生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 257-264.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.006
李少宁1,2( ), 陶雪莹1,2, 李慧敏1,2, 赵娜2, 徐晓天2, 鲁绍伟1,2,*(
), 陶雪莹1,2, 李慧敏1,2, 赵娜2, 徐晓天2, 鲁绍伟1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-22
出版日期:2022-02-18
发布日期:2022-04-14
通讯作者:
*鲁绍伟(1969年生),男,研究员,博士,主要研究方向为生态系统结构与功能研究。E-mail: hblsw8@163.com作者简介:李少宁(1975年生),男,副研究员,博士,主要研究方向为城市森林生态功能研究。E-mail: lishaoning@126.com
基金资助:
LI Shaoning1,2( ), TAO Xueying1,2, LI Huimin1,2, ZHAO Na2, XU Xiaotian2, LU Shaowei1,2,*(
), TAO Xueying1,2, LI Huimin1,2, ZHAO Na2, XU Xiaotian2, LU Shaowei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-22
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
摘要:
选取北京地区典型常绿树种侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)和落叶树种垂柳(Salix babylonica),以生长健康、树龄(8年)相同树种为试材,开展植物释放有益挥发性有机物(BVOCs)动态变化特征研究实验。采用自动热脱附-气相色谱/质谱联用法(Thermal desorption Cold Trap-Gas Chromagraphy/Mass Spectrum,TCT/GC/MS)进行植物BVOCs成分测定,筛选出集景观美化、清新空气、康体保健于一体的园林景观树种,从景观生态学视角为城市绿地植物配置、生态康养森林群落营造提供必要理论依据。针对TCT/GC/MS分析获得的BVOCs原始数据-总离子流图(Total ion current,TIC),其各峰对应化学物质信息利用TurboMass Ver 5.4.2软件、质谱数据库(Nist 2008 Library)检索,经过人工校对和解析后,最终确定各BVOCs成分。结果表明,侧柏在生长季共释放烯烃类、酯类、醛类、酮类、醇类、有机酸类和其他类共7类45种有益挥发物。垂柳较之少一类有机酸,为6类43种;侧柏释放总有益挥发物不同生长季表现为秋季 (61.70%)>春季 (60.99%)>夏季 (60.82%),各季以 (1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯、α-蒎烯、3-蒈烯等烯烃类有益组分相对含量较高;垂柳释放总有益挥发物不同生长季表现为春季 (51.35%)>夏季 (41.09%)>秋季 (32.94%),各季以乙酸叶醇酯、顺-3-己烯-1-醇、(+/-)-薄荷醇、天然壬醛和(1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯等成分相对含量较高,各有益类别化合物季节变化规律明显。
中图分类号:
李少宁, 陶雪莹, 李慧敏, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 侧柏和垂柳释放有益BVOCs组分生长季动态变化特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 257-264.
LI Shaoning, TAO Xueying, LI Huimin, ZHAO Na, XU Xiaotian, LU Shaowei. Study on Dynamic Characteristics of BVOCs Released from Platycladus orientalis and Salix babylonica in Growing Season[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 257-264.
| 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 化合物 Compounds | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||||
| 烯烃类 Alkenes | 1 | (1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯 (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 12.02±1.371 | 21.87±0.618 | 6.91±0.423 |
| 2 | β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | C10H16 | 4.41±1.052 | 0.93±0.383 | 7.01±0.097 | |
| 3 | 右旋萜二烯 (+)-Limonene | C10H16 | 8.24±0.823 | 0.34±0.271 | 4.85±0.142 | |
| 4 | 桧烯 Sabinene | C10H16 | 4.90±0.436 | 5.60±0.242 | 1.50±0.025 | |
| 5 | 萜品油烯 Terpinolene | C10H16 | 2.27±0.194 | 0.84±0.511 | 0.51±0.189 | |
| 6 | (1S)-(-)-α-蒎烯 (1S)-(-)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 0.02±0.011 | 0.29±0.195 | — | |
| 7 | 柠檬烯 2-Ethylbutyl methacrylate | C10H18O2 | 1.29±0.138 | 1.98±0.986 | 0.08±0.024 | |
| 8 | α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | C10H16 | 14.99±2.387 | 4.91±1.495 | 7.73±0.710 | |
| 9 | 松油烯 P-mentha-1, 3-diene | C10H16 | 1.09±0.435 | 0.13±0.007 | 1.56±0.815 | |
| 10 | 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | C10H16 | 2.12±0.149 | 2.08±0.658 | 26.23±1.687 | |
| 11 | (s)-(-)-柠檬烯 (-)-Limonene | C10H16 | 0.69±0.046 | 2.64±1.134 | — | |
| 12 | 柏木烯 Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.21±0.043 | — | — | |
| 13 | 莰烯 Camphene | C10H16 | 0.10±0.005 | 0.08±0.031 | 0.88±0.386 | |
| 14 | 长叶烯 (+)-longifolene | C15H24 | 0.14±0.064 | — | 0.02±0.016 | |
| 15 | 罗勒烯 Ocimene | C10H16 | — | 3.05±0.625 | 0.31±0.008 | |
| 16 | 月桂烯 Myrcene | C10H16 | 2.47±0.058 | 5.40±2.598 | 0.28±0.097 | |
| 17 | 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | C14H22 | — | — | 0.74±0.015 | |
| 18 | α-柏木烯 α-Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.03±0.002 | — | — | |
| 酯类 Esters | 19 | 乙酸松油酯 Alpha-terpinyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.20±0.146 | 0.01±0.012 | 0.11±0.058 |
| 20 | 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | C4H8O2 | 0.24±0.013 | — | 0.95±0.003 | |
| 21 | 丙酸芳樟酯 Linalool propionate | C13H22O2 | 0.01±0.004 | 0.42±0.247 | — | |
| 22 | 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | C12H20O2 | — | 0.01±0.003 | — | |
| 23 | 乙酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenyl acetate | C8H14O2 | — | 2.57±0.852 | — | |
| 24 | 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | C8H8O3 | — | — | 0.10±0.032 | |
| 25 | 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.01±0.006 | — | 0.47±0.022 | |
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 26 | 天然壬醛 Nonyl aldehyde | C9H18O | 2.15±0.013 | 1.57±0.717 | 0.45±0.210 |
| 27 | 己醛 Hexana | C6H12O | 1.61±0.648 | 1.61±0.198 | 0.13±0.034 | |
| 28 | 癸醛 Decanal | C10H20O | 0.76±0.348 | 1.20±0.735 | 0.49±0.315 | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 29 | 甲基庚烯酮 6-Methyl-5-Hepten-2-one | C8H14O | 0.37±0.139 | 0.29±0.044 | — |
| 30 | 异佛尔酮 (z)-P-menthan-3-on | C9H14O | 0.14±0.094 | 1.64±0.048 | — | |
| 31 | 樟脑 Camphor | C10H16O | 0.01±0.006 | 0.03±0.015 | 0.06±0.038 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 32 | 左薄荷脑 L(-)-Menthol | C10H20O | 0.02±0.018 | 0.70±0.447 | 0.01±0.007 |
| 33 | 松油醇 α-Terpineol | C10H18O | — | — | — | |
| 34 | (+/-)-薄荷醇 (+/-)-Menthol | C20H40O2 | 0.08±0.030 | 0.11±0.004 | 0.13±0.108 | |
| 35 | 龙脑 ((1S)-endo)-(-)-borneol | C10H16O | — | 0.02±0.005 | 0.01±0.003 | |
| 36 | 顺-3-己烯-1-醇 Cis-3-Hexen-1-ol | C6H12O | 0.02±0.013 | 0.11±0.124 | — | |
| 37 | 植物醇 Plant alcohol | C20H40O | 0.02±0.024 | 0.19±0.037 | 0.06±0.018 | |
| 38 | 香茅醇 (-)-beta-citronellol | C10H20O | 0.01±0.002 | — | 0.01±0.006 | |
| 39 | 桉树醇 Cineole | C10H18O | 0.06±0.033 | — | — | |
| 40 | 柏木脑 (+)-cedrol | C15H26O | 0.02±0.016 | — | — | |
| 41 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | C10H18O | 0.03±0.005 | — | — | |
| 42 | 环戊醇 Cyclopentanol | C5H10O | 0.20±0.007 | — | — | |
| 有机酸类 Organic acids | 43 | 油酸 Oleic acid | C18H34O2 | 0.04±0.018 | 0.01±0.014 | — |
| 其他类 Others | 44 | 甘菊蓝 Azulene | C10H8 | 0.01±0.002 | 0.01±0.006 | 0.12±0.076 |
| 45 | 左旋樟脑 (-)-Alcanfor | C10H16O | — | 0.17±0.103 | — | |
表1 侧柏释放有益BVOCs在生长季组分和相对含量变化
Table 1 Changes of components and relative contents of beneficial BVOCs of Platycladus orientalis in growing season
| 类型 Type | 序号 No. | 化合物 Compounds | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||||
| 烯烃类 Alkenes | 1 | (1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯 (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 12.02±1.371 | 21.87±0.618 | 6.91±0.423 |
| 2 | β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | C10H16 | 4.41±1.052 | 0.93±0.383 | 7.01±0.097 | |
| 3 | 右旋萜二烯 (+)-Limonene | C10H16 | 8.24±0.823 | 0.34±0.271 | 4.85±0.142 | |
| 4 | 桧烯 Sabinene | C10H16 | 4.90±0.436 | 5.60±0.242 | 1.50±0.025 | |
| 5 | 萜品油烯 Terpinolene | C10H16 | 2.27±0.194 | 0.84±0.511 | 0.51±0.189 | |
| 6 | (1S)-(-)-α-蒎烯 (1S)-(-)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 0.02±0.011 | 0.29±0.195 | — | |
| 7 | 柠檬烯 2-Ethylbutyl methacrylate | C10H18O2 | 1.29±0.138 | 1.98±0.986 | 0.08±0.024 | |
| 8 | α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | C10H16 | 14.99±2.387 | 4.91±1.495 | 7.73±0.710 | |
| 9 | 松油烯 P-mentha-1, 3-diene | C10H16 | 1.09±0.435 | 0.13±0.007 | 1.56±0.815 | |
| 10 | 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | C10H16 | 2.12±0.149 | 2.08±0.658 | 26.23±1.687 | |
| 11 | (s)-(-)-柠檬烯 (-)-Limonene | C10H16 | 0.69±0.046 | 2.64±1.134 | — | |
| 12 | 柏木烯 Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.21±0.043 | — | — | |
| 13 | 莰烯 Camphene | C10H16 | 0.10±0.005 | 0.08±0.031 | 0.88±0.386 | |
| 14 | 长叶烯 (+)-longifolene | C15H24 | 0.14±0.064 | — | 0.02±0.016 | |
| 15 | 罗勒烯 Ocimene | C10H16 | — | 3.05±0.625 | 0.31±0.008 | |
| 16 | 月桂烯 Myrcene | C10H16 | 2.47±0.058 | 5.40±2.598 | 0.28±0.097 | |
| 17 | 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | C14H22 | — | — | 0.74±0.015 | |
| 18 | α-柏木烯 α-Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.03±0.002 | — | — | |
| 酯类 Esters | 19 | 乙酸松油酯 Alpha-terpinyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.20±0.146 | 0.01±0.012 | 0.11±0.058 |
| 20 | 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | C4H8O2 | 0.24±0.013 | — | 0.95±0.003 | |
| 21 | 丙酸芳樟酯 Linalool propionate | C13H22O2 | 0.01±0.004 | 0.42±0.247 | — | |
| 22 | 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | C12H20O2 | — | 0.01±0.003 | — | |
| 23 | 乙酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenyl acetate | C8H14O2 | — | 2.57±0.852 | — | |
| 24 | 水杨酸甲酯 Methyl salicylate | C8H8O3 | — | — | 0.10±0.032 | |
| 25 | 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.01±0.006 | — | 0.47±0.022 | |
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 26 | 天然壬醛 Nonyl aldehyde | C9H18O | 2.15±0.013 | 1.57±0.717 | 0.45±0.210 |
| 27 | 己醛 Hexana | C6H12O | 1.61±0.648 | 1.61±0.198 | 0.13±0.034 | |
| 28 | 癸醛 Decanal | C10H20O | 0.76±0.348 | 1.20±0.735 | 0.49±0.315 | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 29 | 甲基庚烯酮 6-Methyl-5-Hepten-2-one | C8H14O | 0.37±0.139 | 0.29±0.044 | — |
| 30 | 异佛尔酮 (z)-P-menthan-3-on | C9H14O | 0.14±0.094 | 1.64±0.048 | — | |
| 31 | 樟脑 Camphor | C10H16O | 0.01±0.006 | 0.03±0.015 | 0.06±0.038 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 32 | 左薄荷脑 L(-)-Menthol | C10H20O | 0.02±0.018 | 0.70±0.447 | 0.01±0.007 |
| 33 | 松油醇 α-Terpineol | C10H18O | — | — | — | |
| 34 | (+/-)-薄荷醇 (+/-)-Menthol | C20H40O2 | 0.08±0.030 | 0.11±0.004 | 0.13±0.108 | |
| 35 | 龙脑 ((1S)-endo)-(-)-borneol | C10H16O | — | 0.02±0.005 | 0.01±0.003 | |
| 36 | 顺-3-己烯-1-醇 Cis-3-Hexen-1-ol | C6H12O | 0.02±0.013 | 0.11±0.124 | — | |
| 37 | 植物醇 Plant alcohol | C20H40O | 0.02±0.024 | 0.19±0.037 | 0.06±0.018 | |
| 38 | 香茅醇 (-)-beta-citronellol | C10H20O | 0.01±0.002 | — | 0.01±0.006 | |
| 39 | 桉树醇 Cineole | C10H18O | 0.06±0.033 | — | — | |
| 40 | 柏木脑 (+)-cedrol | C15H26O | 0.02±0.016 | — | — | |
| 41 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | C10H18O | 0.03±0.005 | — | — | |
| 42 | 环戊醇 Cyclopentanol | C5H10O | 0.20±0.007 | — | — | |
| 有机酸类 Organic acids | 43 | 油酸 Oleic acid | C18H34O2 | 0.04±0.018 | 0.01±0.014 | — |
| 其他类 Others | 44 | 甘菊蓝 Azulene | C10H8 | 0.01±0.002 | 0.01±0.006 | 0.12±0.076 |
| 45 | 左旋樟脑 (-)-Alcanfor | C10H16O | — | 0.17±0.103 | — | |
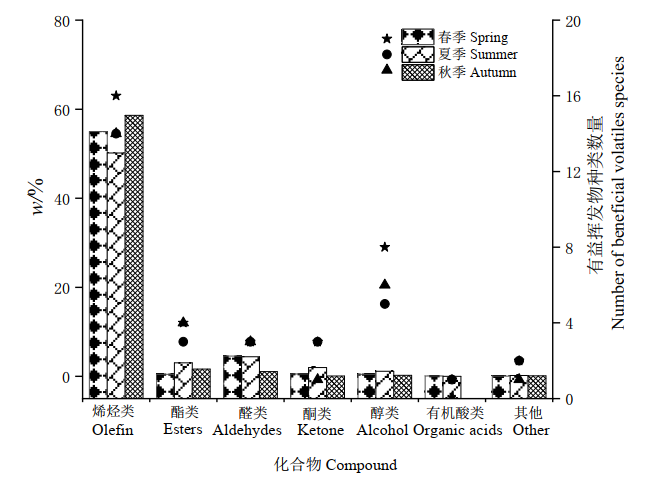
图1 侧柏释放各类有益BVOCs相对含量和种类数量生长季变化
Figure 1 Seasonal variation of relative content and species number of beneficial BVOCs released from Platycladus orientalis
| 类型Type | 序号 No. | 化合物 Compounds | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||||
| 烯烃类 Alkenes | 1 | (1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯 (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 7.49±0.463 | 0.47±0.063 | 3.77±0.214 |
| 2 | (s)-(-)-柠檬烯 (-)-Limonene | C10H16 | 1.04±0.010 | — | — | |
| 3 | β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | C10H16 | 1.09±0.004 | — | — | |
| 4 | 柏木烯 Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.72±0.025 | — | — | |
| 5 | 桧烯 Sabinene | C10H16 | 0.17±0.005 | — | — | |
| 6 | 柠檬烯 2-Ethylbutyl methacrylate | C10H18O2 | 3.49±0.842 | — | — | |
| 7 | 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | C14H22 | 0.14±0.006 | — | — | |
| 8 | 萜品油烯 Terpinolene | C10H16 | 0.08±0.001 | — | — | |
| 9 | 右旋萜二烯 (+)-Limonene | C10H16 | 0.69±0.013 | — | 2.78±0.153 | |
| 10 | 月桂烯 Myrcene | C10H16 | 0.34±0.001 | — | — | |
| 11 | α-柏木烯 α-Cedrene | C15H24 | — | 0.07±0.038 | — | |
| 12 | α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | C10H16 | 0.02±0.016 | 0.05±0.012 | — | |
| 13 | 长叶烯 (+)-longifolene | C15H24 | 0.06±0.024 | 0.49±0.264 | 0.54±0.014 | |
| 14 | 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | C10H16 | — | — | 1.22±0.125 | |
| 15 | 莰烯 Camphene | C10H16 | — | — | 0.12±0.003 | |
| 酯类 Esters | 16 | 甲酸香叶酯 Geranyl formate | C12H20O2 | 0.07±0.005 | — | — |
| 17 | 乙酸松油酯 Alpha-terpinyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.71±0.014 | — | — | |
| 18 | 乙酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenyl acetate | C8H14O2 | 7.15±0.158 | 10.25±1.074 | 2.52±0.058 | |
| 19 | 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | C4H8O2 | 1.18±0.212 | — | 1.37±0.001 | |
| 20 | 乙酸异龙脑酯 Isobornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.14±0.008 | — | 0.01±0.008 | |
| 21 | 丙酸芳樟酯 Linalool propionate | C13H22O2 | — | 0.12±0.047 | 0.41±0.072 | |
| 22 | 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.02±0.012 | 0.03±0.005 | — | |
| 23 | 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.01±0.004 | 0.05±0.001 | — | |
| 24 | γ-己内酯 Gamma-hexalactone | C6H10O2 | — | — | 0.05±0.036 | |
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 25 | 癸醛 Decanal | C10H20O | 1.88±0.116 | 4.24±0.711 | 2.20±0.879 |
| 26 | 己醛 Hexana | C6H12O | 1.46±0.025 | 3.43±1.051 | 2.67±0.216 | |
| 27 | 天然壬醛 Nonyl aldehyde | C9H18O | 3.36±0.018 | 5.09±0.533 | 2.81±1.004 | |
| 28 | 视黄醛 Retinal | C20H28O | — | — | 0.02±0.008 | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 29 | 甲基庚烯酮 6-Methyl-5-Hepten-2-one | C8H14O | 0.85±0.005 | 0.86±0.006 | — |
| 30 | 异佛尔酮 (z)-P-menthan-3-on | C9H14O | 0.17±0.008 | 3.20±0.549 | 0.83±0.513 | |
| 31 | 樟脑 Camphor | C10H16O | — | 0.08±0.061 | 0.29±0.064 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 32 | 桉树醇 Cineole | C10H18O | 0.34±0.021 | — | — |
| 33 | 顺-3-己烯-1-醇 Cis-3-Hexen-1-ol | C6H12O | 6.44±1.085 | 3.12±0.872 | 9.66±2.146 | |
| 34 | α-松油醇 α-Terpineol | C10H18O | — | 0.09±0.010 | — | |
| 35 | (+/-)-薄荷醇 (+/-)-Menthol | C20H40O2 | 11.77±1.769 | 5.29±0.603 | 1.07±0.005 | |
| 36 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | C10H18O | — | 0.03±0.004 | — | |
| 37 | 异植醇 Isophytol | C20H40O | — | 0.10±0.001 | — | |
| 38 | 植物醇 Plant alcohol | C20H40O | — | 0.21±0.028 | 0.04±0.027 | |
| 39 | 左薄荷脑 L(-)-Menthol | C10H20O | 0.12±0.003 | 2.48±1.018 | 0.07±0.008 | |
| 40 | 环戊醇 Cyclopentanol | C5H10O | — | — | 0.25±0.001 | |
| 41 | 龙脑 ((1S)-endo)-(-)-borneol | C10H16O | 0.02±0.011 | — | 0.03±0.016 | |
| 其他类 Others | 42 | 甘菊蓝 Azulene | C10H8 | 0.11±0.001 | 0.43±0.005 | 0.21±0.011 |
| 43 | 左旋樟脑 (-)-Alcanfor | C10H16O | 0.22±0.006 | 0.89±0.426 | — | |
表2 垂柳释放有益BVOCs在生长季组分和相对含量变化
Table 2 Changes of components and relative contents of beneficial BVOCs of Salix babylonica in growing season
| 类型Type | 序号 No. | 化合物 Compounds | 分子式 Molecular formula | 相对含量 Relative content/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | ||||
| 烯烃类 Alkenes | 1 | (1R)-(+)-α-蒎烯 (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene | C10H16 | 7.49±0.463 | 0.47±0.063 | 3.77±0.214 |
| 2 | (s)-(-)-柠檬烯 (-)-Limonene | C10H16 | 1.04±0.010 | — | — | |
| 3 | β-蒎烯 β-Pinene | C10H16 | 1.09±0.004 | — | — | |
| 4 | 柏木烯 Cedrene | C15H24 | 0.72±0.025 | — | — | |
| 5 | 桧烯 Sabinene | C10H16 | 0.17±0.005 | — | — | |
| 6 | 柠檬烯 2-Ethylbutyl methacrylate | C10H18O2 | 3.49±0.842 | — | — | |
| 7 | 石竹烯 Caryophyllene | C14H22 | 0.14±0.006 | — | — | |
| 8 | 萜品油烯 Terpinolene | C10H16 | 0.08±0.001 | — | — | |
| 9 | 右旋萜二烯 (+)-Limonene | C10H16 | 0.69±0.013 | — | 2.78±0.153 | |
| 10 | 月桂烯 Myrcene | C10H16 | 0.34±0.001 | — | — | |
| 11 | α-柏木烯 α-Cedrene | C15H24 | — | 0.07±0.038 | — | |
| 12 | α-蒎烯 α-Pinene | C10H16 | 0.02±0.016 | 0.05±0.012 | — | |
| 13 | 长叶烯 (+)-longifolene | C15H24 | 0.06±0.024 | 0.49±0.264 | 0.54±0.014 | |
| 14 | 3-蒈烯 3-Carene | C10H16 | — | — | 1.22±0.125 | |
| 15 | 莰烯 Camphene | C10H16 | — | — | 0.12±0.003 | |
| 酯类 Esters | 16 | 甲酸香叶酯 Geranyl formate | C12H20O2 | 0.07±0.005 | — | — |
| 17 | 乙酸松油酯 Alpha-terpinyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.71±0.014 | — | — | |
| 18 | 乙酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenyl acetate | C8H14O2 | 7.15±0.158 | 10.25±1.074 | 2.52±0.058 | |
| 19 | 乙酸乙酯 Ethyl acetate | C4H8O2 | 1.18±0.212 | — | 1.37±0.001 | |
| 20 | 乙酸异龙脑酯 Isobornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.14±0.008 | — | 0.01±0.008 | |
| 21 | 丙酸芳樟酯 Linalool propionate | C13H22O2 | — | 0.12±0.047 | 0.41±0.072 | |
| 22 | 乙酸冰片酯 Bornyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.02±0.012 | 0.03±0.005 | — | |
| 23 | 乙酸芳樟酯 Linalyl acetate | C12H20O2 | 0.01±0.004 | 0.05±0.001 | — | |
| 24 | γ-己内酯 Gamma-hexalactone | C6H10O2 | — | — | 0.05±0.036 | |
| 醛类 Aldehyde | 25 | 癸醛 Decanal | C10H20O | 1.88±0.116 | 4.24±0.711 | 2.20±0.879 |
| 26 | 己醛 Hexana | C6H12O | 1.46±0.025 | 3.43±1.051 | 2.67±0.216 | |
| 27 | 天然壬醛 Nonyl aldehyde | C9H18O | 3.36±0.018 | 5.09±0.533 | 2.81±1.004 | |
| 28 | 视黄醛 Retinal | C20H28O | — | — | 0.02±0.008 | |
| 酮类 Ketones | 29 | 甲基庚烯酮 6-Methyl-5-Hepten-2-one | C8H14O | 0.85±0.005 | 0.86±0.006 | — |
| 30 | 异佛尔酮 (z)-P-menthan-3-on | C9H14O | 0.17±0.008 | 3.20±0.549 | 0.83±0.513 | |
| 31 | 樟脑 Camphor | C10H16O | — | 0.08±0.061 | 0.29±0.064 | |
| 醇类 Alcohols | 32 | 桉树醇 Cineole | C10H18O | 0.34±0.021 | — | — |
| 33 | 顺-3-己烯-1-醇 Cis-3-Hexen-1-ol | C6H12O | 6.44±1.085 | 3.12±0.872 | 9.66±2.146 | |
| 34 | α-松油醇 α-Terpineol | C10H18O | — | 0.09±0.010 | — | |
| 35 | (+/-)-薄荷醇 (+/-)-Menthol | C20H40O2 | 11.77±1.769 | 5.29±0.603 | 1.07±0.005 | |
| 36 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | C10H18O | — | 0.03±0.004 | — | |
| 37 | 异植醇 Isophytol | C20H40O | — | 0.10±0.001 | — | |
| 38 | 植物醇 Plant alcohol | C20H40O | — | 0.21±0.028 | 0.04±0.027 | |
| 39 | 左薄荷脑 L(-)-Menthol | C10H20O | 0.12±0.003 | 2.48±1.018 | 0.07±0.008 | |
| 40 | 环戊醇 Cyclopentanol | C5H10O | — | — | 0.25±0.001 | |
| 41 | 龙脑 ((1S)-endo)-(-)-borneol | C10H16O | 0.02±0.011 | — | 0.03±0.016 | |
| 其他类 Others | 42 | 甘菊蓝 Azulene | C10H8 | 0.11±0.001 | 0.43±0.005 | 0.21±0.011 |
| 43 | 左旋樟脑 (-)-Alcanfor | C10H16O | 0.22±0.006 | 0.89±0.426 | — | |
| [1] | BOSSIOLI E, TOMBROU M, PILINIS C, 2002. Adapting the speciation of the VOCs emission inventory in the Greater Athens Area[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution Focus, 2(5-6): 141-153. |
| [2] | BUCHBAUER G, JIROVETZ L, JAGER W, et al., 2010. Fragrance compounds and essential oils with sedative effects upon inhalation[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 82(6): 660664. |
| [3] |
GAO Y, JIN Y J, LI H D, et al., 2005. Volatile organic compounds and their roles in bacteriostasis in five conifer species[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 47(4): 499-507.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
JOUNG D, KIM G, CHOI Y, et al., 2015. The prefrontal cortex activity and psychological effects of viewing forest landscapes in autumn season[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(7): 7235-7243.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KIM D S, LEE H J, JEON Y D, et al., 2015. Alpha-pinene exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through the suppression of MAPKs and the NF-κB pathway in mouse peritoneal macrophages[J]. The American Journal of Chinese medicine, 43(4): 731-742.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LEHRNER J, MARWINSKI G, LEHR S, et al., 2005. Ambient odors of orange and lavender reduce anxiety and improve mood in a dental office[J]. Physiology & Behavior, 86(1-2): 9295.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
NAM S Y, CHUNG C K, SEO J H, et al., 2014. The therapeutic efficacy of α-pinene in an experimental mouse model of allergic rhinitis[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 23(1): 273-282.
DOI URL |
| [8] | RENNER E, MÜNZENBERG A, 2003. Impact of biogenic terpene emissions from Brassica napus on tropospheric ozone over Saxony (Germany): Numerical investigation[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 10(3): 147-153. |
| [9] |
YU C P, LIN C M, TSAI M J, et al., 2017. Effects of short forest bathing program on autonomic nervous system activity and mood states in middle-aged and elderly individuals[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8): 897.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 陈洪伟, 李攻科, 李核, 等, 2001. 大气环境中挥发性有机化合物的测定[J]. 色谱, 19(6): 544-548. |
| CHEN H W, LI G K, LI H, et al., 2001. Determination of volatile organic compounds in atmospheric environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 19(6): 544-548. | |
| [11] | 邓小勇, 2009. 深圳市常见芳香植物挥发性有机物释放特性研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学. |
| DENG X Y, 2009. Study on the dynamic releasing characteristics of plant volatile of the common fragrant plant in Shenzhen[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University. | |
| [12] | 董建华, 2011. 白皮松挥发物释放规律及其对小白鼠自发行为的影响[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| DONG J H, 2011. BVOCS emission and dynamic variation of Pinus bungeana Zucc. And their effects on locomotor activity in mice[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [13] | 付国需, 李为争, 刘珂, 等, 2008. 不同科芳香植物特征挥发物的生源及其对昆虫行为的影响[C]// 华中三省 (湖北、湖南、河南) 昆虫学会2008年学术年会. 咸宁: 14-27. |
| FU G X, LI W Z, LIU K, et al., 2008. Derivations of characteristic volatiles of aroma plants in different families and their effects on insect behaviors[C]// The 2008 Annual Meeting of the Entomological Society of Three Central China (Hubei, Hunan and Henan). Xianning: 14-27. | |
| [14] | 高媛, 2019. 5种园林绿化树种BVOCs排放动态及其影响因素研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| GAO Y, 2019. BVOCs emission dynamics and influencing Factors of five tree species[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [15] | 胡立香, 2007. 白皮松林挥发物及其时空动态变化[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| HU L X, 2007. BVOCs emittion and their Spatio-temporal variation in a Pinus bungeana Zucc. Stand[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [16] | 李平, 贾红婕, 靳毓, 等, 2016. 核桃分心木水提液易挥发性成分分析[J]. 食品科学, 37(16): 142-148. |
| LI P, JIA H G, JIN Y, et al., 2016. Analysis of the volatile compositions of water extracts from walnut diaphragm[J]. Food Science, 37(16): 142-148. | |
| [17] | 李娟, 王成, 彭镇华, 等, 2011. 侧柏春季挥发物浓度日变化规律及其影响因子研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 24(1): 82-90. |
| LI J, WANG C, PENG Z H, et al., 2011. The diurnal variation and influence factors of VOC of platycladus orien talis in spring[J]. Forest Research, 24(1): 82-90. | |
| [18] | 李娟, 2009. 侧柏和油松挥发物动态变化规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| LI J, 2009. The VOCs emittion of two tree species of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus tabulaeformis in urban environment[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry. | |
| [19] | 李天凤, 郭安柱, 张婷, 等, 2017. 核桃举肢蛾对植物挥发物的触角电位反应[J]. 西北林学院学报, 32(5): 161-167. |
| LI T F, GUO A Z, ZHANG T, et al., 2017. Electroantennongram Responses of Atrijuglans hetaohei to Plant Volatiles[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 32(5): 161-167. | |
| [20] | 马亚荣, 杜勇军, 李倩, 等, 2017. 山茱萸叶挥发性成分的SHS-GC-MS分段分析[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 47(3): 401-413. |
| MA Y R, Du Y J, Li Q, et al., 2017. Analysis of volatile constituents of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. leaves by HS-GC-MS[J]. Journal of Northwestern University (Natural Science Edition), 47(3): 401-413. | |
| [21] | 任倩倩, 庄明珠, 蔡晓明, 等, 2020. 小贯小绿叶蝉取食诱导抗、感茶树品种挥发物的释放[J]. 茶叶科学, 40(6): 795-806. |
| REN Q Q, ZHUANG Z M, CAI X M, et al., 2020. The release of volatiles in resistant and susceptible tea cultivars under Empoasca onukii feeding[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 40(6): 795-806. | |
| [22] | 申慧珊, 2019. 马铃薯方便粉丝调味料研制及其风味物质检测分析[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| SHEN H S, 2019. Developmet of potato instant starch noodles seasoning and analysis of flavors substances[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [23] | 王灵艳, 2020. 湿地植物燕子花 (Iris laevigata) 的繁殖对策研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学. |
| WANG L Y, 2020. Reproductive strategy of wetland plant Iris laevigata[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University. | |
| [24] | 奚秋蕙, 2020. 基于健康环境营建的郊野公园规划设计[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| XI Q H, 2020. Planning and design of country parks based on healthy environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [25] | 吴岳华, 周围, 张雅珩, 等, 2013. 热脱附-气相色谱/质谱联用法分析生、炙乳香挥发性成分[J]. 质谱学报, 34(1): 35-39. |
| WU Y H, QIU Z, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2013. Analysis of volatile components of fresh and cooked frankincense by thermal desorption and GC/MS[J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 34(1): 35-39. | |
| [26] | 白建辉, 郝楠, 2018. 亚热带森林植物挥发性有机物 (BVOCs) 排放通量与大气甲醛之间的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(6): 991-999. |
| BAI J H, HAO N, 2018. The relationships between biogenic volatile organic compound (bvoc) emissions and atmospheric formaldehyde in a subtropical pinus plantation in China[J]. Acta Eco-Environmental Sciences, 27(6): 991-999. | |
| [27] | 王君怡, 2020. 北京地区8种典型景观树种释放挥发性有机物 (BVOCs) 动态变化特征研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. |
| WANG J Y, 2020. Study on the characteristics of release BVOCs of eight typical landscape tree species in Beijing[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University. | |
| [28] | 卫强, 杨俊杰, 2019. 安徽4地红豆杉叶中挥发油成分分析[J]. 淮海工学院学报 (自然科学版), 28(3): 26-31. |
| WEI Q, YANG J J, 2019. Chemical components of essential oil from Taxus leaf grown in four places[J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 28(3): 26-31. | |
| [29] | 杨水萌, 2018. 十三种药用植物挥发性成分的SHS/GC-MS研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学. |
| YANG S M, 2018. Study on the Volatile Components of thirteen medicinal plants by SHS/GC-MS[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University. |
| [1] | 李少宁, 李婷婷, 陶雪莹, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 4种落叶树种释放有益挥发性有机物的比较研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 123-128. |
| [2] | 张林, 周飘, 齐实, 张岱, 伍冰晨, 崔冉冉. 侧柏人工林林分空间结构对林下草本多样性的差异性影响及其关联度[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1794-1801. |
| [3] | 孙梦鑫, 张岳, 辛宇, 钟鼎杰, 杨存建. 川西高原近20 a植被物候变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1326-1339. |
| [4] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [5] | 李少宁, 陶雪莹, 李绣宏, 赵娜, 徐晓天, 鲁绍伟. 植物释放有益挥发性有机物研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 187-195. |
| [6] | 雷金睿, 陈宗铸, 陈毅青, 陈小花, 李苑菱, 吴庭天. 1990—2018年海南岛湿地景观格局演变及其驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 59-70. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
