Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 239-247.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Hu1( ), WANG Peiyao1, LI Xiaowei1, WANG Jifei2, YANG Junlong1,*(
), WANG Peiyao1, LI Xiaowei1, WANG Jifei2, YANG Junlong1,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-04
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
Contact:
YANG Junlong
杨虎1( ), 王佩瑶1, 李小伟1, 王继飞2, 杨君珑1,*(
), 王佩瑶1, 李小伟1, 王继飞2, 杨君珑1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
杨君珑
作者简介:杨虎(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤微生物。E-mail: 1986340981@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YANG Hu, WANG Peiyao, LI Xiaowei, WANG Jifei, YANG Junlong. Distribution of Soil Fungal Diversity and Community Structure in Different Vegetation Types on the Eastern Slopes of Helan Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 239-247.
杨虎, 王佩瑶, 李小伟, 王继飞, 杨君珑. 贺兰山东坡不同植被类型的土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 239-247.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.004
| 样地名称 Sample plot | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 土壤类型 Soil type | 优势植物种类 Dominant plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山地荒漠草地 Mountain desert grassland | 38°35'36"‒ 38°52'3″N | 105°54'22″‒ 106°12'6″E | 1110.6‒ 1878.04 | 灰钙土, 粗骨土 | 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus, 细枝补血草 Limonium tenellum, 猪毛蒿 Artemisia scoparia, 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora, 冬青叶兔唇花 Lagochilus ilicifolius |
| 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 38°35'23″‒ 38°56'0.6"N | 105°55'35"‒ 106°10'40″E | 1263.41‒ 1948.41 | 栗钙土, 粗骨土 | 旱榆 Ulmus glaucescens, 小叶金露梅 Potentilla parvifolia, 蒙古扁桃 Amygdalus mongolica, 黄刺玫 Rosa xanthina, 刺旋花 Convolvulus tragacanthoides, 针枝芸香 Haplophyllum tragacanthoides, 绣线菊 Spiraea salicifolia, 紫丁香 Syringa oblata, 置疑小檗 Berberis dubia, 西北栒子 Cotoneaster zabelii, 甘蒙锦鸡儿 Caragana opulens, 荒漠锦鸡儿 Caragana roborovskyi, 小叶鼠李 Rhamnus parvifolia |
| 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 38°35'4.9"‒ 38°56'1.7"N | 105°52'56.6″‒ 106°11'3.1″E | 2206‒ 2697.09 | 灰褐土 | 青海云杉 Picea crassifolia, 杜松 Juniperus rigida |
| 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow | 38°34'59″‒ 38°46'28″N | 105°52′28″‒ 105°53′56″E | 2504.42‒ 2927.88 | 亚高山 草甸土 | 扁穗冰草 Agropyron cristatum, 甘肃蒿 Artemisia gansuensis, 贝加尔针茅 Stipa Baicalensis, 西山委陵菜 Potentilla sischanensis, 阿拉善鹅观草 Roegneria alashanica, 小红菊 Chrysanthemum chanetii, 赖草 Leymus secalinus, 高山苔草 Carex tristachya |
Table 1 Basic overview table of plots of different vegetation types
| 样地名称 Sample plot | 纬度 Latitude | 经度 Longitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 土壤类型 Soil type | 优势植物种类 Dominant plant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山地荒漠草地 Mountain desert grassland | 38°35'36"‒ 38°52'3″N | 105°54'22″‒ 106°12'6″E | 1110.6‒ 1878.04 | 灰钙土, 粗骨土 | 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus, 细枝补血草 Limonium tenellum, 猪毛蒿 Artemisia scoparia, 短花针茅 Stipa breviflora, 冬青叶兔唇花 Lagochilus ilicifolius |
| 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 38°35'23″‒ 38°56'0.6"N | 105°55'35"‒ 106°10'40″E | 1263.41‒ 1948.41 | 栗钙土, 粗骨土 | 旱榆 Ulmus glaucescens, 小叶金露梅 Potentilla parvifolia, 蒙古扁桃 Amygdalus mongolica, 黄刺玫 Rosa xanthina, 刺旋花 Convolvulus tragacanthoides, 针枝芸香 Haplophyllum tragacanthoides, 绣线菊 Spiraea salicifolia, 紫丁香 Syringa oblata, 置疑小檗 Berberis dubia, 西北栒子 Cotoneaster zabelii, 甘蒙锦鸡儿 Caragana opulens, 荒漠锦鸡儿 Caragana roborovskyi, 小叶鼠李 Rhamnus parvifolia |
| 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 38°35'4.9"‒ 38°56'1.7"N | 105°52'56.6″‒ 106°11'3.1″E | 2206‒ 2697.09 | 灰褐土 | 青海云杉 Picea crassifolia, 杜松 Juniperus rigida |
| 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow | 38°34'59″‒ 38°46'28″N | 105°52′28″‒ 105°53′56″E | 2504.42‒ 2927.88 | 亚高山 草甸土 | 扁穗冰草 Agropyron cristatum, 甘肃蒿 Artemisia gansuensis, 贝加尔针茅 Stipa Baicalensis, 西山委陵菜 Potentilla sischanensis, 阿拉善鹅观草 Roegneria alashanica, 小红菊 Chrysanthemum chanetii, 赖草 Leymus secalinus, 高山苔草 Carex tristachya |
| 土壤理化性质和环境因子 Soil physical and chemical properties and environmental factors | 山地荒漠草地 Mountane desert grassland | 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.49±0.28a | 8.10±0.06bc | 7.89±0.12c | 8.18±0.38b |
| 水分质量分数 w(MC)/% | 2.31±1.20d | 8.09±0.82c | 11.07±1.66b | 14.37±3.49a |
| 全氮质量分数 w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.34±0.14a | 0.29±0.07a | 0.29±0.16a | 0.26±0.06a |
| 全磷质量分数 w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.76±0.21a | 0.81±0.52a | 0.97±0.63a | 0.82±0.29a |
| 土壤有机质质量分数 w(SOC)/(g∙kg-1) | 11.22±7.63b | 47.72±60.73ab | 89.73±69.18a | 56.62±49.40ab |
| 海拔 ALT/m | 1415.90±296.40b | 1503.41±296.16b | 2450.88±162.10a | 2644.76±171.58a |
| 年均降雨量MAP/mm | 203.11±28.79c | 208.78±20.87c | 239.56±41.29b | 271.11±12.90a |
| 太阳辐射SRAD/(kJ∙m-2∙d-1) | 16686.79±239.21a | 16671.00±204.54a | 16478.23±356.09a | 16207.64±99.53b |
| 年均温 MAT/℃ | 7.37±1.45a | 6.59±1.65a | 4.11±2.18b | 2.15±0.25c |
| 坡向 ASP/(°) | 127.63±48.82a | 116.31±100.87a | 129.30±133.13a | 70.98±14.75a |
| 坡度 SLOP/(°) 植物多样性指数W 植物丰富度指数R | 11.34±13.99b 1.47±0.47b 1.42±0.47b | 17.89±9.94ab 2.03±0.41a 2.47±0.93a | 21.42±7.52ab 0.42±0.05c 0.26±0.02c | 21.89±3.59a 1.30±0.40b 1.13±0.42b |
Table 2 Soil physical and chemical properties and environmental factors of different vegetation types
| 土壤理化性质和环境因子 Soil physical and chemical properties and environmental factors | 山地荒漠草地 Mountane desert grassland | 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.49±0.28a | 8.10±0.06bc | 7.89±0.12c | 8.18±0.38b |
| 水分质量分数 w(MC)/% | 2.31±1.20d | 8.09±0.82c | 11.07±1.66b | 14.37±3.49a |
| 全氮质量分数 w(TN)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.34±0.14a | 0.29±0.07a | 0.29±0.16a | 0.26±0.06a |
| 全磷质量分数 w(TP)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.76±0.21a | 0.81±0.52a | 0.97±0.63a | 0.82±0.29a |
| 土壤有机质质量分数 w(SOC)/(g∙kg-1) | 11.22±7.63b | 47.72±60.73ab | 89.73±69.18a | 56.62±49.40ab |
| 海拔 ALT/m | 1415.90±296.40b | 1503.41±296.16b | 2450.88±162.10a | 2644.76±171.58a |
| 年均降雨量MAP/mm | 203.11±28.79c | 208.78±20.87c | 239.56±41.29b | 271.11±12.90a |
| 太阳辐射SRAD/(kJ∙m-2∙d-1) | 16686.79±239.21a | 16671.00±204.54a | 16478.23±356.09a | 16207.64±99.53b |
| 年均温 MAT/℃ | 7.37±1.45a | 6.59±1.65a | 4.11±2.18b | 2.15±0.25c |
| 坡向 ASP/(°) | 127.63±48.82a | 116.31±100.87a | 129.30±133.13a | 70.98±14.75a |
| 坡度 SLOP/(°) 植物多样性指数W 植物丰富度指数R | 11.34±13.99b 1.47±0.47b 1.42±0.47b | 17.89±9.94ab 2.03±0.41a 2.47±0.93a | 21.42±7.52ab 0.42±0.05c 0.26±0.02c | 21.89±3.59a 1.30±0.40b 1.13±0.42b |
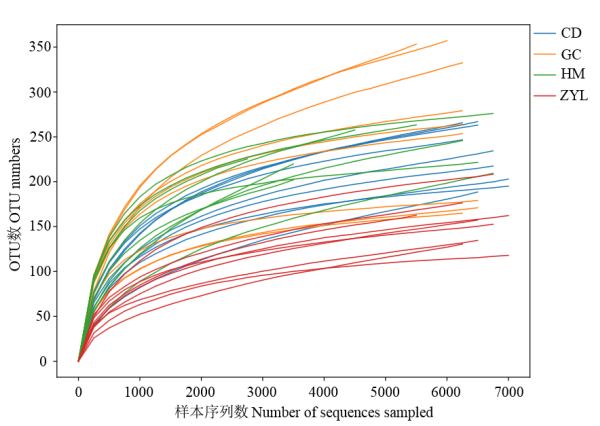
Figure 2 Rarefaction Curve CD: Subalpine meadow; GC: Shallow mountain shrub; HM: Mountane desert grassland; ZYL: Subalpine coniferous forest. The same below
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | OTU数 OTU number | Ace指数 Ace index | Chao1指数 Chao1index | 香浓指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山地荒漠草地 Mountane desert grassland | 237.33±23.75a | 283.04±46.92a | 276.54±32.39a | 5.84±0.99ab | 0.94±0.07a |
| 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 262.11±73.09a | 296.65±101.08a | 298.98±104.08a | 6.23±0.51a | 0.97±0.01a |
| 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 156.22±25.36b | 187.39±26.40b | 182.95±26.71b | 4.43±0.44c | 0.88±0.04b |
| 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow | 231.89±29.61a | 269.89±36.06a | 268.98±35.05a | 5.47±0.57b | 0.93±0.03a |
Table 3 Soil fungi OTU number and α-diversity index of different vegetation types
| 植被类型 Vegetation type | OTU数 OTU number | Ace指数 Ace index | Chao1指数 Chao1index | 香浓指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山地荒漠草地 Mountane desert grassland | 237.33±23.75a | 283.04±46.92a | 276.54±32.39a | 5.84±0.99ab | 0.94±0.07a |
| 浅山灌丛 Shallow mountain shrub | 262.11±73.09a | 296.65±101.08a | 298.98±104.08a | 6.23±0.51a | 0.97±0.01a |
| 亚高山针叶林 Subalpine coniferous forest | 156.22±25.36b | 187.39±26.40b | 182.95±26.71b | 4.43±0.44c | 0.88±0.04b |
| 亚高山草甸 Subalpine meadow | 231.89±29.61a | 269.89±36.06a | 268.98±35.05a | 5.47±0.57b | 0.93±0.03a |
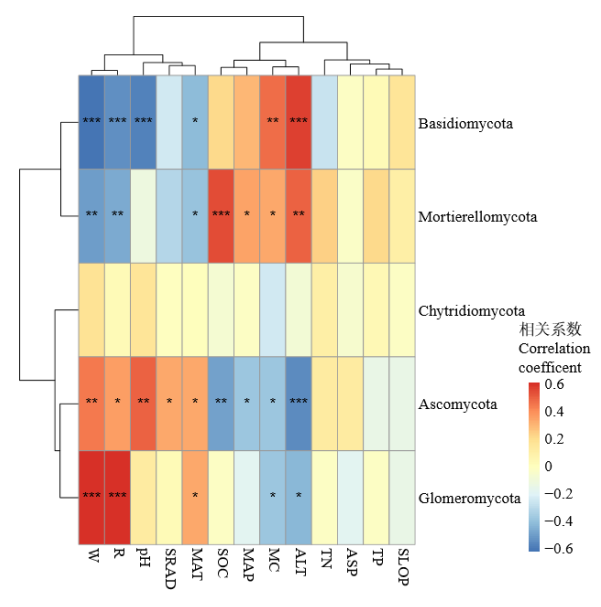
Figure 5 Heat map of the correlation between soil fungal communities and environmental factors at the phylum classification level *P<0.05; **P<0.01***; P<0.001
| [1] |
ADÉLIA V, CELSO M, OSCAR N, et al., 2015. Understanding fungal functional biodiversity during the mitigation of environmentally dispersed pentachlorophenol in cork oak forest soils[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 17(8): 2922-2934.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BEIMFORDE C, FELDBERG K, NYLINDER S, et al., 2014. Estimating the phanerozoic history of the Ascomycota lineages: Combining fossil and molecular data[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 78(5): 386-398.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BELLEMAIN E, CARLSEN T, BROCHMANN C, et al., 2010. ITS as an environmental DNA barcode for fungi: An in silico approach reveals potential PCR biases[J]. BioMed Central, 10(1): 189. |
| [4] |
BOSSUYT H, DENEF K, SIX J, et al., 2001. Influence of microbial populations and residue quality on aggregate stability[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 16(3): 195-208.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
COROI M, SKEFFINGTON M S, GILLER P, et al., 2004. Vegetation diversity and stand structure in streamside forests in the south of Ireland[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 202(1): 39-57.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
COX F, BARSOUM N, LILLESKOV E A, et al., 2010. Nitrogen availability is a primary determinant of conifer mycorrhizas across complex environmental gradients[J]. Ecology Letters, 13(9): 1103-1113.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CUI Y X, BING H J, FANG L C, et al., 2019. Diversity patterns of the rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial communities along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine ecosystem of the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geoderma, 338(5): 118-127.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ELIZABETH A G, HEIDI H K, SEAN C, et al., 2009. Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome[J]. Science (New York, N.Y.), 324(5931): 1190-1192.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FREY S D, KNORR M, PARRENT J L, et al., 2004. Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 196(1): 159-171.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HU H, BORJIGIN S, CHENG Y X, et al., 2014. Effect of abandonment on diversity and abundance of free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria and total bacteria in the cropland soils of Hulun Buir, Inner Mongolia[J]. PLOS ONE, 9(9): e106714.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HU H, CHEN X J, HOU F J, et al., 2017. Bacterial and fungal community structures in loess plateau grasslands with different grazing intensities[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00606.
DOI |
| [12] |
LIU J J, SUI Y Y, YU Z H, et al., 2015. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of Northeast China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 83(5): 29-39.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MA L N, HUANG W W, GUO C Y, et al., 2012. Soil microbial properties and plant growth responses to carbon and water addition in a temperate steppe: the importance of nutrient availability[J]. PLOS ONE, 7(4): e35165.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MENG H, LI K, NIE M, et al., 2013. Responses of bacterial and fungal communities to an elevation gradient in a subtropical montane forest of China[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(5): 2219-2230.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
NI Y Y, YANG T, ZHANG K P, et al., 2018. Fungal communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in an alpine tundra are determined by soil carbon nitrogen ratios[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9(5): 1815.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ROY M, ROCHET J, MANZI S, et al., 2013. What determines Alnus-associated ectomycorrhizal community diversity and specificity? A comparison of host and habitat effects at a regional scale[J]. New Phytologist, 198(4): 1228-1238.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SHENG Y Y, CONG W, YANG L S, et al., 2019. Forest soil fungal community elevational distribution pattern and their ecological assembly processes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10(5): 2226.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TEDERSOO L, BAHRAM M, PÕLME S, et al., 2014. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi[J]. Science (New York, N.Y.), 346(6213): 1256688.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TRIPATHI B M, KIM M, SINGH D, et al., 2012. Tropical soil bacterial communities in Malaysia: pH dominates in the equatorial tropics too[J]. Microbial Ecology, 64(2): 474-484.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J T, ZHENG Y M, HU H W, et al., 2015. Soil pH determines the alpha diversity but not beta diversity of soil fungal community along altitude in a typical Tibetan forest ecosystem[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15(5): 1224-1232.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YANG Y, DOU Y X, HUANG Y M, et al., 2017. Links between soil fungal diversity and plant and soil properties on the Loess Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02198.
DOI |
| [22] |
ZAK D R, HOLMES W E, WHITE D C, et al., 2003. Plant diversity, soil microbial communities, and ecosystem function: Are there anylinks?[J]. Ecology, 84(8): 2042-2050.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. The 3rd edition. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. | |
| [24] | 柴永福, 岳明, 2016. 植物群落构建机制研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 36(15): 4557-4572. |
| CHAI Y F, YUE M, 2016. Research advances in plant community assembly mechanisms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(15): 4557-4572. | |
| [25] | 陈秀波, 朱德全, 赵晨晨, 等, 2019. 不同林型红松林土壤真菌群落组成和多样性[J]. 土壤学报, 56(5): 1221-1234. |
| CHEN X B, ZHU D Q, ZHAO C C, et al., 2019. Community composition and diversity of fungi in soils under different types of Pinus koraiensis forests[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(5): 1221-1234. | |
| [26] | 谷晓楠, 贺红士, 陶岩, 等, 2017. 长白山土壤微生物群落结构及酶活性随海拔的分布特征与影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 37(24): 8374-8384. |
| GU X N, HE H S, TAO Y, et al., 2017. Soil microbial community structure, enzyme activities, and their influencing factors along different altitudes of Changbai Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(24): 8374-8384. | |
| [27] | 刘秉儒, 2010. 贺兰山东坡典型植物群落土壤微生物量碳、氮沿海拔梯度的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 19(4): 883-888. |
| LIU B R, 2010. Changes in soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen under typical plant communies along an altitudinal gradient in east side of Helan Mountain[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19(4): 883-888. | |
| [28] | 刘秉儒, 杨阳, 陈林, 2014. 宁夏荒漠草原4种典型植物群落土壤活性有机碳垂直分布特征[J]. 草地学报, 22(5): 986-990. |
| LIU B R, YANG Y, CHEN L, 2014. Distribution characteristics of soil labile organic carbon of four typical plant communities in desert steppe of Ningxia[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 22(5): 986-990. | |
| [29] | 刘秉儒, 张秀珍, 胡天华, 等, 2013. 贺兰山不同海拔典型植被带土壤微生物多样性[J]. 生态学报, 33(22): 7211-7220. |
|
LIU B R, ZHANG X Z, HU T H, et al., 2013. Soil microbial diversity under typical vegetation zones along an elevation gradient in Helan Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(22): 7211-7220.
DOI URL |
|
| [30] | 李聪, 陆梅, 任玉连, 等, 2020. 文山典型亚热带森林土壤氮组分的海拔分布及其影响因子[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 42(12): 63-73. |
| LI C, LU M, REN Y L, et al., 2020. Distribution of soil nitrogen components of Wenshan typical subtropical forests along an altitude gradient and its influencing factors in Yunnan Province of southwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 42(12): 63-73. | |
| [31] | 刘国华, 叶正芳, 吴为中, 2012. 土壤微生物群落多样性解析法: 从培养到非培养[J]. 生态学报, 32(14): 4421-4433. |
|
LIU G H, YE Z F, WU W Z, 2012. Culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches to studying soil microbial diversity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(14): 4421-4433.
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 刘淑霞, 周平, 赵兰坡, 等, 2008. 吉林黑土区玉米田土壤真菌的多样性[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 4(7): 42-46. |
| LIU S X, ZHOU P, ZHAO L B, et al., 2008. Diversity of soil fungi in black soil planted with corn in Jilin province[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 4(7): 42-46. | |
| [33] | 楼骏, 柳勇, 李延, 2014. 高通量测序技术在土壤微生物多样性研究中的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 30(15): 256-260. |
| LOU J, LIU Y, LI Y, 2014. Review of high-throughput sequencing techniques in studies of soil microbial diversity[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 30(15): 256-260. | |
| [34] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 暴家兵, 等, 2020. 五台山亚高山土壤真菌海拔分布格局与构建机制[J]. 生态学报, 40(19): 7009-7017. |
| LUO Z M, LIU J X, BAO J B, et al., 2020. E levational distribution patterns and assembly mechanisms of soil fungal community in Mount Wutai, Shanxi, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(19): 7009-7017. | |
| [35] | 乔沙沙, 周永娜, 柴宝峰, 等, 2017. 关帝山森林土壤真菌群落结构与遗传多样性特征[J]. 环境科学, 38(6): 2502-2512. |
| QIAO S S, ZHOU Y N, CHAI B F, et al., 2017. Characteristics of fungi community structure and genetic diversity of forests in Guandi mountains[J]. Environmental Science, 38(6): 2502-2512. | |
| [36] | 桑昌鹏, 万晓华, 余再鹏, 等, 2017. 凋落物和根系去除对滨海沙地土壤微生物群落组成和功能的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(4): 1184-1196. |
| SANG C P, WAN X H, YU Z P, et al., 2017. Effects of litter and root exclusion on soil microbial community composition and function of four plantations in subtropical sandy coastal plain area, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(4): 1184-1196. | |
| [37] | 孙倩, 吴宏亮, 陈阜, 等, 2019. 宁夏中部干旱带不同作物根际土壤真菌群落多样性及群落结构[J]. 微生物学通报, 46(11): 2963-2972. |
| SUN Q, WU H L, CHEN F, et al., 2019. Fungal community diversity and structure in rhizosphere soil of different crops in the arid zone of central Ningxia[J]. Microbiology China, 46(11): 2963-2972. | |
| [38] | 盛玉钰, 丛静, 卢慧, 等, 2018. 神农架国家公园林线过渡带土壤真菌多样性[J]. 生态学报, 38(15):5322-5330. |
| SHENG Y Y, CONG J, LU H, et al., 2018. Soil fungal diversity of the timberline ecotone in Shennongjia National Park[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(15): 5322-5330. | |
| [39] | 王诗慧, 常顺利, 李鑫, 等, 2021. 天山林区土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态学报, 41(1): 124-134. |
| WANG S H, CHANG S L, LI X, et al., Soil fungal diversity and its community structure in Tianshan Forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(1): 124-134. | |
| [40] | 袁仁文, 刘琳, 张蕊, 等, 2020. 植物根际分泌物与土壤微生物互作关系的机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(2): 26-35. |
| YUAN R W, LIU L, ZHANG R, et al., 2020. The interaction mechanism between plant rhizosphere secretion and soil microbe: A review[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 36(2): 26-35. | |
| [41] | 张树萌, 黄懿梅, 倪银霞, 等, 2018. 宁南山区人工林草对土壤真菌群落的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(4): 1449-1458. |
| ZHANG S M, HUANG Y M, NI Y X, et al., 2018. Effects of artificial forest and grass on soil fungal community at southern Ningxia mountain[J]. China Environmental Science, 38(4): 1449-1458. | |
| [42] | 周煜杰, 贾夏, 赵永华, 等, 2021. 秦岭火地塘真菌群落海拔分布格局[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(7): 2589-2596. |
| ZHOU Y J, JIA X, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2021. Altitude distribution of fungal community in Huoditang in Qinling Mountains, Northwest, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(7): 2589-2596. |
| [1] | HOU Hui, YAN Peixuan, XIE Qinmi, ZHAO Hongliang, PANG Danbo, CHEN Lin, LI Xuebin, HU Yang, LIANG Yongliang, NI Xilu. Characterization of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community Diversity in the Rhizosphere Soils of Prunus mongolica Scrub of Helan Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [2] | ZHANG Lijin, DU Hu, ZENG Fuping, HUANG Guoqin, SONG Min, SONG Tongqing. Discussion on the Relationship between Productivity and Diversity during Vegetation Restoration in the Karst Peak-cluster Depression [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [3] | MA Huiying, LI Xinzhu, MA Xinyu, GONG Lu. Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Fractions under Different Vegetation Types of the mid-Northern Piedmont of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [4] | ZHU Yihao, LI Qingmei, LIU Xiaoli, LI Na, SONG Fengling, CHEN Weifeng. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community in Newly Cultivated Land under Different Land Consolidation Types [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 909-917. |
| [5] | WANG Yingcheng, YAO Shiting, JIN Xin, YU Wenzhen, LU Guangxin, WANG Junbang. Comparative Study on Soil Bacterial Diversity of Degraded Alpine Meadow in the Sanjiangyuan Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [6] | LIU Hongmei, HAI Xiang, AN Kerui, ZHANG Haifang, WANH Hui, ZHANG Yanjun, WANG Lili, ZHANG Guilong, YANG Dianlin. Effects of Different Fertilization Regimes on Community Structure Diversity of CO2-assimilating Bacteria in Maize Field of Fluvo-aquic Soil in North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 715-722. |
| [7] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [8] | SONG Xiuli, HUANG Ruilong, KE Caijie, HUANG Wei, ZHANG Wu, TAO Bo. Effects of Different Cropping Systems on Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity in Continuous Cropping Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 487-496. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiaoli, WANG Guoli, CHANG Fangdi, ZHANG Hongyuan, PANG Huancheng, ZHANG Jianli, WANG Jing, JI Hongjie, LI Yuyi. Effects of Microbial Agents on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Flora of Rhizosphere Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [10] | SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830. |
| [11] | JIA Chenbo, GUO Yang, MA Chenglian, SU Jianyu, XU Chunyan. Difference on Soil Microbial Community and Function of Healthy and Diseased Plants of Lycium barbarum Ningqi-1 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1831-1841. |
| [12] | YAO Shiting, LU Guangxin, DENG Ye, DANG Ning, WANG Yingcheng, ZHANG Haijuan, YAN Huilin. Effects of Simulated Warming on Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [13] | HAN Fang, BAO Yuanyuan, LIU Xiangyu, ZHANG Xinyong, WEI Denghui, ZHANG Haoran, TIAN Qinglong. Effects of Different Potato Rotation Patterns on Fungal Community Structure in Rhizosphere Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1412-1419. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
