生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2026-2032.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.009
隋阳辉1,2( ), 高继平2, 王延波1,*(
), 高继平2, 王延波1,*( ), 肖万欣1, 刘晶1, 史磊1, 赵海岩1, 张洋1
), 肖万欣1, 刘晶1, 史磊1, 赵海岩1, 张洋1
收稿日期:2021-04-12
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
* 王延波(1966年生),研究员,从事玉米遗传育种与栽培。E-mail: lnwangyanbo@163.com作者简介:隋阳辉(1984年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事玉米栽培生理及生物炭应用基础研究。E-mail: suiyanghui@126.com
基金资助:
SUI Yanghui1,2( ), GAO Jiping2, WANG Yanbo1,*(
), GAO Jiping2, WANG Yanbo1,*( ), XIAO Wanxin1, LIU Jing1, SHI Lei1, ZHAO Haiyan1, ZHANG Yang1
), XIAO Wanxin1, LIU Jing1, SHI Lei1, ZHAO Haiyan1, ZHANG Yang1
Received:2021-04-12
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
为了缓解玉米连作带来的土壤养分失衡及根系早衰,探讨生物炭对土壤养分、玉米根系生长的主要径级水平、玉米干物质积累的后效作用。采用定位试验,设置不施氮肥、不施生物炭为对照(CK),2个施氮量(常规施N量225 kg∙hm-2,N1;减氮10%,N 203 kg∙hm-2,N2),2个生物炭量(8.4 t∙hm-2,C1;21 t∙hm-2,C2)共7个处理。在生物炭施用第二年,测定玉米不同径级根系生长及土壤养分含量。结果表明,与对照(CK)相比,常规施氮配施低量生物炭(N1C1)和减氮配施高量生物炭(N2C2)显著提高了土壤有机质含量;高量生物炭配施氮肥(N1C2和N2C2)分别提高土壤碱解氮储存量29.9%和9.0%;N1C2和N2C1处理显著提高土壤全氮含量。减氮配施低量生物炭(N2C1)促进大喇叭口期玉米0—2 mm径级根系的根长较CK提高38.9%(P˂0.05,下同);低量生物炭配施常规氮肥(N1C1)促进成熟期玉米根系变细13.4%、根系变长32.4%,提高0—2 mm径级根系的总根长37.9%;单施氮肥或配施生物炭对2—3、3—4径级的根长无显著影响;常规单施氮肥(N1C0)较CK显著提高>4 mm径级根系根长约40.5%。低量生物炭配施常规氮肥(N1C1)提高大喇叭口期玉米单株干物质积累53.16 g∙plant-1。综上,研究结果说明,8.4 t∙hm-2生物炭配施225 kg∙hm-2氮肥能更好地促进成熟期玉米细根生长。单施氮肥和配施21 t∙hm-2生物炭均可促进土壤养分的固持。该研究结果为秸秆循环利用提供科学参考,同时为优化玉米根系结构提供新思路。
中图分类号:
隋阳辉, 高继平, 王延波, 肖万欣, 刘晶, 史磊, 赵海岩, 张洋. 氮肥配施生物炭对旱地土壤养分和玉米根系径级分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032.
SUI Yanghui, GAO Jiping, WANG Yanbo, XIAO Wanxin, LIU Jing, SHI Lei, ZHAO Haiyan, ZHANG Yang. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Effects on Soil Nutrient and Root Distribution in Dryland Maize[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032.
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g∙kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen/ (mg∙kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (mg∙g-1) | 全碳 Total carbon/ (mg∙g-1) | 碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.33±0.34c | 114.65±1.35e | 9.47±0.39d | 0.91±0.00d | 9.47±0.02d | 10.36±0.02a |
| N1C0 | 19.15±0.39a | 125.46±2.09cd | 17.17±0.66b | 1.00±0.04c | 8.93±0.00e | 8.97±0.33d |
| N1C1 | 17.39±0.33b | 129.07±1.95bc | 13.42±0.41c | 1.09±0.00b | 10.66±0.01b | 9.82±0.05b |
| N1C2 | 14.52±0.46d | 148.89±2.05a | 4.75±0.27f | 1.13±0.02a | 10.91±0.01a | 9.66±0.19bc |
| N2C0 | 17.78±0.32b | 130.18±1.54b | 22.64±0.83a | 1.09±0.00b | 9.65±0.20c | 8.83±0.15d |
| N2C1 | 15.67±0.49c | 121.66±2.24d | 6.91±0.20e | 1.13±0.01a | 10.69±0.01b | 9.42±0.09c |
| N2C2 | 17.43±0.16b | 124.98±1.94d | 6.81±0.17e | 1.09±0.01b | 10.84±0.10a | 9.93±0.02b |
表1 生物炭与氮肥配施对收获期(0—20 cm)耕层土壤常规养分的影响
Table 1 Effect of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer on topsoil (0-20 cm) nutrient
| 处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter/ (g∙kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen/ (mg∙kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (mg∙g-1) | 全碳 Total carbon/ (mg∙g-1) | 碳氮比 Carbon nitrogen ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.33±0.34c | 114.65±1.35e | 9.47±0.39d | 0.91±0.00d | 9.47±0.02d | 10.36±0.02a |
| N1C0 | 19.15±0.39a | 125.46±2.09cd | 17.17±0.66b | 1.00±0.04c | 8.93±0.00e | 8.97±0.33d |
| N1C1 | 17.39±0.33b | 129.07±1.95bc | 13.42±0.41c | 1.09±0.00b | 10.66±0.01b | 9.82±0.05b |
| N1C2 | 14.52±0.46d | 148.89±2.05a | 4.75±0.27f | 1.13±0.02a | 10.91±0.01a | 9.66±0.19bc |
| N2C0 | 17.78±0.32b | 130.18±1.54b | 22.64±0.83a | 1.09±0.00b | 9.65±0.20c | 8.83±0.15d |
| N2C1 | 15.67±0.49c | 121.66±2.24d | 6.91±0.20e | 1.13±0.01a | 10.69±0.01b | 9.42±0.09c |
| N2C2 | 17.43±0.16b | 124.98±1.94d | 6.81±0.17e | 1.09±0.01b | 10.84±0.10a | 9.93±0.02b |
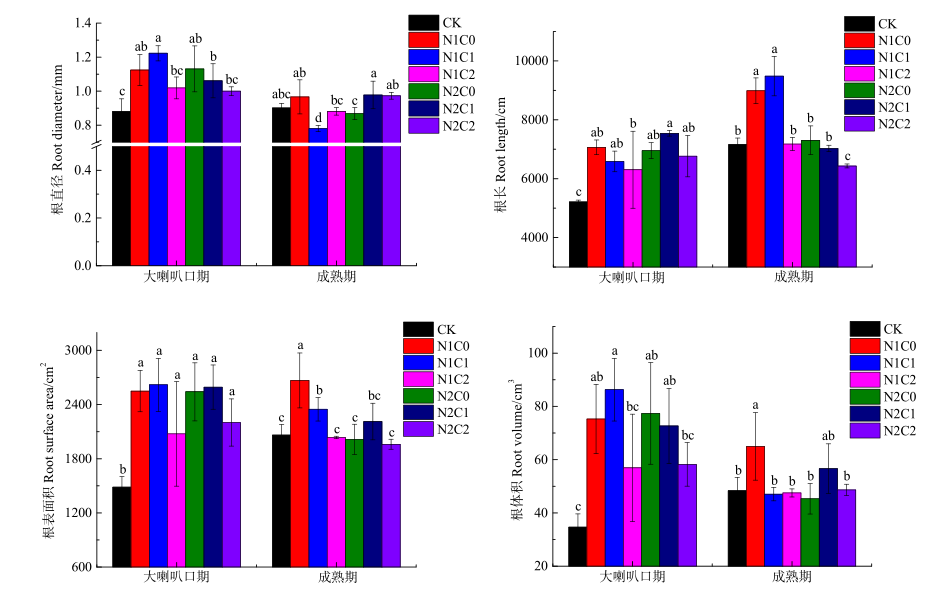
图2 生物炭与氮肥配施对玉米根系生长的影响 平均值±标准差,n=3;不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同
Fig. 2 Effects of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer on maize root develop Means±SD, n=3; Different letters meant significant difference at 0.05 level. The same below
| 处理 Treatment | 大喇叭口期 Large bell stage | 成熟期 Ripening stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0<D<2 | 2<D<3 | 3<D<4 | D>4 | 0<D<2 | 2<D<3 | 3<D<4 | D>4 | ||
| CK | 4671.42±102.77b | 253.27±29.74d | 125.72±28.76b | 160.84±31.71c | 6304.36±198.90c | 356.06±36.70ab | 218.55±25.79abc | 281.63±47.49bc | |
| N1C0 | 6025.78±233.55a | 423.01±42.05a | 210.43±33.77a | 403.23±71.64ab | 7943.97±323.36b | 403.50±42.74a | 241.24±54.86a | 395.55±91.13a | |
| N1C1 | 5575.51±179.41ab | 366.80±70.90ab | 198.17±42.61a | 442.39±63.32a | 8691.10±630.23a | 356.35±22.17ab | 169.08±29.88c | 266.41±29.46bc | |
| N1C2 | 5492.36±1123.71ab | 337.89±79.47cd | 190.92±5.13a | 282.46±108.66bc | 6386.21±196.26c | 329.37±32.20b | 214.60±39.06abc | 245.40±42.79c | |
| N2C0 | 5890.38±280.27a | 418.47±74.42bc | 230.54±51.05a | 412.96±92.69ab | 6516.58±448.54c | 349.37±16.82ab | 175.91±7.61bc | 260.19±39.34bc | |
| N2C1 | 6488.36±205.90a | 462.11±54.74ab | 224.92±28.81a | 362.58±62.01ab | 6147.78±78.22c | 318.26±13.67b | 214.68±6.56abc | 346.19±61.30ab | |
| N2C2 | 5943.47±562.81a | 333.99±52.67ab | 181.69±42.52ab | 303.98±52.22ab | 5584.62±98.27d | 332.22±58.63b | 232.85±20.87ab | 279.72±39.14bc | |
表2 生物炭与氮肥配施对玉米根系径级分布的影响
Table 2 Effect of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer on maize root diameter class distribution
| 处理 Treatment | 大喇叭口期 Large bell stage | 成熟期 Ripening stage | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0<D<2 | 2<D<3 | 3<D<4 | D>4 | 0<D<2 | 2<D<3 | 3<D<4 | D>4 | ||
| CK | 4671.42±102.77b | 253.27±29.74d | 125.72±28.76b | 160.84±31.71c | 6304.36±198.90c | 356.06±36.70ab | 218.55±25.79abc | 281.63±47.49bc | |
| N1C0 | 6025.78±233.55a | 423.01±42.05a | 210.43±33.77a | 403.23±71.64ab | 7943.97±323.36b | 403.50±42.74a | 241.24±54.86a | 395.55±91.13a | |
| N1C1 | 5575.51±179.41ab | 366.80±70.90ab | 198.17±42.61a | 442.39±63.32a | 8691.10±630.23a | 356.35±22.17ab | 169.08±29.88c | 266.41±29.46bc | |
| N1C2 | 5492.36±1123.71ab | 337.89±79.47cd | 190.92±5.13a | 282.46±108.66bc | 6386.21±196.26c | 329.37±32.20b | 214.60±39.06abc | 245.40±42.79c | |
| N2C0 | 5890.38±280.27a | 418.47±74.42bc | 230.54±51.05a | 412.96±92.69ab | 6516.58±448.54c | 349.37±16.82ab | 175.91±7.61bc | 260.19±39.34bc | |
| N2C1 | 6488.36±205.90a | 462.11±54.74ab | 224.92±28.81a | 362.58±62.01ab | 6147.78±78.22c | 318.26±13.67b | 214.68±6.56abc | 346.19±61.30ab | |
| N2C2 | 5943.47±562.81a | 333.99±52.67ab | 181.69±42.52ab | 303.98±52.22ab | 5584.62±98.27d | 332.22±58.63b | 232.85±20.87ab | 279.72±39.14bc | |
| 处理 Treatment | 大喇叭口期 Large bell stage | 成熟期 Ripening stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单株干物质 Dry matter/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length | 单株干物质 Dry matter/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length | ||
| CK | 84.23±12.04c | 0.090±0.002a | 6.21±0.80a | 293.90±24.71b | 0.027±0.002ab | 8.09±0.71a | |
| N1C0 | 149.87±41.85abc | 0.098±0.035a | 4.60±1.49a | 345.37±26.47a | 0.030±0.004a | 7.78±1.70a | |
| N1C1 | 203.03±13.71a | 0.097±0.001a | 2.84±0.19a | 320.60±26.99ab | 0.029±0.003ab | 9.51±0.57a | |
| N1C2 | 133.40±61.32bc | 0.093±0.019a | 4.99±1.88a | 317.53±43.07ab | 0.024±0.003b | 8.55±0.70a | |
| N2C0 | 141.10±51.29abc | 0.096±0.006a | 4.84±1.95a | 293.30±16.11b | 0.027±0.000ab | 8.26±0.37a | |
| N2C1 | 187.73±38.20ab | 0.097±0.011a | 3.77±1.23a | 291.43±51.15ab | 0.024±0.004b | 9.20±1.26a | |
| N2C2 | 123.50±7.18bc | 0.110±0.001a | 4.35±0.15a | 289.57±21.82b | 0.023±0.003b | 8.70±1.68a | |
表3 生物炭与氮肥配施对玉米对根冠生长的影响
Table 3 Effects of biochar combined with nitrogen fertilizer on the growth of shoot and roots
| 处理 Treatment | 大喇叭口期 Large bell stage | 成熟期 Ripening stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单株干物质 Dry matter/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length | 单株干物质 Dry matter/g | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 比根长 Specific root length | ||
| CK | 84.23±12.04c | 0.090±0.002a | 6.21±0.80a | 293.90±24.71b | 0.027±0.002ab | 8.09±0.71a | |
| N1C0 | 149.87±41.85abc | 0.098±0.035a | 4.60±1.49a | 345.37±26.47a | 0.030±0.004a | 7.78±1.70a | |
| N1C1 | 203.03±13.71a | 0.097±0.001a | 2.84±0.19a | 320.60±26.99ab | 0.029±0.003ab | 9.51±0.57a | |
| N1C2 | 133.40±61.32bc | 0.093±0.019a | 4.99±1.88a | 317.53±43.07ab | 0.024±0.003b | 8.55±0.70a | |
| N2C0 | 141.10±51.29abc | 0.096±0.006a | 4.84±1.95a | 293.30±16.11b | 0.027±0.000ab | 8.26±0.37a | |
| N2C1 | 187.73±38.20ab | 0.097±0.011a | 3.77±1.23a | 291.43±51.15ab | 0.024±0.004b | 9.20±1.26a | |
| N2C2 | 123.50±7.18bc | 0.110±0.001a | 4.35±0.15a | 289.57±21.82b | 0.023±0.003b | 8.70±1.68a | |
| [1] |
ARIF M, ILYAS M, RIAZ M, et al., 2017. Biochar improves phosphorus use efficiency of organic-inorganic fertilizers, maize-wheat productivity and soil quality in a low fertility alkaline soil[J]. Field Crops Research, 214:25-37.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BARBERON M, GELDNER N, 2014. Radial Transport of Nutrients: The Plant Root as a Polarized Epithelium[J]. Plant Physiology, 166(2):528-537.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DING Y, LIU Y X, WU W X, et al., 2010. Evaluation of Biochar Effects on Nitrogen Retention and Leaching in Multi-Layered Soil Columns[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 213(1-4):47-55. |
| [4] |
GAO J P, ZHAO Y Z, ZHANG W Z, et al., 2019. Biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures affects urea-nitrogen immobilization and N2O emissions in paddy fields[J]. Peer J, 7:e7027.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
JIN Z W, CHEN C, CHEN X M, et al., 2019. Soil acidity, available phosphorus content, and optimal biochar and nitrogen fertilizer application rates: A five-year field trial in upland red soil, China[J]. Field Crops Research, 232:77-87.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KIM H S, KIM K R, YANG J E, et al., 2016. Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response[J]. Chemosphere, 142:153-159.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LEE C H, WANG C C, LIN H H, et al., 2018. In-situ biochar application conserves nutrients while simultaneously mitigating runoff and erosion of an Fe-oxide-enriched tropical soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 619-620:665-671.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LEHMANN J, 2002. Biochar (Black Carbon) Stability and Stabilization in Soil[C]// Soil Science: Confronting New Realities in the 21st Century. Bangkok: 7th World Congress of Soil Science: 1-12. |
| [9] |
LEHMANN J, DA SILVA JR J P, STEINER C, et al., 2003. Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments[J]. Plant and Soil, 249(2):343-357.
DOI URL |
| [10] | LEHMANN J, JOSEPH S, 2009. Biochar for environmental management: Science and technology. Earthscan. |
| [11] |
MOLLER A L B, PEDAS P, ANDERSEN B, et al., 2011. Responses of barley root and shoot proteomes to long-term nitrogen deficiency, short-term nitrogen starvation and ammonium[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 34(12):2024-2037.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
PAN X, BAQUY M A A, GUAN P, et al., 2020. Effect of soil acidification on the growth and nitrogen use efficiency of maize in Ultisols[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(3):1435-1445.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SANCHEZ P A, VILLACHIA J H, BANDY D E, 1983. Soil fertility dynamics after clearing tropical rainforest in Peru[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 47(6):1171-1178.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUI Y H, GAO J P, LIU C H, et al., 2016. Interactive effects of straw-derived biochar and N fertilization on soil C storage and rice productivity in rice paddies of Northeast China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 544:203-210.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
VAN ZWIETEN L, KIMBER S, MORRIS S, et al., 2010. Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility[J]. Plant and Soil, 327:235-246.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WANG Z, WANG Z, LUO Y, et al., 2020. Biochar increases 15N fertilizer retention and indigenous soil N uptake in a cotton-barley rotation system[J]. Geoderma, DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113944.
DOI |
| [17] |
YU J J, HU H C, WU X D, et al., 2020. Coupling of biochar-mediated absorption and algal-bacterial system to enhance nutrients recovery from swine wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134935.
DOI |
| [18] | 包立, 刘惠见, 邓洪, 等, 2018. 玉米秸秆生物炭对滇池流域大棚土壤磷素利用和小白菜生长的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 55(4):815-825. |
| BAO L, LIU H J, DENG H, et al., 2018. Effect of Straw Biochar on Utilization of Soil Phosphorus and Growth of Bok Choi in Greenhouse in Dianchi Lake Basin[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55(4):815-825. | |
| [19] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [20] | 陈温福, 张伟明, 孟军, 2014. 生物炭与农业环境研究回顾与展望[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 33(5):821-828. |
| CHEN W F, ZHANG W M, MENG J, 2014. Biochar and Agro- ecological Environment: Review and Prospect[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 33(5):821-828. | |
| [21] | 程效义, 孟军, 黄玉威, 等, 2016. 生物炭对玉米根系生长和氮素吸收及产量的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 47(2):218-223. |
| CHENG X Y, MENG J, HUANG Y W, et al., 2016. Effect of Biochar on Root Growth, Absorption of Nitrogen and Maize Yield[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 47(2):218-223. | |
| [22] | 盖霞普, 刘宏斌, 翟丽梅, 等, 2015. 玉米秸秆生物炭对土壤无机氮素淋失风险的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 4(2):310-318. |
| GAI X P, LIU H B, ZHAI LM, et al., 2015. Effects of Corn-Stalk Biochar on Inorganic Nitrogen Leaching from Soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 4(2):310-318. | |
| [23] | 高祥照, 马文奇, 崔勇, 等, 2000. 我国耕地土壤养分变化与肥料投入状况[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 6(4):363-369. |
| GAO X Z, MA W Q, CUI Y, et al., 2000. Changes of soil nutrient contents and input of nutrients in arable of China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 6(4):363-369. | |
| [24] | 郭俊娒, 2015. 不同施肥模式对东北春玉米氮素利用与农田温室气体排放的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. |
| GUO J M, 2015. Effect of Fertilizer Application Models on High Efficient Use of Nitrogen and Greenhouse Gases Emission in Spring Maize in Northeast China [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. | |
| [25] | 蒋健, 王宏伟, 刘国玲, 等, 2015. 生物炭对玉米根系特性及产量的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 23(4):62-66. |
| JIANG J, WANG H W, LIU G L, et al., 2015. Effect of Biochar on Root Characteristics and Yield in Maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 23(4):62-66. | |
| [26] | 巨晓棠, 谷保静, 2014. 我国农田氮肥施用现状、问题及趋势[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20(4):783-795. |
| JU X T, GU B J, 2014. Status-quo, problem and trend of nitrogen fertilization in China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 20(4):783-795. | |
| [27] | 刘赛男, 高尚, 程效义, 等, 2019. 玉米秸秆生物炭对秸秆腐熟进程、养分含量和CO2排放量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(4):1312-1318. |
| LIU S N, GAO S, CHENG X Y, et al., 2019. Effects of corn straw biochar on process, nutrient content, and CO2 emissions of corn straw decomposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(4):1312-1318. | |
| [28] | 刘悦, 黎子涵, 邹博, 等, 2017. 生物炭影响作物生长及其与化肥混施的增效机制研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(3):1030-1038. |
| LIU Y, LI Z H, ZOU B, et al., 2017. Research progress in effects of biochar application on crop growth and synergistic mechanism of biochar with fertilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(3):1030-1038. | |
| [29] | 孟繁昊, 高聚林, 于晓芳, 等, 2018. 生物炭配施氮肥改善表层土壤生物化学性状研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(5):1214-1226. |
| MENG F H, GAO J L, YU X F, et al., 2018. Inprovent of biochemical property of surface soil by combined application of biochar with nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(5):1214-1226. | |
| [30] | 孟繁昊, 于晓芳, 王志刚, 等, 2020. 生物炭配施氮肥对土壤物理性质及春玉米产量的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 28(1):142-150. |
| MENG F H, YU X F, WANG Z G, et al., 2020. Effects of Physical Property of Soil and Yield of Spring Corn by Combined Application of Biochar and Nitrogen[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 28(1):142-150. | |
| [31] | 孟军, 张伟明, 王绍斌, 等, 2011. 农林废弃物炭化还田技术的发展与前景[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 42(4):387-392. |
| MENG J, ZHANG W M, WANG S B, et al., 2011. Development and Prospect of Carbonization and Returning Technology of Agro-forestry Residue[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 42(4):387-392. | |
| [32] | 尚杰, 耿增超, 王月玲, 等, 2016. 施用生物炭对(土娄)土微生物量碳、氮及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 49(6):1142-1151. |
| SHANG J, GENG Z C, WANG Y L, et al., 2016. Effect of Biochar Amendment on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen and Enzyme Activity in Tier Soils[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 49(6):1142-1151. | |
| [33] |
孙宁婷, 王小燕, 周豪, 等, 2021. 生物质炭种类与混施深度对紫色土水分运移和氮磷流失的影响[J]. 土壤学报, DOI: 10.11766/ trxb202008130360.
DOI |
|
SUN N T, WANG X Y, ZHOU H, et al., 2021. Effects of Kind and Incorporation Depth of Biochars on Water Movement and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Purple Soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, DOI: 10.11766/trxb202008130360.
DOI |
|
| [34] | 肖焱波, 李隆, 张福锁, 2005. 用同位素15N直接法和间接法研究小麦/蚕豆间作中根系相互作用对种间竞争及氮转移的影响[C]. 贵州省自然科学优秀学术论文集. |
| XIAO Y B, LI L, ZHANG F S, 2005. Effects of Root Interaction on Interspecific Competition and Nitrogen Transfer in Wheat/Broad Bean Intercropping with Isotope 15N[C]. Guizhou Province Natural Science Excellent Memoirs. | |
| [35] | 谢祖彬, 刘琦, 许燕萍, 等, 2011. 生物炭研究进展及其研究方向[J]. 土壤, 43(6):857-861. |
| XIE Z B, LIU Q, XU Y P, et al., 2011. Advances and Perspectives of Biochar Research[J]. Soils, 43(6):857-861. | |
| [36] | 战秀梅, 彭靖, 王月, 等, 2015. 生物炭及炭基肥改良棕壤理化性状及提高花生产量的作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(6):1633-1641. |
| ZHAN X M, PENG J, WANG Y, et al., 2015. Influences of application of biochar and biochar-based fertilizer on brown soil physiochemical properties and peanut yields[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 21(6):1633-1641. | |
| [37] | 张卫峰, 马林, 黄高强, 等, 2013. 中国氮肥发展、贡献和挑战[J]. 中国农业科学, 46(15):3161-3171. |
| ZHANG W F, MA L, HUANG G Q, et al., 2013. The Development and Contribution of Nitrogenous Fertilizer in China and Challenges Faced by the Country[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 46(15):3161-3171. | |
| [38] | 赵兰坡, 王鸿斌, 刘会青, 等, 2006. 松辽平原玉米带黑土肥力退化机理研究[J]. 土壤学报, 43(1):79-84. |
| ZHAO L P, WANG H B, LIU H Q, et al., 2006. Mechanism of fertility degradation of black soil in corn belt of Songliao Plain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 43(1):79-84. | |
| [39] | 朱倩, 姚兴东, 单玉姿, 等, 2019. 生物炭对R2期大豆根系生长和氮磷吸收利用的影响[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 50(4):385-391. |
| ZHU Q, YAO X D, SHAN Y Z, et al., 2019. Effects of Biochar on Root Growth at R2 Stage, and Nitrogen, Phosphorus Uptake and Utilization of Soybean[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 50(4):385-391. | |
| [40] | 朱艳, 肖清波, 奚永兰, 等, 2020. 改性生物炭制备条件对磷吸附性能的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(9):1897-1903. |
| ZHU Y, XIAO Q B, XI Y L, et al., 2020. Effect of Preparation Conditions on the Phosphorus Adsorption Capacities of Modified Biochar[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(9):1897-1903. |
| [1] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | 潘昱伶, 璩向宁, 李琴, 王磊, 王筱平, 谭鹏, 崔庚, 安雨, 佟守正. 黄河宁夏段典型滩涂湿地土壤理化因子空间分布特征及其对微地形的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | 赵维彬, 唐丽, 王松, 刘玲玲, 王树凤, 肖江, 陈光才. 两种生物炭对滨海盐碱土的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [4] | 张贝儿, 吴建强, 王敏, 熊丽君, 谭娟, 沈城, 黄波涛, 黄沈发. 耕地生态保育工程的土壤健康度评价方法初探[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [5] | 崔远远, 张征云, 刘鹏, 张运春, 张桥英. 镉与聚乙烯微塑料胁迫对小白菜根系的形态特征和分形维数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [6] | 游宏建, 张文文, 兰正芳, 马兰, 张宝娣, 穆晓坤, 李文慧, 曹云娥. 蚯蚓原位堆肥与生物炭对黄瓜根结线虫及根际微生物的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [7] | 李晓晖, 艾仙斌, 李亮, 王玺洋, 辛在军, 孙小艳. 新型改性稻壳生物炭材料对镉污染土壤钝化效果的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1901-1908. |
| [8] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [10] | 钱莲文, 余甜甜, 梁旭军, 王义祥, 陈永山. 茶园土壤酸化改良中生物炭应用5 a后的稳定性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1442-1447. |
| [11] | 夏恩龙, 农珺清, 魏松坡, 刘希珍, 刘广路. 毛竹向阔叶林扩展过程中土壤养分变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [12] | 刘晓红, 刘柳青青, 栗敏, 刘强, 曹东东, 郑浩, 罗先香. 不同粒径的聚乙烯微塑料对玉米和黄瓜种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [13] | 张慧琦, 李子忠, 秦艳. 玉米秸秆生物炭用量对砂土孔隙和持水性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1272-1277. |
| [14] | 邓晓, 武春媛, 杨桂生, 李怡, 李勤奋. 椰壳生物炭对海南滨海土壤的改良效果[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 723-731. |
| [15] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
