生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1901-1908.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.021
李晓晖1( ), 艾仙斌2,*(
), 艾仙斌2,*( ), 李亮1, 王玺洋1, 辛在军1, 孙小艳1
), 李亮1, 王玺洋1, 辛在军1, 孙小艳1
收稿日期:2022-03-29
出版日期:2022-09-18
发布日期:2022-11-07
通讯作者:
*艾仙斌,副研究员,博士,主要从事固废资源化利用。E-mail: axbjxas@163.com作者简介:李晓晖(1985年生),女,副研究员,博士,主要从事环境污染控制研究。E-mail: lixiaohui211121@163.com
基金资助:
LI Xiaohui1( ), AI Xianbin2,*(
), AI Xianbin2,*( ), LI Liang1, WANG Xiyang1, XIN Zaijun1, SUN Xiaoyan1
), LI Liang1, WANG Xiyang1, XIN Zaijun1, SUN Xiaoyan1
Received:2022-03-29
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
摘要:
中国耕地镉污染问题严峻,重金属钝化技术日益受到广泛关注,该技术的关键在于所施用钝化剂的钝化性能。为寻求高效镉污染土壤钝化剂,以稻壳生物炭为基体,采用磷酸化-钙盐复合改性手段制备新型复合稻壳生物炭材料用于镉污染土壤的钝化修复。采用SEM-EDS、FTIR表征材料形貌和表面功能基团,采用盆栽试验研究材料对镉污染土壤的钝化效果及小白菜镉积累的影响。结果表明,复合磷酸化稻壳生物炭(TFQ)材料表面存在大量磷酸根和-OH,大量镉吸附于TFQ材料表面上。与空白对照、稻壳生物炭(DT)和磷酸化稻壳生物炭(DTY)处理相比,TFQ对土壤镉的钝化效果最佳,TFQ处理中土壤镉形态分布规律为铁锰氧化物结合态>残渣态≈可交换态>有机结合态>碳酸盐结合态。与空白对照相比,TFQ处理后土壤中可交换态镉大幅向铁锰氧化物结合态转变,约94%土壤镉以铁锰氧化物结合态存在,残渣态比例较其他处理提高,约占2.3%,明显增强了土壤镉化学稳定性。TFQ显著提高了土壤pH值、电导率和土壤阳离子交换量,促进了小白菜生长,并显著降低小白菜叶片中镉含量。综上所述,TFQ对增强土壤镉稳定性和降低小白菜叶片镉含量具有良好效果。
中图分类号:
李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908.
LI Xiaohui, AI Xianbin, LI Liang, WANG Xiyang, XIN Zaijun, SUN Xiaoyan. Study on Passivation Effects of New Modified Rice Husk Biochar Materials on Cadmium Contaminated Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908.
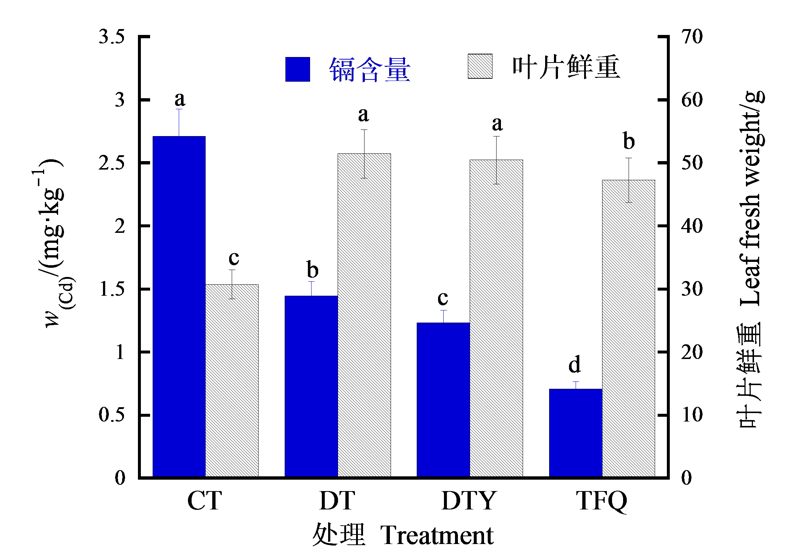
图4 DT、DTY和TFQ对小白菜生长情况及镉积累影响 直方柱上方英文小写字母不同表示处理间镉含量和叶片鲜重差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 4 Effects of DT, DTY and TFQ on growth and cadmium accumulation of Chinese cabbage Different small letters above the square column indicate significant differences in cadmium content and leaf fresh weight between treatments (P<0.05)

图6 DT、DTY和TFQ对土壤阳离子交换量影响 直方柱上方英文小写字母不同表示处理间阳离子交换量差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 6 Effect of DT, DTY and TFQ on soil cation exchange capacity Different small letters above the square column indicate significant differences in cation exchange capacity between treatments (P<0.05)
| [1] | BEATRICE A, VARCO J J, DYGERT A, et al., 2022. Lead immobilization in simulated polluted soil by Douglas fir biochar-supported phosphate[J]. Chemosphere, 292: 133355. |
| [2] | BIAN F Y, ZHONG Z K, ZHANG X P, et al., 2020. Bamboo - An untapped plant resource for the phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 246: 125750. |
| [3] |
BIAN R J, CHEN D, LIU X Y, et al., 2013. Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: Results from a cross-site field experiment[J]. Ecological Engineering, 58: 378-383.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CHEN C, ZHANG X M, CHEN J A, et al., 2020. Assessment of site contaminated soil remediation based on an input output life cycle assessment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 263(1): 121422. |
| [5] |
CUI L Q, PAN G X, LI L Q, et al., 2016. Continuous immobilization of cadmium and lead in biochar amended contaminated paddy soil: A five-year field experiment[J]. Ecological Engineering, 93: 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DAI H P, WEI S H, TWARDOWSKA I, et al., 2017. Hyperaccumulating potential of Bidens pilosa L. for Cd and elucidation of its translocation behavior based on cell membrane permeability[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(29): 23161-23167.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DING K B, WU Q, WEI H, et al., 2016. Ecosystem services provided by heavy metal-contaminated soils in China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18(2): 380-390.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GONG Y Y, ZHAO D Y, WANG Q L, 2018. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade[J]. Water Research, 147: 440-460.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | HAMILTON J G, GROSSKLEG J, HILGER D, et al., 2019. In situ transformations of bonechar and tri-poly phosphate amendments in phosphorus-limited subsurface soils[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 109(1): 104398. |
| [10] | JIANG J, XU R K, JIANG T Y, et al., 2012. Immobilization of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) by the addition of rice straw derived biochar to a simulated polluted Ultisol[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 229-230: 145-150. |
| [11] |
KIZITO S, LUO H Z, LU J X, et al., 2019. Role of nutrient-enriched biochar as a soil amendment during maize growth: Exploring practical alternatives to recycle agricultural residuals and to reduce chemical fertilizer demand[J]. Sustainability, 11(11): 3211-3233.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI H Y, YE X X, GENG Z G, et al., 2016. The influence of biochar type on long-term stabilization for Cd and Cu in contaminated paddy soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 304: 40-48.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | LIANG Y H, LIU C H, LIAO S H, et al., 2012. Cosynthesis of cargo-loaded hydroxyapatite/alginatc core-shell nanoparticles (HAP@Alg) as pH-responsive nanovehicles by a pre-gel method[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4(12): 6720-6727. |
| [14] |
LIANG Y, CAO X D, ZHAO L, et al., 2014. Biochar- and phosphate-induced immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soil and water: Implication on simultaneous remediation of contaminated soil and groundwater[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(6): 4665-4674.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LU K, YANG X, GIELEN G, et al., 2017. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 186(Part 2): 285-292.
DOI URL |
| [16] | MEDHA I, CHANDRA S, RAJA V K, et al., 2021. (3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane and iron rice straw biochar composites for the sorption of Cr (VI) and Zn (II) using the extract of heavymetals contaminated soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 771: 144764. |
| [17] |
MO X X, SIEBECKER M G, GOU W X, et al., 2021. A review of cadmium sorption mechanisms on soil mineral surfaces revealed from synchrotron-based X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy: Implications for soil remediation[J]. Pedosphere, 31(1): 11-27.
DOI URL |
| [18] | O'CONNOR D, PENG T Y, ZHANG J L, et al., 2018. Biochar application for the remediation of heavy metal polluted land: A review of in situ field trials[J]. Science of the Total Environment, (619-620): 815-826. |
| [19] | PALANSOORIYA K N, SHAHEEN S M, CHEN S S, et al., 2020. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review[J]. Environment International, 134(1): 105046. |
| [20] |
PALANSOORIYA K N, WONG J T F, HASHIMOTO Y, et al., 2019. Response of microbial communities to biochar amended soils: A critical review[J]. Biochar, 1(1): 3-22.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
QAYYUM M F, REHMAN M Z, ALI S, et al., 2017. Residual effects of monoammonium phosphate, gypsum and elemental sulfur on cadmium phytoavailability and translocation from soil to wheat in an effluent irrigated field[J]. Chemosphere, 174: 515-523.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
RAMRAKHIANI L, GHOSH S, MAJUMDAR S, 2016. Surface modification of naturally available biomass for enhancement of heavy metal removal efficiency, upscaling prospects, and management aspects of spent biosorbents: A Review[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(1): 41-78.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
TAKEUCHI Y, ARAI H, 1990. Removal of coexisting Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ ions from water by addition of hydroxyapatite power[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 23: 75-80.
DOI URL |
| [24] | WANG G Y, PAN X M, ZHANG S R, et al., 2020. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by biodegradable chelator-induced washing: Efficiencies and mechanisms[J]. Environmental Research, 186(1): 109554. |
| [25] |
YAO A J, WANG Y N, LING X D, et al., 2016. Effects of an iron-silicon material, a synthetic zeolite and an alkaline clay on vegetable uptake of As and Cd from a polluted agricultural soil and proposed remediation mechanisms[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(2): 353-367.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YI Y J, WEN J, ZENG G M, et al., 2017. A comparative study for the stabilization of heavy metal contaminated sediment by limestone, MnO2 and natural zeolite[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1): 795-804.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
YU X L, LU S G, 2016. Micrometer-scale internal structure and element distribution of Fe-Mn nodules in Quaternary red earth of Eastern China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(2): 621-633.
DOI URL |
| [28] | ZHANG S Y, ARKIN K, ZHENG Y X, et al., 2022. Preparation of a composite material based on self-assembly of biomass carbon dots and sodium alginate hydrogel and its green, efficient and visual adsorption performance for Pb2+[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(1): 106921. |
| [29] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [30] | 冯敬云, 聂新星, 刘波, 等, 2021. 镉污染农田原位钝化修复效果及其机理研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 38(5): 764-777. |
| FENG J Y, NIE X X, LIU B, et al., 2021. Efficiency of in-situ passivation remediation in cadmium-contaminated farmland soil and its mechanism: A review[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 38(5): 764-777. | |
| [31] | 辜娇峰, 周航, 吴玉俊, 等, 2016. 复合改良剂对稻田Cd、As活性与累积的协同调控[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(1): 206-214. |
| GU J F, ZHOU H, WU Y J, et al., 2016. Synergistic control of combined amendment on bioavailability and accumulation of Cd and As in rice paddy soil[J]. Chinese Environmental Science, 36(1): 206-214. | |
| [32] | 环境保护部, 国土资源部, 2014. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[EB/OL]. (2014-04-17) [2022-03-22]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417-270670.htm. |
| Ministry of environmental protection, Ministry of land and resources, 2014. National soil pollution survey Bulletin[EB/OL]. (2014-04-17) [2022-03-22]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417-270670.htm. | |
| [33] | 刘丽, 吴燕明, 周航, 等, 2015. 大田条件下施加组配改良剂对蔬菜吸收重金属的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 9(3): 1489-1495. |
| LIU L, WU Y M, ZHOU H, et al., 2015. Effect of combined amendment on vegetable absorption of heavy metals under field conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 9(3): 1489-1495. | |
| [34] | 梅闯, 蔡昆争, 黎紫珊, 等, 2022. 稻秆生物炭对稻田土壤 Cd 形态转化和微生物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(2): 380-390. |
| MEI C, CAI K Z, LI Z S, et al., 2022. Effects of rice-straw biochar on the transformation of cadmium fractions and microbial community in paddy soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(2): 380-390. | |
| [35] | 秦坤, 王志康, 王章鸿, 等, 2022. 木质素-聚乙烯共热解生物炭对Cd(II) 的吸附性能[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(2): 344-353. |
| QIN K, WANG Z K, WANG Z H, et al., 2022. Cd(II) adsorption capability of the biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of lignin and polyethylene[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(2): 344-353. | |
| [36] | 汪涛, 高国龙, 王庆, 等, 2018. 无机有机复合材料对重金属污染土壤的修复效应[J]. 环境科技, 31(5): 29-34. |
| WANG T, GAO G L, WANG Q, et al., 2018. Inorganic-organic amendments for immobilization of heavy metal contaminants in soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(5): 29-34. | |
| [37] | 王亚琢, 周翔, 修磊, 等, 2021. 高铁酸钾改性生物炭的制备及其对水体中Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2380-2386. |
| WANG Y Z, ZHOU X, XIU L, et al., 2021. Preparation of K2FeO4 modified biochar and its adsorption characteristics for Cd(Ⅱ) in aqueous solution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2380-2386. | |
| [38] | 邢金峰, 仓龙, 葛礼强, 等, 2016. 纳米羟基磷灰石钝化修复重金属污染土壤的稳定性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(7): 1271-1277. |
| XING J F, CANG L, GE L Q, et al., 2016. Long-term stability of immobilizing remediation of a heavy metal contaminated soil with nano-hydroxyapatite[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(7): 1271-1277. | |
| [39] | 钟奇伟, 蔡玉荣, 2016. 球形碳酸钙/羟基磷灰石的制备及药物控释[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 35(5): 685-690. |
| ZHONG Q W, CAI Y R, 2016. Preparation of CaCO3 and hydroxyapatite microsphere and its potential application in drug controlled release[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (Nature Science), 35(5): 685-690. | |
| [40] | 邹紫今, 周航, 吴玉俊, 等, 2016. 羟基磷灰石+沸石对稻田土壤中铅镉有效性及糙米中铅镉累积的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(1): 45-52. |
| ZHOU Z J, ZHOU H, WU Y J, et al., 2016. Effects of hydroxyapatitle plus zeolite on bioavailability and rice bioaccumulation of Pb and Cd in soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(1): 45-52. |
| [1] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [2] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [3] | 徐敏, 许超, 余光辉, 尹力初, 张泉, 朱捍华, 朱奇宏, 张杨珠, 黄道友. 地下水位和长期秸秆还田对土壤镉有效性及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 150-157. |
| [4] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [5] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [6] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [7] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [8] | 赵超凡, 周丹丹, 孙建财, 钱坤鹏, 李芳芳. 生物炭中可溶性组分对其吸附镉的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 814-823. |
| [9] | 曾民, 陈佳, 李娥贤, 殷富有, 王玲仙, 曾黎琼, 郭蓉. 元江普通野生稻后代镉分布特点及镉积累动态变化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 565-571. |
| [10] | 李光炫, 石岸, 张黎明, 邢世和, 杨文浩. 不同粒径生物质炭对土壤重金属钝化及细菌群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 583-592. |
| [11] | 文典, 赵沛华, 陈楚国, 李富荣, 杜瑞英, 黄永东, 李蕾, 王富华. 珠三角典型区域蔬菜产地土壤Cd安全阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 603-609. |
| [12] | 石含之, 江棋, 刘帆, 文典, 黄永东, 邓腾灏博, 王旭, 徐爱平, 李富荣, 吴志超, 李梅霞, 彭锦芬, 杜瑞英. 水稻根茬还田对土壤及稻米中镉累积的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 363-369. |
| [13] | 上官宇先, 尹宏亮, 徐懿, 钟红梅, 何明江, 秦鱼生, 郭松, 喻华. 不同钝化剂对水稻小麦籽粒镉吸收的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 370-379. |
| [14] | 秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| [15] | 任珺, 潘佳璇, 陶玲, 仝云龙, 王若安, 孙新妮. 氢氧化钠改性坡缕石对Cd污染土壤的钝化修复效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
