Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1392-1404.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.005
• Research Article [Ecology] • Previous Articles Next Articles
GU Meiying1,3( ), TANG Guangmu2,3, ZHANG Yunshu2,3, HUANG Jian2,3, ZHANG Zhidong1,3, ZHANG Lijuan1,3, ZHU Jing1,3, TANG Qiyong1,3, CHU Min1,3, XU Wanli2,3,*(
), TANG Guangmu2,3, ZHANG Yunshu2,3, HUANG Jian2,3, ZHANG Zhidong1,3, ZHANG Lijuan1,3, ZHU Jing1,3, TANG Qiyong1,3, CHU Min1,3, XU Wanli2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-03-06
Online:2023-08-18
Published:2023-11-08
Contact:
XU Wanli
顾美英1,3( ), 唐光木2,3, 张云舒2,3, 黄建2,3, 张志东1,3, 张丽娟1,3, 朱静1,3, 唐琦勇1,3, 楚敏1,3, 徐万里2,3,*(
), 唐光木2,3, 张云舒2,3, 黄建2,3, 张志东1,3, 张丽娟1,3, 朱静1,3, 唐琦勇1,3, 楚敏1,3, 徐万里2,3,*( )
)
通讯作者:
徐万里
作者简介:顾美英(1974年生),女,研究员,主要研究方向为微生物资源利用和农业微生物生态。E-mail: gmyxj2008@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
GU Meiying, TANG Guangmu, ZHANG Yunshu, HUANG Jian, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHANG Lijuan, ZHU Jing, TANG Qiyong, CHU Min, XU Wanli. Effects of Organic Fertilizers and Biochar on Microorganism Community Characteristics in Saline-alkali Sandy Soil of Xinjiang[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1392-1404.
顾美英, 唐光木, 张云舒, 黄建, 张志东, 张丽娟, 朱静, 唐琦勇, 楚敏, 徐万里. 有机肥与生物炭对新疆盐碱沙化土壤微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1392-1404.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.005
| 处理 | pH | 阳离子交换量/ (cmol∙kg-1) | 电导率/ (μS∙cm-1) | w(全氮)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全磷)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全钾)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有机质)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(速效氮)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效磷)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.21± 0.04a | 2.750± 0.185c | 95.00± 0.10c | 0.160± 0.062b | 0.233± 0.051b | 15.399± 1.037bc | 0.246± 0.007c | 17.678± 2.668c | 3.339± 0.293d | 42.000± 2.000c |
| NPK | 9.10± 0.07a | 2.848± 0.173b | 117.03± 12.82b | 0.133± 0.030c | 0.284± 0.093a | 14.980± 1.541c | 0.316± 0.030b | 17.456± 4.441c | 5.559± 0.246c | 48.333± 5.507b |
| NPK+M | 9.01± 0.03a | 2.899± 0.120b | 145.97± 15.96a | 0.175± 0.012a | 0.270± 0.050a | 15.743± 0.029bc | 0.431± 0.060a | 22.125± 1.388a | 10.455± 3.571a | 65.000± 12.166a |
| NPK+B | 9.11± 0.02a | 3.029± 0.174a | 113.20± 16.18bc | 0.138± 0.042c | 0.275± 0.055a | 16.782± 0.441b | 0.418± 0.059a | 16.344± 4.669c | 5.657± 0.761c | 49.000± 10.440b |
| NPK+M+B | 9.16± 0.09a | 2.841± 0.239b | 109.20± 13.05bc | 0.149± 0.017b | 0.257± 0.073a | 18.320± 0.734a | 0.462± 0.090a | 19.235± 5.094b | 7.517± 1.329b | 67.000± 10.440a |
Table 1 Impacts of organic fertilizer and biochar application on physical and chemical properties of saline-alkali sandy soil
| 处理 | pH | 阳离子交换量/ (cmol∙kg-1) | 电导率/ (μS∙cm-1) | w(全氮)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全磷)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全钾)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有机质)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(速效氮)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效磷)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(速效钾)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.21± 0.04a | 2.750± 0.185c | 95.00± 0.10c | 0.160± 0.062b | 0.233± 0.051b | 15.399± 1.037bc | 0.246± 0.007c | 17.678± 2.668c | 3.339± 0.293d | 42.000± 2.000c |
| NPK | 9.10± 0.07a | 2.848± 0.173b | 117.03± 12.82b | 0.133± 0.030c | 0.284± 0.093a | 14.980± 1.541c | 0.316± 0.030b | 17.456± 4.441c | 5.559± 0.246c | 48.333± 5.507b |
| NPK+M | 9.01± 0.03a | 2.899± 0.120b | 145.97± 15.96a | 0.175± 0.012a | 0.270± 0.050a | 15.743± 0.029bc | 0.431± 0.060a | 22.125± 1.388a | 10.455± 3.571a | 65.000± 12.166a |
| NPK+B | 9.11± 0.02a | 3.029± 0.174a | 113.20± 16.18bc | 0.138± 0.042c | 0.275± 0.055a | 16.782± 0.441b | 0.418± 0.059a | 16.344± 4.669c | 5.657± 0.761c | 49.000± 10.440b |
| NPK+M+B | 9.16± 0.09a | 2.841± 0.239b | 109.20± 13.05bc | 0.149± 0.017b | 0.257± 0.073a | 18.320± 0.734a | 0.462± 0.090a | 19.235± 5.094b | 7.517± 1.329b | 67.000± 10.440a |
| 处理 | 有效序列数 | OTU数量 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | Chao指数 | Ace指数 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 (×104) | 真菌 (×104) | 细菌 (×103) | 真菌 (×102) | 细菌 | 真菌 | 细菌 | 真菌 | 细菌 (×103) | 真菌 (×102) | 细菌(×103) | 真菌(×102) | ||||||
| CK | 4.042d | 7.039c | 2.746b | 5.39a | 9.190b | 4.338b | 0.995a | 0.898a | 2.742c | 5.285a | 2.791c | 5.441a | |||||
| NPK | 4.953c | 7.599b | 3.015b | 5.63a | 9.236b | 5.145a | 0.995a | 0.936a | 3.203 b | 5.598a | 3.216b | 5.790a | |||||
| NPK+M | 5.603b | 7.708b | 3.804a | 4.74b | 9.792a | 4.283b | 0.996a | 0.887a | 4.142 a | 4.694b | 4.192a | 4.970b | |||||
| NPK+B | 3.943d | 8.664a | 2.849b | 5.20ab | 9.223b | 4.305b | 0.994a | 0.881a | 2.767 c | 5.303a | 2.812b | 5.466a | |||||
| NPK+M+B | 6.254a | 5.667d | 3.824a | 2.67c | 9.774ab | 1.296c | 0.996a | 0.272b | 4.332 a | 2.429c | 4.390a | 2.595c | |||||
Table 2 Impacts of organic fertilizer and biochar application on bacteria and fungi community diversities in saline-alkali sandy soil
| 处理 | 有效序列数 | OTU数量 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | Chao指数 | Ace指数 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 细菌 (×104) | 真菌 (×104) | 细菌 (×103) | 真菌 (×102) | 细菌 | 真菌 | 细菌 | 真菌 | 细菌 (×103) | 真菌 (×102) | 细菌(×103) | 真菌(×102) | ||||||
| CK | 4.042d | 7.039c | 2.746b | 5.39a | 9.190b | 4.338b | 0.995a | 0.898a | 2.742c | 5.285a | 2.791c | 5.441a | |||||
| NPK | 4.953c | 7.599b | 3.015b | 5.63a | 9.236b | 5.145a | 0.995a | 0.936a | 3.203 b | 5.598a | 3.216b | 5.790a | |||||
| NPK+M | 5.603b | 7.708b | 3.804a | 4.74b | 9.792a | 4.283b | 0.996a | 0.887a | 4.142 a | 4.694b | 4.192a | 4.970b | |||||
| NPK+B | 3.943d | 8.664a | 2.849b | 5.20ab | 9.223b | 4.305b | 0.994a | 0.881a | 2.767 c | 5.303a | 2.812b | 5.466a | |||||
| NPK+M+B | 6.254a | 5.667d | 3.824a | 2.67c | 9.774ab | 1.296c | 0.996a | 0.272b | 4.332 a | 2.429c | 4.390a | 2.595c | |||||
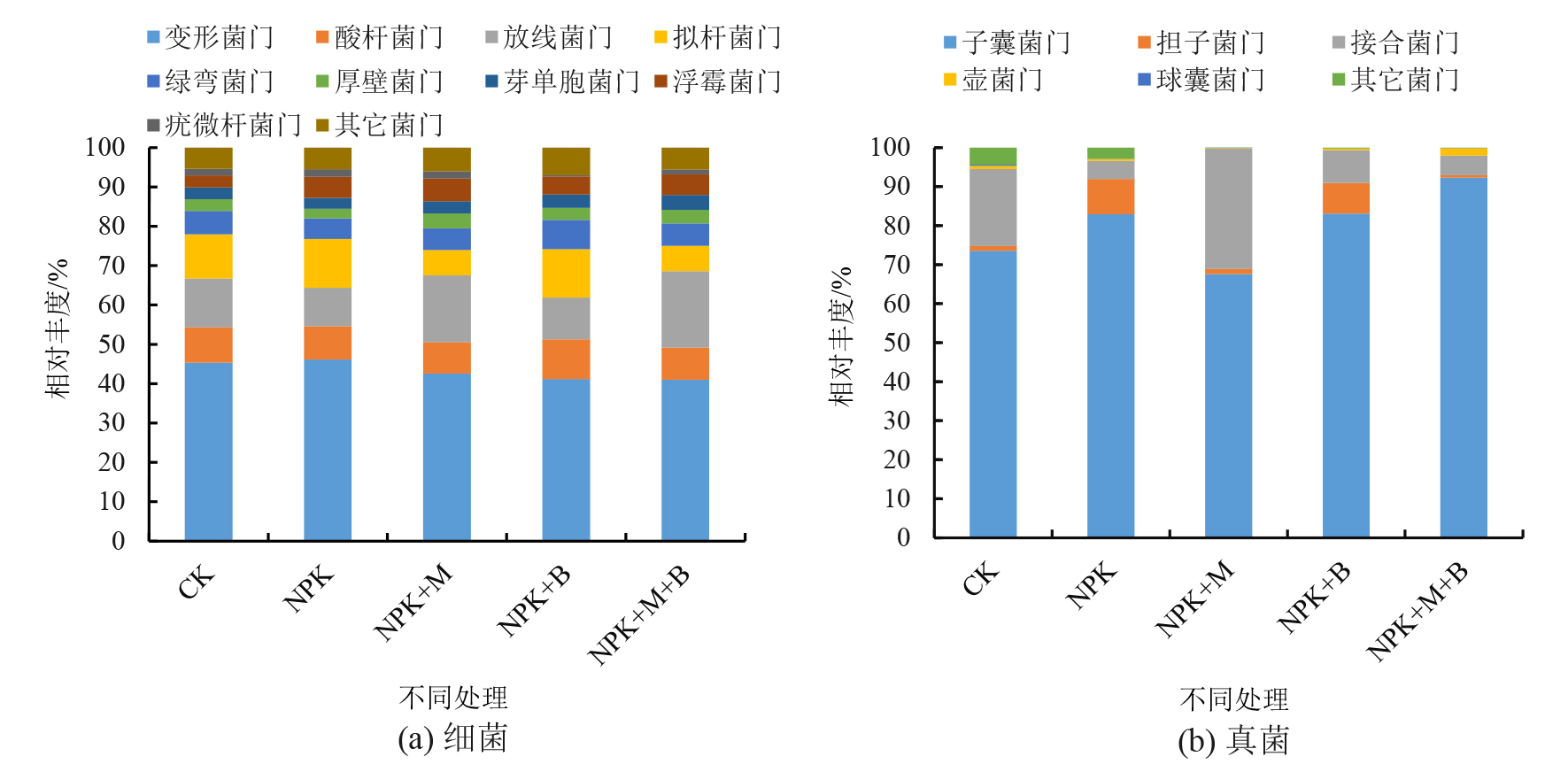
Figure 1 Impacts of organic fertilizer and biochar application on relative abundance of bacterial (a) and fungi (b) at phylum level in saline-alkali sandy soil
| [1] |
BARON N C, POLLO A D S, RIGOBELO E C, 2020. Purpureocillium lilacinum and Metarhizium marquandii as plant growth-promoting fungi[J]. Peer Journal, 8: e9005.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BONANOMI G, ZOTTI M, IDBELLA M, et al., 2021. Mixtures of organic amendments and biochar promote beneficial soil microbiota and affect Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lactucae, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotinia minor disease suppression[J]. Plant Pathology, 71(4): 818-829.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN L, REDMILE-GORDON M, LI J W, et al., 2019. Linking cropland ecosystem services to microbiome taxonomic composition and functional composition in a sandy loam soil with 28-year organic and inorganic fertilizer regimes[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 139: 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CUEVA-YESQUÉN L G, GOULART M C, ATTILI D A D, et al., 2021. Multiple plant growth-promotion traits in endophytic bacteria retrieved in the vegetative stage from passionflower[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11: 621740.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DUAN Y M, ZHANG L S, YANG J F, et al., 2022. Insight to bacteria community response of organic management in apple orchard-bagasse fertilizer combined with biochar[J]. Chemosphere, 286(Part2): 131693.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
EBRAHIMI-ZARANDI M, RISEH R S, TARKKA M T, 2022. Actinobacteria as effective biocontrol agents against plant pathogens, an overview on their role in eliciting plant defense[J]. Microorganisms, 10(9): 1739.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GU Y Y, ZHANG H Y, LIANG X Y, et al., 2022. Effect of different biochar particle sizes together with bio-organic fertilizer on rhizosphere soil microecological environment on saline-alkali land[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10: 949190.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HAMMAM A A, MOHAMED E S, ELNAMAS A E, et al., 2022. Impacted application of water-hyacinth-derived biochar and organic manures on soil properties and barley growth[J]. Sustainability, 14(20): 13096.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HAN Z Q, XU P S, LI Z T, et al., 2022. Microbial diversity and the abundance of keystone species drive the response of soil multifunctionality to organic substitution and biochar amendment in a tea plantation[J]. Global Change Biology Bioenergy, 14(4): 481-495.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KHAN A, KHAN A A, KHAN M J, et al., 2022. Combined effect of organic amendments and seed placement techniques on sorghum yield Under salt-Stressed conditions[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 22(4): 4752-4767.
DOI |
| [11] |
KHAN M A, KHAN S T, 2020. Microbial communities and their predictive functional profiles in the arid soil of Saudi Arabia[J]. Soil, 6(2): 513-521.
DOI URL |
| [12] | KIRUI C K, NJERU E M, RUNO S, 2022. Diversity and phosphate solubilization efficiency of phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from semi-arid agroecosystems of Eastern Kenya[J]. Microbiology Insights, 15: 1-12. |
| [13] |
KHAN M I, ALI N, JAN G, et al., 2022. Salt stress alleviation in Triticum aestivum through primary and secondary metabolites modulation by Aspergillus terreus BTK-1[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13: 779623.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI X K, LANG D Y, WANG J H, et al., 2023. Plant-beneficial Streptomyces dioscori SF1 potential biocontrol and plant growth promotion in saline soil within the arid and semi-arid areas[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(27): 70194-70212.
DOI |
| [15] |
MAO X X, YANG Y, GUAN P B, et al., 2022. Remediation of organic amendments on soil salinization: Focusing on the relationship between soil salts and microbial communities[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 239: 113616.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MINHAL F, MA'AS A, HANUDIN E, et al., 2020. Improvement of the chemical properties and buffering capacity of coastal sandy soil as affected by clays and organic by-product application[J]. Soil and Water Research, 15(2): 93-100.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MUGONZA J, OTIM M H, EGONYU J P, 2020. The comparative virulence of an atoxigenic strain of Aspergillus flavus (Eurotiales: Trichocomaceae) and the commercial ICIPE 69 Metarhizium anisopliae (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) to the bean leaf beetle Ootheca mutabilis (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae)[J]. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, 40(2): 403-411.
DOI |
| [18] |
NAFIS A, RAKLAMI A, BECHTAOUI N, et al., 2019. Actinobacteria from extreme niches in Morocco and their plant growth-promoting potentials[J]. Diversity, 11(8): 139-139.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
OZIMEK E, HANAKA A, 2020. Mortierella species as the plant growth-promoting fungi present in the agricultural soils[J]. Agriculture, 11(1): 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SAFDARIAN M, ASKARI H, NEMATZADEH G, et al., 2020. Halophile plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria induce salt tolerance traits in wheat seedlings ( Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Pedosphere, 30(5): 684-693.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SILVA C C G D, MEDEIROS E V D, FRACETTO G G M, et al., 2021. Biochar and cow manure on chemical and microbial community in regosol with bean[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 21(3): 1552-1564.
DOI |
| [22] |
SOLAIMAN Z M, SHAFI M I, BEAMONT E, et al., 2020. Poultry litter biochar increases mycorrhizal colonisation, soil fertility and cucumber yield in a fertigation system on sandy soil[J]. Agriculture, 10(10): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
TCHAKOUNTÉ G V T, BERGER B, PATZ S, et al., 2018. Community structure and plant growth-promoting potential of cultivable bacteria isolated from Cameroon soil[J]. Microbiological Research, 214: 47-59.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
WANG S B, GAO P L, ZHANG Q W, et al., 2022a. Application of biochar and organic fertilizer to saline-alkali soil in the Yellow River Delta: Effects on soil water, salinity, nutrients, and maize yield[J]. Soil Use and Management, 38(4): 1679-1692.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG S B, GAO P L, ZHANG Q W, et al., 2022b. Biochar improves soil qualit2022y and wheat yield in saline-alkali soils beyond organic fertilizer in a 3-year field trial[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(7): 19097-19110.
DOI |
| [26] |
WANG Y, PAN F, WANG Q, et al., 2022. The effect of different remediation treatments on soil fungal communities in rare earth tailings soil[J]. Forests, 13(12): 1987.
DOI URL |
| [27] | HOU J X, ZHANG J R, LIU X Z, et al., 2023. Effect of biochar addition and reduced irrigation regimes on growth, physiology and water use efficiency of cotton plants under salt stress[J]. Industrial Crops & Products, 198: 116702. |
| [28] |
WU Z X, LI H H, LIU Q L, et al., 2020. Application of bio-organic fertilizer, not biochar, in degraded red soil improves soil nutrients and plant growth[J]. Rhizosphere, 16: 100264.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YANG J J, LI W J, TENG D X, et al., 2022. Metagenomic insights into microbial community structure, function, and salt adaptation in saline soils of arid land, China[J]. Microorganisms, 10(11): 2183-2183.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YAO G S, CHEN X F, ZHENG H W, et al., 2021. Genomic and chemical investigation of bioactive secondary metabolites from a marine-derived fungus Penicillium steckii P2648[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12: 600991.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
YOSHIURA C A, VENTURINI A M, BRAGA L P P, et al., 2021. Responses of low-cost input combinations on the microbial structure of the maize rhizosphere for greenhouse gas mitigation and plant biomass production[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science. 12: 683658.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZAHRA S T, TARIQ M, ABDULLAH M, et al., 2023. Dominance of Bacillus species in the wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere and their plant growth promoting potential under salt stress conditions[J]. Peer Journal, 11: e14621.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHAO P N, YU J, ZHANG X Y, et al., 2022. Trifolium repens and biochar addition affecting soil nutrients and bacteria community[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(12): 33927-33941.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
陈丽美, 李小英, 岳学文, 等, 2019. 竹炭与有机肥混施对火龙果产量和品质影响及其改土作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(11): 2231-2238.
DOI |
| CHEN L M, LI X Y, YUE X W, et al., 2019. Effect of mixed application of bamboo charcoal and organic fertilizer on yield and quality of red pitaya and soil amelioration[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(11): 2231-2238. | |
| [35] | 陈松鹤, 向晓玲, 雷芳, 等, 2022. 秸秆覆盖配施氮肥条件下根际土真菌群落及其与小麦产量关系的研究[J]. 生态学报, 42(21): 8751-8761. |
| CHEN S H, XIANG X L, LEI F, et al., 2022. Relationship between rhizosphere fungal community and wheat yield under straw mulching combined with nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(21): 8751-8761. | |
| [36] |
代金霞, 田平雅, 沈聪, 等, 2021. 耐盐植物根际促生菌筛选及促生效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(5): 968-975.
DOI |
| DAI J X, TIAN P Y, SHEN C, et al., 2022. Screening of rhizosphere bacteria from salt tolerant plants and their growth promoting effects[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(5): 968-975. | |
| [37] | 管鸿智, 黄荣珍, 王金平, 等, 2023. 红壤区退化林地表土真菌群落结构对土壤改良措施的响应[J]. 环境科学, 44(1): 494-501. |
| GUAN H Z, HUANG R Z, WANG J P, et al., 2023. Response of topsoil fungal community structure to soil improvement measures in degraded forest of red soil region[J]. Environmental Science, 44(1): 494-501. | |
| [38] | 顾美英, 徐万里, 马凯, 等, 2021. 不同定植年限核桃园土壤细菌群落多样性及碳代谢功能特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(7): 2045-2056. |
| GU M Y, XU W L, MA K, et al., 2021. Soil bacterial community diversity and carbon source metabolism function in walnut orchard with different stand ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(7): 2045-2056. | |
| [39] | 顾美英, 张志东, 唐光木, 等, 2022. 黑果枸杞不同组织内生真菌群落组成及生态功能分析[J]. 菌物学报, 41(8): 1254-1267. |
| GU M Y, ZHANG Z D, TANG G M, et al., 2022. Community composition and ecological function of endophytic fungi in different tissues of Lycium ruthenicum[J]. Mycosystema, 41(8): 1254-1267. | |
| [40] | 黄俊杰, 陆雅海, 2022. 土壤拟杆菌与梭菌分解多糖类有机物质的研究进展与展望[J]. 微生物学通报, 49(3): 1147-1157. |
| HUANG J J, LU Y H, 2022. Decomposition of soil polymeric organic matter by Bacteroidetes and Clostridia: Progress and perspectives[J]. Microbiology China, 49(3): 1147-1157. | |
| [41] | 胡坤, 张红雪, 郭力铭, 等, 2021. 烟秆炭基肥对薏苡土壤有机碳组分及微生物群落结构和丰度的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 29(9): 1592-1603. |
| HU K, ZHANG H X, GUO L M, et al., 2021. Effects of tobacco stalk biochar-based fertilizer on the organic carbon fractions and microbial community structure of adlay soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29(9): 1592-1603. | |
| [42] | 李依韦, 毕佳欣, 袁琴, 等, 2020. 不同施肥处理玉米根际微生物种群结构及代谢多样性[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 32(1): 21-24, 30. |
| LI Y W, BI J X, YUAN Q, et al., 2020. The population structure and metabolic diversity of microorganisms in rhizosphere soil of corn treated with different fertilizers[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 32(1): 21-24, 30. | |
| [43] | 梁萌, 米晓军, 李晨华, 等, 2022. 新疆准噶尔盆地未开垦盐碱土盐分与盐生植被多样性分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(1): 185-196. |
| LIANG M, MI X J, LI C H, et al., 2022. Salinity characteristics and halophytic vegetation diversity of uncultivated saline-alkali soil in Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 45(1): 185-196. | |
| [44] | 刘广明, 杨劲松, 何丽丹, 等, 2011. 基于模糊综合评判法的新疆典型干旱区土壤盐漠退化风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(3): 1-5. |
| LIU G M, YANG J S, HE L D, et al., 2011. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation based assessment of soil alkaline desertification in typical arid area of Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 27(3): 1-5. | |
| [45] | 鲁如坤. 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agricultural Chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [46] | 南丽丽, 谭杰辉, 郭全恩, 2020. 黄土高原半干旱区轮作休耕模式对土壤真菌的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(23): 8582-8592. |
| NAN L L, TAN J H, GUO Q E, 2020. Effects of fallow rotation modes on soil fungal communities in semi-arid area of the Loess Plateau,northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(23): 8582-8592. | |
| [47] |
申午艳, 冯政君, 秦文芳, 等, 2020. 盐碱胁迫下黑麦草生长及离子微区分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 29(2): 52-63.
DOI |
| SHEN W Y, FENG Z J, QIN W F, et al., 2020. Effects of saline-alkali stress on the growth and ion micro-distribution of ryegrass plants[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 29(2): 52-63. | |
| [48] | 石玉龙, 高佩玲, 刘杏认, 等, 2019. 生物炭和有机肥施用提高了华北平原滨海盐土微生物量[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(4): 555-567. |
| SHI Y L, GAO P L, LIU X R, et al., 2019. Increased microbial biomass in coastal saline fields of North China Plain by application of biochar and organic manure[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 25(4): 555-567. | |
| [49] | 孙强, 杨旭, 孟军, 等, 2022. 生物炭对棕壤团聚体空间分布及有机碳的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 41(11): 2515-2524. |
| SUN Q, YANG X, MENG J, et al., 2022. Effects of biochar on soil aggregate spatial distribution and soil organic carbon in brown earth soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 41(11): 2515-2524. | |
| [50] | 王光飞, 马艳, 郭德杰, 等, 2015. 秸秆生物炭对辣椒疫病的防控效果及机理研究[J]. 土壤, 47(6): 1107-1114. |
| WANG G F, MA Y, GUO D J, et al., 2015. Effect and mechanism of straw biochar on disease control of phytophthora blight of chilli pepper[J]. Soils, 47(6): 1107-1114. | |
| [51] |
王光华, 刘俊杰, 于镇华, 等, 2016. 土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 32(2): 14-20.
DOI |
| WANG G H, LIU J J, YU Z H, et al., 2016. Research progress of Acidobacteria ecology in soils[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 32(2): 14-20. | |
| [52] | 王紫艳, 杨桂玲, 虞轶俊, 等, 2020. 有机肥施用对农产品质量安全及土壤环境的影响研究[J]. 农产品质量与安全 (4): 67-73. |
| WANG Z Y, YANG G L, YU Y J, et al., 2020. Study on the effects of organic fertilizer application on the quality and safety of agricultural products and soil[J]. Quality and Safety of Agro-Products (4): 67-73. | |
| [53] | 王艮梅, 陈捷, 范之馨, 等, 2022. 外源有机物料添加对滨海盐碱土细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 38(1): 85-95. |
| WANG G M, CHEN J, FAN Z X, et al., 2022. The shift of bacterial community structure in coastal saline-alkaline soil upon addition of different organic materials[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 38(1): 85-95. | |
| [54] | 于菲, 赵硕, 赵影, 等, 2022. 长期施用有机肥对松嫩平原西部盐碱土肥力和玉米产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 40(2): 172-180. |
| YU F, ZHAO S, ZHAO Y, et al., 2022. Effects of long-term application of cattle manure on soil fertility and corn yield of saline-sodic soil in western Songnen Plain[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 40(2): 172-180. | |
| [55] | 袁银龙, 孙杰, 徐如玉, 等, 2020. 丛枝菌根真菌与有机肥配施对甜玉米根际土壤关键碳循环功能基因的影响[J]. 福建农业学报, 35(7): 753-763. |
| YUAN Y L, SUN J, XU R Y, et al., 2020. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic fertilizer on key microbial carbon-cycle genes in rhizosphere soil at sweet corn field[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 35(7): 753-763. | |
| [56] | 郑佳华, 赵萌莉, 王琪, 等, 2022. 放牧和刈割对大针茅草原土壤微生物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 42(12): 4998-5008. |
| ZHENG J H, ZHAO M L, WANG Q, et al., 2022. Effects of management regime on soil microbial community structure and diversity of Stipa grandis grassland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(12): 4998-5008. | |
| [57] | 张建兵, 杨劲松, 姚荣江, 等, 2013. 有机肥与覆盖方式对滩涂围垦农田水盐与作物产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 29(15): 116-125. |
| ZHANG J B, YANG J S, YAO R J, et al., 2013. Dynamics of soil water, salt and crop growth under farmyard manure and mulching in coastal tidal flat soil of northern Jiangsu Province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(15): 116-125. | |
| [58] | 张云舒, 唐光木, 蒲胜海, 等, 2020. 减氮配施炭基肥对棉田土壤养分、氮素利用率及产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 29(9): 1372-1377. |
| ZHANG Y S, TANG G M, PU S H, et al., 2020. Effect of biochar-based compound fertilizeron soil nutrients and cotton yield in irrigated sandy soil under nitrogen reduction condition[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 29(9): 1372-1377. | |
| [59] |
赵雅姣, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 等, 2020. 西北半干旱区紫花苜蓿-小黑麦间作对根际土壤养分和细菌群落的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(5): 1645-1652.
DOI |
| ZHAO Y J, LIU X J, WU Y, et al., 2020. Effects of Medicago sativa-Triticale wittmack intercropping system on rhizosphere soil nutrients and bacterial community in semi-arid region of Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(5): 1645-1652. |
| [1] | LI Guiying, LIU Jianying, AN Taicheng. The Formation and Resuscitation Mechanisms of Viable But Nonculturable Bacteria during Water Disinfection Processes [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1333-1343. |
| [2] | LI Haipeng, HUANG Yuehua, SUN Xiaodong, CAO Qimin, FU Fangxing, SUN Chuhan. Correlation Analysis of the Occurrence of the Tomato Bacterial Wilt and Different Types of Texture of Latosols and Its Bacterial Community in Cropland in Hainan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1062-1069. |
| [3] | HUANG Yingmei, ZHONG Songxiong, ZHU Yiwen, WANG Xiangqin, LI Fangbai. Effects and Mechanism of Element Sulfur Inhibiting Methylmercury Accumulation in Rice Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [4] | HOU Hui, YAN Peixuan, XIE Qinmi, ZHAO Hongliang, PANG Danbo, CHEN Lin, LI Xuebin, HU Yang, LIANG Yongliang, NI Xilu. Characterization of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community Diversity in the Rhizosphere Soils of Prunus mongolica Scrub of Helan Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [5] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [6] | QIN Hao, LI Mengai, GAO Jin, CHEN Kailong, ZHANG Yinbo, ZHANG Feng. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Shrub at Different Altitudes in Luya Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [7] | YANG Nie, SUN Xiaoxun, KONG Tianle, SUN Weimin, CHEN Quanyuan, GAO Pin. Response of Microbial Communities to Changes in Antimony Pollution Concentrations in Fluvial Sediment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [8] | YANG Yu, DENG Renjian, LONG Pei, HUANG Zhongjie, Ren Bozhi, WANG Zhenghua. Isolation and Identification of Arsenic-oxidizing Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. AO-1 and Its Oxidation Properties for As(Ⅲ) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| [9] | TONG Yindong, HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Environmental Risk Analysis of Microcystins in Global Water Bodies [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 129-138. |
| [10] | YANG Rui, SUN Weimin, LI Yongbin, GUO Lifang, JIAO Nianyuan. Isolation, Identification and Plant Growth Promotion of Rhizosphere Phosphorus-dissolving Bacteria from Tailings Pioneer Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [11] | XIANG Xing, MAN Baiying, ZHANG Junzhong, LUO Yang, MAO Xiaotao, ZHANG Chao, SUN Binghua, WANG Xi. Vertical Distribution of Bacterial Community and Functional Groups Mediating Nitrogen Cycling in Mount Huangshan, Anhui, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [12] | WANG Zhao, ZHANG Manyin, HU Yukun, LIU Weiwei, ZHANG Miaomiao. Effect of Salinity on Mercury Methylation in Sediments of A Typical Coastal Wetland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [13] | WANG Lixiao, LIU Jinxian, CHAI Baofeng. Response of Soil Bacterial Community and Nitrogen Cycle during the Natural Recovery of Abandoned Farmland in Subalpine of the North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [14] | LIU Ning, LIU Yang, XU Jingping, SONG Huiping, FENG Zhengjun, CHENG Fangqin. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Plant Growth and Water Purification in Constructed Wetlands [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1434-1441. |
| [15] | ZHU Jinfu, HUANG Ruiling, DONG Zhiqiang, MAO Xiaoning, ZHOU Huakun. Response of the Soil Bacterial Community to Nitrogen Addition in Alpine Wetland of Qinghai Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1101-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
