生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1383-1392.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.010
李程程( ), 张子蕤, 宋晓萱, 孔娟娟, 韩阳, 阮亚男*
), 张子蕤, 宋晓萱, 孔娟娟, 韩阳, 阮亚男*
收稿日期:2022-03-22
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*阮亚男,女,副教授。作者简介:李程程(1987年生),女,讲师,博士研究生,研究方向为种群生态学、生态适应、恢复生态学。E-mail: lichengcheng@lnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Chengcheng( ), ZHANG Zirui, SONG Xiaoxuan, KONG Juanjuan, HAN Yang, RUAN Yanan*
), ZHANG Zirui, SONG Xiaoxuan, KONG Juanjuan, HAN Yang, RUAN Yanan*
Received:2022-03-22
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
在全球变化背景下,近地层臭氧(O3)浓度不断升高,将成为影响未来农业生产的重要因素。以大豆(Glycine max)为研究材料,采用OTCs方法,设置3个处理梯度(CK、80 nmol∙mol-1、200 nmol∙mol-1)臭氧熏蒸试验,试验进行9 d,在熏蒸结束后的72 h内(恢复期)分别采集各处理分枝期大豆,分析叶片膜脂过氧化程度、抗氧化酶活性及相关基因表达的变化情况,以及在大豆完熟期测定生长及结实性状。结果表明,(1)低浓度(80 nmol∙mol-1)臭氧处理显著提高了完熟期大豆豆荚数和单株种子粒数,但种子单株粒质量小于对照。(2)低浓度臭氧熏蒸使分枝期大豆叶片抗坏血酸(AsA)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量升高,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)、谷胱甘肽还原酶(GR)活性上升,72 h内的恢复期间,抗氧化酶活性升高,表现出氧化应激反应。(3)高浓度(200 nmol∙mol-1)熏蒸处理使分枝期大豆叶片活性氧水平显著升高,过氧化氢酶(CAT)、APX、GR、脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶(DHAR)、单脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶(MDHAR)活性下降,CAT1、APX、GR表达下调,MDA含量升高。在恢复期,SOD、CAT、APX、GR活性升高,相关酶基因表达上调。该研究表明低浓度(80 nmol∙mol-1)臭氧急性胁迫后,在恢复期大豆能够通过升高抗氧化酶活性及基因表达调控适应臭氧浓度升高带来的氧化胁迫,并在生殖上提高豆荚及单株粒数,保证亲本投入。但急性高浓度(200 nmol∙mol-1)胁迫将对大豆的生长和成株的生殖造成损害,且伤害难以恢复。
中图分类号:
李程程, 张子蕤, 宋晓萱, 孔娟娟, 韩阳, 阮亚男. 臭氧胁迫对大豆抗氧化代谢与生殖生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1383-1392.
LI Chengcheng, ZHANG Zirui, SONG Xiaoxuan, KONG Juanjuan, HAN Yang, RUAN Yanan. Effects of Ozone Stress on Antioxidant Metabolism and Reproductive Growth of Soybean[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1383-1392.
| 数量性状 Traits | x(O3)/(nmol∙mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80 | 200 | |
| 叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 | 51.28±1.76a | 51.70±1.08a | 37.94±2.20b |
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 90.13±6.51a | 89.25±4.37a | 81.00±2.17b |
| 地上生物量 (干质量) Aboveground/g | 13.83±1.95a | 15.25±1.66a | 10.241±0.57b |
| 地下生物量 Underground/g | 2.33±0.58a | 1.46±0.17b | 0.85±0.10b |
| 豆荚数 Pod | 29.25±0.48b | 34.50±2.22a | 25.25±2.87b |
| 单株粒数 Seed | 65.75±4.40b | 80.50±5.56a | 59.00±4.8b |
| 单株粒重 Individual grain weight/g | 11.31±1.18a | 12.31±1.76a | 8.35±1.06b |
| 百粒重 Hundred-gain weight/g | 16.98±0.52a | 16.17±0.62b | 14.35±0.30c |
表1 不同浓度臭氧处理下大豆主要数量性状的多重比较
Table 1 Multiple comparison of main quantitative traits of soybean with different ozone concentrations
| 数量性状 Traits | x(O3)/(nmol∙mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 80 | 200 | |
| 叶面积 Leaf area/cm2 | 51.28±1.76a | 51.70±1.08a | 37.94±2.20b |
| 株高 Plant height/cm | 90.13±6.51a | 89.25±4.37a | 81.00±2.17b |
| 地上生物量 (干质量) Aboveground/g | 13.83±1.95a | 15.25±1.66a | 10.241±0.57b |
| 地下生物量 Underground/g | 2.33±0.58a | 1.46±0.17b | 0.85±0.10b |
| 豆荚数 Pod | 29.25±0.48b | 34.50±2.22a | 25.25±2.87b |
| 单株粒数 Seed | 65.75±4.40b | 80.50±5.56a | 59.00±4.8b |
| 单株粒重 Individual grain weight/g | 11.31±1.18a | 12.31±1.76a | 8.35±1.06b |
| 百粒重 Hundred-gain weight/g | 16.98±0.52a | 16.17±0.62b | 14.35±0.30c |
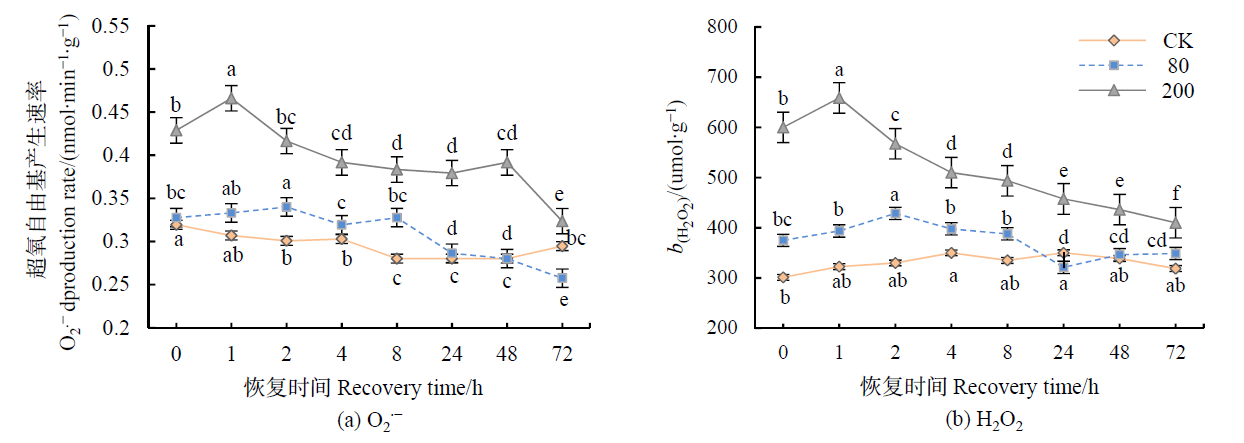
图1 不同浓度臭氧处理结束后对大豆叶片O2∙-产生速率、H2O2含量的影响 CK:自然环境臭氧摩尔分数为 (40.16±8.22) nmol∙mol-1;80:臭氧摩尔分数为80 nmol∙mol-1;200:臭氧摩尔分数为200 nmol∙mol-1,下同
Figure 1 Effects of elevated ozone pretreatment to O2∙-production rate, H2O2 content in soybean leaves CK: ozone mole fraction: 40.16±8.22 nmol∙mol-1; 80: ozone mole fraction: 80 nmol∙mol-1; 200: ozone mole fraction: 200 nmol∙mol-1, The same below
| [1] |
ALSCHER R G, ERTURK N, HEATH L S, 2002. Role of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in controlling oxidative stress in plants[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(372): 1331-1341.
DOI URL |
| [2] | BOWLER C, 1992. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 43(1): 83-116. |
| [3] |
BRITZ S J, ROBINSON J M, 2001. Chronic ozone exposure and photosynthate partitioning into starch in soybean leaves[J]. International Journal of Plant Sciences, 162(1): 111-117.
DOI URL |
| [4] | BUEGE J A, AUST S D, 1978. Microsomal lipid peroxidation[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 52: 302-310. |
| [5] | BULLBOVAS P, SOUZA S R, ESPOSITO J B, et al., 2014. Assessment of the ozone tolerance of two soybean cultivars (Glycine max cv. Sambaíba and Tracajá) cultivated in Amazonian areas[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 21(17): 10514-10524. |
| [6] |
CALATAYUD A, ALVARADO J W, BARRENO E, 2001. Changes in chlorophyll a fluorescence, lipid peroxidation, and detoxificant system in potato plants grown under filtered and non-filtered air in open-top chambers[J]. Photosynthetica, 39(4): 507-513.
DOI URL |
| [7] | CHANGEY F, BAGARD M, SOULEYMANE M, et al., 2018. Cascading effects of elevated ozone on wheat rhizosphere microbial communities depend on temperature and cultivar sensitivity[J]. Environmental Pollution, 242(Part A): 113-125. |
| [8] |
COSTA J H, ROQUE A L M, AZIZ S, et al., 2021. Genome-wide identification of ascorbate-glutathione cycle gene families in soybean (Glycine max) reveals gene duplication events and specificity of gene members linked to development and stress conditions[J]. International journal of biological macromolecules, 187: 528-543.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DU Y Y, WANG P C, CHEN J, et al., 2010. Comprehensive functional analysis of the catalase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 50(10): 1318-1326.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DUMONT J, KESKI-SAARI S, KEINANEN M, et al., 2017. Ozone affects ascorbate and glutathione biosynthesis as well as amino acid contents in three Euramerican poplar genotypes[J]. Tree Physiology, 34(3): 253-266.
DOI URL |
| [11] | EDENHOFER O, PICHS M R, SOKONA Y, 2014. Mitigation of climate change. Climate Change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 111-150. |
| [12] | EMBERSON L, 2020. Effects of ozone on agriculture, forests and grasslands[J]. Philosophical transactions. Series A, Mathematical, physical, and engineering sciences, 378(2183): 20190327. |
| [13] |
GIANNOPOLITIS C N, RIES S K, 1997. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 59(2): 309-314.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
GILL S S, TUTEJA N, 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48(12): 909-930.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
GRIFFITH O W, 1980. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 106(1): 207-212.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
GRULKE N E, HEATH R L, 2020. Ozone effects on plants in natural ecosystems[J]. Plant Biology, 22(Suppl 1): 12-37.
DOI URL |
| [17] | KARAM E A, KERAMAT B, SORBO S, et al., 2017. Interaction of triacontanol and arsenic on the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and their effects on the ultrastructure in Coriandrum sativum L.[J]. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 141: 161-169. |
| [18] |
KASK K, KAURILIND E, TALTS E, et al., 2021. Combined acute ozone and water stress alters the quantitative relationships between O3 uptake, photosynthetic characteristics and volatile emissions in Brassica nigra[J]. Molecules, 26(11): 3114.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
KAUR S, PRAKASH P, BAK D H, et al., 2021. Regulation of Dual Activity of Ascorbate Peroxidase 1 From Arabidopsis thaliana by Conformational Changes and Posttranslational Modifications[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12: 678111.
DOI URL |
| [20] | KE D S, WANG A G, SUN G C, et al., 2002. The effect of active oxygen on the activity of ACC synthase induced by exogenous IAA[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 44(5): 551-556. |
| [21] |
KUERBAN M, WAILI Y, FAN F, et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal patterns of air pollution in China from 2015 to 2018 and implications for health risks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 258:113659.
DOI URL |
| [22] | LEFOHN A S, MALLEY C S, SMITH L, et al., 2018. Tropospheric ozone assessment report: Global ozone metrics for climate change, human health, and crop/ecosystem research[J]. Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene, 6(1): 28. |
| [23] |
LI C H, GU X, WU Z Y, et al., 2021. Assessing the effects of elevated ozone on physiology, growth, yield and quality of soybean in the past 40 years: A meta-analysis[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 208: 111644.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LIANG Z H, JU T Z, DONG H P, et al., 2021. Study on the variation characteristics of tropospheric ozone in Northeast China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(5): 1-16.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D, 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method[J]. METHODS, 25: 402-408.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LU X, HONG J Y, ZHANG L, et al., 2018. Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 5: 487-494. |
| [27] | MACIAS-BENITEZ S, NAVARRO-TORRE S, CABALLERO P, et al., 2021. Biostimulant capacity of an enzymatic extract from rice bran against ozone-induced damage in Capsicum annum [J]. Frontiers in plant science, 12: 749422. |
| [28] | MAHALINGAM R, JAMBUNATHAN N, GUNJAN S K, et al., 2006. Analysis of oxidative signalling induced by ozone in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant Cell & Environment, 29(7): 1357-1371. |
| [29] | MAHMOOD U, HUSSAIN S, HUSSAIN S, et al., 2021. Morpho-physio-biochemical and molecular responses of maize hybrids to salinity and waterlogging during stress and recovery phase[J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 10(7): 345. |
| [30] | MALAIYANDI M, NATARAJAN M, 2014. Impact of Ozone on Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Changes in Cow Pea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.)[J]. Ozone Science & Engineering, 36(1): 36-42. |
| [31] |
MUKHERJEE S P, CHOUDHURI M A, 1985. Implication of hydrogen peroxide-ascorbate system on membrane permeability of water stressed vigna seedlings[J]. New Phytologist, 99(3): 355-360.
DOI URL |
| [32] | NAKANO Y, ASADA K, 1981. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts[J]. Plant & Cell Physiology, 22(5): 867-880. |
| [33] |
OSBORNE S A, MILLS G, HAYES F, et al., 2016. Has the sensitivity of soybean cultivars to ozone pollution increased with time? An analysis of published dose-response data[J]. Global Change Biology, 22(9): 3097-3111.
DOI URL |
| [34] | PANDEY A K, GHOSH A, AGRAWAL M, et al., 2018. Effect of elevated ozone and varying levels of soil nitrogen in two wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars: Growth, gas-exchange, antioxidant status, grain yield and quality[J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 158: 59-68. |
| [35] | PELLEGRINI E, CAMPANELLA A, COTROZZI L, et al., 2017. What about the detoxification mechanisms underlying ozone sensitivity in Liriodendron tulipifera[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 25(9): 1-13. |
| [36] |
PELLEGRINO E, TRIVELLINI A, CAMPANELLA A, et al., 2013. Signaling molecules and cell death in Melissa officinalis plants exposed to ozone[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 32(12): 1965-1980.
DOI URL |
| [37] | PERRY J J, SHIN D S, GETZOFF E D, et al., 2009. The structural biochemistry of the superoxide dismutases[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1804(2): 245-262. |
| [38] | PRYOR W A, 1995. Methods in enzymology: Oxygen radicals in biological systems, part C[J]. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 18(5): 959. |
| [39] |
QIAO X Q, ZHENG Z Z, ZHANG L F, et al., 2015 Lead tolerance mechanism in sterilized seedlings of Potamogeton crispus L.: Subcellular distribution, polyamines and proline[J]. Chemosphere, 120: 179-187.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ROZPĄDEK P, NOSEK M, ŚLESAK I, et al., 2015. Ozone fumigation increases the abundance of nutrients in Brassica vegetables: broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) and Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis)[J]. European Food Research and Technology, 240(2): 459-462.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SALVATORI E, FUSARO L, STRASSER RJ, et al., 2015. Effects of acute O3 stress on PSII and PSI photochemistry of sensitive and resistant snap bean genotypes (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), probed by prompt chlorophyll “a” fluorescence and 820 nm modulated reflectance[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 97: 368-377.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
SHORT E F, NORTH K A, ROBERTS M R, et al., 2012. A stress-specific calcium signature regulating an ozone-responsive gene expression network in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Journal, 71(6): 948-961.
DOI URL |
| [43] | SIM H H, DU H K, JAE C L, 2009. Effects of fertilization on physiological parameters in American sycamore (Platanus occidentalis) during ozone stress and recovery phase[J]. Journal of Ecology and Field Biology, 32(3): 149-158. |
| [44] | SLUPPHAUG G, KAVLI B, KROKAN H E, 2003. The interacting pathways for prevention and repair of oxidative DNA damage[J]. Mutation Research/fundamental & Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 531(1): 231-251. |
| [45] | VAULTIER M N, JOLIVET Y, 2015. Ozone sensing and early signaling in plants: An outline from the cloud[J]. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 114: 144-152. |
| [46] |
WANG N, LYU X P, DENG X J, et al., 2019. Aggravating O3 pollution due to NOx emission control in eastern China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 677: 732-744.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WANG T, XUE L K, PETER B, et al., 2016. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 575: 1582-1596.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YAMAGUCHI M, HOSHINO D, KONDO T, 2015. Evaluation of O3 effect on net photosynthetic rate in flag leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) by stomatal O3 flux and radical scavenging enzyme activities[J]. Journal of Agricultural Meteorology, 71(3): 211-217.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
YANG Q, LI Y L, WANG L H, et al., 2014. Effect of lanthanum (III) on the production of ethylene and reactive oxygen species in soybean seedlings exposed to the enhanced ultraviolet-B radiation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 104: 152-159.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
ZHANG X X, ZHANG X F, WANG T Z, et al., 2021. Metabolic response of soybean leaves induced by short-term exposure of ozone[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 213(114): 112033.
DOI URL |
| [51] | ZHAO T H, SHI Y, HUANG G H, et al., 2005. Respective and interactive effects of doubled CO2 and O3 concentration on membrane lipid peroxidation and antioxidative ability of soybean[J]. Science in China (Series C: Life Sciences), 48(1): 136-141. |
| [52] | 冯兆忠, 2020. 臭氧污染的生态风险和防护对策[J]. 环境保护, 48(15): 20-22. |
| FENG Z Z, 2020. Ecological Risks of Ozone Pollution in China and Countermeasures[J]. Environmental Protection, 48(15): 20-22. | |
| [53] |
冯兆忠, 袁相洋, 李品, 等, 2020. 地表臭氧浓度升高对陆地生态系统影响的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 44(5): 526-542.
DOI |
|
FENG Z Z, YUAN X Y, LI P, et al., 2020. Progress in the effects of elevated ground-level ozone on terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 44(5): 526-542.
DOI URL |
|
| [54] | 阮亚男, 何兴元, 陈玮, 等, 2008. 臭氧浓度升高对植物抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 27(5): 829-834. |
| RUAN Y N, HE X Y, CHEN W, et al., 2008. Effects of elevated ozone on anti-oxidative system in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27(5): 829-834. | |
| [55] | 阮亚男, 徐胜, 郭龙, 等, 2017. 大气臭氧浓度升高对银杏叶片活性氧代谢及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(11): 32-39. |
| RUAN Y N, XU S, GUO L, et al., 2017. Effects of elevated ozone concentrations on reactive oxygen metabolism and related gene expression in Ginkgo biloba leaves[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(11): 32-39. | |
| [56] | 易睿, 王亚林, 张殷俊, 等, 2015. 长江三角洲地区城市臭氧污染特征与影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(8): 2370-2377. |
| YI R, WANG Y L, ZHANG Y J, et al., 2015. Pollution characteristics and influence factors of ozone in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(8): 2370-2377. |
| [1] | 闫学军, 郝赛梅, 张荣荣, 秦华, 高素莲, 王锋, 靳宪忠, 孙友敏, 张桂芹. 家居市场挥发性有机物排放成分谱及排放估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1070-1077. |
| [2] | 许肖云, 饶芝菡, 蒋红斌, 张巍, 陈超, 杨永安, 胡艳丽, 魏海川. 遂宁工业园区夏季VOCs污染特征及其对O3、SOA生成潜势研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 956-968. |
| [3] | 温丽容, 江明, 黄渤, 袁鸾, 周炎, 陆炜梅, 张莹, 刘明, 张力昀. 珠三角典型区域臭氧成因分析与VOCs来源解析——以中山为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 500-513. |
| [4] | 符传博, 丹利, 佟金鹤, 陈红. 海口市区臭氧污染变化特征及潜在源区分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 331-340. |
| [5] | 尹浩均, 龙明亮, 刘维, 倪春林, 李芳柏, 吴云当. 溶氧浓度调控嗜水气单胞菌的砷还原:效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 381-387. |
| [6] | 陈雪泉, 孔彬, 兰青, 余志铨, 谢银斯, 黄俊毅. 胶黏剂生产行业VOCs组分特征及臭氧生成潜势分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 750-758. |
| [7] | 李颖慧, 郭前进, 闫雨龙, 胡冬梅, 邓萌杰, 彭林. 晋城市环境空气中BTEX变化特征及来源[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 504-511. |
| [8] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [9] | 陈瑶瑶, 廖彤, 汪宇, 沈劲, 翟宇虹, 叶斯琪, 陈多宏, 陈靖扬. 2016—2020年广东省臭氧污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2374-2381. |
| [10] | 廖彤, 熊鑫, 王在华, 杨夏捷, 黄映楠, 冯嘉颖. 世界三大湾区大气污染治理经验及对粤港澳大湾区的启示[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2242-2250. |
| [11] | 陈漾, 张金谱, 邱晓暖, 琚鸿, 黄俊. 2021年广州市臭氧污染特征及气象因子影响分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038. |
| [12] | 符传博, 丹利, 刘丽君, 佟金鹤. 2019年秋季三亚市一次典型臭氧污染个例气象成因解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 89-99. |
| [13] | 邓慧颖, 陈立新, 余永江, 王宏. 武夷山市臭氧分布特征及其与气象要素关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1428-1435. |
| [14] | 洪莹莹, 陈辰, 保鸿燕, 沈劲. 珠三角西南部春季臭氧来源与敏感性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 984-994. |
| [15] | 万五星, 张帅, 李洁, 孙旭, 管祖光, 于小红, 杨永宏, 王效科. 河北省城市空气臭氧污染及其对植物伤害的区域差异[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2185-2194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
