Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1434-1441.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.016
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Ning1( ), LIU Yang4, XU Jingping5, SONG Huiping1, FENG Zhengjun2,3,*(
), LIU Yang4, XU Jingping5, SONG Huiping1, FENG Zhengjun2,3,*( ), CHENG Fangqin1
), CHENG Fangqin1
Received:2022-03-04
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
Contact:
FENG Zhengjun
刘宁1( ), 刘洋4, 续京平5, 宋慧平1, 冯政君2,3,*(
), 刘洋4, 续京平5, 宋慧平1, 冯政君2,3,*( ), 程芳琴1
), 程芳琴1
通讯作者:
冯政君
作者简介:刘宁(1995年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事生态修复研究。E-mail: 201924001015@email.sxu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Ning, LIU Yang, XU Jingping, SONG Huiping, FENG Zhengjun, CHENG Fangqin. Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on Plant Growth and Water Purification in Constructed Wetlands[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1434-1441.
刘宁, 刘洋, 续京平, 宋慧平, 冯政君, 程芳琴. 丛枝菌根真菌对人工湿地植物生长及水质净化的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1434-1441.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.016
| 植物种类 Plant species | 种植面积 Planting area/m2 | 种植密度 Planting density/ (pcs∙m-2) | 总株数 Total number of plants/pcs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水葱 Scirpus tabernaemontani | 400 | 10 | 4000 |
| 黄菖蒲 Iris pseudacorus | 400 | 25 | 10000 |
Table 1 Plant planting area and density in the test area
| 植物种类 Plant species | 种植面积 Planting area/m2 | 种植密度 Planting density/ (pcs∙m-2) | 总株数 Total number of plants/pcs |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水葱 Scirpus tabernaemontani | 400 | 10 | 4000 |
| 黄菖蒲 Iris pseudacorus | 400 | 25 | 10000 |
| 监测指标 Monitoring index | 分析方法 Analysis method | 方法来源 Methods the source |
|---|---|---|
| COD | 重铬酸盐滴定法 | HJ 828—2017 (环境保护部, |
| 氨氮NH3-N ammonia nitrogen | 纳氏试剂光度法 | HJ 535—2009 (环境保护部, |
| TP | 钼酸铵分光光度法 | GB 11893-89 (国家环境保护局, |
Table 2 Water sample monitoring index and analysis method
| 监测指标 Monitoring index | 分析方法 Analysis method | 方法来源 Methods the source |
|---|---|---|
| COD | 重铬酸盐滴定法 | HJ 828—2017 (环境保护部, |
| 氨氮NH3-N ammonia nitrogen | 纳氏试剂光度法 | HJ 535—2009 (环境保护部, |
| TP | 钼酸铵分光光度法 | GB 11893-89 (国家环境保护局, |
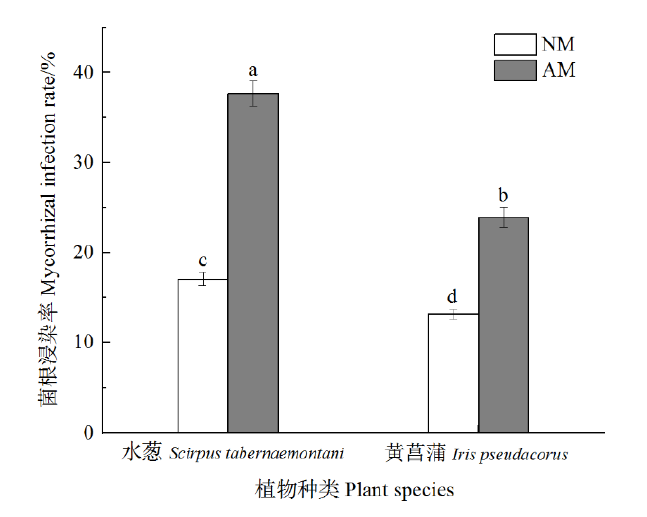
Figure 2 Effects of AM fungi on mycorrhizal infection rate of different plants Data in the figure are the mean values of three repetitives (n=3), different letters indicated significant difference between groups (P<0.05)
| 植物种类 Plant species | 处理 Treament | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm | 鲜重 Fresh weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水葱 Scirpus tabernaemontani | NM | 156.49±9.49b | 16.30±0.92b | 179.77±11.61b |
| AM | 205.55±9.08a | 19.60±1.52a | 389.07±25.30a | |
| 黄菖蒲 Iris pseudacorus | NM | 81.58±6.00b | 28.59±3.84b | 100.02±9.70b |
| AM | 96.09±3.83a | 36.92±2.11a | 154.59±8.19a |
Table 3 Effects of AM fungi on the growth of different plants
| 植物种类 Plant species | 处理 Treament | 株高 Plant height/cm | 根长 Root length/cm | 鲜重 Fresh weight/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水葱 Scirpus tabernaemontani | NM | 156.49±9.49b | 16.30±0.92b | 179.77±11.61b |
| AM | 205.55±9.08a | 19.60±1.52a | 389.07±25.30a | |
| 黄菖蒲 Iris pseudacorus | NM | 81.58±6.00b | 28.59±3.84b | 100.02±9.70b |
| AM | 96.09±3.83a | 36.92±2.11a | 154.59±8.19a |
| 监测指标 Monitoring index | 初始进水质量浓度 Initial inlet concentration/ (mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard | NM区最终出水质量浓度 Final outlet concentration in NM area/(mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard | AM区最终出水质量浓度 Final outlet concentration in AM area/(mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | 36.32±1.21 | V类 | 15.07±0.20 | III类 | 13.97±0.38 | II类 |
| 氨氮NH3-N Ammonia nitrogen | 4.12±0.33 | 劣V类 | 0.17±0.01 | II类 | 0.14±0.02 | I类 |
| TP | 0.49±0.04 | 劣V类 | 0.14±0.01 | III类 | 0.11±0.01 | III类 |
Table 4 The concentration of inlet and outlet water and its quality standard of constructed wetland
| 监测指标 Monitoring index | 初始进水质量浓度 Initial inlet concentration/ (mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard | NM区最终出水质量浓度 Final outlet concentration in NM area/(mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard | AM区最终出水质量浓度 Final outlet concentration in AM area/(mg∙L-1) | 水质标准 Water standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | 36.32±1.21 | V类 | 15.07±0.20 | III类 | 13.97±0.38 | II类 |
| 氨氮NH3-N Ammonia nitrogen | 4.12±0.33 | 劣V类 | 0.17±0.01 | II类 | 0.14±0.02 | I类 |
| TP | 0.49±0.04 | 劣V类 | 0.14±0.01 | III类 | 0.11±0.01 | III类 |
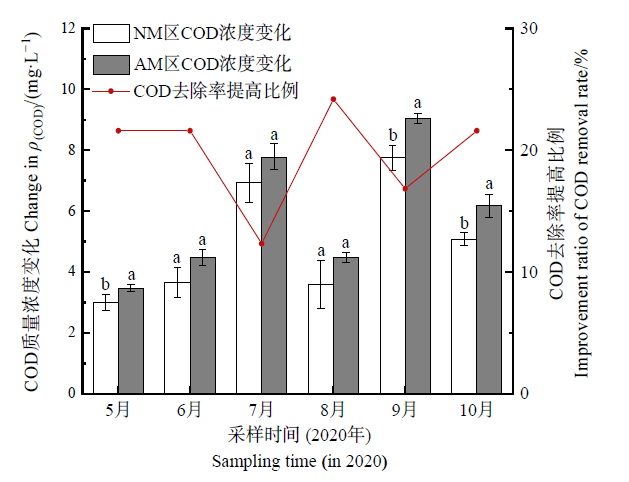
Figure 5 Change and removal improvement ratio of COD mass concentration in inlet and outlet water of constructed wetland Data in the figure are the mean values of three repetitives (n=3). The bar chart shows the change in pollutant concentration, different letters indicate significant difference between groups (P<0.05), and the same letter indicates no significant difference (P>0.05). The point plot represents the improvement ratio of pollutants removal rate, the same below
| [1] |
ANSARI M W, TRIVEDI D K, SAHOO R K, et al., 2013. A critical review on fungi mediated plant responses with special emphasis to Piriformospora indica on improved production and protection of crops[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 70(1): 403-410.
DOI URL |
| [2] | JIANG F Y, ZHANG L, ZHOU J C, et al., 2020. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance mineralization of organic phosphorus (P) by carrying bacteria along their extraradical hyphae[J]. New Phytologist, 78: 1088-1094. |
| [3] |
MOHAMMAD A, MITTRA B, 2011. Effects of inoculation with stress-adapted arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus deserticola on growth of Solanum melogena L. and Sorghum sudanese Staph. seedlings under salinity and heavy metal stress conditions[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 59(2): 173-183.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PHILLIPS J M, HAYMAN D S, 1970. Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection[J]. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 55(1): 158-161.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
RAMÍREZ-VIGA T K, AGUILAR R, CASTILLO-ARGUERO S, et al., 2018. Wetland plant species improve performance when inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: A meta-analysis of experimental pot studies[J]. Mycorrhiza, 28(5-6): 477-493.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG S G, DAI D W, SHUANG S, et al., 2018. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) status in urban wetland plants and its impact factors[J]. Aquatic Botany, 150: 33-45.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XU Z Y, BAN Y H, JIANG Y H, et al., 2016. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in wetland habitats and their application in constructed wetland: A review[J]. Pedosphere, 26(5): 592-617.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
XU Z Y, WU Y, JIANG Y H, et al., 2018. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in two vertical-flow wetlands constructed for heavy metal-contaminated wastewater bioremediation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(2): 12830-12840.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHENG C C, CHAI M M, JIANG S S, et al., 2015. Foraging capability of extraradical mycelium of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to soil phosphorus patches and evidence of carry-over effect on new host plant[J]. Plant and Soil, 387(1-2): 201-217.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 陈明利, 吴晓芙, 胡曰利, 2006. 人工湿地去污机理研究进展[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 26(3): 123-127. |
| CHEN M L, WU X F, HU Y L, 2006. The research review of constructed wetland systems for wastewater treatment[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 26(3): 123-127. | |
| [11] | 陈媛, 2015. AMF-鸢尾-聚氨酯载体生物净化体系对水中氮磷的去除效能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学: 34-62. |
| CHEN Y, 2015. AMF-iris wilsonii C. H. Wright-polyurethane carrier biological removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus in water purification system research[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology: 34-62. | |
| [12] | 丁怡, 王玮, 宋新山, 等, 2017. 人工湿地在水质净化中的应用及研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 37(3): 6-10. |
| DING Y, WANG W, SONG X S, et al., 2017. Application of constructed wetland to water purification and its research progress[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 37(3): 6-10. | |
| [13] | 高文礼, 再努尔∙吐尔逊, 桑钰, 等, 2021. 丛枝菌根真菌对植物氮素吸收作用的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 37(27): 53-58. |
| GAO W L, ZAI N T, SANG Y, et al., 2021. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nitrogen absorption of plant: A review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 37(27): 53-58. | |
| [14] | 国家环境保护局, 1989. 水质总磷的测定钼酸铵分光光度法: GB 11893-89 [S]. 北京: 国家环境保护局: 188-191. |
| State Environmental Protection Administration, 1989. Water quality-Determination of total phosphorus-Ammonium molybdate spectrophotometric method: GB 11893-89 [S]. Beijing: State Environmental Protection Administration: 188-191. | |
| [15] | 郭佳, 王丹, 黄炜, 等, 2014. 不同丛枝菌根对白三叶草生长的影响[J]. 北方园艺 (2): 66-70. |
| GUO J, WANG D, HUANG W, et al., 2014. Influence of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and physiological and biochemical indicators of Triolium repens[J]. Northern Horticulture (2): 66-70. | |
| [16] | 黄锦楼, 陈琴, 许连煌, 2013. 人工湿地在应用中存在的问题及解决措施[J]. 环境科学, 34(1): 401-408. |
| HUANG J L, CHEN Q, XU L H, 2013. Problems and countermeasures in the application of constructed wetlands[J]. Environmental Science, 34(1): 401-408. | |
| [17] | 吉云秀, 丁永生, 丁德文, 2005. 滨海湿地的生物修复[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 31(3): 47-52. |
| JI Y X, DING Y S, DING D W, 2005. Bioremediation in coastal wetland[J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 31(3): 47-52. | |
| [18] | 李世阳, 2010. 芦苇菌根真菌依赖性及其联合环境修复功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学: 46-62. |
| LI S Y, 2010. The reed mycorrhizal fungi dependence and the studies of combinational environmental remediation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology: 46-62. | |
| [19] | 李信茹, 2021. 汞胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌对水稻生长生理特性和吸收积累汞的影响[D]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院:20. |
| LI X R, 2021. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth physiological characteristics and mercury uptake and accumulation in rice under mercury stress[D]. Beijing: Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences:20. | |
| [20] | 梁威, 吴振斌, 周巧红, 等, 2002. 构建湿地基质微生物与净化效果及相关分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 22(3): 282-285. |
| LIANG W, WU Z B, ZHOU Q H, et al., 2002. Analysis of substrate microorganisms in the construction wetland and their correlation with wastewater purification effects[J]. China Environmental Science, 22(3): 282-285. | |
| [21] | 罗鹏程, 2016. 丛枝菌根 (AM) 真菌对生态浮床功能影响的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学:7. |
| LUO P C, 2016. Study on effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the function of ecological floating bed[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology:7. | |
| [22] | 马学淼, 刘晓, 解新宇, 等, 2020. 真菌Glomus mosseae对2个玉米品种产量的影响及生长性状相关分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(19): 8-12. |
| MA X M, LIU X, XIE X Y, et al., 2020. Effects of Glomus mosseae on yield of two maize cultivars and correlation analysis of growth traits[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 36(19): 8-12. | |
| [23] | 莫惠芝, 曾宪军, 何新杰, 等, 2019. 不同AMF接种两种湿地植物的生长效应研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 31(1): 8-13. |
| MO H Z, ZENG X J, HE X J, et al., 2019. Study on growth effect of two wetland plants spiecies infected with different AMFs[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 31(1): 8-13. | |
| [24] | 彭麟, 刘子芳, 肖文雄, 等, 2012. 丛枝菌根真菌 (AMF) 提高人工湿地去污能力及运行稳定性的潜力分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(10): 1869-1878. |
| PENG L, LIU Z F, XIAO W X, et al., 2012. The potential of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) to improve decontamination capability and operational stability of constructed wetland[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(10): 1869-1878. | |
| [25] | 屈明华, 俞元春, 李生, 等, 2019. 丛枝菌根真菌对矿质养分活化作用研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 36(2): 394-405. |
| QU M H, YU Y C, LI S, et al., 2019. Advances in research on activation of mineral nutrients by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 36(2): 394-405. | |
| [26] | 孙秀秀, 贺超兴, 李衍素, 等, 2017. AM真菌对黄瓜根围土壤微生物群落功能的影响[J]. 菌物学报, 36(7): 892-903. |
| SUN X X, HE C X, LI Y S, et al., 2017. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on microbial community and function in the rhizosphere soil of cucumber plants[J]. Mycosystema, 36(7): 892-903. | |
| [27] | 王立, 贾文奇, 马放, 等, 2010. 菌根技术在环境修复领域中的应用及展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(2): 487-493. |
| WANG L, JIA W Q, MA F, et al., 2010. Perspective of mycorrhizal technology application for environmental remediation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(2): 487-493. | |
| [28] | 王宁, 秦艳, 2012. AM真菌对宿主植物三叶鬼针草根系形态的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 40(1): 13-14, 26. |
| WANG N, QIN Y, 2012. Effects of AM fungus on root morphology of Host plant Bidens pilosa L.[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 40(1): 13-14, 26. | |
| [29] | 叶振坤, 陈晓林, 赵培爵, 等, 2020. 复合型人工湿地系统设计及其处理技术开发[J]. 山西建筑, 46(1): 151-153. |
| YE Z K, CHEN X L, ZHAO P J, et al., 2020. Design and treatment technology of compound constructed wetland system[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 46(1): 151-153. | |
| [30] | 鄢金灼, 武发思, 冯虎元, 2008. 湿地植物与丛枝菌根真菌 (AMF) 相互关系的研究进展[J]. 西北植物学报, 28(4): 4836-4842. |
| YAN J Z, WU F S, FENG H Y, 2008. Review on the relationship between wetland plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 28(4): 4836-4842. | |
| [31] |
袁丽环, 闫桂琴, 2010. 丛枝菌根化翅果油树幼苗根际土壤微环境[J]. 植物生态学报, 34(6): 678-686.
DOI |
| YUAN L H, YAN G Q, 2010. Rhizosphere soil of seedlings of Elaeagnus mollis colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(6): 678-686. | |
| [32] | 赵敏, 刘红玲, 邓錡璋, 等, 2021. AM真菌对油樟幼苗生长及土壤养分的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学, 60(17): 74-77. |
| ZHAO M, LIU H L, DENG Q Z, et al., 2021. Effects of AM fungus on camphor seedling growth and soil nutrients[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 60(17): 74-77. | |
| [33] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2009. 水质氨氮的测定纳氏试剂分光光度法: HJ 535-2009 [S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国环境保护部: 1-4. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China, 2009. Water quality-Determination of ammonia nitrogen-Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry: HJ 535-2009 [S]. Beijing: Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: 1-4. | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2017. 水质化学需氧量的测定重铬酸盐法: HJ 828-2017 [S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国环境保护部: 1-8. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2017. Water quality-Determination of the chemical oxygen demand-Dichromate method: HJ 828-2017 [S]. Beijing: Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: 1-8. | |
| [35] | 周霞, 崔明, 秦永胜, 等, 2012. 扩繁条件对3种丛枝菌根真菌 (AMF) 的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 28(12): 83-87. |
| ZHOU X, CUI M, QIN Y S, et al., 2012. The effects of the propagation condition on the three kinds of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 28(12): 83-87. |
| [1] | WANG Tiezheng, QU Xinyue, LIU Chunxiang, LI Youzhi. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Water Quality in the Dongjiang Lake and Their Relationships with Land Use in the Watershed [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 722-732. |
| [2] | CHEN Xiaowan, TIAN Huachuan, CHANG Junjun, CHEN Liqiang, SHU Xingquan, FENG Xiuxiang. Purification Efficiency for Polluted River Water and Microbial Community Characteristics of A Surface-flow Wetland Located at Zhonghe River Estuary near Qilu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| [3] | GUO Lifang, YANG Rui, SUN Weimin. Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Isolation from Mine Tailings and Their Plant Growth Promoting Properties [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2180-2188. |
| [4] | WANG Jin, HAN Zhiyong, FENG Yan, ZHOU Ruoxin, WANG Shuangchao. Morphological Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in the Green Soil of Industrial Zone in Chengdu [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1923-1932. |
| [5] | PAN Guoying, LIN Fenglian, YUAN Feng, LUO Qian, GAO Qianqian, LI Jian, WU Chengzhen, CHEN Can. Study on Purification Ability of 10 Highly Efficient Strains in Artificial Wastewater [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1695-1705. |
| [6] | DAI Jinxia, TIAN Pingya, SHEN Cong, LIU Shuang. Screening of Rhizosphere Bacteria from Salt Tolerant Plants and Their Growth Promoting Effects [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 968-975. |
| [7] | LI Fengmin, CHEN Lin, JIANG Xiaohua, LI Chenguang, ZHAO Shasha, CHONG Yunxiao, HU Hongying, GAO Shuaiqiang. The Construction of Index System for Selecting Aquatic Plant in Water Purification and Ecological Restoration [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2411-2422. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
