生态环境学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 97-104.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.01.011
收稿日期:2019-05-20
出版日期:2020-01-18
发布日期:2020-03-09
通讯作者:
* E-mail: xnxu2007@ahau.edu.cn作者简介:张莎莎(1994年生),女,硕士,主要从事森林生态学研究。E-mail: 247499746@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Shasha( ), LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu*(
), LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu*( )
)
Received:2019-05-20
Online:2020-01-18
Published:2020-03-09
摘要:
为探究不同海拔梯度上杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata)人工林土壤化学计量特征,阐明其对海拔的响应规律,从而有效指导杉木人工林的生产。在安徽省金寨县天马国家自然保护区选取了4个海拔梯度(750、850、1000、1150 m),测定杉木人工林土壤有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)、全磷(TP)含量,并分析化学计量特征。研究结果表明:土壤0—10 cm有机碳、全氮、全磷质量分数为42.15、2.51、0.92 g∙kg-1,均高于我国平均土壤有机碳、全氮、全磷质量分数;土壤C/N比为17.01,高于全国土壤平均值,土壤C/P比为43.59,N/P比为2.63,两者均低于全国平均水平。随着海拔升高不同土层土壤有机碳、全氮均呈先降低后增加的趋势,而土壤全磷呈现先升高后减低的趋势;随海拔增加不同土层土壤碳氮比呈先升高后降低的趋势,碳磷比和氮磷比呈现先降低后升高的趋势;随着土壤深度的增加,不同海拔土壤有机碳、全氮、全磷、碳磷比和氮磷比均呈降低趋势,而土壤碳氮比在不同海拔间变化趋势不一致;土壤有机碳和全氮呈极显著正相关,有机碳和全磷、全氮和全磷显著负相关;土壤碳氮比、碳磷比和氮磷比与海拔不相关,与土壤pH、含水率、容重显著相关。
中图分类号:
张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104.
ZHANG Shasha, LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu. Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation Across An Elevation Gradient[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 97-104.
| 林龄 Age of stand (26‒35 a) | 土层 Soil layer (0‒30 cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/ m | 林分密度 Stand Density/ (DBH≥5 cm, stem∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average DBH/ cm | 平均树高 Average height/ m | 土壤 pH Soil pH | 含水量 Soil moisture/ % | 土壤容重(体积质量) Soil bulk density/ (g∙cm-3) | |
| 750 | 1129±49 | 20.0±1.58 | 13.5±1.02 | 4.64±0.02 | 35.95±0.61 | 0.76±0.05 | |
| 850 | 2216±145 | 17.6±0.63 | 12.5±0.87 | 5.07±0.06 | 17.28±2.63 | 0.92±0.12 | |
| 1000 | 1584±129 | 17.5±0.94 | 12.1±0.24 | 4.80±0.04 | 32.16±1.06 | 0.91±0.09 | |
| 1150 | 2150±58 | 17.7±2.03 | 11.6±0.66 | 4.70±0.03 | 42.45±4.03 | 0.88±0.05 | |
表1 样地基本情况
Table 1 Basic situation of sample plots
| 林龄 Age of stand (26‒35 a) | 土层 Soil layer (0‒30 cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/ m | 林分密度 Stand Density/ (DBH≥5 cm, stem∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average DBH/ cm | 平均树高 Average height/ m | 土壤 pH Soil pH | 含水量 Soil moisture/ % | 土壤容重(体积质量) Soil bulk density/ (g∙cm-3) | |
| 750 | 1129±49 | 20.0±1.58 | 13.5±1.02 | 4.64±0.02 | 35.95±0.61 | 0.76±0.05 | |
| 850 | 2216±145 | 17.6±0.63 | 12.5±0.87 | 5.07±0.06 | 17.28±2.63 | 0.92±0.12 | |
| 1000 | 1584±129 | 17.5±0.94 | 12.1±0.24 | 4.80±0.04 | 32.16±1.06 | 0.91±0.09 | |
| 1150 | 2150±58 | 17.7±2.03 | 11.6±0.66 | 4.70±0.03 | 42.45±4.03 | 0.88±0.05 | |
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/m | ω(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TN)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TP)/(g·kg-1) | ω(C)/ω(N | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 | 35.44±2.81 | 2.23±0.16 | 0.55±0.03 | 15.79±0.21 | 67.19±5.41 | 4.23±0.31 |
| 850 | 21.28±2.60 | 1.17±0.17 | 1.32±0.06 | 19.26±0.53 | 16.53±2.08 | 0.91±0.13 |
| 1000 | 28.96±2.14 | 1.73±0.14 | 0.96±0.34 | 16.99±0.34 | 31.95±3.02 | 1.90±0.18 |
| 1150 | 32.36±3.00 | 1.92±0.17 | 0.61±0.05 | 16.73±0.15 | 58.69±5.45 | 3.48±0.31 |
| 平均值 | 30.26 | 1.82 | 0.82 | 17.01 | 46.05 | 2.79 |
表2 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷含量及其生态化学计量比
Table 2 Soil C, N, P content and their stoichiometry in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/m | ω(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TN)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TP)/(g·kg-1) | ω(C)/ω(N | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 | 35.44±2.81 | 2.23±0.16 | 0.55±0.03 | 15.79±0.21 | 67.19±5.41 | 4.23±0.31 |
| 850 | 21.28±2.60 | 1.17±0.17 | 1.32±0.06 | 19.26±0.53 | 16.53±2.08 | 0.91±0.13 |
| 1000 | 28.96±2.14 | 1.73±0.14 | 0.96±0.34 | 16.99±0.34 | 31.95±3.02 | 1.90±0.18 |
| 1150 | 32.36±3.00 | 1.92±0.17 | 0.61±0.05 | 16.73±0.15 | 58.69±5.45 | 3.48±0.31 |
| 平均值 | 30.26 | 1.82 | 0.82 | 17.01 | 46.05 | 2.79 |
| 因素 Factor | F (and P) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω(SOC) | ω(TN) | ω(TP) | ω(C)/ω(N) | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) | |
| 土层 Soil depth | 42.20(<0.01) | 42.87(<0.01) | 2.23(0.12) | 2.99(<0.01) | 9.28(<0.01) | 8.93(<0.01) |
| 海拔 Elevation gradient | 7.91(<0.01) | 12.34(<0.01) | 53.54(<0.01) | 23.79(0.55) | 27.85(<0.01) | 33.42(<0.01) |
| 土层×海拔 Soil depth×Elevation gradient | 0.39(0.89) | 0.60(0.733) | 0.035(1.00) | 5.06(<0.01) | 0.47(0.83) | 0.55(0.77) |
表3 不同海拔和土壤深度对土壤C、N、P含量及其化学质量比的影响
Table 3 ANOVA results for the effects of elevational gradient and soil depth on soil C, N, P content and their ecological stoichiometric ratios
| 因素 Factor | F (and P) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω(SOC) | ω(TN) | ω(TP) | ω(C)/ω(N) | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) | |
| 土层 Soil depth | 42.20(<0.01) | 42.87(<0.01) | 2.23(0.12) | 2.99(<0.01) | 9.28(<0.01) | 8.93(<0.01) |
| 海拔 Elevation gradient | 7.91(<0.01) | 12.34(<0.01) | 53.54(<0.01) | 23.79(0.55) | 27.85(<0.01) | 33.42(<0.01) |
| 土层×海拔 Soil depth×Elevation gradient | 0.39(0.89) | 0.60(0.733) | 0.035(1.00) | 5.06(<0.01) | 0.47(0.83) | 0.55(0.77) |
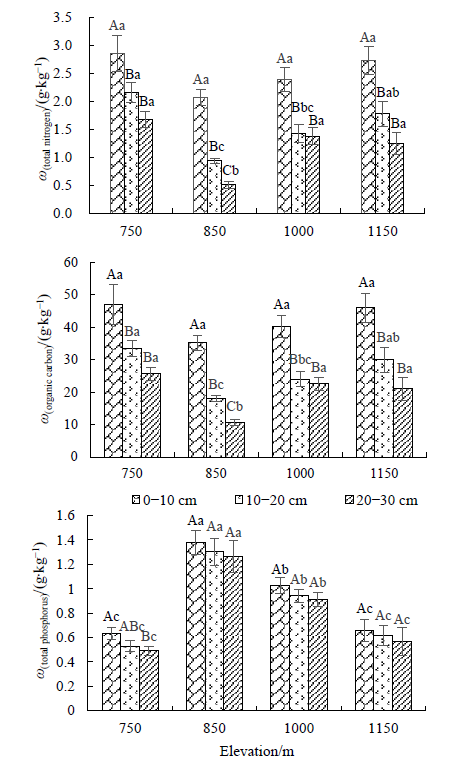
图1 不同海拔土壤的有机碳、全氮、全磷含量 不同大写字母表示相同海拔不同土层在0.05水平上具有显著差异,不同小写字母表示相同土层不同海拔间在0.05水平上具有显著差异(P<0.05)
Fig. 1 Content of organic carbon, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in soil with different elevation gradient Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers at the same elevation (P<0.05), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the different soil layers at different altitudes (P<0.05), the same below
| [1] | CHAPIN F S I, MATSON P A I, MOONEY H A, 2011. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology[M]. Berlin: Springer Verlag: 69-397. |
| [2] |
CHEN X W, LI B L. 2003. Change in soil carbon and nutrient storage after human disturbance of a primary koreanpine forest in northeast china[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 186(1-3): 197-206.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CORYC C, DANIEL L, 2007. C꞉N꞉P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass[J]. Biogeochemistry, 85(3): 235-252.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DON A, SCHUMACHER J, SCHERER-LORENZEN M, 2007. Spatial and vertical variation of soil carbon at two grassland sites-implications for measuring soil carbon stocks[J]. Geoderma, 141(3-4): 272-282.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FAMIGLIETT J S, RUDNICKI J W, RODELL M, 1998. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect: Rattlesnake Hill, Texas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 210(1-4): 259-281.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GÜSEWELL S, KOERSELMAN W, VERHOEVEN J T A, 2003. Biomass N꞉P ratios as indicators of nutrient limitation for plant populations in wetlands[J]. Ecological Applications, 13(2): 372-384.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HOBBIE S E, GOUGH L, 2016. Foliar and soil nutrients in tundra on glacial landscapes of contrasting ages in northern Alaska[J]. Oecologia, 131(3): 453-462.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LIU M, LI Z, ZHANG T, 2016. Changes of soil ecological stoichiometric ratios under different land uses in a small catchment of subtropical China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 66(1): 67-74. |
| [9] |
TESSIER J T, RAYNAL D J, 2003. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 40(3): 523-534.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TIAN H, CHEN G, ZHANG C, et al., 2010. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 98(1-3): 139-151.
DOI URL |
| [11] | YIN X R, LIANG C Z, WANG L X, et al., 2010. Ecological stoichiometry of plant nutrients at different restoration succession stages in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(1): 39-47. |
| [12] | 白小芳, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等, 2015. 华北落叶松人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(6): 68-75. |
| BAI X F, XU F L, WANG W L, et al., 2015. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(6): 68-75. | |
| [13] | 曹娟, 闫文德, 项文化, 等, 2015. 湖南会同3个林龄杉木人工林土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学, 51(7): 1-8. |
| CAO J, YAN W D, XIANG W H, et al., 2015. Stoichiometry Characterization of Soil C, N, and P of Chinese Fir Plantations at Three Different Ages in Huitong, Hunan Province, China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51(7): 1-8. | |
| [14] | 陈安娜, 王光军, 陈婵, 等, 2018. 亚热带不同林龄杉木林叶-根-土氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(11): 4031-4036. |
| CHEN A N, WANG G J, CHEN J, et al., 2018. Variation in the N and P stoichiometry of leaf-root-soil during stand development in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [15] | 陈晓萍, 郭炳桥, 钟全林, 等, 2018. 武夷山不同海拔黄山松细根碳、氮、磷化学计量特征对土壤养分的适应[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 273-281. |
| CHEN X P, GUO B Q, ZHONG Q L, et al., 2018. Response of fine root carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry to soil nutrients in Pinus taiwanensis along an elevation gradient in the Wuyi mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [16] | 胡耀升, 么旭阳, 刘艳红, 2014. 长白山森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤氮磷的化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(3): 632-638. |
| HU Y S, ME X Y, LI Y H, 2014. N and P stoichiometric traits of plant and soil in different forest succession stages in Chang bai Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(3): 632-638. | |
| [17] | 纪文婧, 程小琴, 韩海荣, 等, 2016. 山西太岳山好地方典型植被类型土壤理化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(1): 141-148. |
| JI W J, CHENG X Q, HAN H R, et al., 2016. Soil physicochemical properties of typical vegetation types in Haodifang, Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [18] | 贾国梅, 何立, 程虎, 等, 2016. 三峡库区不同植被土壤微生物量碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 23(4): 23-27. |
| JIA G M, HE L, CHENG H, et al., 2016. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus Under Different Vegetation Covers in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [19] | 李丹维, 王紫泉, 田海霞, 等, 2017. 太白山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 54(1): 160-170. |
| LI D W, WANG Z Q, TIAN H X, et al., 2017. Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents in Soils on Taibai Mountain and Their Ecological Stoichiometry relative to Elevation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54(1): 160-170. | |
| [20] | 李红林, 贡璐, 朱美玲, 等, 2015. 塔里木盆地北缘绿洲土壤化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 52(6): 1345-1355. |
| LI H L, GONG L, ZHU M L, et al., 2015. Stoihiometric characteristics of soil in an oasis on northern edge of tarim basin, Chian[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(6): 13 45- 1355. | |
| [21] | 李玮, 郑子成, 李廷轩, 2015. 不同植茶年限土壤团聚体碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(1): 9-16. |
| LI W, ZHENG Z C, LI Y X, 2015. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus within soil aggregates in tea plantations with different ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(1): 9-16. | |
| [22] | 吕世丽, 李新平, 李文斌, 等, 2013. 牛背梁自然保护区不同海拔高度森林土壤养分特征分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 41(4): 161-168. |
| LV S L, LI X P, LI W B, et al., 2013. Forest soil nutrient characteristics at different altitudes in Niubeiliang National Natural Reserve[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4): 161-168. | |
| [23] | 牛瑞龙, 高星, 徐福利, 等, 2016. 秦岭中幼林龄华北落叶松针叶与土壤的碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7384-7392. |
| NIU R L, GAO X, XU F L, et al., 2016. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of soil and leaves from young and middle aged Larix principis-rupprechtii growing in a Qinling Mountain plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(22): 7384-7392. | |
| [24] | 欧阳林梅, 曾冬萍, 闵庆文, 等, 2014. 鼓山茶园土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(2): 297-301. |
| OUYANG L M, ZENG D P, MIN Q W, et al., 2014. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Tea Garden of Drum Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(2): 297-301. | |
| [25] | 任璐璐, 张炳学, 韩凤朋, 等, 2017. 黄土高原不同年限刺槐土壤化学计量特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(2): 339-344. |
| REN L L, ZHANG B X, HAN F P, et al., 2017. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soils in Robinia pseudoacacia Forests of Different Ages on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(2): 339-344. | |
| [26] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞, 2008. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R, 2008. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| [27] | 王维奇, 曾从盛, 钟春棋, 等, 2010. 人类干扰对闽江河口湿地土壤碳、氮、磷生态化学计量学特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 31(10): 2411-2416. |
| WANG W Q, ZENG C S, ZHONG C Q, et al., 2010. Effect of Human Disturbance on Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Minjiang River Estuarine Wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of environmental science, 31(10): 2411-2416. | |
| [28] |
王雪梅, 闫帮国, 赵广, 等, 2017. 云南元谋不同海拔土壤微生物对车桑子碳、氮、磷化学计量特征及土壤特性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 41(3): 311-324.
DOI |
|
WANG X M, MIN B G, ZHAO G, et al., 2017. Effects of microorganism on carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of Dodonaea viscosa and the soils from different elevations in Yuanmou, Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41(3): 311-324.
DOI URL |
|
| [29] | 肖烨, 黄志刚, 武海涛, 等, 2014. 三江平原4种典型湿地土壤碳氮分布差异和微生物特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(10): 2847-2854. |
| XIAO Y, HUANG Z G, WU H T, et al., 2014. Carbon and nitrogen distributions and microbial characteristics in the soils of four types of wetlands in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(10): 2847-2854. | |
| [30] | 谢锦, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2016. 天山北坡植物土壤生态化学计量特征的垂直地带性[J]. 生态学报, 36(14): 4363-4372. |
| XIE J, CHANG S L, ZHANG M T, et al., 2016. Plant and soil ecological stoichiometry with vertical zonality on the northern slope of the middle Tianshan Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(14): 4363-4372. | |
| [31] | 徐沙, 龚吉蕊, 张梓榆, 等, 2014. 不同利用方式下草地优势植物的生态化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 23(6): 45-53. |
| XU S, GONG J R, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2014. The ecological stoichiometry of dominant species in different land uses type of grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 23(6): 45-53. | |
| [32] |
曾德慧, 陈广生, 2005. 生态化学计量学:复杂生命系统奥秘的探索[J]. 植物生态学报, 29(6): 1007-1019.
DOI |
| ZENG D H, CHEN G S, 2005. Ecological stoichiometay: A science to explore the complexity of living systems[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29(6): 1007-1019. | |
| [33] | 曾全超, 李鑫, 董扬红, 等, 2015. 陕北黄土高原土壤性质及其生态化学计量的纬度变化特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 30(5): 870-879. |
| ZENG Q C, LI X, DONG Y H, et al., 2015. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics and Physical-chemical Properties of Soils at Different Latitudes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(6): 1007-1019. | |
| [34] | 张广帅, 邓浩俊, 杜锟, 等, 2016. 泥石流频发区山地不同海拔土壤化学计量特征--以云南省小江流域为例[J]. 生态学报, 36(3): 675-687. |
| ZHANG G S, DENG H J, DU K, et al., 2016. Soil stoichiometry characteristics at different elevation gradients of a mountain in an area with high frequency debris flow: a case study in Xiaojiang Watershed, Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(3): 675-687. | |
| [35] | 赵维俊, 刘贤德, 金铭, 等, 2016. 祁连山青海云杉林叶片-枯落物-土壤的碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 53(2): 477-489. |
| ZHAO W J, LI X D, JIN M, et al., 2016. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Leaf-Litter-Soil System of Picea Crassifolia Forest in the Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(2): 477-489. | |
| [36] | 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等, 2013. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
|
ZHU Q L, XING X Y, ZHANG H, et al., 2013. Soil ecological stoichiometry under different vegetation area on loess hilly gully region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4674-4682.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [4] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | 刘展航, 张树岩, 侯玉平, 朱书玉, 王立冬, 施欣悦, 李培广, 韩广轩, 谢宝华. 互花米草入侵对黄河口湿地土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369. |
| [6] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [7] | 王小娜, 徐当会, 王谢军, 方向文. 祁连山灌丛群落结构特征随海拔梯度和经度的变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [8] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [9] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [10] | 宋瑞朋, 杨起帆, 郑智恒, 习丹. 3种林下植被类型对杉木人工林土壤有机碳及其组分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [11] | 盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [12] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [13] | 宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [14] | 蔡锡安, 黄娟, 吴彤, 刘菊秀, 蒋芬, 王森浩. 植物叶片排放甲烷的初步研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1842-1847. |
| [15] | 闫东锋, 张妍妍, 吕康婷, 周梦丽, 王婷, 赵宁. 太行山南麓不同海拔梯度天然林优势树种生态位特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1571-1580. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
