生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 2302-2309.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.12.004
盛基峰1,2,3( ), 李垚3,4, 于美佳3,4, 韩艳英1,2,3,4, 叶彦辉1,2,3,4,*(
), 李垚3,4, 于美佳3,4, 韩艳英1,2,3,4, 叶彦辉1,2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-22
出版日期:2022-12-18
发布日期:2023-02-15
通讯作者:
*叶彦辉,E-mail: yeyanhui3554@126.com作者简介:盛基峰(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事高寒草地氮沉降研究。E-mail: 2459993896@qq.com
基金资助:
SHENG Jifeng1,2,3( ), LI Yao3,4, YU MeiJia3,4, HAN Yanying1,2,3,4, YE Yanhui1,2,3,4,*(
), LI Yao3,4, YU MeiJia3,4, HAN Yanying1,2,3,4, YE Yanhui1,2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-22
Online:2022-12-18
Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
土壤是陆地生态系统的重要组分,其养分条件决定了植物生长状况及生产力的大小。氮和磷是植物生长的必需营养元素和主要限制因子,氮磷增加会改变土壤性质,影响土壤中的氮、磷含量,从而对土壤地上植物生长造成影响。为评估氮磷添加对草地土壤养分的影响及为高寒草地如何应对氮磷沉降提供科学依据,在藏东南色季拉山高寒草地开展氮磷添加试验,共设置对照(CK,不添加)、氮添加(N,15 kg?hm?2?a?1)、磷添加(P,75 kg?hm?2?a?1)、氮磷混合添加(NP:15 kg?hm?2?a?1 N;75 kg?hm?2?a?1 P)等4个施肥处理,施肥1年后采集土壤样品在实验室进行相关指标测定。试验结果表明,N、P和NP处理均显著促进高寒草地土壤有机碳、全氮、铵态氮、硝态氮和有效磷含量(P<0.05)。其中,NP添加对有机碳影响最大,增加了50.86%;N添加下土壤全氮、铵态氮、硝态氮和有效磷含量达到最大增幅,分别增加了59.14%、47.58%、333.85%和59.68%;NP添加下显著促进全磷含量(P<0.05),增加了19.41%,表明NP添加对土壤养分含量有积极影响,且影响较大。不同处理均显著促进蔗糖酶、葡萄糖苷酶和脲酶活性(P<0.05),N和NP添加对蔗糖酶和葡萄糖苷酶影响较大,增幅在53.08%—92.63%之间,P添加下脲酶活性增幅最大,达到140.73%。相关性分析表明,土壤有效养分与土壤酶活性之间显著相关,pH与土壤养分和酶活性呈显著相关(P<0.05)。结果表明,NP添加对土壤碳氮相关养分和酶活性影响较大,均呈现显著促进作用,且养分和酶活性之间呈现交互影响。NP添加通过提高土壤酶活性,加快土壤中大分子有机物分解,从而使土壤养分含量增加。N添加对土壤氮相关养分影响较大,表明施氮可缓解青藏高原高寒草地氮限制。
中图分类号:
盛基峰, 李垚, 于美佳, 韩艳英, 叶彦辉. 氮磷添加对高寒草地土壤养分和相关酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309.
SHENG Jifeng, LI Yao, YU MeiJia, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus An Addition on Soil Nutrients and Activity of Related Enzymes in Alpine Grassland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309.
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | 单位 Unit | 养分含量 Nutrient content |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.68 | |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | g∙kg−1 | 42.51 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | g∙kg−1 | 2.78 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | g∙kg−1 | 0.70 |
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 18.60 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 0.68 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | mg∙kg−1 | 14.26 |
表1 试验样地土壤原始状况
Table 1 Original soil conditions of the test plot
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | 单位 Unit | 养分含量 Nutrient content |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.68 | |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | g∙kg−1 | 42.51 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | g∙kg−1 | 2.78 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | g∙kg−1 | 0.70 |
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 18.60 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 0.68 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | mg∙kg−1 | 14.26 |
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | 单位 Unit | 测定方法 Test methods |
|---|---|---|
| pH | pH计测定 | |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | g∙kg−1 | 重铬酸钾氧化-外加热法 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | g∙kg−1 | 凯氏定氮法 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | g∙kg−1 | 钼锑抗比色法 |
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 氯化钾浸提-紫外分光光度法 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 氯化钙浸提-紫外分光光度法 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | mg∙kg−1 | 碳酸氢铵浸提-钼锑抗比色法 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | μg∙g−1∙h−1 | 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸比色法 |
| 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity | U∙g−1 | 标准硫代硫酸钠滴定法 |
| 脲酶 Urease activity | μg∙g−1∙h−1 | 苯酚-次氯酸钠比色法 |
表2 土壤理化性质和酶活性测定方法
Table 2 Methods for determination of soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activity
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | 单位 Unit | 测定方法 Test methods |
|---|---|---|
| pH | pH计测定 | |
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | g∙kg−1 | 重铬酸钾氧化-外加热法 |
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | g∙kg−1 | 凯氏定氮法 |
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | g∙kg−1 | 钼锑抗比色法 |
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 氯化钾浸提-紫外分光光度法 |
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | mg∙kg−1 | 氯化钙浸提-紫外分光光度法 |
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | mg∙kg−1 | 碳酸氢铵浸提-钼锑抗比色法 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | μg∙g−1∙h−1 | 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸比色法 |
| 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity | U∙g−1 | 标准硫代硫酸钠滴定法 |
| 脲酶 Urease activity | μg∙g−1∙h−1 | 苯酚-次氯酸钠比色法 |
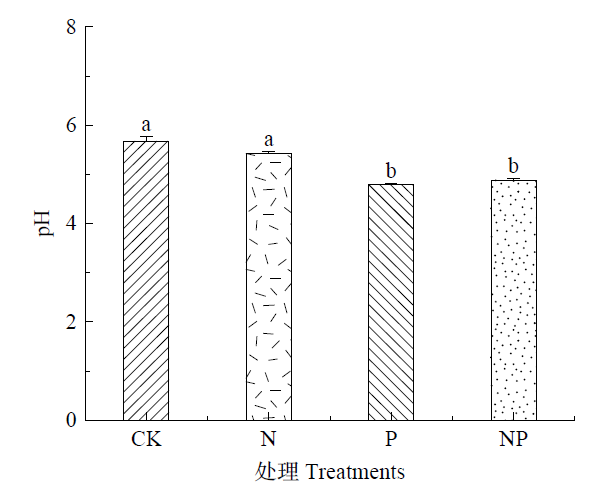
图1 氮磷添加对土壤pH的影响 同行不同小写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 1 Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil pH Different capital letters show significant difference at the 0.05 level in the same row. The same below
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | pH | 有机碳 Organic carbon | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 0.544 | 1 | |||||||
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.704* | −0.195 | 1 | ||||||
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.096 | 0.708* | −0.415 | 1 | |||||
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | 0.960** | 0.543 | 0.697* | 0.156 | 1 | ||||
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 0.969** | 0.395 | 0.814** | −0.053 | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.955** | 0.678* | 0.574 | 0.334 | 0.962** | 0.904** | 1 | ||
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | 0.455 | 0.987** | −0.278 | 0.712* | 0.481 | 0.317 | 0.607 | 1 | |
| 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity | 0.838** | 0.904** | 0.233 | 0.497 | 0.846** | 0.744* | 0.909** | 0.863** | 1 |
| 脲酶 Urease activity | −0.965** | −0.675* | −0.566 | −0.228 | −0.970** | −0.925** | −0.961** | −0.608 | −0.921** |
表3 不同处理后土壤性质Pearson相关性分析
Table 3 Pearson correlation analysis of soil properties after different treatments
| 土壤养分名称 Soil nutrient name | pH | 有机碳 Organic carbon | 全氮 Total nitrogen | 全磷 Total phosphorus | 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机碳 Organic carbon | 0.544 | 1 | |||||||
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.704* | −0.195 | 1 | ||||||
| 全磷 Total phosphorus | 0.096 | 0.708* | −0.415 | 1 | |||||
| 铵态氮 Ammonium nitrogen | 0.960** | 0.543 | 0.697* | 0.156 | 1 | ||||
| 硝态氮 Nitrate nitrogen | 0.969** | 0.395 | 0.814** | −0.053 | 0.962** | 1 | |||
| 有效磷 Available phosphorus | 0.955** | 0.678* | 0.574 | 0.334 | 0.962** | 0.904** | 1 | ||
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrase activity | 0.455 | 0.987** | −0.278 | 0.712* | 0.481 | 0.317 | 0.607 | 1 | |
| 葡萄糖苷酶 Glucosidase activity | 0.838** | 0.904** | 0.233 | 0.497 | 0.846** | 0.744* | 0.909** | 0.863** | 1 |
| 脲酶 Urease activity | −0.965** | −0.675* | −0.566 | −0.228 | −0.970** | −0.925** | −0.961** | −0.608 | −0.921** |
| [1] |
BERENDSE F, NVAN B, RYDIN H, et al., 2001. Raised atmospheric CO2 levels and increased N deposition cause shifts in plant species composition and production in Sphagnum bogs[J]. Global Change Biology, 7(5): 591-598.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FAYIAH M, DONG S K, KHOMERA S W, et al., 2020. Status and challenges of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau’s grasslands: An analysis of causes, mitigation measures, and way forward[J]. Sustainability, 12(3): 1099-1120.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FU G, SHEN Z X, 2017. Response of alpine soils to nitrogen addition on the Tibetan Plateau: A meta-analysis[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 114: 99-104.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GONG S W, ZHANG T, GUO J X, 2020. Warming and nitrogen deposition accelerate soil phosphorus cycling in a temperate meadow ecosystem[J]. Soil Research, 58(1): 109-115.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HARPOLE W S, NGAI J T, CLELAND E E, et al., 2011. Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities[J]. Ecology Letters, 14(9): 852-862.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
HU W J, TAN J R, SHI X R, et al., 2022. Nutrient addition and warming alter the soil phosphorus cycle in grasslands: A global meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22(10): 2608-2619.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JING X, YANG X X, REN F, et al., 2016. Neutral effect of nitrogen addition and negative effect of phosphorus addition on topsoil extracellular enzymatic activities in an alpine grassland ecosystem[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 107: 205-213.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI J H, CHENG B H, ZHANG R, et al., 2020. Nitrogen and phosphorus additions accelerate decomposition of slow carbon pool and lower total soil organic carbon pool in alpine meadows[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 32(4): 1761-1772.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI Q, LÜ J H, PENG C H, et al., 2021. Nitrogen-addition accelerates phosphorus cycling and changes phosphorus use strategy in a subtropical Moso bamboo forest[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 16(2): 024023.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU M H, GAN B P, LI Q, et al., 2022. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Forests[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13: 834184.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIU S B, ZAMANIAN K, SCHLEUSS P, et al., 2018. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles[J]. Agriculture Ecosystem & Environment, 252: 93-104.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LUO R Y, FAN J L, WANG W J, et al., 2019. Nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment accelerates soil organic carbon loss in alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 650: 303-312.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LUO R Y, KUZYAKOV Y, LIU D Y, et al., 2020. Nutrient addition reduces carbon sequestration in a Tibetan grassland soil: Disentangling microbial and physical controls[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 144: 107764-107775.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MOORHEAD D L, RINKES Z L, SINSABAUGH R L, et al., 2013. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: informing enzyme-based decomposition models[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 4: 223-235.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | SONG X Z, PENG C H, CIAIS P, et al., 2020. Nitrogen addition increased CO2 uptake more than non-CO2 greenhouse gases emissions in a Moso bamboo forest[J]. Science Advances, 6(12): 5790-5799. |
| [16] |
ULLAH S, AI C, HUANG S, et al., 2019. The responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community composition under nitrogen addition in an upland soil[J]. PLoS ONE, 14(9): e0223026.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
VANCE C P, UHDE-STONE C, ALLAN D.L, 2003. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource[J]. The New Phytologist, 157(3): 423-447.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG R, BALKANSKI Y, BOUCHER O, CIAIS P, et al., 2015. Significant contribution of combustion related emissions to the atmospheric phosphorus budget[J]. Nature Geoscience, 8: 48-54.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WIDDIG M, HEINTZ B A, SCHLEUSS P M, et al., 2020. Efects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on microbial community composition and element cycling in a grassland soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 151: 108041.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WU Y, ZHOU H K, SUN W, et al., 2022. Temperature sensitivity of soil enzyme kinetics under N and P fertilization in an alpine grassland, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 838(5): 156042.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
XIAO H, YANG H L, ZHAO M L, et al., 2021. Soil extracellular enzyme activities and the abundance of nitrogen-cycling functional genes responded more to N addition than P addition in an Inner Mongolian meadow steppe[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 759(1): 143541.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
YANG S, XU Z W, WANG R Z, et al., 2017. Variations in soil microbial community composition and enzymatic activities inresponse to increased N deposition and precipitation in Inner Mongolian grassland[J]. Applied soil ecology, 119: 275-285.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YU T Y, GUANUAN H, BATELAAN O, et al., 2016. Contrasting responses of water use efficiency to drought across globalterrestrial ecosystems[J]. Scientific reports, 6: 23284.
DOI URL |
| [24] | ZI H B, HU L, WANG C T, 2022. Differentiate responses of soil microbial community and enzyme activities to nitrogen and phosphorus addition rates in an alpine meadow[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 833: 155163-155163. |
| [25] | 曹石榴, 2019. 土壤化学营养元素研究[J]. 农村经济与科技, 30(21): 32-33. |
| CAO S L, 2019. Research on soil chemical nutrient elements[J]. Rural Economy and Technology, 30(21): 32-33. | |
| [26] | 方运霆, 莫江明, 周国逸, 等, 2004. 南亚热带森林土壤有效氮含量及其对模拟氮沉降增加的初期响应[J]. 生态学报, 24(11): 2353-2359. |
| FANG Y T, MO J M, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2004. The short-term responses of soil available nitrogen of Dinghushan forests to simulated N deposition in subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 24(11): 2353-2359. | |
| [27] |
范珍珍, 王鑫, 王超, 等, 2018. 整合分析氮磷添加对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(4): 1266-1272.
DOI |
|
FAN Z Z, WANG X, WANG C, et al., 2018. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil enzyme activities: A meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(4): 1266-1272.
DOI |
|
| [28] | 冯慧芳, 余明, 薛立, 2020. 外源性氮磷添加及林分密度对大叶相思林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(14): 4894-4902. |
| FENG H F, YU M, XUE L, 2020. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil enzyme activities in Acacia auriculiformis stands under different planting densities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(14): 4894-4902. | |
| [29] | 刘红梅, 周广帆, 李洁, 等, 2018. 氮沉降对贝加尔针茅草原土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1387-1394. |
| LIU H M, ZHOU G F, LI J, et al., 2018. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities of Stipa baicalensis steppe[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1387-1394. | |
| [30] | 刘姝萱, 安慧, 张馨文, 等, 2022. 氮磷添加对荒漠草原植物-凋落物-土壤生态化学计量特征的影响[J/OL]. 生态学报, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2031.Q.20220618.1156.010.html. |
| LIU S X, AN H, ZHANG X W, et al., 2022. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on the ecological stoichiometry of plant-litter-soil in desert grassland[J/OL]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, https://kns.cnki.net/ kcms/detail/11.2031.Q.20220618.1156.010.html. | |
| [31] | 宋学贵, 胡庭兴, 鲜骏仁, 等, 2009. 川南天然常绿阔叶林土壤酶活性特征及其对模拟N沉降的响应[J]. 生态学报, 29(3): 1234-1240. |
| SONG X G, HU T X, XIAN J R, et al., 2009. Soil enzyme activities and its response to simulated nitrogen deposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest, southern Sichuan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 29(3): 1234-1240. | |
| [32] | 苏洁琼, 李新荣, 鲍婧婷, 2014. 施氮对荒漠化草原土壤理化性质及酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(3): 664-670. |
| SU J Q, LI X R, BAO J T, 2014. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities in desertified steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(3): 664-670. | |
| [33] | 苏渝钦, 刘何铭, 郑泽梅, 等, 2016. 氮磷添加对中亚热带常绿阔叶林土壤有效氮和pH值的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(9): 2279-2285. |
| SU Y Q, LIU H M, ZHEN Z M, et al., 2016. Effects of N and P addition on soil available nitrogen and pH in a subtropical forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(9): 2279-2285. | |
| [34] | 孙亚男, 李茜, 李以康, 等, 2016. 氮、磷养分添加对高寒草甸土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 25(2): 18-26. |
| SUN Y N, LI Q, LI Y K, et al., 2016. The effect of nitrogen and phosphorus applications on soil enzyme activities in Qinghai-Tibetan alpine meadows[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 25(2): 18-26. | |
| [35] | 史晓鹏, 2018. 施氮磷肥对半干旱区不同生长年限紫花苜蓿地上生物量及土壤养分和水分的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| SHI X P, 2018. The effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on different growing year alfalfa aboveground biomass, soil nutrients and soil water in semi-arid area[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. | |
| [36] | 王常慧, 邢雪荣, 韩兴国, 2004. 草地生态系统中土壤氮素矿化影响因素的研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 15(11): 2184-2188. |
| WANG C H, XING X R, HAN X G, 2004. Research progress on influencing factors of soil nitrogen mineralization in grassland ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15(11): 2184-2188. | |
| [37] | 涂利华, 胡庭兴, 张健, 等, 2009. 华西雨屏区苦竹林土壤酶活性对模拟氮沉降的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 20(12): 2943-2948. |
| TU L H, HU T X, ZHANG J, et al., 2009. Soil enzyme activities in a Pleioblastus amurus plantation in rainy area of west China under simulated nitrogen deposition[J]. Chinese Joumal of Applied Ecology, 20(12): 2943-2948. | |
| [38] | 魏金明, 姜勇, 符明明, 等, 2011. 水、肥添加对内蒙古典型草原土壤碳、氮、磷及pH的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 30(8): 1642-1646. |
| WEI J M, JIANG Y, FU M M, et al., 2011. Effects of water addition and fertilization on soil nutrient contents and pH value of typical grassland in Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30(8): 1642-1646. | |
| [39] |
吴建波, 王小丹, 2021. 藏北高寒草原土壤酶活性对氮添加的响应及其影响因素[J]. 草地学报, 29(3): 555-562.
DOI |
| WU J B, WANG X D, 2021. Responses of soil enzyme activities to nitrogen addition and its impace factors at the alpine steppe of northern Tibet[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica. 29(4): 555-562. | |
| [40] | 文旻, 胡启斌, 阳文静, 等, 2021. 氮、磷添加对鄱阳湖典型苔草湿地土壤养分和植物生物量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(6): 1669-1676. |
| WEN Y, HU Q B, YANG W J, 2021. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil nutrients and plant biomass in a typical Poyang Lake marshland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(8): 1669-1676. | |
| [41] |
叶彦辉, 刘云龙, 韩艳英, 等, 2017. 氮沉降对西藏高山灌丛草甸土壤理化性质的短期影响[J]. 草地学报, 25(5): 973-981.
DOI |
| YE Y H, LIU Y L, HAN Y Y, et al., 2017. Short-term effects of nitrogen deposition on soil physical and chemical properties of alpine shrub meadow in Tibet[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 25(5): 973-981. | |
| [42] | 张进霞, 2014. 氮磷调控对紫花苜蓿生产性能及其土壤养分特性的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. |
| ZHANG J X, 2014. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus supply levels on productivity and the soil nutriment feature of alfalfa[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. | |
| [43] |
赵晓琛, 皇甫超河, 刘红梅, 等, 2016. 贝加尔针茅草原土壤酶活性及微生物量碳氮对养分添加的响应[J]. 草地学报, 24(1): 47-53.
DOI |
| ZHAO X S, HANGFU C H, LIU H M, et al., 2016. Response of soil enzyme activity and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen to the nutrient addition of Stipa baicalensis Steppe in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 24(1): 47-53. | |
| [44] | 翟珈莹, 2020. 氮磷添加对青藏高原高寒草地土壤微生物及化学计量特征的影响[D]. 咸阳: 中国科学院大学 (中国科学院教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心). |
| ZHAI J Y, 2020. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil microbes and stoichiometric characteristic of alpine meadow in Qinghai-Tibet lateau[D]. Xianyang: Research Center of Soil and Water Conservation and Ecological Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Education. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 周沁苑, 董全民, 王芳草, 刘玉祯, 冯斌, 杨晓霞, 俞旸, 张春平, 曹铨, 刘文亭. 放牧方式对高寒草地瑞香狼毒根际土壤团聚体及有机碳特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [3] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [4] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [6] | 杨冲, 王春燕, 王文颖, 毛旭峰, 周华坤, 陈哲, 索南吉, 靳磊, 马华清. 青藏高原黄河源区高寒草地土壤营养特征变化及质量评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 896-908. |
| [7] | 龙靖, 黄耀, 刘占锋, 简曙光, 魏丽萍, 王俊. 西沙热带珊瑚岛典型乔木叶片性状和养分再吸收特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [8] | 余斐, 叶彩红, 许窕孜, 张中瑞, 朱航勇, 张耕, 华雷, 邓鉴锋, 丁晓纲. 韶关市花岗岩地区森林土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [9] | 张晓丽, 王国丽, 常芳弟, 张宏媛, 逄焕成, 张建丽, 王婧, 冀宏杰, 李玉义. 生物菌剂对根际盐碱土壤理化性质和微生物区系的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [10] | 宋贤冲, 蔡雪梅, 陈韬, 潘文, 石媛媛, 唐健, 曹继钊. 不同萌芽代次桉树根际和非根际土壤养分的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [11] | 宗宁, 石培礼, 朱军涛. 高寒草地沙化过程植物群落构成及生态位特征变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1561-1570. |
| [12] | 廖迎春, 段洪浪, 施星星, 孟庆银, 刘文飞, 沈芳芳, 樊后保, 朱涛. 杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolate)人工林生长状况与根系生物量相关性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1121-1128. |
| [13] | 徐文印, 张宇鹏, 段成伟, 柴瑜, 宋娴, 李希来. 黄河源不同区域退化高寒草甸土壤养分空间变异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| [14] | 隋阳辉, 高继平, 王延波, 肖万欣, 刘晶, 史磊, 赵海岩, 张洋. 氮肥配施生物炭对旱地土壤养分和玉米根系径级分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032. |
| [15] | 张子璇, 牛蓓蓓, 李新举. 不同改良模式对滨海盐渍土土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(2): 275-284. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
