生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2124-2133.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.003
收稿日期:2022-08-03
出版日期:2022-11-18
发布日期:2022-12-22
通讯作者:
*田新乐(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为植被动态遥感监测。E-mail: 1713647311@qq.com作者简介:赵安周(1985年生),男,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为城市扩张对生态环境的影响。E-mail: zhaoanzhou@126.com
基金资助:Received:2022-08-03
Online:2022-11-18
Published:2022-12-22
摘要:
基于Google Earth Engine(GEE)云平台,对1986-2021年黄土高原的Landsat地表反射率数据进行去云和融合处理,计算得到归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI),并利用像元二分模型估算植被覆盖度(Fractional Vegetation Coverage,FVC),在此基础上,辅以趋势分析、偏相关和残差分析等方法分析了不同时间段(1986-1999、2000-2021和1986-2021年)黄土高原FVC时空变化及其影响因素。结果表明,(1)时间上,1986-2021年黄土高原FVC呈显著增加的趋势(Trend=0.0044 a-1,P<0.01)。从不同时间段看,2000-2021年FVC的增加趋势(Trend=0.0058 a-1,P<0.01)快于1986-1999年(Trend=0.0038 a-1,P<0.01)。黄土高原所有植被类型的FVC均呈显著上升的趋势(P<0.01),其中草地的上升趋势最大(Trend=0.0066 a-1,P<0.01)。(2)空间上,黄土高原FVC呈东南向西北递减的趋势,1986-2021、1986-1999和2000-2021年FVC呈显著上升的面积分别为53.65%、18.38%和48.12%。(3)地形因子中,高程和坡度对FVC的影响较显著。FVC值随高程呈“下降-上升-下降”的变化趋势,最大值(0.7790)出现在3000-3500 m。FVC随坡度的增加呈上升的趋势,最大值(0.7025)出现在25°-45°。中高等级FVC和高等级FVC比例随坡度呈正相关关系,其中15°-25°面积占比最大(73.93%)。(4)1986-2021年黄土高原FVC与年降水量、年平均气温和太阳辐射(Solar Radiation,RAD)的偏相关系数分别为0.239、0.093和-0.006,其中呈显著正相关(P<0.05)的像元占比分别为48.50%、22.51%和5.96%。残差分析结果表明,人类活动是黄土高原植被动态变化的主要驱动因素,且起正向作用的像元比例为73.20%。
中图分类号:
赵安周, 田新乐. 基于GEE平台的1986-2021年黄土高原植被覆盖度时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2124-2133.
ZHAO Anzhou, TIAN Xinle. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Vegetation Coverage in the Loess Plateau from 1986 to 2021 Based on GEE Platform[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2124-2133.
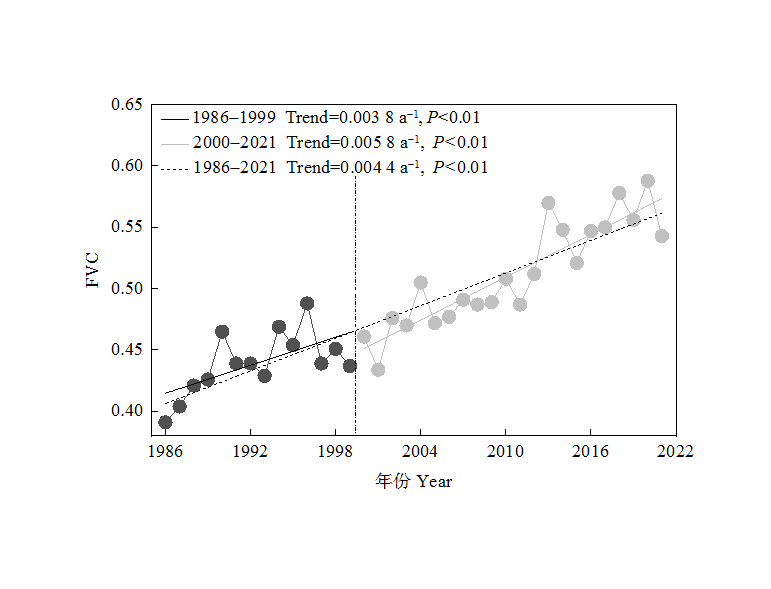
图3 1986-1999、2000-2021和1986-2021年黄土高原FVC年际变化
Figure3 The variation of average annual vegetation cover of the Loess Plateau in 1986-2021, 1986-1999 and 2000-2021
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | 年份 Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986-1999 | 2000-2021 | 1986-2021 | |
| 耕地 Cropland | 0.0033** | 0.0056** | 0.0039** |
| 林地 Woodland | 0.0024** | 0.0032** | 0.0028** |
| 草地 Grassland | 0.0052** | 0.0066** | 0.0055** |
| 灌丛 Thicket | 0.0033** | 0.0036** | 0.0030** |
表1 1986-1999、2000-2021和1986-2021年黄土高原不同植被类型的FVC变化趋势
Table 1 Trends of FVC changes between different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau in 1986-2021, 1986-1999 and 2000-2021
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | 年份 Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1986-1999 | 2000-2021 | 1986-2021 | |
| 耕地 Cropland | 0.0033** | 0.0056** | 0.0039** |
| 林地 Woodland | 0.0024** | 0.0032** | 0.0028** |
| 草地 Grassland | 0.0052** | 0.0066** | 0.0055** |
| 灌丛 Thicket | 0.0033** | 0.0036** | 0.0030** |
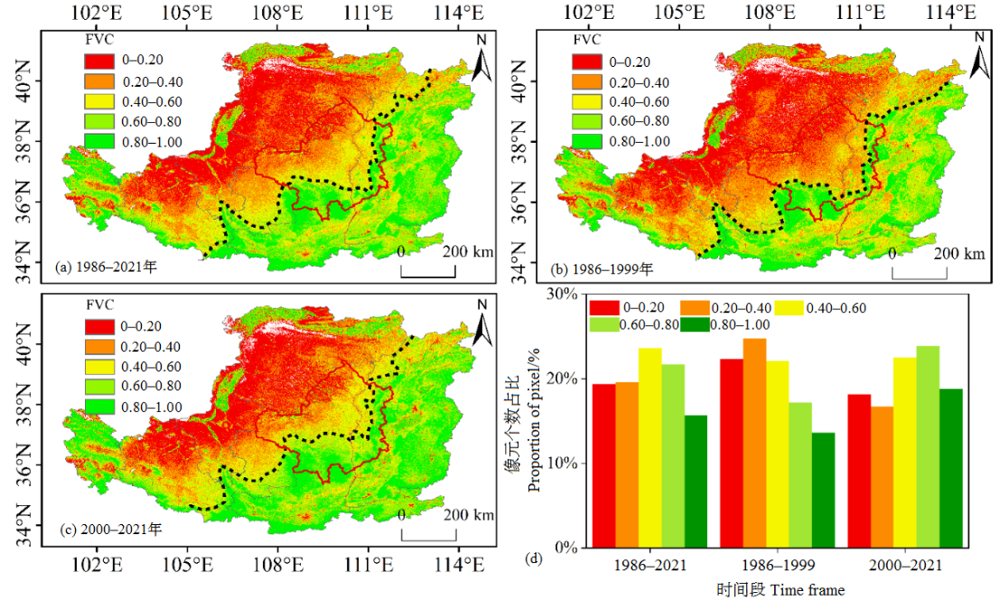
图4 1986-1999、2000-2021和1986-2021年黄土高原FVC均值空间分布及不同等级FVC像元占比 (a)-(c) 图中的虚线表示FVC低于或高于0.60分界线
Figure 4 Spatial distribution and the frequencies of FVC on the Loess Plateau in 1986-2021, 1986-1999 and 2000-2021 The dotted line in the (a-c) figure indicates that the FVC is below or above the 0.60 dividing line
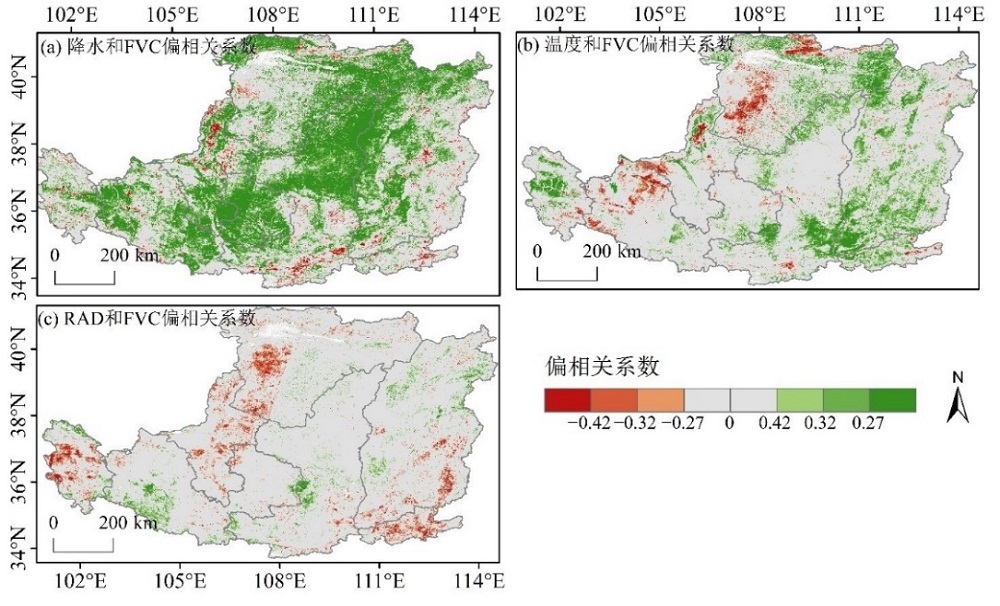
图7 1986-2021年FVC与气候因子偏相关系数的空间分布 显著性水平0.01、0.05、0.1分别对应的偏相关系数为±0.42、±0.32和±0.27
Figure 7 Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficients between FVC and climate factors in 1986-2021 The levels of significance of 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 represent partial correlation coefficient of ±0.42, ±0.32 and ±0.27, respectively
| [1] |
EVANS J, GEERKEN R, 2004. Discrimination between climate and human-induced dryland degradation[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 57(4): 535-554.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FENG X M, FU B J, PIAO S L, et al., 2016. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits[J]. Nature Climate Change, 6(11): 1019-1022.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAO W D, ZHENG C, LIU X H, et al., 2022. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: A case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 137: 108745.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HAN H Z, BAI J J, MA G, 2022. Seasonal responses of net primary productivity of vegetation to phenological dynamics in the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 32(2): 340-357.
DOI URL |
| [5] | KOU P L, XU Q, JIN Z, et al., 2021. Complex anthropogenic interaction on vegetation greening in the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Science of Total Environment, 778(7): 65-146. |
| [6] |
LIU Z Z, WANG H, LI N, et al., 2020. Spatial and temporal characteristics and driving forces of vegetation changes in the Huaihe River Basin from 2003 to 2018[J]. Sustainability, 12(6): 21-98.
DOI URL |
| [7] | WANG Y P, YAN W M, HAN X Y, et al., 2021. Changes in deep soil water content in the process of large-scale apple tree planting on the Loess[J]. Tableland of China. Forests, 12(2): 123. |
| [8] |
XU B, QI B, JI K, et al., 2022. Emerging hot spot analysis and the spatial temporal trends of NDVI in the Jing River Basin of China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(2): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YU H C, BIAN Z F, MU S G, et al., 2020. Effects of climate change on land cover change and vegetation dynamics in Xinjiang, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13): 48-65.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHAO A Z, YU Q Y, WANG D L, et al., 2022. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem water use efficiency over the Chinese Loess Plateau base on long-time satellite data[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(2): 2298-2310.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHENG H, LIN H, ZHOU W J, et al., 2019. Revegetation has increased ecosystem water-use efficiency during 2000-2014 in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Evidence from satellite data[J]. Ecological Indicators, 102: 507-518.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 常铮, 李崇贵, 张家政, 等, 2022. 基于GEE云平台的陕北黄土高原生态修复前后植被变化及原因[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 117(5): 1-10. |
| CHANG Z, LI C G, ZHANG J Z, et al., 2022. Analysis of vegetation changes and causes before and after ecological restoration projects on the Loess Plateau in northern Shaanxi based on Google Earth Engine[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 117(5): 1-10. | |
| [13] | 郭永强, 王乃江, 褚晓升, 等, 2019. 基于Google Earth Engine分析黄土高原植被覆盖变化及原因[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(11): 4804-4811. |
| GUO Y Q, WANG N J, CHU X S, et al., 2019. Analyzing vegetation coverage changes and its reasons on the Loess Plateau based on Google Earth Engine[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(11): 4804-4811. | |
| [14] | 侯学煜, 2001. 中国植被图集(1꞉1000000)[Z]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| HOU X Y, 2001. Vegetation map (1꞉1,000,000) in the Heihe River basin[Z]. BeiJing: Science Press. | |
| [15] | 何亮, 2021. 黄土高原植被覆盖变化特征及驱动力分析[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 51-60. |
| HE L, 2021. Analysis of vegetation cover change characteristics and driving forces in Loess Plateau[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: 51-60. | |
| [16] | 黄栋, 李鹏, 董南, 2021. 近20a环渤海地区GS_NDVI时空分异及其对气候变化和LUCC的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12):2275-2284. |
| HUANG D, LI P, DONG N, 2021. Spatial-temporal Differentiation of GS_NDVI in Recent 20 Years and Its Responses to Climate Change and LUCC in the Bohai Coastal Region[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2275-2284. | |
| [17] | 解晗, 同小娟, 李俊, 等, 2022. 2000-2018年黄河流域生长季植被指数变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(11): 4536-4549. |
| XIE H, TONG X J, LI J, et al., 2022. Changes of NDVI and EVI and their responses to climatic variables in the Yellow River Basin during the growing season of 2000-2018[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(11): 4536-4549. | |
| [18] |
金凯, 王飞, 韩剑桥, 等, 2020. 1982-2015年中国气候变化和人类活动对植被NDVI变化的影响[J]. 地理学报, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
JIN K, WANG F, HAN J Q, et al., 2020. Contribution of climatic change and human activities to vegetation NDVI change over China during 1982-2015[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(5): 961-974.
DOI |
|
| [19] | 李辉霞, 刘国华, 傅伯杰, 2011. 基于NDVI的三江源地区植被生长对气候变化和人类活动的响应研究[J]. 生态学报, 31(19): 5495-5504. |
| LI H X, LIU G H, FU B J, 2011. Response of vegetation to climate change and human activity based on NDVI in the Three-River Headwaters region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(19): 5495-5504. | |
| [20] | 李晶, 闫星光, 闫萧萧, 等, 2021. 基于GEE云平台的黄河流域植被覆盖度时空变化特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 46(5): 1439-1450. |
| LI J, YAN X G, YAN X X, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial variation characteristic of vegetation coverage in the Yellow River Basin based on GEE cloud platform[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 46(5): 1439-1450. | |
| [21] | 李苗苗, 吴炳方, 颜长珍, 等, 2004. 密云水库上游植被覆盖度的遥感估算[J]. 资源科学, 26(4): 153-159. |
| LI M M, WU B F, YAN C Z, et al., 2004. Estimation of vegetation fraction in the upper basin of Miyun Reservoir by remote sensing[J]. Resources Science, 26(4): 153-159. | |
| [22] | 李依璇, 朱清科, 石若莹, 等, 2021. 2000-2018黄土高原植被覆盖时空变化及影响因素[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 19(4): 60-68. |
| LI Y X, ZHU Q K, SHI R Y, et al., 2021. Spatial and temporal changes of vegetation cover and its influencing factors in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2018[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(4): 60-68. | |
| [23] | 马士彬, 安裕伦, 杨广斌, 等, 2019. 不同地形梯度上的植被变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 857-864. |
| MA S B, AN Y L, YANG G B, et al., 2019. The analysis of distribution characteristics and reasons of NDVI change trends along the terrain gradient[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 857-864. | |
| [24] | 宁晓刚, 常文涛, 王浩, 等, 2022. 联合GEE与多源遥感数据的黑龙江流域沼泽湿地信息提取[J]. 遥感学报, 26(2): 386-396. |
| NING X G, CHANG W T, WANG H, et al., 2022. Extraction of marsh wetland in Heilongjiang Basin based on GEE and multi-source remote sensing data[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 26(2): 386-396. | |
| [25] | 聂桐, 董国涛, 蒋晓辉, 等, 2022. 榆林地区植被时空分异特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(1): 26-36. |
| NIE T, DONG G T, JIANG X H, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal Variations and Influencing Factors of Vegetation in Yulin[J]. Ecology and Environment, 31(1): 26-36. | |
| [26] | 孙高鹏, 刘宪锋, 王小红, 等, 2021. 2001-2020年黄河流域植被覆盖变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 41(4): 205-212. |
| SUN G P, LIU X F, WANG X H, et al., 2021. Changes in vegetation coverage and its influencing factors across the Yellow River Basin during 2001-2020[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 41(4): 205-212. | |
| [27] | 田智慧, 任祖光, 魏海涛, 等, 2022. 2000-2020年黄河流域植被时空演化驱动机制[J]. 环境科学, 43(2):743-751. |
|
TIAN Z H, REN Z G, WEI H T, et al., 2022. Driving mechanism of the spatiotemporal evolution of vegetation in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2020[J]. Environmental Science, 43(2):743-751.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] |
王晓蕾, 石守海, 2022. 基于GEE的黄河流域植被时空变化及其地形效应研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 24(6): 1087-1098.
DOI |
| WANG X L, SHI S H, 2022. Spatio-temporal changes of vegetation in the Yellow River Basin and related effect of landform based on GEE[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 24(6): 1087-1098. | |
| [29] | 肖强, 陶建平, 肖洋, 2016. 黄土高原近10年植被覆盖的动态变化及驱动力[J]. 生态学报, 36(23): 7594-7602. |
| XIAO Q, TAO J P, XIAO Y, 2016. Dynamic vegetation cover change over the past 10 years on the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(23): 7594-7602. | |
| [30] | 徐建华, 2014. 计量地理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 159-184. |
| XU J H, 2014. Quantitative geography[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 159-184. | |
| [31] | 徐勇, 黄雯婷, 卢梦缘, 等, 2022. 气候变化和人类活动对西南喀斯特地貌区植被NDVI变化相对作用[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(3): 292-299. |
| XU Y, HUANG W T, LU M Y, et al., 2022. Vegetation cover change and the relative role of climate change and human activities in southwest Karst Areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(3): 292-299. | |
| [32] |
阎世杰, 王欢, 焦珂伟, 2019. 京津冀地区植被时空动态及定量归因[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 21(5): 767-780.
DOI |
| YAN S J, WANG H, JIAO K W, 2019. Spatiotemporal dynamic of NDVI in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on MODIS data and quantitative attribution[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 21(5): 767-780. | |
| [33] | 杨灿, 魏天兴, 李亦然, 等, 2021. 黄土高原典型县域植被覆盖度时空变化及地形分异特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(6): 1830-1838. |
| YANG C, WEI T X, LI Y R, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal variations and topographic differentiation of fractional vegetation cover in typical counties of Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(6): 1830-1838. | |
| [34] | 杨嘉, 郭铌, 黄蕾诺, 等, 2008. 西北地区MODIS-NDVI指数饱和问题分析[J]. 高原气象, 27(4): 896-903. |
| YANG J, GUO N, HUANG L N, et al., 2008. Ananlyses on MODIS-NDVI Index Saturation in Northwest China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 27(4): 896-903. | |
| [35] | 易浪, 任志远, 张翀, 等, 2014. 黄土高原植被覆盖变化与气候和人类活动的关系[J]. 资源科学, 36(1): 166-174. |
| YI L, REN Z Y, ZHANG C, et al., 2014. Vegetation cover, climate and human activities on the Loess Plateau[J]. Resources Science, 36(1): 166-174. | |
| [36] | 袁和第, 2020. 黄土丘陵沟壑区典型小流域水土流失治理技术模式研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 33-57. |
| YUAN H D, 2020. The research on model of soil erosion comprehensive control in typical small watershed in hilly and gully loess region[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 33-57. | |
| [37] | 张宝庆, 田磊, 赵西宁, 等, 2021. 植被恢复对黄土高原局地降水的反馈效应研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 51(7): 1080-1091. |
|
ZHANG B Q, TIAN L, ZHAO X N, et al., 2021. Feedbacks between vegetation restoration and local precipitation over the Loess Plateau in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(6): 920-931.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 张宝庆, 吴普特, 赵西宁, 2011. 近30 a黄土高原植被覆盖时空演变监测与分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(4): 287-293, 400. |
| ZHANG B Q, WU P T, ZHAO X N, 2011. Detecting and analysis of spatial and temporal variation of vegetation cover in the Loess Plateau during 1982-2009[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 27(4): 287-293, 400. | |
| [39] | 张家政, 李崇贵, 王涛, 2022. 黄土高原植被覆盖时空变化及原因[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(1): 224-230, 241. |
| ZHANG J Z, LI C G, WANG T, 2022. Dynamic changes of vegetation coverage on the Loess Plateau and its factors[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(1): 224-230, 241. | |
| [40] |
张园, 袁凤辉, 王安志, 等, 2020. 2001-2018年长白山自然保护区生长季NDVI变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(4): 1213-1222.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Y, YUAN F H, WANG A Z, et al., 2020. Variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climatic change in the growing season of Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve during 2001 and 2018[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(4): 1213-1222.
DOI |
|
| [41] | 赵安周, 张安兵, 刘海新, 等, 2017. 退耕还林(草)工程实施前后黄土高原植被覆盖时空变化分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 32(3): 449-460. |
| ZHAO A Z, ZHANG A B, LIU H X, et al., 2017. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation coverage before and after implementation of grain for green project in the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 19(4): 60-68. |
| [1] | 王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148. |
| [2] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [3] | 王超, 杨倩楠, 张池, 刘同旭, 张晓龙, 陈静, 刘科学. 丹霞山不同土地利用方式土壤磷组分特征及其有效性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [4] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [5] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [6] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [7] | 何艳虎, 龚镇杰, 吴海彬, 蔡宴朋, 杨志峰, 陈晓宏. 粤港澳大湾区城市生态效率时空演变及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [8] | 王嘉丽, 冯婧珂, 杨元征, 俎佳星, 蔡文华, 杨健. 南宁市主城区不透水面与热环境效应的空间关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 525-534. |
| [9] | 郝金虎, 韦玮, 李胜男, 马牧源, 李肖夏, 杨洪国, 姜琦宇, 柴沛东. 基于GEE平台的京津冀长时序水体时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [10] | 张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [11] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [12] | 袁林江, 李梦博, 冷钢, 钟冰冰, 夏大朋, 王景华. 厌氧环境下硫酸盐还原与氨氧化的协同作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [13] | 刘希林, 卓瑞娜. 崩岗崩积体坡面初始产流时间影响因素及其临界阈值[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 36-46. |
| [14] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [15] | 齐月, 张强, 胡淑娟, 蔡迪花, 赵福年, 陈斐, 张凯, 王鹤龄, 王润元. 黄土高原地区气候变化及其对冬小麦生产潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1521-1529. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 528
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 884
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

