生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 469-480.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.005
何艳虎1,2,*( ), 龚镇杰1, 吴海彬1, 蔡宴朋1,2, 杨志峰1,2, 陈晓宏3
), 龚镇杰1, 吴海彬1, 蔡宴朋1,2, 杨志峰1,2, 陈晓宏3
收稿日期:2022-04-22
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
*何艳虎作者简介:何艳虎(1985年生),男,教授,博士,研究方向为水文模拟与水资源合理配置。E-mail: heyanhu456@gdut.edu.cn
基金资助:
HE Yanhu1,2,*( ), GONG Zhenjie1, WU Haibin1, CAI Yanpeng1,2, YANG Zhifeng1,2, CHEN Xiaohong3
), GONG Zhenjie1, WU Haibin1, CAI Yanpeng1,2, YANG Zhifeng1,2, CHEN Xiaohong3
Received:2022-04-22
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
城市生态效率是反映城市发展水平和质量的重要指标,也是绿色可持续发展与生态文明建设成果的重要体现。粤港澳大湾区是中国经济最活跃地区和重要增长极,人口聚集、产业发达,拥有媲美世界一流湾区的优越条件以及成为世界一流城市群的潜力。基于粤港澳大湾区城市2006-2018年面板统计数据,运用Super-SBM模型对湾区城市生态效率值进行测算与评价,结合ArcGIS空间分析方法揭示湾区城市生态效率的时空演变特征,并通过定义空间权重矩阵和构建空间误差模型来识别湾区城市生态效率的主要影响因素。结果表明:(1)湾区城市生态效率在2006-2018年期间均值为1.557,处于中等偏下水平,仍有较大提升空间;(2)湾区城市生态效率区域差异较大,就各城市生态效率均值来看,香港、澳门与深圳大于2,广州、佛山与珠海在1-2之间,东莞、惠州、江门、肇庆与中山小于湾区平均值;(3)香港、澳门、深圳等高生态效率城市对邻接地区产生较强的辐射效应,肇庆、东莞、中山、惠州、江门等低生态效率城市邻接地区的城市生态效率也低。总体上,湾区城市生态效率整体呈现先下降、后上升的趋势,绝大部分处于中低水平,且存在显著的全局空间聚集效应;科学技术支出、人均GDP和利用外资情况是湾区城市生态效率时空演变的主要影响因素,三者对城市生态效率的作用从强到弱,科学技术支出与湾区城市生态效率呈现正相关。研究成果可为制定针对性的湾区城市生态效率提升策略提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480.
HE Yanhu, GONG Zhenjie, WU Haibin, CAI Yanpeng, YANG Zhifeng, CHEN Xiaohong. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban Eco-efficiency and Its Influencing Factors in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 469-480.
| 指标 | 变量 | 变量说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源投入 | 土地投入 | 城市建设用地/km2 |
| 用水投入 | 城市用水总量/(104 t) | |
| 用电投入 | 全社会用电量/(104 kW∙h) | |
| 用气投入 | 液化石油气供气总量/(104 t) | |
| 社会投入 | 劳动投入 | 单位从业人员期末人数/万人 |
| 资本投入 | 固定资产投资总额/万元 | |
| 期望产出 | 经济产出 | 地区生产总值万元/万元 |
| 非期望产出 | 废水排放 | 工业废水排放总量/(104 t) |
| 废气排放 | 工业二氧化硫排放总量/(104 t) | |
| 固废排放 | 工业固废未利用率/% |
表1 城市生态效率指标体系
Table 1 The index system of urban eco-efficiency
| 指标 | 变量 | 变量说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源投入 | 土地投入 | 城市建设用地/km2 |
| 用水投入 | 城市用水总量/(104 t) | |
| 用电投入 | 全社会用电量/(104 kW∙h) | |
| 用气投入 | 液化石油气供气总量/(104 t) | |
| 社会投入 | 劳动投入 | 单位从业人员期末人数/万人 |
| 资本投入 | 固定资产投资总额/万元 | |
| 期望产出 | 经济产出 | 地区生产总值万元/万元 |
| 非期望产出 | 废水排放 | 工业废水排放总量/(104 t) |
| 废气排放 | 工业二氧化硫排放总量/(104 t) | |
| 固废排放 | 工业固废未利用率/% |
| 检验方法 | 统计值 |
|---|---|
| R2检验 | 0.968 |
| F检验 | 24.0 |
| 样本均值检验 | 1.52 |
| LM-lag检验 | 1.06 |
| LM-error检验 | 1.90 |
| 校正决定系数检验 | 0.956 |
| F统计量的P值检验 | 1.66×10-3 |
| 样本标准误差检验 | 1.32 |
| R-LMlag检验 | 0.137 |
| R-LMerr检验 | 1.70 |
表2 空间计量模型模拟效果
Table 2 The simulation effect of the spatial econometric model
| 检验方法 | 统计值 |
|---|---|
| R2检验 | 0.968 |
| F检验 | 24.0 |
| 样本均值检验 | 1.52 |
| LM-lag检验 | 1.06 |
| LM-error检验 | 1.90 |
| 校正决定系数检验 | 0.956 |
| F统计量的P值检验 | 1.66×10-3 |
| 样本标准误差检验 | 1.32 |
| R-LMlag检验 | 0.137 |
| R-LMerr检验 | 1.70 |
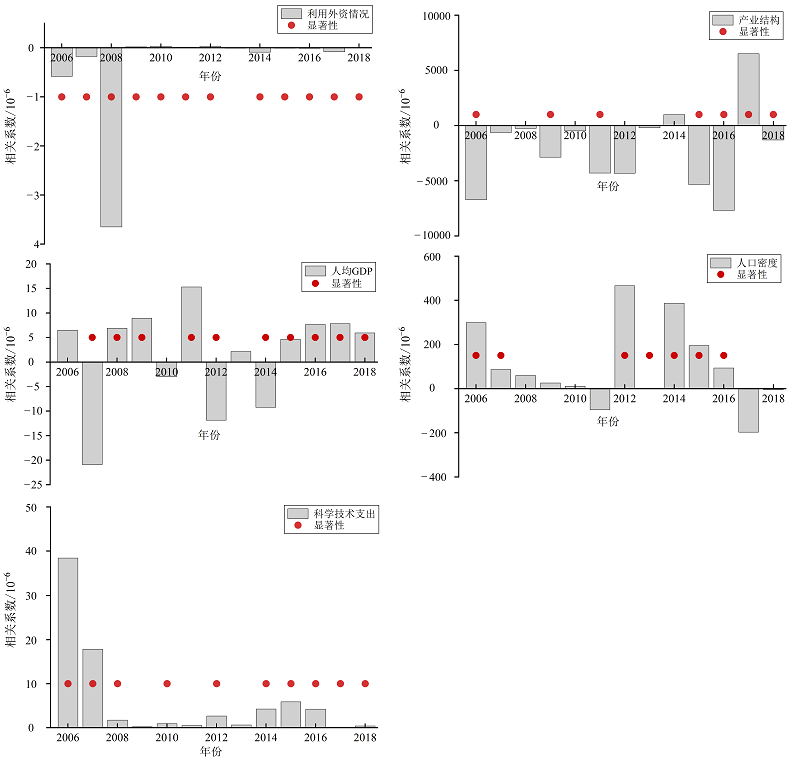
图7 2006-2018年粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率空间计量模型回归结果
Figure 7 The regression results of the spatial econometric model of the urban eco-efficiency in the GD-HK-MA GBA from 2006 to 2018
| [1] |
HE Y H, TANG C C, WANG Z R, 2021. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of sewage treatment plants in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 792: 148430.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SONG C C, SUN C G, XU J H, et al., 2022. Establishing coordinated development index of urbanization based on multi-source data: A case study of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 140: 109030.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
TONE K, 2001. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 130(3): 498-509.
DOI URL |
| [4] | WBCSD, 1996. Eco-efficiency leadership for improved economic environmental performance[M]. World Business Council for Sustainable Development: 4-5. |
| [5] |
ZHANG P, XIE Y L, WANG Y Y, et al., 2021. Water-Energy-Food system in typical cities of the world and China under zero-waste: Commonalities and asynchronous experiences support sustainable development[J]. Ecological Indicators, 132: 108221.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 蔡文博, 韩宝龙, 逯非, 等, 2020. 全球四大湾区生态环境综合评价研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8392-8402. |
| CAI W B, HAN B L, LU F, et al., 2020. Comprehensive evaluation of the eco-environment in the four global bay areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 4(23): 8392-8402. | |
| [7] | 陈浩, 陈平, 罗艳, 2015. 基于超效率DEA模型的中国资源型城市生态效率评价[J]. 大连理工大学学报 (社会科学版), 36(2): 34-40. |
| CHEN H, CHEN P, LUO Y, 2015. Eco-efficiency assessment of resource-based cities of China based on super-efficiency DEA model[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology (Social Sciences), 36(2): 34-40. | |
| [8] | 陈明华, 王山, 刘文斐, 2020. 黄河流域生态效率及其提升路径——基于100个城市的实证研究[J]. 中国人口科学 (4): 46-58, 127. |
| CHEN M H, WANG S, LIU W F, 2020. Eco-efficiency and Its Promotion in the Yellow River Basin: Empirical Evidence from 100 Cities[J]. Chinese Journal of Population Science (4): 46-58, 127. | |
| [9] | 邓志新, 2018. 粤港澳大湾区与世界著名湾区经济的比较分析[J]. 对外经贸实务 (4): 92-95. |
| DENG Z X, 2018. A comparative analysis of the economy of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and the world-famous bay area[J]. Practice in Foreign Economic Relations and Trade (4): 92-95. | |
| [10] | 傅崇辉, 傅愈, 钟柳青, 等, 2022. 粤港澳大湾区人口、经济与环境协同的影响机制研究[J]. 生态经济, 38(2): 158-167. |
| FU C H, FU Y, ZHONG L Q, et al., 2022. The Mechanism of Population, Economy and Environment Synergy in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Ecological Economy, 38(2): 158-167. | |
| [11] | 苟登文, 宫清华, 陈爱兵, 等, 2022. 粤港澳大湾区生态协同治理策略研究综述[J]. 生态科学, 41(2): 249-258. |
| GOU D W, GONG Q H, CHEN A B, et al., 2022. A review of ecological coordination governance strategies in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Ecological Science, 41(2): 249-258. | |
| [12] | 郭国强, 2013. 空间计量模型的理论和应用研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学:26. |
| GUO G Q, 2013. The theoretical and applied research of spatial econometric model[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology:26. | |
| [13] | 高真, 黄本胜, 邱静, 等, 2020. 粤港澳大湾区水安全保障存在的问题及对策研究[J]. 中国水利 (11): 6-9. |
| GAO Z, HUANG B S, QIU J, et al., 2020. Research on the water security issues and suggestions in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. China Water Resources (11): 6-9. | |
| [14] | 韩燕, 邓美玲, 2020. 中原城市群生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 40(14): 4774-4784. |
| HAN Y, DENG M L, 2020. Spatio-temporal evolution of eco-efficiency and influencing factors of central plains urban agglomeration[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(14): 4774-4784. | |
| [15] | 侯孟阳, 姚顺波, 2018. 中国城市生态效率测定及其时空动态演变[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 28(3): 13-21. |
| HOU M Y, YAO S B, 2018. Measurement and temporal-spatial dynamic evolution of urban eco-efficiency in China[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 28(3): 13-21. | |
| [16] | 胡彪, 付业腾, 2016. 中国生态效率测度与空间差异实证基于SBM模型与空间自相关性的分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 30(6): 6-12. |
| HU B, FU Y T, 2016. The measure and the spatial disparity analysis of eco-efficiency in China[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 30(6): 6-12. | |
| [17] |
黄德春, 杨哲成, 2020. 长江经济带环境污染治理投资对生态效率的影响研究[J]. 资源与产业, 22(3): 11-19.
DOI |
| HUANG D C, YANG Z C, 2020. Impacts of environmental pollution management investment on ecological efficiency in Yangtze River economic zone[J]. Resources & Industries, 22(3): 11-19. | |
| [18] | 黄和平, 2015. 基于生态效率的江西省循环经济发展模式[J]. 生态学报, 35(9): 2894-2901. |
| HUANG H P, 2015. Eco-efficiency on the circular economy development pattern in Jiangxi province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(9): 2894-2901. | |
| [19] | 李嘉琪, 黄凤莲, 刘挺, 等, 2020. 长江经济带城市生态效率时空格局及驱动因子探测[J]. 人民长江, 51(5): 1-6. |
| LI J Q, HUANG F L, LIU T, et al., 2020. Temporal and spatial patterns and driving factors of urban ecological efficiency in Yangtze River economic belt[J]. Yangtze River, 51(5): 1-6. | |
| [20] | 刘毅, 王云, 李宏, 2020. 世界级湾区产业发展对粤港澳大湾区建设的启示[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(3): 312-321. |
| LIU Y, WANG Y, LI H, 2020. Industrial development of world-class bay areas and its enlightenment to the guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(3): 312-321. | |
| [21] |
卢燕群, 袁鹏, 2017. 中国省域工业生态效率及影响因素的空间计量分析[J]. 资源科学, 39(7): 1326-1337.
DOI |
|
LU Y Q, YUAN P, 2017. Measurement and spatial econometrics analysis of provincial industrial ecological efficiency in China[J]. Resources Science, 39(7): 1326-1337.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 牛君, 2007. 基于非参数密度估计点样本分析建模的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学:24. |
| NIU J, 2007. Application study based on point sample analysis and modeling using nonparametric density estimation[D]. Ji'nan: Shandong University:24. | |
| [23] | 潘兴侠, 2014. 我国区域生态效率评价、影响因素及收敛性研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学:87. |
| PAN X X, 2014. Study on evaluation, influencing factors and convergence of regional eco-efficiency of China[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University:87. | |
| [24] | 彭薇, 熊科, 2018. 环境压力视角的广东省市域生态效率综合评价[J]. 经济地理, 38(8): 179-186. |
| PENG W, XIONG K, 2018. Ecological efficiency evaluation and spatial evolution of Guangdong province from the perspective of environmental pressure[J]. Economic Geography, 38(8): 179-186. | |
| [25] | 屈文波, 2018. 中国区域生态效率的时空差异及驱动因素[J]. 华东经济管理, 32(3): 59-66. |
| QU W B, 2018. Spatio-temporal differences and driving factors of regional ecological efficiency in China[J]. East China Economic Management, 32(3): 59-66. | |
| [26] | 屈小娥, 2018. 中国生态效率的区域差异及影响因素——基于时空差异视角的实证分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(12): 2673-2683. |
| QU X E, 2018. Regional differentials and influence factors of eco-efficiency in China: An empirical analysis based on the perspective of spatio-temporal differences[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(12): 2673-2683. | |
| [27] | 任红霞, 2019. 基于DEA模型的农业生态效率综合测度[J]. 统计与决策, 35(6): 99-103. |
| REN H X, 2019. Comprehensive measurement of agricultural eco-efficiency based on DEA model[J]. Statistics & Decision, 35(6): 99-103. | |
| [28] |
任宇飞, 方创琳, 蔺雪芹, 2017. 中国东部沿海地区四大城市群生态效率评价[J]. 地理学报, 72(11): 2047-2063.
DOI |
|
REN Y F, FANG C L, LIN X Q, 2017. Evaluation of eco-efficiency of four major urban agglomerations in eastern coastal area of China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(11): 2047-2063.
DOI |
|
| [29] | 孙欣, 赵鑫, 宋马林, 2016. 长江经济带生态效率评价及收敛性分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报 (社会科学版), 15(5): 1-10. |
| SUN X, ZHAO X, SONG M L, 2016. Evaluation of ecological efficiency and convergence of the Yangtze River economic belt from the perspective of coordinated development[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University (Social Science Edition), 15(5): 1-10. | |
| [30] |
田鹏, 汪浩翰, 李加林, 等, 2021. 东海海岸带县域城市生态效率评价及影响因素[J]. 地理研究, 40(8): 2347-2366.
DOI |
|
TIAN P, WANG H H, LI J L, et al., 2021. Eco-efficiency evaluation and influencing factors analysis of county-level cities in the east China Sea coastal zone[J]. Geographical Research, 40(8): 2347-2366.
DOI |
|
| [31] | 万斯斯, 李世杰, 张明空, 等, 2021. 河南省城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 地域研究与开发, 40(6): 51-56. |
| WAN S S, LI S J, ZHANG M K, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban eco-efficiency in Henan province[J]. Areal Research and Development, 40(6): 51-56. | |
| [32] |
王少剑, 崔子恬, 林靖杰, 等, 2021. 珠三角地区城镇化与生态韧性的耦合协调研究[J]. 地理学报, 76(4): 973-991.
DOI |
|
WANG S J, CUI Z T, LIN J J, et al., 2021. Coupling relationship between urbanization and ecological resilience in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(4): 973-991.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 温馨, 朱金勋, 高维新, 2020. 异质体制下粤港澳大湾区九市生态安全协同效率实证分析——基于PSR和GIS-DEA组合模型[J]. 生态经济, 36(4): 200-205. |
| WEN X, ZHU J X, GAO W X, 2020. Empirical analysis on cooperative efficiency of ecological security in nine cities of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area under the heterogeneous system: Based on PSR and GIS-DEA combined model[J]. Ecological Economy, 36(4): 200-205. | |
| [34] | 吴盼, 赵信文, 顾涛, 等, 2021. 粤港澳大湾区水资源现状及其与社会经济协同演化趋势——与国际湾区对比研究[J]. 中国地质, 48(5): 1357-1367. |
| WU P, ZHAO X W, GU T, et al., 2021. Water resources in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and its co-evolution trend with social economy: A comparative study with the international bay area[J]. Geology in China, 48(5): 1357-1367. | |
| [35] | 吴小庆, 王亚平, 何丽梅, 等, 2012. 基于AHP和DEA模型的农业生态效率评价——以无锡市为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 6(21): 714-719. |
| WU X Q, WANG Y P, HE L M, et al., 2012. Agricultural eco-efficiency evaluation based on AHP and DEA model: A Case of Wuxi City[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 6(21): 714-719. | |
| [36] | 吴玉鸣, 徐建华, 2004. 中国区域经济增长集聚的空间统计分析[J]. 地理科学, 24(6): 654-659. |
| WU Y M, XU J H, 2004. A spatial analysis on China's regional economic growth clustering[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 24(6): 654-659. | |
| [37] |
徐维祥, 郑金辉, 王睿, 等, 2022. 黄河流域城市生态效率演化特征及门槛效应[J]. 地理科学, 42(1): 74-82.
DOI |
|
XU W X, ZHENG J H, WANG R, et al., 2022. The evolution characteristics and threshold effects of the ecological efficiency in the Yellow River basin cities[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 42(1): 74-82.
DOI |
|
| [38] |
闫涛, 张晓平, 赵艳艳, 2021. 基于超效率SBM模型的中国城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 38(4): 486-493.
DOI |
|
YAN T, ZHANG X P, ZHAO Y Y, 2021. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban eco-efficiency in china and its influencing factors based on super-efficiency SBM mode[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 38(4): 486-493.
DOI |
|
| [39] | 杨传明, 卓青青, 张莉莉, 2022. 新时代长三角城市群生态效率测度及影响因素研究[J]. 管理现代化, 42(1): 123-128. |
| YANG C M, ZHUO Q Q, ZHANG L L, 2022. Measurement and influencing factors of urban agglomeration of ecological efficiency in Yangtze River Delta in new era[J]. Modernization of Management, 42(1): 123-128. | |
| [40] | 曾庆敏, 陈忠暖, 2007. 基于GIS空间分析法的广东省经济发展区域差异[J]. 经济地理, 27(4): 558-561. |
| ZENG Q M, CHEN Z N, 2007. Research on the regional economic disparity in Guangdong province based on GIS spatial analysis[J]. Economic Geography, 27(4): 558-561. | |
| [41] | 张仁杰, 董会忠, 2020. 基于省级尺度的中国工业生态效率的时空演变及影响因素[J]. 经济地理, 40(7): 124-132. |
| ZHANG R J, DONG H Z, 2020. Spatial and temporal evolution and influencing factors of China's industrial eco-efficiency based on provincial scale[J]. Economic Geography, 40(7): 124-132. | |
| [42] |
郑慧, 贾姗, 赵昕, 2017. 新型城镇化背景下中国区域生态效率分析[J]. 资源科学, 39(7): 1314-1325.
DOI |
|
ZHENG H, JIA S, ZHAO X, 2017. An Analysis of regional eco-efficiency in China under the background of new-type urbanization[J]. Resources Science, 39(7): 1314-1325.
DOI |
|
| [43] |
周春山, 罗利佳, 史晨怡, 等, 2017. 粤港澳大湾区经济发展时空演变特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带地理, 37(6): 802-813.
DOI |
|
ZHOU C S, LUO L J, SHI C Y, et al., 2017. Spatio-temporal evolutionary characteristics of the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and its influencing factors[J]. Tropical Geography, 37(6): 802-813.
DOI |
| [1] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [2] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [3] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [4] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [5] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [6] | 王嘉丽, 冯婧珂, 杨元征, 俎佳星, 蔡文华, 杨健. 南宁市主城区不透水面与热环境效应的空间关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 525-534. |
| [7] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [8] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [9] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [10] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [11] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [12] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [13] | 冯娴慧, 曾芝琳. 粤港澳大湾区植被覆盖特征与变化趋势的自然驱动力研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1713-1724. |
| [14] | 阮惠华, 许剑辉, 张菲菲. 2001—2020年粤港澳大湾区植被和地表温度时空变化研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1510-1520. |
| [15] | 苏泳松, 宋松, 陈叶, 叶子强, 钟润菲, 王昭尧. 珠江三角洲人类活动净氮输入时空特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
