生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 2079-2088.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.10.016
辛未冬*( ), 杜一丹, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 赵浩志, 杨丹
), 杜一丹, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 赵浩志, 杨丹
收稿日期:2022-05-22
出版日期:2022-10-18
发布日期:2022-12-09
通讯作者:
*作者简介:辛未冬(1980年生),女,副教授,博士,主要从事土壤动物生态学方面的教学与科研工作。E-mail: xiny-2005@163.com
基金资助:
XIN Weidong*( ), DU Yidan, LIU Huayu, YANG Yimeng, ZHAO Haozhi, YANG Dan
), DU Yidan, LIU Huayu, YANG Yimeng, ZHAO Haozhi, YANG Dan
Received:2022-05-22
Online:2022-10-18
Published:2022-12-09
摘要:
地表节肢动物是土壤生态系统的重要组成部分,对土壤环境的变化十分敏感。煤矸石山生态退化形势严峻,恢复植被是修复退化煤矸石山生态系统的主要措施,不仅影响土壤理化性质,还影响与土壤有密切联系的地表节肢动物多样性。为探究煤矸石山不同植被恢复方式与地表节肢动物群落多样性之间的关系,于2019年10月选取霍州煤矸石山恢复区的天然恢复植被(草地)、人工恢复植被(石榴地和山楂地)和未受煤矸石影响的玉米地(对照)为研究对象,分析地表节肢动物多样性对煤矸石山不同植被恢复方式的响应及生物指示作用。研究发现,(1)4个样地地表节肢动物活动密度和群落多样性指数均有显著差异。活动密度、Simpson优势度指数和Shannon-wiener多样性指数均表现为石榴地与其他样地存在显著差异;Margalef丰富度指数表现为玉米地显著高于其他样地;Pielou均匀度指数表现为草地最高,石榴地最低。(2)CCA排序结果表明,土壤速效磷和含水量是影响地表节肢动物分布的主要土壤环境因子,且不同地表节肢动物类群对土壤环境因子的响应不同,其中疣跳科(Neanuridae)的活动密度与土壤速效磷和含水量显著正相关。(3)地表节肢动物对不同恢复样地有较强指示作用,其中卷壳虫科(Armadillidae)可指示山楂地,蓟马科(Thripidae)等可指示石榴地,缘腹细蜂科(Scelionidae)等可指示对照玉米地,草地无指示种。研究表明,天然恢复不利于提高地表节肢动物活动密度和类群数,但可以维持较高的Shannon多样性指数;人工恢复虽然有较高的地表节肢动物活动密度和类群数,但Shannon多样性指数和Pielou均匀度指数较低;两种恢复方式在提升地表节肢动物类群数目方面与对照玉米地相比仍有差异,未来还需参考各恢复植被的功能特征,制定因地制宜的恢复策略。
中图分类号:
辛未冬, 杜一丹, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 赵浩志, 杨丹. 地表节肢动物多样性对煤矸石山不同植被恢复方式的响应及生物指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2079-2088.
XIN Weidong, DU Yidan, LIU Huayu, YANG Yimeng, ZHAO Haozhi, YANG Dan. Responses and Biological Indications of Ground-dwelling Arthropods Diversity to Different Vegetation Restoration Patterns in Coal Gangue[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2079-2088.
| 类群 Groups | 草地 WG | 山楂地 HT | 石榴地 GF | 玉米地 CF | 优势度 Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疣跳科 Neanuridae | — | — | — | — | 1327.19 | +++ | 1.94 | ++ | +++ |
| 蚁科 Formicidae | 0.44 | +++ | 0.44 | ++ | 5.63 | + | 18.63 | +++ | ++ |
| 卷壳虫科 Armadillidae | 0.06 | ++ | 19.63 | +++ | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | ++ |
| 长角跳科 Entomobryidae | 0.31 | ++ | 0.63 | ++ | 11.06 | + | 1.00 | ++ | + |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 0.56 | +++ | 0.50 | ++ | 2.56 | + | 1.81 | ++ | + |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 0.06 | ++ | 0.06 | + | 0.13 | + | 5.00 | +++ | + |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 0.25 | ++ | 0.88 | ++ | 0.88 | + | 1.50 | ++ | + |
| 毛蕈甲科 Binphyllidae | 0.13 | ++ | 1.00 | ++ | 0.25 | + | 0.94 | ++ | + |
| 圆跳科 Sminthuridae | 0.38 | ++ | — | — | 1.19 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 细蜂科 Proctotrupidae | — | — | 0.19 | + | — | — | 1.63 | ++ | + |
| 缘腹细蜂科 Scelionidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1.69 | ++ | + |
| 蝗科 Acrididae | 0.88 | +++ | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 食蚜蝇科 Syrphidae | 0.13 | ++ | 0.44 | ++ | 1.00 | + | — | — | + |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 0.06 | ++ | 0.13 | + | 0.19 | + | 0.94 | ++ | + |
| 球蕈甲科 Leiodidae | — | — | — | — | 0.25 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 细蚊科 Dixidae | — | — | 0.31 | ++ | 0.06 | + | 0.38 | + | + |
| 鼠妇科 Porcekkionidae | — | — | 0.25 | ++ | 0.19 | + | 0.31 | + | + |
| 蓟马科 Thripidae | — | — | — | — | 0.69 | + | — | — | + |
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larva | — | — | — | — | 0.19 | + | 0.44 | ++ | + |
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepidoptera larva | 0.13 | ++ | — | — | 0.31 | + | 0.13 | + | + |
| 拟步甲科 Tenebrionidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.44 | ++ | + |
| 实蝇科 Tephritidae | 0.25 | ++ | 0.06 | + | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 甲螨 Oribatidae | 0.19 | ++ | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 象甲科 Curculionidae | — | — | 0.19 | + | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 虎甲科 Cicindelidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.31 | + | + |
| 石蜈蚣科 Lithobiidae | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | 0.13 | + | + |
| 盲蝽科 Miridae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.19 | + | + |
| 盲蛛目 Opiliones | — | — | 0.13 | + | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larva | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 金龟子总科 Scarabaeoidea | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | + |
| 蝽科 Pentatomidae | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 蚊科 Culicidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 小蜂科 Chalalcididae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | + |
| 赤螨 Erythraeidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 叶蝉科 Cicadellidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 木虱科 Psyllidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 网蝽科 Tingidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 夜蛾科 Noctuidae | 0.06 | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 锤角细蜂科 Diapriidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 地蜈蚣科 Geophilomorpha | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 双尾虫科 Campodeidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 蜈蚣科 Scolopendridae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 摇蚊科 Chironomidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 缨小蜂科 Mymaridae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 蚤蝼科 Tridactylidae | 0.06 | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 总类群数 Total groups | 16 | 17 | 29 | 36 | 46 | ||||
| 活动密度 Activity density | 3.88±0.75b | 24.75±10.79b | 1352.06±383.36a | 40.06±12.10b | 101.75 | ||||
表1 不同样地地表节肢动物群落活动密度和优势度
Table 1 Activity density and dominance of ground-dwelling arthropods in four plots
| 类群 Groups | 草地 WG | 山楂地 HT | 石榴地 GF | 玉米地 CF | 优势度 Dominance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疣跳科 Neanuridae | — | — | — | — | 1327.19 | +++ | 1.94 | ++ | +++ |
| 蚁科 Formicidae | 0.44 | +++ | 0.44 | ++ | 5.63 | + | 18.63 | +++ | ++ |
| 卷壳虫科 Armadillidae | 0.06 | ++ | 19.63 | +++ | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | ++ |
| 长角跳科 Entomobryidae | 0.31 | ++ | 0.63 | ++ | 11.06 | + | 1.00 | ++ | + |
| 蚜科 Aphididae | 0.56 | +++ | 0.50 | ++ | 2.56 | + | 1.81 | ++ | + |
| 步甲科 Carabidae | 0.06 | ++ | 0.06 | + | 0.13 | + | 5.00 | +++ | + |
| 蜘蛛目 Araneae | 0.25 | ++ | 0.88 | ++ | 0.88 | + | 1.50 | ++ | + |
| 毛蕈甲科 Binphyllidae | 0.13 | ++ | 1.00 | ++ | 0.25 | + | 0.94 | ++ | + |
| 圆跳科 Sminthuridae | 0.38 | ++ | — | — | 1.19 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 细蜂科 Proctotrupidae | — | — | 0.19 | + | — | — | 1.63 | ++ | + |
| 缘腹细蜂科 Scelionidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1.69 | ++ | + |
| 蝗科 Acrididae | 0.88 | +++ | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 食蚜蝇科 Syrphidae | 0.13 | ++ | 0.44 | ++ | 1.00 | + | — | — | + |
| 叶甲科 Chrysomelidae | 0.06 | ++ | 0.13 | + | 0.19 | + | 0.94 | ++ | + |
| 球蕈甲科 Leiodidae | — | — | — | — | 0.25 | + | 0.63 | ++ | + |
| 细蚊科 Dixidae | — | — | 0.31 | ++ | 0.06 | + | 0.38 | + | + |
| 鼠妇科 Porcekkionidae | — | — | 0.25 | ++ | 0.19 | + | 0.31 | + | + |
| 蓟马科 Thripidae | — | — | — | — | 0.69 | + | — | — | + |
| 鞘翅目幼虫 Coleoptera larva | — | — | — | — | 0.19 | + | 0.44 | ++ | + |
| 鳞翅目幼虫 Lepidoptera larva | 0.13 | ++ | — | — | 0.31 | + | 0.13 | + | + |
| 拟步甲科 Tenebrionidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.44 | ++ | + |
| 实蝇科 Tephritidae | 0.25 | ++ | 0.06 | + | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 甲螨 Oribatidae | 0.19 | ++ | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 象甲科 Curculionidae | — | — | 0.19 | + | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 虎甲科 Cicindelidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.31 | + | + |
| 石蜈蚣科 Lithobiidae | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | 0.13 | + | + |
| 盲蝽科 Miridae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.19 | + | + |
| 盲蛛目 Opiliones | — | — | 0.13 | + | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 双翅目幼虫 Diptera larva | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 金龟子总科 Scarabaeoidea | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | + |
| 蝽科 Pentatomidae | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 蚊科 Culicidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | 0.06 | + | + |
| 小蜂科 Chalalcididae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.13 | + | + |
| 赤螨 Erythraeidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 叶蝉科 Cicadellidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 木虱科 Psyllidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 瓢虫科 Coccinellidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 网蝽科 Tingidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 夜蛾科 Noctuidae | 0.06 | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 锤角细蜂科 Diapriidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 地蜈蚣科 Geophilomorpha | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 双尾虫科 Campodeidae | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | + |
| 蜈蚣科 Scolopendridae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 摇蚊科 Chironomidae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 缨小蜂科 Mymaridae | — | — | — | — | 0.06 | + | — | — | + |
| 蚤蝼科 Tridactylidae | 0.06 | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | + |
| 总类群数 Total groups | 16 | 17 | 29 | 36 | 46 | ||||
| 活动密度 Activity density | 3.88±0.75b | 24.75±10.79b | 1352.06±383.36a | 40.06±12.10b | 101.75 | ||||
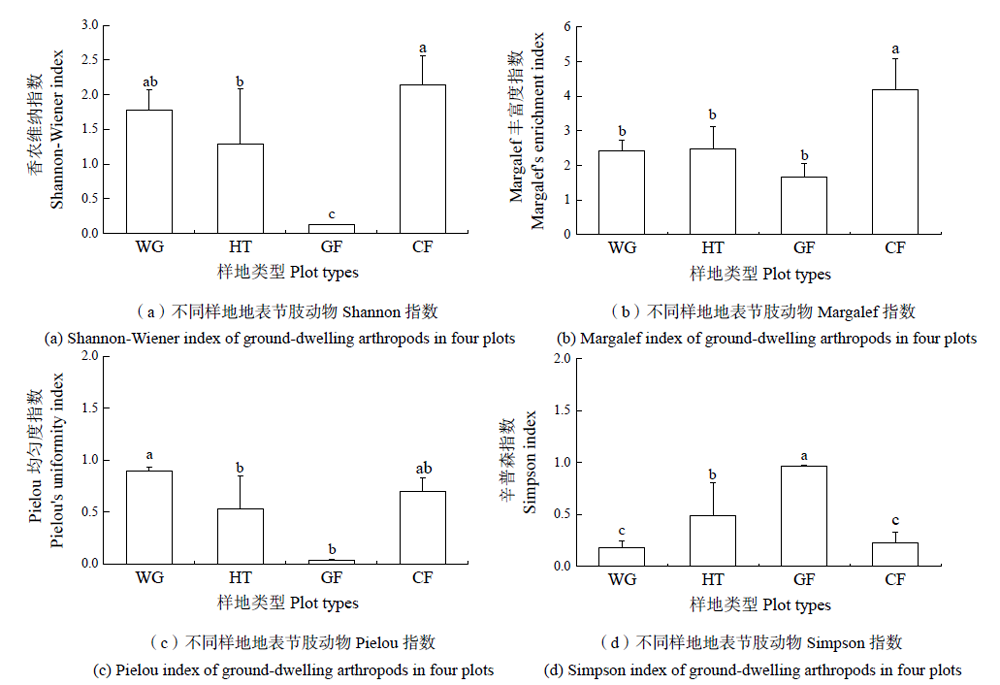
图1 不同样地地表节肢动物多样性 不同字母表示该多样性指数下不同样地之间差异显著(P<0.05);WG:草地;HT:山楂地;GF:石榴地;CF:玉米地
Figure 1 Diversity of ground-dwelling arthropods in four plots Different letters indicate significant differences among plots with diversity index (P<0.05); WG: Waste grassland; HT: Hawthorn field; GF: Granada tree field; CF: Corn field
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 草地WG | 山楂地HT | 石榴地GF | 玉米地CF | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量 Water content | 0.12±0.01c | 0.17±0.01a | 0.17±0.01a | 0.14±0.01b | 19.670 | <0.01 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 1.75±0.16a | 1.67±0.06a | 1.69±0.08a | 1.79±0.06a | 1.197 | 0.352 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 8.04±0.03a | 7.89±0.05b | 8.02±0.12ab | 7.99±0.1ab | 2.426 | 0.116 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter | 8.12±1.43b | 14.62±2.22a | 13.46±3.43a | 16.92±2.21a | 9.409 | <0.01 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 7.05±1.18b | 11.77±2.18b | 39.11±9.36a | 5.49±1.36b | 41.436 | <0.01 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 94.07±15.92c | 145.60±7.64a | 109.30±12.42bc | 126.70±26.25ab | 6.861 | <0.01 |
表2 不同植被恢复样地土壤环境因子状况
Table 2 Soil environmental factors in four plots
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 草地WG | 山楂地HT | 石榴地GF | 玉米地CF | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量 Water content | 0.12±0.01c | 0.17±0.01a | 0.17±0.01a | 0.14±0.01b | 19.670 | <0.01 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 1.75±0.16a | 1.67±0.06a | 1.69±0.08a | 1.79±0.06a | 1.197 | 0.352 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 8.04±0.03a | 7.89±0.05b | 8.02±0.12ab | 7.99±0.1ab | 2.426 | 0.116 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter | 8.12±1.43b | 14.62±2.22a | 13.46±3.43a | 16.92±2.21a | 9.409 | <0.01 |
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 7.05±1.18b | 11.77±2.18b | 39.11±9.36a | 5.49±1.36b | 41.436 | <0.01 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 94.07±15.92c | 145.60±7.64a | 109.30±12.42bc | 126.70±26.25ab | 6.861 | <0.01 |
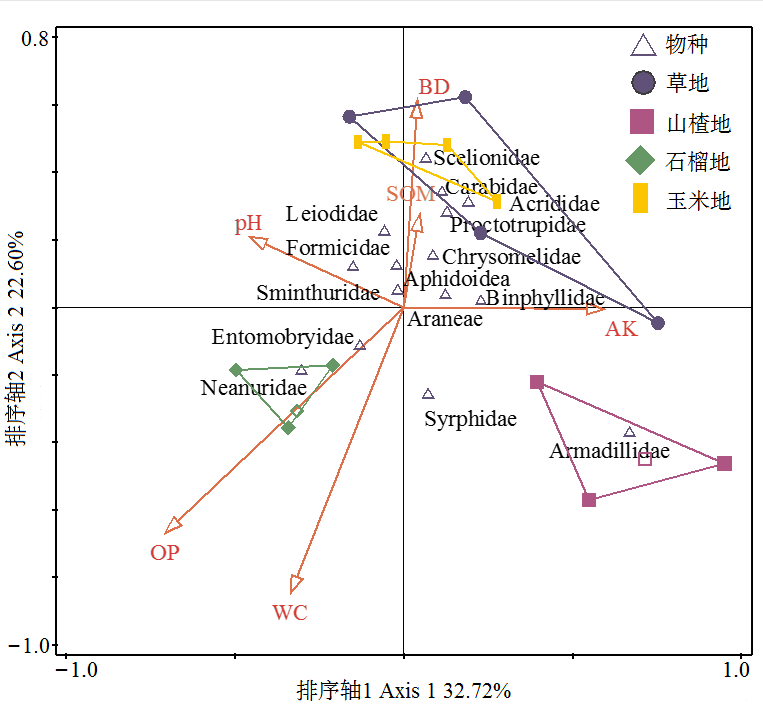
图2 地表节肢动物与土壤环境因子的冗余分析(CCA) Neanuridae:疣跳科;Formicidae:蚁科;Armadillidae:卷壳虫科;Entomobryidae:长角跳科;Aphidoidea:蚜科;Carabidae:步甲科;Araneae:蜘蛛目;Binphyllidae:毛蕈甲科;Sminthuridae:圆跳科;Proctotrupidae:细蜂科;Scelionidae:缘腹细蜂科;Acrididae:蝗科;Syrphidae:食蚜蝇科;Chrysomelidae:叶甲科;Leiodidae:球蕈甲科
Figure 2 CCA among major groups of ground-dwelling arthropods in association with soil environmental factors (CCA)
| 环境变量 Environment variable | 解释率Explains/% | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 26.6 | 39.3 | 5.1 | 0.004 |
| 土壤含水量 Water content | 11.7 | 17.2 | 2.5 | 0.054 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 9.3 | 13.8 | 2.6 | 0.030 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 9.2 | 13.5 | 2.2 | 0.072 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter | 7.5 | 11.1 | 1.7 | 0.130 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 3.5 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 0.442 |
表3 土壤环境因子对地表节肢动物群落分布的相对贡献CCA分析
Table 3 CCA on the relative contribution of environmental factors to ground-dwelling arthropods communities
| 环境变量 Environment variable | 解释率Explains/% | 贡献率 Contribution rate/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 26.6 | 39.3 | 5.1 | 0.004 |
| 土壤含水量 Water content | 11.7 | 17.2 | 2.5 | 0.054 |
| 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 9.3 | 13.8 | 2.6 | 0.030 |
| 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 9.2 | 13.5 | 2.2 | 0.072 |
| 有机质 Soil organic matter | 7.5 | 11.1 | 1.7 | 0.130 |
| 速效钾 Available potassium | 3.5 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 0.442 |
| 项目 Item | 土壤含水量 Water content | 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香农维纳指数 Shannon index | -0.685 | -0.168 | 0.684 | -0.076 | -0.997** | 0.124 |
| 丰富度指数 Margalef index | -0.430 | -0.155 | 0.758 | 0.408 | -0.844 | 0.343 |
| 均匀度指数 Pielou index | -0.789 | -0.063 | 0.631 | -0.340 | -0.961* | -0.076 |
| 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 0.844 | -0.058 | -0.766 | 0.283 | 0.980* | 0.127 |
| 类群数 The number of groups | -0.685 | -0.168 | 0.684 | -0.076 | -0.997** | 0.124 |
| 活动密度 Activity density | 0.717 | 0.147 | -0.428 | 0.474 | 0.864 | 0.091 |
表4 地表节肢动物群落分布与环境因子间的相关关系
Table 4 Correlation between ground-dwelling arthropods communities distribution and environment factors
| 项目 Item | 土壤含水量 Water content | 土壤酸碱度 pH value | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density | 土壤有机质 Soil organic matter | 速效磷 Available phosphorus | 速效钾 Available potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 香农维纳指数 Shannon index | -0.685 | -0.168 | 0.684 | -0.076 | -0.997** | 0.124 |
| 丰富度指数 Margalef index | -0.430 | -0.155 | 0.758 | 0.408 | -0.844 | 0.343 |
| 均匀度指数 Pielou index | -0.789 | -0.063 | 0.631 | -0.340 | -0.961* | -0.076 |
| 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 0.844 | -0.058 | -0.766 | 0.283 | 0.980* | 0.127 |
| 类群数 The number of groups | -0.685 | -0.168 | 0.684 | -0.076 | -0.997** | 0.124 |
| 活动密度 Activity density | 0.717 | 0.147 | -0.428 | 0.474 | 0.864 | 0.091 |
| 样地 Site | 类群 Species | 指示值 IndVal | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 草地WG | — | — | — |
| 山楂地HT | 卷壳虫科Armadillidae | 0.99 | 0.005 |
| 石榴地 GF | 蓟马科Thripidae | 1.00 | 0.003 |
| 疣跳科Neanuridae | 0.99 | 0.004 | |
| 长角跳科Entomobryidae | 0.85 | 0.005 | |
| 玉米地 CF | 缘腹细蜂科Scelionidae | 1.00 | 0.003 |
| 步甲科Carabidae | 0.95 | 0.003 | |
| 虎甲科Cicindelidae | 0.75 | 0.032 | |
| 蚁科Formicidae | 0.74 | 0.012 |
表5 不同恢复植被地表节肢动物指示值
Table 5 IndVal of ground-dwelling arthropods in four plots
| 样地 Site | 类群 Species | 指示值 IndVal | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 草地WG | — | — | — |
| 山楂地HT | 卷壳虫科Armadillidae | 0.99 | 0.005 |
| 石榴地 GF | 蓟马科Thripidae | 1.00 | 0.003 |
| 疣跳科Neanuridae | 0.99 | 0.004 | |
| 长角跳科Entomobryidae | 0.85 | 0.005 | |
| 玉米地 CF | 缘腹细蜂科Scelionidae | 1.00 | 0.003 |
| 步甲科Carabidae | 0.95 | 0.003 | |
| 虎甲科Cicindelidae | 0.75 | 0.032 | |
| 蚁科Formicidae | 0.74 | 0.012 |
| [1] |
BROUGHTON R K, SHORE R F, HEARD M S, 2014. Agri-environment scheme enhances small mammal diversity and abundance at the farm-scale[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 192: 122-129.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
MATSON P A, PARTON W J, POWER A G, et al., 1997. Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties[J]. Science, 277(5325): 504-509.
PMID |
| [3] |
NAKAMURA A, CATTERALL C P, HOUSE A, et al., 2007. The use of ants and other soil and litter arthropods as bio-indicators of the impacts of rainforest clearing and subsequent land use[J]. Journal of Insect Conservation, 11(2): 177-186.
DOI URL |
| [4] | TEAM R C R, 2011. A language and environment for statistical computing[J]. Computing, 1: 12-21. |
| [5] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil chemistry analysis[M]. 3rd Edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [6] | 丁彰琦, 徐国瑞, 张霜, 等, 2022. 北京东灵山土壤动物-植物互作关系对海拔格局的响应[J]. 生态学报, 42(7): 2741-2750. |
| DING Z Q, XU G R, ZAHNG S, et al., 2022. Altitudinal pattern of soil fauna-plant interaction in Dongling mountain, Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(7): 2741-2750. | |
| [7] | 杜亚彬, 马塬淇, 王雪峰, 等, 2020. 刺五加根际效应和土壤环境因子对土壤跳虫群落结构的影响[J]. 植物保护学报, 47(6): 1251-1260. |
| DU Y B, MA Y Q, WANG X F, et al., 2020. Effects of rhizosphere effects of Siberian ginseng Acanthopanax senticosus and soil environmental factors on Collembola community composition in soil[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 47(6): 1251-1260. | |
| [8] |
傅声雷, 2007. 土壤生物多样性的研究概况与发展趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 15(2): 109-115.
DOI |
|
FU S L, 2007. A review and perspective on soil biodiversity research[J]. Biodiversity Science, 15(2): 109-115.
DOI |
|
| [9] | 符亚儒, 张继平, 董强, 等, 2012. 陕北沙区煤矸石废弃地的植被恢复技术研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 27(5): 178-183. |
| FU Y R, ZHANG J P, DONG Q, et al., 2012. Vegetation restoration technologies in the coal gangue waste lands in sandy areas of Northern Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 27(5): 178-183. | |
| [10] | 高光彩, 付必谦, 2009. 步甲作为指示生物的研究进展[J]. 昆虫知识, 46(2): 216-222. |
| GAO G C, FU B Q, 2009. Advances of researches on carabid beetles as bioindicators[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 46(2): 216-222. | |
| [11] | 高金辉, 韩家永, 张厚良, 等, 2022. 刺五加群落多样性海拔梯度变化及相似性[J]. 森林工程, 38(4): 53-60. |
| GAO J H, HAN J Y, ZHANG H L, et al., 2022. Elevational Changes in community diversity and similarity analysis of a Acanthopanax senticosus community[J]. Forest Engineering, 38(4): 53-60. | |
| [12] | 高敏, 马香丽, 杨晋宇, 等, 2017. 冀北山地华北落叶松人工林与白桦混交改造模式对土壤动物群落的影响[J]. 林业科学, 53(1): 70-81. |
| GAO M, MA X L, YANG J Y, et al., 2017. Influence of the mixed modes of larch and birch on soil faunal community in mountain area of northern Hebei, China[J]. Scientla Silvae Cinicae, 53(1): 70-81. | |
| [13] |
侯春雨, 魏雪, 吴鹏飞, 2022. 种植黄连和重楼对小型土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(3): 813-820.
DOI |
| HOU C Y, WEI X, WU P F, 2022. Effects of cultivating Coptis chinensis and Paris polyphylla on soil microarthropod communities[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 33(3): 813-820. | |
| [14] |
黄玉梅, 李向, 张丹桔, 等, 2020. 成都市温江区不同栽植年限园林植物土壤动物群落特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(11): 3859-3868.
DOI |
| HUANG Y M, LI X, ZHANG D J, et al., 2020. Characteristics of soil animal community with different garden plants and various planting periods in Wenjiang district, Chengdu, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(11): 3859-3868. | |
| [15] | 兰洪波, 冉景丞, 王万海, 等, 2017. 茂兰喀斯特森林湿地地表节肢动物群落结构[J]. 森林与环境学报, 37(4): 483-487. |
| LAN H B, RAN J C, WANG W H, et al., 2017. The structure of ground arthropod community of wetland in Maolan karst Forest[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 37(4): 483-487. | |
| [16] | 李欣颖, 张萌, 郭洋楠, 等, 2022. 采煤沉陷区林下植物多样性与土壤因子的关系[J]. 水土保持学报, 36(1): 268-276. |
| LI X Y, ZHANG M, GUO Y N, et al., 2022. Relationship between understory plant diversity and soil factors in coal mining subsidence area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 36(1): 268-276. | |
| [17] | 李雨, 吴鹏飞, 龙伟, 等, 2019. 高寒地区种植不同种类牧草对土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(20): 7697-7708. |
| LI Y, WU P F, LONG W, et al., 2019. Effects of different forage species on soil arthropod communities on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(20): 7697-7708. | |
| [18] | 刘继亮, 赵文智, 李锋瑞, 等, 2018. 人工固沙植被恢复对地表节肢动物群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(4): 1357-1365. |
| LIU J L, ZHAO W Z, LI F R, et al., 2018. Effects of introduced sand-fixing vegetation on community structure and diversity in ground- dwelling arthropods[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(4): 1357-1365. | |
| [19] | 刘汝海, 王起超, 刘景双, 2002. 东北地区煤矸石环境危害及对策[J]. 地理科学, 22(1): 110-113. |
|
LIU R H, WANG Q C, LIU J S, 2002. Hazards and countermeasures of the gangue in northeast of China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 22(1): 110-113.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 刘新民, 杨劼, 2005. 沙坡头地区人工固沙植被演替中大型土壤动物生物指示作用研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 25(1): 42-46. |
| LIU X M, YANG J, 2005. Application of macrofauna as bioindicators of artificial plant succession in Shapotou region[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 25(1): 42-46. | |
| [21] | 龙偲, 陈中吉, 周运超, 等, 2015. 静水和滴水条件下碳酸盐岩溶解与主要元素释放规律初步研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 34(5): 452-459. |
| LONG S, CHEN Z J, ZHOU Y C, et al., 2015. Preliminary research on dissolution of carbonate rocks and major element release under the conditions of stagnant water and dripping water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 34(5): 452-459. | |
| [22] | 吕渡, 杨亚辉, 赵文慧, 等, 2018. 不同恢复类型植被细根分布及与土壤理化性质的耦合关系[J]. 生态学报, 38(11): 3979-3987. |
| LÜ D, YANG Y H, ZHAO W H, et al., 2018. Fine root biomass distribution and coupling to soil physicochemical properties under different restored vegetation types[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 3979-3987. | |
| [23] | 马克平, 刘玉明, 1994. 生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰ. α多样性的测度方法(下)[J]. 生物多样性, 2(4): 231-239. |
| MA K P, LIU Y M, 1994. Measurement of biotic community diversity. Ⅰ. α diversity[J]. Chinese Biodiversity, 2(4): 231-239. | |
| [24] | 彭东海, 侯晓龙, 何宗明, 等, 2015. 金尾矿废弃地不同植被恢复模式对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(6): 137-142. |
| PENG D H, HOU X L, HE Z M, et al., 2015. Effect of different vegetation restoration patterns on soil physical and chemical properties in wasteland of gold tailings[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(6): 137-142. | |
| [25] | 珊丹, 邢恩德, 荣浩, 等, 2019. 草原矿区排土场不同植被配置类型生态恢复[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(2): 336-342. |
| SHAN D, XING E D, RONG H, et al., 2019. Ecological restoration of different vegetation collocations of coal mine dump in typical steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(2): 336-342. | |
| [26] | 邵颖, 曹四平, 曹文文, 2019. 南泥湾湿地退化与管理对土壤动物多样性的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(5): 634-643. |
| SHAO Y, CAO S P, CAO W W, 2019. Effects of degradation and management of Nanniwan wetland on soil fauna diversity[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(5): 634-643. | |
| [27] | 孙彩彩, 董全民, 刘文亭, 等, 2022. 放牧方式对青藏高原高寒草地土壤节肢动物群落结构和多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 31(2): 62-75. |
| SUN C C, DONG Q M, LIU W T, et al., 2022. Effects of grazing modes on the community structure and diversity of soil arthropod in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 31(2): 62-75. | |
| [28] | 王采娥, 黄梅, 王文银, 等, 2022. 三江源区高寒坡地退化植物群落多样性和地上生物量沿海拔梯度的变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 42(9): 3640-3655. |
| WANG C E, HUANG M, WANG W Y, et al., 2022. Variation characteristics of plant community diversity and above-ground biomass in alpine degraded slopes along altitude gradients in the headwaters region of three-river on Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(9): 3640-3655. | |
| [29] |
王嘉元, 秦富仓, 杨振奇, 等, 2021. 黄土残塬沟壑区不同土地利用方式下土壤动物群落特征[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 23(3): 156-165.
DOI |
|
WANG J Y, QIN F C, YANG Z Q, et al., 2021. Characteristics of soil animal communities under different land use in gully area of Loess plateau[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 23(3): 156-165.
DOI |
|
| [30] | 王蕾, 张宇婕, 于亚军, 2019. 煤矸山复垦林、草地土壤有机碳差异及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(12): 3717-3722. |
| WANG L, ZHANG Y J, YU Y J, 2019. The variation of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors between reclaimed woodland and grassland in coal waste pill[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(12): 3717-3722. | |
| [31] | 王邵军, 阮宏华, 汪家社, 等, 2010. 武夷山典型植被类型土壤动物群落的结构特征[J]. 生态学报, 30(19): 5174-5184. |
| WANG S J, RUAN H H, WANG J S, et al., 2010. Composition structure of soil fauna community under the typical vegetations in the Wuyi mountains, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(19): 5174-5184. | |
| [32] | 王尚义, 石瑛, 牛俊杰, 等, 2013. 煤矸石山不同植被恢复模式对土壤养分的影响——以山西省河东矿区1号煤矸石山为例[J]. 地理学报, 68(3): 372-379. |
|
WANG S Y, SHI Y, NIU J J, et al., 2013. Influence of vegetation restoration models on soil nutrient of coal gangue pile: A case study of No.1 coal gangue pile in Hedong, Shanxi[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(3): 372-379.
DOI |
|
| [33] | 王雅雅, 饶鑫, 童升洪, 等, 2020. 西沙永兴岛抗风桐与海岸桐群落凋落叶分解及中型土壤动物的贡献[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8805-8815. |
| WANG Y Y, RAO X, TONG S H, et al., 2020. Leaf litter decomposition and soil mesofauna contribution in Pisonia grandis and Guettarda speciosa plant communities in the Yongxing island of south China sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8805-8815. | |
| [34] | 吴钢, 魏东, 周政达, 等, 2014. 我国大型煤炭基地建设的生态恢复技术研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 34(11): 2812-2820. |
| WU G, WEI D, ZHOU Z D, et al., 2014. A summary of study on ecological restoration technology of large coal bases construction in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(11): 2812-2820. | |
| [35] | 谢林花, 吕家珑, 张一平, 等, 2004. 长期施肥对石灰性土壤磷素肥力的影响Ⅰ.有机质、全磷和速效磷[J]. 应用生态学报, 5(15): 787-789. |
| XIE L H, LÜ J L, ZHANG Y P, et al., 2004. Influence of long-term fertilization on phosphorus fertility of calcareous soil I.organic matter, total phosphorus and available phosphorus[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 5(15): 787-789. | |
| [36] | 辛未冬, 刘华煜, 杨轶萌, 等, 2021. 复垦对煤矸石山地表节肢动物群落特征的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(7): 2213-2222. |
| XIN W D, LIU H Y, YANG Y M, et al., 2021. Effect of reclamation on the characteristics of surface arthropod community in coal gangue[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(7): 2213-2222. | |
| [37] | 辛未冬, 王宇欣, 2019. 霍州煤矸石山大型土壤动物群落特征研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(1): 158-163. |
| XIN W D, WANG Y X, 2019. Study on characteristics of soil macrofauna communities in Huozhou coal waste pile[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 33(1): 158-163. | |
| [38] | 邢树文, 许佳敏, 黄彬, 等, 2021. 钨尾矿重金属污染对茶园土壤动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(9): 1903-1915. |
| XING S W, XU J M, HUANG B, et al., 2021. Effect of heavy metal pollution on the community structure and diversity of soil animals in tea garden located in a tungsten mining area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(9): 1903-1915. | |
| [39] |
徐国良, 文雅, 蔡少燕, 等, 2019. 城市表层土壤对生态健康影响研究述评[J]. 地理研究, 38(12): 2941-2956.
DOI |
|
XU G L, WEN Y, CAI S Y, et al., 2019. Review for the effects of urban topsoil on the ecological health[J]. Geographical Research, 38(12): 2941-2956.
DOI |
|
| [40] | 许洪军, 于立忠, 黄选瑞, 等, 2015. 辽东山区次生林与人工林大型地表节肢动物多样性[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(3): 727-735. |
| XU H J, YU L Z, HUANG X R, et al., 2015. Biodiversity of macro ground-dwelling arthropods in secondary forests and plantation forests of montane region of eastern Liaoning province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(3): 727-735. | |
| [41] | 尹文英, 1998. 中国土壤动物检索图鉴[M]. 北京: 科技出版社. |
| YIN W Y, 1998. Pictorial Keys to Soil Animals of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [42] | 章爱群, 贺立源, 赵会娥, 等, 2009. 有机酸对土壤无机态磷转化和速效磷的影响[J]. 生态学报, 29(8): 4061-4069. |
| ZHANG A Q, HE L Y, ZHAO H E, et al., 2009. Effect of organic acids on inorganic phosphorus transformation in soils and its readily available phosphate[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(8): 4061-4069. | |
| [43] | 张蓉, 于亚军, 2018. 煤矸山复垦林地和草地土壤微生物多样性和群落组成的差异及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(6): 1662-1668. |
| ZHANG R, YU Y J, 2018. Differences of soil microbial diversity and community composition between reclaimed woodland and grassland in coal waste pile and their influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(6): 1662-1668. | |
| [44] | 张振佳, 曹银贵, 王舒菲, 等, 2021. 平朔黄土露天矿区复垦地表层土壤微生物与酶活性分析[J]. 生态学报, 41(1): 110-123. |
| ZHANG Z J, CAO Y G, WANG S F, et al., 2021. Characteristics and differences of surface soil microbial population and enzyme activities in opencast mining area of Pingshuo[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(1): 110-123. | |
| [45] | 郑成卓, 臧建成, 唐晓琴, 2020. 西藏林芝不同植被地表节肢动物群落多样性[J]. 西北农业学报, 29(2): 248-253. |
| ZHENG C Z, ZANG J C, TANG X Q, 2020. Diversity of arthropod community on different vegetation surface in Linzhi of Tibet[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 29(2): 248-253. | |
| [46] | 郑乐怡, 归鸿, 1998. 昆虫分类[M]. 南京: 南京师范大学出版社. |
| ZHENG L Y, GUI H, 1998. Insects Classification[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University Press. | |
| [47] | 钟觉民, 1990. 幼虫分类学[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| ZHONG J M, 1990. Larval Classification[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press. |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 李海鹏, 黄月华, 孙晓东, 曹启民, 符芳兴, 孙楚涵. 海南农田不同质地砖红壤及其细菌群落与番茄青枯病发生的关联分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1062-1069. |
| [3] | 巫晨煜, 许帆帆, 魏士博, 樊晶晶, 刘观鹏, 王坤. 渭河流域地表植被覆盖对气候变化的响应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 835-844. |
| [4] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [5] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [6] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [7] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [8] | 李晖, 李必龙, 葛黎黎, 韩琛惠, 杨倩, 张岳军. 2000-2021年汾河流域植被时空演变特征及地形效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 439-449. |
| [9] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [10] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [11] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [12] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [13] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [14] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [15] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
