Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 1115-1122.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.06.013
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Yingmei1,2,3( ), ZHONG Songxiong3,#(
), ZHONG Songxiong3,#( ), ZHU Yiwen3, WANG Xiangqin3, LI Fangbai3,*(
), ZHU Yiwen3, WANG Xiangqin3, LI Fangbai3,*( )
)
Received:2023-03-16
Online:2023-06-18
Published:2023-09-01
Contact:
LI Fangbai
黄英梅1,2,3( ), 钟松雄3,#(
), 钟松雄3,#( ), 朱忆雯3, 王向琴3, 李芳柏3,*(
), 朱忆雯3, 王向琴3, 李芳柏3,*( )
)
通讯作者:
李芳柏
作者简介:黄英梅(1994年生),女,博士研究生,研究方向为土壤-水稻体系汞的迁移转运机制及修复。E-mail: huangyingmei3691@gmail.com基金资助:CLC Number:
HUANG Yingmei, ZHONG Songxiong, ZHU Yiwen, WANG Xiangqin, LI Fangbai. Effects and Mechanism of Element Sulfur Inhibiting Methylmercury Accumulation in Rice Plants[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122.
黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.06.013
| 功能基因 | 引物名称 | 引物序列(5′-3′) | 扩增程序 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dsrA | DSR1F | ACSCACTGGAAGCACG | 95 ℃ 40 s; 94 ℃ 60 s, 56 ℃ 40 s, 72 ℃ 2 min, 40 cycles; 72 ℃ 4 min |
| DSR1R | GTGTAGCAGTTACCGCA | ||
| dsrB | DSRp2060F | CAACATCGTYCAYACCCAGGG | 95 ℃ 30 s; 95 ℃ 5 s, 55 ℃ 34 s, 72 ℃ 34 s, 40 cycles; 72 ℃ 4 min |
| DSR4R | GTGTAGCAGTTACCGCA |
Table 1 Lists of primer pairs and thermal cycling parameters for qRT-PCR
| 功能基因 | 引物名称 | 引物序列(5′-3′) | 扩增程序 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dsrA | DSR1F | ACSCACTGGAAGCACG | 95 ℃ 40 s; 94 ℃ 60 s, 56 ℃ 40 s, 72 ℃ 2 min, 40 cycles; 72 ℃ 4 min |
| DSR1R | GTGTAGCAGTTACCGCA | ||
| dsrB | DSRp2060F | CAACATCGTYCAYACCCAGGG | 95 ℃ 30 s; 95 ℃ 5 s, 55 ℃ 34 s, 72 ℃ 34 s, 40 cycles; 72 ℃ 4 min |
| DSR4R | GTGTAGCAGTTACCGCA |
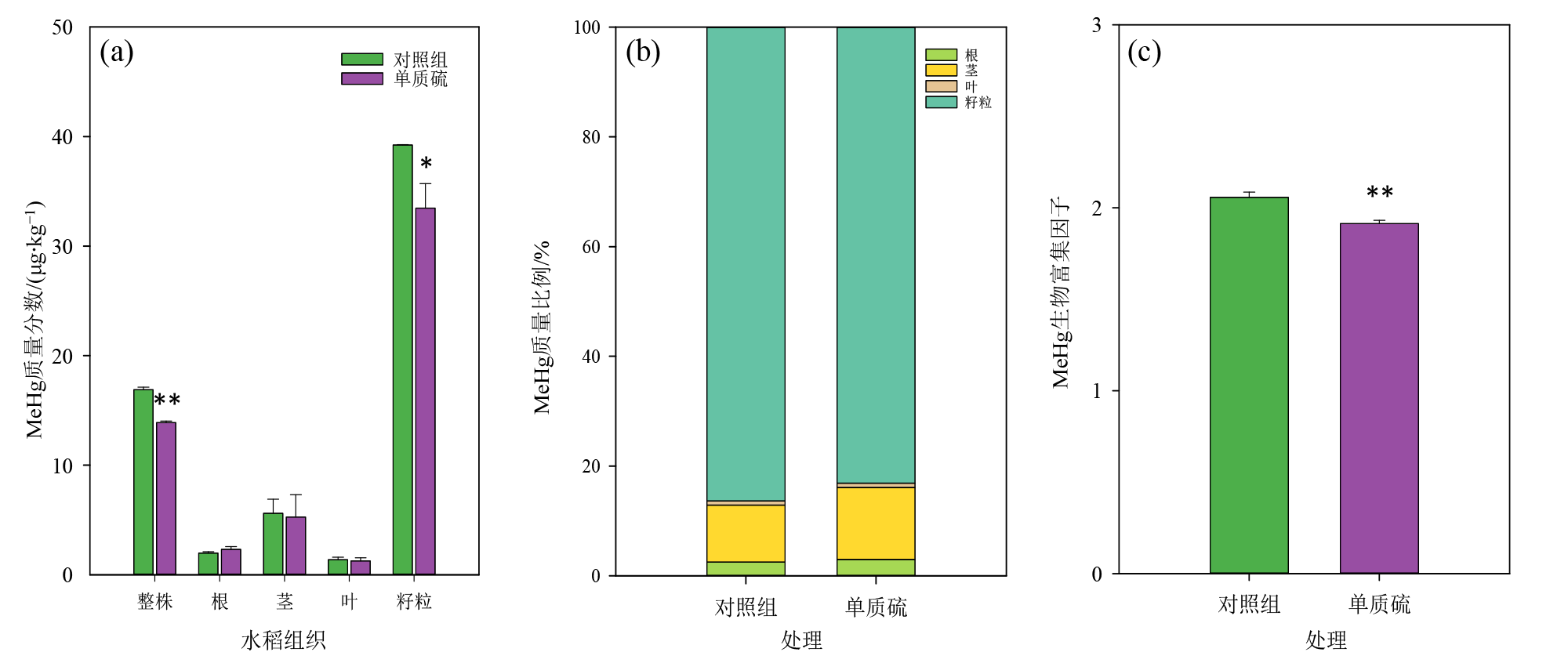
Figure 4 The contents and distribution of MeHg in different tissues of rice plants and bioaccumulation factors of MeHg in control and S(0) (100 mg·kg-1) treatments
| 处理 | 茎-根 | 叶-根 | 籽粒-根 | 叶-茎 | 籽粒-茎 | 籽粒-叶 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 2.83 | 0.696 | 19.8 | 0.246 | 7.00 | 28.5 |
| 单质硫 | 2.28 | 0.548 | 14.5 | 0.240 | 6.36 | 26.4 |
Table 2 The translocation factor of MeHg of rice plants in control and S(0) (100 mg·kg-1) treatments
| 处理 | 茎-根 | 叶-根 | 籽粒-根 | 叶-茎 | 籽粒-茎 | 籽粒-叶 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 2.83 | 0.696 | 19.8 | 0.246 | 7.00 | 28.5 |
| 单质硫 | 2.28 | 0.548 | 14.5 | 0.240 | 6.36 | 26.4 |
| [1] |
BUSCAROLI A, 2017. An overview of indexes to evaluate terrestrial plants for phytoremediation purposes (Review)[J]. Ecological Indicators, 82: 367-380.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN D D, LIU T X, LI X M, et al., 2018. Biological and chemical processes of microbially mediated nitrate-reducing Fe(II) oxidation by Pseudogulbenkiania sp. strain 2002[J]. Chemical Geology, 476(4): 59-69.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DRANGUET P, LE FAUCHEUR S, COSIO C, et al., 2017. Influence of chemical speciation and biofilm composition on mercury accumulation by freshwater biofilms[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 19(1): 38-49. |
| [4] |
FENG X B, LI P, QIU G L, et al., 2008b. Human exposure to methylmercury through rice intake in mercury mining areas, Guizhou province, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(1): 326-332.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FENG X B, QIU G L, 2008a. Mercury pollution in Guizhou, southwestern China-An overview[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 400(1-3): 227-237.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GAO H, WANG C, CHEN J, et al., 2022. Enhancement effects of decabromodiphenyl ether on microbial sulfate reduction in eutrophic lake sediments: A study on sulfate-reducing bacteria using dsrA and dsrB amplicon sequencing[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 843: 157073.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GILMOUR C C, PODAR M, BULLOCK A L, et al., 2013. Mercury methylation by novel microorganisms from new environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47: 11810-11820.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HORVAT M, NOLDE N, FAJON V, et al., 2003. Total mercury, methylmercury and selenium in mercury polluted areas in the province Guizhou, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 304(1-3): 231-256.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
HU Z Y, ZHU Y G, LI M, et al., 2007. Sulfur (S)-induced enhancement of iron plaque formation in the rhizosphere reduces arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings[J]. Environmental Pollution, 147(2): 387-393.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HUANG Y M, YI J C, LI X M, et al., 2024. Transcriptomics and physiological analyses reveal that sulfur alleviates mercury toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 135: 10-25.
DOI URL |
| [11] | KRONBERG R-M, SCHAEFER J K, BJÖRN E, et al., 2018. Mechanisms of methyl mercury net degradation in alder swamps: the role of methanogens and abiotic processes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 5(4): 220-225. |
| [12] |
LI Y Y, WANG Y J, ZHANG Q J, et al., 2019. Elemental sulfur amendment enhance methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in Hg mining polluted soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 379: 120701.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI Y Y, ZHAO J T, GUO J X, et al., 2017. Influence of sulfur on the accumulation of mercury in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) growing in mercury contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 182: 293-300.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIU M D, ZHANG Q R, CHENG M H, et al., 2019. Rice life cycle-based global mercury biotransport and human methylmercury exposure[J]. Nature Communications, 10(1): 5164.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
LIU Y R, YU R Q, ZHENG Y M, et al., 2014. Analysis of the microbial community structure by monitoring an Hg methylation gene (hgcA) in paddy soils along an Hg gradient[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(9): 2874-2879.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU Z X, XU Z Y, XU L F, et al., 2022. Modified biochar: Synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals[J]. Carbon Research, 1(1): 8.
DOI |
| [17] |
LUNDE C, ZYGADLO A, SIMONSEN H T, et al., 2008. Sulfur starvation in rice: the effect on photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and oxidative stress protective pathways[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 134(3): 508-521.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MAN Y, WANG B, WANG J X, et al., 2021. Use of biochar to reduce mercury accumulation in Oryza sativa L.: A trial for sustainable management of historically polluted farmlands[J]. Environment International, 153: 106527.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
MATTIELLO E M, DA SILVA R C, DEGRYSE F, et al., 2017. Sulfur and zinc availability from co-granulated Zn-enriched elemental sulfur fertilizers[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(6): 1108-1115.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
NAJAFI S, RAZAVI S M, KHOSHKAM M, et al., 2020. Effects of green synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles from Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks on physiological and biochemical factors of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)[J]. Physiology Molecular Biology of Plants, 26: 1055-1066.
DOI |
| [21] |
NATASHA, SHAHID M, KHALID S, et al., 2020. A critical review of mercury speciation, bioavailability, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant environment: Ecotoxicology and health risk assessment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 711: 134749.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ONTIVEROS-VALENCIA A, ZIV-EL M, ZHAO H P, et al., 2012. Interactions between nitrate-reducing and sulfate-reducing bacteria coexisting in a hydrogen-fed biofilm[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(20): 11289-11298.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
OREMLAND RONALD S, CULBERTSON CHARLES W, WINFREY MICHAEL R, 1991. Methylmercury decomposition in sediments and bacterial cultures: Involvement of methanogens and sulfate reducers in oxidative demethylation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57(1): 130-137.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
PANDEY S K, BHATTACHARYA T, CHAKRABORTY S, 2016. Metal phytoremediation potential of naturally growing plants on fly ash dumpsite of Patratu thermal power station, Jharkhand, India[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18(1): 87-93.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
PARKS JERRY M, JOHS A, PODAR M, et al., 2013. The genetic basis for bacterial mercury methylation[J]. Science, 339(6125): 1332-1335.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
QIU G L, FENG X B, LI P, et al., 2008. Methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at abandoned mercury mines in Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(7): 2465-2468.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ROTHENBERG S E, ANDERS M, AJAMI N J, et al., 2016. Water management impacts rice methylmercury and the soil microbiome[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 572: 608-617.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SHU R, WANG Y, ZHONG H, 2016. Biochar amendment reduced methylmercury accumulation in rice plants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 313: 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | SINGH S P, SCHWAN A L, 2011. 4.20-Sulfur metabolism in plants and related biotechnologies[M]. Comprehensive Biotechnology (Second Edition). Burlington: Academic Press: 257-271. |
| [30] |
STRICKMAN R J, MITCHELL C P J, 2017. Accumulation and translocation of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in Oryza sativa: An enriched isotope tracer study[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 574: 1415-1423.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
TANG Z Y, FAN F L, DENG S P, et al., 2020. Mercury in rice paddy fields and how does some agricultural activities affect the translocation and transformation of mercury-A critical review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 202: 110950.
DOI URL |
| [32] | USEPA, 1998. Method 1630, Methyl Mercury in Water by Distillation, Aqueous Ethylation, Purge and Trap, and CVAFS[S]. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency. |
| [33] |
WANG G X, HU Z Y, LI S Y, et al., 2020. Sulfur controlled cadmium dissolution in pore water of cadmium-contaminated soil as affected by DOC under waterlogging[J]. Chemosphere, 240: 124846.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
WANG J X, FENG X B, ANDERSON C W, et al., 2012. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites-A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, 221-222: 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YUAN H Y, LIU Q Q, GUO Z, et al., 2021. Sulfur nanoparticles improved plant growth and reduced mercury toxicity via mitigating the oxidative stress in Brassica napus L[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 318(1): 128589.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG H, FENG X B, LARSSEN T, et al., 2010. In inland China, rice, rather than fish, is the major pathway for methylmercury exposure[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 118(9): 1183-1188.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
ZHANG Y F, WANG X Q, YANG Y, et al., 2023. Retention and transformation of exogenous Hg in acidic paddy soil under alternating anoxic and oxic conditions: Kinetic and mechanistic insights[J]. Environmental Pollution, 323: 121335.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHAO C C, DEGRYSE F, GUPTA V, et al., 2015b. Elemental sulfur oxidation in Australian cropping soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 79(1): 89-96.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHAO F J, MA Y B, ZHU Y G, et al., 2015a. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(2): 750-759.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHAO L, MENG B, FENG X, 2020. Mercury methylation in rice paddy and accumulation in rice plant: A review[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 195: 110462.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZHOU X Q, HAO Y Y, GU B H, et al., 2020. Microbial communities associated with methylmercury degradation in paddy soils[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(13): 7952-7960.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHU D W, ZHONG H, ZENG Q L, et al., 2015. Prediction of methylmercury accumulation in rice grains by chemical extraction methods[J]. Environmental Pollution, 199: 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LI Chuanfu, ZHU Taochuan, MING Yufei, YANG Yuxuan, GAO Shu, DONG Zhi, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Shuying. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Desulphurized Gypsum on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon and Its Fractions Contents in the Saline-alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [2] | YANG Kai, YANG Jingrui, CAO Peipei, LÜ Chunhua, SUN Wenjuan, YU Lingfei, DENG Xi. Dynamic Response of Rice Plant Height, Tillering and SPAD under Elevated CO2 Concentration and Their Simulation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [3] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [4] | TANG Haiming, SHI Lihong, WEN Li, CHENG Kaikai, LI Chao, LONG Zedong, XIAO Zhiwu, LI Weiyan, GUO Yong. Effects of Different Long-term Fertilizer Managements on Rhizosphere Soil Nitrogen in the Double-cropping Rice Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [5] | XU Min, XU Chao, YU Guanghui, YIN Lichu, ZHANG Quan, ZHU Hanhua, ZHU Qihong, ZHANG Yangzhu, HUANG Daoyou. Effects of Groundwater Level and Long-term Straw Return on Soil Cadmium Availability and Cadmium Concentration in Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [6] | WANG Zhao, ZHANG Manyin, HU Yukun, LIU Weiwei, ZHANG Miaomiao. Effect of Salinity on Mercury Methylation in Sediments of A Typical Coastal Wetland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [7] | LI Xiaohui, AI Xianbin, LI Liang, WANG Xiyang, XIN Zaijun, SUN Xiaoyan. Study on Passivation Effects of New Modified Rice Husk Biochar Materials on Cadmium Contaminated Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [8] | DENG Tianle, XIE Liyong, ZHANG Fengzhe, ZHAO Hongliang, JIANG Yutong. Competition for Growth Space between Barnyard Grass and Rice under Elevated Atmospheric CO2 Concentration [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1566-1572. |
| [9] | JIANG Chaoqiang, LI Chen, ZHU Qifa, XU Haiqing, LIU Yanhong, SHEN Jia, YAN Yifeng, YU Fei, ZU Chaolong. Evaluation of Carbon Sink and Economic Benefit in Different Planting Patterns in Southern Anhui [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1285-1292. |
| [10] | LI Chengwei, LIU Zhangyong, GONG Songling, YANG Wei, LI Shaoqiu, ZHU Bo. Effects of Changing Rice Cropping Patterns on CH4 and N2O Emissions from Paddy Fields [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 961-968. |
| [11] | LI Jiayi, SUN Weimin, SUN Xiaoxu, KONG Tianle, LI Baoqin, LIU Zhenhong, GAO pin. Isolation, Identification and Functional Verification of Sulfur-oxidizing Microorganisms in Mine Tailing [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 785-792. |
| [12] | XU Meihua, GU Minghua, WANG Chengzhen, LEI Jing, WEI Yanyan, SHEN Fangke. Effect of Manganese on Arsenic Speciation in Soil and Arsenic Migration to Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 802-813. |
| [13] | ZENG Min, CHEN Jia, LI Exian, YIN Fuyou, WANG Linxian, ZENG Liqiong, GUO Rong. Distribution Characteristics and Dynamic Changes of Cadmium Content in the Introgression Lines of Yuanjiang Common Wild Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [14] | SHI Hanzhi, JIANG Qi, LIU Fan, WEN Dian, HUANG Yongdong, DENG Tenghaobo, WANG Xu, XU Aiping, LI Furong, WU Zhichao, LI Meixia, PENG Jinfen, DU Ruiying. Effects of Returning Rice Stubble to Field on Cadmium Accumulation in Soil and Rice [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [15] | SHANG GUAN Yuxian, YIN Hongliang, XU Yi, ZHONG Hongmei, HE Mingjiang, QIN Yusheng, GUO Song, YU Hua. Effects of Different Passivators on Cadmium Absorption in Rice and Wheat Grains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
