生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1754-1764.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.005
肖国举1,2( ), 李秀静2, 郭占强2, 胡延斌3, 王静1
), 李秀静2, 郭占强2, 胡延斌3, 王静1
收稿日期:2021-11-28
出版日期:2022-09-18
发布日期:2022-11-07
作者简介:肖国举(1972年生),男,研究员,博士,主要从事全球气候变化及其对农业生态系统的影响研究。E-mail: xiaoguoju1972@163.com
基金资助:
XIAO Guoju1,2( ), LI Xiujing2, GUO Zhanqiang2, HU Yanbin3, WANG Jing1
), LI Xiujing2, GUO Zhanqiang2, HU Yanbin3, WANG Jing1
Received:2021-11-28
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
摘要:
土壤有机碳是作物生长发育的根基,也是陆地重要的碳汇,在全球碳平衡中起着关键的作用。2017-2020年选择宁夏贺兰山东麓生态试验研究区玉米(Zea mays L.)农田生态系统,采用棋盘式区域布点,GPS定点标记并采集样品,开展土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响研究。研究表明玉米净光合速率随土壤有机碳的增加而升高,蒸腾速率随土壤有机碳的增加表现为先减后增;气孔导度与土壤有机碳呈正相关关系,胞间CO2浓度与土壤有机碳呈负相关关系;叶片水分利用效率在拔节期、大喇叭口期和成熟期,随土壤有机碳的增加而波动增加;叶绿素在拔节期与大喇叭口期,随土壤有机碳的增加而波动升高。玉米穗长、穗粗,穗粒数、穗质量,根、茎、叶、穗干质量,分别随土壤有机碳的增加而增加。土壤有机碳从2.45 g∙kg-1增加到13.52 g∙kg-1,玉米穗长与穗粗分别增加44.3%与21.0%,穗粒数与穗质量分别增加49.3%与70.5%,根、茎、叶、穗干质量分别增加61.8%、30.2%、27.1%、19.0%。土壤有机碳为10.5-12.0 g∙kg-1时,玉米产量达到较高的范围15.5-15.7 t∙hm-2;土壤有机碳超过12.0 g∙kg-1,产量呈现下降趋势。土壤有机碳超过11.5 g∙kg-1,玉米水分利用效率呈现下降。贺兰山东麓黄河灌溉生态试验示范区,农田土壤有机碳保持10.0-12.0 g∙kg-1,能够有效促进玉米生长发育,提高产量及水分利用,是较为合理的阈值范围。
中图分类号:
肖国举, 李秀静, 郭占强, 胡延斌, 王静. 贺兰山东麓土壤有机碳对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764.
XIAO Guoju, LI Xiujing, GUO Zhanqiang, HU Yanbin, WANG Jing. Effects of Soil Organic Carbon on Maize Growth and Water Use at the Eastern Foot of Helan Mountain in Ningxia[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1754-1764.
| 参数 Parameters | 年份 Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation/mm | 195.3 | 280.2 | 145.5 | 186.5 |
| 玉米全生育期降水量 Precipitation during WM/mm | 148.1 | 210.5 | 110.6 | 139.8 |
| 玉米全生育期灌溉量 Irrigation amount during WM/mm | 680.0 | 620.0 | 740.0 | 720.0 |
| 玉米全生育期耗水量 Water consumption during WM/mm | 828.1 | 830.5 | 858.6 | 860.8 |
表1 玉米全生育期降水量、灌溉量及耗水量
Table 1 Precipitation, irrigation amount and water consumption during the whole growth period of corn
| 参数 Parameters | 年份 Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| 年降水量 Annual precipitation/mm | 195.3 | 280.2 | 145.5 | 186.5 |
| 玉米全生育期降水量 Precipitation during WM/mm | 148.1 | 210.5 | 110.6 | 139.8 |
| 玉米全生育期灌溉量 Irrigation amount during WM/mm | 680.0 | 620.0 | 740.0 | 720.0 |
| 玉米全生育期耗水量 Water consumption during WM/mm | 828.1 | 830.5 | 858.6 | 860.8 |
| 理化性质 Physicochemical properties | 年份 Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| 全氮 w(Total nitrogen)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.68 |
| 全磷 w(Total phosphorus)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.68 |
| 碱解氮 w(Alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 48.14 | 57.13 | 72.56 | 66.76 |
| 速效磷 w(Available phosphorus)/(mg∙kg-1) | 13.46 | 17.43 | 21.20 | 19.84 |
| 速效钾 w(Available potassium)/(mg∙kg-1) | 257.97 | 196.61 | 198.11 | 204.78 |
| pH值 Potential of hydrogen | 8.01 | 8.15 | 9.04 | 9.01 |
| 全盐 w(Total salt)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
表2 2017-2020年试验基地玉米耕层土壤理化性质
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties of soil plough layer in field of corn in 2017-2020
| 理化性质 Physicochemical properties | 年份 Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| 全氮 w(Total nitrogen)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.68 |
| 全磷 w(Total phosphorus)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.68 |
| 碱解氮 w(Alkali hydrolyzed nitrogen)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 48.14 | 57.13 | 72.56 | 66.76 |
| 速效磷 w(Available phosphorus)/(mg∙kg-1) | 13.46 | 17.43 | 21.20 | 19.84 |
| 速效钾 w(Available potassium)/(mg∙kg-1) | 257.97 | 196.61 | 198.11 | 204.78 |
| pH值 Potential of hydrogen | 8.01 | 8.15 | 9.04 | 9.01 |
| 全盐 w(Total salt)/(g∙kg-1) | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
| 土壤有机碳分类 Classification of Soil organic carbon/ (g∙kg-1) | 土壤有机碳含量 Soil organic carbon content/(g∙kg-1) | 样品数 Number of samples | 占总样品比例 Proportion of total samples/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 平均 | ||||
| T1 | 0.00-1.00 | 0.84±0.06 | 0.84±0.09 | 0.88±0.01 | 0.88±0.03 | 2.45 | 24 | 16.8 |
| 1.00-2.00 | 1.63±0.30 | 1.64±0.36 | 1.84±0.66 | 1.94±0.36 | ||||
| 2.00-3.00 | 2.63±0.06 | 2.63±0.19 | 2.73±0.01 | 2.83±0.25 | ||||
| T2 | 3.00-4.00 | 3.52±0.08 | 3.58±0.08 | 3.60±0.12 | 3.55±0.62 | 4.95 | 28 | 19.4 |
| 4.00-5.00 | 4.26±0.10 | 4.36±0.13 | 4.44±1.08 | 4.53±0.58 | ||||
| 5.00-6.00 | 5.25±1.05 | 5.35±0.25 | 5.53±1.15 | 5.63±1.41 | ||||
| T3 | 6.00-7.00 | 6.49±1.12 | 6.64±0.17 | 6.64±0.19 | 6.65±0.93 | 7.95 | 32 | 22.2 |
| 7.00-8.00 | 7.43±0.17 | 7.58±0.12 | 7.61±0.07 | 7.68±0.29 | ||||
| 8.00-9.00 | 8.34±0.09 | 8.48±0.01 | 8.48±0.06 | 8.53±0.21 | ||||
| T4 | 9.00-0.00 | 9.17±0.78 | 9.37±0.75 | 9.48±0.27 | 9.48±0.22 | 11.12 | 32 | 22.2 |
| 10.00-11.00 | 10.27±0.54 | 10.47±0.54 | 10.48±0.20 | 10.48±0.28 | ||||
| 11.00-12.00 | 11.26±0.92 | 11.26±0.98 | 11.40±0.92 | 11.42±0.90 | ||||
| T5 | 12.00-13.00 | 12.06±0.15 | 12.26±0.35 | 12.35±0.15 | 12.36±0.25 | 13.52 | 28 | 19.4 |
| 13.00-14.00 | 13.32±0.18 | 13.34±0.19 | 13.46±0.20 | 13.62±0.22 | ||||
| 14.00-15.00 | 14.12±0.18 | 14.42±0.28 | 14.62±0.18 | 14.62±0.48 | ||||
| 样品数 Number of samples | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | - | 144 | 100 | |
表3 2017-2020年土壤耕作层有机碳样品数及分级
Table 3 Sampling number and classification of soil organic carbon in tillage layer from 2017 to 2020
| 土壤有机碳分类 Classification of Soil organic carbon/ (g∙kg-1) | 土壤有机碳含量 Soil organic carbon content/(g∙kg-1) | 样品数 Number of samples | 占总样品比例 Proportion of total samples/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 平均 | ||||
| T1 | 0.00-1.00 | 0.84±0.06 | 0.84±0.09 | 0.88±0.01 | 0.88±0.03 | 2.45 | 24 | 16.8 |
| 1.00-2.00 | 1.63±0.30 | 1.64±0.36 | 1.84±0.66 | 1.94±0.36 | ||||
| 2.00-3.00 | 2.63±0.06 | 2.63±0.19 | 2.73±0.01 | 2.83±0.25 | ||||
| T2 | 3.00-4.00 | 3.52±0.08 | 3.58±0.08 | 3.60±0.12 | 3.55±0.62 | 4.95 | 28 | 19.4 |
| 4.00-5.00 | 4.26±0.10 | 4.36±0.13 | 4.44±1.08 | 4.53±0.58 | ||||
| 5.00-6.00 | 5.25±1.05 | 5.35±0.25 | 5.53±1.15 | 5.63±1.41 | ||||
| T3 | 6.00-7.00 | 6.49±1.12 | 6.64±0.17 | 6.64±0.19 | 6.65±0.93 | 7.95 | 32 | 22.2 |
| 7.00-8.00 | 7.43±0.17 | 7.58±0.12 | 7.61±0.07 | 7.68±0.29 | ||||
| 8.00-9.00 | 8.34±0.09 | 8.48±0.01 | 8.48±0.06 | 8.53±0.21 | ||||
| T4 | 9.00-0.00 | 9.17±0.78 | 9.37±0.75 | 9.48±0.27 | 9.48±0.22 | 11.12 | 32 | 22.2 |
| 10.00-11.00 | 10.27±0.54 | 10.47±0.54 | 10.48±0.20 | 10.48±0.28 | ||||
| 11.00-12.00 | 11.26±0.92 | 11.26±0.98 | 11.40±0.92 | 11.42±0.90 | ||||
| T5 | 12.00-13.00 | 12.06±0.15 | 12.26±0.35 | 12.35±0.15 | 12.36±0.25 | 13.52 | 28 | 19.4 |
| 13.00-14.00 | 13.32±0.18 | 13.34±0.19 | 13.46±0.20 | 13.62±0.22 | ||||
| 14.00-15.00 | 14.12±0.18 | 14.42±0.28 | 14.62±0.18 | 14.62±0.48 | ||||
| 样品数 Number of samples | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | - | 144 | 100 | |
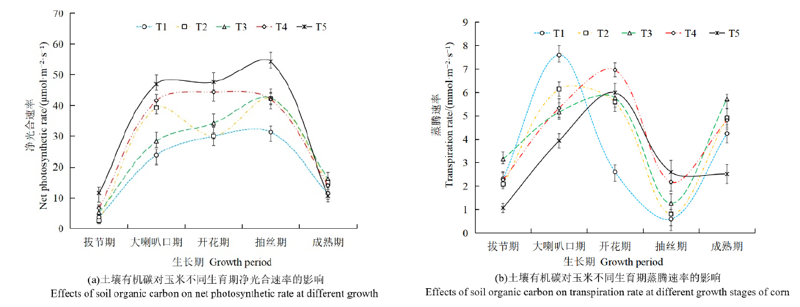
图2 土壤有机碳对玉米不同生育期净光合速率与蒸腾速率的影响
Figure 2 Effects of soil organic carbon on net photosynthetic rate and transpiration rate at different growth stages of corn
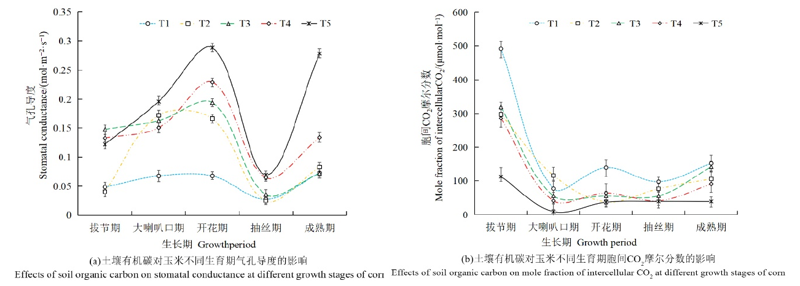
图3 土壤有机碳对玉米不同生育期气孔导度与胞间CO2摩尔分数的影响
Figure 3 Effects of soil organic carbon on stomatal conductance and mole fraction of intercellular CO2 at different growth stages of corn
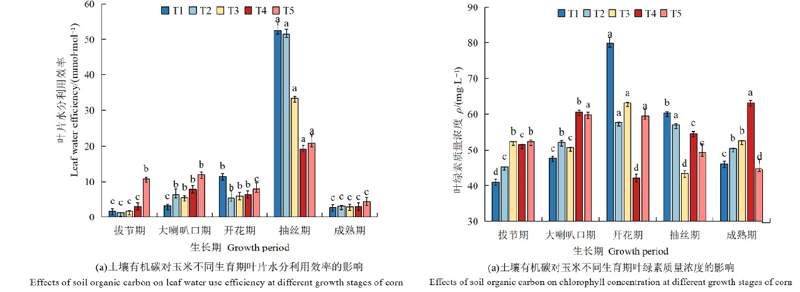
图4 土壤有机碳对玉米不同生育期叶片水分利用效率与叶绿素质量浓度的影响 小写字母代表在5%下差异显著
Figure 4 Effects of soil organic carbon on leaf water use efficiency and chlorophyll at different growth stages of corn Small letters represent significant differences under 5%
| 测定指标 Measure the indicators | 拔节期 Jointing | 大口期 Opening | 开花期 Flowering | 抽丝期 Silking | 成熟期 Maturing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 h/cm | 0.829 | 0.815 | 0.759 | 0.759 | 0.768 |
| 胸径 d/cm | 0.815 | 0.900 | 0.900 | -0.786 | 0.754 |
| 单株叶面积 Leaf area per/cm2 | 0.519 | 0.516 | -0.340 | 0.014 | -0.130 |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | -0.130 | -0.340 | 0.014 | -0.257 | -0.257 |
表4 土壤有机碳与玉米生长发育的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between soil organic carbon and growth at different growth stages of corn
| 测定指标 Measure the indicators | 拔节期 Jointing | 大口期 Opening | 开花期 Flowering | 抽丝期 Silking | 成熟期 Maturing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高 h/cm | 0.829 | 0.815 | 0.759 | 0.759 | 0.768 |
| 胸径 d/cm | 0.815 | 0.900 | 0.900 | -0.786 | 0.754 |
| 单株叶面积 Leaf area per/cm2 | 0.519 | 0.516 | -0.340 | 0.014 | -0.130 |
| 叶面积指数 Leaf area index | -0.130 | -0.340 | 0.014 | -0.257 | -0.257 |
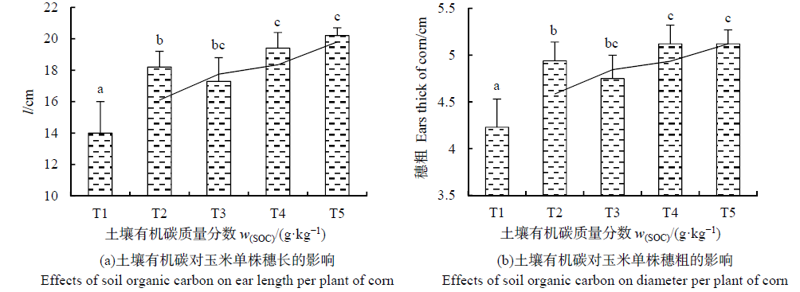
图7 土壤有机碳对玉米单株穗长和穗粗的影响 每行中字母代表在5%下差异显著,a相对于b有显著性差异。下同
Figure 7 Effects of soil organic carbon on ear length and diameter per plant of corn Different letters in a column indicate significant difference (P<0.05). The same below
| [1] |
BOND-LAMBERTY B, THOMSON A, 2010. Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record[J]. Nature, 464(7288): 579-582.
DOI URL |
| [2] | IPCC, 2013. Summary for policymakers//Climate Change 2013:The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M]. Cambridge & New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [3] |
LIU S W, CHENG J, WANG C, et al., 2018. Climatic role of terrestrial ecosystem under elevated CO2: A bottom-up greenhouse gases budget[J]. Ecology Letters, 21(1): 1108-1118.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SCHLESINGER W H, 1990. Evidence from chronosequence studies for a low carbon storage potential of soils[J]. Nature, 348: 232-234.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WILDING L P, LIN H, 2005. Advancing the frontiers of soil science towards a geoscience[J]. Geoderma, 131(3): 257-274.
DOI URL |
| [6] | World Meteorological Organization, 2019. The Global Climate by 2015-2019[R]. Geneva: WMO Report: 1-50. |
| [7] | WU D F, 2020. Effects of combined organic-inorganic fertilization on quality and water use efficiency of spring maize under equal nitrogen fertilization[J]. Asian Agricultural Research, 12(5): 42-46. |
| [8] |
XIA L L, LAM S K, CHEN D L, et al., 2017. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 23(7): 1917-1925.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
XIAO G J, HU Y B, ZHANG Q, et al., 2020. Impact of cultivation on soil organic carbon and carbon sequestration potential in semiarid regions of China[J]. Soil Use and Management, 36(1): 83-92.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 艾俊国, 孟瑶, 于琳, 等, 2015. 沼肥与化肥配施对东北春玉米光合生理特性及产量品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (4): 59-65. |
| AI J G, MENG Y, YU L, et al., 2015. Effects of combined application of biogas manure and chemical fertilizer on leaf photosynthesis, yield and quality of spring maize in Northeast of China[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (4): 59-65. | |
| [11] | 鲍士旦, 2018. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 7. |
| BAO S D, 2018. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 7. | |
| [12] | 陈晓芬, 刘明, 江春玉, 等, 2019. 红壤性水稻土不同粒级团聚体有机碳矿化及其温度敏感性[J]. 土壤学报, 96(5): 1118-1127. |
| CHEN X F, LIU M, JIANG C Y, et al., 2019. Mineralization of soil organic carbon and its sensitivity to temperature in soil aggregates, relative to particle size in red paddy soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 96(5): 1118-1127. | |
| [13] | 刁生鹏, 高宇, 张雄, 等, 2018. 有机肥施用对玉米生长发育及水分利用的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 46(4): 58-63. |
| DIAO S P, GAO Y, ZHANG X, et al., 2018. Effects of organic fertilizer on growth and development and water use of maize[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 46(4): 58-63. | |
| [14] | 高飞, 贾志宽, 路文涛, 等, 2011. 秸秆不同还田量对宁南旱区土壤水分、玉米生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 31(3): 777-0783. |
| GAO F, JIA Z K, LU W T, et al., 2011. Effects of different straw returning treatments on soil water, maize growth and photosynthetic characteristics in the semi-arid area of southern Ningxia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(3): 777-0783. | |
| [15] | 郭洋, 李香兰, 王秀君, 等, 2016. 干旱半干旱区农田土壤碳垂直剖面分布特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 53(6): 1433-1443. |
| GUO Y, LI X L, WANG X J, et al., 2016. Profile distribution of soil inorganic and organic carbon in farmland in arid and semi-arid areas of China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(6): 1433-1443. | |
| [16] | 寒冰, 王效科, 逯飞, 等, 2008. 中国农田土壤生态系统固碳现状和潜力[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 612-615. |
| HAN B, WANG X K, LU F, et al., 2008. Soil carbon sequestration and its potential by cropland ecosystems in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(2): 612-615. | |
| [17] | 贺美, 王迎春, 王立刚, 等, 2017. 应用DNDC模型分析东北黑土有机碳演变规律及其与作物产量之间的协同关系[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(1): 9-19. |
| HE M, WANG Y C, WANG L G, et al., 2017. Using DNDC model to simulate black soil organic carbon dynamics as well as its coordinate relationship with crop yield[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 23(1): 9-19. | |
| [18] | 李北齐, 王倡宪, 孟瑶, 等, 2011. 生物有机肥对盐碱土壤养分及玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 27(21): 182-186. |
| LI B Q, WANG C X, MENG Y, et al., 2011. Effects of microbial organic fertilizer on saline-alkalisoil nutrient and maize production[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27(21): 182-186. | |
| [19] | 李飞跃, 汪建飞, 2013. 中国粮食作物秸秆焚烧排碳量及转化生物炭固碳量的估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 29(14): 1-5. |
| LI F Y, WANG J F, 2013. Estimation of carbon emission from burning and carbon sequestration from biochar producing using crop straw in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(14): 1-5. | |
| [20] | 慕平, 张恩和, 王汉宁, 等, 2012. 不同年限全量玉米秸秆还田对玉米生长发育及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 20(3): 291-296. |
|
MU P, ZHANG E H, WANG H N, et al., 2012. Effects of continuous straw return to soil on maize growth and soil chemical and physical characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20(3): 291-296.
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
潘根兴, 赵其国, 2005. 我国农田土壤碳库演变研究: 全球变化和国家粮食安全[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(4): 384-393.
DOI |
| PAN G X, ZHAO Q G, 2005. Study on evolution of organic carbon stock in agricultural soils of China: Facing the challenge of global change and food security[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 20(4): 384-393. | |
| [22] | 彭辉辉, 刘强, 荣湘民, 等, 2016. 生物炭、有机肥与化肥配施对春玉米光合特征的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 44(7): 132-135. |
| PENG H H, LIU Q, RONG X M, et al., 2016. Effect of biochar, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer distribution on the photosynthetic properties of spring maize[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 44(7): 132-135. | |
| [23] |
秦大河, 2014. 气候变化科学与人类可持续发展[J]. 地理科学进展, 33(7): 874-883.
DOI |
|
QIN D H, 2014. Climate change science and sustainable development[J]. Progress in Geography, 33(7): 874-883.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 邱建军, 王立刚, 李虎, 等, 2009. 农田土壤有机碳含量对作物产量影响的模拟研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 42(1): 154-161. |
| QIU J J, WANG L G, LI H, et al., 2009. Modeling the impacts of soil organic carbon content of croplands on crop yields in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 42(1): 154-161. | |
| [25] | 王宁, 闫洪奎, 王君, 等, 2007. 不同量秸秆还田对玉米生长发育及产量影响的研究[J]. 玉米科学, 15(5): 100-103. |
| WANG N, YAN H K, WANG J, et al., 2007. Research on effects of different amount straws return to field on growth development and yield of maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 15(5): 100-103. | |
| [26] | 王卫, 李秀彬, 2002. 中国耕地有机质含量变化对土地生产力影响的定量研究[J]. 地理科学, 22(1): 24-28. |
|
WANG W, LI X B, 2002. Study on the marginal productivity of cultivated land with change of soil organic matter in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 22(1): 24-28.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 王晓娟, 贾志宽, 梁连友, 等, 2012. 不同有机肥量对旱地玉米光合特性和产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 23(2): 419-425. |
| WANG X J, JIA Z K, LIANG L Y, et al., 2012. Effects of organic fertilizer application rate on leaf photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield of dryland maize[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(2): 419-425. | |
| [28] | 吴萌, 李忠佩, 冯有智, 等, 2016. 长期施肥处理下不同类型水稻土有机碳矿化的动态差异[J]. 中国农业科学, 49(9): 1705-1714 |
| WU M, LI Z P, FENG Y Z, et al., 2016. Dynamic differences of organic carbon mineralization in different types of paddy soil under long-term located fertilization[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49(9): 1705-1714. | |
| [29] | 熊正琴, 张晓旭, 2017. 氮肥高效施用在低碳农业中的关键作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23(6): 1433-1440. |
| XIONG Z Q, ZHANG X X, 2017. Key role of efficient nitrogen application in low carbon agriculture[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 23(6): 1433-1440. | |
| [30] | 余健, 房莉, 卞正富, 等, 2014. 土壤碳库构成研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 34(17): 4830-4831. |
| YU J, FANG L, BIAN Z F, et al., 2014. A review of the composition of soil carbon pool[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(17): 4830-4831. | |
| [31] | 岳杨, 董本春, 李岩, 等, 2020. 不同秸秆还田方式对春玉米生长特性及产量的影响[J]. 农业科技通讯 (10): 41-43, 48. |
| YUE Y, DONG B C, LI Y, et al., 2020. Effects of different straw returning methods on growth characteristics and yield of spring maize[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology (10): 41-43, 48. | |
| [32] | 张维理, KOLBE H, 张认连, 2020. 土壤有机碳作用及转化机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(2): 317-331. |
| ZHANG W L, KOLBE H, ZHANG R L, 2020. Research progress of SOC functions and transformation mechanisms[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(2): 317-331. | |
| [33] | 张影, 刘星, 焦瑞锋, 等, 2017. 生物质炭与有机物料配施的土壤培肥效果及对玉米生长的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 25(9): 1287-1297. |
| ZHANG Y, LIU X, JIAO R F, et al., 2017. Effects of combined biochar and organic matter on soil fertility and maize growth[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 25(9): 1287-1297. |
| [1] | 陈科屹, 林田苗, 王建军, 何友均, 张立文. 天保工程20年对黑龙江大兴安岭国有林区森林碳库的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [2] | 张露, 何雨霏, 陈坦, 杨婷, 张冰, 金军. 2011—2020年汾渭平原农田生态系统碳足迹的时空格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [3] | 朱永乐, 汤家喜, 谭婷, 李玉, 向彪. 氟化工园区周边玉米中全氟/多氟化合物的污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 1001-1006. |
| [4] | 郝蕾, 翟涌光, 戚文超, 兰穹穹. 2001-2020年内蒙古植被碳源/碳汇时空动态及对气候因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 825-834. |
| [5] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [6] | 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 伍冰晨, 张岱, 张岩. 北京山区针阔混交林地土壤有机碳含量的影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [7] | 吴昊平, 秦红杰, 贺斌, 尤毅, 陈金峰, 邹春萍, 杨思雨, 郝贝贝. 基于碳中和的农业面源污染治理模式发展态势刍议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1919-1926. |
| [8] | 姜超强, 李晨, 朱启法, 徐海清, 刘炎红, 沈嘉, 阎轶峰, 余飞, 祖朝龙. 皖南不同种植模式碳汇效应及经济效益评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1285-1292. |
| [9] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [10] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [11] | 杜雪, 王海燕, 邹佳何, 孟海, 赵晗, 崔雪, 董齐琪. 长白山北坡云冷杉阔叶混交林土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 663-669. |
| [12] | 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 姚贤宇, 叶绍明, 喻素芳. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| [13] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [14] | 曹云, 孙应龙, 姜月清, 万君. 黄河流域净生态系统生产力的时空分异特征及其驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2101-2110. |
| [15] | 王浩, 陈永金, 刘加珍, 万波, 张丽. 黄河三角洲新生湿地3种柽柳灌丛对土壤有机碳空间分布的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 9-16. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
