生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2067-2075.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.013
收稿日期:2021-09-18
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
作者简介:丛鑫(1976年生),女,教授,博士,研究方向为土壤环境化学和生态修复。E-mail: congxin1800@163.com
基金资助:
CONG Xin( ), LI Yao, WANG Yu, ZHENG Li
), LI Yao, WANG Yu, ZHENG Li
Received:2021-09-18
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
以牛粪和水稻秸秆为原料,分别在300 ℃和500 ℃条件下制备生物炭,同时通过共沉淀方法制备生物炭基针铁矿复合材料,研究生物炭及生物炭基复合材料对水中莠去津吸附特征。SEM和XRD分析结果表明,复合材料表面粗糙程度增加,2θ在21.2°、33.4°、36.6°、47.6°处出现针铁矿的特征衍射峰,生物炭基针铁矿复合材料制备成功。通过对吸附动力学和等温吸附平衡分析发现,生物炭对莠去津的吸附行为更符合准二级动力学方程,等温吸附过程符合Freundlich模型(r2为0.925—0.996)。在25 ℃条件下,莠去津在300 ℃和500 ℃条件下制备的针铁矿负载牛粪生物炭上的吸附量分别是原生物炭上吸附量的1.59倍和2.99倍,在针铁矿负载水稻秸秆生物炭上的吸附量分别是原生物炭上吸附量的2.02倍和1.73倍。比表面积和孔结构数据显示,生物炭基复合材料的比表面积是原生物炭材料的4.41—20.8倍,制备生物炭材料的孔结构以中孔为主。莠去津在生物炭上的吸附大体表现为吸热的自发过程。对不同材料制备的生物炭及与生物炭基复合材料吸附性能进行对比,结果表明水稻秸秆制备的生物炭对莠去津的吸附性能优于牛粪制备的生物炭,生物炭基针铁矿复合材料对莠去津的吸附效果优于原生物炭。随制备温度的升高,相同材料生物炭对莠去津吸附性能略有增加。研究结果可为生物炭及生物炭基针铁矿复合材料去除水中莠去津的应用提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
丛鑫, 李瑶, 王宇, 郑力. 生物炭基针铁矿复合材料对水中莠去津吸附特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2067-2075.
CONG Xin, LI Yao, WANG Yu, ZHENG Li. Adsorption Characterization of Atrazine in Aqueous Medium on Goethite Biochar Composites[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2067-2075.
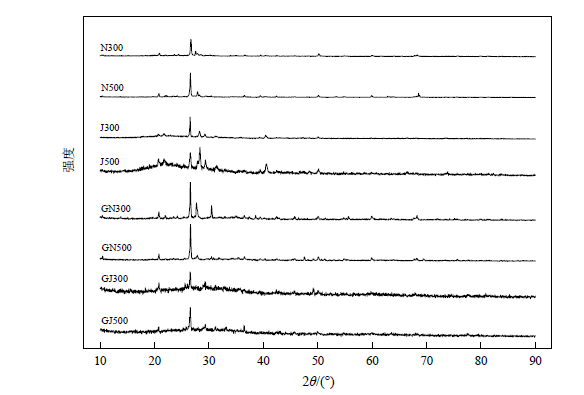
图1 生物炭及生物炭基针铁矿复合材料XRD图谱 N300、N500分别为300、500 ℃下制备的牛粪生物炭;J300和J500分别为300、500 ℃条件下制备的水稻秸秆生物炭。下同
Fig. 1 XRD spectra of biochar and goethite biochar composites
| 生物炭种类 Types of biochar | 元素原子百分比 Atomic percentage of element/% | 比表面积 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔结构分析 Pore structure analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Fe | S | 最可几孔径 Mode pore size/nm | 平均孔径 Mean pore size/nm | 总孔体积 Total pore volume/(cm3∙g-1) | ||
| N300 | 69.28 | 30.21 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 1.995 | 3.452 | 9.055 | 0.0079 |
| N500 | 73.45 | 26.48 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.437 | 3.726 | 14.78 | 0.0785 |
| J300 | 89.74 | 10.22 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 16.11 | 3.048 | 4.575 | 0.0412 |
| J500 | 50.02 | 49.48 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 36.06 | 3.779 | 11.91 | 0.0435 |
| GN300 | 66.28 | 30.65 | 2.84 | 0.22 | 35.43 | 3.396 | 15.83 | 0.1309 |
| GN500 | 90.44 | 8.79 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 92.13 | 3.398 | 15.88 | 0.2086 |
| GJ300 | 84.57 | 13.8 | 1.63 | 0 | 154.2 | 3.402 | 13.61 | 0.5416 |
| GJ500 | 71.35 | 27.62 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 159.1 | 3.403 | 16.39 | 0.6321 |
表1 生物炭及生物炭基针铁矿复合材料理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of biochar and biochar goethite composites
| 生物炭种类 Types of biochar | 元素原子百分比 Atomic percentage of element/% | 比表面积 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 孔结构分析 Pore structure analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Fe | S | 最可几孔径 Mode pore size/nm | 平均孔径 Mean pore size/nm | 总孔体积 Total pore volume/(cm3∙g-1) | ||
| N300 | 69.28 | 30.21 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 1.995 | 3.452 | 9.055 | 0.0079 |
| N500 | 73.45 | 26.48 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.437 | 3.726 | 14.78 | 0.0785 |
| J300 | 89.74 | 10.22 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 16.11 | 3.048 | 4.575 | 0.0412 |
| J500 | 50.02 | 49.48 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 36.06 | 3.779 | 11.91 | 0.0435 |
| GN300 | 66.28 | 30.65 | 2.84 | 0.22 | 35.43 | 3.396 | 15.83 | 0.1309 |
| GN500 | 90.44 | 8.79 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 92.13 | 3.398 | 15.88 | 0.2086 |
| GJ300 | 84.57 | 13.8 | 1.63 | 0 | 154.2 | 3.402 | 13.61 | 0.5416 |
| GJ500 | 71.35 | 27.62 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 159.1 | 3.403 | 16.39 | 0.6321 |
| 生物炭类型 Types of biochar | 准一级动力学方程 Pseudo first-order kinetic equation | 准二级动力学方程 Pseudo second-order kinetic equation | 双常数方程 Double-constant equation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg∙g-1) | k1/h-1 | r2 | qe/(mg∙g-1) | k2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | r2 | lna | Ks/(mg∙g-1∙h-1) | r2 | |||
| N300 | 0.612 | 0.157 | 0.962 | 0.694 | 0.703 | 0.990 | -1.445 | 0.313 | 0.989 | ||
| N500 | 0.452 | 0.211 | 0.898 | 0.528 | 0.513 | 0.995 | -1.347 | 0.201 | 0.972 | ||
| J300 | 4.973 | 0.659 | 0.883 | 5.573 | 0.222 | 0.998 | 1.126 | 0.178 | 0.966 | ||
| J500 | 4.454 | 0.232 | 0.823 | 5.125 | 0.202 | 0.996 | 1.067 | 0.163 | 0.986 | ||
| GN300 | 1.323 | 0.158 | 0.978 | 1.468 | 0.331 | 0.992 | -0.775 | 0.344 | 0.975 | ||
| GN500 | 1.529 | 0.186 | 0.990 | 1.677 | 0.318 | 0.994 | -0.612 | 0.339 | 0.968 | ||
| GJ300 | 10.82 | 0.474 | 0.866 | 12.21 | 0.122 | 0.998 | 2.095 | 0.116 | 0.992 | ||
| GJ500 | 8.097 | 0.237 | 0.729 | 9.274 | 0.112 | 0.997 | 1.617 | 0.178 | 0.967 | ||
表2 莠去津在生物炭及其复合材料上吸附动力学参数
Table 2 Kinetic equation parameters of atrazine adsorption on biochars and their composites
| 生物炭类型 Types of biochar | 准一级动力学方程 Pseudo first-order kinetic equation | 准二级动力学方程 Pseudo second-order kinetic equation | 双常数方程 Double-constant equation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe/(mg∙g-1) | k1/h-1 | r2 | qe/(mg∙g-1) | k2/(g∙mg-1∙h-1) | r2 | lna | Ks/(mg∙g-1∙h-1) | r2 | |||
| N300 | 0.612 | 0.157 | 0.962 | 0.694 | 0.703 | 0.990 | -1.445 | 0.313 | 0.989 | ||
| N500 | 0.452 | 0.211 | 0.898 | 0.528 | 0.513 | 0.995 | -1.347 | 0.201 | 0.972 | ||
| J300 | 4.973 | 0.659 | 0.883 | 5.573 | 0.222 | 0.998 | 1.126 | 0.178 | 0.966 | ||
| J500 | 4.454 | 0.232 | 0.823 | 5.125 | 0.202 | 0.996 | 1.067 | 0.163 | 0.986 | ||
| GN300 | 1.323 | 0.158 | 0.978 | 1.468 | 0.331 | 0.992 | -0.775 | 0.344 | 0.975 | ||
| GN500 | 1.529 | 0.186 | 0.990 | 1.677 | 0.318 | 0.994 | -0.612 | 0.339 | 0.968 | ||
| GJ300 | 10.82 | 0.474 | 0.866 | 12.21 | 0.122 | 0.998 | 2.095 | 0.116 | 0.992 | ||
| GJ500 | 8.097 | 0.237 | 0.729 | 9.274 | 0.112 | 0.997 | 1.617 | 0.178 | 0.967 | ||
| 生物炭类型 Types of biochars | 温度 Temperature/K | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | KF | r2 | Koc/(L·g-1) | Qmax/(mg·L-1) | b | r2 | |||||
| N300 | 298.15 | 0.869 | 0.091 | 0.991 | 0.498 | 8.355 | 0.009 | 0.992 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.858 | 0.107 | 0.995 | 0.687 | 8.853 | 0.009 | 0.991 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.853 | 0.143 | 0.995 | 0.920 | 10.96 | 0.010 | 0.991 | ||||
| N500 | 298.15 | 0.650 | 0.089 | 0.995 | 0.673 | 1.324 | 0.046 | 0.988 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.584 | 0.132 | 0.987 | 1.033 | 1.362 | 0.065 | 0.977 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.544 | 0.193 | 0.982 | 1.492 | 1.584 | 0.084 | 0.973 | ||||
| J300 | 298.15 | 0.393 | 2.090 | 0.958 | 12.17 | 7.823 | 0.266 | 0.951 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.356 | 2.677 | 0.987 | 15.06 | 8.379 | 0.385 | 0.888 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.348 | 3.505 | 0.937 | 19.29 | 10.11 | 0.462 | 0.923 | ||||
| J500 | 298.15 | 0.327 | 2.190 | 0.925 | 23.22 | 6.197 | 0.462 | 0.939 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.364 | 2.726 | 0.940 | 27.85 | 8.785 | 0.363 | 0.881 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.297 | 3.821 | 0.937 | 37.29 | 9.351 | 0.682 | 0.880 | ||||
| GN300 | 298.15 | 0.677 | 0.208 | 0.995 | 1.448 | 3.363 | 0.045 | 0.998 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.716 | 0.126 | 0.996 | 0.852 | 2.924 | 0.030 | 0.990 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.651 | 0.119 | 0.992 | 0.890 | 1.732 | 0.048 | 0.981 | ||||
| GN500 | 298.15 | 0.705 | 0.229 | 0.989 | 1.449 | 4.397 | 0.038 | 0.993 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.691 | 0.249 | 0.993 | 1.588 | 4.576 | 0.038 | 0.997 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.696 | 0.262 | 0.992 | 1.846 | 5.252 | 0.034 | 0.981 | ||||
| GJ300 | 298.15 | 0.371 | 4.378 | 0.991 | 21.48 | 15.42 | 0.253 | 0.959 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.429 | 3.228 | 0.993 | 17.60 | 14.20 | 0.200 | 0.980 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.483 | 2.278 | 0.985 | 12.76 | 13.04 | 0.134 | 0.968 | ||||
| GJ500 | 298.15 | 0.413 | 2.918 | 0.976 | 29.57 | 11.80 | 0.234 | 0.984 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.414 | 3.095 | 0.980 | 31.00 | 12.52 | 0.232 | 0.954 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.374 | 3.716 | 0.994 | 36.04 | 13.19 | 0.254 | 0.924 | ||||
表3 莠去津在生物炭及其复合材料上等温吸附模型参数
Table 3 The parameters of isothermal adsorption model of atrazine on biochars and their composites
| 生物炭类型 Types of biochars | 温度 Temperature/K | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | KF | r2 | Koc/(L·g-1) | Qmax/(mg·L-1) | b | r2 | |||||
| N300 | 298.15 | 0.869 | 0.091 | 0.991 | 0.498 | 8.355 | 0.009 | 0.992 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.858 | 0.107 | 0.995 | 0.687 | 8.853 | 0.009 | 0.991 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.853 | 0.143 | 0.995 | 0.920 | 10.96 | 0.010 | 0.991 | ||||
| N500 | 298.15 | 0.650 | 0.089 | 0.995 | 0.673 | 1.324 | 0.046 | 0.988 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.584 | 0.132 | 0.987 | 1.033 | 1.362 | 0.065 | 0.977 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.544 | 0.193 | 0.982 | 1.492 | 1.584 | 0.084 | 0.973 | ||||
| J300 | 298.15 | 0.393 | 2.090 | 0.958 | 12.17 | 7.823 | 0.266 | 0.951 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.356 | 2.677 | 0.987 | 15.06 | 8.379 | 0.385 | 0.888 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.348 | 3.505 | 0.937 | 19.29 | 10.11 | 0.462 | 0.923 | ||||
| J500 | 298.15 | 0.327 | 2.190 | 0.925 | 23.22 | 6.197 | 0.462 | 0.939 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.364 | 2.726 | 0.940 | 27.85 | 8.785 | 0.363 | 0.881 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.297 | 3.821 | 0.937 | 37.29 | 9.351 | 0.682 | 0.880 | ||||
| GN300 | 298.15 | 0.677 | 0.208 | 0.995 | 1.448 | 3.363 | 0.045 | 0.998 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.716 | 0.126 | 0.996 | 0.852 | 2.924 | 0.030 | 0.990 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.651 | 0.119 | 0.992 | 0.890 | 1.732 | 0.048 | 0.981 | ||||
| GN500 | 298.15 | 0.705 | 0.229 | 0.989 | 1.449 | 4.397 | 0.038 | 0.993 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.691 | 0.249 | 0.993 | 1.588 | 4.576 | 0.038 | 0.997 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.696 | 0.262 | 0.992 | 1.846 | 5.252 | 0.034 | 0.981 | ||||
| GJ300 | 298.15 | 0.371 | 4.378 | 0.991 | 21.48 | 15.42 | 0.253 | 0.959 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.429 | 3.228 | 0.993 | 17.60 | 14.20 | 0.200 | 0.980 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.483 | 2.278 | 0.985 | 12.76 | 13.04 | 0.134 | 0.968 | ||||
| GJ500 | 298.15 | 0.413 | 2.918 | 0.976 | 29.57 | 11.80 | 0.234 | 0.984 | |||
| 308.15 | 0.414 | 3.095 | 0.980 | 31.00 | 12.52 | 0.232 | 0.954 | ||||
| 318.15 | 0.374 | 3.716 | 0.994 | 36.04 | 13.19 | 0.254 | 0.924 | ||||
| Types of biochars | Temperature/ K | ΔG0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔH0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔS0/ (kJ∙mol-1∙K-1) | Types of biochars | Temperature/ K | ΔG0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔH0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔS0/ (kJ∙mol-1∙K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N300 | 298.15 | -11.15 | 18.26 | 0.098 | GN300 | 298.15 | -13.23 | -22.01 | -0.03 |
| 308.15 | -11.97 | 308.15 | -12.31 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -13.12 | 318.15 | -12.65 | ||||||
| N500 | 298.15 | -11.13 | 30.58 | 0.140 | GN500 | 298.15 | -13.47 | 5.35 | 0.06 |
| 308.15 | -12.51 | 308.15 | -14.07 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -13.92 | 318.15 | -14.73 | ||||||
| J300 | 298.15 | -18.95 | 20.37 | 0.132 | GJ300 | 298.15 | -20.78 | -25.73 | -0.02 |
| 308.15 | -20.22 | 308.15 | -20.70 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -21.59 | 318.15 | -20.45 | ||||||
| J500 | 298.15 | -19.07 | 21.89 | 0.137 | GJ500 | 298.15 | -19.78 | 9.48 | 0.10 |
| 308.15 | -20.27 | 308.15 | -20.59 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -21.82 | 318.15 | -21.74 |
表4 莠去津在生物炭及其复合材料上吸附热力学参数
Table 4 Thermodynamic parameters of atrazine adsorption on biochars and their composites
| Types of biochars | Temperature/ K | ΔG0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔH0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔS0/ (kJ∙mol-1∙K-1) | Types of biochars | Temperature/ K | ΔG0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔH0/ (kJ∙mol-1) | ΔS0/ (kJ∙mol-1∙K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N300 | 298.15 | -11.15 | 18.26 | 0.098 | GN300 | 298.15 | -13.23 | -22.01 | -0.03 |
| 308.15 | -11.97 | 308.15 | -12.31 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -13.12 | 318.15 | -12.65 | ||||||
| N500 | 298.15 | -11.13 | 30.58 | 0.140 | GN500 | 298.15 | -13.47 | 5.35 | 0.06 |
| 308.15 | -12.51 | 308.15 | -14.07 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -13.92 | 318.15 | -14.73 | ||||||
| J300 | 298.15 | -18.95 | 20.37 | 0.132 | GJ300 | 298.15 | -20.78 | -25.73 | -0.02 |
| 308.15 | -20.22 | 308.15 | -20.70 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -21.59 | 318.15 | -20.45 | ||||||
| J500 | 298.15 | -19.07 | 21.89 | 0.137 | GJ500 | 298.15 | -19.78 | 9.48 | 0.10 |
| 308.15 | -20.27 | 308.15 | -20.59 | ||||||
| 318.15 | -21.82 | 318.15 | -21.74 |
| [1] |
CASTRO C S, GUERREIRO M C, GONCALVES M, et al., 2009. Activated carbon/iron oxide composites for the removal of atrazine from aqueous medium[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 164(2-3):609-614.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN B L, CHEN Z M, LV S F, 2011. A novel magnetic biochar efficiently sorbs organic pollutants and phosphate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(2):716-723.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GUO X T, DONG H, YANG C, et al., 2016. Application of goethite modified biochar for tylosin removal from aqueous solution[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 502:81-88.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI B, YANG L, WANG C Q, et al., 2017. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derived from different modification processes[J]. Chemosphere, 175:332-340.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU N, CHARRUA A B, WENG C H, et al., 2015. Characterization of biochars derived from agriculture wastes and their adsorptive removal of atrazine from aqueous solution: A comparative study[J]. Bioresource Technology, 198:55-62.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
QU M J, LI H D, LI N, et al., 2017. Distribution of atrazine and its phytoremediation by submerged macrophytes in lake sediments[J]. Chemosphere, 168:1515-1522.
DOI URL |
| [7] | SUN K, GAO B, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2010. Sorption of atrazine and phenanthrene by organic matter fractions in soil and sediment[J]. Envrionmental Pollution, 158(12):3520-3526. |
| [8] |
TAO Y, HU S B, HAN S Y, et al., 2019. Efficient removal of atrazine by iron-modified biochar loaded Acinetobacter lwoffii DNS32[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 682:59-69.
DOI URL |
| [9] | WANG H, CHU Y X, FANG C G, et al., 2017. Sorption of tetracycline on biochar derived from rice straw under different temperatures[J]. Plos One, 12(8):1-14. |
| [10] |
WANG H, FANG C G, WANG Q, et al., 2018. Sorption of tetracycline on biochar derived from rice straw and swine manure[J]. RSC Advances, 8(29):16260-16268.
DOI URL |
| [11] | YANG F, SUN L L, XIE W L, et al., 2017. Nitrogen-functionalization biochars derived from wheat straws via molten salt synjournal: An efficient adsorbent for atrazine removal[J]. Science of the Total Envrionment, 607-608:1391-1399. |
| [12] | ZHANG Z S, WANG X J, WANG Y, et al., 2013. Pb(Ⅱ) removal from water using Fe-coated bamboo charcoal with the assistance of microwaves[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 25(5):1044-1053. |
| [13] | ZHU S H, ZHAO J J, ZHAO N, et al., 2020. Goethite modified biochar as a multifunctional amendment for cationic Cd(Ⅱ), anionic As(Ⅲ), roxarsone, and phosphorus in soil and water[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 247:1-10. |
| [14] | CHARRUA A B, 2015. 生物碳吸附去除溶液中的阿特拉津[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学. |
| CHARRUA A B, 2015. Adsorptive removal of atrazine from aqueous solution by various types of biochars[D]. Jilin: Jilin University. | |
| [15] | 程婉艺, 2020. 改性生物炭有机复合材料的制备及吸附性能的研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学. |
| CHENG W Y, 2020. Preparation and adsorption capability of modified biochar composites[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology. | |
| [16] | 程扬, 沈启斌, 刘子丹, 等, 2019. 两种生物炭的制备及其对水溶液中四环素去除的影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 40(3):1328-1336. |
| CHENG Y, SHEN Q B, LIU Z D, et al., 2019. Preparation of two kinds of biochar and the factors influencing tetracycline removal from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science, 40(3):1328-1336. | |
| [17] | 邓雅雯, 晏彩霞, 聂明华, 等, 2020. 生物炭对抗生素的吸附/解吸研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 42(3):376-384. |
| DENG Y W, YAN C X, NIE M H, et al., 2020. Study on the antibiotic adsorption/desorption of biochar: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 42(3):376-384. | |
| [18] | 樊玉娜, 2019. 高羊茅生物炭对不同类型土壤中阿特拉津及其代谢产物吸附能力的影响研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学. |
| FAN Y N, 2019. Effects of tall festuca biochar on the adsorption capacity of Atrazine and its metabolites in different types of soils[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University. | |
| [19] | 冯婧微, 徐英侠, 兰希平, 2014. 改性纳米零价铁去除水中莠去津[J]. 农药, 53(9):651-654. |
| FENG J W, XU Y X, LAN X P, 2014. Removal of atrazine in wastewater using modified nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. Agrochemicals, 53(9):651-654. | |
| [20] | 李昉泽, 冯丹, 邓惠, 等, 2015. 阿特拉津在5种农业土壤中的吸附解吸特性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(12):2056-2061. |
| LI F Z, FENG D, DENG H, et al., 2015. Adsorption and desorption of atrazine in five agriculture soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(12):2056-2061. | |
| [21] | 廖家辉, 2014. AFT在“氧化铁-腐殖质-Pb2+”系统中的吸附及土壤中AFT/Pb2+检测的生物传感新方法[D]. 重庆: 西南大学. |
| LIAO J H, 2014. Adsorption of AFT in “iron oxide-humus-Pb2+” system and new biosensing methods for AFT/Pb2+ measurement in soil[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University. | |
| [22] | 刘娜, 杨亚冬, ALBERTO B C, 等, 2016. 响应曲面法优化生物质炭去除水溶液中的阿特拉津[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(4):1199-1207. |
| LIU N, YANG Y D, ALBERTO B C, et al., 2016. Optimization of atrazine removal from aqueous solution by biochar using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 46(4):1199-1207. | |
| [23] | 阮梦娜, 王宇芳, 楼筱珺, 等, 2016. 生物炭耦合菌剂法去除污染水体中的苯胺[J]. 环境工程学报, 10(5):2454-2458. |
| RUAN M N, WANG Y F, LOU X J, et al., 2016. Aniline removal with biochar coupling microbial agents[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 10(5):2454-2458. | |
| [24] | 宋桃莉, 伊学农, 王玉琳, 等, 2013. 超声协同Feton法与类Feton法预处理莠去津农药废水研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 24(6):153-156. |
| SONG T L, YI X N, WANG Y L, et al., 2013. Study on pretreatment of atrazine pesticide wastewater by ultrasound coupling with Fenton and Fenton-like methods[J]. Journal of Water Resources and water Engineering, 24(6):153-156. | |
| [25] | 孙莉莉, 2019. 不同粒径生物炭对水溶液中阿特拉津和铅的吸附行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. |
| SUN L L, 2019. Adsorption of atrazine and lead in aqueous solution onto biochars of different particle sizes[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. | |
| [26] | 王靖宜, 王丽, 张文龙, 等, 2019. 生物炭基复合材料制备及其对水体特征污染物的吸附性能[J]. 化工进展, 38(8):3838-3851. |
| WANG J Y, WANG L, ZHANG W L, et al., 2019. Preparation of biochar-based composites and their adsorption performances for characteristic contaminants in wastewater[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 38(8):3838-3851. | |
| [27] | 王晟, 冯翔, 李兵, 等, 2021. 多种铁改性和未改性生物炭对模拟地下水中六价铬的去除[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 51(1):247-255. |
| WANG S, FENG X, LI B, et al., 2021. Removal of hexavalent chromium from simulated groundwater by variety of iron-modified and unmodified biochars[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 51(1):247-255. | |
| [28] | 王旭峰, 郑立安, 刘毛, 等, 2017. 改性玉米芯生物炭对废水中铜和氨氮的吸附[J]. 工业水处理, 37(1):37-41. |
| WANG X F, ZHENG L A, LIU M, et al., 2017. Adsorption characters of Cu2+ and NH4+-N in wastewater by modified corncob biochar[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 37(1):37-41. | |
| [29] | 魏茁, 姜英宇, 陈立飞, 等, 2021. Fe & Cu生物炭复合材料脱除污染水体中金霉素[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4):805-815. |
| WEI Z, JIANG Y Y, CHEN L F, et al., 2021. Fe & Cu-biochar composite material to remove chlortetracycline from polluted water[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(4):805-815. | |
| [30] | 徐雄, 李春梅, 孙静, 等, 2016. 我国重点流域地表水中29种农药污染及其生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 11(2):347-354. |
| XU X, LI C M, SUN J, et al., 2016. Residue characteristics and ecological risk assessment of twenty-nine pesticides in surface water of major river-basin in China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 11(2):347-354. | |
| [31] | 徐雪斌, 丁竹红, 胡忻, 等, 2017. 花生壳基和木屑基生物炭对离子型染料Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 39(9):929-935. |
| XU X B, DING Z H, HU X, et al., 2017. Study on the antibiotic adsorption/desorption of biochar: A review[J]. Environmentl Pollution and Control, 39(9):929-935. | |
| [32] | 俞花美, 2014. 生物质炭对环境中阿特拉津的吸附解吸作用及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京). |
| YU H M, 2014. Sorption/desorption characteristics and mechanisms of bio-chars with atrazine in environment[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing). | |
| [33] | 张海波, 苏龙, 程红艳, 等, 2021. 不同热解温度制备的香菇菌糠生物炭对孔雀石绿的吸附及其机理分析[J]. 核农学报, 35(5):1231-1242. |
| ZHANG H B, SU L, CHENG H Y, et al., 2021. Adsorption and mechanism analysis of Malachite green adsorption by spent Lentinus edodes substrate based biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures[J]. Journal of nuclear agricultural science, 35(5):1231-1242. | |
| [34] | 张苏明, 张建强, 周凯, 等, 2021. 铁基改性椰壳生物炭对砷的吸附效果及机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(7):1503-1512. |
| ZHANG S M, ZHANG J Q, ZHOU K, et al., 2021. Adsorption effect and mechanism of iron-based modified coconut shell biochar to arsenic[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(7):1503-1512. | |
| [35] | 张晓蕾, 薛文平, 徐恒振, 等, 2012. 近海沉积物对粪固醇的等温吸附和热力学研究[J]. 环境科学, 33(10):3547-3553. |
| ZHANG X L, XUE W P, XU H Z, et al., 2012. Sorption isotherms and sorption thermodynamics of faecal sterols on offshore sediment[J]. Environmental Science, 33(10):3547-3553. | |
| [36] | 张照然, 2020. 生物炭基复合材料去除水中磷酸盐的应用研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学. |
| ZHANG Z R, 2020. Applied study on the removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by biochar based composites[D]. Ji’nan: University of Ji’nan. |
| [1] | 王家一, 孙亭亭, 沙润钰, 谌婷红, 邢冉, 秦伯强, 施文卿. 富营养化湖泊蓝藻打捞减污降碳效果模拟研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [2] | 王铁铮, 瞿心悦, 刘春香, 李有志. 东江湖水质时空变化规律及其与流域土地利用的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [3] | 于菲, 曾海龙, 房怀阳, 付玲芳, 林澍, 董家豪. 典型感潮河网浮游藻类功能群时空变化特征及水质评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [4] | 杨秋, 曹英杰, 张宇, 陈建耀, 王诗忠, 田帝. 闭坑铅锌矿区地下水-矿坑水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 361-371. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 杨小琴, 简美鹏, 张晓然. 城市水体中微塑料的来源、赋存及其生态风险研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 407-420. |
| [6] | 童银栋, 黄兰兰, 杨宁, 张奕妍, 李子芃, 邵波. 全球水体微囊藻毒素分布特征及其潜在环境风险分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 129-138. |
| [7] | 张丽聪, 肖凯, 张鹏, 李海龙, 王俊坚, 李镇扬, 王芬芳, 徐华林, 郭跃华. 淤泥质潮滩重金属和溶解性有机质的潮汐变化特征及其环境影响评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2169-2179. |
| [8] | 王海鹤, 孙媛媛, 张帅, 徐小蓉, 商成梅, 黎春想. 贵阳市集中式饮用水源地重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2039-2047. |
| [9] | 刘畅, 罗艳丽, 刘晨通, 郑玉红, 晁博, 董乐乐. 奎屯河下游区域地下水和农田土壤砷的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2070-2078. |
| [10] | 王钊, 张曼胤, 胡宇坤, 刘魏魏, 张苗苗. 盐度对典型滨海湿地沉积物汞甲基化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [11] | 陈小弯, 田华川, 常军军, 陈礼强, 舒兴权, 冯秀祥. 杞麓湖中河河口表流湿地净化河道污染水的效果及其微生物群落特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| [12] | 吴昊平, 秦红杰, 贺斌, 尤毅, 陈金峰, 邹春萍, 杨思雨, 郝贝贝. 基于碳中和的农业面源污染治理模式发展态势刍议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| [13] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [14] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [15] | 樊珂宇, 高原, 赖子尼, 曾艳艺, 刘乾甫, 李海燕, 麦永湛, 杨婉玲, 魏敬欣, 孙金辉, 王超. 珠三角河网鱼类微塑料污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1590-1598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 104
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 170
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
