphere, 160: 323-331.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
CHARTES F J, COCHRANE T A, SULLIVAN A D, 2016. Untreated runoff quality from roof and road surfaces in a low intensity rainfall climate[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 550: 265-272.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DOBROWAKY P H, DEVENTER A, KWAADSTENIET D M, et al., 2014. Prevalence of virulence genes associated with pathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from domestically harvested rainwater during low- and high-rainfall periods[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(5): 1633-1638.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
EKANAYAKE D, ARYAL R, JOHIR M A, et al., 2019. Interrelationship among the pollutants in stormwater in an urban catchment and first flush identification using UV spectroscopy[J]. Chemosphere, 233: 245-251.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
FENG W J, MCARTHY D T, HENRY R, et al., 2018a. Electrochemical oxidation for stormwater disinfection: How does real stormwater chemistry impact on pathogen removal and disinfection by-products level?[J]. Chemosphere, 213: 226-234.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FENG W J, MCARTHY D T, WANG Z Y, et al., 2018b. Stormwater disinfection using electrochemical oxidation: A feasibility investigation[J]. Water Research, 140: 301-310.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GWENZI W, DUNJANA N, PISA C, et al., 2015. Water quality and public health risks associated with roof rainwater harvesting systems for potable supply: Review and perspectives[J]. Sustainability of Water Quality and Ecology, 6: 107-118.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HENNEKINNE J A, BUYSER D M L, DRAGACCI S, 2012. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation[J]. Fems Microbiology Reviews, 36(4): 815-836.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LEE J Y, YANG J S, HAN M, et al., 2010. Comparison of the microbiological and chemical characterization of harvested rainwater and reservoir water as alternative water resources[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 408(4): 896-905.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MA Y K, WANG S H, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2021. Transport process and source contribution of nitrogen in stormwater runoff from urban catchments[J]. Environmental Pollution, 289: 117824.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MAO J, XIA B Y, ZHOU Y, et al., 2021. Effect of roof materials and weather patterns on the quality of harvested rainwater in Shanghai, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 279(Part 2): 123419.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
POLYKOVA O V, ARTAEV V B, LEBEDEV A T, 2018. Priority and emerging pollutants in the Moscow rain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 645: 1126-1134.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SCHANG C, SCHMIDT J, GAO L, et al., 2021. Rainwater for residential hot water supply: Managing microbial risks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 782: 146889.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SHANG C, BLATCHELEY E R, 2001. Chlorination of pure bacterial cultures in aqueous solution[J]. Water Research, 35(1): 244-254.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
SIDHU J P, HODGERS L, AHMED W, et al., 2012. Prevalence of human pathogens and indicators in stormwater runoff in Brisbane, Australia[J]. Water Research, 46(20): 6652-6660.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
SIMMONS G, JURY S, THORNLEY C, et al., 2008. A Legionnaires' disease outbreak: a water blaster and roof-collected rainwater systems[J]. Water Research, 42(6-7): 1449-1458.
PMID |
| [19] |
WANG S, HE Q, AI H, et al., 2013. Pollutant concentrations and pollution loads in stormwater runoff from different land uses in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(3): 502-510.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 高玉婵, 金星龙, 赵乐军, 等, 2019. 屋面径流污染特性及回用分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电 (10): 38-41, 46. |
| GAO Y C, JIN X L, ZHAO L J, et al., 2019. Runoff pollution characteristics of SBS roof[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower (10): 38-41, 46. | |
| [21] |
冯萃敏, 米楠, 王晓彤, 等, 2015. 基于雨型的南方城市道路雨水径流污染物分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(3): 418-426.
DOI |
| FENG C M, MI N, WANG X T, et al., 2015. Analysis of road runoff pollutants in northern city based on the typical rainfall[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(3): 418-426. | |
| [22] |
李倩倩, 李铁龙, 赵倩倩, 等, 2011. 天津市路面雨水径流重金属污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(1): 143-148.
DOI |
| LI Q Q, LI T L, ZHAO Q Q, et al., 2011. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in road rainfall-runoff of Tianjin city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(1): 143-148. | |
| [23] | 林鑫, 王宾, 张富家, 等, 2021. 城市屋面雨水径流水质特征分析[J]. 科技创新与应用, 338(10): 54-56. |
| LIN X, WANG B, ZHANG F J, et al., 2021. Analysis of water quality characteristics of urban roof rainwater runoff[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 338(10): 54-56. | |
| [24] | 仇锦先, 2003. 江苏省淮北丘陵山区雨水集蓄利用灌溉最优化研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学. |
| QIU J X, 2003. Research on the optimization of rainwater harvesting, storage and utilization in the hilly and mountainous areas of Huaibei, Jiangsu Province[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University. | |
| [25] | 王大乐, 2007. 城市园林绿地中雨水利用的景观化探讨[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| WANG D L, 2007. Landscape discussion on rainwater utilization in urban garden green space[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [26] | 肖龙, 甘春娟, 陈颖, 等, 2020. 电化学氧化技术在雨水消毒中的研究进展[J]. 工业用水与废水, 51(4): 6-10, 33. |
| XIAO L, GAN C J, CHEN Y, et al., 2021. Research progress of electrochemical oxidation technology used for rainwater disinfection[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 51(4): 6-10, 33. | |
| [27] | 许秀泉, 2014. 黄土区微型蓄雨设施水体水质变化及对饮水安全影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院 (教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心). |
| XU X Q, 2014. Changes in water quality of micro-rain storage facilities in loess area and its impact on drinking water safety[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [28] | 徐宇婕, 龚玥敏, 毕军鹏, 等, 2020. 宁波市典型城市下垫面雨水径流污染特征解析[J]. 环境科学, 41(7): 3275-3284. |
| XU Y J, GONG YM, BI J P, et al., 2020. Analysis of rainwater runoff pollution characteristics of various typical underlying surfaces in Ningbo[J]. Environmental Science, 41(7): 3275-3284. | |
| [29] | 杨波, 2009. 城市污水再生利用紫外线消毒试验研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学. |
| YANG B, 2009. Experimental study on ultraviolet disinfection of urban sewage recycling and utilization[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology. | |
| [30] | 张科峰, 李贺, 傅大放, 等, 2011. 三种不同屋面雨水径流重金属污染特性及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 31(4): 724-730. |
| ZHANG K F, LI H, FU D F, et al., 2011. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in runoff from three different types of roofs[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(4): 724-730. | |
| [31] |
张娜, 赵乐军, 李铁龙, 等, 2009. 天津城区道路雨水径流水质监测及污染特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 18(6): 2127-2131.
DOI |
| ZHANG N, ZHAO L J, LI T L, et al., 2009. Characteristics of pollution and monitoring of water quality in Tianjin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(6): 2127-2131. | |
| [32] | 张伟, 罗乙兹, 钟兴, 等, 2019. 北京市中心城区某沥青屋面和金属屋面径流污染特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 19(23): 358-365. |
| ZHANG W, LUO Y Z, ZHONG X, et al., 2019. Characteristics of runoff pollution in asphalt roof and metal roof in downtown Beijing[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(23): 358-365. |
| [1] | 雷雅杰, 李雪, 常春艳, 毛雪飞. 聚苯乙烯微塑料对水中汞离子的吸附研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2048-2057. |
| [2] | 汤家喜, 向彪, 李玉, 谭婷, 朱永乐, 甘建平. 硅藻土对水中氟化物的吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 335-343. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
