生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (2): 231-238.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.003
收稿日期:2021-06-29
出版日期:2022-02-18
发布日期:2022-04-14
通讯作者:
*徐当会(1976年生),女,副教授,硕士研究生导师,主要从事群落生态学研究。E-mail: dhxu@lzu.edu.cn作者简介:王小娜(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事群落生态学研究。E-mail: wangxn19@lzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Xiaona( ), XU Danghui(
), XU Danghui( ), WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen
), WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen
Received:2021-06-29
Online:2022-02-18
Published:2022-04-14
摘要:
祁连山是中国西部地区重要的安全屏障和水源涵养区,灌丛群落在水源涵养和安全屏障中起着重要的作用。为了探究祁连山灌丛群落结构随海拔和经度的变化规律,选取了甘肃省永登县奖俊埠林场(祁连山东段)、甘肃省古浪县夏玛林场(祁连山中东段)、甘肃省民乐县海潮坝森林公园(祁连山中段),分析灌丛群落Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Pielou均匀度、物种重要值、地上生物量和盖度在海拔2700—3100 m的变化。结果发现,(1)随着海拔的升高,银露梅(Potentilla glabra)的优势度逐渐下降,金露梅(Potentilla fruticosa)的优势度增加,高山绣线菊(Spiraea alpina)和山生柳(Salix oritrepha)在3个海拔梯度的优势度变化不显著。(2)随着海拔的升高,Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、地上生物量和盖度递增,且各海拔之间差异显著。(3)随着经度的增加(自西向东),地上生物量和盖度呈递增趋势,而Pielou均匀度呈递减趋势;Shannon-Wiener多样性指数在海拔2700 m呈递减趋势,在海拔2900 m和3100 m呈递增趋势。(4)Shannon-Wiener多样性指数与海拔高度、地上生物量、盖度、Pielou均匀度都存在显著相关性。以上结果表明海拔梯度和经度对灌丛群落结构直接或间接产生影响。该研究将为祁连山区灌丛的保护与开发提供一定的理论基础。
中图分类号:
王小娜, 徐当会, 王谢军, 方向文. 祁连山灌丛群落结构特征随海拔梯度和经度的变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 231-238.
WANG Xiaona, XU Danghui, WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen. Changes of Shrub Community Structure with Altitudinal Gradient and Longitude in Qilian Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 231-238.
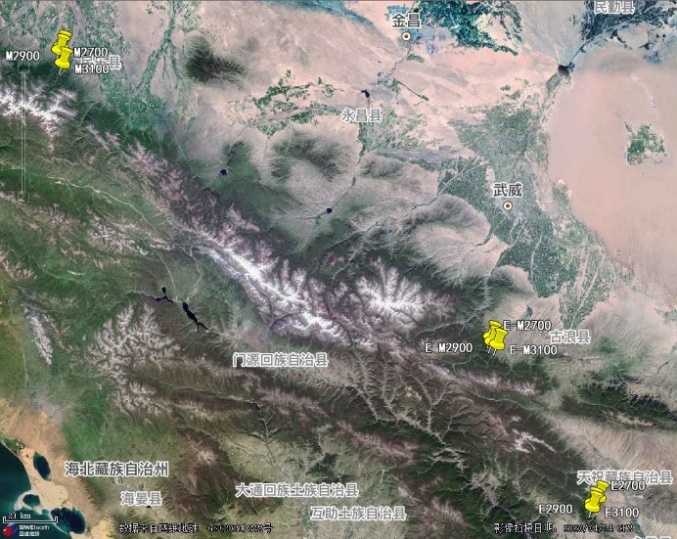
图1 观测样地空间位置 E代表祁连山东段,E-M代表祁连山中东段,M代表祁连山中段;2700、2900、3100分别代表各样地的海拔高度(m)
Figure 1 The spatial position of the sample sites E represents the eastern part of the Qilian Mountains, E-M represents the middle-eastern part of the Qilian Mountains, and M represents the middle part of the Qilian Mountains; 2700, 2900 and 3100 represent the elevations (m) of the sample sites, respectively
| 地点 Sites | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect/(°) | 坡度 Slope/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东段 East | 103°1′44.31ʺE, 36°50′4.78ʺN | 2700 | 110 | 30 |
| 103°0′5.48ʺE, 36°48′37.36ʺN | 2900 | 157 | 25 | |
| 102°59′52.33ʺE, 36°48′32.36ʺN | 3100 | 205 | 32 | |
| 中东段 Middle-east | 102°33′12.83ʺE, 37°23′2.28ʺN | 2700 | 250 | 30 |
| 102°33′18.07ʺE, 37°23′0.47ʺN | 2900 | 151 | 25 | |
| 102°33′48.44ʺE, 37°23′28.6ʺN | 3100 | 178 | 20 |
表 1 样地基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sites
| 地点 Sites | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect/(°) | 坡度 Slope/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东段 East | 103°1′44.31ʺE, 36°50′4.78ʺN | 2700 | 110 | 30 |
| 103°0′5.48ʺE, 36°48′37.36ʺN | 2900 | 157 | 25 | |
| 102°59′52.33ʺE, 36°48′32.36ʺN | 3100 | 205 | 32 | |
| 中东段 Middle-east | 102°33′12.83ʺE, 37°23′2.28ʺN | 2700 | 250 | 30 |
| 102°33′18.07ʺE, 37°23′0.47ʺN | 2900 | 151 | 25 | |
| 102°33′48.44ʺE, 37°23′28.6ʺN | 3100 | 178 | 20 |
| 地点 Sites | 海拔 Altitude/m | 物种 Species | 数量 Quantity/strain | 盖度 Coverage/% | 平均高度 Average height/m | 重要值 Important value/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东段 East | 2700 | 银露梅 P. glabra 甘蒙锦鸡儿 Caragana opulens 绢毛蔷薇 Rosa sericea 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 17±2.00 6±1.41 1±0.20 2±0.58 | 36.7±1.15 5.5±0.71 1.0±0.12 1.3±0.56 | 0.79±0.16 1.12±0.12 1.40±0.05 0.75±0.21 | 58.19±0.05 13.30±0.01 17.53±0.06 10.98±0.01 |
| 2900 | 鲜黄小檗 B. diaphana 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 西北蔷薇 Rosa davidii 金露梅 P. fruticosa 绢毛蔷薇 R. sericea 银露梅 P. glabra | 5±1.53 5±1.53 7±0.58 31±2.65 1±0.00 1±0.00 | 50.0±0.00 15.0±0.00 10.7±1.15 22.7±2.52 2.8±0.35 3.0±0.00 | 1.81±0.26 1.32±0.28 1.25±0.30 0.90±0.17 1.30±0.33 1.53±0.07 | 28.26±0.009 12.61±0.02 13.96±0.02 32.17±0.01 4.60±0.01 8.40±0.01 | |
| 3100 | 山生柳 S. oritrepha 烈香杜鹃 R. anthopogonoides 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鬼箭锦鸡儿 Caragana jubata | 28±2.65 25±1.73 20±1.53 10±2.00 3±1.00 | 23.3±1.53 53.3±1.00 16.0±2.65 10.3±1.53 10.3±1.53 | 1.42±0.07 1.00±0.18 0.82±0.28 0.88±0.26 1.22±0.28 | 26.40±0.009 31.47±0.001 18.02±0.009 12.35±0.01 11.76±0.02 | |
| 中东段 Middle-east | 2700 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鲜黄小檗 B. diaphana 银露梅 P. glabra | 25±2.65 12±1.41 11±0.58 1±0.00 | 26.3± 1.24 4.0±1.41 9.0±2.00 1.0±0.00 | 0.54±0.09 0.46±0.007 0.52±0.16 0.5±0.003 | 11.34±0.06 13.32±0.01 25.23±0.06 51.11±0.02 |
| 2900 | 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鲜黄小檗 Berberis diaphana 银露梅 P. glabra | 26±3.61 12±2.65 5±1.00 | 70.7±2.08 36.7±2.08 5±0.00 | 1.12±0.09 1.24±0.25 0.75±0.01 | 53.72±0.01 33.60±0.008 12.68±0.01 | |
| 3100 | 烈香杜鹃 R. anthopogonoides 雪层杜鹃 R. nivale 头花杜鹃 R. capitatum 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 山生柳 S. oritrepha | 3±0.00 45±1.53 24±1.53 7±0.71 9±1.00 11±0.58 | 7.5±0.70 50.0±1.73 31.0±1.15 5.0±0.00 3.0±0.58 12.0±1.00 | 1.33±0.18 0.96±0.08 1.07±0.09 0.95±0.01 0.65±0.04 1.36±0.14 | 6.86±0.002 37.99±0.03 24.80±0.03 5.81±0.005 8.30±0.02 16.24±0.02 | |
| 中段 Middle | 2700 | 银露梅 P. glabra 金露梅 P. fruticosa 鲜黄小檗 Berberis diaphana 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 13±0.58 8±1.15 3±1.15 3±0.71 | 11.0±1.00 6.0±1.73 1.2±0.76 2.5±0.71 | 0.66±0.13 0.48±0.12 0.73±0.17 0.51±0.04 | 45.85±0.05 28.45±0.03 16.67±0.02 9.03±0.02 |
| 2900 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 山生柳 S. oritrepha 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 16±2.08 10±2.08 3±1.00 | 12.0±2.08 8.7±2.00 1.0±0.00 | 0.48±0.08 0.63±0.02 0.53±0.007 | 46.32±0.02 38.37±0.01 15.31±0.008 | |
| 3100 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 34±1.41 13±3.51 | 39.0±1.41 3.5±1.50 | 0.62±0.12 0.44±0.03 | 73.82±0.01 26.18±0.001 |
表2 不同海拔灌丛群落结构变化
Table 2 The community structure changes of shrub at different elevations
| 地点 Sites | 海拔 Altitude/m | 物种 Species | 数量 Quantity/strain | 盖度 Coverage/% | 平均高度 Average height/m | 重要值 Important value/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东段 East | 2700 | 银露梅 P. glabra 甘蒙锦鸡儿 Caragana opulens 绢毛蔷薇 Rosa sericea 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 17±2.00 6±1.41 1±0.20 2±0.58 | 36.7±1.15 5.5±0.71 1.0±0.12 1.3±0.56 | 0.79±0.16 1.12±0.12 1.40±0.05 0.75±0.21 | 58.19±0.05 13.30±0.01 17.53±0.06 10.98±0.01 |
| 2900 | 鲜黄小檗 B. diaphana 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 西北蔷薇 Rosa davidii 金露梅 P. fruticosa 绢毛蔷薇 R. sericea 银露梅 P. glabra | 5±1.53 5±1.53 7±0.58 31±2.65 1±0.00 1±0.00 | 50.0±0.00 15.0±0.00 10.7±1.15 22.7±2.52 2.8±0.35 3.0±0.00 | 1.81±0.26 1.32±0.28 1.25±0.30 0.90±0.17 1.30±0.33 1.53±0.07 | 28.26±0.009 12.61±0.02 13.96±0.02 32.17±0.01 4.60±0.01 8.40±0.01 | |
| 3100 | 山生柳 S. oritrepha 烈香杜鹃 R. anthopogonoides 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鬼箭锦鸡儿 Caragana jubata | 28±2.65 25±1.73 20±1.53 10±2.00 3±1.00 | 23.3±1.53 53.3±1.00 16.0±2.65 10.3±1.53 10.3±1.53 | 1.42±0.07 1.00±0.18 0.82±0.28 0.88±0.26 1.22±0.28 | 26.40±0.009 31.47±0.001 18.02±0.009 12.35±0.01 11.76±0.02 | |
| 中东段 Middle-east | 2700 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鲜黄小檗 B. diaphana 银露梅 P. glabra | 25±2.65 12±1.41 11±0.58 1±0.00 | 26.3± 1.24 4.0±1.41 9.0±2.00 1.0±0.00 | 0.54±0.09 0.46±0.007 0.52±0.16 0.5±0.003 | 11.34±0.06 13.32±0.01 25.23±0.06 51.11±0.02 |
| 2900 | 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 鲜黄小檗 Berberis diaphana 银露梅 P. glabra | 26±3.61 12±2.65 5±1.00 | 70.7±2.08 36.7±2.08 5±0.00 | 1.12±0.09 1.24±0.25 0.75±0.01 | 53.72±0.01 33.60±0.008 12.68±0.01 | |
| 3100 | 烈香杜鹃 R. anthopogonoides 雪层杜鹃 R. nivale 头花杜鹃 R. capitatum 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina 山生柳 S. oritrepha | 3±0.00 45±1.53 24±1.53 7±0.71 9±1.00 11±0.58 | 7.5±0.70 50.0±1.73 31.0±1.15 5.0±0.00 3.0±0.58 12.0±1.00 | 1.33±0.18 0.96±0.08 1.07±0.09 0.95±0.01 0.65±0.04 1.36±0.14 | 6.86±0.002 37.99±0.03 24.80±0.03 5.81±0.005 8.30±0.02 16.24±0.02 | |
| 中段 Middle | 2700 | 银露梅 P. glabra 金露梅 P. fruticosa 鲜黄小檗 Berberis diaphana 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 13±0.58 8±1.15 3±1.15 3±0.71 | 11.0±1.00 6.0±1.73 1.2±0.76 2.5±0.71 | 0.66±0.13 0.48±0.12 0.73±0.17 0.51±0.04 | 45.85±0.05 28.45±0.03 16.67±0.02 9.03±0.02 |
| 2900 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 山生柳 S. oritrepha 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 16±2.08 10±2.08 3±1.00 | 12.0±2.08 8.7±2.00 1.0±0.00 | 0.48±0.08 0.63±0.02 0.53±0.007 | 46.32±0.02 38.37±0.01 15.31±0.008 | |
| 3100 | 金露梅 P. fruticosa 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 34±1.41 13±3.51 | 39.0±1.41 3.5±1.50 | 0.62±0.12 0.44±0.03 | 73.82±0.01 26.18±0.001 |
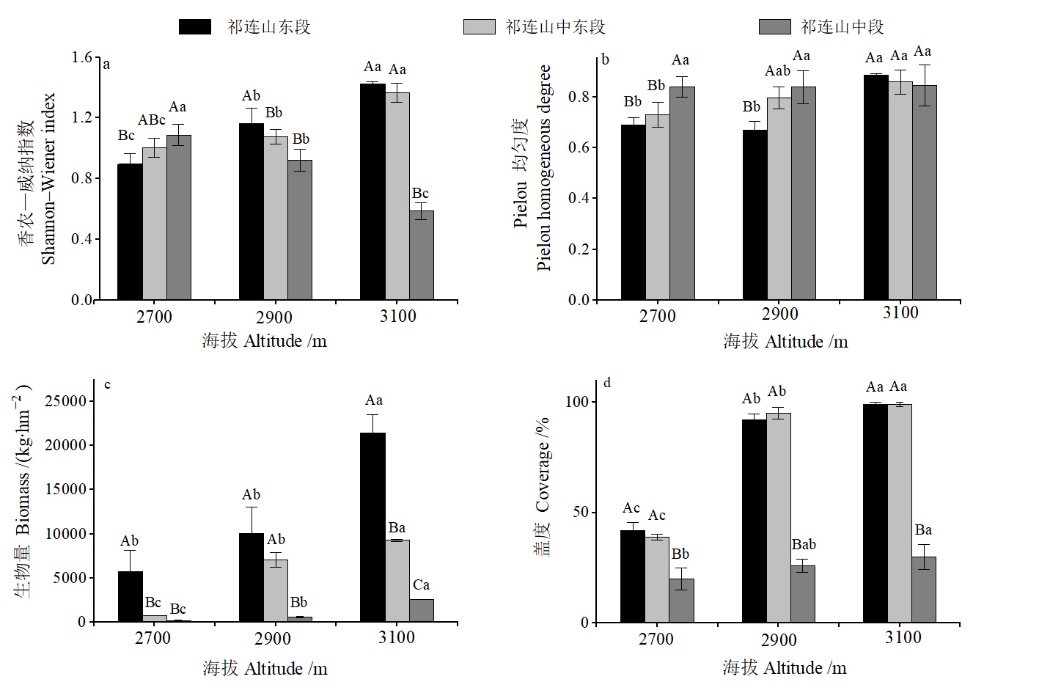
图2 香农—威纳指数(a)、Pielou均匀度(b)、地上生物量(c)、盖度(d)随海拔梯度的变化 n=3;不同小写字母表示同一经度、不同海拔高度差异显著(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示同一海拔高度、不同经度差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 2 Changes of Shannon-Wiener index (a), Pielou homogeneous degree (b), Biomass (c) and coverage (d) with altitude gradient n=3; Different lowercase letters indicated significant difference in the same longitude and different elevations (P<0.05). Different capital letters indicated significant difference at the same altitude and different longitude (P<0.05)
| 影响因子 Impact factor | 生物量 Biomass | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 盖度 Coverage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 82.871 | 0.000 | 106.131 | 0.000 | 13.659 | 0.000 | 402.137 | 0.000 |
| 经度 Longitude | 134.954 | 0.000 | 3.131 | 0.068 | 8.402 | 0.003 | 953.265 | 0.000 |
| 海拔×经度 Altitude & Longitude | 19.178 | 0.000 | 9.880 | 0.001 | 4.968 | 0.007 | 107.064 | 0.000 |
表3 海拔和经度对地上生物量、Shannon-Wiener指数、Pielou均匀度、盖度双因素分析
Table 3 Two-factor analysis of elevation and longitude on aboveground biomass, Shannon-Wiener index, Pielou homogeneous degree and Coverage
| 影响因子 Impact factor | 生物量 Biomass | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 盖度 Coverage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 82.871 | 0.000 | 106.131 | 0.000 | 13.659 | 0.000 | 402.137 | 0.000 |
| 经度 Longitude | 134.954 | 0.000 | 3.131 | 0.068 | 8.402 | 0.003 | 953.265 | 0.000 |
| 海拔×经度 Altitude & Longitude | 19.178 | 0.000 | 9.880 | 0.001 | 4.968 | 0.007 | 107.064 | 0.000 |
| Pearson相关性 Pearson correlation | 生物量 Biomass | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 盖度 Coverage | 海拔 Altitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物量 Biomass Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 1 | ||||
| 0.943** | 1 | ||||
| Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 0.855** | 0.776* | 1 | ||
| 盖度 Coverage | 0.740* | 0.872** | 0.455 | 1 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.926** | 0.965** | 0.762* | 0.913** | 1 |
表4 灌丛生物量,Shannon-Wiener指数,Pielou均匀度,盖度,海拔相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of shrub biomass, Shannon-Wiener index, Pielou homogeneous degree, Coverage and Altitude
| Pearson相关性 Pearson correlation | 生物量 Biomass | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 盖度 Coverage | 海拔 Altitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物量 Biomass Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 1 | ||||
| 0.943** | 1 | ||||
| Pielou均匀度 Pielou homogeneous degree | 0.855** | 0.776* | 1 | ||
| 盖度 Coverage | 0.740* | 0.872** | 0.455 | 1 | |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.926** | 0.965** | 0.762* | 0.913** | 1 |
| [1] |
DORJI T, MOE S R, KLEINl J A, et al., 2014. Plant species richness, evenness, and composition along environmental gradients in an alpine meadow grazing ecosystem in central Tibet, China[J]. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research, 46(2): 308-326.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
EVANS R D, FONDA R W, 1990. The influence of snow on sub-alpine meadow community pattern, North-Cascades, Washington[J]. Canadian Journal of Botany, 68(1): 212-220.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GASTON K, 2000. Global patterns in biodiversity[J]. Nature, 405(6783): 220-227.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PIAO S L, FANG J Y, CIAIS P, et al., 2009. The carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems in China[J]. Nature, 458(7241): 1009-1013.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
RAHBEK C, 2005. The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns[J]. Ecology Letters, 8(2): 224-239.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XU Z F, HU T X, WANG K Y, et al., 2009. Short-term responses of phenology, shoot growth and leaf traits of four alpine shrubs in a timberline ecotone to simulated global warming, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Plant Species Biology, 24(1): 27-34.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 蔡蔚, 刘学录, 宋洁, 等, 2020. 基于土地利用变化的生态系统服务价值动态研究--以祁连山自然保护区为例[J]. 国土与自然资源研究(4): 32-37. |
| CAI W, LIU X L, SONG J, et al., 2020. Dynamic research on ecosystem service value based on land use change: A case study of Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve[J]. Territory & Natural Resources Study (4): 32-37. | |
| [8] | 陈泓, 黎燕琼, 郑绍伟, 等, 2007. 岷江上游干旱河谷灌丛生物量与坡向及海拔梯度相关性研究[J]. 成都大学学报: 自然科学版, 26(1): 14-18. |
| CHEN H, LI Y Q, ZHENG S W, et al., 2007. Research on the correlations of shrub biomass with slope-aspect and altitude in dry valley of the upper reach of the Minjiang River[J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition), 26(1): 14-18. | |
| [9] | 陈祖刚, 巴图娜存, 徐芝英, 等, 2014. 基于数码相机的草地植被盖度测量方法对比研究[J]. 草业学报, 23(6): 20-27. |
| CHEN Z G, BATU N C, XU Z Y, et al., 2014. Measuring grassland vegetation cover using digital camera images[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 23(6): 20-27. | |
| [10] | 邓清月, 张晓龙, 牛俊杰, 等, 2019. 晋西北饮马池山植物群落物种多样性沿海拔梯度的变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(5): 865-872. |
| DENG Q Y, ZHANG X L, NIU J J, et al., 2019. Species diversity of plant communities along an altitude gradient in Yinmachi Mountain, northwestern Shanxi, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 865-872. | |
| [11] | 邓少福, 2013. 祁连山气候变化对植被的影响研究 (2000-2011)[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学: 34-38. |
| DENG S F, 2013. Impacts of climate change on vegetation in Qilian Mountains from 2000 to 2011 [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou university: 34-38. | |
| [12] | 丁松爽, 苏培玺, 2010. 黑河上游祁连山区植物群落随海拔生境的变化特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 32(4): 829-836. |
| DING S S, SU P X, 2010. Altitudinal variation characteristics of plant community on tne upper reaches of Heihe River in tne Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 32(4): 829-836. | |
| [13] | 方精云, 黄耀, 朱江玲, 等, 2015. 森林生态系统碳收支及其影响机制[J]. 中国基础科学, 17(3): 20-25. |
| FANG J Y, HUANG Y, ZHU J L, et al., 2015. Carbon budget of forest ecosystems and its driving forces[J]. China Basic Science, 17(3): 20-25. | |
| [14] | 付建新, 曹广超, 郭文炯, 2020. 1998-2017年祁连山南坡不同海拔、坡度和坡向生长季NDVI变化及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(4): 1203-1212. |
| FU J X, CAO G C, GUO W J, 2020. Changes of NDVI of growing season at different elevations, slopes, slope aspects and its relationship with meteorological factors in the southern slope of the Qilian Mountains, China from 1998 to 2017 [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(4): 1203-1212. | |
| [15] |
胡会峰, 王志恒, 刘国华, 等, 2006. 中国主要灌丛植被碳储量[J]. 植物生态学报, 30(4): 539-544.
DOI |
| HU H F, WANG Z H, LIU G H, et al., 2006. Vegetation carbon storage of major shrublands in China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 30(4): 539-544. | |
| [16] | 梁倍, 邸利, 赵传燕, 等, 2013. 祁连山天涝池流域典型灌丛地上生物量沿海拔梯度变化规律的研究[J]. 草地学报, 21(4): 664-669. |
| LIANG B, DI L, ZHAO C Y, et al., 2013. Altitude distribution of aboveground biomass of typical shrubs in the Tianlaochi watershed of Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 21(4): 664-669. | |
| [17] | 雷蕾, 刘贤德, 王顺利, 等, 2011. 祁连山高山灌丛生物量分配规律及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(11): 1602-1607. |
| LEI L, LIU X D, WANG S L, et al., 2011. Assignment rule of alpine shrubs biomass and its relationships to environmental factors in Qilian Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(11): 1602-1607. | |
| [18] | 雷蕾, 2012. 祁连山高山灌丛生物量沿海拔梯度分配特征研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学: 12-42. |
| LEI L, 2012. Distributon character of alpine shrubs biomass along an elevation gradient in Qilian mountains[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University: 12-42. | |
| [19] | 刘国华, 马克明, 傅伯杰, 等, 2003. 岷江干旱河谷主要灌丛类型地上生物量研究[J]. 生态学报, 23(9): 1757-1764. |
| LIU G H, MA K M, FU B J, et al., 2003. Aboveground biomass of main shrubs in dry valley of Minjiang River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(9): 1757-1764. | |
| [20] | 刘玉祯, 曹文侠, 王金兰, 等, 2019. 祁连山东段不同类型灌丛斑块土壤特征对围封的响应[J]. 草业学报, 28(11): 32-45. |
| LIU Y Z, CAO W X, WANG J L, et al., 2019. Response of soil characteristics of different types of shrub patches to enclosure on eastern Qilian Mountain[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 28(11): 32-45. | |
| [21] | 罗黎鸣, 苗彦军, 武建双, 等, 2014. 拉萨河谷山地灌丛草地物种多样性随海拔升高的变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 23(6): 320-326. |
| LUO L M, MIAO Y J, WU J S, et al., 2014. Variation in the biodiversity of montane shrub grassland communities along an altitudinal gradient in Lhasa River basin valley[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 23(6): 320-326. | |
| [22] | 齐鹏, 刘贤德, 赵维俊, 等, 2015. 祁连山中段青海云杉林土壤养分特征[J]. 山地学报, 33(5): 538-545. |
| QI P, LIU X D, ZHAO W J, et al., 2015. Soil nutrient characteristics of Picea crassifolia forest in the middle segment of Qilian Mountain[J]. Mountain Research, 33(5): 538-545. | |
| [23] | 唐志红, 尉秋实, 刘虎俊, 等, 2020. 祁连山东段高寒植被群落特征及其与地形气候因子关系研究[J]. 生态学报, 40(1): 223-232. |
| TANG Z H, WEI Q S, LIU H J, et al., 2020. Characteristics of alpine vegetation community and its relationship to topographic climmate factors in the eastern Qilian mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1): 223-232. | |
| [24] | 王飞, 屠彩芸, 曹秀文, 等, 2018. 白龙江干旱河谷不同坡向主要灌丛群落随海拔梯度变化的物种多样性研究[J]. 植物研究, 38(1): 26-36. |
| WANG F, TU C Y, CAO X W, et al., 2018. The different altitude gradient change rules of the main shrub community in arid valleys of the Bailongjiang river with different slope[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 38(1): 26-36. | |
| [25] |
王晶, 张钦弟, 许强, 等, 2016. 山西庞泉沟银露梅群落物种多样性的海拔格局[J]. 植物学报, 51(3): 335-342.
DOI |
| WANG J, ZHANG Q D, XU Q, et al., 2016. Elevational patterns of community species diversity of Potentilla glabra in Pangquangou of Shanxi province[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 51(3): 335-342. | |
| [26] | 王金兰, 曹文侠, 张德罡, 等, 2019. 东祁连山高寒杜鹃灌丛群落结构和物种多样性对海拔梯度的响应[J]. 草原与草坪, 39(5): 1-9. |
| WANG J L, CAO W X, ZHANG D G, et al., 2019. Structure and species diversity of Rhododendron shrub-herb community and its response to altitude gradients in eastern Qilian Mountains[J]. Grassland and Turf, 39(5): 1-9. | |
| [27] | 温静, 张世雄, 杨晓艳, 等, 2019. 青藏高原高寒草地物种多样性的海拔梯度格局及其对模拟增温的响应[J]. 农学学报, 9(4): 66-73. |
| WEN J, ZHANG S X, YANG X Y, et al., 2019. Species diversity in alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: altitudinal gradient pattern and its response to simulated warming[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 9(4): 66-73. | |
| [28] | 武龙庆, 金铭, 敬文茂, 等, 2021. 祁连山肃南县大野口至小孤山公路边坡生态防护措施探索[J]. 农业与技术, 41(6): 127-130. |
| WU L Q, JIN M, JING W M, et al., 2021. Exploration of ecological protection measures for slope of highway from Dayekou to Xiaogushan in Sunan County, Qilian Mountains[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 41(6): 127-130. | |
| [29] | 占玉芳, 马力, 滕玉风, 等, 2015. 祁连圆柏群落物种多样性的海拔梯度效应研究[J]. 中国水土保持 (8): 52-55, 77. |
| ZFAN Y F, MA L, TENG Y F, et al., 2015. Altitude gradient effect of species diversity in Sabina przewalskii Community[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China (8): 52-55, 77. | |
| [30] | 赵维俊, 敬文茂, 赵永宏, 等 2017. 祁连山大野口流域典型灌丛植物与土壤中氮磷的化学计量特征[J]. 土壤, 49(3): 572-579. |
| ZHAO W J, JING W M, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2017. Nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of plants and soils of typical shrubs in Dayekou Basin of Qilian Mountains[J]. Soil, 49(3): 572-579. |
| [1] | 王雪梅, 杨雪峰, 赵枫, 安柏耸, 黄晓宇. 基于机器学习算法的干旱区绿洲地上生物量估算[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1007-1015. |
| [2] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [3] | 李海鹏, 黄月华, 孙晓东, 曹启民, 符芳兴, 孙楚涵. 海南农田不同质地砖红壤及其细菌群落与番茄青枯病发生的关联分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1062-1069. |
| [4] | 陈俊芳, 吴宪, 刘啸林, 刘娟, 杨佳绒, 刘宇. 不同土壤水分下元素化学计量对微生物多样性的塑造特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [5] | 姜永伟, 丁振军, 袁俊斌, 张峥, 李杨, 问青春, 王业耀, 金小伟. 辽宁省主要河流底栖动物群落结构及水质评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [6] | 李阳, 侯志勇, 陈薇, 于晓英, 谢永宏, 黄鑫, 谭佩阳, 李继承, 黎尚林, 杨辉. 大围山高山湿地植物多样性与区系组成研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [7] | 李善家, 王兴敏, 刘海锋, 孙梦格, 雷雨昕. 河西走廊荒漠植物多样性及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [8] | 秦浩, 李蒙爱, 高劲, 陈凯龙, 张殷波, 张峰. 芦芽山不同海拔灌丛土壤细菌群落组成和多样性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [9] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [10] | 宋志斌, 周佳诚, 谭路, 唐涛. 高原河流着生藻类群落沿海拔梯度的变化特征--以西藏黑曲、雪曲为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 274-282. |
| [11] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [12] | 李威闻, 黄金权, 齐瑜洁, 刘小岚, 刘纪根, 毛治超, 高绣纺. 土壤侵蚀条件下土壤微生物生物量碳含量变化及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 47-55. |
| [13] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [14] | 黄伟佳, 刘春, 刘岳, 黄斌, 李定强, 袁再健. 南岭山地不同海拔土壤生态化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [15] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
