生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 593-602.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.018
收稿日期:2021-12-04
出版日期:2022-03-18
发布日期:2022-05-25
通讯作者:
*苏小娟,E-mail: sl_505@126.com作者简介:苏焱(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为重金属污染修复。E-mail: suy88888888@163.com
基金资助:
SU Yan( ), QUAN Yanhong, HUAN Ziyan, YAO Jia, SU Xiaojuan*(
), QUAN Yanhong, HUAN Ziyan, YAO Jia, SU Xiaojuan*( )
)
Received:2021-12-04
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
摘要:
以烟杆炭(Y)和竹炭(Z)及磷改性烟杆炭(PY)和磷改性竹炭(PZ)作为修复材料,通过室内培养试验研究不同生物炭施用量(质量分数分别为1%、3%和5%)对矿区附近农田重金属复合污染土壤pH,有效磷,水溶态Pb、Zn及其赋存形态转化的影响,并通过毒性淋溶提取法(TCLP法)对4种钝化材料的钝化效果及环境风险进行评价。结果表明,(1)施用生物炭可明显提高土壤pH和有效磷含量,与CK相比,土壤pH增加了0.01—0.30个单位,土壤有效磷含量增加了6.4%—72.9%。(2)土壤水溶态Pb和Zn含量随生物炭施用量的增加而降低,与CK相比,培养结束后生物炭和磷改性生物炭处理土壤水溶态Pb和Zn分别降低了17.5%—92.6%和15.2%—76.8%,其中PY5处理效果最显著。(3)与CK相比,随着生物炭施用的增加,土壤弱酸态和可还原态Pb、Zn含量显著降低,而可氧化态和残渣态Pb、Zn所占比例则明显增加。(4)培养结束后,PY5(添加量为5%的 PY处理)土壤TCLP提取态Pb、Zn浓度降至最低,分别为14.53、21.88 mg∙L-1。(5)相关分析表明,土壤pH、有效磷含量与重金属形态显著相关。综上所述,生物炭及磷改性生物炭促进土壤重金属形态向残渣态转化,降低了土壤重金属的有效性,磷改性生物炭钝化效果优于未改性生物炭。
中图分类号:
苏焱, 全妍红, 宦紫嫣, 姚佳, 苏小娟. 磷改性生物炭对云南某铅锌矿周边农田铅锌污染土壤修复效果的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 593-602.
SU Yan, QUAN Yanhong, HUAN Ziyan, YAO Jia, SU Xiaojuan. Effect of phosphate-modified Biochar on Remediation of Pb- and Zn-polluted Farmlands Around A Pb/Zn Mine in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 593-602.
| 生物炭 Biochars | pH | 比表面积 Specific surface area/(m2∙g-1) | 有效磷含量 w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 总Pb含量 w(Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 总Zn含量 w(Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟杆炭 Tobacco stem biochar | 9.25 | 19.52 | 1199 | — | 130 |
| 竹炭 Bamboo biochar | 9.38 | 2.53 | 543 | — | 30 |
| 磷改性烟杆炭 Phosphorus-modified tobacco stem biochar | 8.56 | 10.52 | 1672 | — | 50 |
| 磷改性竹炭 Phosphorus-modified bamboo biochar | 8.56 | 1.82 | 833 | — | 20 |
表1 生物炭及磷改性生物炭基本性质
Table 1 Basic properties of biochars
| 生物炭 Biochars | pH | 比表面积 Specific surface area/(m2∙g-1) | 有效磷含量 w(AP)/(mg∙kg-1) | 总Pb含量 w(Pb)/(mg∙kg-1) | 总Zn含量 w(Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟杆炭 Tobacco stem biochar | 9.25 | 19.52 | 1199 | — | 130 |
| 竹炭 Bamboo biochar | 9.38 | 2.53 | 543 | — | 30 |
| 磷改性烟杆炭 Phosphorus-modified tobacco stem biochar | 8.56 | 10.52 | 1672 | — | 50 |
| 磷改性竹炭 Phosphorus-modified bamboo biochar | 8.56 | 1.82 | 833 | — | 20 |
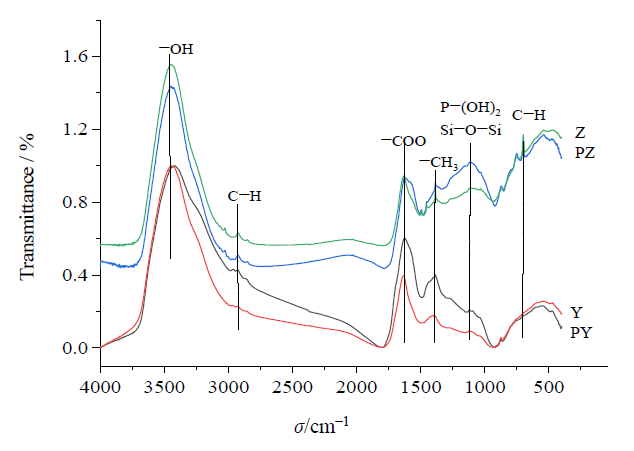
图1 生物炭及磷改性生物炭红外光谱图 Y:烟杆炭; Z:竹炭; PY:磷改性烟杆炭; PZ:磷改性竹炭。下同
Figure 1 Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of biochar and phosphorus-modified biochar Y: Tobacco charcoal; Z: Bamboo charcoal; PY: Phosphorus modified tobacco charcoal; PZ: Phosphorus modified bamboo charcoal. The same below
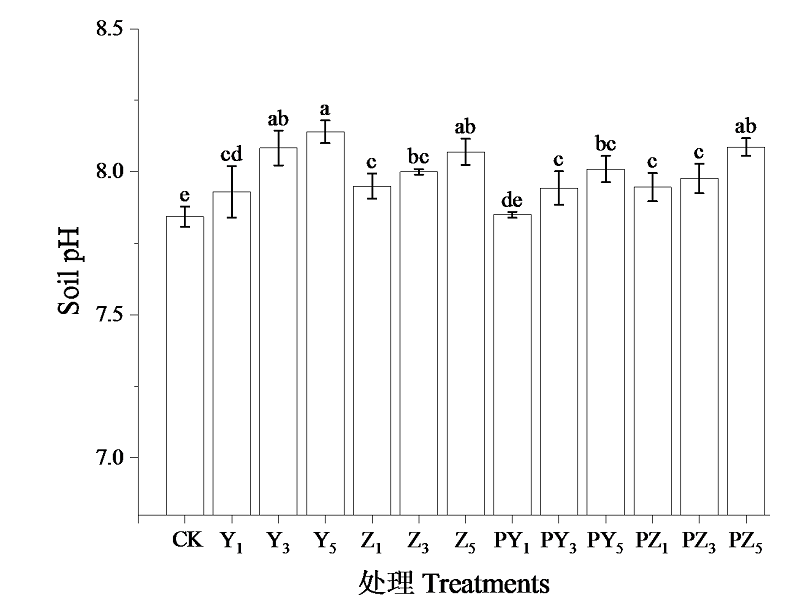
图3 不同处理对土壤pH的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异性显著(P<0.05,n=3)。CK:对照组,未添加生物炭的处理;Y1、Y2、Y3:添加质量分数1%、3%、5%的烟杆炭处理;Z1、Z2、Z3:添加质量分数1%、3%、5%的竹炭处理;PY1、PY2、PY3:添加质量分数1%、3%、5%的磷改性烟杆炭处理;PZ1、PZ2、PZ3:添加质量分数1%、3%、5%的磷改性竹炭处理;下同
Figure 3 Effect of different biochar treatments on soil pH Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference among different treatments (P<0.05, n=3). CK: control group(without biochar). Y1, Y2, Y3: the addition amount was 1%, 3%, 5% (w/w) tobacco stem carbon treatment, respectively. Z1, Z2, Z3: the addition amount was 1%, 3%, 5% (w/w) bamboo charcoal treatment, respectively. PY1, PY2, PY3: the addition amount was 1%, 3%, 5% (w/w) phosphorus modified tobacco carbon treatment, respectively. PZ1, PZ2, PZ3: the addition amount was 1%, 3%, 5% (w/w) phosphorus modified bamboo charcoal treatment, respectively. the same below
| 重金属Heavy metals | 生物炭Biochar | 弱酸提取态 Acid fraction | 可还原态 Reducible fraction | 可氧化态 Oxidizable fraction | 残渣态 Residual fraction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | |||||
| 铅 Pb | Y | -0.875** | -0.852** | -0.678* | -0.875** | 0.844** | 0.980** | 0.778** | 0.671* | |||
| Z | -0.884** | -0.796** | -0.875** | -0.791** | 0.906** | 0.842** | 0.777** | 0.629* | ||||
| PY | -0.611* | -0.999** | -0.568 | -0.997** | 0.608* | 0.999** | 0.547 | 0.995** | ||||
| PZ | -0.765** | -0.877** | -0.784** | -0.874** | 0.675* | 0.887** | 0.894** | 0.719** | ||||
| 锌 Zn | Y | -0.858** | -0.856** | -0.915** | -0.948** | 0.818** | 0.679* | 0.833** | 0.998** | |||
| Z | -0.887** | -0.801** | -0.933** | -0.914** | 0.933** | 0.927** | 0.827** | 0.701* | ||||
| PY | -0.554 | -0.995** | -0.560 | -0.995** | 0.417 | 0.956** | 0.777** | 0.926** | ||||
| PZ | -0.776** | -0.977** | -0.747** | -0.972** | 0.723** | 0.959** | 0.803** | 0.984** | ||||
表2 土壤pH和有效P含量与不同形态重金属含量之间的相关系数
Table 2 Correlation coefficients of fractions and contents of different forms of heavy metals with soil pH and available phosphorus
| 重金属Heavy metals | 生物炭Biochar | 弱酸提取态 Acid fraction | 可还原态 Reducible fraction | 可氧化态 Oxidizable fraction | 残渣态 Residual fraction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | pH | 有效磷 AP | |||||
| 铅 Pb | Y | -0.875** | -0.852** | -0.678* | -0.875** | 0.844** | 0.980** | 0.778** | 0.671* | |||
| Z | -0.884** | -0.796** | -0.875** | -0.791** | 0.906** | 0.842** | 0.777** | 0.629* | ||||
| PY | -0.611* | -0.999** | -0.568 | -0.997** | 0.608* | 0.999** | 0.547 | 0.995** | ||||
| PZ | -0.765** | -0.877** | -0.784** | -0.874** | 0.675* | 0.887** | 0.894** | 0.719** | ||||
| 锌 Zn | Y | -0.858** | -0.856** | -0.915** | -0.948** | 0.818** | 0.679* | 0.833** | 0.998** | |||
| Z | -0.887** | -0.801** | -0.933** | -0.914** | 0.933** | 0.927** | 0.827** | 0.701* | ||||
| PY | -0.554 | -0.995** | -0.560 | -0.995** | 0.417 | 0.956** | 0.777** | 0.926** | ||||
| PZ | -0.776** | -0.977** | -0.747** | -0.972** | 0.723** | 0.959** | 0.803** | 0.984** | ||||
| [1] |
BEREK A K, HUE N V, 2016. Characterization of Biochars and Their Use as an Amendment to Acid Soils[J]. Soil Science, 181(9-10): 412-426.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CAI L M, WANG Q S, LUO J, et al., 2019. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment for children near a large Cu-smelter in central China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 650(Pt 1): 725-733.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HUANG G, SU X, RIZWAN M S, et al., 2016. Chemical immobilization of Pb, Cu, and Cd by phosphate materials and calcium carbonate in contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(16): 16845-16856.
DOI URL |
| [4] | KONG L L, LIU W T, ZHOU Q X, 2014. Biochar: An Effective Amendment for Remediating Contaminated Soil[M]// WHITACRE D M. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 228. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 228: 83-99. |
| [5] |
LAHORI A H, GUO Z, ZHANG Z, et al., 2017. Use of Biochar as an Amendment for Remediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils: Prospects and Challenges[J]. Pedosphere, 27(6): 991-1014.
DOI URL |
| [6] | LI B, YANG L, WANG C Q, et al., 2017. Adsorption of Cd (II) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derived from different modification processes[J]. Chemosphere Environmental Toxicology & Risk Assessment, 175: 332-340. |
| [7] |
LIU H, XU F, XIE Y, et al., 2018. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 645: 702-709.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
OMAR N A, PRAVEENA S M, ARIS A Z, et al., 2015. Health Risk Assessment using in vitro digestion model in assessing bioavailability of heavy metal in rice: A preliminary study[J]. Food Chemistry, 188: 46-50.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
QUEVAUVILLER Ph, RAURET G, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F, et al., 1997. Certification of trace metal extractable contents in a sediment reference material (CRM 601) following a three-step sequential extraction procedure[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 205(2-3): 223-234.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
REGMI P, GARCIA MOSCOSO J L, KUMAR S, et al., 2012. Removal of copper and cadmium from aqueous solution using switchgrass biochar produced via hydrothermal carbonization process[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 109: 61-69.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
XU G, SUN J N, SHAO H B, et al., 2014. Biochar had effects on phosphorus sorption and desorption in three soils with differing acidity[J]. Ecological Engineering, 62: 54-60.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XU Y, LIANG X F, XU Y M, et al., 2017. Remediation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Agricultural Soils Using Clay Minerals: A Review[J]. Pedosphere, 27(2): 193-204.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG J Y, HANG Z, GU J F, et al., 2020. Effects of nano-Fe3O4-modified biochar on iron plaque ormation and Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113970.
DOI |
| [14] |
ZHANG Y N, ZHANG Y J, AKAKURU O U, et al., 2021. Research progress and mechanism of nanomaterials-mediated in-situ remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil: A critical review[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 104(6): 351-364.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 北京农业出版社: 79-81. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: Beijing Agriculture Press: 79-81. | |
| [16] | 蔡键, 2018. 富磷改性毛竹生物炭对水体中重金属镉的吸附研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学: 1-33. |
| CAI J, 2018. The study of adsorption of cadmium in aqueous solution by phosphate-modified bamboo biochar[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology: 1-33. | |
| [17] | 陈航, 王颖, 王澍, 2021. 铜山矿区周边农田土壤重金属来源解析及污染评价[J/OL]. 环境科学, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202108281. |
| CHEN H, WANG Y, WANG S, 2021. Source analysis and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around Tongshan Mining Area[J/OL]. Environmental Science, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx. 202108281. | |
| [18] | 陈志良, 袁志辉, 黄玲, 等, 2016. 生物炭来源、性质及其在重金属污染土壤修复中的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(11): 1879-1884. |
| CHEN Z L, YUAN Z H, HUANG L, et al., 2016. Pyrolysis materials, characteristics of biochar and its application on remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: A review[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(11): 1879-1884. | |
| [19] | 丁振亮, 赵玲, 续晓云, 等, 2015. 改性天然磷灰石促进Pb/Zn复合污染土壤的稳定化修复[J]. 环境化学, 34(6): 1049-1056. |
| DING Z L, ZHAO L, XU X Y, et al., 2015. Enhanced immobilization of Pb/Zn in compound contaminated soil by modified natural phosphate rock[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(6): 1049-1056. | |
| [20] | 房彬, 张建, 季民, 等, 2018. 生物炭复配磷酸盐对Pb-Cd污染土壤原位钝化修复的研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 40(12): 1389-1393. |
| FANG B, ZHANG J, JI M, et al., 2018. Effect of biochar with phosphate on in-situ immobilization of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 40(12): 1389-1393. | |
| [21] | 郭丹丹, 2020. 生物炭和改性生物炭对重金属Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学: 9-23. |
| GUO D D, 2020. Research on the adsorption performance of heavy metals Pb(Ⅱ), Cd(Ⅱ) by biochar and modified biochar[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology:9-23. | |
| [22] | 葛启隆, 田琦, 丰开庆, 等, 2022. 磷改性生物炭与沸石配施对土壤有效磷释放的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(1): 219-229. |
| GE Q L, TIAN Q, FENG K Q, et al., Effect of co-application of phosphorus-modified hydrochar and zeolite on release of soil available phosphorus[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(1): 219-229. | |
| [23] | 高瑞丽, 朱俊, 汤帆, 等, 2016. 水稻秸秆生物炭对镉、铅复合污染土壤中重金属形态转化的短期影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(1): 251-256. |
| GAO R L, ZHU J, TANG F, et al., 2016. Short-term effects of rice straw biochar on speciation transformation of heavy metals in cadmium and lead contaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 36(1): 251-256. | |
| [24] | 胡红青, 黄益宗, 黄巧云, 等, 2017. 农田土壤重金属污染化学钝化修复研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(6): 1676-1685. |
| HU H Q, HUANG Y Z, HUANG Q Y, et al., 2017. Research progress of heavy metals chemical immobilization in farmland[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 23(6): 1676-1685. | |
| [25] | 李洪达, 李艳, 周薇, 等, 2018. 稻壳生物炭对矿区重金属复合污染土壤中Cd、Zn形态转化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(9): 1856-1865. |
| LI H D, LI Y, ZHOU W, et al., 2018. Effects of rice-husk-derived biochar on the morphological transformation of Cd and Zn in mining area soils polluted by heavy metals[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(9): 1856-1865. | |
| [26] | 刘广深, 许中坚, 周根娣, 等, 2004. 模拟酸雨作用下红壤镉释放的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 24(4): 36-40. |
| LIU G S, XU Z J, ZOU G D, et al., 2004. Studies on the character and rule of cadmium release from red soils under the action of acid rain[J]. Chinese Environmental Science, 24(4): 36-40. | |
| [27] | 刘蕾, 韩枫, 武西社, 等, 2021. 磷基改性生物炭的制备及对重金属Pb(Ⅱ) 的吸附[J/OL]. 应用化工, https://doi.org/10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20211021.005. |
| LIU L, HAN F, WU X S, et al., 2021. Preparation of phosphorus based modified biochar and its adsorption on Pb(Ⅱ) in water[J/OL]. Application of Chemical, https://doi.org/10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.20211021.005. | |
| [28] | 刘洋, 何朝辉, 牛学奎, 等, 2021. 云南某矿区小流域土壤重金属健康风险评价[J/OL]. 环境科学, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202105114. |
| LIU Y, HE C H, NIU X K, et al., 2021. Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in a Small Watershed of a Mining Area in Yunnan[J/OL]. Environmental Science, https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202105114. | |
| [29] | 刘玉学, 唐旭, 杨生茂, 等, 2016. 生物炭对土壤磷素转化的影响及其机理研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 22(6): 1690-1695. |
| LIU Y X, TANG X, YANG S M, et al., 2016. Review on the effect of biochar on soil phosphorus transformation and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 22(6): 1690-1695. | |
| [30] | 靳辉勇, 2017. 土壤调理剂对镉、铅污染土壤及烟叶化学成分的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学: 23-24. |
| JIN H Y, 2017. Effects of soil conditioner on chemical constituents of cadmium and lead contaminated soil and tobacco leaves[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University: 23-24. | |
| [31] | 梅闯, 王衡, 蔡昆争, 等, 2021. 生物炭对土壤重金属化学形态影响的作用机制研究进展[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 37(4): 421-429. |
| MEI C, WANG H, CAI K Z, et al., 2021. Advances on effects and mechanisms of biochar on chemical forms of heavy metals in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37(4): 421-429. | |
| [32] | 申建波, 白洋, 韦中, 等, 2021. 根际生命共同体: 协调资源、环境和粮食安全的学术思路与交叉创新[J]. 土壤学报, 58(4): 805-813. |
| SHEN J B, BAI Y, WEI Z, et al., 2021. Rhizobiont: An interdisciplinary innovation and perspective for harmonizing resources, environment, and food security[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58(4): 805-813. | |
| [33] | 王秋君, 徐丽萍, 郭德杰, 等, 2021. 设施土壤中连续施用生物炭对土壤磷形态及吸附与释放特性的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 37(11): 114-121. |
| WANG Q J, XU L P, GUO D J, et al., 2021. Effect of continuous application of biochar on soil phosphorus forms and adsorption and release characteristics in greenhouse[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 37(11): 114-121. | |
| [34] | 王荣萍, 余炜敏, 梁嘉伟, 等, 2016. 改性生物炭对菜地土壤磷素形态转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(5): 872-876. |
| WANG R P, YU W M, LIANG J W, et al., 2016. Effects of modified biochar on soil phosphorus transformation in vegetable fields[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(5): 872-876. | |
| [35] | 王孝堂, 1991. 土壤酸度对重金属形态分配的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 28(1): 103-107. |
| WANG X T, 1991. Effects of soil acidity on speciation and distribution of heavy metals[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 28(1): 103-107. | |
| [36] | 王鑫宇, 孟海波, 沈玉君, 等, 2021. 改性生物炭特性表征及对冶炼厂周边农田土壤铜镉形态的影响[J]. 环境科学, 42(9): 4441-4451. |
| WANG X Y, MENG H B, SENG Y J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of modified biochars and their immobilization effect on Cu and Cd in polluted farmland soil around smelter[J]. Environmental Science, 42(9): 4441-4451. | |
| [37] | 吴萍萍, 李录久, 王家嘉, 等, 2017. 秸秆生物炭对矿区污染土壤重金属形态转化的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 33(5): 453-459. |
| WU P P, LI L J, WANG J J, et al., 2017. Effects of application of straw-derived biochar on forms of heavy metals in mining contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 33(5): 453-459. | |
| [38] | 杨兰, 李冰, 王昌全, 等, 2016. 改性生物炭材料对稻田原状和外源镉污染土钝化效应[J]. 环境科学, 37(9): 3562-3574. |
| YANG L, LI B, WANG C Q, et al., 2016. Effect of modified biochars on soil cadmium stabilization in paddy soil suffered from original or exogenous contamination[J]. Environmental Science, 37(9): 3562-3574. | |
| [39] | 杨惟薇, 张超兰, 曹美珠, 等, 2015. 4种生物炭对镉污染潮土钝化修复效果研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(1): 239-243. |
| YANG W W, ZHANG C L, CAO M Z, et al., 2015. Immobilization and remediation of cadmium contaminated soil with four kinds of biochars[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(1): 239-243. | |
| [40] | 叶金利, 田路萍, 吴文卫, 等, 2019. 云南会泽者海镇典型矿区场地重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 31(3): 36-40. |
| YE J L, TIAN L P, WU W W, et al., 2019. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in typical mining area in Zhehai, Huize County, Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Monitoring Management and Technology, 31(3): 36-40. | |
| [41] | 袁兴超, 李博, 朱仁凤, 等, 2019. 不同钝化剂对铅锌矿区周边农田镉铅污染钝化修复研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(4): 807-817. |
| YUAN X C, LI B, ZHU R F, et al., 2019. Immobilization of Cd and Pb using different amendments of cultivated soils around lead-zinc mines[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(4): 807-817. | |
| [42] | 张龙, 张云霞, 宋波, 等, 2020. 云南兰坪铅锌矿区优势植物重金属富集特性及应用潜力[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4210-4217. |
| ZHANG L, ZHANG Y X, SONG B, et al., 2020. Potential of accumulation and application of dominant plants in lanping lead-zinc mine, Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4210-4217. | |
| [43] | 张学庆, 费宇红, 田夏, 等, 2017. 磷改性生物炭对Pb、Cd复合污染土壤的钝化效果[J]. 环境污染与防治, 39(9): 1017-1020. |
| ZHANG X Q, FEI Y H, TIAN X, et al., 2017. The passivation effect of Pb, Cd composite polluted soil by phosphorus-modified biochar[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 39(9): 1017-1020. | |
| [44] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2012. 农田土壤环境质量检测技术规范NY/T395-2012 [S]. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China, 2012. Technical rules for monitoring of environmental quality of farmland soil: NY/T395-2012 [S]. | |
| [45] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 (试行): GB 15618-2018 [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团: 2-3. |
| Ministry of Ecology Environment of the People's Republic of China, 2018. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land: GB 15618-2018 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Publishing Group: 2-3. | |
| [46] | 周涵君, 韩秋静, 马静, 等, 2019. 生物炭对红壤和褐土中镉形态的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(3): 433-442. |
| ZHOU H J, HAN Q J, MA J, et al., 2019. Effects of biochar on Cd forms in red soil and cinnamon soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(3): 433-442. | |
| [47] | 周会平, 2019. 生物质竹炭的制备、表征及其对甲苯气体动态吸附特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学: 23-38. |
| ZHOU H P, 2019. Research on preparation and characterization of biomass bamboo charcoal and its dynamic adsorption properties for toluene gas[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Technology: 23-38. |
| [1] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [2] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [3] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [4] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [5] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [6] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [7] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [9] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [10] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [11] | 程文远, 李法云, 吕建华, 吝美霞, 王玮. 碱改性向日葵秸秆生物炭对多环芳烃菲吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 824-834. |
| [12] | 丛鑫, 王宇, 李瑶, 何洋洋. 生物炭及氧化石墨烯/生物炭复合材料对水中抗生素吸附性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 326-334. |
| [13] | 秦坤, 王志康, 王章鸿, 杨成, 刘杰刚, 沈德魁. 木质素-聚乙烯共热解生物炭对Cd(II)的吸附性能[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 344-353. |
| [14] | 梅闯, 蔡昆争, 黎紫珊, 徐美丽, 黄飞. 稻秆生物炭对稻田土壤Cd形态转化和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 380-390. |
| [15] | 秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
