生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 802-813.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.019
徐梅华1( ), 顾明华1, 王骋臻1, 雷静2,*(
), 顾明华1, 王骋臻1, 雷静2,*( ), 韦燕燕1, 沈方科1
), 韦燕燕1, 沈方科1
收稿日期:2021-11-08
出版日期:2022-04-18
发布日期:2022-06-22
通讯作者:
*雷静(1973年生),女,讲师,硕士,研究方向为环境生态。E-mail: ljfy1173@126.com作者简介:徐梅华(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤学。E-mail: xu_meihua02@163.com
基金资助:
XU Meihua1( ), GU Minghua1, WANG Chengzhen1, LEI Jing2,*(
), GU Minghua1, WANG Chengzhen1, LEI Jing2,*( ), WEI Yanyan1, SHEN Fangke1
), WEI Yanyan1, SHEN Fangke1
Received:2021-11-08
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
摘要:
土壤中铁锰氧化物是影响土壤砷形态及其生物有效性的重要因素。通过盆栽试验法,利用土壤理化性质相近而锰质量分数相差大的两种自然土壤混合得到土壤锰质量分数(mg·kg-1)分别为580(Mn1)、980(Mn2)、1900(Mn3)、3030(Mn4)、4230(Mn5)的5个土壤,种植水稻(Oryza sativa L.)后,分别在水稻分蘖期、抽穗期和成熟期采集土壤孔隙水、水稻和土壤样品进行分析,探讨锰质量分数对土壤中铁、锰氧化物形态和砷形态转变及其对水稻吸收砷的影响和作用机制。结果表明,随着土壤锰质量分数增加,土壤Eh呈升高趋势;土壤中无定形铁氧化物、锰氧化物和游离态锰氧化物质量分数增加,成熟期Mn1和Mn5处理土壤无定形态铁氧化物、锰氧化物分别比分蘖期增加11.9%、40.5%和3.6%、35.7%;随着土壤锰质量分数增加,土壤中非专性吸附砷和专性吸附砷比例呈下降趋势,土壤砷更大比例以无定形铁氧化物结合态、晶质铁氧化物结合态和残渣态存在,从水稻分蘖期到成熟期处理Mn1土壤晶质铁氧化物结合态砷和残渣态砷的质量分数共减少了2.7%,Mn2至Mn5处理晶质铁氧化物结合砷和残渣砷的质量分数共增加了6.3%—14.0%,土壤孔隙水Fe(Ⅱ)、As(Ⅲ) 质量浓度降低;随着土壤锰质量分数增加,水稻根、茎、叶和籽粒砷质量分数减少,各部位的砷富集系数减小,水稻各部位砷质量分数与土壤非专性吸附态砷质量分数呈现极显著正相关,与无定形铁氧化物结合态砷质量分数显著负相关。综上所述,土壤中高质量分数锰可以延缓Eh下降,促进土壤中无定形态铁氧化物、锰氧化物和游离态锰氧化物的形成及对砷的氧化和吸附固定,降低土壤砷的有效性,从而减少水稻对砷的吸收。
中图分类号:
徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813.
XU Meihua, GU Minghua, WANG Chengzhen, LEI Jing, WEI Yanyan, SHEN Fangke. Effect of Manganese on Arsenic Speciation in Soil and Arsenic Migration to Rice[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 802-813.
| 土壤类型 Soil types | 土壤基本性质 Basic properties of soils | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(总铁 Total Fe)/ % | w(总锰 Total Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总砷 Total As)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总氮 Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Effective phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效钾 Effective potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | |
| 低锰土 Soil with low Mn mass fraction | 6.56 | 582.67 | 57.54 | 6 | 24 | 1.82 | 0.55 | 410.25 |
| 高锰土 Soil with high Mn mass fraction | 6.85 | 4232.66 | 69.75 | 6.6 | 26.4 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 398.47 |
表1 供试土壤相关性质
Table 1 Related properties of tested soils
| 土壤类型 Soil types | 土壤基本性质 Basic properties of soils | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(总铁 Total Fe)/ % | w(总锰 Total Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总砷 Total As)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总氮 Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Effective phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效钾 Effective potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | |
| 低锰土 Soil with low Mn mass fraction | 6.56 | 582.67 | 57.54 | 6 | 24 | 1.82 | 0.55 | 410.25 |
| 高锰土 Soil with high Mn mass fraction | 6.85 | 4232.66 | 69.75 | 6.6 | 26.4 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 398.47 |
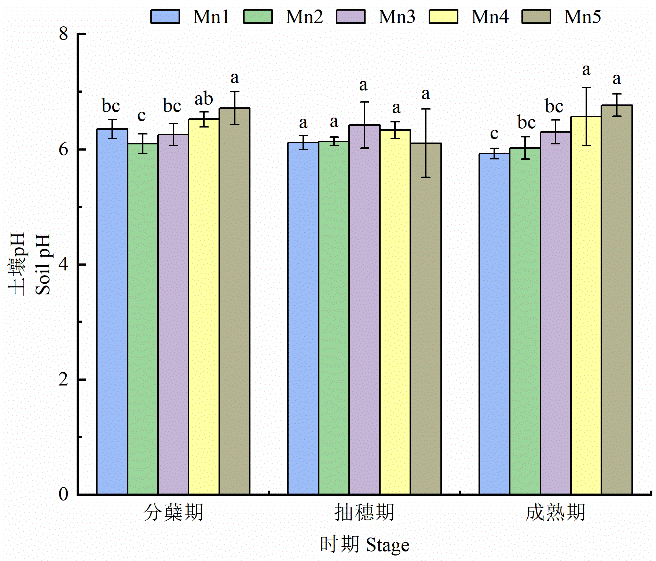
图1 不同处理对土壤pH的影响 不同字母表示同一时期处理之间有,下同
Figure 1 Effects of different treatments on soil pH Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments during the same period (P<0.05), n=4, the same as below
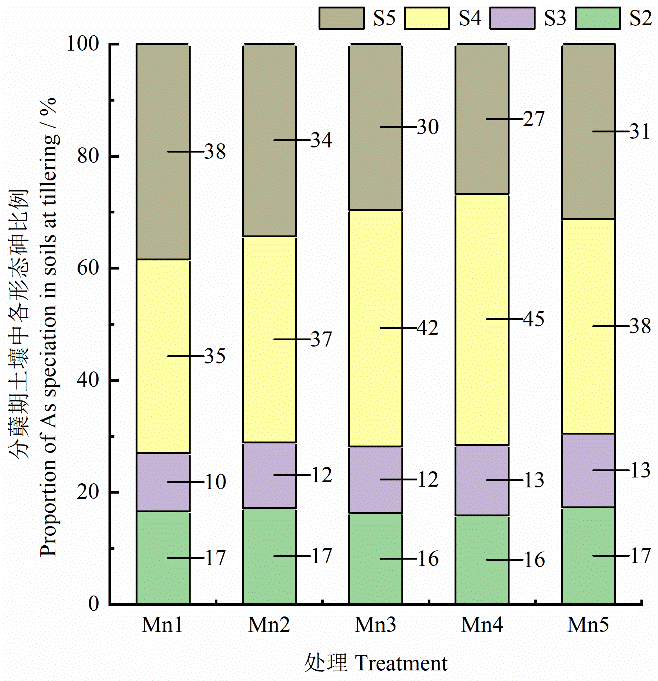
图5 不同处理对分蘖期土壤各砷形态质量分数的影响 S2、S3、S4、S5分别为专性吸附态砷,无定形态铁氧化物结合态砷,晶质铁氧化物结合态砷和残渣态砷,n=4,下同
Figure 5 Effects of different treatments on mass fractions of As speciation in soils at tillering stage S2, S3, S4, S5 denote obligate adsorbed As, amorphous Fe oxides bound As, crystalline Fes oxide bound As and residual As, respectively, n=4, The same as below
| 处理 Treatment | 非专性吸附态砷质量分数的比例 Proportion of non-obligate adsorbed As mass fraction in soils/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖期 Tillering | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |
| Mn1 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Mn2 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Mn3 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| Mn4 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Mn5 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
表2 不同处理对土壤中非专性吸附态砷质量分数占总砷质量分数比例的影响
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on the mass fraction ratio of non-obligate adsorbed As to total As in soils
| 处理 Treatment | 非专性吸附态砷质量分数的比例 Proportion of non-obligate adsorbed As mass fraction in soils/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖期 Tillering | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |
| Mn1 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Mn2 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Mn3 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| Mn4 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Mn5 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 土壤砷形态 Speciation of As in soil | 土壤铁锰氧化物形态 Speciation of Fe oxides and Mn oxides in soils | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无定形铁 氧化物 Amorphous Fe oxides | 无定形锰 氧化物 Amorphous Mn oxides | 游离铁 氧化物 Free Fe oxides | 游离锰 氧化物 Free Mn oxides | |
| S1 | 0.035 | -0.409** | -0.071 | -0.438** |
| S2 | -0.137 | 0.114 | 0.429** | 0.182 |
| S3 | 0.278* | 0.652** | -0.258* | 0.747** |
| S4 | 0.370** | 0.365** | -0.282* | 0.387** |
| S5 | 0.238 | 0.302* | -0.0816 | 0.272* |
表3 土壤砷形态质量分数与土壤铁锰氧化物质量分数相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis between As speciation and Fe/Mn oxides in soils
| 土壤砷形态 Speciation of As in soil | 土壤铁锰氧化物形态 Speciation of Fe oxides and Mn oxides in soils | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无定形铁 氧化物 Amorphous Fe oxides | 无定形锰 氧化物 Amorphous Mn oxides | 游离铁 氧化物 Free Fe oxides | 游离锰 氧化物 Free Mn oxides | |
| S1 | 0.035 | -0.409** | -0.071 | -0.438** |
| S2 | -0.137 | 0.114 | 0.429** | 0.182 |
| S3 | 0.278* | 0.652** | -0.258* | 0.747** |
| S4 | 0.370** | 0.365** | -0.282* | 0.387** |
| S5 | 0.238 | 0.302* | -0.0816 | 0.272* |
| 孔隙水离子 Ion in pore water | 土壤铁、锰、砷形态和Eh Speciation of Fe, Mn, As in soils and soil Eh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | 无定形铁 Amorphous Fe | 无定形锰 Amorphous Mn | 游离铁 Free Fe | 游离锰 Free Mn | Eh | |
| As(III) | 0.052 | 0.331** | -0.245 | -0.522** | 0.252 | -0.476** | -0.48** | 0.097 | -0.447** | -0.759** |
表4 土壤孔隙水As(III) 质量浓度与土壤砷形态质量分数相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between As (III) concentration in soil pore water and As speciation of in soils, Fe/Mn oxides mass fraction, Eh value
| 孔隙水离子 Ion in pore water | 土壤铁、锰、砷形态和Eh Speciation of Fe, Mn, As in soils and soil Eh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | 无定形铁 Amorphous Fe | 无定形锰 Amorphous Mn | 游离铁 Free Fe | 游离锰 Free Mn | Eh | |
| As(III) | 0.052 | 0.331** | -0.245 | -0.522** | 0.252 | -0.476** | -0.48** | 0.097 | -0.447** | -0.759** |
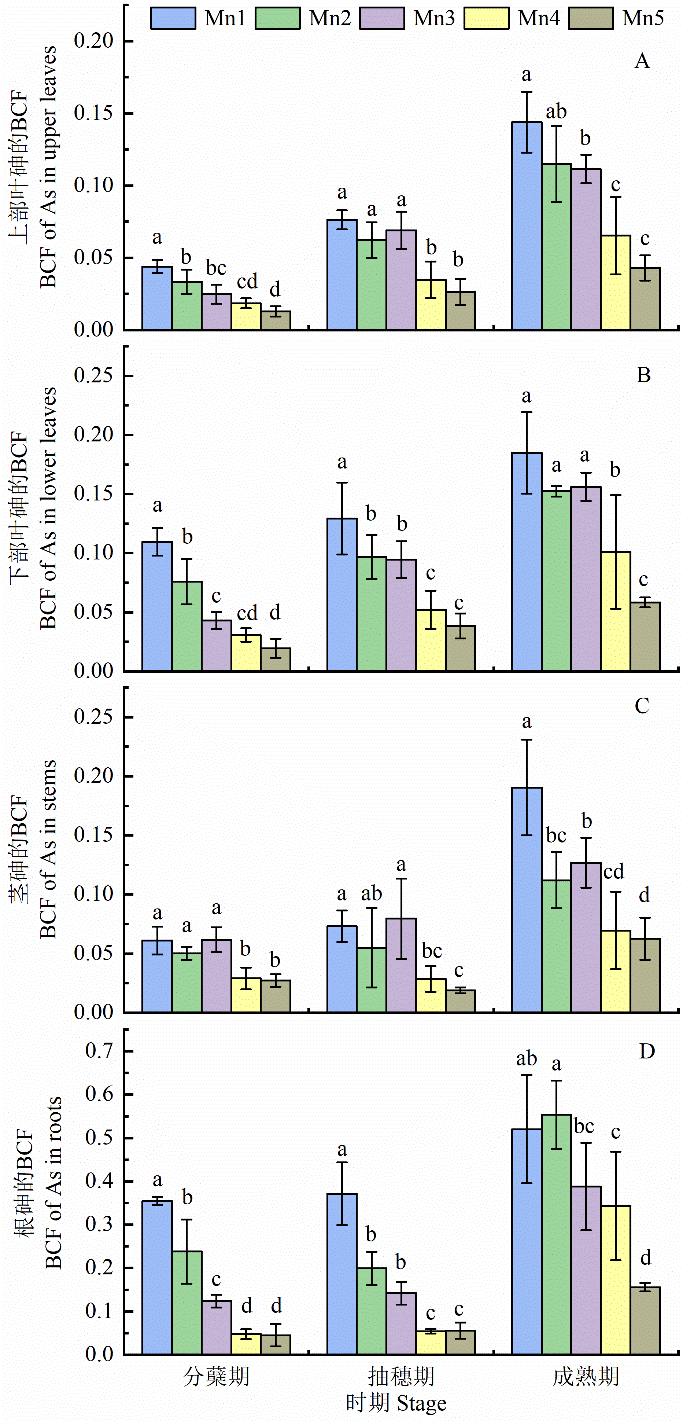
图12 不同处理对水稻上部叶、下部叶、茎、根砷富集系数的影响
Figure 12 Effects of different treatments on As enrichment coefficients in upper leaves, lower leaves, stems and roots of rice
| 砷形态 As speciation | 水稻各部位的总砷质量分数 Total As mass fraction in different parts of rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stems | 根 Roots | 上部叶 Upper leaves | 下部叶 Lower leaves | 籽粒 Grains | |
| S1 | 0.582** | 0.574** | 0.809** | 0.798** | 0.745** |
| S2 | -0.237 | -0.243 | -0.299* | -0.329* | -0.032 |
| S3 | -0.413** | -0.616** | -0.597** | -0.721** | -0.519* |
| S4 | 0.182 | -0.117 | 0.151 | -0.076 | 0.191 |
| S5 | -0.174 | -0.137 | -0.241 | -0.069 | -0.683** |
表5 水稻各部位砷质量分数与土壤中各形态砷质量分数的相关性分析
Table 5 Correlation analysis between As mass fraction in different parts of rice and As mass fraction in soils
| 砷形态 As speciation | 水稻各部位的总砷质量分数 Total As mass fraction in different parts of rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stems | 根 Roots | 上部叶 Upper leaves | 下部叶 Lower leaves | 籽粒 Grains | |
| S1 | 0.582** | 0.574** | 0.809** | 0.798** | 0.745** |
| S2 | -0.237 | -0.243 | -0.299* | -0.329* | -0.032 |
| S3 | -0.413** | -0.616** | -0.597** | -0.721** | -0.519* |
| S4 | 0.182 | -0.117 | 0.151 | -0.076 | 0.191 |
| S5 | -0.174 | -0.137 | -0.241 | -0.069 | -0.683** |
| [1] |
ABBASI S, LAMB D T, KADER M, et al., 2021. The influence of long-term ageing on arsenic ecotoxicity in soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124819.
DOI |
| [2] |
CAO Z Z, PAN J Y, YANG Y J, et al., 2020. Water management affects arsenic uptake and translocation by regulating arsenic bioavailability, transporter expression and thiol metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020. 111208.
DOI |
| [3] |
CHEN H, LEI J, TONG H, et al., 2019. Effects of Mn (II) on the oxidation of Fe in soils and the uptake of cadmium by rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(8): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHIU V Q, HERING J G, 2000. Arsenic adsorption and oxidation at manganite surfaces. 1. method for simultaneous determination of adsorbed and dissolved arsenic species[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(10): 2029-2034.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DIXIT S, HERING J G, 2003. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(18): 4182-4189.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG G W, HAN R W, PAN Y J, et al., 2021. Role of MnO2 in controlling iron and arsenic mobilization from illuminated flooded arsenic-enriched soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020. 123362.
DOI |
| [7] |
GEBEL T, 2000. Confounding variables in the environmental toxicology of arsenic[J]. Toxicology, 144(1-3): 155-162.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HIMENO S, SUMI D, FUJISHIRO H, 2019. Toxicometallomics of cadmium, manganese and arsenic with special reference to the roles of metal transporters[J]. Toxicological Research, 35(4): 311-317.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HOU J T, LUO J L, SONG S X, et al., 2017. The remarkable effect of the coexisting arsenite and arsenate species ratios on arsenic removal by manganese oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 315: 159-166.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KEIMOWITZ A R, MAILLOUX B J, WOVKULICH K, et al., 2017. Manganese redox buffering limits arsenic release from contaminated sediments, Union Lake, New Jersey[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 77: 24-30.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI J H, DONG F, LU Y, et al., 2014. Mechanisms controlling arsenic uptake in rice grown in mining impacted regions in south China[J]. PloS One, 9(9): e108300.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIN L N, SONG Z G, LIU X W, et al., 2019. Arsenic volatilization in flooded paddy soil by the addition of Fe-Mn-modified biochar composites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 674: 327-335.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIU H J, ZHANG J L, CHRISTIE P, et al., 2008. Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 394(2-3): 361-368.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MA L, CAI D M, TU S X, 2020. Arsenite simultaneous sorption and oxidation by natural ferruginous manganese ores with various ratios of Mn/Fe[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123040.
DOI |
| [15] |
MAGUFFIN S C, ABU-ALI L, TAPPERO R V, et al., 2020. Influence of manganese abundances on iron and arsenic solubility in rice paddy soils[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 276: 50-69.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MATSUMOTO S, KASUGA J, MAKINO T, et al., 2016. Evaluation of the effects of application of iron materials on the accumulation and speciation of arsenic in rice grain grown on uncontaminated soil with relatively high levels of arsenic[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 125: 42-51.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
NIAZI N K, SINGH B, SHAH P. 2011. Arsenic Speciation and Phytoavailability in Contaminated Soils Using a Sequential Extraction Procedure and XANES Spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17): 7135-7142.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
QIAN Z Y, XUE S G, CUI M Q, et al., 2021. Arsenic availability and transportation in soil-rice system affected by iron-modified biochar[J]. Journal of Central South University, 28(6): 1901-1918.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
RAHMAN M S, CLARK M W, YEE L H, et al., 2017. Arsenic solid-phase speciation and reversible binding in long-term contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 168: 1324-1336.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SARWAR T, KHAN S, MUHAMMAD S, et al., 2021. Arsenic speciation, mechanisms, and factors affecting rice uptake and potential human health risk: A systematic review[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, DOI: 10.1016/j.eti.2021.101392.
DOI |
| [21] |
ULTRA V U J E, NAKAYAMA A, TANAKA S, et al., 2009. Potential for the alleviation of arsenic toxicity in paddy rice using amorphous iron-(hydr)oxide amendments[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (Tokyo), 55(1): 160-169.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG J, WANG P M, GU Y, et al., 2019. Iron-Manganese (Oxyhydro) oxides, rather than oxidation of sulfides, determine mobilization of Cd during soil drainage in paddy soil systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(5): 2500-2508.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WENZEL W W, KIRCHBAUMER N, PROHASKA T, et al., 2001. Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 436(2): 309-323.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XU X W, CHEN C, WANG P, et al., 2017. Control of arsenic mobilization in paddy soils by manganese and iron oxides[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231(Part 1): 37-47.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YANG H, HAN M X, JIANG P P, 2021. Research Progress on the treatment of arsenic pollution by manganese oxide[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, DOI: 10.1051/e3sconf/202126104032.
DOI |
| [26] |
ZANG X Y, ZHOU Z G, ZHANG T L, et al., 2021. Aging of exogenous arsenic in flooded paddy soils: Characteristics and predictive models[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116561.
DOI |
| [27] |
ZHANG G S, LIU F D, LIU H J, et al., 2014. Respective role of Fe and Mn oxide contents for arsenic sorption in iron and manganese binary oxide: An X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(17): 10316-10322.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHANG L Y, XIAO J, JI J F, et al., 2021. Arsenate Adsorption on Different Fractions of Iron Oxides in the Paddy Soil from the Karst Region of China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 106(1): 126-133.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 鲍士旦, 2013. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 100-115. |
| BAO S D, 2013. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House: 100-115. | |
| [30] | 陈家坊, 何群, 邵宗臣, 1983. 土壤中氧化铁的活化过程的探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 20(4): 387-393. |
| CHEN J F, HE Q, SHAO Z C, 1983. Discussion on the activation process of iron oxide in soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 20(4): 387-393. | |
| [31] | 陈耀祖, 汪宜敏, 李明, 等, 2019. 老化对Cd-As污染土壤上金属形态及其生物效应的影响[J]. 环境科技, 32(6): 35-40. |
| CHEN Y Z, WANG Y M, LI M, et al., 2019. Effect of Aging on Metal Morphology and Biological Effects of Cd-As Contaminated Soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(6): 35-40. | |
| [32] | 杜艳艳, 王欣, 谢伟城, 等, 2017. 负载铁生物炭对土壤-水稻系统As溶出特性与生物有效性的影响与机理解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(8): 3158-3168. |
| DU Y Y, WANG X, XIE W C, et al., 2017. Effects and mechanisms of Fe-impregnated biochar on arsenic solubility and bioavailability in soil-rice system[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(8): 3158-3168. | |
| [33] | 顾明华, 李志明, 陈宏, 等, 2020. 施锰对土壤锰氧化物形成及镉固定的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(2): 360-368. |
| GU M H, LI Z M, CHEN H, et al., 2020. Effects of manganese application on the formation of manganese oxides and cadmium fixation in soil[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(2): 360-368. | |
| [34] | 何群, 陈家坊, 许祖诒, 1981. 土壤中氧化铁的转化及其对土壤结构的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 18(4): 326-334. |
| HE Q, CHEN J F, XU Z Y, 1981. Transformation of iron oxide in soil and its effect on soil structure[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 18(4): 326-334. | |
| [35] | 黄永东, 杜应琼, 陈永坚, 等, 2020. 水淹条件下锰改性生物炭对水稻砷吸收及形态分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(11): 2288-2295. |
| HUANG Y D, DU Y Q, CHEN Y J, et al., 2020. Effects of manganese-modified biochar on arsenic uptake and its species distribution in rice under flooding[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(11): 2288-2295. | |
| [36] | 李志明, 丁氏祝, 奇奇格, 等, 2020. 施用铁锰对土壤砷形态及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 33(8): 1722-1728. |
| LI Z M, DING S Z, QI Q G, et al., 2020. Effects of Fe and Mn application on arsenic speciation in soil and arsenic uptake by rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 33(8): 1722-1728. | |
| [37] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 20-347. |
| LU R K, 1999. Soil agrochemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 20-347. | |
| [38] | 律兆, 松徐琪, 1995. 中国白浆土研究Ⅱ白浆土机械组成特点及元素地球化学分异特征[J]. 土壤学报, 32(1): 274-288. |
| LU Z, SONG X Q, 1995. Study on Chinese Albic Soil Ⅱ Characteristics of mechanical composition and element geochemical differentiation of albic soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 32(1): 274-288. | |
| [39] | 毛凌晨, 叶华, 2018. 氧化还原电位对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 31(10): 1669-1676. |
| MAO L C, YE H, 2018. Research progress on the effect of redox potential on the environmental behavior of heavy metals in soil[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 31(10): 1669-1676. | |
| [40] | 王欣, 钟松雄, 陈志良, 等, 2018. 厌氧条件水稻土铁对砷释放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(6): 2912-2918. |
|
WANG X, ZHONG C X, CHEN Z L, et al., 2018. Effects of anaerobic conditions on arsenic release from paddy soil iron[J]. Environmental Science, 39(6): 2912-2918.
DOI URL |
|
| [41] | 薛培英, 刘文菊, 刘会玲, 等, 2010. 中轻度砷污染土壤-水稻体系中砷迁移行为研究[J]. 土壤学报, 47(5): 872-879. |
| XUE P Y, LIU W J, LIU H L, et al., 2010. Study on arsenic migration behavior in soil rice system with moderate and mild arsenic pollution[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 47(5): 872-879. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 2015. 食品中总砷及无机砷的测定: GB 5009.11—2014 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, 2015. Determination of total arsenic and abio-arsenic in foods: GB 5009.11—2014 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. | |
| [43] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2008. 土壤中总砷的测定: GB/T 22105.2—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2008. Analysis of total arsenic contents in soils: GB/T 22105.2—2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. |
| [1] | 黄英梅, 钟松雄, 朱忆雯, 王向琴, 李芳柏. 单质硫抑制水稻植株甲基汞累积的效应与机制[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [2] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | 张露, 何雨霏, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 金军. 2011—2020年汾渭平原农田生态系统碳足迹的时空格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [4] | 李传福, 朱桃川, 明玉飞, 杨宇轩, 高舒, 董智, 李永强, 焦树英. 有机肥与脱硫石膏对黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤团聚体及其有机碳组分的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [5] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [6] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [7] | 杨凯, 杨靖睿, 曹培培, 吕春华, 孙文娟, 于凌飞, 邓希. CO2浓度升高下水稻株高、茎蘖与SPAD动态响应及其模拟[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [8] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [9] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [10] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [11] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [12] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [13] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [14] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [15] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
